Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Body Mass Index (BMI), The Waist Circumference and The Waist/hip Ratio. Although Not A
Body Mass Index (BMI), The Waist Circumference and The Waist/hip Ratio. Although Not A
Uploaded by
LucyellowOttemoesoeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Breast Cancer Case StudyDocument3 pagesBreast Cancer Case Studyyohans TeferiNo ratings yet
- Calgary Cambridge ModelDocument25 pagesCalgary Cambridge ModelHumera Sarwar100% (1)
- Jarvis Chapter 18 Study GuideDocument5 pagesJarvis Chapter 18 Study GuideEmily Cheng100% (2)
- Nurs 5002 - Case Study 3Document14 pagesNurs 5002 - Case Study 3api-308904543No ratings yet
- Obesity in Adults - Prevalence, Screening, and Evaluation - UpToDateDocument18 pagesObesity in Adults - Prevalence, Screening, and Evaluation - UpToDateGabrielle AndersonNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument18 pagesObesityShakil KhanNo ratings yet
- Thesis D ObesidadDocument35 pagesThesis D ObesidadIllya Godoy de MojicaNo ratings yet
- Obesity PDFDocument20 pagesObesity PDFAhmed JabbarNo ratings yet
- TOOL E3 Measurement and Assessment of Overweight and Obesity - ADULTSDocument8 pagesTOOL E3 Measurement and Assessment of Overweight and Obesity - ADULTSMok Chu ZhenNo ratings yet
- The Complete Weight Loss Guide: Brought To You byDocument6 pagesThe Complete Weight Loss Guide: Brought To You bySam YoussefNo ratings yet
- Definition of Overweight and ObesityDocument4 pagesDefinition of Overweight and ObesityHamemi Binti Mohd FaripNo ratings yet
- Adiposity and Fat Distribution Outcome Measures: Assessment and Clinical ImplicationsDocument8 pagesAdiposity and Fat Distribution Outcome Measures: Assessment and Clinical ImplicationsSofa Nasir BasalamahNo ratings yet
- Body Mass Index - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesBody Mass Index - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSanthosh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Obesity and PreventionDocument12 pagesObesity and Preventionsalman hasanNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument6 pagesObesityOde BukolaNo ratings yet
- Obesity in AustraliaDocument2 pagesObesity in AustraliareneeNo ratings yet
- Hphe UsingbmiDocument3 pagesHphe UsingbmiAMIT SOLANKINo ratings yet
- Body Mass IndexDocument11 pagesBody Mass IndexAbdul QuyyumNo ratings yet
- Reference Material I 11Document19 pagesReference Material I 11Maru Mengesha Worku 18BBT0285No ratings yet
- Obesity and Overweight: Baskoro AbdiansyahDocument8 pagesObesity and Overweight: Baskoro AbdiansyahBASKORO AbdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Obesity: Scope, Lifestyle Interventions, and Medical ManagementDocument8 pagesObesity: Scope, Lifestyle Interventions, and Medical ManagementFafafafa FafafafaNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument20 pagesObesitygheorghesimedrumaxxNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument11 pagesObesityBNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument32 pagesObesityRao MehakNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument17 pagesObesityYukii ChunNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument11 pagesObesitysalini dasNo ratings yet
- Obesity and Type 2 DiabetesDocument18 pagesObesity and Type 2 DiabetespritaultimardianNo ratings yet
- Journal of Occupational Health - 2003 - Anuurad - The New BMI Criteria For Asians by The Regional Office For The WesternDocument9 pagesJournal of Occupational Health - 2003 - Anuurad - The New BMI Criteria For Asians by The Regional Office For The Westernjokeshua34No ratings yet
- Chapters 1-5 FINALDocument55 pagesChapters 1-5 FINALGwen NamNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument3 pagesINTRODUCTIONMarebel ManabatNo ratings yet
