Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syllabus - Session 2014-15 (Odd Sem)
Syllabus - Session 2014-15 (Odd Sem)
Uploaded by
nitin_johri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views4 pagesThis document contains the syllabus for the course NME-302 Mechanics of Solids. It outlines 5 units that will be covered over the semester: compound stress and strains, stresses in beams, torsion, helical and leaf springs, and columns and struts. It also includes the syllabus for the related labs NME-352 Machine Drawing-I Lab and NME-351 Fluid Mechanics Lab, which involve hands-on exercises, as well as references for the courses.
Original Description:
Syllabus --Session 2014-15 (Odd Sem)
Original Title
Syllabus --Session 2014-15 (Odd Sem)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains the syllabus for the course NME-302 Mechanics of Solids. It outlines 5 units that will be covered over the semester: compound stress and strains, stresses in beams, torsion, helical and leaf springs, and columns and struts. It also includes the syllabus for the related labs NME-352 Machine Drawing-I Lab and NME-351 Fluid Mechanics Lab, which involve hands-on exercises, as well as references for the courses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views4 pagesSyllabus - Session 2014-15 (Odd Sem)
Syllabus - Session 2014-15 (Odd Sem)
Uploaded by
nitin_johriThis document contains the syllabus for the course NME-302 Mechanics of Solids. It outlines 5 units that will be covered over the semester: compound stress and strains, stresses in beams, torsion, helical and leaf springs, and columns and struts. It also includes the syllabus for the related labs NME-352 Machine Drawing-I Lab and NME-351 Fluid Mechanics Lab, which involve hands-on exercises, as well as references for the courses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
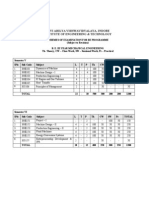
Syllabus [ Session 2014-15 (odd Sem)]
NME-302: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS L T P
3 1 0
UNIT-I
Compound stress and strains: Introduction, normal stress and strain, shear stress and strain, stresses
on
inclines sections, strain energy, impact loads and stresses, state of plane stress, principal stress and
strain,
maximum shear stress, Mohrs stress circle, three dimensional state of stress & strain, equilibrium
equations, generalized Hooks law, theories of failure
8
UNIT II
Stresses in Beams: Pure Bending, normal stresses in beams, shear stresses in beams due to transverse
and axial loads, composite beams.
2
Deflection of Beams: Equation of elastic curve, cantilever and simply supported beams, Macaulays
method, area moment method, fixed and continuous beams
4
Torsion: Torsion, combined bending & torsion of solid & hollow shafts, torsion of thin walled tubes
2
UNIT-III
Helical and Leaf Springs: Deflection of springs by energy method, helical springs under axial load
and
under axial twist (respectively for circular and square cross sections) axial load and twisting moment
acting simultaneously both for open and closed coiled springs, laminated springs.
4
Columns and Struts: Buckling and stability, slenderness ratio, combined bending and direct stress,
middle third and middle quarter rules, struts with different end conditions, Eulers theory for pin
ended
columns, effect of end conditions on column buckling, Ranking Gordon formulae, examples of
columns
in mechanical equipments and machines.
4
UNIT-IV
Thin cylinders & spheres: Introduction, difference between thin walled and thick walled pressure
vessels, Thin walled spheres and cylinders, hoop and axial stresses and strain, volumetric strain.
2
Thick cylinders:
Radial, axial and circumferential stresses in thick cylinders subjected to internal or external pressures,
compound cylinders, stresses in rotating shaft and cylinders, stresses due to interference fits.
4
UNIT-V
Curved Beams: Bending of beams with large initial curvature, position of neutral axis for
rectangular,
trapezoidal and circular cross sections, stress in crane hooks, stress in circular rings subjected to
tension
or compression.
4
Unsymmetrical Bending: Properties of beam cross-section, slope of neutral axis, stress and
deflection in
unsymmetrical bending, determination of shear center and flexural axis (for symmetry about both axis
and about one axis) for I-section and channel section.
