Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RS - Calculating Damages CHECKLIST2
RS - Calculating Damages CHECKLIST2
Uploaded by
superxl20090 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views1 pageThis document provides a checklist for calculating damages from a breach of contract. It addresses whether the contract has a damages clause, how to calculate the benefit of the bargain if not, whether the elements of calculation are foreseeable, and whether any elements could have been avoided. It also discusses alternative remedies to consider such as reliance interest, restitution interest, and specific performance.
Original Description:
Outline
Original Title
RS_Calculating Damages CHECKLIST2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a checklist for calculating damages from a breach of contract. It addresses whether the contract has a damages clause, how to calculate the benefit of the bargain if not, whether the elements of calculation are foreseeable, and whether any elements could have been avoided. It also discusses alternative remedies to consider such as reliance interest, restitution interest, and specific performance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views1 pageRS - Calculating Damages CHECKLIST2
RS - Calculating Damages CHECKLIST2
Uploaded by
superxl2009This document provides a checklist for calculating damages from a breach of contract. It addresses whether the contract has a damages clause, how to calculate the benefit of the bargain if not, whether the elements of calculation are foreseeable, and whether any elements could have been avoided. It also discusses alternative remedies to consider such as reliance interest, restitution interest, and specific performance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
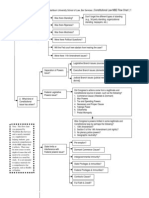
CHECKLIST: CALCULATING DAMAGES
DOES THE CONTRACT HAVE A DAMAGES CLAUSE?
The parties may specify the amount of damages due upon breach of contract in a damages clause
of the contract. Although U.C.C. Section 2-719 permits liquidated damages that approximate loss,
courts will not enforce punitive damage clauses.
F NOT, HOW DO YOU CALCULATE THE BENEFIT OF THE BARGAIN?
Generally, the court attempts to put the promisee in the position he would have been in had the
promise been performed. The plaintif's beneft of the bargain includes both the decline in his
position caused by breach and the gains he expected to make on the deal.
ARE THE ELEMENTS OF THE CALCULUS FORESEEABLE?
To import certainty and stability to the contract regime, contract law excludes speculative
and unforeseeable movements of plaintif's economic position from the calculation of damages.
Plaintifs cannot recover speculative profts nor unusual damages; defendants cannot reduce the
damage award by speculating on the benefts conferred to plaintif through breach.
WERE ANY ELEMENTS OF THE CALCULUS AVOIDABLE?
To keep economic waste to a minimum, contract law does not award compensation for a particular
element of damages that plaintif could have avoided without undue risk, expenses or humiliation.
Where plaintif retains exclusive control of the goods or services under contract, he may not
increase recovery through unreasonable failure to avoid harm.
CONSIDER: RELIANCE INTEREST AS ALTERNATIVE
A plaintif who incurs costs in the pursuit of speculative proft may seek remedy for the reliance
interest disappointed at breach. Courts awarding reasonable damages made in reliance on
defendant's promise in order to put the plaintif in as good a position as never making the
agreement in the frst place.
CONSIDER: RESTITUTION INTEREST AS ALTERNATIVE
In some cases the breaching party may be entitled to the defendant's money to remedy unjust
enrichment. One measure of this restitution interest is the market value of beneft conferred to
defendant by the plaintif's partial performance of the contract. These plaintif do not sue on the
contract but rather by the doctrine of quantum meruit ("as much as he deserves.")
CONSIDER: SPECIFIC PERFORMANCE INSTEAD
When money is not enough to equitably remedy plaintif's disappointed expectations, the non-
breaching plaintif may demand that defendant perform as specifed in the contract or that the
court impose an injunction against defendant behavior destructive to plaintif.
