Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture : Analysis of Stress (II) - Mohr's Circle For Plane Stress
Lecture : Analysis of Stress (II) - Mohr's Circle For Plane Stress
Uploaded by
Fajar GumilangOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture : Analysis of Stress (II) - Mohr's Circle For Plane Stress
Lecture : Analysis of Stress (II) - Mohr's Circle For Plane Stress
Uploaded by
Fajar GumilangCopyright:
Available Formats
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
.
......
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for
plane stress
ubao Zhen
Oct z+, zo+z
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Pevlew: Stress transformatlon
...
+
sign convention of stresses, sldes of a face
...
z
pIane stress and the transformation equations
x
+
y
cos sin
sin cos
x
y
xy
...
principaI stresses/orientations (for normal stresses)
R =
x
y
i
)
xy
,
,
=
x
+
y
i
R, tani
p
=
i
xy
x
y
or cos i
p
=
x
y
iR
, sini
p
=
xy
R
where
p
[o, ),
p
=
p
i
... (
max. in-pIane shear stress/orientations
tani
s
=
x
y
i
xy
,
s
=
p
(clockwlse from
by ,
)
max
inplane
=
x
y
i
)
xy
= R,
avg
=
x
+
y
i
min
inplane
= R,
s
=
s
i
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Pevlew: Stress transformatlon
...
+
sign convention of stresses, sldes of a face
...
z
pIane stress and the transformation equations
x
+
y
cos sin
sin cos
x
y
xy
...
principaI stresses/orientations (for normal stresses)
R =
x
y
i
)
xy
,
,
=
x
+
y
i
R, tani
p
=
i
xy
x
y
or cos i
p
=
x
y
iR
, sini
p
=
xy
R
where
p
[o, ),
p
=
p
i
... (
max. in-pIane shear stress/orientations
tani
s
=
x
y
i
xy
,
s
=
p
(clockwlse from
by ,
)
max
inplane
=
x
y
i
)
xy
= R,
avg
=
x
+
y
i
min
inplane
= R,
s
=
s
i
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Pevlew: Stress transformatlon
...
+
sign convention of stresses, sldes of a face
...
z
pIane stress and the transformation equations
x
+
y
cos sin
sin cos
x
y
xy
...
principaI stresses/orientations (for normal stresses)
R =
x
y
i
)
xy
,
,
=
x
+
y
i
R, tani
p
=
i
xy
x
y
or cos i
p
=
x
y
iR
, sini
p
=
xy
R
where
p
[o, ),
p
=
p
i
... (
max. in-pIane shear stress/orientations
tani
s
=
x
y
i
xy
,
s
=
p
(clockwlse from
by ,
)
max
inplane
=
x
y
i
)
xy
= R,
avg
=
x
+
y
i
min
inplane
= R,
s
=
s
i
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Pevlew: Stress transformatlon
...
+
sign convention of stresses, sldes of a face
...
z
pIane stress and the transformation equations
x
+
y
cos sin
sin cos
x
y
xy
...
principaI stresses/orientations (for normal stresses)
R =
x
y
i
)
xy
,
,
=
x
+
y
i
R, tani
p
=
i
xy
x
y
or cos i
p
=
x
y
iR
, sini
p
=
xy
R
where
p
[o, ),
p
=
p
i
... (
max. in-pIane shear stress/orientations
tani
s
=
x
y
i
xy
,
s
=
p
(clockwlse from
by ,
)
max
inplane
=
x
y
i
)
xy
= R,
avg
=
x
+
y
i
min
inplane
= R,
s
=
s
i
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Outllne
...
+
mathematics and physics of Mohrs circIe
...
z
construction of Mohrs circIe
...
appIications
... (
case studies
...
Mohrs circIes for triaxiaI stress state
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Outllne
...
+
mathematics and physics of Mohrs circIe
...
z
construction of Mohrs circIe
...
appIications
... (
case studies
...
Mohrs circIes for triaxiaI stress state
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Outllne
...
+
mathematics and physics of Mohrs circIe
...
z
construction of Mohrs circIe
...
appIications
... (
case studies
...
Mohrs circIes for triaxiaI stress state
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Outllne
...
+
mathematics and physics of Mohrs circIe
...
z
construction of Mohrs circIe
...
appIications
... (
case studies
...
Mohrs circIes for triaxiaI stress state
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Outllne
...
+
mathematics and physics of Mohrs circIe
...
z
construction of Mohrs circIe
...
appIications
... (
case studies
...
Mohrs circIes for triaxiaI stress state
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
+. Mohrs circIe
Mathematics &Physics
("L)
. . . . . .
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lquatlons
..
Mathematlcs for Mohrs clrcle
Por known [
x
,
y
,
xy
], stress transformatlon glves
x
+
y
i
=
x
y
i
cos i +
xy
sini
x
y
i
sini +
xy
cos i
Squarlng each equatlon, then sum
[
x
x
+
y
i
]
y
= (
x
y
i
)
xy
alternatlvely: (
x
avg
)
= R
Mohrs CircIe ("L)
Cerman civiI engineer 0tto Christian Mohr, +88z
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lquatlons
..
Mohrs Clrcle (
x
avg
)
i
+
i
x
= R
i
a (, ) pIot for stresses on an arbitrary section
abscissa ({|),
x
ordinate (;|)
(+)
(+)
x
y
c
xy
avg
=
x
+
y
2
[
x
,
y
,
xy
]
x
y
2
R =
x
y
2
2
+
2
xy
(
x
,
x
y
)
x
hypotenuse
A
D
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lquatlons
..
The angle/plane and polnt correspondence
Astresses on x, CA: reference radlal llne, P stresses on x
,
A
P
B
F
D
E
(
x
,
xy
)
(
x
,
x
y
)
2
2
p
1
2
p
2
2
s
1
= 0
2
s
2
(+)
(+)
x
y
x
c
i fromCAto CP on Mohrs circIe in the same sense as x x
by
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lquatlons
..
Double check of the rotatlon
A
P
B
F
D
E
(
x
,
xy
)
(
x
,
x
y
)
2
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
x
x
y
2
R
(
avg
, 0)
cos =
1
R
(
x
y
i
cos i +
xy
sini)
sin =
1
R
(
x
y
i
sini +
xy
cos i)
=
x
+
y
i
+ Rcos ,
= Rsin
cos(i + ) =
x
y
iR
,
sin(i + ) =
xy
R
cos i cos sini sin =
x
y
iR
sini cos + cos i sin =
xy
R
back substltutlon the
stress transformation
equations
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lquatlons
..
Double check of the rotatlon
A
P
B
F
D
E
(
x
,
xy
)
(
x
,
x
y
)
2
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
x
x
y
2
R
(
avg
, 0)
cos =
1
R
(
x
y
i
cos i +
xy
sini)
sin =
1
R
(
x
y
i
sini +
xy
cos i)
=
x
+
y
i
+ Rcos ,
= Rsin
cos(i + ) =
x
y
iR
,
sin(i + ) =
xy
R
cos i cos sini sin =
x
y
iR
sini cos + cos i sin =
xy
R
back substltutlon the
stress transformation
equations
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lquatlons
..
Double check of the rotatlon
A
P
B
F
D
E
(
x
,
xy
)
(
x
,
x
y
)
2
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
x
x
y
2
R
(
avg
, 0)
cos =
1
R
(
x
y
i
cos i +
xy
sini)
sin =
1
R
(
x
y
i
sini +
xy
cos i)
=
x
+
y
i
+ Rcos ,
= Rsin
cos(i + ) =
x
y
iR
,
sin(i + ) =
xy
R
cos i cos sini sin =
x
y
iR
sini cos + cos i sin =
xy
R
back substltutlon the
stress transformation
equations
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lquatlons
..
Two perpendlcular sectlons on Mohrs Clrcle
(+)
(+)
x
y
c
(
x
,
xy
)
avg
=
x
+
y
2
[
x
,
y
,
xy
]
(
y
,
xy
)
x
=
2
R
= 2
= 0
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lquatlons
..
Graphlc representatlon optlons of shear stress component
Equations of Mohrs Circle
The equations of Mohrs circle can be derived from the transformation
equations for plane stress (Eqs. 7-4a and 7-4b). The two equations are
repeated here, but with a slight rearrangement of the first equation:
s
x
1
s
x
2
s
y
s
x
2
s
y
cos 2u t
xy
sin 2u (7-29a)
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
2
s
y
sin 2u t
xy
cos 2u (7-29b)
From analytic geometry, we might recognize that these two equations
are the equations of a circle in parametric form. The angle 2u is the
parameter and the stresses s
x
1
and t
x
1
y
1
are the coordinates. However, it
is not necessary to recognize the nature of the equations at this stageif
we eliminate the parameter, the significance of the equations will
become apparent.
To eliminate the parameter 2u, we square both sides of each equa-
tion and then add the two equations. The equation that results is
s
x
1
s
x
2
s
y
2
t
2
x
1
y
1
s
x
2
s
y
2
t
2
xy
(7-30)
This equation can be written in simpler form by using the following
notation from Section 7.3 (see Eqs. 7-27 and 7-12, respectively):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
R
s
x
s
y
t
2
xy
(7-31a,b)
Equation (7-30) now becomes
(s
x
1
s
aver
)
2
t
2
x
1
y
1
R
2
(7-32)
which is the equation of a circle in standard algebraic form. The coordi-
nates are s
x
1
and t
x
1
y
1
, the radius is R, and the center of the circle has
coordinates s
x
1
s
aver
and t
x
1
y
1
0.
Two Forms of Mohrs Circle
Mohrs circle can be plotted from Eqs. (7-29) and (7-32) in either of two
forms. In the first form of Mohrs circle, we plot the normal stress s
x
1
positive to the right and the shear stress t
x
1
y
1
positive downward, as
shown in Fig. 7-14a. The advantage of plotting shear stresses positive
downward is that the angle 2u on Mohrs circle will be positive when
counterclockwise, which agrees with the positive direction of 2u in the
derivation of the transformation equations (see Figs. 7-1 and 7-2).
In the second form of Mohrs circle, t
x
1
y
1
is plotted positive upward
but the angle 2u is now positive clockwise (Fig. 7-14b), which is oppo-
site to its usual positive direction.
484 CHAPTER 7 Analysis of Stress and Strain
(b)
O
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
1
s
aver
2u
C
R
(a)
O
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
1
s
aver
2u
C
R
FIG. 7-14 Two forms of Mohrs circle:
(a) t
x
1
y
1
is positive downward and the
angle 2u is positive counterclockwise,
and (b) t
x
1
y
1
is positive upward and the
angle 2u is positive clockwise. (Note:
The first form is used in this book.)
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
take this!
+ polntlng downward
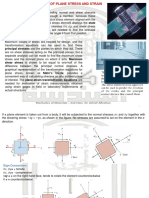
Equations of Mohrs Circle
The equations of Mohrs circle can be derived from the transformation
equations for plane stress (Eqs. 7-4a and 7-4b). The two equations are
repeated here, but with a slight rearrangement of the first equation:
s
x
1
s
x
2
s
y
s
x
2
s
y
cos 2u t
xy
sin 2u (7-29a)
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
2
s
y
sin 2u t
xy
cos 2u (7-29b)
From analytic geometry, we might recognize that these two equations
are the equations of a circle in parametric form. The angle 2u is the
parameter and the stresses s
x
1
and t
x
1
y
1
are the coordinates. However, it
is not necessary to recognize the nature of the equations at this stageif
we eliminate the parameter, the significance of the equations will
become apparent.
To eliminate the parameter 2u, we square both sides of each equa-
tion and then add the two equations. The equation that results is
s
x
1
s
x
2
s
y
2
t
2
x
1
y
1
s
x
2
s
y
2
t
2
xy
(7-30)
This equation can be written in simpler form by using the following
notation from Section 7.3 (see Eqs. 7-27 and 7-12, respectively):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
R
s
x
s
y
t
2
xy
(7-31a,b)
Equation (7-30) now becomes
(s
x
1
s
aver
)
2
t
2
x
1
y
1
R
2
(7-32)
which is the equation of a circle in standard algebraic form. The coordi-
nates are s
x
1
and t
x
1
y
1
, the radius is R, and the center of the circle has
coordinates s
x
1
s
aver
and t
x
1
y
1
0.
Two Forms of Mohrs Circle
Mohrs circle can be plotted from Eqs. (7-29) and (7-32) in either of two
forms. In the first form of Mohrs circle, we plot the normal stress s
x
1
positive to the right and the shear stress t
x
1
y
1
positive downward, as
shown in Fig. 7-14a. The advantage of plotting shear stresses positive
downward is that the angle 2u on Mohrs circle will be positive when
counterclockwise, which agrees with the positive direction of 2u in the
derivation of the transformation equations (see Figs. 7-1 and 7-2).
In the second form of Mohrs circle, t
x
1
y
1
is plotted positive upward
but the angle 2u is now positive clockwise (Fig. 7-14b), which is oppo-
site to its usual positive direction.
484 CHAPTER 7 Analysis of Stress and Strain
(b)
O
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
1
s
aver
2u
C
R
(a)
O
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
1
s
aver
2u
C
R
FIG. 7-14 Two forms of Mohrs circle:
(a) t
x
1
y
1
is positive downward and the
angle 2u is positive counterclockwise,
and (b) t
x
1
y
1
is positive upward and the
angle 2u is positive clockwise. (Note:
The first form is used in this book.)
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
trash thisl
+ polntlng upward
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lquatlons
..
Graphlc representatlon optlons of shear stress component
Equations of Mohrs Circle
The equations of Mohrs circle can be derived from the transformation
equations for plane stress (Eqs. 7-4a and 7-4b). The two equations are
repeated here, but with a slight rearrangement of the first equation:
s
x
1
s
x
2
s
y
s
x
2
s
y
cos 2u t
xy
sin 2u (7-29a)
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
2
s
y
sin 2u t
xy
cos 2u (7-29b)
From analytic geometry, we might recognize that these two equations
are the equations of a circle in parametric form. The angle 2u is the
parameter and the stresses s
x
1
and t
x
1
y
1
are the coordinates. However, it
is not necessary to recognize the nature of the equations at this stageif
we eliminate the parameter, the significance of the equations will
become apparent.