- Body Mass Index - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesBody Mass Index - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRupam DasNo ratings yet
- OBESITYDocument1 pageOBESITYlxmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 36 - Morbid Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Nonsurgical Weight ManagementDocument11 pagesChapter 36 - Morbid Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Nonsurgical Weight ManagementCharbel AounNo ratings yet
- Obesity in Adults - Overview of Management - UpToDateDocument17 pagesObesity in Adults - Overview of Management - UpToDateGabrielle AndersonNo ratings yet
- An20220812 505Document7 pagesAn20220812 505Marthee BaticanNo ratings yet
- Progress SerminarDocument32 pagesProgress SerminarFavourNo ratings yet
- Script Obesity - TANGII - Nhóm 11Document4 pagesScript Obesity - TANGII - Nhóm 11thvl3105No ratings yet
- Hubungan Diabetes Mellitus Dengan Obesitas Berdasarkan Indeks Massa Tubuh Dan Lingkar Pinggang Data Riskesdas 2007Document7 pagesHubungan Diabetes Mellitus Dengan Obesitas Berdasarkan Indeks Massa Tubuh Dan Lingkar Pinggang Data Riskesdas 2007Titik HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Project Pictures SPMDocument4 pagesAdd Maths Project Pictures SPMdanushvar maheswaranNo ratings yet
- Some Exceptions To The BMI RuleDocument3 pagesSome Exceptions To The BMI RuleSyed fayas thanveer SNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guidelines On The Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in AdultsDocument11 pagesClinical Guidelines On The Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in AdultsCelia DiazNo ratings yet
- Bariatric Surgery in Class I Obesity (Body Mass Index 30-35 KG/M)Document10 pagesBariatric Surgery in Class I Obesity (Body Mass Index 30-35 KG/M)David PereiraNo ratings yet
- Obesity KnowledgeDocument35 pagesObesity KnowledgeledahosnNo ratings yet
- BMI Classification Percentile and Cut Off Points: ArticleDocument6 pagesBMI Classification Percentile and Cut Off Points: ArticlePoonam SengarNo ratings yet
- 08-8 Obesity - Diet and ExerciseDocument68 pages08-8 Obesity - Diet and ExerciseAhmad SobihNo ratings yet
- Home/health & Living Health Center/diet & Weight Management A-Z List/obesity Weight Loss Center /obesity (Weight Loss) ArticleDocument5 pagesHome/health & Living Health Center/diet & Weight Management A-Z List/obesity Weight Loss Center /obesity (Weight Loss) ArticleHannah LNo ratings yet
- Obesity Disease: Polikandrioti Maria, Stefanou EvageliaDocument7 pagesObesity Disease: Polikandrioti Maria, Stefanou Evageliaali amineNo ratings yet
- Body Mass IndexDocument3 pagesBody Mass IndexAyesha KhalilNo ratings yet
- NCDs 2Document100 pagesNCDs 2Fauziyah Farah RNo ratings yet
- Normal Weight or Underweight (BMI Under 24.9) Overweight (BMI of 25 To 29.9) Obesity (BMI of 30+) Extreme Obesity (BMI of 40+)Document3 pagesNormal Weight or Underweight (BMI Under 24.9) Overweight (BMI of 25 To 29.9) Obesity (BMI of 30+) Extreme Obesity (BMI of 40+)Kavi RobertsNo ratings yet
- Sustainability and Environment 2Document28 pagesSustainability and Environment 2Navnoor Kaur 48No ratings yet
- Body Mass Index (BMI) : DefinitionDocument2 pagesBody Mass Index (BMI) : DefinitionVenkata Ramana Murty GandiNo ratings yet
- Obesity: Body Mass Index (BMI) Waist-Hip Ratio Percentage Body FatDocument6 pagesObesity: Body Mass Index (BMI) Waist-Hip Ratio Percentage Body FatRichmond AmuraoNo ratings yet
- Overweight and Obesity: Global Health Observatory (GHO) DataDocument1 pageOverweight and Obesity: Global Health Observatory (GHO) DataMuhammad Fakhrian IrsaliNo ratings yet
- Kehe 202Document68 pagesKehe 202RuchikaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting BmiDocument9 pagesFactors Affecting BmiJashmine RachlyNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument35 pagesObesitysohilaw210No ratings yet
