Professional Documents
Culture Documents
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
517 viewsLegg Calve Perthes
Legg Calve Perthes
Uploaded by
Adrian MallarLegg Calve Perthes (LCPD) is a degenerative disease of the hip joint typically found in young children where loss of blood supply to the femoral head leads to bone death and deformity of the hip ball and socket. Symptoms include limping, hip or groin pain exacerbated by movement, and leg length inequality. The disease progresses through four stages and treatment aims to reduce pain and hip irritability while preventing femoral head collapse and maintaining mobility. This can involve medical management, surgery such as osteotomies, or nonsurgical treatments like casting and bracing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Front of Me. She Is A Good Cook." For The Past Few Months, Mrs. Jenaro HasDocument5 pagesFront of Me. She Is A Good Cook." For The Past Few Months, Mrs. Jenaro Hasnct thomasNo ratings yet
- Reflective Essay-Rexson A. DalanginDocument3 pagesReflective Essay-Rexson A. DalanginRexson Alcantara DalanginNo ratings yet
- CertificatesDocument13 pagesCertificatesbkmurthy78100% (1)
- Vii. NCPDocument4 pagesVii. NCPmariaNo ratings yet
- FractureDocument4 pagesFractureRaveen mayiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER I The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument10 pagesCHAPTER I The Problem and Its BackgroundPaola EncilaNo ratings yet
- Kocher (Ochsner) .: (Kelly Curve) - Use To Clamp Larger Tissues or VesselsDocument5 pagesKocher (Ochsner) .: (Kelly Curve) - Use To Clamp Larger Tissues or VesselsKevin AliasasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Emergency DrugsDocument6 pagesDrug Study Emergency DrugsJhessa Curie PitaganNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Discharge PlanningDocument3 pagesCerebral Palsy Discharge Planningjints poterNo ratings yet
- Lacerated WoundDocument38 pagesLacerated Wounddomzlr18100% (2)
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- HypophysectomyDocument19 pagesHypophysectomyjoel david knda mj100% (1)
- Problem PRIORITIZATION and NCP 1, 2, 3 of CataractDocument7 pagesProblem PRIORITIZATION and NCP 1, 2, 3 of CataractEries Lacanlale LumbaNo ratings yet
- Module Activity Week 18 Evaluation of Community Project ActivityDocument1 pageModule Activity Week 18 Evaluation of Community Project ActivityErickson V. LibutNo ratings yet
- Aminogen Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAminogen Drug Studymilesmin100% (1)
- Valacyclovir HydrochlorideDocument3 pagesValacyclovir HydrochlorideAndrea Huecas TriaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyXio PauNo ratings yet
- Atracurium BesylateDocument3 pagesAtracurium BesylateAP TOROBXNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study TelmisartanDocument9 pagesDrug-Study TelmisartanAngelica FloritaNo ratings yet
- ItoprideDocument2 pagesItoprideLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Circulating Nurse ScriptDocument1 pageCirculating Nurse Scriptmaga.abigail.bsnNo ratings yet
- EndocrinedisorderDocument3 pagesEndocrinedisorderDyan LazoNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument3 pagesNarrative ReportRoxenette Gil Bernales PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Copaxone - Ms Drug StudyDocument1 pageCopaxone - Ms Drug StudygraceNo ratings yet
- Npi NCMHDocument6 pagesNpi NCMHJoshua DauzNo ratings yet
- Coa ReviewersDocument269 pagesCoa Reviewersmary ann corsanesNo ratings yet
- Corpuz, Lorelyn S - NCP (Colostomy and Ileostomy)Document3 pagesCorpuz, Lorelyn S - NCP (Colostomy and Ileostomy)Lorelyn Santos CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide: Ngeles Niversity OundationDocument9 pagesLearning Guide: Ngeles Niversity OundationNYCA GRACIA TUAZONNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEChezka Orton Swift BolintiamNo ratings yet
- NCP RheumatoidDocument5 pagesNCP RheumatoidJane Elizabeth Gonzales MacahiaNo ratings yet
- Post Operative Acute PainDocument1 pagePost Operative Acute Painالأغا محمد زكارنةNo ratings yet
- DolcetDocument2 pagesDolcetmarc_hansen_1312No ratings yet
- BactidolDocument1 pageBactidolRryje SallevaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Allopurinol (Purinase)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY Allopurinol (Purinase)DennMarkTaponNo ratings yet
- Drugs Mechanism of Action Nursing Responsibilities OMXDocument5 pagesDrugs Mechanism of Action Nursing Responsibilities OMXEmmanuelRodriguezNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument4 pagesConcept MapgeejeiNo ratings yet
