Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsThe Pricing Approaches: Product Cost Competitor's Offers & Other Internal and External Factors High Price (No Demand)
The Pricing Approaches: Product Cost Competitor's Offers & Other Internal and External Factors High Price (No Demand)
Uploaded by
Saud Alnooh1. There are several factors to consider when setting a product price, including production costs, competitor prices, and customer perceived value.
2. For new products, companies can use either market skimming pricing by setting a high initial price to target early adopters, or market penetration pricing using lower prices to target a wider customer base.
3. Pricing strategies also depend on balancing product quality with price, targeting either premium, good value, overcharging, or economy customer segments. Cost-based pricing considers production costs while value-based pricing focuses on customer perceived value.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Back Bay Battery Simulation PDFDocument3 pagesBack Bay Battery Simulation PDFHugs100% (2)
- Problem 5-19 Basic CVP Analysis Graphing (LO1, LO2, LO4, LO6)Document16 pagesProblem 5-19 Basic CVP Analysis Graphing (LO1, LO2, LO4, LO6)Chamrith SophearaNo ratings yet
- Relevant Costing AnalysisDocument11 pagesRelevant Costing Analysisrajeshaisdu009100% (1)
- Compl7th QuizDocument67 pagesCompl7th QuizSaeym SegoviaNo ratings yet
- Marketing 1Document4 pagesMarketing 1Crisielyn BuyanNo ratings yet
- Unit 7. Pricing DecisionDocument27 pagesUnit 7. Pricing DecisionGunjan GuptaNo ratings yet
- PricingDocument12 pagesPricingSupreet Singh BediNo ratings yet
- Pricing & Its ObjectivesDocument33 pagesPricing & Its ObjectivesshoaibNo ratings yet
- Marketing Managment - Unit 3 (Part Iv)Document5 pagesMarketing Managment - Unit 3 (Part Iv)amritaNo ratings yet
- CH 6 PricingDocument20 pagesCH 6 PricingkichuubmcNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 - Marketing PPT AcctDocument42 pagesCHAPTER 5 - Marketing PPT AcctAmanuel AbebawNo ratings yet
- Price' Is What You Give/pay in Return For Goods or Services. It Is The Most Flexible Marketing Mix ElementDocument5 pagesPrice' Is What You Give/pay in Return For Goods or Services. It Is The Most Flexible Marketing Mix ElementSagar ParekhNo ratings yet
- Abdullah Nisar and Jameel TalibDocument16 pagesAbdullah Nisar and Jameel Talibfatimadilawaiz1No ratings yet
- Pricing StrategyDocument33 pagesPricing Strategyumar yousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Marketing Chapter 5Document9 pagesMarketing Chapter 5wiki121.agsNo ratings yet
- Pricing & Channels of DistributionDocument60 pagesPricing & Channels of Distributionsumeet kcNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 KMB N MK 03Document13 pagesUnit 3 KMB N MK 03Mohammad ShahvanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Marketing: Pricing: Understanding and Capturing Customer ValueDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Marketing: Pricing: Understanding and Capturing Customer ValueMustakim Mehmud TohaNo ratings yet
- Various Pricing Strategies: A Review: Dr. Satyajeet S DeshpandeDocument5 pagesVarious Pricing Strategies: A Review: Dr. Satyajeet S DeshpandeGis PeeNo ratings yet
- Pricing StratagyDocument47 pagesPricing StratagyKranthiNalla100% (1)
- Marketing - Chapter 12Document35 pagesMarketing - Chapter 12Jawad AzizNo ratings yet
- Factors of ProductionDocument29 pagesFactors of Productionxhai vhieNo ratings yet
- Pricing StrategiesDocument9 pagesPricing StrategiesramyagolluNo ratings yet
- PRICING CH SixDocument31 pagesPRICING CH SixBelay AdamuNo ratings yet
