Professional Documents
Culture Documents
All About Data Transfer Process (DTP) - SAP BW 7 - SCN
All About Data Transfer Process (DTP) - SAP BW 7 - SCN
Uploaded by
loknathtanikantiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
All About Data Transfer Process (DTP) - SAP BW 7 - SCN
All About Data Transfer Process (DTP) - SAP BW 7 - SCN
Uploaded by
loknathtanikantiCopyright:
Available Formats
7/6/2014 All about Data Transfer Process (DTP) - SAP BW 7 | SCN
http://scn.sap.com/docs/DOC-31781 1/6
Getting Started Newsletters Store
Products Services & Support About SCN Downloads
Industries Training & Education Partnership Developer Center
Lines of Business University Alliances Events & Webinars Innovation
Log On Join Us Hi, Guest Search the Community
Activity Communications Actions
Browse
5 Tweet 0
created by Bhushan Raval on Sep 16, 2012 6:20 PM, last modif ied by Bhushan Raval on Sep 17, 2012 9:54 AM
Data Transfer Process (DTP)
DTP determines the process for transfer of data between two persistent objects within BI.
As of SAP NetWeaver 7.0, InfoPackage loads data from a Source System only up to PSA. It is DTP that determines the
further loading of data thereafter.
Use
Loading data from PSA to InfoProvider(s).
Transfer of data from one InfoProvider to another within BI.
Data distribution to a target outside the BI system; e.g. Open HUBs, etc.
In the process of transferring data within BI, the Transformations define mapping and logic of data updating to the
data targets whereas, the Extraction mode and Update mode are determined using a DTP.
NOTE: DTP is used to load data within BI system only; except when they are used in the scenarios of Virtual
InfoProviders where DTP can be used to determine a direct data fetch from the source system at run time.
Key Benefits of using a DTP over conventional IP loading
1. DTP follows one to one mechanism between a source and a Target i.e. one DTP sources data to only one
data target whereas, IP loads data to all data targets at once. This is one of the major advantages over
the InfoPackage method as it helps in achieving a lot of other benefits.
2. Isolation of Data loading from Source to BI system (PSA) and within BI system. This helps in scheduling
data loads to InfoProviders at any time after loading data from the source.
3. Better Error handling mechanism with the use of Temporary storage area, Semantic Keys and Error
Stack.
Extraction
There are two types of Extraction modes for a DTP Full and Delta.
Full:
Update mode full is same as that in an InfoPackage.
It selects all the data available in the source based on the Filter conditions mentioned in the DTP.
When the source of data is any one from the below InfoProviders, only FULL Extraction Mode is available.
InfoObjects
InfoSets
DataStore Objects for Direct Update
Delta is not possible when the source is anyone of the above.
Delta:
All about Data Transfer Process (DTP) - SAP
BW 7
Share 3
20 Like
Version 3
7/6/2014 All about Data Transfer Process (DTP) - SAP BW 7 | SCN
http://scn.sap.com/docs/DOC-31781 2/6
Unlike InfoPackage, delta transfer using a DTP doesnt require an explicit initialization. When DTP is executed with
Extraction mode Delta for the first time, all existing request till then are retrieved from the source and the delta is
automatically initialized.
The below 3 options are available for a DTP with Extraction Mode: Delta.
Only Get Delta Once.
Get All New Data Request By Request.
Retrieve Until No More New Data.
I Only get delta once:
If this indicator is set, a snapshot scenario is built. The Data available in the Target is an exact replica
of the Source Data.
Scenario:
Let us consider a scenario wherein Data is transferred from a Flat File to an InfoCube. The Target
needs to contain the data from the latest Flat File data load only. Each time a new Request is
loaded, the previous request needs to be deleted from the Target. For every new data load, any
previous Request loaded with the same selection criteria is to be removed from the InfoCube
automatically. This is necessary, whenever the source delivers only the last status of the key
figures, similar to a Snap Shot of the Source Data.
Solution Only Get Delta Once
A DTP with a Full load should suffice the requirement. However, it is not recommended to use a Full
DTP; the reason being, a full DTP loads all the requests from the PSA regardless of whether these
were loaded previously or not. So, in order to avoid the duplication of data due to full loads, we have
to always schedule PSA deletion every time before a full DTP is triggered again.
Only Get Delta Once does this job in a much efficient way; as it loads only the latest request
(Delta) from a PSA to a Data target.
1. Delete the previous Request from the data target.
2. Load data up to PSA using a Full InfoPackage.
3. Execute DTP in Extraction Mode: Delta with Only Get Delta Once checked.
The above 3 steps can be incorporated in a Process Chain which avoids any manual intervention.
