Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 3 Nutrition Revision A1 Poster
1 3 Nutrition Revision A1 Poster
Uploaded by
api-263322904Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sources of CarbohydratesDocument17 pagesSources of Carbohydratesjcee2008No ratings yet
- Bio Molecules PPT For P AP BiologyDocument34 pagesBio Molecules PPT For P AP BiologyDivineDoctorNo ratings yet
- Food Defense PlanDocument11 pagesFood Defense Planshyamalababu100% (3)
- The Chemicals of LifeDocument31 pagesThe Chemicals of Lifeapi-406307933No ratings yet
- The Chemicals of LifeDocument31 pagesThe Chemicals of Lifeapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Lectures by Tariq Alalwan, PH.D.: Biology, 12/e Mader & WindelspechtDocument74 pagesLectures by Tariq Alalwan, PH.D.: Biology, 12/e Mader & WindelspechtSulaiman Dawood Saif AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PresentationDocument174 pagesUnit 2 PresentationYASH WANKHEDENo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument42 pagesBiological MoleculesMerita DanushiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of The CellDocument11 pagesChapter 4: Chemical Composition of The CellAeda NurynnaNo ratings yet
- Molecules of LifeDocument55 pagesMolecules of LifeAnabelle Gonzales MontevirgenNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules (KH, Lemak, Protein) - Topik 3 FBS 1Document47 pagesBiomolecules (KH, Lemak, Protein) - Topik 3 FBS 1Teofilus Dani PNo ratings yet
- Valence Shell Electrons: Chemical Composition of Organisms Organic Carbon Is Chemically Combined With TheDocument7 pagesValence Shell Electrons: Chemical Composition of Organisms Organic Carbon Is Chemically Combined With TheSoung HuiNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & Physiology Chemical Basis of Life: Chapter 2 (Emphasis On Pages 47-58)Document68 pagesHuman Anatomy & Physiology Chemical Basis of Life: Chapter 2 (Emphasis On Pages 47-58)Jera'anah OwenNo ratings yet
- Cytolgy 2Document7 pagesCytolgy 2Mohammad RajabNo ratings yet
- 2 Cytology ChemistryDocument47 pages2 Cytology ChemistrySamNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Composition of Organisms: What Makes Compounds Inorganic or Organic?Document18 pagesThe Chemical Composition of Organisms: What Makes Compounds Inorganic or Organic?Mohd NizamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Molecules of LifeDocument8 pagesChapter 3: The Molecules of LifeCourtney FazioNo ratings yet
- Homework Biologia Gadiel GómezDocument4 pagesHomework Biologia Gadiel GómezGADIEL ADRIAN GOMEZ SALAZARNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument9 pagesBIOMOLECULESanujbhagat031No ratings yet
- 2.1 Molecules To Metabolism: Molecular Biology Is The Chemistry of Living OrganismsDocument25 pages2.1 Molecules To Metabolism: Molecular Biology Is The Chemistry of Living OrganismsAbdul HalimNo ratings yet
- Molecules of CellsDocument98 pagesMolecules of CellsKd123No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Biological MoleculesDocument28 pagesChapter 4 - Biological MoleculesshammmssNo ratings yet
- CAPE Biology UNIT 1carbohydrates - BiomoleculesDocument98 pagesCAPE Biology UNIT 1carbohydrates - BiomoleculesKemoy FrancisNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument13 pagesCarbohydratesyr44grf94kNo ratings yet
- CH 07 CellsDocument29 pagesCH 07 Cellsshikaku.88hokoriNo ratings yet
- Proteins and Amino AcidsDocument24 pagesProteins and Amino Acidsqwerty masterNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules: Self-Preparation Biology Assessment TestDocument36 pagesMacromolecules: Self-Preparation Biology Assessment Testmay ann dimaanoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Lipids: Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty AcidsDocument53 pagesCarbohydrate Lipids: Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty AcidsSyamila YusofNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument14 pagesBiology ReviewerForkensteinNo ratings yet
- General Biology All About BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology All About BiomoleculeskimberlyfritzzunigaNo ratings yet
