Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
103 viewsBewakoof
Bewakoof
Uploaded by
Akhil AroraThis document provides course information for four courses:
1. Network and Systems (EE 211/EE 211H) which covers topics like signals and transforms, resistive circuits, analysis methods, graph theory, three phase circuits, and network functions.
2. Electrical Measurements and Instrumentation (EE 212/EE 212H) which covers topics like introduction to instrumentation, analog instruments, sensors and transducers, bridge measurements, electronic instruments, signal generators and analyzers, and storage/display devices.
3. Electrical Machines-I (EE 214/EE 214H) which covers topics like principles of electromechanical energy conversion, transformers, DC machines, and three-phase induction motors.
4.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- SPSC SyllabusDocument3 pagesSPSC SyllabusNirmal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cfmi Cfm56 NDTM Cfmi-Tp - nt.11 Rev 36 May 31, 2000Document392 pagesCfmi Cfm56 NDTM Cfmi-Tp - nt.11 Rev 36 May 31, 2000gm&o100% (3)
- 3 SemDocument8 pages3 Semdelinquent_abhishekNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Ph. D. (Engg.) Admission Test (From Electrical Engineering Department)Document5 pagesSyllabus of Ph. D. (Engg.) Admission Test (From Electrical Engineering Department)PradyumnaRoyNo ratings yet
- Electrical New SyallabusDocument65 pagesElectrical New SyallabusSuraj KanojiaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Ug - BeDocument35 pagesSyllabus Ug - Bevbose0555No ratings yet
- Detailed Syllabus FOR 5 Semester: Anpat Niversity U. V. Patel College of Engineering Ganpat Vidyanagar, Kherva-382711Document10 pagesDetailed Syllabus FOR 5 Semester: Anpat Niversity U. V. Patel College of Engineering Ganpat Vidyanagar, Kherva-382711Maulik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Shivaji University, Kolhapur: T.E. (Electrical Engineering) (Semester - VI)Document15 pagesShivaji University, Kolhapur: T.E. (Electrical Engineering) (Semester - VI)sudhirdhadge39No ratings yet
- Paper - I 1. Engineering MathematicsDocument3 pagesPaper - I 1. Engineering MathematicsSURYAPRATAPREDDY BHUMANo ratings yet
- Mathematics Iii: Unit I: (Laplace Transform)Document11 pagesMathematics Iii: Unit I: (Laplace Transform)HhhhNo ratings yet
- SRMS ManualDocument41 pagesSRMS ManualHarshit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ETC SyllabusDocument46 pagesETC SyllabusLavanya ChavaNo ratings yet
- EE Engg. 6 Sem.Document15 pagesEE Engg. 6 Sem.krishna universityNo ratings yet
- BE-EEE Courses DescriptionDocument7 pagesBE-EEE Courses DescriptionShrayan BarmanNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. Mechanical Engineering Scheme PDFDocument87 pagesB. Tech. Mechanical Engineering Scheme PDFshubham.aggarwalNo ratings yet
- 43203notice 04232019 PDFDocument59 pages43203notice 04232019 PDFHgNo ratings yet
- Be EeeDocument38 pagesBe EeeGopinathblNo ratings yet
- Branch/Discipline: Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pagesBranch/Discipline: Electrical EngineeringSravan ReddyNo ratings yet
- EE1101Document2 pagesEE1101balajiNo ratings yet
- Curriculum S T R U C T U R E of S.Y.-B.Tech (Electrical Engineering) (Regularstudents)Document56 pagesCurriculum S T R U C T U R E of S.Y.-B.Tech (Electrical Engineering) (Regularstudents)Bhushan RaneNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Control Systems: RationaleDocument15 pages3.1 Control Systems: RationaleSoumya BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering: Ea6210: Switchgear and ProtectionDocument5 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering: Ea6210: Switchgear and ProtectionAvi PokiNo ratings yet
- em Theory:: Paper IDocument3 pagesem Theory:: Paper IDeepthi Madhav AnnavarapuNo ratings yet
- Previewpage - Do RemovedDocument16 pagesPreviewpage - Do RemovedGona SujathaNo ratings yet
- Branch/Discipline: Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesBranch/Discipline: Electrical EngineeringsixfacerajNo ratings yet
- CCCC C C C CCDocument3 pagesCCCC C C C CCManoj MeenaNo ratings yet
- D) Electrical Engineering Syllabus Ies 2015: Paper I 1. EM TheoryDocument4 pagesD) Electrical Engineering Syllabus Ies 2015: Paper I 1. EM TheorysyamalaNo ratings yet
- Elect Et Syllabus 2013 For SJVNDocument3 pagesElect Et Syllabus 2013 For SJVNBest KvansNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabi Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument12 pagesCourse Syllabi Department of Electrical EngineeringPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Electrical EngineeringbasabNo ratings yet
- AKU Patna Syllabus 3rd YearDocument20 pagesAKU Patna Syllabus 3rd Yearडाँ सूर्यदेव चौधरीNo ratings yet
- Nikesh Indus Final SyllabusDocument15 pagesNikesh Indus Final Syllabusvatsalshah24No ratings yet
- Syllabus ESEDocument3 pagesSyllabus ESESuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
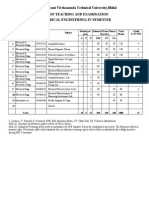
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekananda Technical University, Bhilai Scheme of Teaching and Examination Be (Electrical Engineering) Iv SemesterDocument12 pagesChhattisgarh Swami Vivekananda Technical University, Bhilai Scheme of Teaching and Examination Be (Electrical Engineering) Iv SemesterAnonymous l5X3VhTNo ratings yet
- EE May 04 2011Document40 pagesEE May 04 2011ChandanUpadhyayNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Mizoram: Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Btech SyllabusDocument32 pagesNational Institute of Technology Mizoram: Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Btech SyllabustoshaliNo ratings yet
- EEE 4th SemesterDocument5 pagesEEE 4th SemesterKeyern MwihandiNo ratings yet
- Ese Ee PDFDocument4 pagesEse Ee PDFJfttgjugNo ratings yet
- Sem6 SyllabusDocument5 pagesSem6 SyllabusSamsung TabletNo ratings yet
- Stage I - Paper I, Objective Type, Common To All Candidates, 2 Hours Duration, 200 Marks MaximumDocument3 pagesStage I - Paper I, Objective Type, Common To All Candidates, 2 Hours Duration, 200 Marks MaximumAayushGoyalNo ratings yet
