Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vitamin or Mineral Source
Vitamin or Mineral Source
Uploaded by
thorat82Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vitamin or Mineral Source
Vitamin or Mineral Source
Uploaded by
thorat82Copyright:
Available Formats
Vitamin or
Mineral
Examples of
Good Food
Sources
What It
Does
Recommended Daily
Amount
(RDA) or Adequate
Upper Limit
(The Highest Amount
You Can Take Without
Risk
Calcium Milk, yogurt, hard
cheeses, fortified
cereals, spinach
Essential for
bone growth and
strength, blood
clotting, muscle
contraction, and
the transmission
of nerve signals
Adults age 19-50: 1,000
milligrams/day
Adults age 51 and
up: 1,200 milligrams/day
2,500 milligrams/day
Choline
(Vitamin B
complex)
Milk, liver, eggs,
peanuts
Plays a key role
in the production
of cells and
neurotransmitter
s
Men: 550 milligrams/day
Women: 425
milligrams/day
Pregnantwomen: 450
milligrams/day
Breastfeedingwomen: 55
0 milligrams/day
3,500 milligrams/day
Chromium Meats, poultry,
fish, some cereals
Helps contro
lblood sugar
levels
Adult men age 19-50: 35
micrograms/day
Adult men age 51 and
up: 30 micrograms/day
Adult women age 19-
50: 25 micrograms/day
Adult women age 51 and
up:20 micrograms/day
Pregnant women: 30
micrograms/day
Breastfeeding
women: 45
micrograms/day
Unknown
Copper Seafood, nuts,
seeds, wheat
bran cereals,
whole grains
Important in
themetabolism o
f iron
Adults: 900
micrograms/dayPregnant
women: 1,000
micrograms/dayBreastfee
ding women: 1,300
micrograms/day
10,000 micrograms/day
Fiber Bran cereal, peas,
lentils, black
beans, fruits,
vegetables
Helps with
digestion and
the maintenance
of blood sugar
levels; reduces
the risk
of heartdisease
Adult men age 19-50: 38
grams/dayAdult men age
51 and up: 30
grams/dayAdult women
age 19-50: 25
grams/dayAdult women
age 51 and up:21
grams/dayPregnant
women: 28
grams/dayBreastfeeding
women: 29 grams/day
None
Fluoride Fluoridated water,
some sea fish,
sometoothpastes
and mouth rinses
Prevents the
formation
oftoothcavities a
nd stimulates
the growth of
bone
Adult men: 4
milligrams/dayAdult
women (including
pregnant and
breastfeeding):3
milligrams/day
10 milligrams/day
Folic Acid
(Folate)
Oranges,
Grapefruit,
Strawberries,
Spinach, Green
Peas,Bhendi,
beet,
cauliflower,
kanis,
Gajar,sunflower
Seed,brusell
Key for the
development of
cells, protein
metabolism
andheart health;
in pregnant
women, helps
prevent birth
defects
Adults: 400
micrograms/dayPregnant
women: 600
micrograms/dayBreastfee
ding women: 500
micrograms/day
1,000 micrograms/day
Iodine Processed foods
and iodized salt
Important in the
production
ofthyroid hormon
es
Adults: 150
micrograms/day Pregnant
women: 220
micrograms/day
Breastfeeding women: 290
micrograms/day
1,100 micrograms/day
Iron Fortified cereals,
beans, lentils,
beef, eggs
Key component
of red blood
cells and many
enzymes
Men: 8
milligrams/dayWomen age
19-50: 18
milligrams/dayWomen age
51 and up: 8
milligrams/dayPregnant
women: 27 milligrams/day
Breastfeeding women: 9
milligrams/day
45 milligrams/day
Magnesium Green leafy
vegetables, Brazil
nuts, almonds,
soybeans, halibut,
quinoa
Helps with heart
rhythm, muscle
and nerve
function, bone
strength
Adult men age 19-30: 400
milligrams/dayAdult men
age 31 and up: 420
milligrams/dayAdult
women age 19-30: 310
milligrams/day Adult
women age 31 and up:
320
milligrams/dayPregnant
women: 350-360
milligrams/dayBreastfeedi
ng women: 310-320
milligrams/day
For magnesium in food
and water, there is no
upper limit.