- Serving Sterile GownDocument2 pagesServing Sterile GownGelo BallartaNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies (DMII) (Humulin, NACh03, Losartan, Vessel Due F)Document5 pagesDrug Studies (DMII) (Humulin, NACh03, Losartan, Vessel Due F)Alvin OrizaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilitiesangel cenaNo ratings yet
- AlendronateDocument3 pagesAlendronateAdhaNo ratings yet
- HTP of AsthmaDocument1 pageHTP of AsthmaMarland Faith Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityShiva TorinsNo ratings yet
- Surgery JournalDocument1 pageSurgery JournalPhilippe CANTORIA (SHS)No ratings yet
- GC COURSEWORK (Maternal April 13, 2020) - VARGASDocument5 pagesGC COURSEWORK (Maternal April 13, 2020) - VARGASKathleen VargasNo ratings yet
- Reflection Video Why Mrs. X Die MATERNALDocument2 pagesReflection Video Why Mrs. X Die MATERNALQueenzee AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone, MetropololDocument7 pagesAzithromycin, Ceftriaxone, Metropolollei_odanNo ratings yet
- MG Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMG Drug StudySandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Epidural AnesthesiaDocument5 pagesDrug Study - Epidural AnesthesiaMarie PotayreNo ratings yet
- Lung CancerDocument2 pagesLung CancerLezTeѓ Recto LaddaranNo ratings yet
- MAHILOM NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesMAHILOM NCP Impaired Physical Mobilitykasandra dawn BerisoNo ratings yet
- NCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalDocument13 pagesNCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZNo ratings yet
- Pedia Care Study - Appendix B - Drug StudyDocument8 pagesPedia Care Study - Appendix B - Drug Studyryan100% (1)
- AB Critical Thinking ExercisesDocument4 pagesAB Critical Thinking ExercisesAhmad BaolayyanNo ratings yet
- DS (Fenofibrate)Document5 pagesDS (Fenofibrate)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument4 pagesNCP Finalmarkanthony39030% (1)
- Enalapril MaleateDocument3 pagesEnalapril MaleatelichunghkNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Clausii ErcefloraDocument1 pageBacillus Clausii ErcefloraCezhille BattadNo ratings yet
- Ameloblastoma PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAmeloblastoma PathophysiologyAshok KpNo ratings yet
- Legg Calve PerthesDocument7 pagesLegg Calve PerthesNelhbenson LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document27 pagesChapter 13Zaky DavidiaNo ratings yet
- Paget's Disease: Support. Bones Provide A Framework For The Attachment of Muscles andDocument11 pagesPaget's Disease: Support. Bones Provide A Framework For The Attachment of Muscles andAndrew MckinleyNo ratings yet
- Casestudy FractureDocument22 pagesCasestudy FractureAdrian Mallar0% (1)
- Flail Chest (Tayug)Document25 pagesFlail Chest (Tayug)Adrian MallarNo ratings yet
- HyperkalemiaDocument10 pagesHyperkalemiaAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing p.31-55Document25 pagesCommunity Health Nursing p.31-55Adrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) Is A Disease of The Human Immune System Caused byDocument7 pagesAcquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) Is A Disease of The Human Immune System Caused byAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric NursingDocument15 pagesPsychiatric NursingAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient KnowledgeDocument1 pageNCP Deficient KnowledgeAdrian Mallar67% (3)
- HyperkalemiaDocument10 pagesHyperkalemiaAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Potts Disease Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesPotts Disease Case AnalysisAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Potts Disease Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesPotts Disease Case AnalysisAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Case StudyDocument8 pagesOrthopedic Case StudyAdrian Mallar100% (1)
- Case Study On SchizophreniaDocument21 pagesCase Study On SchizophreniaAdrian Mallar100% (2)
- College of Nursing: Homer D. Elegado BSN 3ADocument12 pagesCollege of Nursing: Homer D. Elegado BSN 3AAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Stab Wound Case StudyDocument33 pagesStab Wound Case StudyAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Homer D. Elegado BSN 3ADocument16 pagesCollege of Nursing: Homer D. Elegado BSN 3AAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Case in Herniorraphy BESTCASEDocument23 pagesCase in Herniorraphy BESTCASEAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Renal Pathology Unit ExamDocument50 pagesRenal Pathology Unit ExamCherry RahimaNo ratings yet