- FRM Course Syllabus IPDownloadDocument1 pageFRM Course Syllabus IPDownloadMovie ClipsNo ratings yet
- JNTUK DAP Course Structure and Syllabus EEE II YEAR R10 Students 3Document32 pagesJNTUK DAP Course Structure and Syllabus EEE II YEAR R10 Students 3Shravan RaoNo ratings yet
- 2007-08 M.sc. ElectronicsDocument19 pages2007-08 M.sc. ElectronicsUlhasNo ratings yet
- Eee 8th Sem r2008Document18 pagesEee 8th Sem r2008Ashok VannanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines & Measurement B.E. 4 SemesterDocument4 pagesElectrical Machines & Measurement B.E. 4 Semestersameerpatel15770No ratings yet
- Elecives CombinedDocument32 pagesElecives CombinedmeetNo ratings yet
- IV B.E. (Electrical Engineering)Document8 pagesIV B.E. (Electrical Engineering)9y9aNo ratings yet
- BainganDocument3 pagesBainganDebadrita BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Ies Syllabus: Part A: General EnglishDocument4 pagesIes Syllabus: Part A: General EnglishRaj RaushanNo ratings yet
- PSU's Common Syllabus For Electrical Engineering Non-Technical: General StudyDocument2 pagesPSU's Common Syllabus For Electrical Engineering Non-Technical: General StudyJitendra TambeNo ratings yet
- IES Electrical Engg.Document2 pagesIES Electrical Engg.Anil BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between IES 2016 and 2017 Syllabus For Electrical EngineeringEEDocument5 pagesComparison Between IES 2016 and 2017 Syllabus For Electrical EngineeringEERishi KamalNo ratings yet
- Eec403: Microwave EngineeringDocument1 pageEec403: Microwave EngineeringNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- IES Electrical Engineering SyllabusDocument4 pagesIES Electrical Engineering SyllabusAvinash Arya100% (1)
- Syllabus B ElectricalDocument6 pagesSyllabus B ElectricalnetprosenjitNo ratings yet
- II ND YEAR SEM B U.G. Elex and TC Syllabus 2022-23Document12 pagesII ND YEAR SEM B U.G. Elex and TC Syllabus 2022-23Mitali KhareNo ratings yet
- EEE1001 - ELECTRIC-CIRCUITS-AND-SYSTEMS - LTP - 1.3 - 53 - EEE1001 - Electric Circuits and Systems - LTP - 4 - V1.3Document2 pagesEEE1001 - ELECTRIC-CIRCUITS-AND-SYSTEMS - LTP - 1.3 - 53 - EEE1001 - Electric Circuits and Systems - LTP - 4 - V1.3devmewada2505No ratings yet
- UEE001 SyllabusDocument2 pagesUEE001 SyllabusashNo ratings yet
- Creation of Rare Heavy Elements Witnessed in Neutron-Star CollisDocument3 pagesCreation of Rare Heavy Elements Witnessed in Neutron-Star CollisEkkoNo ratings yet
- Governmental Legal and Regulatory Framework For SafetyDocument63 pagesGovernmental Legal and Regulatory Framework For Safetychrissbans100% (1)
- The Environment Is A Very Complex PhenomenonDocument2 pagesThe Environment Is A Very Complex PhenomenonAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Physics Past Paper - P2 - 2015-20 PDFDocument424 pagesPhysics Past Paper - P2 - 2015-20 PDF123 456No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/41Document28 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/41Raghav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Complete Chemistry Notes: Unit 1: States of MatterDocument72 pagesIgcse Complete Chemistry Notes: Unit 1: States of MatterYoga RomdoniNo ratings yet
- Enrico FermiDocument3 pagesEnrico FermiEsha MishraNo ratings yet
- IGCSE PhysicsDocument15 pagesIGCSE PhysicsLailla MarlinaNo ratings yet
- Wide Energy Range Efficiency Calibration Method For Ge DetectorsDocument20 pagesWide Energy Range Efficiency Calibration Method For Ge DetectorsシリーズスーパNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument28 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelSaeeda KhiljiNo ratings yet
- 198471Document5 pages198471Clarice ArañezNo ratings yet
- Physics 3204: UNIT 3 - Test - Matter Energy InterfaceDocument7 pagesPhysics 3204: UNIT 3 - Test - Matter Energy InterfaceRaJA ViNoDNo ratings yet
- Physics in Focus Year 12 Student Book 2Nd Edition Robert Farr Download PDF ChapterDocument51 pagesPhysics in Focus Year 12 Student Book 2Nd Edition Robert Farr Download PDF Chaptergary.taylor799100% (8)
- G.C.E. (Advanced Level) CHEMISTRYDocument297 pagesG.C.E. (Advanced Level) CHEMISTRYMaliNo ratings yet
- Advanced Burn Life SupportDocument118 pagesAdvanced Burn Life SupportIntan Noa100% (1)
- Atomic StructureDocument5 pagesAtomic StructureMustafa OmerNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On RadioactivityDocument11 pagesLiterature Review On Radioactivityafdtrqaau100% (1)
- Inverse Sqaure Law For Gamma RadiationDocument7 pagesInverse Sqaure Law For Gamma RadiationAhmedAmer1100% (2)
- Grade 7 ForceDocument23 pagesGrade 7 ForceJuan Miguel Sapad AlpañoNo ratings yet
- Final Mock 5 Paper2Document11 pagesFinal Mock 5 Paper2Dewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- Chem Final ExamDocument42 pagesChem Final ExamWild RiftNo ratings yet
- Applications MATH 404Document32 pagesApplications MATH 404Rocel Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- Thesis AnttirtyDocument84 pagesThesis Anttirtynagatopein6No ratings yet
- Physics STPM Past Year Questions With Answer 2006Document18 pagesPhysics STPM Past Year Questions With Answer 2006Chan Q ON100% (1)
- 0625/s 19/qp/42Document16 pages0625/s 19/qp/42n.No ratings yet
- General Physics 2 4Q Week 9.pubDocument13 pagesGeneral Physics 2 4Q Week 9.pubShane June DemetrialNo ratings yet
- Final Coaching 4Document12 pagesFinal Coaching 4Cliff Sotto Omayan100% (1)
- Wa0004.Document13 pagesWa0004.shahbikky67No ratings yet
- Modul Analisis Fizik Merbau Miri SPM 2014 SkemaDocument5 pagesModul Analisis Fizik Merbau Miri SPM 2014 SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
Bewakoof
Bewakoof
Uploaded by
Akhil Arora0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
103 views10 pagesThis document provides course information for four courses:
1. Network and Systems (EE 211/EE 211H) which covers topics like signals and transforms, resistive circuits, analysis methods, graph theory, three phase circuits, and network functions.