For magnesium
in supplementsor fortified
foods: 350 milligrams/day
Manganese Nuts, beans and
other legumes,
tea, whole grains
Important in
forming bones
and some
enzymes
Men: 2.3 milligrams/day
Adult women: 1.8
milligrams/day Pregnant
women: 2.0 milligrams/day
Breastfeeding women: 2.6
milligrams/day
11 milligrams/day
Molybdenum Legumes, grains,
nuts
Key in the
production of
some enzymes
Adults: 45
micrograms/dayPregnant
and breastfeeding
women: 50
micrograms/day
2,000 micrograms/day
Phosphorus Milk and other
dairy products,
peas, meat, eggs,
some cereals and
Allows cells to
function
normally; helps
the body
Adults: 700 milligrams/day Adults up to age
70: 4,000
milligrams/dayAdults
over age 70: 3,000
breads produce energy;
key in bone
growth
milligrams/dayPregnant
women: 3500
milligrams/dayBreastfee
ding women: 4,000
milligrams/day
Potassium Sweet potato,
bananas, yogurt,
yellowfin tuna,
soybeans
Important in
maintaining
normal fluid
balance; helps
control blood
pressure;
reduces risk of
kidney stones
Adults: 4,700 milligrams
per dayBreastfeeding
women: 5,100
milligrams/day
Unknown
Selenium Organ meats,
seafood, some
plants (if grown in
soil with
selenium) Brazil
nuts.
Protects cells
from damage;
regulates thyroid
hormone
Adults: 55
micrograms/dayPregnant
women: 60
micrograms/dayBreastfee
ding women: 70
micrograms/day
400 micrograms/day
Sodium Foods to which
sodium chloride
(salt) has been
added, like salted
meats, nuts,
butter, and a vast
number of
processed foods
Important for
fluid balance
Adults age 19-50: 1500
milligrams/dayAdults age
51-70: 1,300
milligrams/dayAdults age
71 and up: 1,200
milligrams/day
2,300 milligrams/day
Vitamin A Sweet potato with
peel, carrots,
spinach, fortified
cereals
Necessary for
normal vision,
immune
function,
reproduction
Men: 900
micrograms/dayWomen: 7
00 micrograms/day
3,000 micrograms/day
Vitamin
B
1
(Thiamin)
Whole grain,
enriched, fortified
products; bread;
cereals
Allows the body
to process
carbohydrates
and some
protein.
Men: 1.2
milligrams/dayWomen: 1.1
milligrams/dayPregnant
and breastfeeding
women: 1.4
milligrams/day
Unknown
Vitamin
B
2
(Riboflavin
)
Milk, bread
products, fortified
cereals
Key in
metabolism and
the conversion
of food into
energy; helps
produce red
blood cells
Men: 1.3 milligrams/day
Women: 1.1 milligrams/day
Pregnant Women: 1.4
milligrams/day
Breastfeeding Women: 1.6
milligrams/day
Unknown
Vitamin
B
3
(Niacin)
Meat, fish,
poultry, enriched
and whole grain
breads, fortified
cereals
Assists in
digestion and
the conversion
of food into
energy;
important in the
production of
cholesterol
Men: 16
milligrams/dayWomen: 14
milligrams/dayPregnant
Women: 18 milligrams/day
?Breastfeeding
women: 17 milligrams/day
For niacin in natural
sources, there is no
upper limit.