- Lecture Pricing StrategyDocument34 pagesLecture Pricing StrategyTin PerezNo ratings yet
- Pricing MethodsDocument7 pagesPricing MethodsakmohideenNo ratings yet
- "You Don't Sell Through Price. You Sell The Price" Price Is The Marketing-Mix Element That Produces Revenue The Others Produce CostDocument22 pages"You Don't Sell Through Price. You Sell The Price" Price Is The Marketing-Mix Element That Produces Revenue The Others Produce Cost200eduNo ratings yet
- Ch. 2 PricingDocument10 pagesCh. 2 PricingAshu DrwalNo ratings yet
- Pricing Strategies 1Document17 pagesPricing Strategies 1Pule JackobNo ratings yet
- Pricing StrategyDocument9 pagesPricing StrategyVindhya ShankerNo ratings yet
- 4Ps PriceDocument39 pages4Ps PriceCaesar AmigoNo ratings yet
- Group 1 (Marketing)Document21 pagesGroup 1 (Marketing)Kim Andrhea RoazolNo ratings yet
- Unit 07 PricingDocument13 pagesUnit 07 PricingKhan AshfaqueNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Marketing ManagementDocument18 pagesUnit 3 Marketing ManagementvasantharaoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Definition of PricingDocument15 pagesUnit - 4 Definition of PricingmussaiyibNo ratings yet
- Economics NotesDocument11 pagesEconomics NotesRuthveek FadteNo ratings yet
- Pricing: Pricing Pricing Objectives or Goals Give Direction To The WholeDocument4 pagesPricing: Pricing Pricing Objectives or Goals Give Direction To The WholeClaudette ClementeNo ratings yet
- Price PlanningDocument42 pagesPrice Planningaqsakhan78681No ratings yet
- Major Pricing StrategyDocument3 pagesMajor Pricing Strategy35Phạm Ngọc ThyNo ratings yet
- The Second P: PRICEDocument22 pagesThe Second P: PRICEJudy Ann PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Pricing MethodsDocument12 pagesPricing MethodsAtharva DumbreNo ratings yet
- Marketing MangementDocument26 pagesMarketing MangementPopuri Nagasai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Pricing Objectives and Price DeterminationDocument7 pagesChapter 3 - Pricing Objectives and Price DeterminationChierhy Jane BayudanNo ratings yet
- Theme 9 Price and PricingDocument10 pagesTheme 9 Price and PricingMuzaffar SaleemNo ratings yet
- PriceDocument37 pagesPriceSahana S MendonNo ratings yet
- Group 3: A. Demonstrate The Different Concepts B. Collect The Appropriate Pricing StrategiesDocument12 pagesGroup 3: A. Demonstrate The Different Concepts B. Collect The Appropriate Pricing StrategiesErica May BurgosNo ratings yet
- Designing Pricing StrategiesDocument17 pagesDesigning Pricing Strategiesrahulravi4uNo ratings yet
- Pricing DecisionsDocument44 pagesPricing DecisionsTejaswiniNo ratings yet
- The Marketing Mix PriceDocument3 pagesThe Marketing Mix PriceraheemeeaaishaNo ratings yet
- Different Pricing Strategies in Marketing Adopted by CompaniesDocument2 pagesDifferent Pricing Strategies in Marketing Adopted by CompaniesHKHNo ratings yet
- Different Pricing Strategies in Marketing Adopted by CompaniesDocument2 pagesDifferent Pricing Strategies in Marketing Adopted by CompaniesHKHNo ratings yet
- Pricing in MarketingDocument4 pagesPricing in Marketingdaniela carvajal guarinNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document12 pagesUnit 4shivumasaraddi0No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PriceDocument25 pagesChapter 5 PriceNur Atikah GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Unit 8-Revenue Analysis and Pricing PoliciesDocument17 pagesUnit 8-Revenue Analysis and Pricing PoliciesGayl Ignacio TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument21 pagesUnit IiiAnuradha MauryaNo ratings yet
- Pricing PolicyDocument1 pagePricing PolicyHend HelmyNo ratings yet