- 04 Biological MoleculesDocument6 pages04 Biological MoleculeskaderovichNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Life: WaterDocument3 pagesChemistry of Life: WaterRiy KimNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Handout Week5-6Document19 pagesPhysical Science Handout Week5-6Jhay Lorraine Sadian PalacpacNo ratings yet
- 3 Essential Chemicals of Life PPTDocument82 pages3 Essential Chemicals of Life PPTBhoni KumariNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Proteins Water LipidsDocument94 pagesBiomolecules: Proteins Water LipidsRochelleCasador180No ratings yet
- Tabaco National High School Tabaco City: Giane Marie Buela 10-CharityDocument9 pagesTabaco National High School Tabaco City: Giane Marie Buela 10-CharityElla Mae Red BarbadilloNo ratings yet
- Bio 93 Midterm Review For The FinalDocument1 pageBio 93 Midterm Review For The Finalsarah_choi_21No ratings yet
- Zoology 1Document53 pagesZoology 1Nouran SamyNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesgershom03No ratings yet
- L 14 BiomoleculesDocument20 pagesL 14 Biomoleculesshahin appuNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules and Living ThingsDocument33 pagesMacromolecules and Living ThingsDana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Dicussion Forum: Carbohydrates ProteinsDocument3 pagesDicussion Forum: Carbohydrates ProteinsKim Angelo del CastilloNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Biological MoleculesDocument38 pagesModule 7 Biological MoleculesJoana CastilloNo ratings yet
- B1.1 Ib Biology NotesDocument12 pagesB1.1 Ib Biology NotesAashi AdsuleNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomolecules: CarbohydratesDocument20 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomolecules: CarbohydratesSOUMYODEEP NAYAKNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument4 pagesBio MoleculesShishir AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of CellsDocument79 pagesBiochemistry of CellsketakeeNo ratings yet
- Intro Macromolecule LectureDocument34 pagesIntro Macromolecule Lectureapi-300252239No ratings yet
- Lecture 4, 5: Chemical Reactions Acids, Bases & SaltsDocument13 pagesLecture 4, 5: Chemical Reactions Acids, Bases & Saltstenzin bhutiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates and Lipidshibadesi00No ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument5 pagesAtoms and MoleculesRelaisa CimafrancaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules (Hints)Document2 pagesBiomolecules (Hints)hchawla421No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document53 pagesChapter 4Corinne ChooNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 3 AoS1Document21 pagesBiology Unit 3 AoS1Kerry JiangNo ratings yet
- BIOMACROMOLECULESDocument25 pagesBIOMACROMOLECULESAina Mira PalouNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Chemistry 2020-1Document99 pagesCarbohydrate Chemistry 2020-1WixHal MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Biological MoleculesDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Biological Moleculessaim adeelNo ratings yet
- Lecture17 Carbohydrates Preview-KeywordsDocument5 pagesLecture17 Carbohydrates Preview-KeywordsthedecieverNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument27 pagesBio MoleculesAceres John HenryNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules GRADE 12Document26 pagesBiomolecules GRADE 12Jericho Anthiel de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Revision Book For Senior BiologyDocument85 pagesRevision Book For Senior Biologyapi-263322904No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Gas LawsDocument5 pagesChemistry Notes Gas Lawsapi-263322904100% (1)
- 28 02 14 The Exchange System in PlantsDocument53 pages28 02 14 The Exchange System in Plantsapi-263322904No ratings yet
- Leaving Cert EnglishDocument4 pagesLeaving Cert Englishapi-263322904No ratings yet
- 1 Male Structure and HormonesDocument39 pages1 Male Structure and Hormonesapi-263322904No ratings yet