For niacin in supplements
or fortified foods: 35
milligrams/day
Vitamin
B
5
(Pantothen
ic Acid)
Chicken, beef,
potatoes, oats,
cereals, tomatoes
Important in fatty
acid metabolism
Adults: 5
milligrams/dayPregnant
women: 6
milligrams/dayBreastfeedi
ng women: 7
milligrams/day
Unknown
Vitamin B
6
Fortified cereals,
fortified soy
products, organ
meats
Important for the
nervous system;
helps the body
metabolize
proteins and
sugar
Men age 19-50:1.3
milligrams/dayMen age 51
up: 1.7
milligrams/dayWomen age
19-50: 1.3
milligrams/dayWomen age
51 up: 1.5
milligrams/dayPregnant
women: 1.9
milligrams/dayBreastfeedi
ng women: 2
milligrams/day
100 milligrams/day
Vitamin
B
7
(Biotin)
Liver, fruits,
meats
Helps with the
synthesis of fats,
glycogen and
amino acids
Adults: 30
micrograms/dayBreastfee
ding women: 35
micrograms/day
Unknown
Vitamin
B
12
(Cobalami
n)
Fish, poultry,
meat, fortified
cereals
Important in the
production of red
blood cells
Adults: 2.4
micrograms/dayPregnant
women: 2.6
micrograms/dayBreastfee
ding women: 2.8
micrograms/day
Unknown
Vitamin C Red and green
peppers, kiwis,
oranges,
strawberries,
broccoli
Antioxidant that
protects against
cell damage,
boosts the
immune system,
forms collagen
in the body
Men: 90
milligrams/dayWomen: 75
milligrams/dayPregnant
women: 85
milligrams/dayBreastfeedi
ng women: 120
milligrams/day
2,000 milligrams/day
Vitamin D
(Calciferol)
Fish liver oils,
fatty fish, fortified
milk products,
fortified cereals;
also, formed
naturally as a
result of sunlight
exposure
Crucial in
metabolizing
calcium for
healthy bones
Adults age 18-50: 5
micrograms/dayAdults
age 51-70: 10
micrograms/dayAdults
over age 70: 15
micrograms/dayPregnant
and breastfeeding
women: 5 micrograms/day
50 micrograms/day
Vitamin E
(alpha-
tocopherol)
Fortified cereals,
sunflower seeds,
almonds, peanut
butter, vegetable
oils
Antioxidant that
protects cells
against damage
Adults (including
pregnant women): 15
milligrams/dayBreastfeedi
ng women: 19
1,000 milligrams/day
Vitamin K Green vegetables
like spinach,
collards, and
broccoli; brussels
sprouts; cabbage
Important in
blood clotting
and bone health
Men: 120 micrograms/day
___
Women (including
pregnant and
breastfeeding):90
micrograms/day
Unknown
Zinc Red meats, some
seafood, fortified
cereals
Supports the
body's immunity
and nerve
function;
important in
reproduction
Men: 11 milligrams/day
___
Women: 8
milligrams/dayPregnant
women: 11
milligrams/dayBreastfeedi
ng women: 12
milligrams/day
40 milligrams/
You might also like
- Vitamin ChartDocument5 pagesVitamin ChartHimNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Nutrition FlyerDocument3 pagesPregnancy Nutrition Flyerapi-234728337No ratings yet
- Seminar PPT SangeethaDocument142 pagesSeminar PPT SangeethasangeethaNo ratings yet
- Hirarc For Tower CraneDocument2 pagesHirarc For Tower CraneShirako TakamotoNo ratings yet
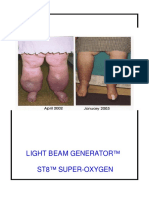
- Wow Light Beam Generator St8 Super-OxygenDocument44 pagesWow Light Beam Generator St8 Super-OxygenMilan Valachovic100% (1)
- English Name Indian / Hindi NameDocument9 pagesEnglish Name Indian / Hindi NameMantuNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Second Trimester PregnancyDocument8 pagesNutrition For Second Trimester PregnancysanthanalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Nutrition During PregnancyDocument11 pagesNutrition During PregnancyTjoema AsriNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & Minerals ChartDocument6 pagesVitamins & Minerals ChartfarhanyazdaniNo ratings yet
- Nutrition On Pregnant and Lactating MothersDocument11 pagesNutrition On Pregnant and Lactating Mothersclalaguna100% (1)
- Vitamins and Minerals - Google DriveDocument3 pagesVitamins and Minerals - Google DriveadriennenunnNo ratings yet