You might also like
- ConLaw FlowChartDocument2 pagesConLaw FlowChartAisha Lesley81% (16)
- Evidence FlowchartDocument2 pagesEvidence Flowchartsuperxl200990% (10)
- Kucc FlowchartDocument1 pageKucc Flowchartsuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Lec 7Document20 pagesLec 7babitasaini6402No ratings yet
- Remedies For The Breach of ContractDocument8 pagesRemedies For The Breach of ContractakhilgambhirNo ratings yet
- Scrutiny Categorization ChartDocument1 pageScrutiny Categorization Chartsuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Answers To Case1Document3 pagesAnswers To Case1Dinesh Raghavendra100% (2)
- Notes - DamagesDocument7 pagesNotes - DamagesRichard CoatesNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Breach of Contract Damages 1 PDFDocument24 pagesUnit Iii Breach of Contract Damages 1 PDFAzriSafarNo ratings yet
- Follow The Settlements Andfollow The FortunesDocument9 pagesFollow The Settlements Andfollow The FortunesDean Rodriguez100% (1)
- 5 PDFDocument1 page5 PDFDan ManNo ratings yet
- Remedies of Breach of Contract: Chapter - 07Document10 pagesRemedies of Breach of Contract: Chapter - 07Okasha AliNo ratings yet
- Defences Used in Breach of ContractDocument5 pagesDefences Used in Breach of ContractNeha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Consequences of Breach of ContractDocument4 pagesConsequences of Breach of Contract201360190No ratings yet
- 2019 SC-A 85 Translated SummaryDocument3 pages2019 SC-A 85 Translated SummaryD'avocats ChambersNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document8 pagesModule 9Shruti SumanNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document7 pagesModule 9Shaman KingNo ratings yet
- Lecture2022 Lecture13 - On Remedies - DamagesDocument16 pagesLecture2022 Lecture13 - On Remedies - DamagesJacksonVanHerdenAlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Remedies For Breach of ContractDocument17 pagesRemedies For Breach of ContractAreeb AsifNo ratings yet
- Debt and Damages: (2201) Reason For Distinguishing Debt and Damages. The Action To Recover A Debt Due ForDocument3 pagesDebt and Damages: (2201) Reason For Distinguishing Debt and Damages. The Action To Recover A Debt Due ForAndika PramatamaNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 130421 - American Home Assurance Co. v. ChuaDocument10 pagesG.R. No. 130421 - American Home Assurance Co. v. ChuaApay GrajoNo ratings yet
- Contract Disputes Practical Guide Series Guide 9Document20 pagesContract Disputes Practical Guide Series Guide 9harrisonsimbamaNo ratings yet
- Liquidated DamageDocument16 pagesLiquidated DamageJason RodriguezNo ratings yet
- InsuranceDocument5 pagesInsuranceabhithanotesNo ratings yet
- Indemnity ContractsDocument5 pagesIndemnity Contractsjitmanyu satpatiNo ratings yet
- Breachof ContractDocument6 pagesBreachof ContractShubham KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17Document5 pagesLecture 17adeelkhan17.akNo ratings yet
- RemediesDocument5 pagesRemediesAria XoNo ratings yet
- International Newsletter-Liquidated Damages in Middle EastDocument4 pagesInternational Newsletter-Liquidated Damages in Middle EastRanjith PriyanagaNo ratings yet
- Remedies For Breach of ContractDocument4 pagesRemedies For Breach of ContractRameen AyubNo ratings yet
- Breach of Contract RemediesDocument6 pagesBreach of Contract RemediesAbdul Salam khuhro100% (3)
- Unit 4 Contracts 1Document10 pagesUnit 4 Contracts 1poovizhikalyani.m2603No ratings yet
- CFAS. Pages 6Document3 pagesCFAS. Pages 6Julienne CaitNo ratings yet
- Remedies For Breach of ContractDocument6 pagesRemedies For Breach of Contract'Sånjîdå KåBîr'No ratings yet
- American Home Assurance Company, Petitioner, vs. Antonio CHUA, RespondentDocument20 pagesAmerican Home Assurance Company, Petitioner, vs. Antonio CHUA, RespondentMaan ManagaytayNo ratings yet
- The Law of Damages Under Indian Contract ActDocument5 pagesThe Law of Damages Under Indian Contract Actvaibhav singh boraNo ratings yet
- BEDA - CaseZ-Doctrines-InsuranceDocument5 pagesBEDA - CaseZ-Doctrines-InsuranceMalcolm CruzNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Financial GuaranteesDocument4 pagesAccounting For Financial GuaranteesABC 123No ratings yet
- Title 10 Variable ContractsDocument3 pagesTitle 10 Variable ContractsAlvin PateresNo ratings yet
- Loss of ProfitsDocument2 pagesLoss of Profitsjuan dsouzaNo ratings yet