- ObesityDocument52 pagesObesityAdy Micoara100% (1)
- Healthy Weight, Overweight, and Obesity Among U.S. AdultsDocument2 pagesHealthy Weight, Overweight, and Obesity Among U.S. Adultsحسين جاموسNo ratings yet
- Name: Zeshan Khan Roll No: 04 Department: Physical Education and Sports. Discipline: Bs Semester: 5thDocument24 pagesName: Zeshan Khan Roll No: 04 Department: Physical Education and Sports. Discipline: Bs Semester: 5thHaroon KhanNo ratings yet
- KPSV ThesisDocument166 pagesKPSV ThesissvgvtrainingNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument5 pagesObesityAliNor2425No ratings yet
- Review: The Medical Complications of ObesityDocument15 pagesReview: The Medical Complications of ObesitysilmiNo ratings yet
- Tubulointerstitial DiseaseDocument94 pagesTubulointerstitial DiseaseLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Chelators and Heavy MetalsDocument3 pagesChelators and Heavy MetalsLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- IM IBD IBsDocument1 pageIM IBD IBsLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Dr. N. Collantes - Learning To CommunicateDocument11 pagesDr. N. Collantes - Learning To CommunicateLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- IM Clinics History 2Document4 pagesIM Clinics History 2LucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LeukemiaDocument51 pagesIntroduction To LeukemiaLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Action Potential: Cardiac CycleDocument1 pageVentricular Action Potential: Cardiac CycleLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- ENT Diseases of Paranasal SinusesDocument3 pagesENT Diseases of Paranasal SinusesLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- White Blood Cell DisordersDocument18 pagesWhite Blood Cell DisordersLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- ENT Benign Laryngeal DisordersDocument6 pagesENT Benign Laryngeal DisordersLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- ENT Benign Neck MassesDocument2 pagesENT Benign Neck MassesLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Volumes and CapacitiesDocument1 pageRespiratory Volumes and CapacitiesLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- ENT Anatomy and Physiology of The Esophagus and Tracheobronchial TreeDocument1 pageENT Anatomy and Physiology of The Esophagus and Tracheobronchial TreeLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- IM Infective Endocarditis Pericardial DiseaseDocument4 pagesIM Infective Endocarditis Pericardial DiseaseLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis: Navigation SearchDocument15 pagesCystic Fibrosis: Navigation SearchLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Principles of GeneticsDocument4 pagesPrinciples of GeneticsLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Bowman's Capsule Proximal Tubule Distal TubuleDocument1 pageBowman's Capsule Proximal Tubule Distal TubuleLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- 2 PneumoniaDocument53 pages2 PneumoniaLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Pohon Masalah AnsietasDocument16 pagesPohon Masalah AnsietasDeva NatarummandaNo ratings yet
- New Corona Form Revised Version-7Document1 pageNew Corona Form Revised Version-7Rishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Resume Tutorial A Skenario 1 Blok 14Document74 pagesResume Tutorial A Skenario 1 Blok 14Istaz MaulanaNo ratings yet
- NizoralDocument4 pagesNizoralianecunar100% (2)
- Unusual Presentation of Pancreatic Insulinoma:a Case ReportDocument5 pagesUnusual Presentation of Pancreatic Insulinoma:a Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprungs Disease: What Is Hirschsprung's Disease?Document9 pagesHirschsprungs Disease: What Is Hirschsprung's Disease?Karina Jane Farnacio PuruggananNo ratings yet