- Nutrient - Daily Amount Needed Information Fruit Sources Vegetable Sources Nut SourcesDocument10 pagesNutrient - Daily Amount Needed Information Fruit Sources Vegetable Sources Nut SourcesGopal PodderNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Pregnancy and Lactation PDFDocument33 pagesNutrition in Pregnancy and Lactation PDFmichael jan de celisNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument4 pagesVitaminsHemanth KokaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin ChartDocument4 pagesVitamin ChartBanu Priya100% (1)
- SMA AWiS Nutrition For Active WomenDocument2 pagesSMA AWiS Nutrition For Active WomenenergisemeNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients For HealthDocument4 pagesMicronutrients For HealthIsaac GoldNo ratings yet
- Expectant MotherDocument58 pagesExpectant MotherRex PaulrajNo ratings yet
- Nutrition During PregnancyDocument44 pagesNutrition During PregnancyMohnnad Hmood AlgaraybhNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PregnancyDocument52 pagesNutrition in Pregnancyboragam.saisharanyaNo ratings yet
- Continuation of Antepartal Care - NutritionDocument3 pagesContinuation of Antepartal Care - NutritionGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- The Best Vitamins and Supplements To Boost Your Fertility - ProgynyDocument3 pagesThe Best Vitamins and Supplements To Boost Your Fertility - ProgynyVanessa Maria de Miranda PontesNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy AllowancesDocument5 pagesPregnancy AllowancesAlyssa MercadoNo ratings yet
- MOST Assign1 VitaminsDocument6 pagesMOST Assign1 VitaminsbubblingbrookNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & Minerals: Presented By-Ms. Sumit Kumari Nursing Tutor SionDocument28 pagesVitamins & Minerals: Presented By-Ms. Sumit Kumari Nursing Tutor SionSumit YadavNo ratings yet
- Vitamin C WrittenDocument11 pagesVitamin C WrittenKimberly MolatoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Childhood & AdolescenceDocument13 pagesNutrition in Childhood & AdolescenceRonald A. SagangNo ratings yet
- Women's Health Booklet 1-10Document16 pagesWomen's Health Booklet 1-10Komala SariNo ratings yet
- Nutrients For FertilityDocument3 pagesNutrients For Fertilitykanishka upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Maternal Health - Nutritional Care During Pregnancy (Mumbai Mirror - 3 June 2010)Document2 pagesMaternal Health - Nutritional Care During Pregnancy (Mumbai Mirror - 3 June 2010)National Child Health Resource Centre (NCHRC)No ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Tamag, Vigan City 2700 Ilocos SurDocument26 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Tamag, Vigan City 2700 Ilocos SurJewel Ramos GalinatoNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A: A Pre-Formed Vitamin RETINOL and A Pro-Vitamin, Beta CaroteneDocument21 pagesVitamin A: A Pre-Formed Vitamin RETINOL and A Pro-Vitamin, Beta CarotenezuhaibjokhioNo ratings yet
- Vitamin & MineralsDocument18 pagesVitamin & MineralsdedefreddyNo ratings yet
- NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS DURING PREGNANCY by G.swathi - 20231213 - 223250 - 0000Document17 pagesNUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS DURING PREGNANCY by G.swathi - 20231213 - 223250 - 0000jamalNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 6Document37 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 6skeltenboiNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument7 pagesVitaminswol3No ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument18 pagesVitaminsAbdul QuddusNo ratings yet
- Physical Changes of Pregnant WomanDocument5 pagesPhysical Changes of Pregnant WomanLODY LEAN CRUZNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 9 - CompressedDocument14 pagesKelompok 9 - CompressedZiana BastariNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and LactationDocument62 pagesPregnancy and LactationFe Mina NisperosNo ratings yet
- Group3 Nutrition in The Adult YearsDocument20 pagesGroup3 Nutrition in The Adult YearsKAREN PEARL BAYUBAYNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Vegetarian NutritionDocument2 pagesPregnancy Vegetarian NutritionAles SandraNo ratings yet