II Get all new data request by request:
If you set this indicator in combination with Retrieve Until No More New Data, a DTP gets data from
one request in the source. When it completes processing, the DTP checks whether the source
contains any further new requests. If the source contains more requests, a new DTP request is
automatically generated and processed.
NOTE: If Retrieve Until No More New Data is unchecked, the above option automatically changes
to Get One Request Only. This would in turn get only one request from the source.
Also, once DTP is activated, the option Retrieve Until No More New Data no more appears
in the DTP maintenance.
Package Size
The number of Data records contained in one individual Data package is determined here.
Default value is 50,000.
7/6/2014 All about Data Transfer Process (DTP) - SAP BW 7 | SCN
http://scn.sap.com/docs/DOC-31781 3/6
Filter
The selection Criteria for fetching the data from the source is determined / restricted by filter.
We have following options to restrict a value / range of values:
Multiple selections
OLAP variable
ABAP Routine
A on the right of the Filter button indicates the Filter selections exist for the DTP.
Semantic Groups
Choose Semantic Groups to specify how you want to build the data packages that are read from the source
(DataSource or InfoProvider). To do this, define key fields. Data records that have the same key are combined in a
single data package.
This setting is only relevant for DataStore objects with data fields that are overwritten. This setting also defines the key
fields for the error stack. By defining the key for the error stack, you ensure that the data can be updated in the target in
the correct order once the incorrect data records have been corrected.
A on the right side of the Semantic Groups button indicates the Semantic keys exist for the DTP.
Update
Error Handling
7/6/2014 All about Data Transfer Process (DTP) - SAP BW 7 | SCN
http://scn.sap.com/docs/DOC-31781 4/6
Deactivated:
If an error occurs, the error is reported at the package level and not at the data record level.
The incorrect records are not written to the error stack since the request is terminated and has to be
updated again in its entirety.
This results in faster processing.
No Update, No Reporting:
If errors occur, the system terminates the update of the entire data package. The request is not released for
reporting. The incorrect record is highlighted so that the error can be assigned to the data record.
The incorrect records are not written to the error stack since the request is terminated and has to be
updated again in its entirety.
Valid Records Update, No Reporting (Request Red):
This option allows you to update valid data. This data is only released for reporting after the administrator
checks the incorrect records that are not updated and manually releases the request (by a QM action, that
is, setting the overall status on the Status tab page in the monitor).
The incorrect records are written to a separate error stack in which the records are edited and can be
updated manually using an error DTP.
Valid Records Update, Reporting Possible (Request Green):
Valid records can be reported immediately. Automatic follow-up actions, such as adjusting the aggregates,
are also carried out.
The incorrect records are written to a separate error stack in which the records are edited and can be
updated manually using an error DTP.
Error DTP
Erroneous records in a DTP load are written to a stack called Error Stack.
Error Stack is a request-based table (PSA table) into which erroneous data records from a data transfer process
(DTP) are written. The error stack is based on the data source (PSA, DSO or Info Cube), that is, records from the
source are written to the error stack.
In order to upload data to the Data Target, we need to correct the data records in the Error Stack and manually run the
Error DTP.
Execute
Processing Mode
Serial Extraction, Immediate Parallel Processing:
A request is processed in a background process when a DTP is started in a process chain or manually.
Serial in dialog process (for debugging):
A request is processed in a dialog process when it is started in debug mode from DTP maintenance.
This mode is ideal for simulating the DTP execution in Debugging mode. When this mode is selected, we have the
option to activate or deactivate the session Break Points at various stages like Extraction, Data Filtering, Error
Handling, Transformation and Data Target updating.
7/6/2014 All about Data Transfer Process (DTP) - SAP BW 7 | SCN
http://scn.sap.com/docs/DOC-31781 5/6
You cannot start requests for real-time data acquisition in debug mode.
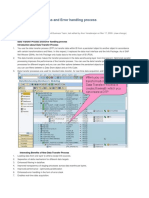
Debugging Tip:
When you want to debug the DTP, you cannot set a session breakpoint in the editor where you write the ABAP code
(e.g. DTP Filter). You need to set a session break point(s) in the Generated program as shown below:
No data transfer; delta status in source: fetched:
This processing is available only when DTP is operated in Delta Mode. It is similar to Delta Initialization without data
transfer as in an InfoPackage.
In this mode, the DTP executes directly in Dialog. The request generated would mark the data found from the source
as fetched, but does not actually load any data to the target.