- Adult Brain Tumours: DR M.P. Okemwa PathologistDocument39 pagesAdult Brain Tumours: DR M.P. Okemwa PathologistSalman MajidNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever DR Moses KazevuDocument12 pagesTyphoid Fever DR Moses KazevuMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis StepDocument2 pagesVasculitis Stepcsa yanisis hernandezNo ratings yet
- 1-крок-1-ЛС-KROK 2007-2017-English - microbiologyDocument58 pages1-крок-1-ЛС-KROK 2007-2017-English - microbiologyAbhani MøhitNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Ulkus KorneaDocument10 pagesJurnal Ulkus KorneaPutri Dery CahyaniNo ratings yet
- Acid Base 2Document5 pagesAcid Base 2itiswhatitis55No ratings yet
- CPFGrantDoc 77632Document2 pagesCPFGrantDoc 77632Khánh ChiNo ratings yet
- Qol JournalDocument14 pagesQol JournalAgus Tamil ArifinNo ratings yet
- Fungal Infections: Alma E. Malilong, MD, FPSPDocument33 pagesFungal Infections: Alma E. Malilong, MD, FPSPQurrataini IbanezNo ratings yet
- Vol.35 - No.1.2019 InmunohematologiaDocument48 pagesVol.35 - No.1.2019 InmunohematologiaZuleynis MendozaNo ratings yet
- WLD Disease Perceptions Society Views Infographic 070417Document1 pageWLD Disease Perceptions Society Views Infographic 070417Pslem SelangorNo ratings yet
- Zambia PHF Exit Interview QuestionnaireDocument37 pagesZambia PHF Exit Interview QuestionnairenomdeplumNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercises For EpidemiologyDocument8 pagesPractice Exercises For Epidemiologyninja-2001100% (2)
- KHA Emergency Cervical Spine 2Document65 pagesKHA Emergency Cervical Spine 2Kyaw Htet AungNo ratings yet
- MENT. Med. 2Document25 pagesMENT. Med. 2kwakyegrace1991No ratings yet
- Questions and Answers: MumpsDocument4 pagesQuestions and Answers: MumpsHannahNo ratings yet
- Movement DisordersDocument10 pagesMovement DisordersAli 10No ratings yet
- Pet Owner's Guide To Infectious DiseasesDocument38 pagesPet Owner's Guide To Infectious DiseasesAnonymous qYLCf4eANo ratings yet
- The Triangle OperationDocument7 pagesThe Triangle OperationJaldo FreireNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Dr. Jasmina Begum Assistant Professor AIIMS, BhubaneswarDocument80 pagesAbnormal Uterine Bleeding: Dr. Jasmina Begum Assistant Professor AIIMS, BhubaneswarSharoon KumarNo ratings yet
Body Mass Index (BMI), The Waist Circumference and The Waist/hip Ratio. Although Not A
Body Mass Index (BMI), The Waist Circumference and The Waist/hip Ratio. Although Not A
Uploaded by
LucyellowOttemoesoeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Body Mass Index (BMI), The Waist Circumference and The Waist/hip Ratio. Although Not A
Body Mass Index (BMI), The Waist Circumference and The Waist/hip Ratio. Although Not A
Uploaded by
LucyellowOttemoesoeCopyright:
Available Formats
In a webcast from the medical website, www.medscape.com in July 2007, Dr.
Zimmet
decries the problem as, "Diabesity-The Biggest Epidemic in Human History." He continues,
"What HIV/AIDS was in the last 20 years of the 20th century diabetes and obesity and their
consequences will almost certainly be in the first 2 decades of the 21st century."
There is even more. Among the top ten countries with diabetes by 2030, six are from Asia
(neighbors India, number 1; China, number 2; Indonesia, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Japan).
The Philippines ranks number 9, definitely a top 10 that we as a nation, should not aspire
too. The 6th National Nutrition Health Survey of 1993 warns us that its time to wake up!
Diabesity is a global health threat, so much so, that the United Nations General Assembly
fast-tracked a unanimous resolution in December 2006-with lobbying from the International
Diabetes Federation (IDF), Paul Zimmet, one of its most ferocious and passionate
proponents-"declaring diabetes an inter national public health issue, only the second disease
after HW/AIDS to attain that unenviable status."