- Abdikamalov Xodjabay Ismamutovich, Najimov Paraxat Ibrayimovich, Abstract. The Article Discusses The Importance and Necessity of PhysicalDocument7 pagesAbdikamalov Xodjabay Ismamutovich, Najimov Paraxat Ibrayimovich, Abstract. The Article Discusses The Importance and Necessity of PhysicalNurnazar PirnazarovNo ratings yet
- Railway Accounting: Indian Railway Accounts ServiceDocument5 pagesRailway Accounting: Indian Railway Accounts ServiceAbhijeet AsthanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Environmental Health 2012Document66 pagesIntroduction To Environmental Health 2012Mark Lopez100% (1)
- Escalator Switches AdjustmentDocument6 pagesEscalator Switches AdjustmentSANAL KUMAR SNo ratings yet
- CIMON IXT15 Datasheet 2023.06.06Document1 pageCIMON IXT15 Datasheet 2023.06.06habacuc8891No ratings yet
- CACR21 January 2015Document19 pagesCACR21 January 2015maikaNo ratings yet
- Ichi The KillerDocument7 pagesIchi The KillerShaul RechterNo ratings yet
- SOLON Black Blue 230 07 enDocument4 pagesSOLON Black Blue 230 07 enstulemanskiNo ratings yet
- DRRMH 4 Schematic Area Final Budget 2023-2025 As of Oct 17 2023Document4 pagesDRRMH 4 Schematic Area Final Budget 2023-2025 As of Oct 17 2023Roel AbricaNo ratings yet
- 48 Weeks To Total M-Powerment!Document18 pages48 Weeks To Total M-Powerment!sundevil2010usa4605No ratings yet
- NiBallast TM BWMS v-2021Document21 pagesNiBallast TM BWMS v-2021王杰No ratings yet
- Biography of John Mordecai Gottman 1Document4 pagesBiography of John Mordecai Gottman 1kalitkalitNo ratings yet
- HollywoodmusclesylvesterstalloneinspiredworkoutroutineDocument1 pageHollywoodmusclesylvesterstalloneinspiredworkoutroutinefernandocmbenedetteNo ratings yet
- A Cultural Herpetology of Nile Crocodiles in AfricaDocument18 pagesA Cultural Herpetology of Nile Crocodiles in Africabudi biozooNo ratings yet
- People vs. LikiranDocument3 pagesPeople vs. LikiranRoyce Ann PedemonteNo ratings yet
- ETP Plant AsignmentDocument11 pagesETP Plant AsignmentFzUsman100% (2)
- Electrical Resistivity and ConductivityDocument10 pagesElectrical Resistivity and ConductivityMsKarolyNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument14 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesJanna GunioNo ratings yet
- Eat Right For A Healthy Life (PE)Document15 pagesEat Right For A Healthy Life (PE)Yan100% (4)
- Managing People - AssignmentDocument10 pagesManaging People - AssignmentayeshaNo ratings yet
- Developmental DisordersDocument58 pagesDevelopmental DisordersEsraRamos67% (3)
- UD150L-40E Ope M501-E053GDocument164 pagesUD150L-40E Ope M501-E053GMahmoud Mady100% (3)
- CobasDocument145 pagesCobasAugia Nur IftihatunnisaNo ratings yet
- Desoldering Tool: Designed For Lead FreeDocument2 pagesDesoldering Tool: Designed For Lead FreeMarco Antonio Ortiz RomeroNo ratings yet
- RULE 1160 - BoilerDocument24 pagesRULE 1160 - Boilerteddy tavaresNo ratings yet
- LOROFF, Nicole - Gender and Sexuality in Nazi Germany PDFDocument13 pagesLOROFF, Nicole - Gender and Sexuality in Nazi Germany PDFClara LimaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument50 pagesCell Divisionbknishad100% (2)
- RS 232 Repeater KFD2-FF-Ex2.RS232: FunctionDocument4 pagesRS 232 Repeater KFD2-FF-Ex2.RS232: FunctionEder AlexandreNo ratings yet
- Upda-Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument39 pagesUpda-Multiple Choice QuestionsAnonymous GllSJsUNo ratings yet
1 3 Nutrition Revision A1 Poster
1 3 Nutrition Revision A1 Poster
Uploaded by
api-263322904Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 3 Nutrition Revision A1 Poster
1 3 Nutrition Revision A1 Poster
Uploaded by
api-263322904Copyright:
Available Formats
N U T R I T I O N
ELEMENTS IN FOOD:
Bimolecular units: The elements in
food combine in different ratios to form
different food components
Common Elements: Carbon (C) ,
Hydrogen (H) ,Oxygen (O), Nitrogen
(N), Phosphorus (P), Sulphur (S)
Salts of: Sodium (Na), Magnesium
(Mg), Chlorine (Cl), Potassium (K),
Calcium (Ca)
Trace elements : Iron (Fe), Copper
(Cu), Zinc (Zn)
FATS
Contain elements: C, O, H.