We can choose this mode even if the data has already been transferred previously using the DTP.
Delta DTP on a DSO
There are special data transfer options when the Data is sourced from a DTP to other Data Target.
Active Table (with Archive)
The data is read from the DSO active table and from the archived data.
Active Table (Without Archive)
The data is only read from the active table of a DSO. If there is data in the archive or in near-line storage
at the time of extraction, this data is not extracted.
Archive (Full Extraction Only)
The data is only read from the archive data store. Data is not extracted from the active table.
Change Log
7/6/2014 All about Data Transfer Process (DTP) - SAP BW 7 | SCN
http://scn.sap.com/docs/DOC-31781 6/6
Follow SCN
Site Index Contact Us SAP Help Portal
Privacy Terms of Use Legal Disclosure Copyright
Average User Rating
(38 ratings)
5 Tweet 0
The data is read from the change log and not the active table of the DSO.
43798 Views
Share 3
20 Like
5 Comments
Like (0)
Bhushan Raval Dec 30, 2012 5:15 AM
Thank you guys!
I wish you a wonderful journey with SAP BI.
Like (0)
Janardhan Sudhir Kumar Chanda May 23, 2013 6:21 AM
Hi Bhushan raval,
Very informative , explained in simple terms.
Hope to see more such articles.
Best Rgds
Chanda
Like (0)
Manimaran A Oct 9, 2013 5:58 AM
I have a doubt,
If i do delta load, it's always fetching data from "change log only", even though i checked active table
(radio button).
Do u have any idea.
Thanks.
Like (0)
Saikat Pal Jun 7, 2014 6:40 PM
Very good document to read.
Like (0)
Prakash k Jun 26, 2014 2:55 PM
Great detailed explanation would love to see more such blogs on various topics.
You might also like
- Performance Optimization in BODSDocument67 pagesPerformance Optimization in BODSisskumar67% (3)
- 01 - SAP Data Transfer Made EasyDocument13 pages01 - SAP Data Transfer Made Easylluizfellipe0% (1)
- TIBCO DesignerDocument65 pagesTIBCO Designeravinashkakarla0% (1)
- CoDeSys SP 32 Bit Embedded - EDocument70 pagesCoDeSys SP 32 Bit Embedded - EKamalakannan Karuppiah100% (1)
- All About Data Transfer Process (DTP) - SAPDocument9 pagesAll About Data Transfer Process (DTP) - SAPsunkrish1No ratings yet
- Creating Data Transfer Processes Using Process ChainsDocument10 pagesCreating Data Transfer Processes Using Process ChainssyellaneniNo ratings yet
- Creating Data Transfer ProcessesDocument4 pagesCreating Data Transfer Processeskoolraj.eeeNo ratings yet
- InfopackageDocument5 pagesInfopackageBW HinjewadiNo ratings yet
- Integration Approach of SAP BW 3.x and 7.0 With Data Transfer ProcessDocument17 pagesIntegration Approach of SAP BW 3.x and 7.0 With Data Transfer ProcessKiran MallavelliNo ratings yet
- Data Transfer ProcessDocument34 pagesData Transfer ProcessabapvinayNo ratings yet
- Infopackages in DetailDocument2 pagesInfopackages in DetailManohar GoudNo ratings yet
- Why Data Transfer Process (DTP) Over Info Package (IP) in SAP BI 7Document2 pagesWhy Data Transfer Process (DTP) Over Info Package (IP) in SAP BI 7Sree DharNo ratings yet
- Creating ODS Objects: Prerequisites ProcedureDocument4 pagesCreating ODS Objects: Prerequisites ProcedurebuddydavisNo ratings yet
- BW - Migration of 3x To 70Document2 pagesBW - Migration of 3x To 70Rogerio Vaz de SouzaNo ratings yet
- LSMW CattDocument4 pagesLSMW CattSrinivasa Rao MullapudiNo ratings yet
- SAP NetWeaver Business Warehouse111docxDocument3 pagesSAP NetWeaver Business Warehouse111docxkksrisriNo ratings yet
- SAP Certified Technology Associate - SystemDocument14 pagesSAP Certified Technology Associate - SystemTeja AripiralaNo ratings yet
- Delta Queue CleanupDocument10 pagesDelta Queue CleanupBadari Nadh GelliNo ratings yet
- Spot Rate2Document3 pagesSpot Rate2pawans8110No ratings yet
- Reporting: Classical ReportsDocument14 pagesReporting: Classical ReportsAshish RajputNo ratings yet