- Nama ObatDocument4 pagesNama ObatMayha Gyu1803No ratings yet
- 13 Necrotizing Ulcerative GingivitisDocument9 pages13 Necrotizing Ulcerative GingivitisGerard Andrei Arlovski100% (1)
- Pharmacology of Antiviral DrugsDocument1 pagePharmacology of Antiviral Drugssarah90222100% (1)
- ST Johns Tel DirectoryDocument1 pageST Johns Tel DirectoryeshariffNo ratings yet
- CME Palliative Medicine (126358) : Self-Assessment QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesCME Palliative Medicine (126358) : Self-Assessment Questionnairealialison7666No ratings yet
- Advances in Heart Failure, Patient Management, ST2 TestingDocument44 pagesAdvances in Heart Failure, Patient Management, ST2 TestingPhan QuanNo ratings yet
- TamifluDocument20 pagesTamiflukiwikid718635No ratings yet
- Pathology & Clinical Laboratory (M) SDN - BHD: Scan QR For VerificationDocument2 pagesPathology & Clinical Laboratory (M) SDN - BHD: Scan QR For VerificationAdnan Md SaatNo ratings yet
- Molecular Prevalence of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Prisons: Case of The Central Prison of FrancevilleDocument8 pagesMolecular Prevalence of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Prisons: Case of The Central Prison of FrancevilleInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Assessment of Foetal Wellbeing.Document30 pagesAntenatal Assessment of Foetal Wellbeing.Kavya S MohanNo ratings yet
- Gi Pathogens Profile Sample ReportDocument2 pagesGi Pathogens Profile Sample ReportPuneet Kumar DhimanNo ratings yet
- OR AnesthesiaDocument6 pagesOR AnesthesiaLipa Alliza CaÑaNo ratings yet
- What Is Hypospadias?Document5 pagesWhat Is Hypospadias?Anonymous MWd5UOUuiyNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: Colorectal Cancer, Also Called Colon Cancer or Large Bowel Cancer, IncludesDocument18 pagesSigns and Symptoms: Colorectal Cancer, Also Called Colon Cancer or Large Bowel Cancer, Includesphvega06No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 and 1Document31 pagesChapter 2 and 1AduNo ratings yet
- TM194853GL HOTLINE White Paper HighlightsDocument2 pagesTM194853GL HOTLINE White Paper HighlightsAphichetNo ratings yet
- 9 Essential CBT Techniques and Tools PsychotherapyDocument4 pages9 Essential CBT Techniques and Tools Psychotherapyآئمہ توصيف100% (1)
- Fluids, PH, Ions and ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesFluids, PH, Ions and ElectrolytesthedancingseaNo ratings yet
- Emphysema: Pathophysiology / Drug Studies / Nursing Care Plans /health TeachingsDocument24 pagesEmphysema: Pathophysiology / Drug Studies / Nursing Care Plans /health TeachingsGeoffrey Sintaan RiveraNo ratings yet
- Data and Modeling Update VSHARE 729206 7 (MDHHS)Document40 pagesData and Modeling Update VSHARE 729206 7 (MDHHS)Caleb HollowayNo ratings yet
- NeutrophilDocument61 pagesNeutrophilJenivic Empig PuedanNo ratings yet
- MOSH-Chapter 10 Occupational VibrationDocument13 pagesMOSH-Chapter 10 Occupational Vibrationsiti zubaidahNo ratings yet
- Terpinen 4 OlDocument8 pagesTerpinen 4 OlDouglas RussellNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Part 2 DRAFTDocument6 pagesEndocrine Part 2 DRAFTPreeti Joan BuxaniNo ratings yet
- Elekta Versa HDDocument12 pagesElekta Versa HDHaider RabeeNo ratings yet
- uk-spc-nexium-sachet-10mg-DRESS-update-GI 21 0012aDocument17 pagesuk-spc-nexium-sachet-10mg-DRESS-update-GI 21 0012aDeisy ClerkeNo ratings yet
- Anti-MUM1 Antibody Ab104803: 1 Abreviews 2 ImagesDocument3 pagesAnti-MUM1 Antibody Ab104803: 1 Abreviews 2 Imageshorace35No ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument10 pagesCardiopulmonary ResuscitationLilay MakulayNo ratings yet
Legg Calve Perthes
Legg Calve Perthes
Uploaded by
Adrian Mallar100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
517 views7 pagesLegg Calve Perthes (LCPD) is a degenerative disease of the hip joint typically found in young children where loss of blood supply to the femoral head leads to bone death and deformity of the hip ball and socket. Symptoms include limping, hip or groin pain exacerbated by movement, and leg length inequality. The disease progresses through four stages and treatment aims to reduce pain and hip irritability while preventing femoral head collapse and maintaining mobility. This can involve medical management, surgery such as osteotomies, or nonsurgical treatments like casting and bracing.
