Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Map AAA
Concept Map AAA
Uploaded by
Sandrine Barredo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
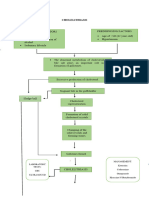
479 views6 pagesThis document outlines the pathophysiology and risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). It describes the process as beginning with predisposing factors like age, gender, and smoking that cause damage to the aortic wall. Over time, this results in thinning of the wall, loss of elastic tissue, and accumulation of lipids and inflammatory cells that form plaques. The plaques enlarge the vessel and put it at risk of rupture, which can lead to hemorrhage and death. Complications of AAA include embolism, hypertension, renal failure, and shock due to blood loss from rupture. Signs and symptoms may include back or abdominal pain, pulsations, and hypotension. Diagnostic tests involve ultrasound, CT
Original Description:
pathophysiology of AAA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the pathophysiology and risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). It describes the process as beginning with predisposing factors like age, gender, and smoking that cause damage to the aortic wall. Over time, this results in thinning of the wall, loss of elastic tissue, and accumulation of lipids and inflammatory cells that form plaques. The plaques enlarge the vessel and put it at risk of rupture, which can lead to hemorrhage and death. Complications of AAA include embolism, hypertension, renal failure, and shock due to blood loss from rupture. Signs and symptoms may include back or abdominal pain, pulsations, and hypotension. Diagnostic tests involve ultrasound, CT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as xlsx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
479 views6 pagesConcept Map AAA
Concept Map AAA
Uploaded by
Sandrine BarredoThis document outlines the pathophysiology and risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). It describes the process as beginning with predisposing factors like age, gender, and smoking that cause damage to the aortic wall. Over time, this results in thinning of the wall, loss of elastic tissue, and accumulation of lipids and inflammatory cells that form plaques. The plaques enlarge the vessel and put it at risk of rupture, which can lead to hemorrhage and death. Complications of AAA include embolism, hypertension, renal failure, and shock due to blood loss from rupture. Signs and symptoms may include back or abdominal pain, pulsations, and hypotension. Diagnostic tests involve ultrasound, CT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as xlsx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Predisposing factors:
- Age: 67 years old
- Gender: male
- Genetics
Precipitating factors:
- Cigarette smoking
- Atherosclerosis
- Trauma
- Hypertension
- Obesity,diet (high
cholesterol and fat), lack
High wall tension
Hypermeable vessels allow establishment
of chemotactic gradients for endothelial
cell migration
Elimination of elastin from the media
Increased expression and activity of
matrix metalloproteinases
Accumulation of lipids in foam cells, extracellular
free cholesterol crystals, calcifications, thrombosis,
and ulcerations
Chemotactic gradient also allows
recruitment of inflammatory cells
Atherosclerosis
reduced amount of vasa vasorum
Medial Neovascularization
Degradation of extracellular matrix in
media allows endothelial cell migration
Degradation of elastin and collagen
Inflammatory Infiltration
production of proteases
Production of
cytotoxic mediators
Decrease in smooth muscle cells density
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Wall thinning and focal dilation
Plaque formation
Ulceration of the wall
Damage of endothelial lining
Development of intraluminal thrombus
Narrows the vessel
Hypertension
Rupture of aneurysm
Hemorrhage
Death
- Feeling of heart beat
on the abdomen when
lying
- abdominal/back pain
- Duplex
ultrasonography
- X-ray examination
- Echocardiography
- CT scan
- MRI
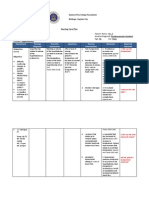
Altered comfort: Acute pain related
to nerve compression
Decreased cardiac output related
to increased systemic vascular
resistance
Anxiety related to threat to health
status
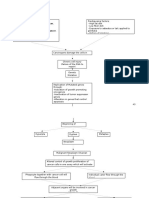
Swept along with the blood and
becomes an emboli
Arterial embolism
Emboli travels to the brain Emboli travels to the heart
Stroke Myocardial infarction
Death
Emboli travels to the renal artery
Complete blockage of blood flow
Kidney failure
Emboli lodges in the interosseous
or digital artery
Ineffective cerebral tissue
perfusion related to occlusion in
the carotid artery
- Altered level of
consciousness
- restlessness
- Changes in
motor/sensory
responses
Excess Fluid Volume related
to compromised regulatory
mechanism
- Intake greater than
output
- oliguria
- changes in urine specific
gravity
- Decreased
Hb/hematocrit (Hct)
- altered electrolytes
- Urinalysis
- CBC
- GCS
Altered comfort: Acute
pain related to coronary
artery occlusion
- chest pain
- Restlessness
- Facial grimacing
- Fatigue
- Peripheral cyanosis
- Weak pulse
- Pulse
Risk for super infection
related to presence of
bacteria on the bladder
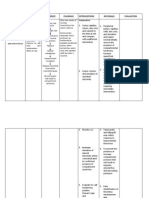
Legends:
Nursing dx------------------------
Complications-------------------
Signs and symptoms-----------
Medications----------------------
Surgical interventions---------
Disease condition---------------
Diagnostic tests------------------
Hypovolemic shock
- tachycardia
- hypotension
- pale clammy skin
- decreased urine output
-altered sensorium
- abdominal tenderness on palpation
- Diuretics
- beta-blockers
- ACE inhibitors
- Angiotensin II receptor antagonists
- Calcium channel blockers
- Open aneurysm repair
- Endovascular grafting
Risk for fluid volume deficit related
to hemorrhage
Deficient knowledge (preoperative
and postoperative care) related to
newly identified need for aortic
surgery
cyanosis
mottling of toes
Ineffective peripheral tissue
perfusion related to occlusion the
digital artery
Risk for super infection
related to presence of
bacteria on the bladder
You might also like
- Client Personal Training QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesClient Personal Training QuestionnaireFrancesco100% (4)
- ISSA Client Intake Forms PDFDocument24 pagesISSA Client Intake Forms PDFscorpion999No ratings yet
- Case Analysis On Respiratory DisordersDocument5 pagesCase Analysis On Respiratory DisordersAaron ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Worksheet Mary Richards Heart Failure Jasgou1752Document3 pagesConcept Map Worksheet Mary Richards Heart Failure Jasgou1752Jasmyn Rose100% (1)
- 1 Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionDocument1 page1 Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusionjean_fabulaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute PancreatitisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute PancreatitisHarvin FrancoNo ratings yet
- DomperidoneDocument1 pageDomperidoneSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- DomperidoneDocument1 pageDomperidoneSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- GENERIC NAME: Alprazolam DRUG CLASS: Benzodiazepine, AnxiolyticDocument1 pageGENERIC NAME: Alprazolam DRUG CLASS: Benzodiazepine, AnxiolyticSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- NATTBFIT Guide 2Document63 pagesNATTBFIT Guide 21THROUGH10100% (3)
- 5 - Respiratory AssessmentDocument61 pages5 - Respiratory AssessmentAbboud Ali100% (1)
- Milieu Therapy (1) FINAL)Document10 pagesMilieu Therapy (1) FINAL)Marie Nelle Escriba LimpocoNo ratings yet
- Basilar Skull FractureDocument16 pagesBasilar Skull FractureRindahMDNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of InfectionDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Infectionchristianemmanuel18No ratings yet
- Papillary Thyroid Ca: Group. 1 B Grand CaseDocument16 pagesPapillary Thyroid Ca: Group. 1 B Grand CaseAdora Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- HCVD Cad Cva InfarctionDocument2 pagesHCVD Cad Cva InfarctionPamela DomingoNo ratings yet
- Ordonio, Alyn Kyla S. BSN-1C TFN-MW7:40-9:10: Name of Theorist Theory Description Florence NightingaleDocument4 pagesOrdonio, Alyn Kyla S. BSN-1C TFN-MW7:40-9:10: Name of Theorist Theory Description Florence NightingaleKyla OrdonioNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesCholelithiasis PathophysiologyShinrin SukehiroNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology HeadinjuryDocument1 pagePathophysiology HeadinjuryK.b. Dequiña100% (1)
- Subjective Data: Baseline Data of Client.: Reference: Nurse's Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Interventions, and RationalesDocument4 pagesSubjective Data: Baseline Data of Client.: Reference: Nurse's Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Interventions, and RationalesJor GarciaNo ratings yet
- Modified Radical MastectomyDocument6 pagesModified Radical Mastectomymetch isulatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) : Date and Time Nursing Diagnosis Short - Term and Long - Term OutcomesDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP) : Date and Time Nursing Diagnosis Short - Term and Long - Term OutcomesDeanne Carla DalilisNo ratings yet
- Cva Concept MapDocument1 pageCva Concept MapAnn Justine OrbetaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Cad NstemiDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Cad Nstemianreilegarde100% (1)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosis Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosis Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- 403 Full PDFDocument10 pages403 Full PDFKuroto YoshikiNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument5 pagesNCP Acute PainEzra TuanNo ratings yet
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAngina Pectoris PathophysiologyALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONo ratings yet
- Cushing's SyndromeDocument5 pagesCushing's SyndromesummerduskNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PsoriasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PsoriasisKim LegastoNo ratings yet
- E000779 FullDocument19 pagesE000779 Fullmartina silalahiNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument16 pagesMyasthenia Graviszarka wahid buxNo ratings yet
- Whitening Injection Informed ConsentDocument3 pagesWhitening Injection Informed ConsentCalix Jr Rambuyon0% (1)
- Esophagea L Cancer: By: Krizzia S. Bunagan-Legasi, RNDocument20 pagesEsophagea L Cancer: By: Krizzia S. Bunagan-Legasi, RNAnn SalvatierraNo ratings yet
- PT EducationDocument4 pagesPT Educationapi-248017509No ratings yet
- NCP 1Document3 pagesNCP 1kat2111993No ratings yet
- Acute Pyelonephritis Nursing Care PlansDocument2 pagesAcute Pyelonephritis Nursing Care PlansJoannah Marie Juloya Kiat-ong100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Head TraumaDocument12 pagesPathophysiology of Head TraumaMohammad ZianuddinNo ratings yet
- Cholecystectomy (: Laparoscopic GallstonesDocument4 pagesCholecystectomy (: Laparoscopic GallstonesAlexia BatungbacalNo ratings yet
- Intracerebral HemorrageDocument13 pagesIntracerebral HemorrageChristian JuarezNo ratings yet
- Addison's Disease. FinalDocument10 pagesAddison's Disease. FinalAnn KelseaNo ratings yet
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" IntroDocument6 pages"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" IntroCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- DX Fracture PDFDocument8 pagesDX Fracture PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- NCP CvaDocument4 pagesNCP CvaMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- NeuroblastomaDocument4 pagesNeuroblastomaGeleine Curutan - OniaNo ratings yet
- CarboplatinDocument10 pagesCarboplatinapi-273179395No ratings yet
- OsteomyelitisDocument7 pagesOsteomyelitis4kscribd100% (1)
- Predisposing Factors: Independent:: Assessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Schematic Diagram Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesPredisposing Factors: Independent:: Assessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Schematic Diagram Rationale EvaluationCarla Tongson MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Stroke - NewDocument4 pagesNursing Care of Stroke - Newninda saputriNo ratings yet
- Potts DiseaseDocument8 pagesPotts Diseaseaimeeros0% (2)
- Malignant Neoplasm (Ovarian Cancer)Document4 pagesMalignant Neoplasm (Ovarian Cancer)nursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route Indication Action Drug Interaction Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Generic Name: Brand NameDocument3 pagesDrug Dosage, Frequency, Route Indication Action Drug Interaction Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Generic Name: Brand NameRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- Risk For Peripheral NeurovacularDocument4 pagesRisk For Peripheral NeurovacularRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDocument2 pagesScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DNo ratings yet
- Understanding Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument43 pagesUnderstanding Traumatic Brain InjurySilvanaPutriNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Diabetes InsipidusDocument6 pagesLab 5 Diabetes InsipidusLisa EkapratiwiNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord InjuryDocument3 pagesSpinal Cord InjuryDan Leo UnicoNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Document34 pagesOsteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Angelic khanNo ratings yet
- A Case Report of Classical Hodgkin's Lymphoma Presented With Anemia of Chronic Disease As Microcytic Hypochromic TypeDocument3 pagesA Case Report of Classical Hodgkin's Lymphoma Presented With Anemia of Chronic Disease As Microcytic Hypochromic TypeIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Shock Sepsis and Organ Failure PDFDocument1,179 pagesPathophysiology of Shock Sepsis and Organ Failure PDFNotInterested100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 pagesDecreased Cardiac Outputshuang81No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pressure UlcerDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Pressure UlcerSTORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- Case Presentation OsteomylitisDocument64 pagesCase Presentation OsteomylitisDemi Rose Bolivar100% (1)
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Avascular Necrosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAvascular Necrosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Pathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsErrol B. TiozonNo ratings yet
- Cues and Evidences Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues and Evidences Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- Arcoxia (Etoricoxib)Document1 pageArcoxia (Etoricoxib)Sandrine Barredo100% (1)
- GliclazideDocument2 pagesGliclazideSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- Clarithromycin & AvamysDocument1 pageClarithromycin & AvamysSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- Terbutaline NasoclearDocument1 pageTerbutaline NasoclearSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- Salbutamol (Ventolin Neb)Document1 pageSalbutamol (Ventolin Neb)Sandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- LinaglipitinDocument1 pageLinaglipitinSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- Terbutaline NasoclearDocument1 pageTerbutaline NasoclearSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- Budesonide (Asmavent)Document1 pageBudesonide (Asmavent)Sandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- Mosegor, Nacl, Nahco 3, Fondaparinux, RamiprilDocument2 pagesMosegor, Nacl, Nahco 3, Fondaparinux, RamiprilSandrine Barredo100% (2)
- FebuxostatDocument1 pageFebuxostatSandrine Barredo100% (4)
- Sodium Chloride (Nacl)Document1 pageSodium Chloride (Nacl)Sandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- LantusDocument1 pageLantusSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- ClonitidineDocument1 pageClonitidineSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- School Form 8 (SF 8)Document3 pagesSchool Form 8 (SF 8)Jessa Desiree PorrasNo ratings yet
- Muscle Fatigue TestDocument8 pagesMuscle Fatigue TestKhaled ToffahaNo ratings yet
- 64 Year Old Male With COPDDocument14 pages64 Year Old Male With COPDKyle MangononNo ratings yet
- E61 PDFDocument39 pagesE61 PDFElizabeth SniderNo ratings yet
- ELC501 - English For Critical Academic Reading: Individual Assignment - Written Article AnalysisDocument6 pagesELC501 - English For Critical Academic Reading: Individual Assignment - Written Article AnalysisNur Shazleen Afina100% (1)
- Weight Loss ChartDocument7 pagesWeight Loss ChartAton MoshidiNo ratings yet
- Gastric Sleeve Surgery by DR Nagi SafaDocument3 pagesGastric Sleeve Surgery by DR Nagi SafaDr Nagi SafaNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain-Orthoinfo - AaosDocument13 pagesLow Back Pain-Orthoinfo - AaosBang mantoNo ratings yet
- 2009 WHO Lifestyle Manual Module1 Overview NCDDocument49 pages2009 WHO Lifestyle Manual Module1 Overview NCDRazel Kinette AzotesNo ratings yet
- Hiw Many Pullups Can The Average Human Do - Google SearchDocument1 pageHiw Many Pullups Can The Average Human Do - Google SearchMathew GiddensNo ratings yet
- Cataracts Diabetes Diuretics EyeDocument4 pagesCataracts Diabetes Diuretics Eyevandana singhNo ratings yet
- Analysis: Dietary and Nutritional Approaches For Prevention and Management of Type 2 DiabetesDocument9 pagesAnalysis: Dietary and Nutritional Approaches For Prevention and Management of Type 2 DiabetesMr. LNo ratings yet
- Muscle Fibers - An in Depth Analysis Part 3 AbcbodybuildingDocument7 pagesMuscle Fibers - An in Depth Analysis Part 3 AbcbodybuildingsupiulilumaNo ratings yet
- Intermedio KEY 2014Document14 pagesIntermedio KEY 2014juanpepito24No ratings yet
- E003290 FullDocument9 pagesE003290 FullANGELA CAMILA JARA LUZURIAGANo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument50 pagesObesityKetan JainNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument9 pagesDiabetes MellitusElifah RahmadhaniNo ratings yet
- Brain MetabolismDocument10 pagesBrain MetabolismDr. Kaushal Kishor SharmaNo ratings yet
- Causes of The UterineDocument7 pagesCauses of The UterineDurgaValliNo ratings yet
- Blood Gas AnalysisDocument3 pagesBlood Gas AnalysisChameera Bandara100% (2)
- February 16, 2018 Strathmore TimesDocument24 pagesFebruary 16, 2018 Strathmore TimesStrathmore Times100% (1)
- Off-Season Football Training - Muscle & StrengthDocument12 pagesOff-Season Football Training - Muscle & StrengthTom HochhalterNo ratings yet
- 50 Third ConditionalDocument7 pages50 Third ConditionalRaphael LoboNo ratings yet
- Obesity PDFDocument7 pagesObesity PDFRoderick RichardNo ratings yet
- Gestational DiabetesDocument6 pagesGestational DiabetesZAY EMNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Nursing (Report)Document101 pagesBasic Concepts in Nursing (Report)NDJNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 On Regulation of MetabolismDocument23 pagesLecture 11 On Regulation of MetabolismSaad KazmiNo ratings yet