Of the several ways to measure degree of obesity available to us, the simplest would be a
body mass index (BMI), the waist circumference and the waist/hip ratio. Although not a
direct measure of adiposity, the BMI is most widely used method. It is calculated from the
height and weight as follows:
BMI = body weight (in kg) / square of stature (height, in meters) BMI defines the degree of
risk for cardiovascular morbidity. A BMI between 25 and 30 kg/m2 is low risk, above 30
kg/m2 is moderate risk. A BMI between 25 and 30 is significant and requires therapeutic
intervention when other risk factors like hypertension and glucose intolerance co-exist.
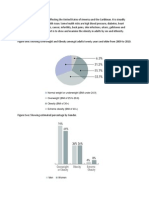
The survey says that five percent of the population has a BMI greater than 30, and 19.6
percent are overweight. Twenty four percent of the population is overweight or obese, an
increase from 20 percent in 1998. Seven percent of the obese are women, and 3 percent
are men. Obesity is most prevalent among those aged 40-59 years.
Classification of weight by BMI in - adult Asians (WHO-Western Pacific Region 2000) See
table.
CLASSIFICATION BMI KG/M2 RISK OF CO-MORBIDITIES
Underweight <18.5
Low (but increased risk of
other clinical problems)
Normal 18.5-22.9 Average
Overweight >23
At risk 23-24.9 Increased
Obese I 25-29.9 Moderate
Obese II >30 Severe
For Asians, this classification had been modified - the normal BMI is only up to 23, the
individual is already overweight if BMI is between 23 and 25, and obese if BMI is more than 25.
Waist Circumference. For Asians, waist circumference is more predictive of body fat excess,
and is most useful if BMI is less than 35. One is considered obese if they exceed the cut-off
values of 102 cm for men and 88 cm for women.
Waist to Hip Ratio. Values are gender-specific: >1.0 for men; > 0.85 for women.
You might also like
- Breast Cancer Case StudyDocument3 pagesBreast Cancer Case Studyyohans TeferiNo ratings yet
- Calgary Cambridge ModelDocument25 pagesCalgary Cambridge ModelHumera Sarwar100% (1)
- Jarvis Chapter 18 Study GuideDocument5 pagesJarvis Chapter 18 Study GuideEmily Cheng100% (2)
- Nurs 5002 - Case Study 3Document14 pagesNurs 5002 - Case Study 3api-308904543No ratings yet
- Obesity in Adults - Prevalence, Screening, and Evaluation - UpToDateDocument18 pagesObesity in Adults - Prevalence, Screening, and Evaluation - UpToDateGabrielle AndersonNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument18 pagesObesityShakil KhanNo ratings yet
- Thesis D ObesidadDocument35 pagesThesis D ObesidadIllya Godoy de MojicaNo ratings yet
- Obesity PDFDocument20 pagesObesity PDFAhmed JabbarNo ratings yet
- TOOL E3 Measurement and Assessment of Overweight and Obesity - ADULTSDocument8 pagesTOOL E3 Measurement and Assessment of Overweight and Obesity - ADULTSMok Chu ZhenNo ratings yet
- The Complete Weight Loss Guide: Brought To You byDocument6 pagesThe Complete Weight Loss Guide: Brought To You bySam YoussefNo ratings yet
- Definition of Overweight and ObesityDocument4 pagesDefinition of Overweight and ObesityHamemi Binti Mohd FaripNo ratings yet
- Adiposity and Fat Distribution Outcome Measures: Assessment and Clinical ImplicationsDocument8 pagesAdiposity and Fat Distribution Outcome Measures: Assessment and Clinical ImplicationsSofa Nasir BasalamahNo ratings yet
- Body Mass Index - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesBody Mass Index - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSanthosh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Obesity and PreventionDocument12 pagesObesity and Preventionsalman hasanNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument6 pagesObesityOde BukolaNo ratings yet
- Obesity in AustraliaDocument2 pagesObesity in AustraliareneeNo ratings yet
- Hphe UsingbmiDocument3 pagesHphe UsingbmiAMIT SOLANKINo ratings yet