2. Electrical Measurements and Instrumentation (EE 212/EE 212H) which covers topics like introduction to instrumentation, analog instruments, sensors and transducers, bridge measurements, electronic instruments, signal generators and analyzers, and storage/display devices.
3. Electrical Machines-I (EE 214/EE 214H) which covers topics like principles of electromechanical energy conversion, transformers, DC machines, and three-phase induction motors.
4.
Original Description:
timepass
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides course information for four courses:
1. Network and Systems (EE 211/EE 211H) which covers topics like signals and transforms, resistive circuits, analysis methods, graph theory, three phase circuits, and network functions.
2. Electrical Measurements and Instrumentation (EE 212/EE 212H) which covers topics like introduction to instrumentation, analog instruments, sensors and transducers, bridge measurements, electronic instruments, signal generators and analyzers, and storage/display devices.
3. Electrical Machines-I (EE 214/EE 214H) which covers topics like principles of electromechanical energy conversion, transformers, DC machines, and three-phase induction motors.
4.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
103 views10 pagesBewakoof
Bewakoof
Uploaded by
Akhil AroraThis document provides course information for four courses:
1. Network and Systems (EE 211/EE 211H) which covers topics like signals and transforms, resistive circuits, analysis methods, graph theory, three phase circuits, and network functions.
2. Electrical Measurements and Instrumentation (EE 212/EE 212H) which covers topics like introduction to instrumentation, analog instruments, sensors and transducers, bridge measurements, electronic instruments, signal generators and analyzers, and storage/display devices.
3. Electrical Machines-I (EE 214/EE 214H) which covers topics like principles of electromechanical energy conversion, transformers, DC machines, and three-phase induction motors.
4.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 10
Course Name: NETWORK AND SYSTEMS
Course Code: EE 211/EE 211H Credits: 4 L T P : 4-0-0
Pre Req: ---
Lecture wise break up Number of Lectures
1. SIGNALS AND TRANSFORMS [06]
Basic continuous time signals, Laplace transform of basic signals and functions, initial
and final value theorems, inverse Laplace transform, convolution theorem, Fourier
integral and Fourier transform, transform of common functions and periodic wave forms,
applications of Laplace and Fourier transforms to network analysis.
2. RESISTIVE CIRCUITS [08]
Sources and Loads, review of KCL and KVL, Duality, Circuits with controlled sources,
Linear elements and circuits, proportionality principle, superposition theorem, Thevenin,
Norton, reciprocity, Millman and Tellegens theorems, source conversions.
3. ANALYSIS METHODS [06]
Node analysis, mesh analysis, analysis with controlled sources, delta-wye
transformations, network topology concepts, AC circuit analysis, series and parallel
resonance,
4. GRAPH THEORY [05]
Graph of a network, definitions, tree, co tree, link, basic loop and basic cut set,
incidence matrix, cut set matrix, tie set matrix duality, loop and nodal methods of
analysis
3. THREE PHASE CIRCUITS [05]
Balanced and unbalanced three phase wye and delta loads, symmetrical components,
three phase power measurements.
4. MAGNETIC COUPLING AND MUTUAL INDUCTANCE [03]
Analysis of circuits with mutual inductance, dot convention.
5. NETWORK FUNCTIONS [04]
Transform impedances, Network functions, concepts of poles and zeros,
properties of driving point and transfer functions, time response and stability from pole
zero plot.
6. TWO PORT NETWORKS [06]
Characterization of two port networks, Z, Y, ABCD and h-parameters, inter-relationships
between the parameters, interconnection of two port networks, ladder and lattice
networks, T and representations.
7. FILTERS [05]
Image parameters and characteristics impedance, passive and active filter fundamentals,
low pass, high pass, band pass filters, introduction to active filters
BOOKS:
1 Circuits Engineering Concepts and Analysis of Linear Electric Circuits by A.
Bruce Carlson, Thomson Brooks/Cole.
2 Network and Systems by D. Roy Choudhary, Wiley Eastern Ltd.
REFERENCES:
1. Network Analysis & Synthesis by FF Kuo, Wiley International
2. Circuit Analysis: A Systems Approach by Russell M. Mersereau et.al, Pearson
Education Inc., 2006.
Honors: Students opting for Honors course will have to over reach academic
performance through learning of advanced topics and evaluation in terms of assignments
working on related field problems and additional questions for honors students in the
examinations.