- MM Module 4Document8 pagesMM Module 4Sonal GowdaNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Price PDFDocument8 pagesTopic 10 Price PDFIntan SyuhadaNo ratings yet
- Price Analysis: Submitted To: Mrs. Arlene Gabriel Submitted By: Kailyn Cris B. RuaboroDocument4 pagesPrice Analysis: Submitted To: Mrs. Arlene Gabriel Submitted By: Kailyn Cris B. RuaboroJerico ManaloNo ratings yet
- Marketing 1Document6 pagesMarketing 1VIDHI KAMATH 2122084No ratings yet
- Group 6Document41 pagesGroup 6Ej RubioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. PricingDocument26 pagesChapter 6. PricingTadele BekeleNo ratings yet
- Value-based Intelligent Pricing: Marketing and Business, #1From EverandValue-based Intelligent Pricing: Marketing and Business, #1No ratings yet
- The WogDocument21 pagesThe WogSaud Alnooh0% (3)
- Security Part 1 Auditing OS & NDocument59 pagesSecurity Part 1 Auditing OS & NSaud AlnoohNo ratings yet
- Bernie Madoff CaseDocument15 pagesBernie Madoff CaseSaud AlnoohNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 12 - Marketing CommunicationDocument30 pagesCHAPTER 12 - Marketing CommunicationSaud AlnoohNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 12 - Marketing CommunicationDocument30 pagesCHAPTER 12 - Marketing CommunicationSaud AlnoohNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 - Integrated Marketing CommunicationsDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 10 - Integrated Marketing CommunicationsSaud AlnoohNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 - The New Product Development ProcessDocument16 pagesCHAPTER 5 - The New Product Development ProcessSaud Alnooh100% (2)
- CHAPTER 2 - Marketing Environmwnt & SWOT AnalysisDocument24 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Marketing Environmwnt & SWOT AnalysisSaud AlnoohNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - An Overview of MarketingDocument49 pagesCHAPTER 1 - An Overview of MarketingSaud AlnoohNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit Analysis (Bridal Shoppe Sells Wedding Dresses)Document7 pagesCost Volume Profit Analysis (Bridal Shoppe Sells Wedding Dresses)Asma HatamNo ratings yet
- Mas 10 Exercises For UploadDocument5 pagesMas 10 Exercises For UploadChristine Joy Duterte RemorozaNo ratings yet
- Senior Auditor Cost-Accounting-McqsDocument101 pagesSenior Auditor Cost-Accounting-McqsMuhammad HamidNo ratings yet
- Topics: Break-Even Analysis, Operating and Financial Leverage, and Optimal Capital StructureDocument5 pagesTopics: Break-Even Analysis, Operating and Financial Leverage, and Optimal Capital StructuremagoimoiNo ratings yet
- CVPDocument20 pagesCVPDen Potxsz100% (1)
- Model Exit Exam of Cost & Managerial CostDocument10 pagesModel Exit Exam of Cost & Managerial Costnewaybeyene5No ratings yet
- Strategic Cost Management QuizDocument9 pagesStrategic Cost Management Quizctarenas.studentNo ratings yet
- 2011 AICPA Business QuestionsDocument45 pages2011 AICPA Business Questionsjklein2588100% (1)
- Relevant Costing Short Term Non Routine DecisionsDocument10 pagesRelevant Costing Short Term Non Routine DecisionsMitch fabayNo ratings yet
- Cost Analysis, Concepts & ClassificationsDocument43 pagesCost Analysis, Concepts & Classificationsmarget85% (13)
- BTEC HND Management Accounting Assignment 1Document18 pagesBTEC HND Management Accounting Assignment 1Suranga SamaranayakeNo ratings yet
- Solving A CVP ProblemDocument11 pagesSolving A CVP ProblemMahruf OpuNo ratings yet
- Standard Cost and Variance AnalysisDocument22 pagesStandard Cost and Variance AnalysisAbbas Jan Bangash100% (1)