- What Are Vitamins ?Document91 pagesWhat Are Vitamins ?muhammad amjadNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Requirements in Different AgeDocument58 pagesNutritional Requirements in Different AgeKate Emily YbañezNo ratings yet
- Why Do People Take Vitamin K?Document27 pagesWhy Do People Take Vitamin K?JamesBuensalidoDellavaNo ratings yet
- Article About VitaminsDocument12 pagesArticle About VitaminsMarvin Xylon M. JaenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Maternal Nutrition - 3.4.2024Document49 pagesLecture 7 - Maternal Nutrition - 3.4.2024Mohamed HamdyNo ratings yet
- Maternal Nutrition - AntepartumDocument25 pagesMaternal Nutrition - AntepartumServices CentreNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Mineral TABLEDocument1 pageVitamin and Mineral TABLEHibozoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition During Pregnancy: Joy Carsten and Emerson HartDocument18 pagesNutrition During Pregnancy: Joy Carsten and Emerson HartAntarnet AntarNo ratings yet
- Good Nutrition in Pregnancy: A Healthy Pregnancy Is Important For You and Your BabyDocument12 pagesGood Nutrition in Pregnancy: A Healthy Pregnancy Is Important For You and Your Babymicky mouseNo ratings yet
- 4 Idol Ko Si Nanay Module 4Document18 pages4 Idol Ko Si Nanay Module 4Mash JumahariNo ratings yet
- Food PyramidDocument12 pagesFood PyramidAgnes Enya LorraineNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Guidelines For A Multiple Pregnancy: Obstetrical Health PromotionDocument19 pagesNutritional Guidelines For A Multiple Pregnancy: Obstetrical Health PromotionLini Anisfatus SholihahNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 VITAMINSDocument36 pagesTopic 6 VITAMINSnaem nadzriNo ratings yet
- Basic-Grow Taller Nutrition GuideDocument18 pagesBasic-Grow Taller Nutrition GuideVlad VladNo ratings yet
- Doh 06Document26 pagesDoh 06Malack ChagwaNo ratings yet
- Healthy Food in Pregnancy and Mediterain Type of Food PyramidDocument14 pagesHealthy Food in Pregnancy and Mediterain Type of Food Pyramidfawzia rashediNo ratings yet
- Formatted Food N Nutrition EVS Notes 27th AugDocument5 pagesFormatted Food N Nutrition EVS Notes 27th AugGauravNo ratings yet
- Health and ofDocument35 pagesHealth and ofShinkaSihhahNo ratings yet
- Nutrional ProfileDocument117 pagesNutrional ProfileYash SuriNo ratings yet
- MCQ Financial Regulatory FrameworkDocument13 pagesMCQ Financial Regulatory Frameworkthorat82No ratings yet
- Placmnet Notice 1 4.8..15Document7 pagesPlacmnet Notice 1 4.8..15thorat82No ratings yet
- Application No. Rv0000280 REGISTRATION NO. 11021001606Document1 pageApplication No. Rv0000280 REGISTRATION NO. 11021001606thorat82No ratings yet
- Padmashree Dr. D.Y. Patil Institute of Master of Computer Applications, MBA (2 Shift)Document5 pagesPadmashree Dr. D.Y. Patil Institute of Master of Computer Applications, MBA (2 Shift)thorat82No ratings yet
- Accounting Basics Word Scramble QuestionsDocument1 pageAccounting Basics Word Scramble Questionsthorat82No ratings yet
- MBA 3rd Sem ListDocument115 pagesMBA 3rd Sem Listthorat82No ratings yet
- Pravin Thorat Lecturer Plan 2015 PDFDocument26 pagesPravin Thorat Lecturer Plan 2015 PDFthorat82No ratings yet
- Guidlines Final-2015-16 MbaDocument30 pagesGuidlines Final-2015-16 Mbathorat82No ratings yet
- Padmashree Dr. D.Y. Patil Institute of Master of Computer Applications, MBA (2 Shift)Document5 pagesPadmashree Dr. D.Y. Patil Institute of Master of Computer Applications, MBA (2 Shift)thorat82No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Students: First Year MBA Academic Year: 2015 - 2016Document4 pagesGuidelines For Students: First Year MBA Academic Year: 2015 - 2016thorat82No ratings yet
- Induction Schedule 2015-17 BatchDocument1 pageInduction Schedule 2015-17 Batchthorat82No ratings yet
- Microsoft: Get Up To SpeedDocument65 pagesMicrosoft: Get Up To Speedthorat82No ratings yet