Course Name: ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION
Course Code: EE 212/EE 212H Credits: 4 L T P :4 0 0
Pre Req: ---
Design Points: 2
Lecture wise break up Number of Lecturers
1. INTRODUCTION (06)
Functional elements of an instrument, static and dynamic characteristics, errors in
measurement, statistical evaluation of measurement data, standard and calibration.
Measurement of error, Accuracy and Precision, significant figures, types of error,
Statistical analysis of data, probability of errors, limiting errors. Unit and Measurement:
Fundamental and derived units, systems of units electric and magnetic units, international
system of units, conversion of units.
2. ANALOG INSTRUMENTS (08)
Electro-mechanical instruments moving, coil, moving iron, electrodynamics,
rectifier, electrostatic instruments, current voltage and power measurements, induction
type energy meter, q meter, frequency meter, power factor meter.
3. SENSOR AS TRANSDUCERS (07)
Classification of transducers - selection of transducers resistive, capacitive and
inductive transducers- piezo electric transducers - optical and digital transducers - pH
electrodes -transducers for measurement of displacement, temperature, level, flows,
pressure, velocity and acceleration.
4. BRIDGE MEASUREMENT (06)
Wheatstone bridge, Kelvin bridge, a.c. bridge and their application for the
measurement of self inductance and mutual inductance, Wagner Ground connection,
measurement of capacitance, Measurement of low and high resistance.
5. ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTS (07)
Principle and analog and digital ammeters and volt-meters-single and three phase
watt meters and energy meter- magnetic measurements -instruments transformers.
6. SIGNAL GENERATORS AND ANALYSERS (07)
Sweep frequency generator, frequency synthesized signal generator signal generator
and function generator, wave analyzer harmonic distortion and spectrum analyzer.
7. STORAGE AND DISPLAY DEVICES (07)
Magnetic disc and tape recorders, digital plotters and printers, CRT display, digital
CRO, LED, LCD and Dot matrix displays.
BOOKS:
1. Doebeling, E.O.: Measurement Systems- Application and Design, McGraw Hill
Publishing Company, 1990
2. A.K. Sawhney, A course in Electrical and Electronics Measurements and
Instrumentation, Dhanpat Rai & Co., (Pvt) Ltd., 2000.
REFERENCES
1. Stout MoB., Basic Electrical Measurement, Prentice Hall of India, 1986.
2. Dalley, J.W., Riley, W.F. and Meconnel, K.G., Instrumentation for Engineering
Measurement, John Wiley & Sons, 1999.
3. Moorthy, D.V.S., Transducers and Instrumentation, Prentice Hall of India, 1995.
4. Mooris. A.S., Principle of Measurement and Instrumentation, Prentice Hall of
India, 1999.
Honors: Students opting for Honors course will have to over reach academic
performance through learning of advanced topics and evaluation in terms of assignments
working on related field problems and additional questions for honors students in the
examinations.
Course Name: ELECTRICAL MACHINES-I
Course Code: EE 214/EE 214H Credits: 4 L T P: 4 -0- 0
Pre Req: ---
Design Points: 2
Lecture wise breakup No. of lectures
1 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRO-MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION
(07)
Review of magnetic circuits, magnetic materials and their properties, flow of
energy in electromagnetic devices, singly excited systems, determination of mechanical
force, mechanical energy, torque equation, doubly excited systems, energy stored in
magnetic field, electromagnetic torque, generation emf in machines, torque in machines
with cylindrical air gap.
2 TRANSFORMERS (13)
Construction, ideal transformer, no-load and on-load operation, real transformer
and equivalent circuit, transformer losses, testing of transformer and determination of its
parameters, the per unit system, efficiency and voltage regulation, autotransformer,
parallel operation, three phase transformers construction and connections applications.
3 DC MACHINES (14)
Construction, emf and torque equations, circuit model, armature reaction and
commutation, methods of excitation, characteristics of generators and motors, starting
and speed control of dc motors, starters, losses, efficiency and testing of dc machines.
4 THREE-PHASE INDUCTION MOTORS (14)
Construction, torque production, slip, equivalent circuit, power and torque
expressions, torque-slip characteristics, testing, circle diagram, calculations of
performance, starting and speed control techniques, cogging and crawling.
BOOKS:
1. Electrical Machines by I. J. Nagrath and D. P. Kothari, Tata McGraw Hill
2. Electric Machinery by A.E. Fitzgerald, Charles Kingsley, Jr. and Stephen D.
Umans, Tata McGraw-Hill.
REFERENCES:
1. Electrical Machinery by P. S. Bimbhra, Khanna Publishers
2. Electrical Machinery by M. G. Say, C.B.S. Publisher
Honors: Students opting for Honors course will have to over reach academic
performance through learning of advanced topics and evaluation in terms of assignments
working on related field problems and additional questions for honors students in the
examinations.