4
Books and References :
1. Mechanics of Materials by Hibbeler, Pearson.
2. Mechanics of Materials by.Beer, Jhonston, DEwolf and Mazurek, TMH
3. Strength of Materials by Pytel and Singer, Harper Collins
4. Strength of Materials by Ryder, Macmillan.
5. Strength of Materials by Timoshenko and & Yungs, East West Press.
6. Introduction to Solid Mechanics by Shames, PHI
7. Strength of Materials by Nag and Chandra, Wiley India.
8. Strength of Materials by Nash (Sp Indian Edition), TMH
9. Strength of Materials by Jindal, Pearson Education
10. Strength of Material by Bhavikatti, Vikas Publishing.
11. Fundamentals of Solid Mechanics by Gambhir, PHI
12. Strength of Materials by Basavajaiah and Mahadevappa, University Press.
NME-352: MACHINE DRAWING -I LAB L T P
0 0 3
Introduction (1 drawing sheets)
Introduction, classification of machine drawings, principles of drawing, conventional representation
of
machine components and materials, lines, types of lines, dimensioning types, lines and rules of
dimensioning.
2
Orthographic Projections (3 drawing sheets)
Introduction to orthographic projection, concept of first angle and third angle projection, drawing of
simple machine elements in first angle projection, missing line problems, principle of visualization of
objects, sectional views, full and half sectional views, auxiliary views.
3
Fasteners (2 drawing sheets)
Temporary and permanent fasteners, thread nomenclature and forms, thread series, designation,
representation of threads, bolted joints, locking arrangement of nuts, screws, washers, foundation
bolts
etc., keys, types of keys, cotter and knuckle joints.
2
Riveted joints (1 drawing sheet)
Introduction, rivets and riveting, types of rivets, types of riveted joints, drawing of boiler joints etc.
1
Assembly drawing (2 drawing sheets)
Introduction to assembly drawing, drawing assembly drawing of simple machine elements like rigid
or
flexible coupling, muff coupling, plummer block, footstep bearing, bracket etc.
2
Free hand sketching (1 drawing sheet)
Introduction, Need for free hand sketching, Free hand sketching of foundation bolts, studs, pulleys,
couplings etc.
1
Computer aided drafting (1 drawing)
Introduction to computer aided drafting; advantages and applications of CAD, concepts of computer
aided 2D drafting using any drafting software like AutoCAD, Solid Edge, Draft Sight etc., basic draw
and
modify commands, making 2D drawings of simple machine parts
1
Books and References:
1. Fundamentals of Machine Drawing by Sadhu Singh & Shah, PHI
2. Engineering Drawing by Bhat, & Panchal, Charotar Publishing House
3. Machine Drawing with AutoCAD by Pohit and Ghosh, Pearson
4. Machine Drawing-KL Narayana, P Kannaiah, KV Reddy, New Age
5. Machine Drawing, N. Siddeshswar, P Kannaiah, VVS Shastry, Tata McGraw Hill
6. Engineering Drawing, Pathak, Wiley
7. Textbook of Machine Drawing, K C John, PHI
8. AutoCAD 2014 for Engineers & Designers, Bhatt, WILEY
9. Engineering Graphics with AutoCAD, Bethune, PHI
NME- 351: FLUID MECHANICS LAB. L T P
0 0 3
Note: Ensure to conduct at least 10 experiments from the list:
1. To verify the momentum equation using the experimental set-up on impact of jet.
2. To determine the coefficient of discharge of an orifice of a given shape. Also to determine the
coefficient of velocity and the coefficient of contraction of the orifice mouth piece.
3. To calibrate an orifice meter and study the variation of the co-efficient of discharge with the
Reynolds number.
4. To calibrate a Venturimeter and study the variation of the co-efficient of discharge with the
Reynolds number.
5. To calibrate a bend meter and study the variation of the co-efficient of discharge with the Reynolds
number.
6. To draw a flow-net using Electrical Analogy Method.
7. To study the transition from laminar to turbulent flow and to determine the lower critical Reynolds
number.