Original Description:
case study
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLegg Calve Perthes (LCPD) is a degenerative disease of the hip joint typically found in young children where loss of blood supply to the femoral head leads to bone death and deformity of the hip ball and socket. Symptoms include limping, hip or groin pain exacerbated by movement, and leg length inequality. The disease progresses through four stages and treatment aims to reduce pain and hip irritability while preventing femoral head collapse and maintaining mobility. This can involve medical management, surgery such as osteotomies, or nonsurgical treatments like casting and bracing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
517 views7 pagesLegg Calve Perthes
Legg Calve Perthes
Uploaded by
Adrian MallarLegg Calve Perthes (LCPD) is a degenerative disease of the hip joint typically found in young children where loss of blood supply to the femoral head leads to bone death and deformity of the hip ball and socket. Symptoms include limping, hip or groin pain exacerbated by movement, and leg length inequality. The disease progresses through four stages and treatment aims to reduce pain and hip irritability while preventing femoral head collapse and maintaining mobility. This can involve medical management, surgery such as osteotomies, or nonsurgical treatments like casting and bracing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Legg Calve Perthes (LCPD)
Is a degenerative disease of the hip joint, where growth/loss
of bone mass leads to some degree of collapse of the hip joint and
to deformity of the ball of the femur and the surface of the hip
socket. The disease is characterized by idiopathic avascular
osteonecrosis of the capital femoral epiphysis of the femoral head
leading to an interruption of the blood supply of the head of the
femur close to the hip joint. The disease is typically found in young
children, and it can lead to osteoarthritis in adults. The effects of
the disease can sometimes continue into adulthood.
Also known as:
Perthes disease
Ischemic necrosis of the hip
o!a plana
"steochondritis
#ascular necrosis of the femoral head
Causes$
The e!act cause is unknown
%eduction in blood flow to the joint
It is thought that the artery of the ligamentum teres femoris
closes too early, not allowing time for the medical circumfle!
femoral artery to take over
&bnormal blood clotting
Infection
'alnourishment
(enetic
Trauma
Incidence
Perthes is rare, occurring in appro!imately ).) of *++,+++ children.
Signs & Symtoms$
,irst -igns$
complaint of sourness from the child .often dismissed
as growing pain/
limping
guarding of the joint
"ther -ymptoms$
hip, knee .reffered pain/, or groin pain, e!acerbated
by hip/leg movement.
%educe %"' at the hip joint and a painful or antalgic
gait
&trophy of thigh muscles from disuse
Ine0uality of the leg length.
Pathohysiology
Predisposing/ %isk factors$
"besity
,amily history
1ow birth weight
&bnormal presentation at birth
%ace2 &sians, 3skimos, whites
(enetic, Infection, Trauma, 'alnutrition, &bnormal 4lood lotting,
Idiopathic.
%apid (rowth 5 6evelopment of the -upply of the -econdary "ssification
enters in the 3piphysis.
Interrupted of ade0uate blood flow
Prone to avascular necrosis
%esult in necrosis
6eformity of the ball of the hip, knee or groin
pain
femur and the surface of the
hip socket
1imping, guarding of
the joint
ine0uality of leg length
antalgic gait
6isuse
&trophy thigh muscles
!our Stages o" LCPD
1. ,emoral head becomes more dense with possible fracture
of supporting bone7
2. ,ragmentation and reabsorption of bone7
3. %eossification when new bone has regrown7 and
4. 8ealing, when new bone reshapes.