Course Name: PHYSICS - II
Course Code: PY 201 Credits: 4 L T P: 4 0 0
Pre-requisite: PY 101
Lecture-wise breakup (No. of Lectures)
1. QUANTUM MECHANICS & ATOMS
Quantum theory of light, X-rays production, spectrum & diffraction (Braggs law),
photoelectric effect, Compton effect, pair production, photons & gravity, black holes, de-
Broglie hypothesis, particle diffraction, uncertainty principle and applications (7)
Postulates of quantum mechanics, Schrodinger theory, time-dependent and time-
independent Schrodinger equation, wave function, Born interpretation and normalization,
expectation values (3)
Particle in a box (infinite potential well), finite potential step and barrier problems,
tunneling, linear harmonic oscillator (one-dimensional) (4)
Hydrogen atom, radiative transitions and selection rules, electron spin, Stern-Gerlach
experiment, Spin-orbit coupling, exclusion principle, symmetric and antisymmetric
wavefunctions (6)
ADDITIONAL TOPICS FOR HONOURS STUDENTS: -decay, Zeeman effect,
Correspondence Principle, Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics
2. NUCLEAR PHYSICS
Natural radioactivity, successive radioactive transformations, radioactive
equilibrium, radioactive series, radiometric dating (3)
Nuclear force and its characteristics, Elementary description of shell model,
explanation of magic numbers, liquid drop model and semi-empirical binding energy
formula (3)
Nuclear fission, fission products, mass and energy distribution of fission products,
neutron emission and energy distribution of neutrons emitted in fission, theory of fission
process, nuclear reactors classification, neutron cycle in thermal reactors and four-
factor formula for neutron reproduction, nuclear fusion controlled thermonuclear
reactions. (5)
ADDITIONAL TOPICS FOR HONOURS STUDENTS: Artificial radioactivity and
its applications, -decay (energy spectrum & discovery of neutrino), Fusion Reactions in
stars
3. STATISTICAL PHYSICS
Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics, molecular energies in an ideal gas, Bose-Einstein and
Fermi-Dirac statistics, black body radiation, Rayleigh-Jeans and Plancks radiation laws,
free electrons in a metal, electron-energy distribution, Fermi energy, electronic specific
heat, conduction in metals, thermionic emission (9)
ADDITIONAL TOPICS FOR HONOURS STUDENTS: Specific heat of solids,
Bose-Einstein condensation
4. SOLIDS AND SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS
Band theory of solids, Kronig-Penney Model (qualitative), conductors, insulators and
semiconductors, p-type and n-type semiconductors, statistics of electrons and holes, Hall
effect (for single as well as both type of charge carriers) (5)
ADDITIONAL TOPICS FOR HONOURS STUDENTS: p-n junction, rectifier, LED,
tunnel diode
5. SUPER CONDUCTIVITY
Occurrence, destruction of super conductivity, Meissner effect, type I and type II
Super-conductors; heat capacity, isotope effect, thermodynamical considerations, London
equations & penetration depth, coherence length, BCS theory (elementary description),
applications of superconductors. (5)
ADDITIONAL TOPICS FOR HONOURS STUDENTS: High temperature
superconductivity, Josephson junctions
TEXT BOOK: Concepts of Modern Physics, by Arthur Beiser (McGraw-Hill)
REFERENCE BOOKS:
1. Nuclear Physics, by I. Kaplan (Addison-Wesley)
2. Solid State Physics, by C. Kittel (Wiley Eastern)
3. Solid State Physics, by S.O. Pillai (New Age International)
4. Introduction to Modern Physics, by Richtmyer, Kennard & Cooper (
McGraw Hill)
5. Introduction to Modern Physics, by Mani & Mehta (East West Press)
Modern Physics, by Bernstein, Fishbane & Gasiorowicz (Pearson Education)
Course Name: PHYSICS LAB
Course Code: PY 202 Credits: 2 L T P: 0 0 3
Pre-requisite: None
Lecture-wise breakup (No. of Lectures)
TWELVE EXERCISES OUT OF THE FOLLOWING:
1. Familiarization with various measuring instruments Vernier calipers, screw gauge,
spherometer, spectrometer etc. (3)
2. To find the wavelength of sodium light using Fresnels biprism. (3)
3. (i) To determine the wavelength of He-Ne laser using transmission grating.
(ii) To determine the slit width using the diffraction pattern. (3)
4. To determine the wave length of sodium light by Newtons rings method.
(3)
5. To determine the wave length of sodium light using a diffraction grating.
(3)
6. To find the specific rotation of sugar solution using a Bi-quartz Polarimeter.
(3)
7. To find the energy band gap of the given semiconductor by four probe method.
(3)
8. To find the angle of prism and the angle of minimum deviation with the help of a
spectrometer, and hence to determine the refractive index of the material of the prism.
(3)
9. To design a method to draw equipotential lines with various geometries of electrodes
kept at different potentials. (3)
10. To study the Hall effect of a given semiconductor. (3)
11. To determine the dielectric constant of the given materials. (3)
12. To study the photoelectric effect. (3)
13. To study the B-H curve of the ferromagnetic materials. (3)
14. To design a hollow prism and used it find the refractive index of a given liquid.
(3)
TEXT BOOKS:
1. Practical Physics, by Gupta & Kumar (Pragati Prakashan)
2. B.Sc. Practical Physics, by C.L.Arora (S. Chand)
COURSE NAME : COMPUTER NETWORKS
COURSE CODE : ENN 206
CREDITS : 04
L T P : 4 00
LECTURE WISE BREAKUP NO. OF LECTURES
Computer Networks and the Internet: 10
Internet and its Architecture, ISPs and Internet Backbones, Delay and Loss in Packet-
Switched Networks, Protocol Layers and Service Models, Brief History of Computer
Networking and the Internet.
Application Layer: 10
Principles of Network applications, The Web and HTTP, File Transfer: FTP, Electronic
Mail in the Internet, DNS - The Internet's Directory Service, P2P file sharing, Socket
Programming with TCP & UDP
Transport Layer: 10
Introduction and Transport-Layer Services and Principles, Multiplexing and
Demultiplexing, Connectionless Transport: UDP, Principles of Reliable of Data Transfer,
Connection-Oriented Transport: TCP, Principles of Congestion Control, TCP Congestion
Control
The Network Layer: 10
Introduction, Virtual circuit and datagram networks, Router Internals, Internet
Protocol(IP): Forwarding and addressing in the Internet, Subnetting, Routing Algorithms
, shortest path, flooding, distance vector routing and link state routing, Routing in the
Internet, Broadcast and Multicast Routing, Other troubleshooting protocols
The Data Link Layer: 10
Link Layer: Introduction and Services, Error Detection and Correction Techniques,
Multiple Access Protocols, Link-layer Addressing, Ethernet, Hub and Switches, PPP,
Link Virtualization: a network as a link layer.