- Acknowledgement C LanguageDocument1 pageAcknowledgement C Languagethorat82No ratings yet
- Brigada Eskwela 2019 Sportsfest Narrative Report I. RationaleDocument3 pagesBrigada Eskwela 2019 Sportsfest Narrative Report I. RationaleJilian MeiNo ratings yet
- FIH 6e Ch01 NotesDocument13 pagesFIH 6e Ch01 NotesCamilo Soto CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Precision MedicineDocument23 pagesPrecision Medicinecelecosib100% (1)
- SALVO Newsletter Apr 15Document2 pagesSALVO Newsletter Apr 15Women's Health Research UnitNo ratings yet
- The Role of Complementary and Alternative Therapies in Managing Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument1 pageThe Role of Complementary and Alternative Therapies in Managing Rheumatoid Arthritisjelena_bojovic1No ratings yet
- Executive Summary (1-3)Document3 pagesExecutive Summary (1-3)Jennelyn Solomon PaduaNo ratings yet
- Ictm FinalsreviewerDocument13 pagesIctm FinalsreviewerDenize Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Tacrolimus Ointment Is Used To Treat The Symptoms of EczemaDocument2 pagesTacrolimus Ointment Is Used To Treat The Symptoms of EczemaSharan SahotaNo ratings yet
- Rabies Vaccine and Rabies Immune Globulin Fact Sheet PDFDocument3 pagesRabies Vaccine and Rabies Immune Globulin Fact Sheet PDFWelly WongNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in MAPEH (Health 7) Semi DetailedDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in MAPEH (Health 7) Semi DetailedZchecsh Blace AceNo ratings yet
- Interferential TherapyDocument12 pagesInterferential TherapySherief MansourNo ratings yet
- Summary Maulik SiddhantDocument46 pagesSummary Maulik SiddhantErshad Shafi AhmedNo ratings yet
- TOPIC: Financial Stability of Grade 11 Students: Firsts Question 1.what Is The Topic/problem About?Document2 pagesTOPIC: Financial Stability of Grade 11 Students: Firsts Question 1.what Is The Topic/problem About?Heinrich VergaraNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Setera Case 8Document10 pagesDRUG STUDY Setera Case 8Ceria Dorena Fe SeteraNo ratings yet
- Rapid Risk Assessment of Acute Public Health EventsDocument44 pagesRapid Risk Assessment of Acute Public Health EventsdinahajjarNo ratings yet
- Clinical ExperienceDocument2 pagesClinical Experienceapi-509074425No ratings yet
- Zeva 1 - MSDSDocument6 pagesZeva 1 - MSDSRowi ArifudinNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 1: Medical Ethics IiiDocument16 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Type 1: Medical Ethics IiiGiane DavidNo ratings yet
- CV Rachael CostelloDocument3 pagesCV Rachael Costellorachael costelloNo ratings yet
- Fuo, Sepsis and Septic Shock: Clinical Clerk Mary Christine S. IlangaDocument62 pagesFuo, Sepsis and Septic Shock: Clinical Clerk Mary Christine S. IlangaPraise BechaydaNo ratings yet
- Simulation Integration Simulation Integration: Strategies For The Effective Implementation of Scenario-Based TrainingDocument20 pagesSimulation Integration Simulation Integration: Strategies For The Effective Implementation of Scenario-Based TrainingCuty GomezNo ratings yet
- Fi ADocument67 pagesFi AalfonsoNo ratings yet
- The Sadvaidyasla Private Limited Catalogue of MedicinesDocument39 pagesThe Sadvaidyasla Private Limited Catalogue of MedicinesHiramandalam PatanjaliNo ratings yet
- 4 .unit-IVDocument73 pages4 .unit-IVPriya bhattiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Tool For The Geriatric PatientDocument5 pagesAssessment Tool For The Geriatric PatientGlaizalyn Fabella Tagoon100% (1)
- Brain Tumor: Basics .. What Is Primary Brain Tumor ?. Initiating Care Plan For Primary Brain Tumor PatientDocument20 pagesBrain Tumor: Basics .. What Is Primary Brain Tumor ?. Initiating Care Plan For Primary Brain Tumor Patientahmed_alkiady100% (1)
- Dating Violence ThesisDocument4 pagesDating Violence Thesisafjrqokne100% (2)
- Benefits of Listening To Music - Nino ChigogaDocument2 pagesBenefits of Listening To Music - Nino ChigogaNino ShergelashviliNo ratings yet