Phase I takes about 92: months, Phase : takes one year or
more, and Phase ; and < may go on for many years.
Diagnosis:
=2%ay
'agnetic %esonance Imaging .'%I/
bone scan
#reatment
The goal of treatment is four2fold$
I/ to reduce hip irritability
:/ restore and maintain hip mobility
;/ to prevent the ball from e!truding or collapsing
</ to regain a spherical femoral head
$edical $%#$
>-&I6 .'otrin) ? for pain
@oledponic &cid .under investigation/
Surgical $%#:
-urgery is indicated for children greater that age 9 years.
3!cision of e!truded portion of the head for hinge abduction
&cetabular osteotomy
1ateral shelf osteotomy
hiari osteotomy
#algus osteotomy
&rthrodesis
&on'surgical treatment:
cast
traction
braces
Prevention
There is no known effective preventative measure
&ursing $%#:
6istraction method ? for pain
&dvice refrains from contacts sports or game/activities which
impact the pain.
%eneral Interventions:
1. Instruct patient to report pain as soon as it begins
2. Provide 0uite environment, calm activities.
3. 3ncourage use of diversional activity .T#, %adio,
socializing/
4. 3ncourage ade0uate rest periods to prevent fatigue
evaluate in pain behavior
&ursing D(:
&cute pain related to inflammation of joint secondary to legg
calve perthes disease.
Impaired physical mobility related to abnormal gait secondary
to legg calve perthes disease.
%isk for injury related to altered mobility secondary to
unsteady gait.
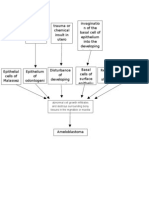
Avascular &ecrosis
Is a disease resulting from the temporary or permanent loss
of the blood supply to the bone. Aithout blood, the bone tissue dies
and causes the bone to collapse. If the process involves the bones
near a joint, it often leads to collapse of the joint surface.
Also known as:
"steonecrosis
&septic necrosis
Ischemic bone necrosis
)tiologies$
&lcohol abuse
aisson .decompression/ disease
igarette smoking
,at emboli
(out
%adiation therapy
%aynauld phenomenon
-ickle cell disease with increase blood viscosity
-ystemic steroids
Trauma, such as fracture, disruption circulation in the bone
Bnknown cause, known as idiopathic &#>
Causes$
,ollowing is a list of causes or underlying conditions .see also
'isdiagnosis of underlying causes of &vascular necrosis/ that could
possibly cause &vascular necrosis includes$
Traumatic injury
,racture
6islocation
6islocated hip .see 8ip symptoms/
&lcoholism
3!cessive alcohol
Pathohysiology
%isk factors$
injury
steroid use
(aucher disease
alcohol use
blood disorders, such as sickle cell anemia
radiation treatments
chemotherapy
pancreatitis
decompression disease
Traumatic causes non2traumatic causes
Temporary or permanent loss of blood supply to the bone
Ahen blood supply is cut off, the bone tissue dies
minimal early joint pain
4one collapses
increased joint pain as bone and joint begin to collapse
If it occurs near a joint, collapse of the joint surface may occur
limited range of motion due to pain
Diagnostic #ests
The list of diagnostic tests mentioned in various sources as used
in the diagnosis of &vascular necrosis includes$
=2rays
'%I 2 good for diagnosis in the early stages
4one scintigraphy .bone scan/
T scan
4one biopsy
#reatments "or Avascular necrosis
The list of treatments mentioned in various sources for &vascular
necrosis includes the following list. &lways seek professional medical
advice about any treatment or change in treatment plans.
>-&I6s 2 for pain
&void weight bearing 2 take pressure off the joint .e.g.
crutches/7 in some cases this allows the body to self2heal.
%ange2of2motion e!ercises
3lectrical stimulation 2 to stimulate natural growth of the
bone.
&void alcohol
Treat alcoholism 2 if the problem is caused by alcoholism.
6iscontinue corticosteroid use 2 slowly under medical advice,
since stopping 0uickly causes problems.