8. To study the velocity distribution in a pipe and also to compute the discharge by integrating the
velocity profile.
9. To study the variation of friction factor, f for turbulent flow in commercial pipes.
10. To study the boundary layer velocity profile over a flat plate and to determine the boundary layer
thickness.
11. To determine Meta-centric height of a given ship model.
12. To determine the head loss for a sudden enlargement
13. To determine the head loss for a sudden Contraction.
Seminar:
NME-152/NME/252 : Engineering Mechanics Lab
L T P [0 0 2]
(Any 10 experiments of the following or similar experiments suitably designed)
1. To verify the law of parallelogram of forces.
2. To study the equilibrium of a body under three forces.
3. To determine the coefficient of friction of a flat surface.
4. Friction experiment on screw-jack.
5. Experiment based on analysis of truss.
6. To determine the mass moment of inertia of a rotating disc.
7. To conduct the tensile test and determine the ultimate tensile strength, percentage elongation for a
mild steel specimen.
8. To conduct the Impact-tests (Izod / Charpy) on Impact-testing machine to find the Impact
Strength of the specimen.
9. To determine the hardness of the given specimen using Vicker/Brinell/Rockwell hardness testing
machine.
10. Simple & compound gear-train experiment.
11. Worm & worm-wheel experiment for load lifting.
12. Belt-Pulley experiment.
13. Bending of simply-supported and cantilever beams for theoretical & experimental deflection.
14. Dynamics experiment on momentum conservation
15. Dynamics experiment on collision for determining coefficient of restitution.
16. Experiment on Torsion of Rod/wire
You might also like
- Condenser DesignDocument1 pageCondenser DesignNaqqash SajidNo ratings yet
- Report Fatigue TestDocument20 pagesReport Fatigue TestCherif Chokeir75% (4)
- SQR 472 Engine: Service Manual For Mechanical PartDocument57 pagesSQR 472 Engine: Service Manual For Mechanical PartjamesmotuvNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials (9024)Document6 pagesStrength of Materials (9024)rajyamgarNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Strength of MaterialsDocument17 pages3.1 Strength of Materialsengr_sehranNo ratings yet
- Syllabus PDFDocument66 pagesSyllabus PDFPardeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Third Year Mechanical Engineering SyllabusDocument54 pagesThird Year Mechanical Engineering SyllabusTonya WhitneyNo ratings yet
- 1ST YearDocument5 pages1ST YearVikas KunduNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material QuantumDocument349 pagesStrength of Material QuantumAkash Singh100% (2)
- S. E. Mech. Engg. June 2013 PDFDocument34 pagesS. E. Mech. Engg. June 2013 PDFDinesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Production Engineering SyllabusDocument10 pagesProduction Engineering SyllabusKavan PanneerselvamNo ratings yet
- Report Torsion TestDocument27 pagesReport Torsion TestCherif ChokeirNo ratings yet
- Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, I Dore I Stitute of E Gi Eeri G & Tech OlogyDocument20 pagesDevi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, I Dore I Stitute of E Gi Eeri G & Tech OlogySonal MahajanNo ratings yet
- B Tech Mechanical Engineering Syllabus For Batch 2013-14Document30 pagesB Tech Mechanical Engineering Syllabus For Batch 2013-14ra44993541No ratings yet
- Applied MathematicsDocument9 pagesApplied MathematicsbhabadnileshNo ratings yet
- 5th Sem Mech Syllabus Vssut, BurlaDocument5 pages5th Sem Mech Syllabus Vssut, BurlaDeepak AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical SyllabusDocument35 pagesMechanical SyllabusTanuj Deshmukh0% (1)