- Error Stack PsaDocument9 pagesError Stack PsaAsitNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions: 1. Which RFC Will Be Used To "Read System Data Remote" From Transaction SMSY?Document30 pagesSample Questions: 1. Which RFC Will Be Used To "Read System Data Remote" From Transaction SMSY?Ajay SainiNo ratings yet
- SAP BI Production Support IssuesDocument15 pagesSAP BI Production Support IssuesKalyanaraman ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- WorkShop BI AdquisitionDocument90 pagesWorkShop BI Adquisitionalfredo_erubielNo ratings yet
- How To Improve Performance of Sap Bods JobsDocument2 pagesHow To Improve Performance of Sap Bods JobssatishNo ratings yet
- Data HubDocument152 pagesData Hub威王No ratings yet
- How To Minimize The Reporting Downtime During The Initial Data LoadDocument2 pagesHow To Minimize The Reporting Downtime During The Initial Data LoadSuresh BabuNo ratings yet
- LSMW 14 StepsDocument31 pagesLSMW 14 StepsNiks WanNo ratings yet
- Batch Data Communication (BDC) in SAP R/3Document4 pagesBatch Data Communication (BDC) in SAP R/3Vivek SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Handling Error Stack in DTPDocument13 pagesHandling Error Stack in DTPavinash kumar gautamNo ratings yet
- LSMWDocument7 pagesLSMWPatil MgNo ratings yet
- DTP and Error HandlingDocument4 pagesDTP and Error HandlingVinoth Kumar PeethambaramNo ratings yet
- Back To TopDocument5 pagesBack To Topanjali AnjuNo ratings yet
- BC0058 AssignmentDocument8 pagesBC0058 AssignmentAlok EkkaNo ratings yet
- SAP BW Repair Full RequestDocument6 pagesSAP BW Repair Full RequestDavid TownsendNo ratings yet
- SAP BW Performance OptimizationDocument11 pagesSAP BW Performance OptimizationHemanth JanyavulaNo ratings yet
- Data Loading Mechanisms For Spend Performance Management (SPM)Document8 pagesData Loading Mechanisms For Spend Performance Management (SPM)Nikunj KachaNo ratings yet
- Azure Data FactoryDocument47 pagesAzure Data FactorygoldenNo ratings yet
- TrainersguidetoDataEntryv1 1Document9 pagesTrainersguidetoDataEntryv1 1hmounguiNo ratings yet
- ProtcopDocument3 pagesProtcopArunts SoundharajanNo ratings yet
- Data Load IssuesDocument11 pagesData Load IssuesSanjeev SinghNo ratings yet
- Informatica Interview Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesInformatica Interview Questions and AnswersPreethaNo ratings yet
- Assessment 2: Data Cleansing & Conversion (20%) : Overview of TasksDocument3 pagesAssessment 2: Data Cleansing & Conversion (20%) : Overview of TasksAounaiza AhmedNo ratings yet
- Data Migration SAPDocument6 pagesData Migration SAPআবু উবাইদাNo ratings yet
- 13 Steps To Simple LSMW Using Record MethodDocument13 pages13 Steps To Simple LSMW Using Record MethodAbhijeet ZawareNo ratings yet
- Oracle Golden Gate PresentationDocument20 pagesOracle Golden Gate Presentationsuganya88No ratings yet
- Powercenter Server On Windows Can Connect To Following Databases: Ibm Db2 Informix Microsoft Access Microsoft Excel Microsoft SQL Server Oracle Sybase TeradataDocument9 pagesPowercenter Server On Windows Can Connect To Following Databases: Ibm Db2 Informix Microsoft Access Microsoft Excel Microsoft SQL Server Oracle Sybase Teradatavpv0002No ratings yet
- SAP Business Intelligence NotesDocument10 pagesSAP Business Intelligence NoteskadosiNo ratings yet
- BDCDOCUMENTATIONDocument48 pagesBDCDOCUMENTATIONapi-3730718No ratings yet
- Sap Catt ToolDocument5 pagesSap Catt ToolsapreaderNo ratings yet
- SAP BW Interview QuestionDocument102 pagesSAP BW Interview Questionmkumar260% (1)
- Assignment4 PadillaRuizMartaDocument28 pagesAssignment4 PadillaRuizMartaMarta Padilla RuizNo ratings yet
- Production IssuesDocument4 pagesProduction IssuessolankikavitaNo ratings yet
- Data PageDocument4 pagesData PageMEGHANADH REDDYNo ratings yet
- How To Improve ASCP Data Collections PerformanceDocument6 pagesHow To Improve ASCP Data Collections PerformancePramodNo ratings yet
- Support IssuesDocument9 pagesSupport Issuesapi-3753683100% (1)
- What Is Sap LSMWDocument13 pagesWhat Is Sap LSMWVinay PavanNo ratings yet
- BDC - Batch InputDocument52 pagesBDC - Batch InputRoberto MartínezNo ratings yet
- SAS Programming Guidelines Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandSAS Programming Guidelines Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- Infineon-AN58009 Serial (UART) Port Debugging of FX1 FX2LP Firmware-ApplicationNotes-v06 00-ENDocument15 pagesInfineon-AN58009 Serial (UART) Port Debugging of FX1 FX2LP Firmware-ApplicationNotes-v06 00-ENNugroho Widi JatmikoNo ratings yet
- Hackaday USSSSSBTalkingUSBFromPython OFlynn PDFDocument165 pagesHackaday USSSSSBTalkingUSBFromPython OFlynn PDFjokcy codeNo ratings yet
- APIs by ExampleDocument12 pagesAPIs by ExampleTaufik RamdaniNo ratings yet
- Compiling, Linking, and LocatingDocument20 pagesCompiling, Linking, and LocatingAravindNo ratings yet
- USB Debugging and Profiling TechniquesDocument39 pagesUSB Debugging and Profiling Techniquesmiora6ny6ainaNo ratings yet
- Qm852 Troubleshooting Guide CiscoDocument90 pagesQm852 Troubleshooting Guide CiscoKajen VmvNo ratings yet
- v2 GTM Data Layer Cheat Sheet Analytics ManiaDocument20 pagesv2 GTM Data Layer Cheat Sheet Analytics ManiaRobertNo ratings yet
- Programming LanguagesDocument27 pagesProgramming LanguagesziggatronNo ratings yet
- Abap Debugging BasicDocument53 pagesAbap Debugging BasicramakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ricoh MP 9000/1100/1350 Service ManualDocument862 pagesRicoh MP 9000/1100/1350 Service ManualFuriousBK100% (2)
- 1.1 General: 1.2 Scope of The ProjectDocument55 pages1.1 General: 1.2 Scope of The Projectvenkatesh reddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter #1 Concepts of Computer ProgrammingDocument35 pagesChapter #1 Concepts of Computer Programmingsqamar68No ratings yet
- Somachine Software Suite: PresentationDocument4 pagesSomachine Software Suite: PresentationSalih Ahmed ObeidNo ratings yet
- Control Expeert Operation GuideDocument44 pagesControl Expeert Operation GuideJuan ZarateNo ratings yet
- B3 Debuging IMS 200902Document37 pagesB3 Debuging IMS 200902Suresh BabuNo ratings yet
- 001-66390 CY3674 CY3684 EZ USB R Development Kit User GuideDocument99 pages001-66390 CY3674 CY3684 EZ USB R Development Kit User GuideAlexisNo ratings yet
- Design of Object Oriented Debugger ModelDocument14 pagesDesign of Object Oriented Debugger ModelHaylemichael AbateNo ratings yet
- Ricoh - mp5000 S.M.Document836 pagesRicoh - mp5000 S.M.Nikolaos Mavridis100% (1)
- C Programming and Assembly LanguageDocument8 pagesC Programming and Assembly LanguagePallavi Kumari 11 DNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument295 pagesUntitledWilian MoranNo ratings yet
- Infopage Testing and Repairing nRF24LE1 ModulesDocument3 pagesInfopage Testing and Repairing nRF24LE1 ModulesMaxHSBNo ratings yet
- General Info - Tenderly DocsDocument30 pagesGeneral Info - Tenderly DocsSouradeepDasNo ratings yet
- Base SAS Interview QuestionsDocument26 pagesBase SAS Interview Questionsmamatha_mba269690No ratings yet
- PRPC Rule Config Clist 33Document13 pagesPRPC Rule Config Clist 33Ekta ParabNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Foundations of Software TestingDocument45 pagesChapter-1 Foundations of Software TestingNaveen Kumar0% (1)
- Debugging Techniques For Embedded SystemsDocument9 pagesDebugging Techniques For Embedded SystemsJames DoolinNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Introduction To Programming - UpdatedDocument30 pagesModule 2 - Introduction To Programming - UpdatedKen FirmalanNo ratings yet
- Jonathan Valvano University of Texas at Austin Valvano@mail - Utexas.eduDocument44 pagesJonathan Valvano University of Texas at Austin Valvano@mail - Utexas.eduFreya OlamitNo ratings yet
- CUADocument10 pagesCUASunita CMNo ratings yet