-urgical treatments
o ore decompression
o "steotomy
o 4one graft
o Coint replacement .arthroplasty/
&ursing D(:
Impair physical mobility related to &#> of femoral head or
tarsal navicular bone.
&cute pain related to ischemic changes and degeneration of
involved bone.
You might also like
- Front of Me. She Is A Good Cook." For The Past Few Months, Mrs. Jenaro HasDocument5 pagesFront of Me. She Is A Good Cook." For The Past Few Months, Mrs. Jenaro Hasnct thomasNo ratings yet
- Reflective Essay-Rexson A. DalanginDocument3 pagesReflective Essay-Rexson A. DalanginRexson Alcantara DalanginNo ratings yet
- CertificatesDocument13 pagesCertificatesbkmurthy78100% (1)
- Vii. NCPDocument4 pagesVii. NCPmariaNo ratings yet
- FractureDocument4 pagesFractureRaveen mayiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER I The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument10 pagesCHAPTER I The Problem and Its BackgroundPaola EncilaNo ratings yet
- Kocher (Ochsner) .: (Kelly Curve) - Use To Clamp Larger Tissues or VesselsDocument5 pagesKocher (Ochsner) .: (Kelly Curve) - Use To Clamp Larger Tissues or VesselsKevin AliasasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Emergency DrugsDocument6 pagesDrug Study Emergency DrugsJhessa Curie PitaganNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Discharge PlanningDocument3 pagesCerebral Palsy Discharge Planningjints poterNo ratings yet
- Lacerated WoundDocument38 pagesLacerated Wounddomzlr18100% (2)
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- HypophysectomyDocument19 pagesHypophysectomyjoel david knda mj100% (1)
- Problem PRIORITIZATION and NCP 1, 2, 3 of CataractDocument7 pagesProblem PRIORITIZATION and NCP 1, 2, 3 of CataractEries Lacanlale LumbaNo ratings yet
- Module Activity Week 18 Evaluation of Community Project ActivityDocument1 pageModule Activity Week 18 Evaluation of Community Project ActivityErickson V. LibutNo ratings yet
- Aminogen Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAminogen Drug Studymilesmin100% (1)
- Valacyclovir HydrochlorideDocument3 pagesValacyclovir HydrochlorideAndrea Huecas TriaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyXio PauNo ratings yet
- Atracurium BesylateDocument3 pagesAtracurium BesylateAP TOROBXNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study TelmisartanDocument9 pagesDrug-Study TelmisartanAngelica FloritaNo ratings yet
- ItoprideDocument2 pagesItoprideLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Circulating Nurse ScriptDocument1 pageCirculating Nurse Scriptmaga.abigail.bsnNo ratings yet
- EndocrinedisorderDocument3 pagesEndocrinedisorderDyan LazoNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument3 pagesNarrative ReportRoxenette Gil Bernales PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Copaxone - Ms Drug StudyDocument1 pageCopaxone - Ms Drug StudygraceNo ratings yet
- Npi NCMHDocument6 pagesNpi NCMHJoshua DauzNo ratings yet
- Coa ReviewersDocument269 pagesCoa Reviewersmary ann corsanesNo ratings yet
- Corpuz, Lorelyn S - NCP (Colostomy and Ileostomy)Document3 pagesCorpuz, Lorelyn S - NCP (Colostomy and Ileostomy)Lorelyn Santos CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide: Ngeles Niversity OundationDocument9 pagesLearning Guide: Ngeles Niversity OundationNYCA GRACIA TUAZONNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEChezka Orton Swift BolintiamNo ratings yet
- NCP RheumatoidDocument5 pagesNCP RheumatoidJane Elizabeth Gonzales MacahiaNo ratings yet
- Post Operative Acute PainDocument1 pagePost Operative Acute Painالأغا محمد زكارنةNo ratings yet
- DolcetDocument2 pagesDolcetmarc_hansen_1312No ratings yet
- BactidolDocument1 pageBactidolRryje SallevaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Allopurinol (Purinase)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY Allopurinol (Purinase)DennMarkTaponNo ratings yet
- Drugs Mechanism of Action Nursing Responsibilities OMXDocument5 pagesDrugs Mechanism of Action Nursing Responsibilities OMXEmmanuelRodriguezNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument4 pagesConcept MapgeejeiNo ratings yet