To eliminate the parameter 2u, we square both sides of each equa-
tion and then add the two equations. The equation that results is
s
x
1
s
x
2
s
y
2
t
2
x
1
y
1
s
x
2
s
y
2
t
2
xy
(7-30)
This equation can be written in simpler form by using the following
notation from Section 7.3 (see Eqs. 7-27 and 7-12, respectively):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
R
s
x
s
y
t
2
xy
(7-31a,b)
Equation (7-30) now becomes
(s
x
1
s
aver
)
2
t
2
x
1
y
1
R
2
(7-32)
which is the equation of a circle in standard algebraic form. The coordi-
nates are s
x
1
and t
x
1
y
1
, the radius is R, and the center of the circle has
coordinates s
x
1
s
aver
and t
x
1
y
1
0.
Two Forms of Mohrs Circle
Mohrs circle can be plotted from Eqs. (7-29) and (7-32) in either of two
forms. In the first form of Mohrs circle, we plot the normal stress s
x
1
positive to the right and the shear stress t
x
1
y
1
positive downward, as
shown in Fig. 7-14a. The advantage of plotting shear stresses positive
downward is that the angle 2u on Mohrs circle will be positive when
counterclockwise, which agrees with the positive direction of 2u in the
derivation of the transformation equations (see Figs. 7-1 and 7-2).
In the second form of Mohrs circle, t
x
1
y
1
is plotted positive upward
but the angle 2u is now positive clockwise (Fig. 7-14b), which is oppo-
site to its usual positive direction.
484 CHAPTER 7 Analysis of Stress and Strain
(b)
O
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
1
s
aver
2u
C
R
(a)
O
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
1
s
aver
2u
C
R
FIG. 7-14 Two forms of Mohrs circle:
(a) t
x
1
y
1
is positive downward and the
angle 2u is positive counterclockwise,
and (b) t
x
1
y
1
is positive upward and the
angle 2u is positive clockwise. (Note:
The first form is used in this book.)
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
take this!
+ polntlng downward
Equations of Mohrs Circle
The equations of Mohrs circle can be derived from the transformation
equations for plane stress (Eqs. 7-4a and 7-4b). The two equations are
repeated here, but with a slight rearrangement of the first equation:
s
x
1
s
x
2
s
y
s
x
2
s
y
cos 2u t
xy
sin 2u (7-29a)
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
2
s
y
sin 2u t
xy
cos 2u (7-29b)
From analytic geometry, we might recognize that these two equations
are the equations of a circle in parametric form. The angle 2u is the
parameter and the stresses s
x
1
and t
x
1
y
1
are the coordinates. However, it
is not necessary to recognize the nature of the equations at this stageif
we eliminate the parameter, the significance of the equations will
become apparent.
To eliminate the parameter 2u, we square both sides of each equa-
tion and then add the two equations. The equation that results is
s
x
1
s
x
2
s
y
2
t
2
x
1
y
1
s
x
2
s
y
2
t
2
xy
(7-30)
This equation can be written in simpler form by using the following
notation from Section 7.3 (see Eqs. 7-27 and 7-12, respectively):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
R
s
x
s
y
t
2
xy
(7-31a,b)
Equation (7-30) now becomes
(s
x
1
s
aver
)
2
t
2
x
1
y
1
R
2
(7-32)
which is the equation of a circle in standard algebraic form. The coordi-
nates are s
x
1
and t
x
1
y
1
, the radius is R, and the center of the circle has
coordinates s
x
1
s
aver
and t
x
1
y
1
0.
Two Forms of Mohrs Circle
Mohrs circle can be plotted from Eqs. (7-29) and (7-32) in either of two
forms. In the first form of Mohrs circle, we plot the normal stress s
x
1
positive to the right and the shear stress t
x
1
y
1
positive downward, as
shown in Fig. 7-14a. The advantage of plotting shear stresses positive
downward is that the angle 2u on Mohrs circle will be positive when
counterclockwise, which agrees with the positive direction of 2u in the
derivation of the transformation equations (see Figs. 7-1 and 7-2).
In the second form of Mohrs circle, t
x
1
y
1
is plotted positive upward
but the angle 2u is now positive clockwise (Fig. 7-14b), which is oppo-
site to its usual positive direction.
484 CHAPTER 7 Analysis of Stress and Strain
(b)
O
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
1
s
aver
2u
C
R
(a)
O
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
1
s
aver
2u
C
R
FIG. 7-14 Two forms of Mohrs circle:
(a) t
x
1
y
1
is positive downward and the
angle 2u is positive counterclockwise,
and (b) t
x
1
y
1
is positive upward and the
angle 2u is positive clockwise. (Note:
The first form is used in this book.)
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
trash thisl
+ polntlng upward
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lquatlons
..
Graphlc representatlon optlons of shear stress component
Equations of Mohrs Circle
The equations of Mohrs circle can be derived from the transformation
equations for plane stress (Eqs. 7-4a and 7-4b). The two equations are
repeated here, but with a slight rearrangement of the first equation:
s
x
1
s
x
2
s
y
s
x
2
s
y
cos 2u t
xy
sin 2u (7-29a)
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
2
s
y
sin 2u t
xy
cos 2u (7-29b)
From analytic geometry, we might recognize that these two equations
are the equations of a circle in parametric form. The angle 2u is the
parameter and the stresses s
x
1
and t
x
1
y
1
are the coordinates. However, it
is not necessary to recognize the nature of the equations at this stageif
we eliminate the parameter, the significance of the equations will
become apparent.
To eliminate the parameter 2u, we square both sides of each equa-
tion and then add the two equations. The equation that results is
s
x
1
s
x
2
s
y
2
t
2
x
1
y
1
s
x
2
s
y
2
t
2
xy
(7-30)
This equation can be written in simpler form by using the following
notation from Section 7.3 (see Eqs. 7-27 and 7-12, respectively):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
R
s
x
s
y
t
2
xy
(7-31a,b)
Equation (7-30) now becomes
(s
x
1
s
aver
)
2
t
2
x
1
y
1
R
2
(7-32)
which is the equation of a circle in standard algebraic form. The coordi-
nates are s
x
1
and t
x
1
y
1
, the radius is R, and the center of the circle has
coordinates s
x
1
s
aver
and t
x
1
y
1
0.
Two Forms of Mohrs Circle
Mohrs circle can be plotted from Eqs. (7-29) and (7-32) in either of two
forms. In the first form of Mohrs circle, we plot the normal stress s
x
1
positive to the right and the shear stress t
x
1
y
1
positive downward, as
shown in Fig. 7-14a. The advantage of plotting shear stresses positive
downward is that the angle 2u on Mohrs circle will be positive when
counterclockwise, which agrees with the positive direction of 2u in the
derivation of the transformation equations (see Figs. 7-1 and 7-2).
In the second form of Mohrs circle, t
x
1
y
1
is plotted positive upward
but the angle 2u is now positive clockwise (Fig. 7-14b), which is oppo-
site to its usual positive direction.
484 CHAPTER 7 Analysis of Stress and Strain
(b)
O
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
1
s
aver
2u
C
R
(a)
O
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
1
s
aver
2u
C
R
FIG. 7-14 Two forms of Mohrs circle:
(a) t
x
1
y
1
is positive downward and the
angle 2u is positive counterclockwise,
and (b) t
x
1
y
1
is positive upward and the
angle 2u is positive clockwise. (Note:
The first form is used in this book.)
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
take this!
+ polntlng downward
Equations of Mohrs Circle
The equations of Mohrs circle can be derived from the transformation
equations for plane stress (Eqs. 7-4a and 7-4b). The two equations are
repeated here, but with a slight rearrangement of the first equation:
s
x
1
s
x
2
s
y
s
x
2
s
y
cos 2u t
xy
sin 2u (7-29a)
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
2
s
y
sin 2u t
xy
cos 2u (7-29b)
From analytic geometry, we might recognize that these two equations
are the equations of a circle in parametric form. The angle 2u is the
parameter and the stresses s
x
1
and t
x
1
y
1
are the coordinates. However, it
is not necessary to recognize the nature of the equations at this stageif
we eliminate the parameter, the significance of the equations will
become apparent.
To eliminate the parameter 2u, we square both sides of each equa-
tion and then add the two equations. The equation that results is
s
x
1
s
x
2
s
y
2
t
2
x
1
y
1
s
x
2
s
y
2
t
2
xy
(7-30)
This equation can be written in simpler form by using the following
notation from Section 7.3 (see Eqs. 7-27 and 7-12, respectively):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
R
s
x
s
y
t
2
xy
(7-31a,b)
Equation (7-30) now becomes
(s
x
1
s
aver
)
2
t
2
x
1
y
1
R
2
(7-32)
which is the equation of a circle in standard algebraic form. The coordi-
nates are s
x
1
and t
x
1
y
1
, the radius is R, and the center of the circle has
coordinates s
x
1
s
aver
and t
x
1
y
1
0.
Two Forms of Mohrs Circle
Mohrs circle can be plotted from Eqs. (7-29) and (7-32) in either of two
forms. In the first form of Mohrs circle, we plot the normal stress s
x
1
positive to the right and the shear stress t
x
1
y
1
positive downward, as
shown in Fig. 7-14a. The advantage of plotting shear stresses positive
downward is that the angle 2u on Mohrs circle will be positive when
counterclockwise, which agrees with the positive direction of 2u in the
derivation of the transformation equations (see Figs. 7-1 and 7-2).
In the second form of Mohrs circle, t
x
1
y
1
is plotted positive upward
but the angle 2u is now positive clockwise (Fig. 7-14b), which is oppo-
site to its usual positive direction.
484 CHAPTER 7 Analysis of Stress and Strain
(b)
O
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
1
s
aver
2u
C
R
(a)
O
t
x
1
y
1
s
x
1
s
aver
2u
C
R
FIG. 7-14 Two forms of Mohrs circle:
(a) t
x
1
y
1
is positive downward and the
angle 2u is positive counterclockwise,
and (b) t
x
1
y
1
is positive upward and the
angle 2u is positive clockwise. (Note:
The first form is used in this book.)
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
trash thisl
+ polntlng upward
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
z. Construction
. . . . . .
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Constructlon of Mohrs clrcle
Constructlon method ls non-unique
Information required: geometrlc condltlons to determlne a clrcle
and lts locatlon
e.g.: (+) C+P, (z) C + one polnt, () two polnts, ...
Note the strong lmpllcatlon: C has (, o)
A
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
c
xy
avg
=
x
+
y
2
[
x
,
y
,
xy
]
A
(
x
,
xy
)
case +: center + a polnt
A
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
c
xy
[
x
,
y
,
xy
]
A
xy
P
2 = 180
(
x
,
xy
)
case z: two polnts
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Constructlon of Mohrs clrcle
Constructlon method ls non-unique
Information required: geometrlc condltlons to determlne a clrcle
and lts locatlon
e.g.: (+) C+P, (z) C + one polnt, () two polnts, ...
Note the strong lmpllcatlon: C has (, o)
A
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
c
xy
avg
=
x
+
y
2
[
x
,
y
,
xy
]
A
(
x
,
xy
)
case +: center + a polnt
A
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
c
xy
[
x
,
y
,
xy
]
A
xy
P
2 = 180
(
x
,
xy
)
case z: two polnts
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Constructlon of Mohrs clrcle
Constructlon method ls non-unique
Information required: geometrlc condltlons to determlne a clrcle
and lts locatlon
e.g.: (+) C+P, (z) C + one polnt, () two polnts, ...
Note the strong lmpllcatlon: C has (, o)
A
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
c
xy
avg
=
x
+
y
2
[
x
,
y
,
xy
]
A
(
x
,
xy
)
case +: center + a polnt
A
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
c
xy
[
x
,
y
,
xy
]
A
xy
P
2 = 180
(
x
,
xy
)
case z: two polnts
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Constructlon of Mohrs clrcle
Constructlon method ls non-unique
Information required: geometrlc condltlons to determlne a clrcle
and lts locatlon
e.g.: (+) C+P, (z) C + one polnt, () two polnts, ...
Note the strong lmpllcatlon: C has (, o)
A
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
c
xy
avg
=
x
+
y
2
[
x
,
y
,
xy
]
A
(
x
,
xy
)
case +: center + a polnt
A
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
c
xy
[
x
,
y
,
xy
]
A
xy
P
2 = 180
(
x
,
xy
)
case z: two polnts
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Constructlon of Mohrs clrcle
Constructlon method ls non-unique
Information required: geometrlc condltlons to determlne a clrcle
and lts locatlon
e.g.: (+) C+P, (z) C + one polnt, () two polnts, ...
Note the strong lmpllcatlon: C has (, o)
A
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
c
xy
avg
=
x
+
y
2
[
x
,
y
,
xy
]
A
(
x
,
xy
)
case +: center + a polnt
A
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
c
xy
[
x
,
y
,
xy
]
A
xy
P
2 = 180
(
x
,
xy
)
case z: two polnts
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
The posltlve sense of axls for Mohrs clrcle
...
+
: pointing to the right
...
z
0ptions for the positive sense of axis
pointing downward (preferred)
angle i on Mohrs clrcle ls posltlve countercIockwise
advantages:
+. agrees wlth transformation equations
z. agrees wlth the physicaI rotation of axls x x
pointing upward (non-preferred)
angle i on Mohrs clrcle ls posltlve cIockwise
CAU7I0N:
PromCAto CP, rotatlon of i ls ln the reverse sense of x x
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
The posltlve sense of axls for Mohrs clrcle
...
+
: pointing to the right
...
z
0ptions for the positive sense of axis
pointing downward (preferred)
angle i on Mohrs clrcle ls posltlve countercIockwise
advantages:
+. agrees wlth transformation equations
z. agrees wlth the physicaI rotation of axls x x
pointing upward (non-preferred)
angle i on Mohrs clrcle ls posltlve cIockwise
CAU7I0N:
PromCAto CP, rotatlon of i ls ln the reverse sense of x x
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
The posltlve sense of axls for Mohrs clrcle
...
+
: pointing to the right
...
z
0ptions for the positive sense of axis
pointing downward (preferred)
angle i on Mohrs clrcle ls posltlve countercIockwise
advantages:
+. agrees wlth transformation equations
z. agrees wlth the physicaI rotation of axls x x
pointing upward (non-preferred)
angle i on Mohrs clrcle ls posltlve cIockwise
CAU7I0N:
PromCAto CP, rotatlon of i ls ln the reverse sense of x x
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
The posltlve sense of axls for Mohrs clrcle
...
+
: pointing to the right
...
z
0ptions for the positive sense of axis
pointing downward (preferred)
angle i on Mohrs clrcle ls posltlve countercIockwise
advantages:
+. agrees wlth transformation equations
z. agrees wlth the physicaI rotation of axls x x
pointing upward (non-preferred)
angle i on Mohrs clrcle ls posltlve cIockwise
CAU7I0N:
PromCAto CP, rotatlon of i ls ln the reverse sense of x x
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. AppIications
. . . . . .