Different ratio to carbohydrates have
more oxygen
Fats are solid at room temperature
Oils are liquid at room temperature
Structural role: protect the body
organs
Metabolic role Source of energy for
metabolism
Triglycerides: made up of three Fatty
acids and one Glycerol
Phospholipids formed when one
fatty acid of a lipid molecule is
replaced by a phosphate group
PROTEINS
Contain elements: C, O, H, N
They sometimes contain P, S
They are made up of amino acids
Structural role: they join with
phospholipids to form the cell
membrane
Metabolic role: all enzymes are
proteins and they control the cells
chemical reactions
ENERGY TRANSFER
REACTION
Anabolic reactions: Small
molecules are built up into large
ones, using energy e.g.
photosynthesis
Catabolic reactions: large
molecules are broken down into
smaller ones, energy is released
e.g. respiration
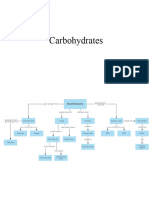
CARBOHYDRATES
Contain elements: C, O, H.
General formula: C
x
(H
2
O)
y
Structural role: cellulose forms part of
the cell wall
Metabolic role Source of energy for
metabolism
Types of Carbohydrate
Monosaccharides e.g. glucose
Disaccharides e.g. sucrose
Polysaccharides e.g. cellulose
WATER
Properties of water:
Gives cells their shape
Transports materials
A universal solvent
A medium for metabolism
Vitamin Type Source Function Deficiency
C
Water
soluble
Lemons
Connective tissue
formation
Scurvy
D
Fat
soluble
Cod-liver oil Absorb calcium Rickets
MINERALS
Plants need Magnesium to make
chlorophyll and calcium for the cell
walls
Animals need iron to make
haemoglobin and calcium for
healthy bones.
VITAMINS
The Function of Food: Growth, Repair, Energy
N U T R I T I O N
N U T R I T I O N
ELEMENTS IN FOOD:
Bimolecular units: The elements in
food combine in different ratios to form
different food components
Common Elements: Carbon (C) ,
Hydrogen (H) ,Oxygen (O), Nitrogen
(N), Phosphorus (P), Sulphur (S)
Salts of: Sodium (Na), Magnesium
(Mg), Chlorine (Cl), Potassium (K),
Calcium (Ca)
Trace elements : Iron (Fe), Copper
(Cu), Zinc (Zn)
FATS
Contain elements: C, O, H.
Different ratio to carbohydrates have
more oxygen
Fats are solid at room temperature
Oils are liquid at room temperature
Structural role: protect the body
organs
Metabolic role Source of energy for
metabolism
Triglycerides: made up of three Fatty
acids and one Glycerol
Phospholipids formed when one
fatty acid of a lipid molecule is
replaced by a phosphate group
PROTEINS
Contain elements: C, O, H, N
They sometimes contain P, S
They are made up of amino acids
Structural role: they join with
phospholipids to form the cell
membrane
Metabolic role: all enzymes are
proteins and they control the cells
chemical reactions
ENERGY TRANSFER
REACTION
Anabolic reactions: Small
molecules are built up into large
ones, using energy e.g.
photosynthesis
Catabolic reactions: large
molecules are broken down into
smaller ones, energy is released
e.g. respiration
CARBOHYDRATES
Contain elements: C, O, H.