- Ammy Contract 2020Document3 pagesAmmy Contract 2020Mkushi FedarhNo ratings yet
- DPC Module-2 (Can See)Document20 pagesDPC Module-2 (Can See)xakij19914No ratings yet
- Module-8,-Law of Contract-I - II SemDocument9 pagesModule-8,-Law of Contract-I - II SemRAJARAJESHWARI M GNo ratings yet
- Dil Warranties and ContractDocument33 pagesDil Warranties and ContractDilbahadur YadavNo ratings yet
- Notes Ica and SogaDocument38 pagesNotes Ica and SogahaloXDNo ratings yet
- Breach of ContractDocument6 pagesBreach of Contractbharti35No ratings yet
- The Propriety of Claiming Damages in Administrative Proceedings in The HLURBDocument12 pagesThe Propriety of Claiming Damages in Administrative Proceedings in The HLURBEnrique Paolo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Contract of Sale of GoodsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Contract of Sale of GoodsKristina Cassandra CababatNo ratings yet
- Professional Practice AssignmentDocument7 pagesProfessional Practice Assignmenttejaswini C gaur100% (1)
- Types of Damages Sec 73 To 75Document6 pagesTypes of Damages Sec 73 To 75rahuldoshi53No ratings yet
- Grno July: July Philippine Supreme Court Decisions On Commercial LawDocument2 pagesGrno July: July Philippine Supreme Court Decisions On Commercial LawMisc EllaneousNo ratings yet
- Contracts RemediesDocument18 pagesContracts RemediesТетяна КульгаNo ratings yet
- BreachDocument18 pagesBreachVijaya BanuNo ratings yet
- 4.01. Kinds or Components of Actual DamagesDocument6 pages4.01. Kinds or Components of Actual DamagesDeeej cartalNo ratings yet
- FRIADocument3 pagesFRIAErikha AranetaNo ratings yet
- Damages Under Contract ActDocument27 pagesDamages Under Contract ActSHRUTINo ratings yet
- Liquidated DamagesDocument25 pagesLiquidated Damagesvirfann01No ratings yet
- Remedies Available For Breach of ContractDocument6 pagesRemedies Available For Breach of Contractsyed_arshed15No ratings yet
- Understanding Named, Automatic and Additional Insureds in the CGL PolicyFrom EverandUnderstanding Named, Automatic and Additional Insureds in the CGL PolicyNo ratings yet
- Structured Settlements: A Guide For Prospective SellersFrom EverandStructured Settlements: A Guide For Prospective SellersNo ratings yet
- Life, Accident and Health Insurance in the United StatesFrom EverandLife, Accident and Health Insurance in the United StatesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 9, Insurance Requirements for the Urgent Care CenterFrom EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 9, Insurance Requirements for the Urgent Care CenterNo ratings yet
- The Complete Defense: of Risk, Risk RiskDocument1 pageThe Complete Defense: of Risk, Risk Risksuperxl2009No ratings yet
- MBE Handscore FormDocument1 pageMBE Handscore Formsuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Post Nuptial and Prenuptual Agreement EnforceabilityDocument1 pagePost Nuptial and Prenuptual Agreement Enforceabilitysuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Homicide Approach For The Bar ExamDocument1 pageHomicide Approach For The Bar Examsuperxl2009100% (1)
- Professional ResponsibilityDocument1 pageProfessional Responsibilitysuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Civil Pro ChecklistDocument1 pageCivil Pro Checklistsuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Prop I Attack Outline Ehrlich 2014Document6 pagesProp I Attack Outline Ehrlich 2014superxl2009No ratings yet
- Contracts Where Courts Are Divided: ConsiderationDocument1 pageContracts Where Courts Are Divided: Considerationsuperxl2009No ratings yet
- DOS SLTort ChartDocument1 pageDOS SLTort Chartsuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Cases and Materials On Employment DiscriminationDocument1 pageCases and Materials On Employment Discriminationsuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Pa Contracts BarDocument1 pagePa Contracts Barsuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Week 5-Family Law CohabitationDocument1 pageWeek 5-Family Law Cohabitationsuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Law Outline For Chapter 5 TermsDocument2 pagesLaw Outline For Chapter 5 Termssuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Week 9 - Family Law The Family, Children, Parentage, and GrandparentsDocument2 pagesWeek 9 - Family Law The Family, Children, Parentage, and Grandparentssuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Model Penal Code (1) : Citizen Would Observe. Citizen Would Observe. Citizen Would ObserveDocument1 pageModel Penal Code (1) : Citizen Would Observe. Citizen Would Observe. Citizen Would Observesuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Parentage Finding Form-PS4 - 0350Document5 pagesParentage Finding Form-PS4 - 0350superxl2009No ratings yet