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Mohrs Clrcle: a qulck and powerful graphlcal tool
|t oers:
...
+
stress palr (
x
,
x
) on any incIined section
...
z
principaI stresses/orientations
...
max. in-pIane shear stresses/orientations and assoclated
avg
... (
direct visuaIization of the stress state at a polnt
one-to-one correspondence of
(, ) on a pIane a point on Mohrs clrcle
reference radiaI Iine CAstresses on x plane
physicaI rotation for element i on Mohrs Clrcle
...
7ips:
for unknowns, use trlgonometry and geometry,
for problemsolvlng or double check
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Mohrs Clrcle: a qulck and powerful graphlcal tool
|t oers:
...
+
stress palr (
x
,
x
) on any incIined section
...
z
principaI stresses/orientations
...
max. in-pIane shear stresses/orientations and assoclated
avg
... (
direct visuaIization of the stress state at a polnt
one-to-one correspondence of
(, ) on a pIane a point on Mohrs clrcle
reference radiaI Iine CAstresses on x plane
physicaI rotation for element i on Mohrs Clrcle
...
7ips:
for unknowns, use trlgonometry and geometry,
for problemsolvlng or double check
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Mohrs Clrcle: a qulck and powerful graphlcal tool
|t oers:
...
+
stress palr (
x
,
x
) on any incIined section
...
z
principaI stresses/orientations
...
max. in-pIane shear stresses/orientations and assoclated
avg
... (
direct visuaIization of the stress state at a polnt
one-to-one correspondence of
(, ) on a pIane a point on Mohrs clrcle
reference radiaI Iine CAstresses on x plane
physicaI rotation for element i on Mohrs Clrcle
...
7ips:
for unknowns, use trlgonometry and geometry,
for problemsolvlng or double check
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Mohrs Clrcle: a qulck and powerful graphlcal tool
|t oers:
...
+
stress palr (
x
,
x
) on any incIined section
...
z
principaI stresses/orientations
...
max. in-pIane shear stresses/orientations and assoclated
avg
... (
direct visuaIization of the stress state at a polnt
one-to-one correspondence of
(, ) on a pIane a point on Mohrs clrcle
reference radiaI Iine CAstresses on x plane
physicaI rotation for element i on Mohrs Clrcle
...
7ips:
for unknowns, use trlgonometry and geometry,
for problemsolvlng or double check
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Mohrs Clrcle: a qulck and powerful graphlcal tool
|t oers:
...
+
stress palr (
x
,
x
) on any incIined section
...
z
principaI stresses/orientations
...
max. in-pIane shear stresses/orientations and assoclated
avg
... (
direct visuaIization of the stress state at a polnt
one-to-one correspondence of
(, ) on a pIane a point on Mohrs clrcle
reference radiaI Iine CAstresses on x plane
physicaI rotation for element i on Mohrs Clrcle
...
7ips:
for unknowns, use trlgonometry and geometry,
for problemsolvlng or double check
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Mohrs Clrcle: a qulck and powerful graphlcal tool
|t oers:
...
+
stress palr (
x
,
x
) on any incIined section
...
z
principaI stresses/orientations
...
max. in-pIane shear stresses/orientations and assoclated
avg
... (
direct visuaIization of the stress state at a polnt
one-to-one correspondence of
(, ) on a pIane a point on Mohrs clrcle
reference radiaI Iine CAstresses on x plane
physicaI rotation for element i on Mohrs Clrcle
...
7ips:
for unknowns, use trlgonometry and geometry,
for problemsolvlng or double check
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Mohrs Clrcle: a qulck and powerful graphlcal tool
|t oers:
...
+
stress palr (
x
,
x
) on any incIined section
...
z
principaI stresses/orientations
...
max. in-pIane shear stresses/orientations and assoclated
avg
... (
direct visuaIization of the stress state at a polnt
one-to-one correspondence of
(, ) on a pIane a point on Mohrs clrcle
reference radiaI Iine CAstresses on x plane
physicaI rotation for element i on Mohrs Clrcle
...
7ips:
for unknowns, use trlgonometry and geometry,
for problemsolvlng or double check
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Mohrs Clrcle: a qulck and powerful graphlcal tool
|t oers:
...
+
stress palr (
x
,
x
) on any incIined section
...
z
principaI stresses/orientations
...
max. in-pIane shear stresses/orientations and assoclated
avg
... (
direct visuaIization of the stress state at a polnt
one-to-one correspondence of
(, ) on a pIane a point on Mohrs clrcle
reference radiaI Iine CAstresses on x plane
physicaI rotation for element i on Mohrs Clrcle
...
7ips:
for unknowns, use trlgonometry and geometry,
for problemsolvlng or double check
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Mohrs Clrcle: a qulck and powerful graphlcal tool
|t oers:
...
+
stress palr (
x
,
x
) on any incIined section
...
z
principaI stresses/orientations
...
max. in-pIane shear stresses/orientations and assoclated
avg
... (
direct visuaIization of the stress state at a polnt
one-to-one correspondence of
(, ) on a pIane a point on Mohrs clrcle
reference radiaI Iine CAstresses on x plane
physicaI rotation for element i on Mohrs Clrcle
...
7ips:
for unknowns, use trlgonometry and geometry,
for problemsolvlng or double check
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Mohrs Clrcle: a qulck and powerful graphlcal tool
|t oers:
...
+
stress palr (
x
,
x
) on any incIined section
...
z
principaI stresses/orientations
...
max. in-pIane shear stresses/orientations and assoclated
avg
... (
direct visuaIization of the stress state at a polnt
one-to-one correspondence of
(, ) on a pIane a point on Mohrs clrcle
reference radiaI Iine CAstresses on x plane
physicaI rotation for element i on Mohrs Clrcle
...
7ips:
for unknowns, use trlgonometry and geometry,
for problemsolvlng or double check
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Typlcal appllcatlon +: Prlnclpal stresses
A
B
D
(
x
,
xy
)
2
p
1
2
p
2
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
x
c
P
(
1
, 0)
(
2
, 0)
(
x
y
)/2
E
principaI stresses: B
, D
,
,
=
avg
R, z
p
cos i
p
=
x
y
iR
, sini
p
=
xy
R
, i
p
i
p
=
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Typlcal appllcatlon z: Maxlmum ln-plane shear stresses
A
P
F
E
(
x
,
xy
)
2
s
1
= 0
2
s
2
(+)
(+)
x
y
x
c
(
avg
,
min
inplane
)
(
avg
, max
inplane
)
max. ln-plane shear: /F
max/min
inplane
,
avg
and i
s
cos i
s
=
xy
R
, sini
s
x
y
iR
, i
s
i
s
=
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Pemarks on the appllcatlons
key points:
construction and reference radiaI Iine ( = o)
generaI ruIes:
...
+
mark the known condltlons,
...
z
nd the relevant angles (note: i wlth sense),
...
do the math
probIem-soIving techniques: non-unlque
analytlcal, graphlcal, seml-analytlcal/seml-graphlcal
Mohrs clrcles for typlcal stress states
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Pemarks on the appllcatlons
key points:
construction and reference radiaI Iine ( = o)
generaI ruIes:
...
+
mark the known condltlons,
...
z
nd the relevant angles (note: i wlth sense),
...
do the math
probIem-soIving techniques: non-unlque
analytlcal, graphlcal, seml-analytlcal/seml-graphlcal
Mohrs clrcles for typlcal stress states
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Pemarks on the appllcatlons
key points:
construction and reference radiaI Iine ( = o)
generaI ruIes:
...
+
mark the known condltlons,
...
z
nd the relevant angles (note: i wlth sense),
...
do the math
probIem-soIving techniques: non-unlque
analytlcal, graphlcal, seml-analytlcal/seml-graphlcal
Mohrs clrcles for typlcal stress states
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Pemarks on the appllcatlons
key points:
construction and reference radiaI Iine ( = o)
generaI ruIes:
...
+
mark the known condltlons,
...
z
nd the relevant angles (note: i wlth sense),
...
do the math
probIem-soIving techniques: non-unlque
analytlcal, graphlcal, seml-analytlcal/seml-graphlcal
Mohrs clrcles for typlcal stress states
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Pemarks on the appllcatlons
key points:
construction and reference radiaI Iine ( = o)
generaI ruIes:
...
+
mark the known condltlons,
...
z
nd the relevant angles (note: i wlth sense),
...
do the math
probIem-soIving techniques: non-unlque
analytlcal, graphlcal, seml-analytlcal/seml-graphlcal
Mohrs clrcles for typlcal stress states
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Pemarks on the appllcatlons
key points:
construction and reference radiaI Iine ( = o)
generaI ruIes:
...
+
mark the known condltlons,
...
z
nd the relevant angles (note: i wlth sense),
...
do the math
probIem-soIving techniques: non-unlque
analytlcal, graphlcal, seml-analytlcal/seml-graphlcal
Mohrs clrcles for typlcal stress states
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress
..
Pemarks on the appllcatlons
key points:
construction and reference radiaI Iine ( = o)
generaI ruIes:
...
+
mark the known condltlons,
...
z
nd the relevant angles (note: i wlth sense),
...
do the math
probIem-soIving techniques: non-unlque
analytlcal, graphlcal, seml-analytlcal/seml-graphlcal
Mohrs clrcles for typlcal stress states
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
q. SpeciaI Cases
. . . . . .
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Case study +: unlaxlal stress state
A
P
(B)
F
D
E
(
1
, 0)
(
x
,
x
y
)
2
2
p
1
= 0
2
p
2
= 180
2
s
1
= 90
= 0
2
s
2
= 90
(+)
(+)
x
y
x
c
(0, 0)
1
> 0
A
(
1
/2, 0)
B
E
F
D
D
F
E
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Pallure of ductlle and brlttle materlals on unlaxlal tenslon
ductiIe materiaIs (|])
(fall on shear stress )
max
at = ,
brittIe materiaIs (j])
(fall on normal stress )
max
at = o,
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Pallure of ductlle and brlttle materlals on unlaxlal tenslon
ductiIe materiaIs (|])
(fall on shear stress )
max
at = ,
brittIe materiaIs (j])
(fall on normal stress )
max
at = o,
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Pallure of ductlle and brlttle materlals on unlaxlal tenslon
ductiIe materiaIs (|])
(fall on shear stress )
max
at = ,
brittIe materiaIs (j])
(fall on normal stress )
max
at = o,
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Case study z: blaxlal stress state
A
P
(B)
F
D
E
(
1
, 0)
(
x
,
x
y
)
2
2
p
1
= 0
2
p
2
= 180
2
s
1
= 90
= 0
2
s
2
= 90
(+)
(+)
x
y
x
c
(
2
, 0)
1
> 0
A
2
< 0
2
> 0
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Case study : hydrostatlc stress state
A
P
(B)
F
D
E
(
1
, 0)
(
x
,
x
y
)
= 0
(+)
(+)
x
y
x
c
(
2
, 0)
1
=
2
A
0
,
2
0
(
0
, 0)
a slngle polnt on the axls
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Case study (: pure shear stress state
A
P
B
F
D
E
(
xy
, 0)
(
x
,
x
y
)
2
2
p
1
= 90
2
p
2
= 90
2
s
1
= 0
= 0
2
s
2
= 180
(+)
(+)
x
y
x
c
(
xy
, 0)
xy
> 0
A
(0, 0)
xy
xy
B
D
E
F
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Pallure of ductlle and brlttle materlals on pure torslon
ductiIe (fall on shear stress )
max
at = o,
brittIe (fall on normal stress )
max
at = ,
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Pallure of ductlle and brlttle materlals on pure torslon
ductiIe (fall on shear stress )
max
at = o,
brittIe (fall on normal stress )
max
at = ,
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Pallure of ductlle and brlttle materlals on pure torslon
ductiIe (fall on shear stress )
max
at = o,
brittIe (fall on normal stress )
max
at = ,
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample + prlnclpal state
An element at a polnt ls sub[ected to the state of stress shown. Determlne
the prlnclpal stresses actlng at thls polnt.
SoIution:
...
+
Llst the stress state ln xoy: [
x
,
y
,
xy
] = [1i, o, o] MPa,
...
z
Calculate the center:
avg
=
x
+
y
i
=
1i + o
i
= o MPa
A
B
F
D
E
(
1
, 0)
2
p
1
2
p
2
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
(
2
, 0)
12 MPa
6 MPa
(-12,-6)
2
s
1
(-6,0)
C
A
2.49 MPa
14.5 MPa
O
22.5
= 0
...
Use A(-+z,-6) and
C(-6,o) to
construct Mohrs
circIe
R =
o
+ o
=
o
i = 8. MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample + prlnclpal state
An element at a polnt ls sub[ected to the state of stress shown. Determlne
the prlnclpal stresses actlng at thls polnt.
SoIution:
...
+
Llst the stress state ln xoy: [
x
,
y
,
xy
] = [1i, o, o] MPa,
...
z
Calculate the center:
avg
=
x
+
y
i
=
1i + o
i
= o MPa
A
B
F
D
E
(
1
, 0)
2
p
1
2
p
2
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
(
2
, 0)
12 MPa
6 MPa
(-12,-6)
2
s
1
(-6,0)
C
A
2.49 MPa
14.5 MPa
O
22.5
= 0
...
Use A(-+z,-6) and
C(-6,o) to
construct Mohrs
circIe
R =
o
+ o
=
o
i = 8. MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample + prlnclpal state
An element at a polnt ls sub[ected to the state of stress shown. Determlne
the prlnclpal stresses actlng at thls polnt.
SoIution:
...
+
Llst the stress state ln xoy: [
x
,
y
,
xy
] = [1i, o, o] MPa,
...
z
Calculate the center:
avg
=
x
+
y
i
=
1i + o
i
= o MPa
A
B
F
D
E
(
1
, 0)
2
p
1
2
p
2
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
(
2
, 0)
12 MPa
6 MPa
(-12,-6)
2
s
1
(-6,0)
C
A
2.49 MPa
14.5 MPa
O
22.5
= 0
...
Use A(-+z,-6) and
C(-6,o) to
construct Mohrs
circIe
R =
o
+ o
=
o
i = 8. MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample + prlnclpal state
An element at a polnt ls sub[ected to the state of stress shown. Determlne
the prlnclpal stresses actlng at thls polnt.
SoIution:
...