- Body Mass IndexDocument11 pagesBody Mass IndexAbdul QuyyumNo ratings yet
- Reference Material I 11Document19 pagesReference Material I 11Maru Mengesha Worku 18BBT0285No ratings yet
- Obesity and Overweight: Baskoro AbdiansyahDocument8 pagesObesity and Overweight: Baskoro AbdiansyahBASKORO AbdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Obesity: Scope, Lifestyle Interventions, and Medical ManagementDocument8 pagesObesity: Scope, Lifestyle Interventions, and Medical ManagementFafafafa FafafafaNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument20 pagesObesitygheorghesimedrumaxxNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument11 pagesObesityBNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument32 pagesObesityRao MehakNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument17 pagesObesityYukii ChunNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument11 pagesObesitysalini dasNo ratings yet
- Obesity and Type 2 DiabetesDocument18 pagesObesity and Type 2 DiabetespritaultimardianNo ratings yet
- Journal of Occupational Health - 2003 - Anuurad - The New BMI Criteria For Asians by The Regional Office For The WesternDocument9 pagesJournal of Occupational Health - 2003 - Anuurad - The New BMI Criteria For Asians by The Regional Office For The Westernjokeshua34No ratings yet
- Chapters 1-5 FINALDocument55 pagesChapters 1-5 FINALGwen NamNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument3 pagesINTRODUCTIONMarebel ManabatNo ratings yet
- Body Mass Index - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesBody Mass Index - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRupam DasNo ratings yet
- OBESITYDocument1 pageOBESITYlxmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 36 - Morbid Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Nonsurgical Weight ManagementDocument11 pagesChapter 36 - Morbid Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Nonsurgical Weight ManagementCharbel AounNo ratings yet
- Obesity in Adults - Overview of Management - UpToDateDocument17 pagesObesity in Adults - Overview of Management - UpToDateGabrielle AndersonNo ratings yet
- An20220812 505Document7 pagesAn20220812 505Marthee BaticanNo ratings yet
- Progress SerminarDocument32 pagesProgress SerminarFavourNo ratings yet
- Script Obesity - TANGII - Nhóm 11Document4 pagesScript Obesity - TANGII - Nhóm 11thvl3105No ratings yet
- Hubungan Diabetes Mellitus Dengan Obesitas Berdasarkan Indeks Massa Tubuh Dan Lingkar Pinggang Data Riskesdas 2007Document7 pagesHubungan Diabetes Mellitus Dengan Obesitas Berdasarkan Indeks Massa Tubuh Dan Lingkar Pinggang Data Riskesdas 2007Titik HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Project Pictures SPMDocument4 pagesAdd Maths Project Pictures SPMdanushvar maheswaranNo ratings yet
- Some Exceptions To The BMI RuleDocument3 pagesSome Exceptions To The BMI RuleSyed fayas thanveer SNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guidelines On The Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in AdultsDocument11 pagesClinical Guidelines On The Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in AdultsCelia DiazNo ratings yet
- Bariatric Surgery in Class I Obesity (Body Mass Index 30-35 KG/M)Document10 pagesBariatric Surgery in Class I Obesity (Body Mass Index 30-35 KG/M)David PereiraNo ratings yet
- Obesity KnowledgeDocument35 pagesObesity KnowledgeledahosnNo ratings yet
- BMI Classification Percentile and Cut Off Points: ArticleDocument6 pagesBMI Classification Percentile and Cut Off Points: ArticlePoonam SengarNo ratings yet
- 08-8 Obesity - Diet and ExerciseDocument68 pages08-8 Obesity - Diet and ExerciseAhmad SobihNo ratings yet