- Serving Sterile GownDocument2 pagesServing Sterile GownGelo BallartaNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies (DMII) (Humulin, NACh03, Losartan, Vessel Due F)Document5 pagesDrug Studies (DMII) (Humulin, NACh03, Losartan, Vessel Due F)Alvin OrizaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilitiesangel cenaNo ratings yet
- AlendronateDocument3 pagesAlendronateAdhaNo ratings yet
- HTP of AsthmaDocument1 pageHTP of AsthmaMarland Faith Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityShiva TorinsNo ratings yet
- Surgery JournalDocument1 pageSurgery JournalPhilippe CANTORIA (SHS)No ratings yet
- GC COURSEWORK (Maternal April 13, 2020) - VARGASDocument5 pagesGC COURSEWORK (Maternal April 13, 2020) - VARGASKathleen VargasNo ratings yet
- Reflection Video Why Mrs. X Die MATERNALDocument2 pagesReflection Video Why Mrs. X Die MATERNALQueenzee AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone, MetropololDocument7 pagesAzithromycin, Ceftriaxone, Metropolollei_odanNo ratings yet
- MG Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMG Drug StudySandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Epidural AnesthesiaDocument5 pagesDrug Study - Epidural AnesthesiaMarie PotayreNo ratings yet
- Lung CancerDocument2 pagesLung CancerLezTeѓ Recto LaddaranNo ratings yet
- MAHILOM NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesMAHILOM NCP Impaired Physical Mobilitykasandra dawn BerisoNo ratings yet
- NCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalDocument13 pagesNCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZNo ratings yet
- Pedia Care Study - Appendix B - Drug StudyDocument8 pagesPedia Care Study - Appendix B - Drug Studyryan100% (1)
- AB Critical Thinking ExercisesDocument4 pagesAB Critical Thinking ExercisesAhmad BaolayyanNo ratings yet
- DS (Fenofibrate)Document5 pagesDS (Fenofibrate)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument4 pagesNCP Finalmarkanthony39030% (1)
- Enalapril MaleateDocument3 pagesEnalapril MaleatelichunghkNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Clausii ErcefloraDocument1 pageBacillus Clausii ErcefloraCezhille BattadNo ratings yet
- Ameloblastoma PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAmeloblastoma PathophysiologyAshok KpNo ratings yet
- Legg Calve PerthesDocument7 pagesLegg Calve PerthesNelhbenson LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document27 pagesChapter 13Zaky DavidiaNo ratings yet
- Paget's Disease: Support. Bones Provide A Framework For The Attachment of Muscles andDocument11 pagesPaget's Disease: Support. Bones Provide A Framework For The Attachment of Muscles andAndrew MckinleyNo ratings yet
- Casestudy FractureDocument22 pagesCasestudy FractureAdrian Mallar0% (1)
- Flail Chest (Tayug)Document25 pagesFlail Chest (Tayug)Adrian MallarNo ratings yet
- HyperkalemiaDocument10 pagesHyperkalemiaAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing p.31-55Document25 pagesCommunity Health Nursing p.31-55Adrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) Is A Disease of The Human Immune System Caused byDocument7 pagesAcquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) Is A Disease of The Human Immune System Caused byAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric NursingDocument15 pagesPsychiatric NursingAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient KnowledgeDocument1 pageNCP Deficient KnowledgeAdrian Mallar67% (3)
- HyperkalemiaDocument10 pagesHyperkalemiaAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Potts Disease Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesPotts Disease Case AnalysisAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Potts Disease Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesPotts Disease Case AnalysisAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Case StudyDocument8 pagesOrthopedic Case StudyAdrian Mallar100% (1)
- Case Study On SchizophreniaDocument21 pagesCase Study On SchizophreniaAdrian Mallar100% (2)
- College of Nursing: Homer D. Elegado BSN 3ADocument12 pagesCollege of Nursing: Homer D. Elegado BSN 3AAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Stab Wound Case StudyDocument33 pagesStab Wound Case StudyAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Homer D. Elegado BSN 3ADocument16 pagesCollege of Nursing: Homer D. Elegado BSN 3AAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Case in Herniorraphy BESTCASEDocument23 pagesCase in Herniorraphy BESTCASEAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- Renal Pathology Unit ExamDocument50 pagesRenal Pathology Unit ExamCherry RahimaNo ratings yet
- Nama ObatDocument4 pagesNama ObatMayha Gyu1803No ratings yet
- 13 Necrotizing Ulcerative GingivitisDocument9 pages13 Necrotizing Ulcerative GingivitisGerard Andrei Arlovski100% (1)
- Pharmacology of Antiviral DrugsDocument1 pagePharmacology of Antiviral Drugssarah90222100% (1)
- ST Johns Tel DirectoryDocument1 pageST Johns Tel DirectoryeshariffNo ratings yet
- CME Palliative Medicine (126358) : Self-Assessment QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesCME Palliative Medicine (126358) : Self-Assessment Questionnairealialison7666No ratings yet
- Advances in Heart Failure, Patient Management, ST2 TestingDocument44 pagesAdvances in Heart Failure, Patient Management, ST2 TestingPhan QuanNo ratings yet
- TamifluDocument20 pagesTamiflukiwikid718635No ratings yet
- Pathology & Clinical Laboratory (M) SDN - BHD: Scan QR For VerificationDocument2 pagesPathology & Clinical Laboratory (M) SDN - BHD: Scan QR For VerificationAdnan Md SaatNo ratings yet
- Molecular Prevalence of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Prisons: Case of The Central Prison of FrancevilleDocument8 pagesMolecular Prevalence of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Prisons: Case of The Central Prison of FrancevilleInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Assessment of Foetal Wellbeing.Document30 pagesAntenatal Assessment of Foetal Wellbeing.Kavya S MohanNo ratings yet
- Gi Pathogens Profile Sample ReportDocument2 pagesGi Pathogens Profile Sample ReportPuneet Kumar DhimanNo ratings yet
- OR AnesthesiaDocument6 pagesOR AnesthesiaLipa Alliza CaÑaNo ratings yet
- What Is Hypospadias?Document5 pagesWhat Is Hypospadias?Anonymous MWd5UOUuiyNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: Colorectal Cancer, Also Called Colon Cancer or Large Bowel Cancer, IncludesDocument18 pagesSigns and Symptoms: Colorectal Cancer, Also Called Colon Cancer or Large Bowel Cancer, Includesphvega06No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 and 1Document31 pagesChapter 2 and 1AduNo ratings yet
- TM194853GL HOTLINE White Paper HighlightsDocument2 pagesTM194853GL HOTLINE White Paper HighlightsAphichetNo ratings yet
- 9 Essential CBT Techniques and Tools PsychotherapyDocument4 pages9 Essential CBT Techniques and Tools Psychotherapyآئمہ توصيف100% (1)
- Fluids, PH, Ions and ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesFluids, PH, Ions and ElectrolytesthedancingseaNo ratings yet
- Emphysema: Pathophysiology / Drug Studies / Nursing Care Plans /health TeachingsDocument24 pagesEmphysema: Pathophysiology / Drug Studies / Nursing Care Plans /health TeachingsGeoffrey Sintaan RiveraNo ratings yet
- Data and Modeling Update VSHARE 729206 7 (MDHHS)Document40 pagesData and Modeling Update VSHARE 729206 7 (MDHHS)Caleb HollowayNo ratings yet
- NeutrophilDocument61 pagesNeutrophilJenivic Empig PuedanNo ratings yet
- MOSH-Chapter 10 Occupational VibrationDocument13 pagesMOSH-Chapter 10 Occupational Vibrationsiti zubaidahNo ratings yet
- Terpinen 4 OlDocument8 pagesTerpinen 4 OlDouglas RussellNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Part 2 DRAFTDocument6 pagesEndocrine Part 2 DRAFTPreeti Joan BuxaniNo ratings yet
- Elekta Versa HDDocument12 pagesElekta Versa HDHaider RabeeNo ratings yet
- uk-spc-nexium-sachet-10mg-DRESS-update-GI 21 0012aDocument17 pagesuk-spc-nexium-sachet-10mg-DRESS-update-GI 21 0012aDeisy ClerkeNo ratings yet
- Anti-MUM1 Antibody Ab104803: 1 Abreviews 2 ImagesDocument3 pagesAnti-MUM1 Antibody Ab104803: 1 Abreviews 2 Imageshorace35No ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument10 pagesCardiopulmonary ResuscitationLilay MakulayNo ratings yet