+
Llst the stress state ln xoy: [
x
,
y
,
xy
] = [1i, o, o] MPa,
...
z
Calculate the center:
avg
=
x
+
y
i
=
1i + o
i
= o MPa
A
B
F
D
E
(
1
, 0)
2
p
1
2
p
2
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
(
2
, 0)
12 MPa
6 MPa
(-12,-6)
2
s
1
(-6,0)
C
A
2.49 MPa
14.5 MPa
O
22.5
= 0
...
Use A(-+z,-6) and
C(-6,o) to
construct Mohrs
circIe
R =
o
+ o
=
o
i = 8. MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample + prlnclpal state
An element at a polnt ls sub[ected to the state of stress shown. Determlne
the prlnclpal stresses actlng at thls polnt.
SoIution:
...
+
Llst the stress state ln xoy: [
x
,
y
,
xy
] = [1i, o, o] MPa,
...
z
Calculate the center:
avg
=
x
+
y
i
=
1i + o
i
= o MPa
A
B
F
D
E
(
1
, 0)
2
p
1
2
p
2
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
(
2
, 0)
12 MPa
6 MPa
(-12,-6)
2
s
1
(-6,0)
C
A
2.49 MPa
14.5 MPa
O
22.5
= 0
...
Use A(-+z,-6) and
C(-6,o) to
construct Mohrs
circIe
R =
o
+ o
=
o
i = 8. MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample + prlnclpal state
An element at a polnt ls sub[ected to the state of stress shown. Determlne
the prlnclpal stresses actlng at thls polnt.
SoIution:
...
+
Llst the stress state ln xoy: [
x
,
y
,
xy
] = [1i, o, o] MPa,
...
z
Calculate the center:
avg
=
x
+
y
i
=
1i + o
i
= o MPa
A
B
F
D
E
(
1
, 0)
2
p
1
2
p
2
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
(
2
, 0)
12 MPa
6 MPa
(-12,-6)
2
s
1
(-6,0)
C
A
2.49 MPa
14.5 MPa
O
22.5
= 0
...
Use A(-+z,-6) and
C(-6,o) to
construct Mohrs
circIe
R =
o
+ o
=
o
i = 8. MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample + (cont.)
A
B
F
D
E
(
1
, 0)
2
p
1
2
p
2
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
(
2
, 0)
12 MPa
6 MPa
(-12,-6)
2
s
1
(-6,0)
C
A
2.49 MPa
14.5 MPa
O
22.5
= 0
... (
Read fromgure:
prlnclpal stresses:
= o + R = i. MPa,
= o R = 1., MPa
orlentatlons: i
p
= tan
o
1i o
= ,
= ii.,
=
p
= o,.,
...
Plot the prlnclpal state.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample + (cont.)
A
B
F
D
E
(
1
, 0)
2
p
1
2
p
2
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
(
2
, 0)
12 MPa
6 MPa
(-12,-6)
2
s
1
(-6,0)
C
A
2.49 MPa
14.5 MPa
O
22.5
= 0
... (
Read fromgure:
prlnclpal stresses:
= o + R = i. MPa,
= o R = 1., MPa
orlentatlons: i
p
= tan
o
1i o
= ,
= ii.,
=
p
= o,.,
...
Plot the prlnclpal state.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample z max. ln-plane shear
An element at a polnt ls sub[ected to the state of stress shown. Determlne
the maxlmum ln-plane shear stresses and the orlentatlon of the element
upon whlch they act.
SoIution:
...
+
Llst the stress state ln xoy: [
x
,
y
,
xy
] = [io, o, oo] MPa,
A
B
F
D
E
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
20 MPa
(-20, 60)
2
s
1
(35, 0)
C
A
81.4 MPa
35 MPa
O
21.3
= 0
60 MPa
90 MPa
60
20
35
xy
x
...
z
the center:
avg
=
x
+
y
i
=
io + o
i
= , MPa
...
Use A(-zo,6o) and
C(,o) to construct
Mohrs circIe
R =
,,
+ oo
=
81. MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample z max. ln-plane shear
An element at a polnt ls sub[ected to the state of stress shown. Determlne
the maxlmum ln-plane shear stresses and the orlentatlon of the element
upon whlch they act.
SoIution:
...
+
Llst the stress state ln xoy: [
x
,
y
,
xy
] = [io, o, oo] MPa,
A
B
F
D
E
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
20 MPa
(-20, 60)
2
s
1
(35, 0)
C
A
81.4 MPa
35 MPa
O
21.3
= 0
60 MPa
90 MPa
60
20
35
xy
x
...
z
the center:
avg
=
x
+
y
i
=
io + o
i
= , MPa
...
Use A(-zo,6o) and
C(,o) to construct
Mohrs circIe
R =
,,
+ oo
=
81. MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample z max. ln-plane shear
An element at a polnt ls sub[ected to the state of stress shown. Determlne
the maxlmum ln-plane shear stresses and the orlentatlon of the element
upon whlch they act.
SoIution:
...
+
Llst the stress state ln xoy: [
x
,
y
,
xy
] = [io, o, oo] MPa,
A
B
F
D
E
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
20 MPa
(-20, 60)
2
s
1
(35, 0)
C
A
81.4 MPa
35 MPa
O
21.3
= 0
60 MPa
90 MPa
60
20
35
xy
x
...
z
the center:
avg
=
x
+
y
i
=
io + o
i
= , MPa
...
Use A(-zo,6o) and
C(,o) to construct
Mohrs circIe
R =
,,
+ oo
=
81. MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample z max. ln-plane shear
An element at a polnt ls sub[ected to the state of stress shown. Determlne
the maxlmum ln-plane shear stresses and the orlentatlon of the element
upon whlch they act.
SoIution:
...
+
Llst the stress state ln xoy: [
x
,
y
,
xy
] = [io, o, oo] MPa,
A
B
F
D
E
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
20 MPa
(-20, 60)
2
s
1
(35, 0)
C
A
81.4 MPa
35 MPa
O
21.3
= 0
60 MPa
90 MPa
60
20
35
xy
x
...
z
the center:
avg
=
x
+
y
i
=
io + o
i
= , MPa
...
Use A(-zo,6o) and
C(,o) to construct
Mohrs circIe
R =
,,
+ oo
=
81. MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample z max. ln-plane shear
An element at a polnt ls sub[ected to the state of stress shown. Determlne
the maxlmum ln-plane shear stresses and the orlentatlon of the element
upon whlch they act.
SoIution:
...
+
Llst the stress state ln xoy: [
x
,
y
,
xy
] = [io, o, oo] MPa,
A
B
F
D
E
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
20 MPa
(-20, 60)
2
s
1
(35, 0)
C
A
81.4 MPa
35 MPa
O
21.3
= 0
60 MPa
90 MPa
60
20
35
xy
x
...
z
the center:
avg
=
x
+
y
i
=
io + o
i
= , MPa
...
Use A(-zo,6o) and
C(,o) to construct
Mohrs circIe
R =
,,
+ oo
=
81. MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample z max. ln-plane shear
An element at a polnt ls sub[ected to the state of stress shown. Determlne
the maxlmum ln-plane shear stresses and the orlentatlon of the element
upon whlch they act.
SoIution:
...
+
Llst the stress state ln xoy: [
x
,
y
,
xy
] = [io, o, oo] MPa,
A
B
F
D
E
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
20 MPa
(-20, 60)
2
s
1
(35, 0)
C
A
81.4 MPa
35 MPa
O
21.3
= 0
60 MPa
90 MPa
60
20
35
xy
x
...
z
the center:
avg
=
x
+
y
i
=
io + o
i
= , MPa
...
Use A(-zo,6o) and
C(,o) to construct
Mohrs circIe
R =
,,
+ oo
=
81. MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample z: (cont.)
A
B
F
D
E
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
20 MPa
(-20, 60)
2
s
1
(35, 0)
C
A
81.4 MPa
35 MPa
O
21.3
= 0
60 MPa
90 MPa
60
20
35
xy
x
... (
Read fromgure:
max ln-plane shear stress: max
inplane
= R = 81. MPa
orlentatlons: i
s
= tan
,,
oo
= i.,
= i1.
=
s
= o8.,
...
Plot the state.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample z: (cont.)
A
B
F
D
E
2
s
2
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
x
y
x
20 MPa
(-20, 60)
2
s
1
(35, 0)
C
A
81.4 MPa
35 MPa
O
21.3
= 0
60 MPa
90 MPa
60
20
35
xy
x
... (
Read fromgure:
max ln-plane shear stress: max
inplane
= R = 81. MPa
orlentatlons: i
s
= tan
,,
oo
= i.,
= i1.
=
s
= o8.,
...
Plot the state.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample : Lxerclse z-+o (p.zp, Chlnese textbook, H|T)
Plane stress state at K.
Determlne the principaI stresses.
20 MPa
K
20 MPa
60 MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample : (cont.))
A
B
D
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
20 MPa
(20, 60)
C
K
O
20 MPa
20
20
(R 20, 0)
60
60 MPa
(-20, 0)
R
x
y
H
...
+
two glven polnts
A (io, oo) MPa,
D (io, o)
...
z
center C (R io, o)
...
(io
avg
)
+ oo
= R
R = o, MPa
... (
principaI stresses:
= iR io = 11o MPa,
= io MPa
...
lncluded angle of the
wedge:
1
i
aictan
oo
R o
= .o
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample : (cont.))
A
B
D
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
20 MPa
(20, 60)
C
K
O
20 MPa
20
20
(R 20, 0)
60
60 MPa
(-20, 0)
R
x
y
H
...
+
two glven polnts
A (io, oo) MPa,
D (io, o)
...
z
center C (R io, o)
...
(io
avg
)
+ oo
= R
R = o, MPa
... (
principaI stresses:
= iR io = 11o MPa,
= io MPa
...
lncluded angle of the
wedge:
1
i
aictan
oo
R o
= .o
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample : (cont.))
A
B
D
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
20 MPa
(20, 60)
C
K
O
20 MPa
20
20
(R 20, 0)
60
60 MPa
(-20, 0)
R
x
y
H
...
+
two glven polnts
A (io, oo) MPa,
D (io, o)
...
z
center C (R io, o)
...
(io
avg
)
+ oo
= R
R = o, MPa
... (
principaI stresses:
= iR io = 11o MPa,
= io MPa
...
lncluded angle of the
wedge:
1
i
aictan
oo
R o
= .o
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample : (cont.))
A
B
D
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
20 MPa
(20, 60)
C
K
O
20 MPa
20
20
(R 20, 0)
60
60 MPa
(-20, 0)
R
x
y
H
...
+
two glven polnts
A (io, oo) MPa,
D (io, o)
...
z
center C (R io, o)
...
(io
avg
)
+ oo
= R
R = o, MPa
... (
principaI stresses:
= iR io = 11o MPa,
= io MPa
...
lncluded angle of the
wedge:
1
i
aictan
oo
R o
= .o
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample : (cont.))
A
B
D
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
20 MPa
(20, 60)
C
K
O
20 MPa
20
20
(R 20, 0)
60
60 MPa
(-20, 0)
R
x
y
H
...
+
two glven polnts
A (io, oo) MPa,
D (io, o)
...
z
center C (R io, o)
...
(io
avg
)
+ oo
= R
R = o, MPa
... (
principaI stresses:
= iR io = 11o MPa,
= io MPa
...
lncluded angle of the
wedge:
1
i
aictan
oo
R o
= .o
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample : (cont.))
A
B
D
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
20 MPa
(20, 60)
C
K
O
20 MPa
20
20
(R 20, 0)
60
60 MPa
(-20, 0)
R
x
y
H
...
+
two glven polnts
A (io, oo) MPa,
D (io, o)
...
z
center C (R io, o)
...
(io
avg
)
+ oo
= R
R = o, MPa
... (
principaI stresses:
= iR io = 11o MPa,
= io MPa
...
lncluded angle of the
wedge:
1
i
aictan
oo
R o
= .o
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample : (cont.))
A
B
D
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
20 MPa
(20, 60)
C
K
O
20 MPa
20
20
(R 20, 0)
60
60 MPa
(-20, 0)
R
x
y
H
...
+
two glven polnts
A (io, oo) MPa,
D (io, o)
...
z
center C (R io, o)
...
(io
avg
)
+ oo
= R
R = o, MPa
... (
principaI stresses:
= iR io = 11o MPa,
= io MPa
...
lncluded angle of the
wedge:
1
i
aictan
oo
R o
= .o
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample : (cont.))
A
B
D
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
20 MPa
(20, 60)
C
K
O
20 MPa
20
20
(R 20, 0)
60
60 MPa
(-20, 0)
R
x
y
H
...
+
two glven polnts
A (io, oo) MPa,
D (io, o)
...
z
center C (R io, o)
...
(io
avg
)
+ oo
= R
R = o, MPa
... (
principaI stresses:
= iR io = 11o MPa,
= io MPa
...
lncluded angle of the
wedge:
1
i
aictan
oo
R o
= .o
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6, page (((
Por the glven plane stress state, determlne
...
+
the stresses on an element at = ,
...
z
the prlnclpal stresses
...
the maxlmum shear stresses (only the ln-plane ones)
At a point on the surface of a generator shaft the stresses are s
x
50 MPa,
s
y
10 MPa, and t
xy
40 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7-21a.
Using Mohrs circle, determine the following quantities: (a) the stresses
acting on an element inclined at an angle u 45, (b) the principal stresses, and
(c) the maximum shear stresses. (Consider only the in-plane stresses, and show
all results on sketches of properly oriented elements.)
SECTION 7.4 Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress 497
Example 7-6
(a)
(b)
10 MPa
50 MPa
40 MPa
P
2
(u
p
2
= 26.6)
A B
y
x
O
C
D (u = 45)
P
1
(u
p
1
= 116.6)
A (u = 0)
B (u = 90)
t
x
1
y
1
20 10
s
x
1
40
50
5
0
D'
5
0
5
0
(u
s
1
= 71.6)
S
1
S
2
O
40
36.87
5
0
53.13
90
FIG. 7-21 Example 7-6. (a) Element in
plane stress, and (b) the corresponding
Mohrs circle. (Note: All stresses on the
circle have units of MPa.)
Solution
Construction of Mohrs circle. The axes for the normal and shear stresses
are shown in Fig. 7-21b, with s
x
1
positive to the right and t
x
1
y
1
positive down-
ward. The center C of the circle is located on the s
x
1
axis at the point where the
stress equals the average normal stress (Eq. 7-31a):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
20 MPa
Point A, representing the stresses on the x face of the element (u 0), has
coordinates
s
x
l
50 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
Similarly, the coordinates of point B, representing the stresses on the y face
(u 90), are
s
x
l
10 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
continued
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6, page (((
Por the glven plane stress state, determlne
...
+
the stresses on an element at = ,
...
z
the prlnclpal stresses
...
the maxlmum shear stresses (only the ln-plane ones)
At a point on the surface of a generator shaft the stresses are s
x
50 MPa,
s
y
10 MPa, and t
xy
40 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7-21a.
Using Mohrs circle, determine the following quantities: (a) the stresses
acting on an element inclined at an angle u 45, (b) the principal stresses, and
(c) the maximum shear stresses. (Consider only the in-plane stresses, and show
all results on sketches of properly oriented elements.)
SECTION 7.4 Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress 497
Example 7-6
(a)
(b)
10 MPa
50 MPa
40 MPa
P
2
(u
p
2
= 26.6)
A B
y
x
O
C
D (u = 45)
P
1
(u
p
1
= 116.6)
A (u = 0)
B (u = 90)
t
x
1
y
1
20 10
s
x
1
40
50
5
0
D'
5
0
5
0
(u
s
1
= 71.6)
S
1
S
2
O
40
36.87
5
0
53.13
90
FIG. 7-21 Example 7-6. (a) Element in
plane stress, and (b) the corresponding
Mohrs circle. (Note: All stresses on the
circle have units of MPa.)
Solution
Construction of Mohrs circle. The axes for the normal and shear stresses
are shown in Fig. 7-21b, with s
x
1
positive to the right and t
x
1
y
1
positive down-
ward. The center C of the circle is located on the s
x
1
axis at the point where the
stress equals the average normal stress (Eq. 7-31a):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
20 MPa
Point A, representing the stresses on the x face of the element (u 0), has
coordinates
s
x
l
50 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
Similarly, the coordinates of point B, representing the stresses on the y face
(u 90), are
s
x
l
10 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
continued
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6, page (((
Por the glven plane stress state, determlne
...
+
the stresses on an element at = ,
...
z
the prlnclpal stresses
...
the maxlmum shear stresses (only the ln-plane ones)
At a point on the surface of a generator shaft the stresses are s
x
50 MPa,
s
y
10 MPa, and t
xy
40 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7-21a.
Using Mohrs circle, determine the following quantities: (a) the stresses
acting on an element inclined at an angle u 45, (b) the principal stresses, and
(c) the maximum shear stresses. (Consider only the in-plane stresses, and show
all results on sketches of properly oriented elements.)
SECTION 7.4 Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress 497
Example 7-6
(a)
(b)
10 MPa
50 MPa
40 MPa
P
2
(u
p
2
= 26.6)
A B
y
x
O
C
D (u = 45)
P
1
(u
p
1
= 116.6)
A (u = 0)
B (u = 90)
t
x
1
y
1
20 10
s
x
1
40
50
5
0
D'
5
0
5
0
(u
s
1
= 71.6)
S
1
S
2
O
40
36.87
5
0
53.13
90
FIG. 7-21 Example 7-6. (a) Element in
plane stress, and (b) the corresponding
Mohrs circle. (Note: All stresses on the
circle have units of MPa.)
Solution
Construction of Mohrs circle. The axes for the normal and shear stresses
are shown in Fig. 7-21b, with s
x
1
positive to the right and t
x
1
y
1
positive down-
ward. The center C of the circle is located on the s
x
1
axis at the point where the
stress equals the average normal stress (Eq. 7-31a):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
20 MPa
Point A, representing the stresses on the x face of the element (u 0), has
coordinates
s
x
l
50 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
Similarly, the coordinates of point B, representing the stresses on the y face
(u 90), are
s
x
l
10 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
continued
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6 (cont.)
At a point on the surface of a generator shaft the stresses are s
x
50 MPa,
s
y
10 MPa, and t
xy
40 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7-21a.
Using Mohrs circle, determine the following quantities: (a) the stresses
acting on an element inclined at an angle u 45, (b) the principal stresses, and
(c) the maximum shear stresses. (Consider only the in-plane stresses, and show
all results on sketches of properly oriented elements.)
SECTION 7.4 Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress 497
Example 7-6
(a)
(b)
10 MPa
50 MPa
40 MPa
P
2
(u
p
2
= 26.6)
A B
y
x
O
C
D (u = 45)
P
1
(u
p
1
= 116.6)
A (u = 0)
B (u = 90)
t
x
1
y
1
20 10
s
x
1
40
50
5
0
D'
5
0
5
0
(u
s
1
= 71.6)
S
1
S
2
O
40
36.87
5
0
53.13 90
FIG. 7-21 Example 7-6. (a) Element in
plane stress, and (b) the corresponding
Mohrs circle. (Note: All stresses on the
circle have units of MPa.)
Solution
Construction of Mohrs circle. The axes for the normal and shear stresses
are shown in Fig. 7-21b, with s
x
1
positive to the right and t
x
1
y
1
positive down-
ward. The center C of the circle is located on the s
x
1
axis at the point where the
stress equals the average normal stress (Eq. 7-31a):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
20 MPa
Point A, representing the stresses on the x face of the element (u 0), has
coordinates
s
x
l
50 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
Similarly, the coordinates of point B, representing the stresses on the y face
(u 90), are
s
x
l
10 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
continued
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
SoIution:
...
+
avg
= io MPa
...
z
= o
A(,o, o), =
o
B(1o, o)
...
stresses at = ,
i = o
,
DCP
= o
aictan(
) = o.8,
D
=
avg
Rcos DCP
,
D
= RsinDCP
,
D (oo, o) MPa D
(io, o) MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6 (cont.)
At a point on the surface of a generator shaft the stresses are s
x
50 MPa,
s
y
10 MPa, and t
xy
40 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7-21a.
Using Mohrs circle, determine the following quantities: (a) the stresses
acting on an element inclined at an angle u 45, (b) the principal stresses, and
(c) the maximum shear stresses. (Consider only the in-plane stresses, and show
all results on sketches of properly oriented elements.)
SECTION 7.4 Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress 497
Example 7-6
(a)
(b)
10 MPa
50 MPa
40 MPa
P
2
(u
p
2
= 26.6)
A B
y
x
O
C
D (u = 45)
P
1
(u
p
1
= 116.6)
A (u = 0)
B (u = 90)
t
x
1
y
1
20 10
s
x
1
40
50
5
0
D'
5
0
5
0
(u
s
1
= 71.6)
S
1
S
2
O
40
36.87
5
0
53.13 90
FIG. 7-21 Example 7-6. (a) Element in
plane stress, and (b) the corresponding
Mohrs circle. (Note: All stresses on the
circle have units of MPa.)
Solution
Construction of Mohrs circle. The axes for the normal and shear stresses
are shown in Fig. 7-21b, with s
x
1
positive to the right and t
x
1
y
1
positive down-
ward. The center C of the circle is located on the s
x
1
axis at the point where the
stress equals the average normal stress (Eq. 7-31a):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
20 MPa
Point A, representing the stresses on the x face of the element (u 0), has
coordinates
s
x
l
50 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
Similarly, the coordinates of point B, representing the stresses on the y face
(u 90), are
s
x
l
10 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
continued
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
SoIution:
...
+
avg
= io MPa
...
z
= o
A(,o, o), =
o
B(1o, o)
...
stresses at = ,
i = o
,
DCP
= o
aictan(
) = o.8,
D
=
avg
Rcos DCP
,
D
= RsinDCP
,
D (oo, o) MPa D
(io, o) MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6 (cont.)
At a point on the surface of a generator shaft the stresses are s
x
50 MPa,
s
y
10 MPa, and t
xy
40 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7-21a.
Using Mohrs circle, determine the following quantities: (a) the stresses
acting on an element inclined at an angle u 45, (b) the principal stresses, and
(c) the maximum shear stresses. (Consider only the in-plane stresses, and show
all results on sketches of properly oriented elements.)
SECTION 7.4 Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress 497
Example 7-6
(a)
(b)
10 MPa
50 MPa
40 MPa
P
2
(u
p
2
= 26.6)
A B
y
x
O
C
D (u = 45)
P
1
(u
p
1
= 116.6)
A (u = 0)
B (u = 90)
t
x
1
y
1
20 10
s
x
1
40
50
5
0
D'
5
0
5
0
(u
s
1
= 71.6)
S
1
S
2
O
40
36.87
5
0
53.13 90
FIG. 7-21 Example 7-6. (a) Element in
plane stress, and (b) the corresponding
Mohrs circle. (Note: All stresses on the
circle have units of MPa.)
Solution
Construction of Mohrs circle. The axes for the normal and shear stresses
are shown in Fig. 7-21b, with s
x
1
positive to the right and t
x
1
y
1
positive down-
ward. The center C of the circle is located on the s
x
1
axis at the point where the
stress equals the average normal stress (Eq. 7-31a):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
20 MPa
Point A, representing the stresses on the x face of the element (u 0), has
coordinates
s
x
l
50 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
Similarly, the coordinates of point B, representing the stresses on the y face
(u 90), are
s
x
l
10 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
continued
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
SoIution:
...
+
avg
= io MPa
...
z
= o
A(,o, o), =
o
B(1o, o)
...
stresses at = ,
i = o
,
DCP
= o
aictan(
) = o.8,
D
=
avg
Rcos DCP
,
D
= RsinDCP
,
D (oo, o) MPa D
(io, o) MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6 (cont.)
At a point on the surface of a generator shaft the stresses are s
x
50 MPa,
s
y
10 MPa, and t
xy
40 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7-21a.
Using Mohrs circle, determine the following quantities: (a) the stresses
acting on an element inclined at an angle u 45, (b) the principal stresses, and
(c) the maximum shear stresses. (Consider only the in-plane stresses, and show
all results on sketches of properly oriented elements.)
SECTION 7.4 Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress 497
Example 7-6
(a)
(b)
10 MPa
50 MPa
40 MPa
P
2
(u
p
2
= 26.6)
A B
y
x
O
C
D (u = 45)
P
1
(u
p
1
= 116.6)
A (u = 0)
B (u = 90)
t
x
1
y
1
20 10
s
x
1
40
50
5
0
D'
5
0
5
0
(u
s
1
= 71.6)
S
1
S
2
O
40
36.87
5
0
53.13 90
FIG. 7-21 Example 7-6. (a) Element in
plane stress, and (b) the corresponding
Mohrs circle. (Note: All stresses on the
circle have units of MPa.)
Solution
Construction of Mohrs circle. The axes for the normal and shear stresses
are shown in Fig. 7-21b, with s
x
1
positive to the right and t
x
1
y
1
positive down-
ward. The center C of the circle is located on the s
x
1
axis at the point where the
stress equals the average normal stress (Eq. 7-31a):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
20 MPa
Point A, representing the stresses on the x face of the element (u 0), has
coordinates
s
x
l
50 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
Similarly, the coordinates of point B, representing the stresses on the y face
(u 90), are
s
x
l
10 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
continued
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
SoIution:
...
+
avg
= io MPa
...
z
= o
A(,o, o), =
o
B(1o, o)
...
stresses at = ,
i = o
,
DCP
= o
aictan(
) = o.8,
D
=
avg
Rcos DCP
,
D
= RsinDCP
,
D (oo, o) MPa D
(io, o) MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6 (cont.)
At a point on the surface of a generator shaft the stresses are s
x
50 MPa,
s
y
10 MPa, and t
xy
40 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7-21a.
Using Mohrs circle, determine the following quantities: (a) the stresses
acting on an element inclined at an angle u 45, (b) the principal stresses, and
(c) the maximum shear stresses. (Consider only the in-plane stresses, and show
all results on sketches of properly oriented elements.)
SECTION 7.4 Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress 497
Example 7-6
(a)
(b)
10 MPa
50 MPa
40 MPa
P
2
(u
p
2
= 26.6)
A B
y
x
O
C
D (u = 45)
P
1
(u
p
1
= 116.6)
A (u = 0)
B (u = 90)
t
x
1
y
1
20 10
s
x
1
40
50
5
0
D'
5
0
5
0
(u
s
1
= 71.6)
S
1
S
2
O
40
36.87
5
0
53.13 90
FIG. 7-21 Example 7-6. (a) Element in
plane stress, and (b) the corresponding
Mohrs circle. (Note: All stresses on the
circle have units of MPa.)
Solution
Construction of Mohrs circle. The axes for the normal and shear stresses
are shown in Fig. 7-21b, with s
x
1
positive to the right and t
x
1
y
1
positive down-
ward. The center C of the circle is located on the s
x
1
axis at the point where the
stress equals the average normal stress (Eq. 7-31a):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
20 MPa
Point A, representing the stresses on the x face of the element (u 0), has
coordinates
s
x
l
50 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
Similarly, the coordinates of point B, representing the stresses on the y face
(u 90), are
s
x
l
10 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
continued
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
SoIution:
...
+
avg
= io MPa
...
z
= o
A(,o, o), =
o
B(1o, o)
...
stresses at = ,
i = o
,
DCP
= o
aictan(
) = o.8,
D
=
avg
Rcos DCP
,
D
= RsinDCP
,
D (oo, o) MPa D
(io, o) MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6 (cont.)
At a point on the surface of a generator shaft the stresses are s
x
50 MPa,
s
y
10 MPa, and t
xy
40 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7-21a.
Using Mohrs circle, determine the following quantities: (a) the stresses
acting on an element inclined at an angle u 45, (b) the principal stresses, and
(c) the maximum shear stresses. (Consider only the in-plane stresses, and show
all results on sketches of properly oriented elements.)
SECTION 7.4 Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress 497
Example 7-6
(a)
(b)
10 MPa
50 MPa
40 MPa
P
2
(u
p
2
= 26.6)
A B
y
x
O
C
D (u = 45)
P
1
(u
p
1
= 116.6)
A (u = 0)
B (u = 90)
t
x
1
y
1
20 10
s
x
1
40
50
5
0
D'
5
0
5
0
(u
s
1
= 71.6)
S
1
S
2
O
40
36.87
5
0
53.13 90
FIG. 7-21 Example 7-6. (a) Element in
plane stress, and (b) the corresponding
Mohrs circle. (Note: All stresses on the
circle have units of MPa.)
Solution
Construction of Mohrs circle. The axes for the normal and shear stresses
are shown in Fig. 7-21b, with s
x
1
positive to the right and t
x
1
y
1
positive down-
ward. The center C of the circle is located on the s
x
1
axis at the point where the
stress equals the average normal stress (Eq. 7-31a):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
20 MPa
Point A, representing the stresses on the x face of the element (u 0), has
coordinates
s
x
l
50 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
Similarly, the coordinates of point B, representing the stresses on the y face
(u 90), are
s
x
l
10 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
continued
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
SoIution:
...
+
avg
= io MPa
...
z
= o
A(,o, o), =
o
B(1o, o)
...
stresses at = ,
i = o
,
DCP
= o
aictan(
) = o.8,
D
=
avg
Rcos DCP
,
D
= RsinDCP
,
D (oo, o) MPa D
(io, o) MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6 (cont.)
At a point on the surface of a generator shaft the stresses are s
x
50 MPa,
s
y
10 MPa, and t
xy
40 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7-21a.
Using Mohrs circle, determine the following quantities: (a) the stresses
acting on an element inclined at an angle u 45, (b) the principal stresses, and
(c) the maximum shear stresses. (Consider only the in-plane stresses, and show
all results on sketches of properly oriented elements.)
SECTION 7.4 Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress 497
Example 7-6
(a)
(b)
10 MPa
50 MPa
40 MPa
P
2
(u
p
2
= 26.6)
A B
y
x
O
C
D (u = 45)
P
1
(u
p
1
= 116.6)
A (u = 0)
B (u = 90)
t
x
1
y
1
20 10
s
x
1
40
50
5
0
D'
5
0
5
0
(u
s
1
= 71.6)
S
1
S
2
O
40
36.87
5
0
53.13 90
FIG. 7-21 Example 7-6. (a) Element in
plane stress, and (b) the corresponding
Mohrs circle. (Note: All stresses on the
circle have units of MPa.)
Solution
Construction of Mohrs circle. The axes for the normal and shear stresses
are shown in Fig. 7-21b, with s
x
1
positive to the right and t
x
1
y
1
positive down-
ward. The center C of the circle is located on the s
x
1
axis at the point where the
stress equals the average normal stress (Eq. 7-31a):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
20 MPa
Point A, representing the stresses on the x face of the element (u 0), has
coordinates
s
x
l
50 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
Similarly, the coordinates of point B, representing the stresses on the y face
(u 90), are
s
x
l
10 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
continued
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
... (
principaI stresses
=
avg
+ R = o MPa,
=
1
i
(18o
,.1
) =
o.
=
avg
R = ,o MPa,
=
1
i
(,.1
) = io.o
...
max
=
1
i
(,.1
+ o
) =
,1.o
max
= R = ,o MPa
=
s
= 18.
min
= R = ,o MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6 (cont.)
At a point on the surface of a generator shaft the stresses are s
x
50 MPa,
s
y
10 MPa, and t
xy
40 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7-21a.
Using Mohrs circle, determine the following quantities: (a) the stresses
acting on an element inclined at an angle u 45, (b) the principal stresses, and
(c) the maximum shear stresses. (Consider only the in-plane stresses, and show
all results on sketches of properly oriented elements.)
SECTION 7.4 Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress 497
Example 7-6
(a)
(b)
10 MPa
50 MPa
40 MPa
P
2
(u
p
2
= 26.6)
A B
y
x
O
C
D (u = 45)
P
1
(u
p
1
= 116.6)
A (u = 0)
B (u = 90)
t
x
1
y
1
20 10
s
x
1
40
50
5
0
D'
5
0
5
0
(u
s
1
= 71.6)
S
1
S
2
O
40
36.87
5
0
53.13 90
FIG. 7-21 Example 7-6. (a) Element in
plane stress, and (b) the corresponding
Mohrs circle. (Note: All stresses on the
circle have units of MPa.)
Solution
Construction of Mohrs circle. The axes for the normal and shear stresses
are shown in Fig. 7-21b, with s
x
1
positive to the right and t
x
1
y
1
positive down-
ward. The center C of the circle is located on the s
x
1
axis at the point where the
stress equals the average normal stress (Eq. 7-31a):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
20 MPa
Point A, representing the stresses on the x face of the element (u 0), has
coordinates
s
x
l
50 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
Similarly, the coordinates of point B, representing the stresses on the y face
(u 90), are
s
x
l
10 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
continued
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
... (
principaI stresses
=
avg
+ R = o MPa,
=
1
i
(18o
,.1
) =
o.
=
avg
R = ,o MPa,
=
1
i
(,.1
) = io.o
...
max
=
1
i
(,.1
+ o
) =
,1.o
max
= R = ,o MPa
=
s
= 18.
min
= R = ,o MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6 (cont.)
At a point on the surface of a generator shaft the stresses are s
x
50 MPa,
s
y
10 MPa, and t
xy
40 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7-21a.
Using Mohrs circle, determine the following quantities: (a) the stresses
acting on an element inclined at an angle u 45, (b) the principal stresses, and
(c) the maximum shear stresses. (Consider only the in-plane stresses, and show
all results on sketches of properly oriented elements.)
SECTION 7.4 Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress 497
Example 7-6
(a)
(b)
10 MPa
50 MPa
40 MPa
P
2
(u
p
2
= 26.6)
A B
y
x
O
C
D (u = 45)
P
1
(u
p
1
= 116.6)
A (u = 0)
B (u = 90)
t
x
1
y
1
20 10
s
x
1
40
50
5
0
D'
5
0
5
0
(u
s
1
= 71.6)
S
1
S
2
O
40
36.87
5
0
53.13 90
FIG. 7-21 Example 7-6. (a) Element in
plane stress, and (b) the corresponding
Mohrs circle. (Note: All stresses on the
circle have units of MPa.)
Solution
Construction of Mohrs circle. The axes for the normal and shear stresses
are shown in Fig. 7-21b, with s
x
1
positive to the right and t
x
1
y
1
positive down-
ward. The center C of the circle is located on the s
x
1
axis at the point where the
stress equals the average normal stress (Eq. 7-31a):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
20 MPa
Point A, representing the stresses on the x face of the element (u 0), has
coordinates
s
x
l
50 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
Similarly, the coordinates of point B, representing the stresses on the y face
(u 90), are
s
x
l
10 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
continued
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
... (
principaI stresses
=
avg
+ R = o MPa,
=
1
i
(18o
,.1
) =
o.
=
avg
R = ,o MPa,
=
1
i
(,.1
) = io.o
...
max
=
1
i
(,.1
+ o
) =
,1.o
max
= R = ,o MPa
=
s
= 18.
min
= R = ,o MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6 (cont.)
At a point on the surface of a generator shaft the stresses are s
x
50 MPa,
s
y
10 MPa, and t
xy
40 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7-21a.
Using Mohrs circle, determine the following quantities: (a) the stresses
acting on an element inclined at an angle u 45, (b) the principal stresses, and
(c) the maximum shear stresses. (Consider only the in-plane stresses, and show
all results on sketches of properly oriented elements.)
SECTION 7.4 Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress 497
Example 7-6
(a)
(b)
10 MPa
50 MPa
40 MPa
P
2
(u
p
2
= 26.6)
A B
y
x
O
C
D (u = 45)
P
1
(u
p
1
= 116.6)
A (u = 0)
B (u = 90)
t
x
1
y
1
20 10
s
x
1
40
50
5
0
D'
5
0
5
0
(u
s
1
= 71.6)
S
1
S
2
O
40
36.87
5
0
53.13 90
FIG. 7-21 Example 7-6. (a) Element in
plane stress, and (b) the corresponding
Mohrs circle. (Note: All stresses on the
circle have units of MPa.)
Solution
Construction of Mohrs circle. The axes for the normal and shear stresses
are shown in Fig. 7-21b, with s
x
1
positive to the right and t
x
1
y
1
positive down-
ward. The center C of the circle is located on the s
x
1
axis at the point where the
stress equals the average normal stress (Eq. 7-31a):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
20 MPa
Point A, representing the stresses on the x face of the element (u 0), has
coordinates
s
x
l
50 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
Similarly, the coordinates of point B, representing the stresses on the y face
(u 90), are
s
x
l
10 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
continued
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
... (
principaI stresses
=
avg
+ R = o MPa,
=
1
i
(18o
,.1
) =
o.
=
avg
R = ,o MPa,
=
1
i
(,.1
) = io.o
...
max
=
1
i
(,.1
+ o
) =
,1.o
max
= R = ,o MPa
=
s
= 18.
min
= R = ,o MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6 (cont.)
At a point on the surface of a generator shaft the stresses are s
x
50 MPa,
s
y
10 MPa, and t
xy
40 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7-21a.
Using Mohrs circle, determine the following quantities: (a) the stresses
acting on an element inclined at an angle u 45, (b) the principal stresses, and
(c) the maximum shear stresses. (Consider only the in-plane stresses, and show
all results on sketches of properly oriented elements.)
SECTION 7.4 Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress 497
Example 7-6
(a)
(b)
10 MPa
50 MPa
40 MPa
P
2
(u
p
2
= 26.6)
A B
y
x
O
C
D (u = 45)
P
1
(u
p
1
= 116.6)
A (u = 0)
B (u = 90)
t
x
1
y
1
20 10
s
x
1
40
50
5
0
D'
5
0
5
0
(u
s
1
= 71.6)
S
1
S
2
O
40
36.87
5
0
53.13 90
FIG. 7-21 Example 7-6. (a) Element in
plane stress, and (b) the corresponding
Mohrs circle. (Note: All stresses on the
circle have units of MPa.)
Solution
Construction of Mohrs circle. The axes for the normal and shear stresses
are shown in Fig. 7-21b, with s
x
1
positive to the right and t
x
1
y
1
positive down-
ward. The center C of the circle is located on the s
x
1
axis at the point where the
stress equals the average normal stress (Eq. 7-31a):
s
aver
s
x
2
s
y
20 MPa
Point A, representing the stresses on the x face of the element (u 0), has
coordinates
s
x
l
50 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
Similarly, the coordinates of point B, representing the stresses on the y face
(u 90), are
s
x
l
10 MPa t
x
l
y
l
40 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
continued
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
... (
principaI stresses
=
avg
+ R = o MPa,
=
1
i
(18o
,.1
) =
o.
=
avg
R = ,o MPa,
=
1
i
(,.1
) = io.o
...
max
=
1
i
(,.1
+ o
) =
,1.o
max
= R = ,o MPa
=
s
= 18.
min
= R = ,o MPa
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Lxamples
..
Lxample (: example ;-6 (cont.)
state sketches on stress elements
The circle is now drawn through points A and B with center at C and radius R
(from Eq. 7-31b) equal to
R
s
x
2
s
y
2
t
2
xy
2
(
40 MP
a)
2
50 MPa
(a) Stresses on an element inclined at u 45. The stresses acting on a
plane oriented at an angle u 45 are given by the coordinates of point D,
which is at an angle 2u 90 from point A (Fig. 7-21b). To evaluate these coor-
dinates, we need to know the angle between line CD and the negative s
x
1
axis
(that is, angle DCP
2
), which in turn requires that we know the angle between
line CA and the negative s
x
1
axis (angle ACP
2
). These angles are found from the
geometry of the circle as follows:
tan AC P
2
4
3
0
0
M
M
P
P
a
a
4
3
ACP
2
53.13
DCP
2
90 A CP
2
90 53.13 36.87
Knowing these angles, we can obtain the coordinates of point D directly from
the figure:
(Point D) s
x
1
20 MPa (50 MPa)(cos 36.87) 60 MPa
t
x
1
y
1
(50 MPa)(sin 36.87) 30 MPa
50 MPa 10 MPa
2
498 CHAPTER 7 Analysis of Stress and Strain
(b) (c)
y
x
O
y
O
(a)
x
y
x
O
20 MPa
30 MPa
30 MPa
20 MPa
20 MPa
50 MPa
60 MPa
70 MPa
u = 45 u
p
2
= 26.6
u
s
1
= 71.6
D'
D
P
1
P
2
S
2
S
1
FIG. 7-22 Example 7-6 (continued).
(a) Stresses acting on an element
oriented at u 45, (b) principal
stresses, and (c) maximum shear stresses
Copyright 2004 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.
= ,
principaI stresses max shear stresses
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
y. 7riaxiaI stress state
. . . . . .
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Generallzatlon of zD stress state
Maxlmum ln-plane shear stress: an alternatlve form
,
=
x
+
y
i
R, max
inplane
= R =
i
CeneraIization of plane stress state to three dlmenslons
...
+
for plane stress state:
...
z
The out-of-pIane principaI stress:
z
= o
(lndependent of ln-plane stresses)
...
ln-plane (xy) prlnclpals (> o, < o, = o )
... (
conventlon on three principaIs (aIgebraicaIIy):
In-pIane (xy) and out-of-pIane max. shear stresses
(
xy
)
max
=
i
(in-pIane)
{(
zx
)
max
, (
zy
)
max
} = {
o
i
,
o
i
} (out-of-pIane)
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Generallzatlon of zD stress state
Maxlmum ln-plane shear stress: an alternatlve form
,
=
x
+
y
i
R, max
inplane
= R =
i
CeneraIization of plane stress state to three dlmenslons
...
+
for plane stress state:
...
z
The out-of-pIane principaI stress:
z
= o
(lndependent of ln-plane stresses)
...
ln-plane (xy) prlnclpals (> o, < o, = o )
... (
conventlon on three principaIs (aIgebraicaIIy):
In-pIane (xy) and out-of-pIane max. shear stresses
(
xy
)
max
=
i
(in-pIane)
{(
zx
)
max
, (
zy
)
max
} = {
o
i
,
o
i
} (out-of-pIane)
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Generallzatlon of zD stress state
Maxlmum ln-plane shear stress: an alternatlve form
,
=
x
+
y
i
R, max
inplane
= R =
i
CeneraIization of plane stress state to three dlmenslons
...
+
for plane stress state:
...
z
The out-of-pIane principaI stress:
z
= o
(lndependent of ln-plane stresses)
...
ln-plane (xy) prlnclpals (> o, < o, = o )
... (
conventlon on three principaIs (aIgebraicaIIy):
In-pIane (xy) and out-of-pIane max. shear stresses
(
xy
)
max
=
i
(in-pIane)
{(
zx
)
max
, (
zy
)
max
} = {
o
i
,
o
i
} (out-of-pIane)
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Generallzatlon of zD stress state
Maxlmum ln-plane shear stress: an alternatlve form
,
=
x
+
y
i
R, max
inplane
= R =
i
CeneraIization of plane stress state to three dlmenslons
...