- Home/health & Living Health Center/diet & Weight Management A-Z List/obesity Weight Loss Center /obesity (Weight Loss) ArticleDocument5 pagesHome/health & Living Health Center/diet & Weight Management A-Z List/obesity Weight Loss Center /obesity (Weight Loss) ArticleHannah LNo ratings yet
- Obesity Disease: Polikandrioti Maria, Stefanou EvageliaDocument7 pagesObesity Disease: Polikandrioti Maria, Stefanou Evageliaali amineNo ratings yet
- Body Mass IndexDocument3 pagesBody Mass IndexAyesha KhalilNo ratings yet
- NCDs 2Document100 pagesNCDs 2Fauziyah Farah RNo ratings yet
- Normal Weight or Underweight (BMI Under 24.9) Overweight (BMI of 25 To 29.9) Obesity (BMI of 30+) Extreme Obesity (BMI of 40+)Document3 pagesNormal Weight or Underweight (BMI Under 24.9) Overweight (BMI of 25 To 29.9) Obesity (BMI of 30+) Extreme Obesity (BMI of 40+)Kavi RobertsNo ratings yet
- Sustainability and Environment 2Document28 pagesSustainability and Environment 2Navnoor Kaur 48No ratings yet
- Body Mass Index (BMI) : DefinitionDocument2 pagesBody Mass Index (BMI) : DefinitionVenkata Ramana Murty GandiNo ratings yet
- Obesity: Body Mass Index (BMI) Waist-Hip Ratio Percentage Body FatDocument6 pagesObesity: Body Mass Index (BMI) Waist-Hip Ratio Percentage Body FatRichmond AmuraoNo ratings yet
- Overweight and Obesity: Global Health Observatory (GHO) DataDocument1 pageOverweight and Obesity: Global Health Observatory (GHO) DataMuhammad Fakhrian IrsaliNo ratings yet
- Kehe 202Document68 pagesKehe 202RuchikaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting BmiDocument9 pagesFactors Affecting BmiJashmine RachlyNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument35 pagesObesitysohilaw210No ratings yet
- ObesityDocument52 pagesObesityAdy Micoara100% (1)
- Healthy Weight, Overweight, and Obesity Among U.S. AdultsDocument2 pagesHealthy Weight, Overweight, and Obesity Among U.S. Adultsحسين جاموسNo ratings yet
- Name: Zeshan Khan Roll No: 04 Department: Physical Education and Sports. Discipline: Bs Semester: 5thDocument24 pagesName: Zeshan Khan Roll No: 04 Department: Physical Education and Sports. Discipline: Bs Semester: 5thHaroon KhanNo ratings yet
- KPSV ThesisDocument166 pagesKPSV ThesissvgvtrainingNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument5 pagesObesityAliNor2425No ratings yet
- Review: The Medical Complications of ObesityDocument15 pagesReview: The Medical Complications of ObesitysilmiNo ratings yet
- Tubulointerstitial DiseaseDocument94 pagesTubulointerstitial DiseaseLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Chelators and Heavy MetalsDocument3 pagesChelators and Heavy MetalsLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- IM IBD IBsDocument1 pageIM IBD IBsLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Dr. N. Collantes - Learning To CommunicateDocument11 pagesDr. N. Collantes - Learning To CommunicateLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- IM Clinics History 2Document4 pagesIM Clinics History 2LucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LeukemiaDocument51 pagesIntroduction To LeukemiaLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Action Potential: Cardiac CycleDocument1 pageVentricular Action Potential: Cardiac CycleLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- ENT Diseases of Paranasal SinusesDocument3 pagesENT Diseases of Paranasal SinusesLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- White Blood Cell DisordersDocument18 pagesWhite Blood Cell DisordersLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- ENT Benign Laryngeal DisordersDocument6 pagesENT Benign Laryngeal DisordersLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- ENT Benign Neck MassesDocument2 pagesENT Benign Neck MassesLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Volumes and CapacitiesDocument1 pageRespiratory Volumes and CapacitiesLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- ENT Anatomy and Physiology of The Esophagus and Tracheobronchial TreeDocument1 pageENT Anatomy and Physiology of The Esophagus and Tracheobronchial TreeLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- IM Infective Endocarditis Pericardial DiseaseDocument4 pagesIM Infective Endocarditis Pericardial DiseaseLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis: Navigation SearchDocument15 pagesCystic Fibrosis: Navigation SearchLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Principles of GeneticsDocument4 pagesPrinciples of GeneticsLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Bowman's Capsule Proximal Tubule Distal TubuleDocument1 pageBowman's Capsule Proximal Tubule Distal TubuleLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- 2 PneumoniaDocument53 pages2 PneumoniaLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Pohon Masalah AnsietasDocument16 pagesPohon Masalah AnsietasDeva NatarummandaNo ratings yet
- New Corona Form Revised Version-7Document1 pageNew Corona Form Revised Version-7Rishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Resume Tutorial A Skenario 1 Blok 14Document74 pagesResume Tutorial A Skenario 1 Blok 14Istaz MaulanaNo ratings yet
- NizoralDocument4 pagesNizoralianecunar100% (2)
- Unusual Presentation of Pancreatic Insulinoma:a Case ReportDocument5 pagesUnusual Presentation of Pancreatic Insulinoma:a Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprungs Disease: What Is Hirschsprung's Disease?Document9 pagesHirschsprungs Disease: What Is Hirschsprung's Disease?Karina Jane Farnacio PuruggananNo ratings yet
- Adult Brain Tumours: DR M.P. Okemwa PathologistDocument39 pagesAdult Brain Tumours: DR M.P. Okemwa PathologistSalman MajidNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever DR Moses KazevuDocument12 pagesTyphoid Fever DR Moses KazevuMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis StepDocument2 pagesVasculitis Stepcsa yanisis hernandezNo ratings yet
- 1-крок-1-ЛС-KROK 2007-2017-English - microbiologyDocument58 pages1-крок-1-ЛС-KROK 2007-2017-English - microbiologyAbhani MøhitNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Ulkus KorneaDocument10 pagesJurnal Ulkus KorneaPutri Dery CahyaniNo ratings yet
- Acid Base 2Document5 pagesAcid Base 2itiswhatitis55No ratings yet
- CPFGrantDoc 77632Document2 pagesCPFGrantDoc 77632Khánh ChiNo ratings yet
- Qol JournalDocument14 pagesQol JournalAgus Tamil ArifinNo ratings yet
- Fungal Infections: Alma E. Malilong, MD, FPSPDocument33 pagesFungal Infections: Alma E. Malilong, MD, FPSPQurrataini IbanezNo ratings yet
- Vol.35 - No.1.2019 InmunohematologiaDocument48 pagesVol.35 - No.1.2019 InmunohematologiaZuleynis MendozaNo ratings yet
- WLD Disease Perceptions Society Views Infographic 070417Document1 pageWLD Disease Perceptions Society Views Infographic 070417Pslem SelangorNo ratings yet
- Zambia PHF Exit Interview QuestionnaireDocument37 pagesZambia PHF Exit Interview QuestionnairenomdeplumNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercises For EpidemiologyDocument8 pagesPractice Exercises For Epidemiologyninja-2001100% (2)
- KHA Emergency Cervical Spine 2Document65 pagesKHA Emergency Cervical Spine 2Kyaw Htet AungNo ratings yet
- MENT. Med. 2Document25 pagesMENT. Med. 2kwakyegrace1991No ratings yet
- Questions and Answers: MumpsDocument4 pagesQuestions and Answers: MumpsHannahNo ratings yet
- Movement DisordersDocument10 pagesMovement DisordersAli 10No ratings yet
- Pet Owner's Guide To Infectious DiseasesDocument38 pagesPet Owner's Guide To Infectious DiseasesAnonymous qYLCf4eANo ratings yet
- The Triangle OperationDocument7 pagesThe Triangle OperationJaldo FreireNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Dr. Jasmina Begum Assistant Professor AIIMS, BhubaneswarDocument80 pagesAbnormal Uterine Bleeding: Dr. Jasmina Begum Assistant Professor AIIMS, BhubaneswarSharoon KumarNo ratings yet