- Civil - Sem - 3Document28 pagesCivil - Sem - 3Garima RajdevaNo ratings yet
- Btech 2Document17 pagesBtech 2Divyesh SindhiNo ratings yet
- 7ME7: P.E. LAB.-II 3 P MM 100 Minimum Any Ten Experiments Can Be PerformedDocument7 pages7ME7: P.E. LAB.-II 3 P MM 100 Minimum Any Ten Experiments Can Be PerformedappannusaNo ratings yet
- FMD 3141907Document3 pagesFMD 3141907Hitesh RanaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Mech 3rd YearDocument130 pagesSyllabus - Mech 3rd YearAbhishek AmarNo ratings yet
- MarineDocument71 pagesMarineRENGANATHAN P67% (3)
- Strength of MaterialsDocument3 pagesStrength of Materialsvp0209198825% (4)
- SOM CivilDocument7 pagesSOM CivilVikram RaoNo ratings yet
- Elements of Mechanical Engineering Syllabus For 1st Sem B.TechDocument6 pagesElements of Mechanical Engineering Syllabus For 1st Sem B.TechDebarshi BaruahNo ratings yet
- S.E.mechanicalEngg SyllabusDocument32 pagesS.E.mechanicalEngg SyllabusBalaji MundeNo ratings yet
- Se Ce SyllabusDocument23 pagesSe Ce SyllabusPrashant PatilNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engg SyllabusDocument33 pagesMechanical Engg SyllabusKRISHNA KANT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Me RRB JeDocument5 pagesMe RRB JeErin BarryNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Me-3 III Sem All SubjectDocument7 pagesSyllabus Me-3 III Sem All SubjectDeepak prasadNo ratings yet
- 3 Second Year First Semester-1Document8 pages3 Second Year First Semester-1SiddharthaShahNo ratings yet
- Second Year First Semester: Department of Mechanical Engineering - Course CatalogueDocument8 pagesSecond Year First Semester: Department of Mechanical Engineering - Course CatalogueRojan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solid: PME3I101Document3 pagesMechanics of Solid: PME3I101Anonymous kTVBUxrNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation On Torsional Rigidity of Power ScrewsDocument4 pagesExperimental Investigation On Torsional Rigidity of Power ScrewsIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- Veer Surendra Sai University of Technology:Orissa: Syllabus For First Year B.TechDocument24 pagesVeer Surendra Sai University of Technology:Orissa: Syllabus For First Year B.TechSohamsi BeheraNo ratings yet
- The Benefits and Drawbacks of eDocument5 pagesThe Benefits and Drawbacks of esaikumarNo ratings yet
- Proposed Scheme and Syllabus From Academic Year 2010-11 Aeronautical Engineering V SemesterDocument41 pagesProposed Scheme and Syllabus From Academic Year 2010-11 Aeronautical Engineering V SemestershivurbNo ratings yet
- Fatigue 2Document16 pagesFatigue 2kalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument58 pagesSyllabusRediraNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids CT 205Document2 pagesMechanics of Solids CT 205Hassan0% (2)
- Mos - Practice Book PDFDocument69 pagesMos - Practice Book PDFDipika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - DevdevDocument19 pagesExperiment 1 - DevdevVinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- 01 - Session 00 Course IntroductionDocument14 pages01 - Session 00 Course Introductionyagrazz33No ratings yet
- Machine Design and Drawing-IDocument75 pagesMachine Design and Drawing-IJomis MathewsNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics Syllabus 27-11-16 1Document3 pagesSolid Mechanics Syllabus 27-11-16 1atif shaikhNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics M203 PDFDocument4 pagesEngineering Mechanics M203 PDFPawan SahuNo ratings yet
- 3rd Smester PDFDocument17 pages3rd Smester PDFVijayKumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Solid Mechanics Basic ConceptDocument9 pages1 Solid Mechanics Basic ConceptRahulNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering B.techDocument35 pagesMechanical Engineering B.techRamBabuInkolluNo ratings yet
- Curriculum (B. TECH) : Undergraduate ProgrammeDocument43 pagesCurriculum (B. TECH) : Undergraduate ProgrammeHarman Singh NagpalNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of B. Tech. in Mechanical Engineering Semester III Cs 1312:numerical Analysis & Computer Program (C & C++) (2-1-0)Document8 pagesSyllabus of B. Tech. in Mechanical Engineering Semester III Cs 1312:numerical Analysis & Computer Program (C & C++) (2-1-0)gopalchandramahatoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Manual 2021-22 - Sem-III - MOS - MITSOEDocument97 pagesTutorial Manual 2021-22 - Sem-III - MOS - MITSOEJeetender MishraNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityDhaval PatelNo ratings yet
- Civil 4th SemDocument12 pagesCivil 4th Semwaseem akramNo ratings yet
- Course Structure and Teaching Schedule (5 Semester)Document12 pagesCourse Structure and Teaching Schedule (5 Semester)Gladiatordiv OutlawNo ratings yet
- 66 Handbook Me V SemDocument62 pages66 Handbook Me V Semkanishkakhurana240% (1)
- Mechanical Characterization of Materials and Wave Dispersion: Instrumentation and Experiment InterpretationFrom EverandMechanical Characterization of Materials and Wave Dispersion: Instrumentation and Experiment InterpretationYvon ChevalierNo ratings yet
- Plate and Shell Structures: Selected Analytical and Finite Element SolutionsFrom EverandPlate and Shell Structures: Selected Analytical and Finite Element SolutionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Question-Bank-Machine Design-II (NME-602)Document10 pagesQuestion-Bank-Machine Design-II (NME-602)nitin_johriNo ratings yet
- Assignment No-1 EME-051 orDocument1 pageAssignment No-1 EME-051 ornitin_johriNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1 NME 602 MD 2Document2 pagesAssignment No 1 NME 602 MD 2nitin_johri0% (1)
- MD-2 Lab NME-652 C++ Programs - 6th Sem ME Section ADocument8 pagesMD-2 Lab NME-652 C++ Programs - 6th Sem ME Section Anitin_johri100% (3)
- MD-2 EME-602 AttendanceDocument2 pagesMD-2 EME-602 Attendancenitin_johriNo ratings yet
- Urgent - Notice For Weak StudentsDocument1 pageUrgent - Notice For Weak Studentsnitin_johriNo ratings yet
- MD-2 Short AttendanceDocument1 pageMD-2 Short Attendancenitin_johriNo ratings yet
- MD-2 EME-602 AttendanceDocument2 pagesMD-2 EME-602 Attendancenitin_johriNo ratings yet
- UPTU 2013-14 Machine Design - II EME 602Document4 pagesUPTU 2013-14 Machine Design - II EME 602nitin_johriNo ratings yet
- Machine Design-II EME602 2012-13Document4 pagesMachine Design-II EME602 2012-13nitin_johriNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2 Mechanics of Solids (NME-302)Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2 Mechanics of Solids (NME-302)nitin_johriNo ratings yet
- Previous Year UPTU End Sem Exam Papers - SOM / MOSDocument4 pagesPrevious Year UPTU End Sem Exam Papers - SOM / MOSnitin_johriNo ratings yet
- Previous Year UPTU End Sem Exam Papers - SOM / MOS Paper 7Document3 pagesPrevious Year UPTU End Sem Exam Papers - SOM / MOS Paper 7nitin_johri0% (1)
- Previous Year UPTU End Sem Exam Papers - SOM / MOSDocument4 pagesPrevious Year UPTU End Sem Exam Papers - SOM / MOSnitin_johriNo ratings yet
- Previous Year UPTU End Sem Exam Papers - SOM / MOS Paper 4Document4 pagesPrevious Year UPTU End Sem Exam Papers - SOM / MOS Paper 4nitin_johriNo ratings yet
- Relation Between Elastic ConstantsDocument5 pagesRelation Between Elastic Constantsnitin_johri100% (1)
- Shear Force & Bending MomentDocument17 pagesShear Force & Bending Momentnitin_johriNo ratings yet
- Direct & Shear Stress & Mohr's CircleDocument19 pagesDirect & Shear Stress & Mohr's Circlenitin_johri0% (1)
- Chapter4performanceparav2 28student 29Document19 pagesChapter4performanceparav2 28student 29Thiuyah A/p RajandranNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Heat Transfer Ten Remaining Hot Gas Path ChallengesDocument9 pagesGas Turbine Heat Transfer Ten Remaining Hot Gas Path Challengeseankibo100% (2)
- BFC20903 - Ch5 (Transverse Shear)Document27 pagesBFC20903 - Ch5 (Transverse Shear)azrinaishakNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of DryingDocument14 pagesFundamentals of DryingAlisha AnchearyNo ratings yet
- Air Solution: Outdoor UnitDocument49 pagesAir Solution: Outdoor UnitYoyok PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Installation Instructions W10436749 RevC PDFDocument36 pagesInstallation Instructions W10436749 RevC PDFCarlos Alberto VentreNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 WorkDocument15 pagesLesson 2 WorkprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Diagrama ElectricoDocument2 pagesDiagrama ElectricodptecnicocmspNo ratings yet
- Manual 700Document58 pagesManual 700Romanhnap100% (1)
- Unit 3Document8 pagesUnit 3bvnareshNo ratings yet
- The Design and Construction of The 16 Hectare Basement at Marina Bay Sands, SingaporeDocument14 pagesThe Design and Construction of The 16 Hectare Basement at Marina Bay Sands, SingaporeTrần KhươngNo ratings yet
- Abreviaciones de PipingDocument13 pagesAbreviaciones de PipingCesar HernandezNo ratings yet
- TW Groeneweg - Shield Driven Tunnels in UHSCDocument141 pagesTW Groeneweg - Shield Driven Tunnels in UHSCSérgio BernardesNo ratings yet
- List of Oil ZF PDFDocument16 pagesList of Oil ZF PDFJhon SyalfiandyNo ratings yet
- Naresh KumarDocument3 pagesNaresh KumarMasidur RahamanNo ratings yet
- Snap Tie SpecsDocument108 pagesSnap Tie SpecsJames PittsNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of A Particle Live Class-1 Teacher NotesDocument28 pagesKinematics of A Particle Live Class-1 Teacher NotesYash sharmaNo ratings yet
- HondaDocument5 pagesHondadixon_12No ratings yet
- The First Law of Thermodynamics: Pre-Reading 19.1Document25 pagesThe First Law of Thermodynamics: Pre-Reading 19.1Umair Afzal ChNo ratings yet
- GE Appliances - Air & Water - Page 1 - GE AppliancesDocument7 pagesGE Appliances - Air & Water - Page 1 - GE Appliancesabdalla AljzNo ratings yet
- Greensmaster 1000Document36 pagesGreensmaster 1000Raúl TorresNo ratings yet
- 7 Gas Turbine Plant: G. Boxer, Applications of Engineering Thermodynamics © G. Boxer 1979Document2 pages7 Gas Turbine Plant: G. Boxer, Applications of Engineering Thermodynamics © G. Boxer 1979WestNo ratings yet
- Aleyna Ceyhan, İpek Erdinç, Nijat Tarverdiyev, Elif Toprak, İlayda Nur GüzelDocument2 pagesAleyna Ceyhan, İpek Erdinç, Nijat Tarverdiyev, Elif Toprak, İlayda Nur Güzelilayda güzelNo ratings yet
- SteelDesign BeamColumn Fu 455Document4 pagesSteelDesign BeamColumn Fu 455mavessNo ratings yet
- Problem9-113 (Thermal Decomposition of Parallel Plates)Document15 pagesProblem9-113 (Thermal Decomposition of Parallel Plates)youga SriNo ratings yet
- Heat and Power Networks in Process Design Part1 - Bodo LinnhoffDocument7 pagesHeat and Power Networks in Process Design Part1 - Bodo Linnhoffkim haksongNo ratings yet
- P103 Temperature, Heat, ExpansionDocument33 pagesP103 Temperature, Heat, ExpansionAnonymous 88kXqKNo ratings yet
- Supreme CPVC PipeDocument1 pageSupreme CPVC PiperajanvidyarthiNo ratings yet