+
for plane stress state:
...
z
The out-of-pIane principaI stress:
z
= o
(lndependent of ln-plane stresses)
...
ln-plane (xy) prlnclpals (> o, < o, = o )
... (
conventlon on three principaIs (aIgebraicaIIy):
In-pIane (xy) and out-of-pIane max. shear stresses
(
xy
)
max
=
i
(in-pIane)
{(
zx
)
max
, (
zy
)
max
} = {
o
i
,
o
i
} (out-of-pIane)
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Generallzatlon of zD stress state
Maxlmum ln-plane shear stress: an alternatlve form
,
=
x
+
y
i
R, max
inplane
= R =
i
CeneraIization of plane stress state to three dlmenslons
...
+
for plane stress state:
...
z
The out-of-pIane principaI stress:
z
= o
(lndependent of ln-plane stresses)
...
ln-plane (xy) prlnclpals (> o, < o, = o )
... (
conventlon on three principaIs (aIgebraicaIIy):
In-pIane (xy) and out-of-pIane max. shear stresses
(
xy
)
max
=
i
(in-pIane)
{(
zx
)
max
, (
zy
)
max
} = {
o
i
,
o
i
} (out-of-pIane)
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Generallzatlon of zD stress state
Maxlmum ln-plane shear stress: an alternatlve form
,
=
x
+
y
i
R, max
inplane
= R =
i
CeneraIization of plane stress state to three dlmenslons
...
+
for plane stress state:
...
z
The out-of-pIane principaI stress:
z
= o
(lndependent of ln-plane stresses)
...
ln-plane (xy) prlnclpals (> o, < o, = o )
... (
conventlon on three principaIs (aIgebraicaIIy):
In-pIane (xy) and out-of-pIane max. shear stresses
(
xy
)
max
=
i
(in-pIane)
{(
zx
)
max
, (
zy
)
max
} = {
o
i
,
o
i
} (out-of-pIane)
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Generallzatlon of zD stress state
Maxlmum ln-plane shear stress: an alternatlve form
,
=
x
+
y
i
R, max
inplane
= R =
i
CeneraIization of plane stress state to three dlmenslons
...
+
for plane stress state:
...
z
The out-of-pIane principaI stress:
z
= o
(lndependent of ln-plane stresses)
...
ln-plane (xy) prlnclpals (> o, < o, = o )
... (
conventlon on three principaIs (aIgebraicaIIy):
In-pIane (xy) and out-of-pIane max. shear stresses
(
xy
)
max
=
i
(in-pIane)
{(
zx
)
max
, (
zy
)
max
} = {
o
i
,
o
i
} (out-of-pIane)
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
|n-plane and out-of-plane max. shear stresses
x
y
z
3
(
xy
)
max
(
zy
)
max
(
zx
)
max
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Prlnclpal stresses for trlaxlal stress state
Stress transformatlon for generaI stress state
doable, but not requlred
x
max
int
min
...
+
Pesults: three (nonzero) principaI
stresses:
max
int
min
along x
, y
and z
,
respectlvely
...
z
Mohrs clrcle ls appllcable for each zD
plane: y
, x
, x
...
Determlnatlon of maxlmum of ln-plane shear stresses
Potatlon axls: x
, ln y
, (
y
)
max
= (
int
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: y
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: z
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
int
)/i
(
x
)
max
ls the absoIute max.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Prlnclpal stresses for trlaxlal stress state
Stress transformatlon for generaI stress state
doable, but not requlred
x
max
int
min
...
+
Pesults: three (nonzero) principaI
stresses:
max
int
min
along x
, y
and z
,
respectlvely
...
z
Mohrs clrcle ls appllcable for each zD
plane: y
, x
, x
...
Determlnatlon of maxlmum of ln-plane shear stresses
Potatlon axls: x
, ln y
, (
y
)
max
= (
int
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: y
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: z
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
int
)/i
(
x
)
max
ls the absoIute max.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Prlnclpal stresses for trlaxlal stress state
Stress transformatlon for generaI stress state
doable, but not requlred
x
max
int
min
...
+
Pesults: three (nonzero) principaI
stresses:
max
int
min
along x
, y
and z
,
respectlvely
...
z
Mohrs clrcle ls appllcable for each zD
plane: y
, x
, x
...
Determlnatlon of maxlmum of ln-plane shear stresses
Potatlon axls: x
, ln y
, (
y
)
max
= (
int
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: y
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: z
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
int
)/i
(
x
)
max
ls the absoIute max.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Prlnclpal stresses for trlaxlal stress state
Stress transformatlon for generaI stress state
doable, but not requlred
x
max
int
min
...
+
Pesults: three (nonzero) principaI
stresses:
max
int
min
along x
, y
and z
,
respectlvely
...
z
Mohrs clrcle ls appllcable for each zD
plane: y
, x
, x
...
Determlnatlon of maxlmum of ln-plane shear stresses
Potatlon axls: x
, ln y
, (
y
)
max
= (
int
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: y
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: z
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
int
)/i
(
x
)
max
ls the absoIute max.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Prlnclpal stresses for trlaxlal stress state
Stress transformatlon for generaI stress state
doable, but not requlred
x
max
int
min
...
+
Pesults: three (nonzero) principaI
stresses:
max
int
min
along x
, y
and z
,
respectlvely
...
z
Mohrs clrcle ls appllcable for each zD
plane: y
, x
, x
...
Determlnatlon of maxlmum of ln-plane shear stresses
Potatlon axls: x
, ln y
, (
y
)
max
= (
int
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: y
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: z
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
int
)/i
(
x
)
max
ls the absoIute max.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Prlnclpal stresses for trlaxlal stress state
Stress transformatlon for generaI stress state
doable, but not requlred
x
max
int
min
...
+
Pesults: three (nonzero) principaI
stresses:
max
int
min
along x
, y
and z
,
respectlvely
...
z
Mohrs clrcle ls appllcable for each zD
plane: y
, x
, x
...
Determlnatlon of maxlmum of ln-plane shear stresses
Potatlon axls: x
, ln y
, (
y
)
max
= (
int
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: y
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: z
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
int
)/i
(
x
)
max
ls the absoIute max.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Prlnclpal stresses for trlaxlal stress state
Stress transformatlon for generaI stress state
doable, but not requlred
x
max
int
min
...
+
Pesults: three (nonzero) principaI
stresses:
max
int
min
along x
, y
and z
,
respectlvely
...
z
Mohrs clrcle ls appllcable for each zD
plane: y
, x
, x
...
Determlnatlon of maxlmum of ln-plane shear stresses
Potatlon axls: x
, ln y
, (
y
)
max
= (
int
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: y
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: z
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
int
)/i
(
x
)
max
ls the absoIute max.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Prlnclpal stresses for trlaxlal stress state
Stress transformatlon for generaI stress state
doable, but not requlred
x
max
int
min
...
+
Pesults: three (nonzero) principaI
stresses:
max
int
min
along x
, y
and z
,
respectlvely
...
z
Mohrs clrcle ls appllcable for each zD
plane: y
, x
, x
...
Determlnatlon of maxlmum of ln-plane shear stresses
Potatlon axls: x
, ln y
, (
y
)
max
= (
int
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: y
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: z
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
int
)/i
(
x
)
max
ls the absoIute max.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Prlnclpal stresses for trlaxlal stress state
Stress transformatlon for generaI stress state
doable, but not requlred
x
max
int
min
...
+
Pesults: three (nonzero) principaI
stresses:
max
int
min
along x
, y
and z
,
respectlvely
...
z
Mohrs clrcle ls appllcable for each zD
plane: y
, x
, x
...
Determlnatlon of maxlmum of ln-plane shear stresses
Potatlon axls: x
, ln y
, (
y
)
max
= (
int
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: y
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
min
)/i
Potatlon axls: z
, ln x
, (
x
)
max
= (
max
int
)/i
(
x
)
max
ls the absoIute max.
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Mohrs clrcle for D
(+)
(+)
z
min
int
max
(
y
z
)
max
(
x
z
)
max
=
abs
max
(
x
y
)
max
x
min
max
int
cubic
abs
max
= (
x
)
max
=
max
min
i
,
avg
=
max
+
min
i
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Mohrs clrcle for D the proof
|n prlnclpal stress space:
n
+
n
= Tn
= (l
+ (m
+ (n
n
= Tn n = l
+ m
+ n
+ m
+ n
= 1
we get
l
n
+ (
n
)(
n
)
(
)(
)
m
n
+ (
n
)(
n
)
(
)(
)
n
n
+ (
n
)(
n
)
(
)(
)
Assume
n
+ (
n
i
)
i
)
n
+ (
n
i
)
i
)
n
+ (
n
i
)
i
)
P
1
P
2
P
3
n
M
Mohrs CircIe for D
(
n
,
n
) falls on or lnslde the
shaded area bounded by the
three clrcles wlth
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Mohrs clrcle for D the proof
|n prlnclpal stress space:
n
+
n
= Tn
= (l
+ (m
+ (n
n
= Tn n = l
+ m
+ n
+ m
+ n
= 1
we get
l
n
+ (
n
)(
n
)
(
)(
)
m
n
+ (
n
)(
n
)
(
)(
)
n
n
+ (
n
)(
n
)
(
)(
)
Assume
n
+ (
n
i
)
i
)
n
+ (
n
i
)
i
)
n
+ (
n
i
)
i
)
P
1
P
2
P
3
n
M
Mohrs CircIe for D
(
n
,
n
) falls on or lnslde the
shaded area bounded by the
three clrcles wlth
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Mohrs clrcle for D the proof
|n prlnclpal stress space:
n
+
n
= Tn
= (l
+ (m
+ (n
n
= Tn n = l
+ m
+ n
+ m
+ n
= 1
we get
l
n
+ (
n
)(
n
)
(
)(
)
m
n
+ (
n
)(
n
)
(
)(
)
n
n
+ (
n
)(
n
)
(
)(
)
Assume
n
+ (
n
i
)
i
)
n
+ (
n
i
)
i
)
n
+ (
n
i
)
i
)
P
1
P
2
P
3
n
M
Mohrs CircIe for D
(
n
,
n
) falls on or lnslde the
shaded area bounded by the
three clrcles wlth
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Peduced case for x
plane stress
(
z
=
min
= , llke slgns (') (+) for
max,int
)
(+)
(+)
z
min
int
max
(
y
z
)
max
(
x
z
)
max
=
abs
max
(
x
y
)
max
x
min
= 0
max
int
cubic
Absolute Max Shear Stress
Max In-plane Shear Stress
abs
max
= (
x
)
max
=
max
o
i
=
max
i
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Peduced case for x
plane stress
(
z
=
int
= , unllke slgns (]) for
max,min
)
(+)
(+)
z
min
int
= 0
max
(
y
z
)
max
(
x
y
)
max
=
abs
max
(
x
z
)
max
x
min
max
cubic
int
= 0
Max In-plane and Absolute
Max Shear Stress
abs
max
= (
x
)
max
=
max
min
i
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Lxample
An element ls sub[ected to the state of plane stress shown. Determlne the
prlnclpal stresses and the absolute maxlmum shear stress at the polnt.
A
B
D
= 0
(MPa)
(MPa)
(-20, -40)
C
O
10
20
R =
10
2
+ 40
2
= 41.2 MPa
H (-10,0)
20 MPa
40 MPa
(
min
, 0) (
max
, 0)
51.2 Mpa
31.2 MPa
10 MPa
41.2 MPa
38
83
76
(-51.2, 0)
(31.2, 0)
abs
max
= R
principal
max abs shear
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Prlnclpal stresses/planes for general D stress states
(N07 RUIRD)
...
+
an eigenvaIue probIem(),_)
t(n) = Tn = n
Cauchys stress formuIa (|.)
t(n): tractlon on a dlerentlal area wlth normal n
T: Cauchy stress tensor (|;) (one matrlx),
...
z
the symbols
T =
x
xy
xz
yx
y
yz
zx
zy
z
: eigenvaIues ()) (prlnclpal values)
n: eigen-vector ()() (normal of prlnclpal planes)
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Prlnclpal stresses/planes for general D stress states
(N07 RUIRD)
...
+
an eigenvaIue probIem(),_)
t(n) = Tn = n
Cauchys stress formuIa (|.)
t(n): tractlon on a dlerentlal area wlth normal n
T: Cauchy stress tensor (|;) (one matrlx),
...
z
the symbols
T =
x
xy
xz
yx
y
yz
zx
zy
z
: eigenvaIues ()) (prlnclpal values)
n: eigen-vector ()() (normal of prlnclpal planes)
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
The reduced zD case
T =
x
xy
o
yx
y
o
o o
z
T = [
x
xy
yx
y
]
Tn = n
x
xy
yx
y
= o
(
x
+
y
) + (
x
xy
) = o
,
=
(
x
+
y
)
(
x
y
)
xy
i
=
avg
R
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Summary
Mohrs circIe: mathematlcs & physlcs (
x
avg
)
= R
correspondence: polnts on clrcle (, ) on lncllned sectlons
construction of Mohrs clrcle
full appllcatlon of the glven condltlons, non-unlque
positive sense of axls
+ polntlng downward: conslstent wlth physlcal sense of rotatlon
appIications: i rotatlon relatlve to reference
+. stresses on an arbltrary sectlon (trlgonometry requlred),
z. prlnclpals,
. max. ln-plane shear
(. lnformatlon on orlentatlons
overaII: a powerfuI graphicaI tooI for stress analysls
Mohrs clrcle for D prlnclpal stress state
ln-plane, out-of-plane max. shear, absoIute max shear
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Summary
Mohrs circIe: mathematlcs & physlcs (
x
avg
)
= R
correspondence: polnts on clrcle (, ) on lncllned sectlons
construction of Mohrs clrcle
full appllcatlon of the glven condltlons, non-unlque
positive sense of axls
+ polntlng downward: conslstent wlth physlcal sense of rotatlon
appIications: i rotatlon relatlve to reference
+. stresses on an arbltrary sectlon (trlgonometry requlred),
z. prlnclpals,
. max. ln-plane shear
(. lnformatlon on orlentatlons
overaII: a powerfuI graphicaI tooI for stress analysls
Mohrs clrcle for D prlnclpal stress state
ln-plane, out-of-plane max. shear, absoIute max shear
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Summary
Mohrs circIe: mathematlcs & physlcs (
x
avg
)
= R
correspondence: polnts on clrcle (, ) on lncllned sectlons
construction of Mohrs clrcle
full appllcatlon of the glven condltlons, non-unlque
positive sense of axls
+ polntlng downward: conslstent wlth physlcal sense of rotatlon
appIications: i rotatlon relatlve to reference
+. stresses on an arbltrary sectlon (trlgonometry requlred),
z. prlnclpals,
. max. ln-plane shear
(. lnformatlon on orlentatlons
overaII: a powerfuI graphicaI tooI for stress analysls
Mohrs clrcle for D prlnclpal stress state
ln-plane, out-of-plane max. shear, absoIute max shear
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Summary
Mohrs circIe: mathematlcs & physlcs (
x
avg
)
= R
correspondence: polnts on clrcle (, ) on lncllned sectlons
construction of Mohrs clrcle
full appllcatlon of the glven condltlons, non-unlque
positive sense of axls
+ polntlng downward: conslstent wlth physlcal sense of rotatlon
appIications: i rotatlon relatlve to reference
+. stresses on an arbltrary sectlon (trlgonometry requlred),
z. prlnclpals,
. max. ln-plane shear
(. lnformatlon on orlentatlons
overaII: a powerfuI graphicaI tooI for stress analysls
Mohrs clrcle for D prlnclpal stress state
ln-plane, out-of-plane max. shear, absoIute max shear
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Summary
Mohrs circIe: mathematlcs & physlcs (
x
avg
)
= R
correspondence: polnts on clrcle (, ) on lncllned sectlons
construction of Mohrs clrcle
full appllcatlon of the glven condltlons, non-unlque
positive sense of axls
+ polntlng downward: conslstent wlth physlcal sense of rotatlon
appIications: i rotatlon relatlve to reference
+. stresses on an arbltrary sectlon (trlgonometry requlred),
z. prlnclpals,
. max. ln-plane shear
(. lnformatlon on orlentatlons
overaII: a powerfuI graphicaI tooI for stress analysls
Mohrs clrcle for D prlnclpal stress state
ln-plane, out-of-plane max. shear, absoIute max shear
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
. . . . . .
Mohrs clrcle Constructlon Apps Cases Trlaxlal stress Trlaxlal stress Absolute Maxlmum Shear Stress Lxamples
..
Homework o6
Chap. ) zq, z6, z
Due: +c.zq.zc+z (Wed.)
Lecture p: Analysls of Stress (||) Mohrs clrcle for plane stress
You might also like
- 6 DOF Equations of MotionDocument62 pages6 DOF Equations of Motionmimi_chan_17No ratings yet
- LECTURE No. 11. ADVANCED MATERIALS-SMART MATERIALS-BIOMATERIALS-NANOMATERIALSDocument13 pagesLECTURE No. 11. ADVANCED MATERIALS-SMART MATERIALS-BIOMATERIALS-NANOMATERIALSBizuayehu Tadesse AzeneNo ratings yet
- WIT CWI Fudamentls PDFDocument43 pagesWIT CWI Fudamentls PDFOscar Leonardo Roa CaceresNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of The Repetitive Failure in An Aircraft EngineDocument15 pagesAn Investigation of The Repetitive Failure in An Aircraft EnginemanelouchkaNo ratings yet
- Zero DynamicsDocument10 pagesZero DynamicsKarthiNo ratings yet
- Met 1Document46 pagesMet 1Ahmed AbdelhamedNo ratings yet
- 3d Stresses GoodDocument71 pages3d Stresses Goodiiscraja100% (1)
- Phys 101 - Chapter-V (1) ..Document27 pagesPhys 101 - Chapter-V (1) ..MD NAYM MIANo ratings yet
- Paper 3Document4 pagesPaper 3Yessica RosasNo ratings yet
- Stress6 ht08 2Document26 pagesStress6 ht08 2fredrikalloNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 1 PDFDocument22 pagesTutorial 1 1 PDFSuresh g.s.No ratings yet
- Lecture - 8 Real Analysis IBADocument3 pagesLecture - 8 Real Analysis IBAWisha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Application of Mohr's CircleDocument22 pagesApplication of Mohr's CircleMohit ShivaneNo ratings yet
- Taylor's SeriesDocument4 pagesTaylor's Seriesdibakarde72No ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibration CH 3 Harmonically Excited SystemsDocument57 pagesMechanical Vibration CH 3 Harmonically Excited SystemsPutro Adi nugrohoNo ratings yet
- Calculatioyjrtfgjdof Revolution With ArbitraryDocument12 pagesCalculatioyjrtfgjdof Revolution With ArbitrarySmileNo ratings yet
- 6-Transformation of Stress & Strain (Jan2013)Document49 pages6-Transformation of Stress & Strain (Jan2013)Mohammad HanafiNo ratings yet
- Theme 2: Mohr Diagram: Exercise 2 - Mathematical Demonstration of The Existence of Principal StressesDocument8 pagesTheme 2: Mohr Diagram: Exercise 2 - Mathematical Demonstration of The Existence of Principal StressesNAFISSA BOURQUIANo ratings yet
- Dynamic Rigid BodiesDocument50 pagesDynamic Rigid Bodiesamul_kambleNo ratings yet
- EM Predavanja 10 2015 2Document64 pagesEM Predavanja 10 2015 2DaliborNo ratings yet
- The Slope of A Polar GraphDocument2 pagesThe Slope of A Polar GraphKevin ZhangNo ratings yet
- Lec5 PDFDocument25 pagesLec5 PDFRavi Kiran MeesalaNo ratings yet
- IGC Basic Elasticity Volumetric Strain Thermal StressesDocument14 pagesIGC Basic Elasticity Volumetric Strain Thermal StressesKumar RNo ratings yet
- ENTC 376 Chapter 9 Lecture Notes-III-Stress TransformationDocument27 pagesENTC 376 Chapter 9 Lecture Notes-III-Stress TransformationYahia Raad Al-AniNo ratings yet
- Principal Stresses (Civil Engg. For AUST EEE 1/1)Document25 pagesPrincipal Stresses (Civil Engg. For AUST EEE 1/1)Fazlay ElahiNo ratings yet
- GATE AEROSPACE Engineering Aircraft Structures BasicsDocument11 pagesGATE AEROSPACE Engineering Aircraft Structures BasicsAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- 1385106121Document70 pages1385106121Abhishek AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structures Basics/SOM Basics (GATE Aerospace & GATE Mechanical) by MR Dinesh KumarDocument17 pagesAircraft Structures Basics/SOM Basics (GATE Aerospace & GATE Mechanical) by MR Dinesh Kumarspace bethNo ratings yet
- Principal StressesDocument5 pagesPrincipal Stressesavinashn1No ratings yet
- Part 1-Mechanics Review: Prof. Ramesh SinghDocument23 pagesPart 1-Mechanics Review: Prof. Ramesh SinghDrMohamed MansourNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress TransformDocument24 pagesPlane Stress Transformsandrock92No ratings yet
- These are NOT conditional probabilities; θ is NOT randomDocument3 pagesThese are NOT conditional probabilities; θ is NOT randomapi-246008426No ratings yet
- Stress Tensor Lec.2Document24 pagesStress Tensor Lec.2Malak ShatiNo ratings yet
- FEM FullDocument423 pagesFEM FullHarish LambadiNo ratings yet
- EN380 Naval Materials Science and Engineering Course Notes, U.S. Naval AcademyDocument7 pagesEN380 Naval Materials Science and Engineering Course Notes, U.S. Naval Academysrinivas pavan kumar ANo ratings yet
- Susskind Classical Mechanics NotesDocument13 pagesSusskind Classical Mechanics NotesGary SheaNo ratings yet
- Short MCMC SupplementaryDocument5 pagesShort MCMC SupplementaryccsunfanNo ratings yet
- Static Equilibrium: M M M F F FDocument41 pagesStatic Equilibrium: M M M F F FINMENo ratings yet
- R x f ξ n+1 ! x−x: Taylorov red (Mac Laurinov red)Document13 pagesR x f ξ n+1 ! x−x: Taylorov red (Mac Laurinov red)Hinko FušNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress LoadingDocument19 pagesPlane Stress LoadingAjeet Kumar100% (1)
- Mohr S CircleDocument8 pagesMohr S Circlelalala uNo ratings yet
- Summary. Consideration of The Associativity EquationDocument7 pagesSummary. Consideration of The Associativity Equationmark_villarino7158No ratings yet
- Lec02 2012eightDocument5 pagesLec02 2012eightPhạm Ngọc HòaNo ratings yet
- Teknik Kekuatan BahanDocument29 pagesTeknik Kekuatan BahanfayuangNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Formulas: X X X X X XDocument3 pagesTrigonometry Formulas: X X X X X XMahendraKumarNo ratings yet
- Arena Stanfordlecturenotes11Document9 pagesArena Stanfordlecturenotes11Victoria MooreNo ratings yet
- CE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations: Stresses in A Soil Mass I (Das, Ch. 9)Document27 pagesCE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations: Stresses in A Soil Mass I (Das, Ch. 9)jorge.jimenezNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Solving The Robust Maximal Covering Location ProblemDocument12 pagesModeling and Solving The Robust Maximal Covering Location ProblemEduardo FernandesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Brute Force StudentDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Brute Force StudentHùng Nguyễn MạnhNo ratings yet
- Ljgldldytfjg IolkjhgfdsfghjgfdDocument5 pagesLjgldldytfjg IolkjhgfdsfghjgfdGaming with SambhavNo ratings yet
- Muller Method: Where Z - 2c B B - 4acDocument3 pagesMuller Method: Where Z - 2c B B - 4acKantharaj Chinnappa0% (1)
- Lecture 6Document5 pagesLecture 6Abhilash MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Rolle, MVT TheoremDocument16 pagesRolle, MVT Theorem01795494168nazmulhasanNo ratings yet
- 5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Ii : Mit OpencoursewareDocument6 pages5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Ii : Mit OpencoursewareMohd Zeeshan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- X y Xy: of Plane Stress at A Point (Normal StressesDocument11 pagesX y Xy: of Plane Stress at A Point (Normal Stressesİlker ÇirkinNo ratings yet
- Lect1a 2022Document12 pagesLect1a 2022Qixian FengNo ratings yet
- Sec5_Castigliano TheoremsDocument22 pagesSec5_Castigliano Theoremshusamlabsha6060No ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Applsci 09 00376 v2 PDFDocument40 pagesApplsci 09 00376 v2 PDFFajar GumilangNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CCD Camera: Observational Astronomy 2011/2012Document19 pagesIntroduction To CCD Camera: Observational Astronomy 2011/2012Fajar GumilangNo ratings yet
- APAexamples PDFDocument2 pagesAPAexamples PDFFajar GumilangNo ratings yet
- Examples of Assessor Feedback From A Variety of AU Programs Presentation and Front End PiecesDocument15 pagesExamples of Assessor Feedback From A Variety of AU Programs Presentation and Front End PiecesFajar GumilangNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Cramers RuleDocument3 pages3.3 Cramers RuleFajar GumilangNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Concrete TanksDocument10 pagesRectangular Concrete Tanksferchov_coNo ratings yet
- Bending Moment in A Beam Lab Report - Green MechanicDocument9 pagesBending Moment in A Beam Lab Report - Green Mechanicmohdiqbal93No ratings yet
- Presstres MidDocument2 pagesPresstres MidTarun KumarNo ratings yet
- Crown Wedge CVCDocument40 pagesCrown Wedge CVCledaswanNo ratings yet
- Applied Surface Science: Full Length ArticleDocument10 pagesApplied Surface Science: Full Length Articlesreeiitm09No ratings yet
- The Solid State Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 1 - Learn CBSEDocument3 pagesThe Solid State Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 1 - Learn CBSEpofacoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Polymer Melt Compressibility On Mold Filling in Micro Injection MoldingDocument10 pagesEffects of Polymer Melt Compressibility On Mold Filling in Micro Injection MoldingOakmeNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - POWDER METALLURGY LABORATORYDocument9 pagesLab 2 - POWDER METALLURGY LABORATORYNur Anisa Wasilah Binti Mohd Noor ShahrinNo ratings yet
- Aci - 108-M04Document9 pagesAci - 108-M04Denglei TangNo ratings yet
- "Baseplt9" - Steel Column Base Plate Analysis: Program DescriptionDocument11 pages"Baseplt9" - Steel Column Base Plate Analysis: Program DescriptionMustafa RupawalaNo ratings yet
- Is 7001 1989Document14 pagesIs 7001 1989Kevin100% (1)
- Syllabus CE207fall2223Document2 pagesSyllabus CE207fall2223Dully CleverNo ratings yet
- Designation by Standards: Steel Vcmo230 (Mat - No. 1.7707, Din 30crmov9, Aisi 4340)Document5 pagesDesignation by Standards: Steel Vcmo230 (Mat - No. 1.7707, Din 30crmov9, Aisi 4340)janjicbojanNo ratings yet
- Metals 107908 PDFDocument20 pagesMetals 107908 PDFiban tecnaliaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Sylomer SR 18 ENDocument4 pagesData Sheet Sylomer SR 18 ENlpczyfansNo ratings yet
- The ASME Impact Test RequirementDocument7 pagesThe ASME Impact Test Requirementrosli2503No ratings yet
- Polymer Structures: Issues To Address..Document34 pagesPolymer Structures: Issues To Address..Eugene Embalzado Jr.No ratings yet
- Rotor Hot Spot Treatment PDFDocument10 pagesRotor Hot Spot Treatment PDFramnadh803181No ratings yet
- HW #7Document8 pagesHW #7Jigoku KuroakaNo ratings yet
- Abaqus - Nonlinear Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Beam Experimentation2015Document5 pagesAbaqus - Nonlinear Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Beam Experimentation2015oioNo ratings yet
- Bolt Grades: Mark's Standard Handbook For Mechanical Engineers Lists Grade 5Document4 pagesBolt Grades: Mark's Standard Handbook For Mechanical Engineers Lists Grade 5maverick79c100% (2)
- Prem Prakash Choudhary: Premsprakash@gmail - Co MDocument4 pagesPrem Prakash Choudhary: Premsprakash@gmail - Co Mvipul_khattar20026144No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lectures 2 (Convection)Document18 pagesHeat Transfer Lectures 2 (Convection)Haider100% (6)
- 03 - Rolling of MetalsDocument79 pages03 - Rolling of MetalsIrfan MahyunisNo ratings yet
- EM-20-020 - Full - Conf. Paper - IIT KGPDocument11 pagesEM-20-020 - Full - Conf. Paper - IIT KGPSatyajit SahuNo ratings yet
- Book Review: Applied Tribology - Bearing Design and LubricationDocument3 pagesBook Review: Applied Tribology - Bearing Design and LubricationBilly BetancourtNo ratings yet