NETWORK TECHNOLGIES
Overview of Local Area Networks and Wide Area Networks, LAN Standards, How
LANs operate, LAN Topologies, ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CD, Overview of Ethernet
BOOK:
1. James F. Kurose and Keith W. Ross, Computer Networking: A top down approach
featuring the Internet, Pearson Education, third ed.
REFERENCES:
1. A.S. Tanenbaum, Computer Networks, 4th Edition, PHI, 2004.
2. D. Bertesekas and R. Gallager, Data Networks, 2nd Edition, PHI, 2000.
3. U. Black, Computer Networks, PHI, 1997.
4. S. Keshav, An engineering approach to computer networking, Addison Wesley,
1999.
5. William Stallings, Data & Computer Communication, PHI, 6th Edition, 2002.
6. B.A. Forouzan, Data communications and networking, TMH, 1st ed, 2000.
Course Name: POWER ELECTRONICS
Course No.: ENN 204 Credit: 4 L T P : 4-0-0
Design Points: 2
Pre Req: ---
Lecture wise break up No of Lectures
1. INTRODUCTION (07)
Applications of Power Electronics, Power Semiconductor Devices : Power
diodes, Thyristors and Power Transistors, Control Characteristics of Power devices,
Characteristics and Specifications of Switches, Types of power Electronic circuits,
Design of Power Electronics Equipment, Peripheral Effects, Power and Intelligent
Modules
2. POWER TRANSISTORS (05)
Bipolar Junction transistors, Power MOSFETs, IGBTs and Comparisons of
Transistors.
3. THYRISTORS (08)
Thyristor Characteristics, Two- Transistor Model of Thyristors, Transistor Turn-
on, Transistor Turn-off, Phase Controlled Thyristors , Fast-Switching Thyristors,
LASCRs, GTOs, IGCTs, MCTs, SITHs, Comparisons of Thyristors, Series Operation of
Thyristors, Parallel Operation of Thyristors, di/dt Protection, dv/dt Protection.
4. CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS (10)
Principle of Phase controlled converter operation, Single Phase Full converters,
Single Phase dual converters, Principle of three phase Half wave converters, Three Phase
Full Converters , Three Phase Dual Converters, Single Phase Semi Converters, Three
Phase semi Converters, Effects of Load and Source Inductances
5. DC-DC CONVERTERS (07)
Principle of Step Down Operation, Step-Down Converter with RL Load, Principle
of Step-up Operation, Step-up converter with a Resistive Load, Converter Classification
6. INVERTERS (08)
Principle of Operation, Performance Parameters, Single-Phase bridge Inverters,
Three Phase Inverters, Voltage control of single phase Inverters, Series Resonant
Inverters, Parallel Resonant Inverters
7. AC VOLTAGE CONTROLLERS (03)
Principle of ON-OFF control, Principle of Phase control, Cycloconverters.
8. APPLICATIONS OF POWER ELECTRONICS (04)
Uninterrupted power supply, switch mode power supply, zero voltage switch,
speed control of dc drives.
BOOKS:
1. Power Electronics by Dr. P.S.Bhimra, Khanna Publishers.
2. Power Electronics, by Muhammad H. Rashid, Pearson Education, Third Edition
Honors For students registering for honors course in this subject are to be given
advanced problem to check their capabilities to earn in the subject. The
assignment/projects/exploring an idea using e-support involving independent effort of the
student.
Course Name : SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS
Course Code : ENN 203
Credits : 4
L T P : 4 0 0
Rationale:
After going through this course students would be able to analyze signals for
communication systems in time and frequency domain. It would enable them to
troubleshoot the communication systems hence with.
Lecture wise break up No of Lectures
SIGNALSAND
SYSTEMS (05)
Signals and their classification, size of the signal, continuous and discrete time signals,
Systems and their classification, signal operations on elementary CT/DT signals:
Shifting, flipping, multiplication, addition, modulation, windows and pulse, Impulse.
Continuous and discrete time systems and their applications.
FOURIER
SERIES (09)
Overview of trigonometric, compact and exponential fourier series, Fourier spectrum of
signals, properties of fourier series components, distribution of average power in
frequencies, parsevals theorem.
FOURIER
TRANSFORM (15)
Aperiodic signal representation by Fourier integral, concept of continuous and discrete
spectrum, essential and absolute bandwidth, convolution, correlation, auto-correlation
and cross-correlation and their properties, energy spectral density, power spectral density,
calculation of the energy and power signal respectively, sampling theorem, properties of
Fourier transform and applications
RANDOM SIGNAL THEORY AND
NOISE (12)
Sample space, random variables-discrete and continuous variable, conditional
probability, probability density function, cumulative density function and their properties,
noise and its types, white noise, noise calculations, noise figure and its calculations for
cascaded networks, nose equivalent temperature, optimum detection and matched filters.
INFORMATION
THEORY (09)
Concept of information, entropies of discrete system, rate of transmission-redundancy,
efficiency and information rate, channel capacity theorem, source encoding including
Huffman encoding, Shannon coding theorem, comparisons of analog and digital
communication systems on the basis of the ideal channel capacity theorem.
BOOK:
1. Modern Digital & Analog Communication Systems by B.P.Lathi, pub. Oxford Univ.
Press, 3rd Edition
REFERENCES:
Signal And System by M.J.Robert, TMH, Third Edition.
Signals and systems by A.V.Oppenheim & A.S. willisky, 2nd edition, Pearson education.