- COPA Configuration and Painter GuideDocument217 pagesCOPA Configuration and Painter Guideresky surbakti0% (1)
- Class Question CVPDocument2 pagesClass Question CVPTanuj LalchandaniNo ratings yet
- Profits and MarginsDocument4 pagesProfits and Marginsrishifiib08No ratings yet
- Fixed Cost: Marginal CostingDocument6 pagesFixed Cost: Marginal CostingJebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Homework Chapter 5 EX 5-18Document9 pagesHomework Chapter 5 EX 5-18K59 Lai Hoang SonNo ratings yet
- CVP Finance AssignmentDocument12 pagesCVP Finance AssignmentVivek VashisthaNo ratings yet
- MA CHAPTER 4 Marginal Costing 1Document79 pagesMA CHAPTER 4 Marginal Costing 1Mohd Zubair KhanNo ratings yet
- SAP Profitability AnalysisDocument49 pagesSAP Profitability Analysisrohitmandhania95% (22)
- Relevant Costing by A BobadillaDocument99 pagesRelevant Costing by A BobadillaShailene DavidNo ratings yet
- Acctg Le3 BocotaDocument3 pagesAcctg Le3 BocotaAngela KlaraNo ratings yet
- Operating and Financial LeverageDocument43 pagesOperating and Financial LeverageMARIBEL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- ACT-project-og-123456 (Money Bag)Document17 pagesACT-project-og-123456 (Money Bag)Zidan ZaifNo ratings yet
- Actg 10 - MAS Midterm ExamDocument24 pagesActg 10 - MAS Midterm Examjoemel091190100% (1)
The Pricing Approaches: Product Cost Competitor's Offers & Other Internal and External Factors High Price (No Demand)
The Pricing Approaches: Product Cost Competitor's Offers & Other Internal and External Factors High Price (No Demand)
Uploaded by
Saud Alnooh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pages1. There are several factors to consider when setting a product price, including production costs, competitor prices, and customer perceived value.
2. For new products, companies can use either market skimming pricing by setting a high initial price to target early adopters, or market penetration pricing using lower prices to target a wider customer base.
3. Pricing strategies also depend on balancing product quality with price, targeting either premium, good value, overcharging, or economy customer segments. Cost-based pricing considers production costs while value-based pricing focuses on customer perceived value.
Original Description:
Original Title
Chapter 8
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. There are several factors to consider when setting a product price, including production costs, competitor prices, and customer perceived value.
2. For new products, companies can use either market skimming pricing by setting a high initial price to target early adopters, or market penetration pricing using lower prices to target a wider customer base.
3. Pricing strategies also depend on balancing product quality with price, targeting either premium, good value, overcharging, or economy customer segments. Cost-based pricing considers production costs while value-based pricing focuses on customer perceived value.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesThe Pricing Approaches: Product Cost Competitor's Offers & Other Internal and External Factors High Price (No Demand)
The Pricing Approaches: Product Cost Competitor's Offers & Other Internal and External Factors High Price (No Demand)
Uploaded by
Saud Alnooh1. There are several factors to consider when setting a product price, including production costs, competitor prices, and customer perceived value.
2. For new products, companies can use either market skimming pricing by setting a high initial price to target early adopters, or market penetration pricing using lower prices to target a wider customer base.
3. Pricing strategies also depend on balancing product quality with price, targeting either premium, good value, overcharging, or economy customer segments. Cost-based pricing considers production costs while value-based pricing focuses on customer perceived value.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Chapter 8
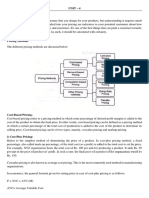
The pricing approaches
Things to conceder in setting the price:
1. Product cost (fixed cost + variable cost).
2. Competitors offers & other internal and external factors.
3. Consumers perception of value.
New product pricing strategies:
If a company is setting a new product there two options:
1. To set a high price if the company is setting a high price for their products it should
be backed up with a strong promotional effort it is called
Market skimming pricing
Advantage {the company initially sets high prices to skim revenues layer by layer from the
market}
Disadvantage {it may lead to lower demand}
Product cost
Competitors
offers & other
internal and
external factors
High Price (no
demand)
2. To set a low price
If the company is setting for a low price but it should also be backed up by strong promotional
support called market penetration pricing
The advantage {the company can penetrate the market quickly and deeply to attract a large
number of buyers and capture a large market share in the process}
Disadvantage{ revenues may be filled by more substantial demand }
To know which is better it depends on the button line ( profit) although it may be the same in
both options.
(Table 3)
the different between the two options are:
1. In skimming pricing is to make a swift return on investment by offering product at a high price
2. In penetration pricing the objective is to capture a large market share by attracting buyers
through low prices.
The low pricing is more beneficial to a firm over a long period of time.
the companies that are adopting the skimming pricing strategy need to be caution of their
marketing program and ensure that they justify the high price they charge for their products to
win customers confidence, support and eventually loyalty.
An alternative the two pricing strategies is establishing a relationship between the price and the
quality of the product to come up with 4 possible strategies:
1. Selling a High- quality product at a high price (premium pricing strategy)
2. Selling High- quality product at low price ( good value pricing strategy)
3. Selling Low- quality product at high price( overcharging pricing strategy)
4. Selling a low- quality product at a low price (economy pricing strategy)
Figure 3
Cost based pricing:
The cost is primary considered under the cost based pricing
Cost based pricing has 3 pricing approaches:
1. Cost -plus pricing. It requires a standard mark-up in the cost of the product ( called the mark-
up pricing) total cost of product per unit + (total cost of product per unit * Mark-up)= selling
price
2. Break -even pricing the company neither earns profit nor incurs loss ( net income equals to 0)
Q= T F C/ SP/u-VC/u where Q= break- even quantity, TFC= total fixed cost, SP/u= selling price
per unit and VC/u= variable cost per unit
The dominator (SP/u-VC/u) is also known as the contribution margin which is the amount os
sales contribution to pay for the companys fixed costs.
If a company sells more than the break- even it is sure to earn profit but if below it will incur
loss
Sales
Less: variable cost
Contribution margin
Less fixed cost
Net income
3. Target profit pricing a strategy in variation of the break-even the company will set a target
profit to be earned and use the break even analysis to meet the said target.
TPP= TP/Q+ CSP where TPP= breakeven price, TP= target profit, Q= estimated quantity to be
sold and CSP= current selling price.
Value- based pricing strategy: it considers the buyers perception value as the main ingredient in pricing.
The starting point is the customers perception value not the cost
Figure 4
Competition- based pricing strategy:
There 2 kind of Competition- based pricing strategy:
1. Going rate pricing
2. Sealed- bid pricing
You might also like
- Back Bay Battery Simulation PDFDocument3 pagesBack Bay Battery Simulation PDFHugs100% (2)
- Problem 5-19 Basic CVP Analysis Graphing (LO1, LO2, LO4, LO6)Document16 pagesProblem 5-19 Basic CVP Analysis Graphing (LO1, LO2, LO4, LO6)Chamrith SophearaNo ratings yet
- Relevant Costing AnalysisDocument11 pagesRelevant Costing Analysisrajeshaisdu009100% (1)
- Compl7th QuizDocument67 pagesCompl7th QuizSaeym SegoviaNo ratings yet
- Marketing 1Document4 pagesMarketing 1Crisielyn BuyanNo ratings yet
- Unit 7. Pricing DecisionDocument27 pagesUnit 7. Pricing DecisionGunjan GuptaNo ratings yet
- PricingDocument12 pagesPricingSupreet Singh BediNo ratings yet
- Pricing & Its ObjectivesDocument33 pagesPricing & Its ObjectivesshoaibNo ratings yet
- Marketing Managment - Unit 3 (Part Iv)Document5 pagesMarketing Managment - Unit 3 (Part Iv)amritaNo ratings yet
- CH 6 PricingDocument20 pagesCH 6 PricingkichuubmcNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 - Marketing PPT AcctDocument42 pagesCHAPTER 5 - Marketing PPT AcctAmanuel AbebawNo ratings yet
- Price' Is What You Give/pay in Return For Goods or Services. It Is The Most Flexible Marketing Mix ElementDocument5 pagesPrice' Is What You Give/pay in Return For Goods or Services. It Is The Most Flexible Marketing Mix ElementSagar ParekhNo ratings yet
- Abdullah Nisar and Jameel TalibDocument16 pagesAbdullah Nisar and Jameel Talibfatimadilawaiz1No ratings yet
- Pricing StrategyDocument33 pagesPricing Strategyumar yousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Marketing Chapter 5Document9 pagesMarketing Chapter 5wiki121.agsNo ratings yet
- Pricing & Channels of DistributionDocument60 pagesPricing & Channels of Distributionsumeet kcNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 KMB N MK 03Document13 pagesUnit 3 KMB N MK 03Mohammad ShahvanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Marketing: Pricing: Understanding and Capturing Customer ValueDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Marketing: Pricing: Understanding and Capturing Customer ValueMustakim Mehmud TohaNo ratings yet
- Various Pricing Strategies: A Review: Dr. Satyajeet S DeshpandeDocument5 pagesVarious Pricing Strategies: A Review: Dr. Satyajeet S DeshpandeGis PeeNo ratings yet
- Pricing StratagyDocument47 pagesPricing StratagyKranthiNalla100% (1)
- Marketing - Chapter 12Document35 pagesMarketing - Chapter 12Jawad AzizNo ratings yet
- Factors of ProductionDocument29 pagesFactors of Productionxhai vhieNo ratings yet
- Pricing StrategiesDocument9 pagesPricing StrategiesramyagolluNo ratings yet
- PRICING CH SixDocument31 pagesPRICING CH SixBelay AdamuNo ratings yet
- Lecture Pricing StrategyDocument34 pagesLecture Pricing StrategyTin PerezNo ratings yet
- Pricing MethodsDocument7 pagesPricing MethodsakmohideenNo ratings yet
- "You Don't Sell Through Price. You Sell The Price" Price Is The Marketing-Mix Element That Produces Revenue The Others Produce CostDocument22 pages"You Don't Sell Through Price. You Sell The Price" Price Is The Marketing-Mix Element That Produces Revenue The Others Produce Cost200eduNo ratings yet
- Ch. 2 PricingDocument10 pagesCh. 2 PricingAshu DrwalNo ratings yet
- Pricing Strategies 1Document17 pagesPricing Strategies 1Pule JackobNo ratings yet
- Pricing StrategyDocument9 pagesPricing StrategyVindhya ShankerNo ratings yet
- 4Ps PriceDocument39 pages4Ps PriceCaesar AmigoNo ratings yet
- Group 1 (Marketing)Document21 pagesGroup 1 (Marketing)Kim Andrhea RoazolNo ratings yet
- Unit 07 PricingDocument13 pagesUnit 07 PricingKhan AshfaqueNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Marketing ManagementDocument18 pagesUnit 3 Marketing ManagementvasantharaoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Definition of PricingDocument15 pagesUnit - 4 Definition of PricingmussaiyibNo ratings yet
- Economics NotesDocument11 pagesEconomics NotesRuthveek FadteNo ratings yet
- Pricing: Pricing Pricing Objectives or Goals Give Direction To The WholeDocument4 pagesPricing: Pricing Pricing Objectives or Goals Give Direction To The WholeClaudette ClementeNo ratings yet
- Price PlanningDocument42 pagesPrice Planningaqsakhan78681No ratings yet
- Major Pricing StrategyDocument3 pagesMajor Pricing Strategy35Phạm Ngọc ThyNo ratings yet
- The Second P: PRICEDocument22 pagesThe Second P: PRICEJudy Ann PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Pricing MethodsDocument12 pagesPricing MethodsAtharva DumbreNo ratings yet
- Marketing MangementDocument26 pagesMarketing MangementPopuri Nagasai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Pricing Objectives and Price DeterminationDocument7 pagesChapter 3 - Pricing Objectives and Price DeterminationChierhy Jane BayudanNo ratings yet
- Theme 9 Price and PricingDocument10 pagesTheme 9 Price and PricingMuzaffar SaleemNo ratings yet
- PriceDocument37 pagesPriceSahana S MendonNo ratings yet
- Group 3: A. Demonstrate The Different Concepts B. Collect The Appropriate Pricing StrategiesDocument12 pagesGroup 3: A. Demonstrate The Different Concepts B. Collect The Appropriate Pricing StrategiesErica May BurgosNo ratings yet
- Designing Pricing StrategiesDocument17 pagesDesigning Pricing Strategiesrahulravi4uNo ratings yet
- Pricing DecisionsDocument44 pagesPricing DecisionsTejaswiniNo ratings yet
- The Marketing Mix PriceDocument3 pagesThe Marketing Mix PriceraheemeeaaishaNo ratings yet
- Different Pricing Strategies in Marketing Adopted by CompaniesDocument2 pagesDifferent Pricing Strategies in Marketing Adopted by CompaniesHKHNo ratings yet
- Different Pricing Strategies in Marketing Adopted by CompaniesDocument2 pagesDifferent Pricing Strategies in Marketing Adopted by CompaniesHKHNo ratings yet
- Pricing in MarketingDocument4 pagesPricing in Marketingdaniela carvajal guarinNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document12 pagesUnit 4shivumasaraddi0No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PriceDocument25 pagesChapter 5 PriceNur Atikah GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Unit 8-Revenue Analysis and Pricing PoliciesDocument17 pagesUnit 8-Revenue Analysis and Pricing PoliciesGayl Ignacio TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument21 pagesUnit IiiAnuradha MauryaNo ratings yet
- Pricing PolicyDocument1 pagePricing PolicyHend HelmyNo ratings yet
- MM Module 4Document8 pagesMM Module 4Sonal GowdaNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Price PDFDocument8 pagesTopic 10 Price PDFIntan SyuhadaNo ratings yet
- Price Analysis: Submitted To: Mrs. Arlene Gabriel Submitted By: Kailyn Cris B. RuaboroDocument4 pagesPrice Analysis: Submitted To: Mrs. Arlene Gabriel Submitted By: Kailyn Cris B. RuaboroJerico ManaloNo ratings yet
- Marketing 1Document6 pagesMarketing 1VIDHI KAMATH 2122084No ratings yet
- Group 6Document41 pagesGroup 6Ej RubioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. PricingDocument26 pagesChapter 6. PricingTadele BekeleNo ratings yet
- Value-based Intelligent Pricing: Marketing and Business, #1From EverandValue-based Intelligent Pricing: Marketing and Business, #1No ratings yet
- The WogDocument21 pagesThe WogSaud Alnooh0% (3)
- Security Part 1 Auditing OS & NDocument59 pagesSecurity Part 1 Auditing OS & NSaud AlnoohNo ratings yet
- Bernie Madoff CaseDocument15 pagesBernie Madoff CaseSaud AlnoohNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 12 - Marketing CommunicationDocument30 pagesCHAPTER 12 - Marketing CommunicationSaud AlnoohNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 12 - Marketing CommunicationDocument30 pagesCHAPTER 12 - Marketing CommunicationSaud AlnoohNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 - Integrated Marketing CommunicationsDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 10 - Integrated Marketing CommunicationsSaud AlnoohNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 - The New Product Development ProcessDocument16 pagesCHAPTER 5 - The New Product Development ProcessSaud Alnooh100% (2)
- CHAPTER 2 - Marketing Environmwnt & SWOT AnalysisDocument24 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Marketing Environmwnt & SWOT AnalysisSaud AlnoohNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - An Overview of MarketingDocument49 pagesCHAPTER 1 - An Overview of MarketingSaud AlnoohNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit Analysis (Bridal Shoppe Sells Wedding Dresses)Document7 pagesCost Volume Profit Analysis (Bridal Shoppe Sells Wedding Dresses)Asma HatamNo ratings yet
- Mas 10 Exercises For UploadDocument5 pagesMas 10 Exercises For UploadChristine Joy Duterte RemorozaNo ratings yet
- Senior Auditor Cost-Accounting-McqsDocument101 pagesSenior Auditor Cost-Accounting-McqsMuhammad HamidNo ratings yet
- Topics: Break-Even Analysis, Operating and Financial Leverage, and Optimal Capital StructureDocument5 pagesTopics: Break-Even Analysis, Operating and Financial Leverage, and Optimal Capital StructuremagoimoiNo ratings yet
- CVPDocument20 pagesCVPDen Potxsz100% (1)
- Model Exit Exam of Cost & Managerial CostDocument10 pagesModel Exit Exam of Cost & Managerial Costnewaybeyene5No ratings yet
- Strategic Cost Management QuizDocument9 pagesStrategic Cost Management Quizctarenas.studentNo ratings yet
- 2011 AICPA Business QuestionsDocument45 pages2011 AICPA Business Questionsjklein2588100% (1)
- Relevant Costing Short Term Non Routine DecisionsDocument10 pagesRelevant Costing Short Term Non Routine DecisionsMitch fabayNo ratings yet
- Cost Analysis, Concepts & ClassificationsDocument43 pagesCost Analysis, Concepts & Classificationsmarget85% (13)
- BTEC HND Management Accounting Assignment 1Document18 pagesBTEC HND Management Accounting Assignment 1Suranga SamaranayakeNo ratings yet
- Solving A CVP ProblemDocument11 pagesSolving A CVP ProblemMahruf OpuNo ratings yet
- Standard Cost and Variance AnalysisDocument22 pagesStandard Cost and Variance AnalysisAbbas Jan Bangash100% (1)
- COPA Configuration and Painter GuideDocument217 pagesCOPA Configuration and Painter Guideresky surbakti0% (1)
- Class Question CVPDocument2 pagesClass Question CVPTanuj LalchandaniNo ratings yet
- Profits and MarginsDocument4 pagesProfits and Marginsrishifiib08No ratings yet
- Fixed Cost: Marginal CostingDocument6 pagesFixed Cost: Marginal CostingJebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Homework Chapter 5 EX 5-18Document9 pagesHomework Chapter 5 EX 5-18K59 Lai Hoang SonNo ratings yet
- CVP Finance AssignmentDocument12 pagesCVP Finance AssignmentVivek VashisthaNo ratings yet
- MA CHAPTER 4 Marginal Costing 1Document79 pagesMA CHAPTER 4 Marginal Costing 1Mohd Zubair KhanNo ratings yet
- SAP Profitability AnalysisDocument49 pagesSAP Profitability Analysisrohitmandhania95% (22)
- Relevant Costing by A BobadillaDocument99 pagesRelevant Costing by A BobadillaShailene DavidNo ratings yet
- Acctg Le3 BocotaDocument3 pagesAcctg Le3 BocotaAngela KlaraNo ratings yet
- Operating and Financial LeverageDocument43 pagesOperating and Financial LeverageMARIBEL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- ACT-project-og-123456 (Money Bag)Document17 pagesACT-project-og-123456 (Money Bag)Zidan ZaifNo ratings yet
- Actg 10 - MAS Midterm ExamDocument24 pagesActg 10 - MAS Midterm Examjoemel091190100% (1)