- Federal Income Tax - Block - Fall 2003Document1 pageFederal Income Tax - Block - Fall 2003superxl2009No ratings yet
- Superior Court of Washington County ofDocument6 pagesSuperior Court of Washington County ofsuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Contracts: Requirements ListDocument1 pageContracts: Requirements Listsuperxl2009No ratings yet
- FacebookDocument3 pagesFacebookvinodNo ratings yet
- Current ContentDocument41 pagesCurrent Contentrishi284No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Economics As Applied ScienceDocument14 pagesLesson 2 Economics As Applied ScienceMichelin Danan75% (4)
- 时间改写,逻辑转换Document3 pages时间改写,逻辑转换S ZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 The Theory of Individual BehaviorDocument51 pagesChapter 4 The Theory of Individual BehaviorAyelle AdeNo ratings yet
- WK 3 Tutorial 4 Is LM Model (Solution)Document3 pagesWK 3 Tutorial 4 Is LM Model (Solution)Ivan TenNo ratings yet
- SPM 421-Strategic Supply Chain Management Notes - IukDocument63 pagesSPM 421-Strategic Supply Chain Management Notes - IukSserwadda Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- The PESTLE Analysis Is The Analysis of The Environment As A Whole in Which A Business Operates or Tends To Offer Its TradeDocument3 pagesThe PESTLE Analysis Is The Analysis of The Environment As A Whole in Which A Business Operates or Tends To Offer Its TradeFarhana RomanaNo ratings yet
- 5th-7th Lecture - Economy in The Long RunDocument58 pages5th-7th Lecture - Economy in The Long Runshubham solankiNo ratings yet
- Factors That Influence Exchange RatesDocument2 pagesFactors That Influence Exchange RatesJoelene ChewNo ratings yet
- Snap Fitness Franchise OpportunityDocument7 pagesSnap Fitness Franchise OpportunityrtphockjockNo ratings yet
- Valuation: Source: BSE: 500290 DCF 1st Stage: Next 10 Years Cash Flow ForecastDocument2 pagesValuation: Source: BSE: 500290 DCF 1st Stage: Next 10 Years Cash Flow ForecastAman KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Aggregate PlanningDocument22 pagesChapter-4 Aggregate PlanningYonatanNo ratings yet
- Eco 448 Economic Planning IIDocument135 pagesEco 448 Economic Planning IIprincessprecious013No ratings yet
- The Rise and Fall of The Dependency Movement - Omar SanchezDocument20 pagesThe Rise and Fall of The Dependency Movement - Omar SanchezAnonymous 74rXuCTNo ratings yet
- Economic theories-REAL LIFE EXAMPLESDocument5 pagesEconomic theories-REAL LIFE EXAMPLESDaksh MorNo ratings yet
- Atlantic Computers: A Bundle of Pricing Options: Presented by Team A6Document13 pagesAtlantic Computers: A Bundle of Pricing Options: Presented by Team A6Pallabi NagNo ratings yet
- Econ 223Document52 pagesEcon 223Patricia RuizNo ratings yet
- Capital Markets & Investments (Lochstoer) SU2014Document5 pagesCapital Markets & Investments (Lochstoer) SU2014darwin12No ratings yet
- Victory INCR Investment Grade Convertible Fund 2022 - 1QDocument3 pagesVictory INCR Investment Grade Convertible Fund 2022 - 1Qag rNo ratings yet
- FINS1613 File 04 - All 3 Topics Practice Questions PDFDocument16 pagesFINS1613 File 04 - All 3 Topics Practice Questions PDFisy campbellNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Business - Assignment BriefDocument7 pagesUnit 1 Business - Assignment BriefMuhammad UMERNo ratings yet
- Strategic Information SystemsDocument16 pagesStrategic Information SystemsDr Rushen SinghNo ratings yet
- 10 Mg2451 Eeca QBDocument22 pages10 Mg2451 Eeca QBDarshan KumarNo ratings yet
- Wk9 - Ch6b - Comparison & Selection Among AlternativesDocument13 pagesWk9 - Ch6b - Comparison & Selection Among AlternativesrashiNo ratings yet
- Setting Manufacturing Strategy For A Factory-Within-A-FactoryDocument17 pagesSetting Manufacturing Strategy For A Factory-Within-A-FactoryTania Amórtegui ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- A Profitability IndexDocument2 pagesA Profitability Indexkavitachordiya86No ratings yet
- Prob14 45Document2 pagesProb14 45Shai ManahanNo ratings yet