Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Body Systems Essential Vocabulary
Human Body Systems Essential Vocabulary
Uploaded by
api-261172766Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Body Systems Essential Vocabulary
Human Body Systems Essential Vocabulary
Uploaded by
api-261172766Copyright:
Available Formats
Human Body Systems Vocabulary
characteristics
quality of an organism
DNA
material in life forms that transfers genetic characteristics
inherited
characteristics from parents
likeness
similarity
organism
individual living system
traits
distinguishing characteristics
cell
the basic unit of life
multicellular
composed of several or many cells
unicellular
(single cell)
composed of one cell
permeable
able to pass through
tissue
similar cells with a specific function
direct evidence
evidence you collect yourself
indirect
evidence
evidence that you do not collect yourself, but rely on evidence collected by others
fitness
state of being healthy
Skeletal System
ball/socket joint
joint that allows twisting and turning movements; example: hip joint
bones
forms the substance of a skeleton, support the body
cartilage
flexible connective tissue
cranium
skull
femur
longest, largest, and strongest bone in the human body; located in the leg
fracture
to break or crack
framework
supports, i.e. human skeleton
gliding joint
joint that allows to flat bones to slide over each other; example: foot, wrist
hinge joint
joint that allows movement in a certain spot, like the opening and closing of a door;
example: elbow, knee, ankle
humerus
long bone in arm extending from the shoulder to the elbow
immovable
not able to be moved
joints
place where two parts are joined or united to allow motion
mandible
jaw bone
patella
flat moveable bone in the front of the knee, also known as the knee bone
pelvis
funnel-shaped, part of skeleton supporting lower limbs
phalanges
bones that make up the fingers or feet
radius
bone of forearm on the thumb side
ribs
bones that support and protect organs such as the lungs
scapula
shoulder blade
skeleton
framework that support the body
skull
head bone
spine
backbone
sternum
breastbone
tarsals
bones in the feet
tibia
shinbone
torso
upper part of the body
ulna
forearm bone, located on the side opposite the thumb
vertebrae
bones in the spine
Muscular System
bicep
muscle at the front of the upper arm
cardiac muscle
type of muscle in the heart
contract
to draw together
endurance
ability or strength to continue or last without becoming tired
exertion
activity of using your muscles in various ways to keep fit
extend
to increase in length
flex
to bend
involuntary
muscle controlled without thinking about it (pumping heart)
ligaments
tissues that connect bones, hold organs in place
muscles
tissues that cause motion in the body when contracted
musculoskeletal
muscular and skeletal systems
resistance
Exercise that involves working your muscles against free weights or your body's own
weight (walking, running, pushups)
skeletal muscle
muscle connected at either end with a bone
smooth muscle
found in the walls of internal organs, blood vessels, hair follicles
tendons
connects muscle to bone
tricep
muscle located at the back of the upper arm
voluntary
muscle whose action is controlled by the person (example: lifting an arm)
atrophy
to waste away or decrease in size
autonomic
nervous system
system of nerves that control involuntary functions
axon
part of neuron that takes information away from a cell body
brain
controls mental and physical actions, located in the cranium (skull)
brain stem
part of brain near spinal cord; controls reflexes, breathing, and heartbeat
cerebellum
large portion of the brain, controls voluntary motions
cerebrum
largest part of the brain, controls voluntary movements and mental actions
dendrites
part of a neuron that brings information to a cell body
nerves
bundle of fibers that send impulses from the brain to other parts of the body
neurons
specialized, impulse-conducting cells (composed of cell body, axon, dendrites)
peripheral
nervous system
lies outside brain and spinal cord, includes nerves to arms, legs, and sense organs
relay
to transmit a signal
signals
messages sent from brain to nerves
spinal cord
cord of nerve tissue extending through the spinal column
spinal nerve
nerves that start in the spinal cord
stimuli
something that causes an action (example-stimulus: hot stove, response: moving hand
away from hot stove)
synapse
place where nerve messages are sent and received
Nervous System
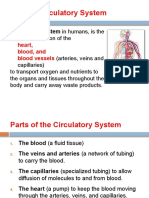
Circulatory and Cardiovascular Systems
blood
a fluid that circulates throughout the body to sustain life
cholesterol
found in animal tissues, too much can lead to heart disease
red blood cells
blood cells constantly traveling through your body delivering oxygen and removing
waste
white blood cells
blood cells that help protect the body by fighting off infections and diseases
platelets
smallest blood cells to help form clots if you have an injury
plasma
liquid part of the blood; contains blood's proteins, suspends blood cells
aerobic exercise
exercise that increases the need for oxygen
anaerobic
exercise
exercise that builds muscles through tension
aorta
part of the heart, circulates blood from the heart to all of the body (except the lungs)
arteries
blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart
atrium
two upper chambers on each side of the heart, receives blood from veins and forces
blood into ventricles
blood vessels
any of the vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) through which the blood circulates
capillaries
small blood vessels between the ending of the arteries and the beginning of the veins
cardiac
relating to the heart
circulation
flowing (such as the flow of blood throughout the body)
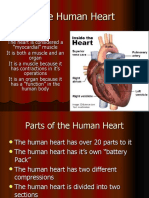
heart
organ (consisting of four chambers) that circulates blood, divided into four chambers
(valves)
heart rate
number of heartbeats in one minute
pulmonary
artery
transports blood from the heart to the lungs
pulse
regular throbbing of arteries caused by heart contractions
veins
blood vessels that carry blood toward the heart
ventricles
located in the heart, left and right, pumps blood to the entire body
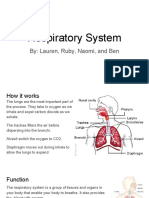
Respiratory System
air sac
air-filled spaces in the body
alveoli
very small air sacs; where air breathed in goes
bronchial tubes
two tubes at the end of the trachea, brings in air from trachea and helps clean lungs; one tube
goes to right lung, one to left
diaphragm
sheet-like muscle separating the chest from the abdominal cavity; creates suction to draw in
air and expand lungs
exhale
to breathe out
inhale
to breathe in
larynx
voice box
lungs
two respiratory organs
nasal passages
(nasal cavity)
helps with inhaling and exhaling of air through the nose
pharynx
throat; collects incoming air from the nose and passes air to the trachea
respiration
inhaling and exhaling air, breathing
ribs
bones that protect and support the chest
sinuses
hollow spaces in the bones of the head, helps regulate temperature of air breathed in
trachea
windpipe; passage from pharynx to lungs
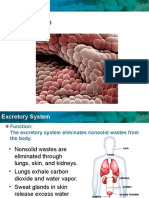
Digestive and Excretory Systems
anus
where solid waste exits through the body
appendix
located near the small and large intestine, purpose unknown
bile duct
stores bile (yellow, green liquid from the liver)
digestion
processing food in the body
epiglottis
located in the back of the mouth; prevents food and drink from entering the larynx
esophagus
muscular passage connecting the mouth and the stomach, rhythmic motion
large intestine
where stool (solid waste) accumulates
liver
filters blood coming from the digestive tract, releases bile, helps take toxins (poisons) from
chemicals in the body
mouth
where digestion begins
pancreas
about 6" long, located behind the stomach, secretes insulin
rectum
straight section of the intestine, ending in the anus, stores solid waste
saliva
watery fluid for tasting and swallowing food, chewing, keeping mouth moist
salivary glands
secretes (releases) saliva
small intestine
helps in the passage of food that comes from the stomach
stomach
organ in the digestive system that stores and digests food
tongue
organ in the mouth; functions include eating, tasting, speaking
You might also like
- The Chase TemplateDocument19 pagesThe Chase Templatejonscott141No ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Study GuideDocument1 pageHuman Body Systems Study Guideapi-323141584No ratings yet
- Local History Research of Barangay Ayala in Zambo City (Caminos, Keen Jude)Document6 pagesLocal History Research of Barangay Ayala in Zambo City (Caminos, Keen Jude)Keen Jude Caminos0% (1)
- Antonov 225 - The Largest - Airliner in The WorldDocument63 pagesAntonov 225 - The Largest - Airliner in The WorldFridayFunStuffNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument45 pagesCardiovascular SystemAlyssa VillaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Circulatory Systemolivia majcherNo ratings yet
- Notes About BiologyDocument81 pagesNotes About BiologyRichard Coffey100% (1)
- Human Body Systems Study GuideDocument1 pageHuman Body Systems Study Guideapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument25 pagesHeat Transferapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Sedona Unit PlanDocument3 pagesSedona Unit Planapi-404546120No ratings yet
- CS3 Mods PDFDocument6 pagesCS3 Mods PDFAnonymous LgJH9UE2jNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Study GuideDocument1 pageHuman Body Systems Study Guideapi-261172766No ratings yet
- 3.6 - The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pages3.6 - The Respiratory SystemDjej100% (1)
- Lec-21,22,23 - Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesLec-21,22,23 - Circulatory SystemAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- Muscular System WorksheetDocument1 pageMuscular System Worksheetapi-238647540No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory SystemKent Clark VillaNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System - The Dermis: T. RickDocument17 pagesThe Integumentary System - The Dermis: T. Rickapi-464344582No ratings yet
- Answer Key End of Chapter QuestionsDocument102 pagesAnswer Key End of Chapter QuestionsPhoebe Faye LyNo ratings yet
- Pollution Is The Introduction of Contaminants Into A Natural Environment That Causes Instability, DisorderDocument16 pagesPollution Is The Introduction of Contaminants Into A Natural Environment That Causes Instability, DisorderJassi Layal100% (2)
- Introduction of Anatomy PDFDocument34 pagesIntroduction of Anatomy PDFUohna MoienNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology - Coordination&ResponseDocument16 pagesForm 5 Biology - Coordination&ResponseAcapSuiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Chapter 19 - Lecture NotesDocument73 pagesCardiovascular System: The Heart: Chapter 19 - Lecture Noteshersheys72002No ratings yet
- Sheep Brain Dissection With Labeled ImagesDocument13 pagesSheep Brain Dissection With Labeled Imagesapi-275510930No ratings yet
- Basic Biology: 1. Cellular StructureDocument3 pagesBasic Biology: 1. Cellular StructureAbhay VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology: Topic 1: Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument63 pagesIgcse Biology: Topic 1: Characteristics of Living OrganismsIndia IB 2020No ratings yet
- Workshop About The Heart and Cardiac CycleDocument4 pagesWorkshop About The Heart and Cardiac CycleLina Mafla100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Respiration 1.1 The Human Breathing MechanismDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Respiration 1.1 The Human Breathing MechanismWindy SanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Worksheet: Axon Myelin Sheath Cell Body Dendrites Muscle Fibers Axon TerminalsDocument2 pagesNervous System Worksheet: Axon Myelin Sheath Cell Body Dendrites Muscle Fibers Axon Terminalsdwi choirinaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System WorksheetDocument7 pagesSkeletal System Worksheet마스러버100% (1)
- Chemistry 11 Concept ReviewDocument31 pagesChemistry 11 Concept ReviewJames Ernest Baker-taylor100% (1)
- Chapter 15 - Cardiovascular SystemDocument89 pagesChapter 15 - Cardiovascular SystemOliver Namyalo100% (1)
- Sheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Document4 pagesSheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Leo MatsuokaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument30 pagesCirculatory SystemIra Lavigne De VillaNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument16 pagesHomeostasisDr M K GuptaNo ratings yet
- Istology: Lymphatic SystemDocument48 pagesIstology: Lymphatic Systemninja-2001No ratings yet
- ANATOMY: Muscular System Quiz Study Guide Part 1Document4 pagesANATOMY: Muscular System Quiz Study Guide Part 1jbradeeNo ratings yet
- The Human Heart ...Document20 pagesThe Human Heart ...Prateek JainNo ratings yet
- 12 Transport of O2 & Co2Document169 pages12 Transport of O2 & Co2Bakhtiar Effendi YahyaNo ratings yet
- Heart Dissection WorksheetDocument5 pagesHeart Dissection Worksheetapi-237875296100% (1)
- Animal Transport Systems: Blood VesselsDocument24 pagesAnimal Transport Systems: Blood VesselsRabia KhalilNo ratings yet
- Biology - Circulatory System Notes 1Document13 pagesBiology - Circulatory System Notes 1archit.kulkarni7756No ratings yet
- Osmosis and Diffusion NotesDocument3 pagesOsmosis and Diffusion Notesapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument71 pagesNervous SystemSyra May PadlanNo ratings yet
- Life Processes and Cells: Chapter 1:-Longman GCSE BiologyDocument16 pagesLife Processes and Cells: Chapter 1:-Longman GCSE BiologynkllaeNo ratings yet
- 1 BloodDocument77 pages1 BloodVisaNathan100% (1)
- Concept 3 Notes - Anatomy Basics For StudentsDocument39 pagesConcept 3 Notes - Anatomy Basics For StudentsKaranNo ratings yet
- Body System ChecklistDocument6 pagesBody System Checklistapi-422967453No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesRespiratory Systemapi-272862164100% (1)
- 511-525chapter 6-8 (1) An Introduction To The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pages511-525chapter 6-8 (1) An Introduction To The Skeletal Systemtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Worksheet: I. Read The Passage and Answer The Questions That FollowDocument2 pagesMuscular System Worksheet: I. Read The Passage and Answer The Questions That FollowJulie Anne Bergado CortezNo ratings yet
- Systems BookletDocument8 pagesSystems Bookletapi-383568582No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Coordination and ControlDocument22 pagesChapter 12 Coordination and ControlXaundrae McDonaldNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 Endocrine GlandDocument73 pagesUnit 13 Endocrine GlandChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Cell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleDocument43 pagesCell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleJomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- Human Muscular & Skeletal System - Grade 11 & 12Document24 pagesHuman Muscular & Skeletal System - Grade 11 & 12Ishita SinghNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Parts and FunctionsDocument9 pagesIntegumentary System: Parts and FunctionsJat GomezNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint #5: Honors BiologyDocument19 pagesPowerpoint #5: Honors BiologyNylan AnyerNo ratings yet
- Skeleton Axial and AppendicularDocument33 pagesSkeleton Axial and AppendicularAnnisa Safira100% (1)
- Excretory System CiegoDocument2 pagesExcretory System CiegoMagui Jambrina Martín100% (1)
- 1 - Kidney Anatomy and HistologyDocument7 pages1 - Kidney Anatomy and HistologyLaura TorpeyNo ratings yet
- Study NotesDocument74 pagesStudy NotesCandyMaryoomNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument87 pagesEpithelial Tissueabubeker mohammed100% (1)
- Excretory System FinalDocument15 pagesExcretory System FinalJames AysonNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems VocabularyDocument4 pagesHuman Body Systems Vocabularyapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Human Body VocabularyDocument11 pagesHuman Body Vocabularyapi-323449449100% (1)
- Body Systems: By: Veda PurnithaDocument60 pagesBody Systems: By: Veda PurnithaVeda PurnithaNo ratings yet
- Themes in Fiction 1Document1 pageThemes in Fiction 1api-261172766No ratings yet
- Convection Conduction Radiation Fact SheetDocument1 pageConvection Conduction Radiation Fact Sheetapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Multiply or DivideDocument1 pageMultiply or Divideapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Weather ToolsDocument20 pagesWeather Toolsapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Mapping The West Lewis and ClarkDocument2 pagesMapping The West Lewis and Clarkapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Introduction To Westward ExpansionDocument1 pageIntroduction To Westward Expansionapi-261172766No ratings yet
- 50 Chapter 1 - The Seers of StrokDocument14 pages50 Chapter 1 - The Seers of StrokALFREDNo ratings yet
- JBL Ctrl24C CT.v1 PDFDocument4 pagesJBL Ctrl24C CT.v1 PDFZefRy D'e DSNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Vocabulary PracticeDocument2 pagesUnit 1: Vocabulary PracticeReka KutasiNo ratings yet
- 06 Chapter 01 PDFDocument23 pages06 Chapter 01 PDFbibaNo ratings yet
- 0-Ecolier CompressedDocument8 pages0-Ecolier CompressedIshaq HashmiNo ratings yet
- Embroidery StitchesDocument15 pagesEmbroidery StitchesVanrick Arino100% (1)
- OSPF Part1 - Study Notes CheatSheet - (Waqas Karim) WK v2Document1 pageOSPF Part1 - Study Notes CheatSheet - (Waqas Karim) WK v2Heera SinghNo ratings yet
- Lee LabradaDocument7 pagesLee Labradaviky100% (1)
- Calendrier SuperbikeDocument2 pagesCalendrier SuperbikeLe Journal du CentreNo ratings yet
- Scribd - Read Unlimited Books PDFDocument16 pagesScribd - Read Unlimited Books PDFfgsdfgdsg0% (1)
- Axis Bank Credit CardsDocument19 pagesAxis Bank Credit Cardsamit singhNo ratings yet
- Mapeh Long QuizDocument2 pagesMapeh Long QuizRehyna Relos CrudaNo ratings yet
- Indra-Normarc 7710 0Document2 pagesIndra-Normarc 7710 0nemyaNo ratings yet
- Symbolism in The Devil and Tom WalkerDocument20 pagesSymbolism in The Devil and Tom Walkeranon_980674024No ratings yet
- RE3 AIO ExtraPrac 8 L1Document3 pagesRE3 AIO ExtraPrac 8 L1Elba LazoNo ratings yet
- Snow White. Cuentos Tradicionales en Inglés para NiñosDocument4 pagesSnow White. Cuentos Tradicionales en Inglés para Niñosvictorposadas0% (1)
- Software - AvaxHomeDocument11 pagesSoftware - AvaxHomeisaias.prestesNo ratings yet
- Audiolab 8000A Owner's Manual PDFDocument10 pagesAudiolab 8000A Owner's Manual PDFspyrosNo ratings yet
- EquestrianCatalogue - 2014 As at 26th NovemberDocument29 pagesEquestrianCatalogue - 2014 As at 26th NovemberAnne HjorthNo ratings yet
- AKLATech Entrepreneurship - Week3-6 FinalDocument15 pagesAKLATech Entrepreneurship - Week3-6 FinalCharmaine Joemaica SapigaoNo ratings yet
- Team 2 Section 5 Final Business Plan 1Document27 pagesTeam 2 Section 5 Final Business Plan 1api-636075808No ratings yet
- Paititi DeyermenjianDocument26 pagesPaititi DeyermenjianjorgenarcisoNo ratings yet
- MAXPRO® NVRs Family Data SheetDocument4 pagesMAXPRO® NVRs Family Data SheetMarlonNo ratings yet
- Ernst Krenek-Tonal Counterpoint - in The Style of The Eighteenth Century (BH Scores and Books) PDFDocument50 pagesErnst Krenek-Tonal Counterpoint - in The Style of The Eighteenth Century (BH Scores and Books) PDFLurian Lima100% (1)
- Tabuada PDFDocument4 pagesTabuada PDF7869aqNo ratings yet