General formula: C
x
(H
2
O)
y
Structural role: cellulose forms part of
the cell wall
Metabolic role Source of energy for
metabolism
Types of Carbohydrate
Monosaccharides e.g. glucose
Disaccharides e.g. sucrose
Polysaccharides e.g. cellulose
WATER
Properties of water:
Gives cells their shape
Transports materials
A universal solvent
A medium for metabolism
Vitamin Type Source Function Deficiency
C
Water
soluble
Lemons
Connective tissue
formation
Scurvy
D
Fat
soluble
Cod-liver oil Absorb calcium Rickets
MINERALS
Plants need Magnesium to make
chlorophyll and calcium for the cell
walls
Animals need iron to make
haemoglobin and calcium for
healthy bones.
VITAMINS
The Function of Food: Growth, Repair, Energy
N U T R I T I O N
You might also like
- Sources of CarbohydratesDocument17 pagesSources of Carbohydratesjcee2008No ratings yet
- Bio Molecules PPT For P AP BiologyDocument34 pagesBio Molecules PPT For P AP BiologyDivineDoctorNo ratings yet
- Food Defense PlanDocument11 pagesFood Defense Planshyamalababu100% (3)
- The Chemicals of LifeDocument31 pagesThe Chemicals of Lifeapi-406307933No ratings yet
- The Chemicals of LifeDocument31 pagesThe Chemicals of Lifeapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Lectures by Tariq Alalwan, PH.D.: Biology, 12/e Mader & WindelspechtDocument74 pagesLectures by Tariq Alalwan, PH.D.: Biology, 12/e Mader & WindelspechtSulaiman Dawood Saif AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PresentationDocument174 pagesUnit 2 PresentationYASH WANKHEDENo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument42 pagesBiological MoleculesMerita DanushiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of The CellDocument11 pagesChapter 4: Chemical Composition of The CellAeda NurynnaNo ratings yet
- Molecules of LifeDocument55 pagesMolecules of LifeAnabelle Gonzales MontevirgenNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules (KH, Lemak, Protein) - Topik 3 FBS 1Document47 pagesBiomolecules (KH, Lemak, Protein) - Topik 3 FBS 1Teofilus Dani PNo ratings yet
- Valence Shell Electrons: Chemical Composition of Organisms Organic Carbon Is Chemically Combined With TheDocument7 pagesValence Shell Electrons: Chemical Composition of Organisms Organic Carbon Is Chemically Combined With TheSoung HuiNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & Physiology Chemical Basis of Life: Chapter 2 (Emphasis On Pages 47-58)Document68 pagesHuman Anatomy & Physiology Chemical Basis of Life: Chapter 2 (Emphasis On Pages 47-58)Jera'anah OwenNo ratings yet
- Cytolgy 2Document7 pagesCytolgy 2Mohammad RajabNo ratings yet
- 2 Cytology ChemistryDocument47 pages2 Cytology ChemistrySamNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Composition of Organisms: What Makes Compounds Inorganic or Organic?Document18 pagesThe Chemical Composition of Organisms: What Makes Compounds Inorganic or Organic?Mohd NizamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Molecules of LifeDocument8 pagesChapter 3: The Molecules of LifeCourtney FazioNo ratings yet
- Homework Biologia Gadiel GómezDocument4 pagesHomework Biologia Gadiel GómezGADIEL ADRIAN GOMEZ SALAZARNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument9 pagesBIOMOLECULESanujbhagat031No ratings yet
- 2.1 Molecules To Metabolism: Molecular Biology Is The Chemistry of Living OrganismsDocument25 pages2.1 Molecules To Metabolism: Molecular Biology Is The Chemistry of Living OrganismsAbdul HalimNo ratings yet
- Molecules of CellsDocument98 pagesMolecules of CellsKd123No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Biological MoleculesDocument28 pagesChapter 4 - Biological MoleculesshammmssNo ratings yet
- CAPE Biology UNIT 1carbohydrates - BiomoleculesDocument98 pagesCAPE Biology UNIT 1carbohydrates - BiomoleculesKemoy FrancisNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument13 pagesCarbohydratesyr44grf94kNo ratings yet
- CH 07 CellsDocument29 pagesCH 07 Cellsshikaku.88hokoriNo ratings yet
- Proteins and Amino AcidsDocument24 pagesProteins and Amino Acidsqwerty masterNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules: Self-Preparation Biology Assessment TestDocument36 pagesMacromolecules: Self-Preparation Biology Assessment Testmay ann dimaanoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Lipids: Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty AcidsDocument53 pagesCarbohydrate Lipids: Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty AcidsSyamila YusofNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument14 pagesBiology ReviewerForkensteinNo ratings yet
- General Biology All About BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology All About BiomoleculeskimberlyfritzzunigaNo ratings yet
- 04 Biological MoleculesDocument6 pages04 Biological MoleculeskaderovichNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Life: WaterDocument3 pagesChemistry of Life: WaterRiy KimNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Handout Week5-6Document19 pagesPhysical Science Handout Week5-6Jhay Lorraine Sadian PalacpacNo ratings yet
- 3 Essential Chemicals of Life PPTDocument82 pages3 Essential Chemicals of Life PPTBhoni KumariNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Proteins Water LipidsDocument94 pagesBiomolecules: Proteins Water LipidsRochelleCasador180No ratings yet
- Tabaco National High School Tabaco City: Giane Marie Buela 10-CharityDocument9 pagesTabaco National High School Tabaco City: Giane Marie Buela 10-CharityElla Mae Red BarbadilloNo ratings yet
- Bio 93 Midterm Review For The FinalDocument1 pageBio 93 Midterm Review For The Finalsarah_choi_21No ratings yet
- Zoology 1Document53 pagesZoology 1Nouran SamyNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesgershom03No ratings yet
- L 14 BiomoleculesDocument20 pagesL 14 Biomoleculesshahin appuNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules and Living ThingsDocument33 pagesMacromolecules and Living ThingsDana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Dicussion Forum: Carbohydrates ProteinsDocument3 pagesDicussion Forum: Carbohydrates ProteinsKim Angelo del CastilloNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Biological MoleculesDocument38 pagesModule 7 Biological MoleculesJoana CastilloNo ratings yet
- B1.1 Ib Biology NotesDocument12 pagesB1.1 Ib Biology NotesAashi AdsuleNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomolecules: CarbohydratesDocument20 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomolecules: CarbohydratesSOUMYODEEP NAYAKNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument4 pagesBio MoleculesShishir AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of CellsDocument79 pagesBiochemistry of CellsketakeeNo ratings yet
- Intro Macromolecule LectureDocument34 pagesIntro Macromolecule Lectureapi-300252239No ratings yet
- Lecture 4, 5: Chemical Reactions Acids, Bases & SaltsDocument13 pagesLecture 4, 5: Chemical Reactions Acids, Bases & Saltstenzin bhutiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates and Lipidshibadesi00No ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument5 pagesAtoms and MoleculesRelaisa CimafrancaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules (Hints)Document2 pagesBiomolecules (Hints)hchawla421No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document53 pagesChapter 4Corinne ChooNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 3 AoS1Document21 pagesBiology Unit 3 AoS1Kerry JiangNo ratings yet
- BIOMACROMOLECULESDocument25 pagesBIOMACROMOLECULESAina Mira PalouNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Chemistry 2020-1Document99 pagesCarbohydrate Chemistry 2020-1WixHal MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Biological MoleculesDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Biological Moleculessaim adeelNo ratings yet
- Lecture17 Carbohydrates Preview-KeywordsDocument5 pagesLecture17 Carbohydrates Preview-KeywordsthedecieverNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument27 pagesBio MoleculesAceres John HenryNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules GRADE 12Document26 pagesBiomolecules GRADE 12Jericho Anthiel de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Revision Book For Senior BiologyDocument85 pagesRevision Book For Senior Biologyapi-263322904No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Gas LawsDocument5 pagesChemistry Notes Gas Lawsapi-263322904100% (1)
- 28 02 14 The Exchange System in PlantsDocument53 pages28 02 14 The Exchange System in Plantsapi-263322904No ratings yet
- Leaving Cert EnglishDocument4 pagesLeaving Cert Englishapi-263322904No ratings yet
- 1 Male Structure and HormonesDocument39 pages1 Male Structure and Hormonesapi-263322904No ratings yet
- Abdikamalov Xodjabay Ismamutovich, Najimov Paraxat Ibrayimovich, Abstract. The Article Discusses The Importance and Necessity of PhysicalDocument7 pagesAbdikamalov Xodjabay Ismamutovich, Najimov Paraxat Ibrayimovich, Abstract. The Article Discusses The Importance and Necessity of PhysicalNurnazar PirnazarovNo ratings yet
- Railway Accounting: Indian Railway Accounts ServiceDocument5 pagesRailway Accounting: Indian Railway Accounts ServiceAbhijeet AsthanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Environmental Health 2012Document66 pagesIntroduction To Environmental Health 2012Mark Lopez100% (1)
- Escalator Switches AdjustmentDocument6 pagesEscalator Switches AdjustmentSANAL KUMAR SNo ratings yet
- CIMON IXT15 Datasheet 2023.06.06Document1 pageCIMON IXT15 Datasheet 2023.06.06habacuc8891No ratings yet
- CACR21 January 2015Document19 pagesCACR21 January 2015maikaNo ratings yet
- Ichi The KillerDocument7 pagesIchi The KillerShaul RechterNo ratings yet
- SOLON Black Blue 230 07 enDocument4 pagesSOLON Black Blue 230 07 enstulemanskiNo ratings yet
- DRRMH 4 Schematic Area Final Budget 2023-2025 As of Oct 17 2023Document4 pagesDRRMH 4 Schematic Area Final Budget 2023-2025 As of Oct 17 2023Roel AbricaNo ratings yet
- 48 Weeks To Total M-Powerment!Document18 pages48 Weeks To Total M-Powerment!sundevil2010usa4605No ratings yet
- NiBallast TM BWMS v-2021Document21 pagesNiBallast TM BWMS v-2021王杰No ratings yet
- Biography of John Mordecai Gottman 1Document4 pagesBiography of John Mordecai Gottman 1kalitkalitNo ratings yet
- HollywoodmusclesylvesterstalloneinspiredworkoutroutineDocument1 pageHollywoodmusclesylvesterstalloneinspiredworkoutroutinefernandocmbenedetteNo ratings yet
- A Cultural Herpetology of Nile Crocodiles in AfricaDocument18 pagesA Cultural Herpetology of Nile Crocodiles in Africabudi biozooNo ratings yet
- People vs. LikiranDocument3 pagesPeople vs. LikiranRoyce Ann PedemonteNo ratings yet
- ETP Plant AsignmentDocument11 pagesETP Plant AsignmentFzUsman100% (2)
- Electrical Resistivity and ConductivityDocument10 pagesElectrical Resistivity and ConductivityMsKarolyNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument14 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesJanna GunioNo ratings yet
- Eat Right For A Healthy Life (PE)Document15 pagesEat Right For A Healthy Life (PE)Yan100% (4)
- Managing People - AssignmentDocument10 pagesManaging People - AssignmentayeshaNo ratings yet
- Developmental DisordersDocument58 pagesDevelopmental DisordersEsraRamos67% (3)
- UD150L-40E Ope M501-E053GDocument164 pagesUD150L-40E Ope M501-E053GMahmoud Mady100% (3)
- CobasDocument145 pagesCobasAugia Nur IftihatunnisaNo ratings yet
- Desoldering Tool: Designed For Lead FreeDocument2 pagesDesoldering Tool: Designed For Lead FreeMarco Antonio Ortiz RomeroNo ratings yet
- RULE 1160 - BoilerDocument24 pagesRULE 1160 - Boilerteddy tavaresNo ratings yet
- LOROFF, Nicole - Gender and Sexuality in Nazi Germany PDFDocument13 pagesLOROFF, Nicole - Gender and Sexuality in Nazi Germany PDFClara LimaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument50 pagesCell Divisionbknishad100% (2)
- RS 232 Repeater KFD2-FF-Ex2.RS232: FunctionDocument4 pagesRS 232 Repeater KFD2-FF-Ex2.RS232: FunctionEder AlexandreNo ratings yet
- Upda-Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument39 pagesUpda-Multiple Choice QuestionsAnonymous GllSJsUNo ratings yet