Introduction to Communication Theory by P.D. Sharma
Signals and systems by HAWI.P. HSU, Schaum Series by TMH
You might also like
- SPSC SyllabusDocument3 pagesSPSC SyllabusNirmal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cfmi Cfm56 NDTM Cfmi-Tp - nt.11 Rev 36 May 31, 2000Document392 pagesCfmi Cfm56 NDTM Cfmi-Tp - nt.11 Rev 36 May 31, 2000gm&o100% (3)
- 3 SemDocument8 pages3 Semdelinquent_abhishekNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Ph. D. (Engg.) Admission Test (From Electrical Engineering Department)Document5 pagesSyllabus of Ph. D. (Engg.) Admission Test (From Electrical Engineering Department)PradyumnaRoyNo ratings yet
- Electrical New SyallabusDocument65 pagesElectrical New SyallabusSuraj KanojiaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Ug - BeDocument35 pagesSyllabus Ug - Bevbose0555No ratings yet
- Detailed Syllabus FOR 5 Semester: Anpat Niversity U. V. Patel College of Engineering Ganpat Vidyanagar, Kherva-382711Document10 pagesDetailed Syllabus FOR 5 Semester: Anpat Niversity U. V. Patel College of Engineering Ganpat Vidyanagar, Kherva-382711Maulik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Shivaji University, Kolhapur: T.E. (Electrical Engineering) (Semester - VI)Document15 pagesShivaji University, Kolhapur: T.E. (Electrical Engineering) (Semester - VI)sudhirdhadge39No ratings yet
- Paper - I 1. Engineering MathematicsDocument3 pagesPaper - I 1. Engineering MathematicsSURYAPRATAPREDDY BHUMANo ratings yet
- Mathematics Iii: Unit I: (Laplace Transform)Document11 pagesMathematics Iii: Unit I: (Laplace Transform)HhhhNo ratings yet
- SRMS ManualDocument41 pagesSRMS ManualHarshit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ETC SyllabusDocument46 pagesETC SyllabusLavanya ChavaNo ratings yet
- EE Engg. 6 Sem.Document15 pagesEE Engg. 6 Sem.krishna universityNo ratings yet
- BE-EEE Courses DescriptionDocument7 pagesBE-EEE Courses DescriptionShrayan BarmanNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. Mechanical Engineering Scheme PDFDocument87 pagesB. Tech. Mechanical Engineering Scheme PDFshubham.aggarwalNo ratings yet
- 43203notice 04232019 PDFDocument59 pages43203notice 04232019 PDFHgNo ratings yet
- Be EeeDocument38 pagesBe EeeGopinathblNo ratings yet
- Branch/Discipline: Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pagesBranch/Discipline: Electrical EngineeringSravan ReddyNo ratings yet
- EE1101Document2 pagesEE1101balajiNo ratings yet
- Curriculum S T R U C T U R E of S.Y.-B.Tech (Electrical Engineering) (Regularstudents)Document56 pagesCurriculum S T R U C T U R E of S.Y.-B.Tech (Electrical Engineering) (Regularstudents)Bhushan RaneNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Control Systems: RationaleDocument15 pages3.1 Control Systems: RationaleSoumya BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering: Ea6210: Switchgear and ProtectionDocument5 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering: Ea6210: Switchgear and ProtectionAvi PokiNo ratings yet
- em Theory:: Paper IDocument3 pagesem Theory:: Paper IDeepthi Madhav AnnavarapuNo ratings yet
- Previewpage - Do RemovedDocument16 pagesPreviewpage - Do RemovedGona SujathaNo ratings yet
- Branch/Discipline: Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesBranch/Discipline: Electrical EngineeringsixfacerajNo ratings yet
- CCCC C C C CCDocument3 pagesCCCC C C C CCManoj MeenaNo ratings yet
- D) Electrical Engineering Syllabus Ies 2015: Paper I 1. EM TheoryDocument4 pagesD) Electrical Engineering Syllabus Ies 2015: Paper I 1. EM TheorysyamalaNo ratings yet
- Elect Et Syllabus 2013 For SJVNDocument3 pagesElect Et Syllabus 2013 For SJVNBest KvansNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabi Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument12 pagesCourse Syllabi Department of Electrical EngineeringPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Electrical EngineeringbasabNo ratings yet
- AKU Patna Syllabus 3rd YearDocument20 pagesAKU Patna Syllabus 3rd Yearडाँ सूर्यदेव चौधरीNo ratings yet
- Nikesh Indus Final SyllabusDocument15 pagesNikesh Indus Final Syllabusvatsalshah24No ratings yet
- Syllabus ESEDocument3 pagesSyllabus ESESuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekananda Technical University, Bhilai Scheme of Teaching and Examination Be (Electrical Engineering) Iv SemesterDocument12 pagesChhattisgarh Swami Vivekananda Technical University, Bhilai Scheme of Teaching and Examination Be (Electrical Engineering) Iv SemesterAnonymous l5X3VhTNo ratings yet
- EE May 04 2011Document40 pagesEE May 04 2011ChandanUpadhyayNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Mizoram: Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Btech SyllabusDocument32 pagesNational Institute of Technology Mizoram: Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Btech SyllabustoshaliNo ratings yet
- EEE 4th SemesterDocument5 pagesEEE 4th SemesterKeyern MwihandiNo ratings yet
- Ese Ee PDFDocument4 pagesEse Ee PDFJfttgjugNo ratings yet
- Sem6 SyllabusDocument5 pagesSem6 SyllabusSamsung TabletNo ratings yet
- Stage I - Paper I, Objective Type, Common To All Candidates, 2 Hours Duration, 200 Marks MaximumDocument3 pagesStage I - Paper I, Objective Type, Common To All Candidates, 2 Hours Duration, 200 Marks MaximumAayushGoyalNo ratings yet
- FRM Course Syllabus IPDownloadDocument1 pageFRM Course Syllabus IPDownloadMovie ClipsNo ratings yet
- JNTUK DAP Course Structure and Syllabus EEE II YEAR R10 Students 3Document32 pagesJNTUK DAP Course Structure and Syllabus EEE II YEAR R10 Students 3Shravan RaoNo ratings yet
- 2007-08 M.sc. ElectronicsDocument19 pages2007-08 M.sc. ElectronicsUlhasNo ratings yet
- Eee 8th Sem r2008Document18 pagesEee 8th Sem r2008Ashok VannanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines & Measurement B.E. 4 SemesterDocument4 pagesElectrical Machines & Measurement B.E. 4 Semestersameerpatel15770No ratings yet
- Elecives CombinedDocument32 pagesElecives CombinedmeetNo ratings yet
- IV B.E. (Electrical Engineering)Document8 pagesIV B.E. (Electrical Engineering)9y9aNo ratings yet
- BainganDocument3 pagesBainganDebadrita BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Ies Syllabus: Part A: General EnglishDocument4 pagesIes Syllabus: Part A: General EnglishRaj RaushanNo ratings yet
- PSU's Common Syllabus For Electrical Engineering Non-Technical: General StudyDocument2 pagesPSU's Common Syllabus For Electrical Engineering Non-Technical: General StudyJitendra TambeNo ratings yet
- IES Electrical Engg.Document2 pagesIES Electrical Engg.Anil BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between IES 2016 and 2017 Syllabus For Electrical EngineeringEEDocument5 pagesComparison Between IES 2016 and 2017 Syllabus For Electrical EngineeringEERishi KamalNo ratings yet
- Eec403: Microwave EngineeringDocument1 pageEec403: Microwave EngineeringNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- IES Electrical Engineering SyllabusDocument4 pagesIES Electrical Engineering SyllabusAvinash Arya100% (1)
- Syllabus B ElectricalDocument6 pagesSyllabus B ElectricalnetprosenjitNo ratings yet
- II ND YEAR SEM B U.G. Elex and TC Syllabus 2022-23Document12 pagesII ND YEAR SEM B U.G. Elex and TC Syllabus 2022-23Mitali KhareNo ratings yet
- EEE1001 - ELECTRIC-CIRCUITS-AND-SYSTEMS - LTP - 1.3 - 53 - EEE1001 - Electric Circuits and Systems - LTP - 4 - V1.3Document2 pagesEEE1001 - ELECTRIC-CIRCUITS-AND-SYSTEMS - LTP - 1.3 - 53 - EEE1001 - Electric Circuits and Systems - LTP - 4 - V1.3devmewada2505No ratings yet
- UEE001 SyllabusDocument2 pagesUEE001 SyllabusashNo ratings yet
- Creation of Rare Heavy Elements Witnessed in Neutron-Star CollisDocument3 pagesCreation of Rare Heavy Elements Witnessed in Neutron-Star CollisEkkoNo ratings yet
- Governmental Legal and Regulatory Framework For SafetyDocument63 pagesGovernmental Legal and Regulatory Framework For Safetychrissbans100% (1)
- The Environment Is A Very Complex PhenomenonDocument2 pagesThe Environment Is A Very Complex PhenomenonAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Physics Past Paper - P2 - 2015-20 PDFDocument424 pagesPhysics Past Paper - P2 - 2015-20 PDF123 456No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/41Document28 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/41Raghav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Complete Chemistry Notes: Unit 1: States of MatterDocument72 pagesIgcse Complete Chemistry Notes: Unit 1: States of MatterYoga RomdoniNo ratings yet
- Enrico FermiDocument3 pagesEnrico FermiEsha MishraNo ratings yet
- IGCSE PhysicsDocument15 pagesIGCSE PhysicsLailla MarlinaNo ratings yet
- Wide Energy Range Efficiency Calibration Method For Ge DetectorsDocument20 pagesWide Energy Range Efficiency Calibration Method For Ge DetectorsシリーズスーパNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument28 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelSaeeda KhiljiNo ratings yet
- 198471Document5 pages198471Clarice ArañezNo ratings yet
- Physics 3204: UNIT 3 - Test - Matter Energy InterfaceDocument7 pagesPhysics 3204: UNIT 3 - Test - Matter Energy InterfaceRaJA ViNoDNo ratings yet
- Physics in Focus Year 12 Student Book 2Nd Edition Robert Farr Download PDF ChapterDocument51 pagesPhysics in Focus Year 12 Student Book 2Nd Edition Robert Farr Download PDF Chaptergary.taylor799100% (8)
- G.C.E. (Advanced Level) CHEMISTRYDocument297 pagesG.C.E. (Advanced Level) CHEMISTRYMaliNo ratings yet
- Advanced Burn Life SupportDocument118 pagesAdvanced Burn Life SupportIntan Noa100% (1)
- Atomic StructureDocument5 pagesAtomic StructureMustafa OmerNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On RadioactivityDocument11 pagesLiterature Review On Radioactivityafdtrqaau100% (1)
- Inverse Sqaure Law For Gamma RadiationDocument7 pagesInverse Sqaure Law For Gamma RadiationAhmedAmer1100% (2)
- Grade 7 ForceDocument23 pagesGrade 7 ForceJuan Miguel Sapad AlpañoNo ratings yet
- Final Mock 5 Paper2Document11 pagesFinal Mock 5 Paper2Dewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- Chem Final ExamDocument42 pagesChem Final ExamWild RiftNo ratings yet
- Applications MATH 404Document32 pagesApplications MATH 404Rocel Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- Thesis AnttirtyDocument84 pagesThesis Anttirtynagatopein6No ratings yet
- Physics STPM Past Year Questions With Answer 2006Document18 pagesPhysics STPM Past Year Questions With Answer 2006Chan Q ON100% (1)
- 0625/s 19/qp/42Document16 pages0625/s 19/qp/42n.No ratings yet
- General Physics 2 4Q Week 9.pubDocument13 pagesGeneral Physics 2 4Q Week 9.pubShane June DemetrialNo ratings yet
- Final Coaching 4Document12 pagesFinal Coaching 4Cliff Sotto Omayan100% (1)
- Wa0004.Document13 pagesWa0004.shahbikky67No ratings yet
- Modul Analisis Fizik Merbau Miri SPM 2014 SkemaDocument5 pagesModul Analisis Fizik Merbau Miri SPM 2014 SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet