Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prob5 33s
Prob5 33s
Uploaded by
martinreakyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prob5 33s
Prob5 33s
Uploaded by
martinreakyCopyright:
Available Formats
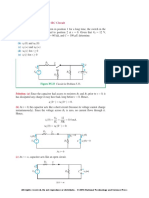
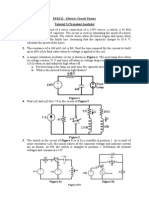
Problem 5.
33 After having been in position 1 for a long time, the switch in the
circuit of Fig. P5.33 was moved to position 2 at t = 0. Given that V
0
= 12 V,
R
1
= 30 k, R
2
= 120 k, R
3
= 60 k, and C = 100 F, determine:
(a) i
C
(0
) and
C
(0
)
(b) i
C
(0) and
C
(0)
(c) i
C
() and
C
()
(d)
C
(t) for t 0
(e) i
C
(t) for t 0
R
1
R
2
C
i
C
C
i
1
V
0
R
3
1
2
+
_
Figure P5.33: Circuit for Problem 5.33.
Solution: (a) Since the capacitor had access to resistors R
2
and R
3
prior to t = 0, it
has dissipated any charge it may have had, long before t = 0. Hence,
i
C
(0
) =
C
(0
) = 0.
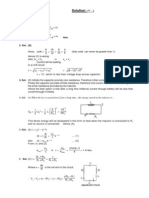
(b) At t = 0, the capacitor acts like a short circuit (because its voltage cannot change
instantaneously). Since the voltage across R
3
is zero, no current ows through it.
Hence,
i
1
(0) =
V
0
R
1
=
12
30k
= 0.4 mA.
C
(0) =
C
(0
) = 0.
At t = 0
R
1
C
(0) = 0
C
i
1
(0)
i
C
(0)
V
0
R
3
2
+
_
i
R
3
= 0
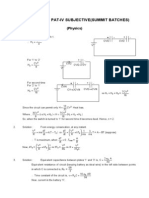
(c) At t =, capacitor acts like an open circuit.
At t = 8
R
1
v
C
( )
C
i
1
V
0
R
3
2
+
_
8
All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. c 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Hence,
i
C
() = 0
C
() =
V
0
R
3
R
1
+R
3
=
1260
30+60
= 8 V.
(d)
C
(t) =
C
() +(
C
(0)
C
())e
t/
= 8+(08)e
t/
= 8(1e
t/
) (V), for t 0,
where
=
R
1
R
3
R
1
+R
3
C =
3060
30+60
10
3
10
4
= 2 s.
(e)
i
C
(t) =C
d
C
dt
= 10
4
d
dt
[8(1e
0.5t
)]
= 0.4e
0.5t
(mA) for t 0.
All rights reserved. Do not reproduce or distribute. c 2013 National Technology and Science Press
You might also like
- RL RC CircuitDocument8 pagesRL RC CircuitDavex GwapoNo ratings yet
- Section 5-4: Response of The RC Circuit: Problem 5.33Document2 pagesSection 5-4: Response of The RC Circuit: Problem 5.33JOAQUIN ALESSANDRO CABRERA CHAMORRONo ratings yet
- HW12 SolDocument16 pagesHW12 SolAdtiya Kulkarni0% (1)
- Solution:: DT DQ e RC C V BDocument5 pagesSolution:: DT DQ e RC C V BAritra LahiriNo ratings yet
- Techtutor Academy: Electrical Circuits Sheet-5 (First Order Circuits)Document10 pagesTechtutor Academy: Electrical Circuits Sheet-5 (First Order Circuits)Masum BillahNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Pat-Iv Subjective (Summit Batches) : (Physics)Document2 pagesSolutions To Pat-Iv Subjective (Summit Batches) : (Physics)blue_l1No ratings yet
- PreLab3 NguyenQuocKhanh ITITIU18186Document4 pagesPreLab3 NguyenQuocKhanh ITITIU18186Kay NguyenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial #4.2 (Circuit Analysis by Classical Method, part-III)Document2 pagesTutorial #4.2 (Circuit Analysis by Classical Method, part-III)Jcb NitinNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits Response of First Order RL and RC CircuitsDocument56 pagesElectric Circuits Response of First Order RL and RC CircuitsAlexander_Tir_91570% (1)
- RC Circuits TutorialDocument9 pagesRC Circuits TutorialPiyush DubeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document115 pagesChapter 6heryj12No ratings yet
- Examination Nov 2012Document16 pagesExamination Nov 2012Mahesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Circuitry Ch07 First-Order CircuitsDocument50 pagesCircuitry Ch07 First-Order CircuitsGeorge VargheeseNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional Piston Problem: Tel: 631-5736 Email:atassi.1@nd - EduDocument4 pagesOne Dimensional Piston Problem: Tel: 631-5736 Email:atassi.1@nd - EdumohammadtariNo ratings yet
- Solve Problems in RC Series CircuitsDocument6 pagesSolve Problems in RC Series CircuitsAmer ArtesanoNo ratings yet
- Natural and Step Response of Series andDocument71 pagesNatural and Step Response of Series andManar HosnyNo ratings yet
- Detailed Solution of IES 2103 (ECE) Objective Paper - I: Set - A'Document12 pagesDetailed Solution of IES 2103 (ECE) Objective Paper - I: Set - A'vijaynarayan guptaNo ratings yet
- 08 Differential Equations - Second Order LDE ApplicationsDocument25 pages08 Differential Equations - Second Order LDE ApplicationsRemo Rubian EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Saturation CT Because of DC OffsetDocument20 pagesSaturation CT Because of DC OffsetAngga Wira PramanaNo ratings yet
- 6.1 The Capacitor 6.2 The Inductor 6.3 Series - Parallel Combinations of Capacitance and Inductance 6.4 Mutual InductanceDocument28 pages6.1 The Capacitor 6.2 The Inductor 6.3 Series - Parallel Combinations of Capacitance and Inductance 6.4 Mutual Inductancejayant5253No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document4 pagesTutorial 3Dhivya NNo ratings yet
- Ke16203 Assignement-1Document3 pagesKe16203 Assignement-1Kah MingNo ratings yet
- GATE EE 2010 With SolutionsDocument49 pagesGATE EE 2010 With SolutionsKumar GauravNo ratings yet
- RL RC CircuitsDocument29 pagesRL RC CircuitsKrishnaveni Subramani SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - DC Transient AnalysisDocument45 pagesChapter 5 - DC Transient AnalysisMohamed Awad100% (1)
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Solution For Problem 1Document7 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology: Solution For Problem 1Jeniffer OngNo ratings yet
- 4.work SheatDocument21 pages4.work SheatOdaa ClassNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Problem 2 A 20 F Capacitor Has Energy 10cos 377Document5 pagesChapter 6 Problem 2 A 20 F Capacitor Has Energy 10cos 377Wad ZzupNo ratings yet
- Solution - Tutorial 3Document11 pagesSolution - Tutorial 3zgalionoooNo ratings yet
- Cc19 Group 1 Lab Report 6Document8 pagesCc19 Group 1 Lab Report 6PHƯỚC DƯƠNG THANHNo ratings yet
- ES-1 Natural and Forced ResponseDocument39 pagesES-1 Natural and Forced ResponseGanesh DharmireddyNo ratings yet
- Experiment-11 Time Response of R-C CircuitDocument8 pagesExperiment-11 Time Response of R-C CircuitabhimanyuNo ratings yet
- Ee PDFDocument8 pagesEe PDFabhimanyuNo ratings yet
- EE102 Lab6Document8 pagesEE102 Lab6Ankit NadanNo ratings yet
- GATE EE 2006 With SolutionsDocument56 pagesGATE EE 2006 With Solutionspwnkumar63100% (1)
- JEE (Main) Model Paper: Physics SolutionsDocument1 pageJEE (Main) Model Paper: Physics Solutionssarma410437No ratings yet
- R-L & R-C CircuitsDocument41 pagesR-L & R-C CircuitsAlamgir Kabir ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Mae 3800 Pset 1Document3 pagesMae 3800 Pset 1lqmurraNo ratings yet
- Cap. 32 PDFDocument75 pagesCap. 32 PDFwallaNo ratings yet
- SP AC KL - PhasorDocument10 pagesSP AC KL - PhasorstavenschistudentNo ratings yet
- GATE EE 2008 With SolutionsDocument60 pagesGATE EE 2008 With SolutionsAbhishek Mohan67% (3)
- P, P Z (O / P) OFF OFF OFF OFF ON ON ON OFF ON ON ON OFF: EC-GATE-2013 PAPERDocument31 pagesP, P Z (O / P) OFF OFF OFF OFF ON ON ON OFF ON ON ON OFF: EC-GATE-2013 PAPERa_barbate1147No ratings yet
- Exam III PHY 2049 Summer C July 16, 2008Document7 pagesExam III PHY 2049 Summer C July 16, 2008Ytzel NëssieNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document31 pagesLab Report 1Kristi GadeshiNo ratings yet
- Gate - in 2007Document30 pagesGate - in 2007prabhjot singh1No ratings yet
- Transient Response in Electric Circuits: V (T) I R) DT' I (T' C 1 DT Di M DT Di L (T) VDocument16 pagesTransient Response in Electric Circuits: V (T) I R) DT' I (T' C 1 DT Di M DT Di L (T) VNeas GintingNo ratings yet
- A Capacitor Paradox: Q On Its PlatesDocument7 pagesA Capacitor Paradox: Q On Its PlatesJoseph LeeNo ratings yet
- HW 4 ADocument8 pagesHW 4 ABelayneh Tadesse100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document15 pagesChapter 3Gemechis AsfawNo ratings yet
- Rland RCDocument33 pagesRland RCSyed Muhammad DanishNo ratings yet
- ECE QuestionsDocument12 pagesECE QuestionsSimran SiNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Circuit Analysis and Design (Victor Nelson, Troy Nagle, David Irwin & Bill Carroll)Document866 pagesDigital Logic Circuit Analysis and Design (Victor Nelson, Troy Nagle, David Irwin & Bill Carroll)Juvenal Eduardo Saucedo Arizpe100% (5)
- Deliverables: Two Separate and Complete Lab Reports: 1. A Sketch That Simulates A 4 Position SwitchDocument1 pageDeliverables: Two Separate and Complete Lab Reports: 1. A Sketch That Simulates A 4 Position SwitchmartinreakyNo ratings yet
- Prob5 37sDocument2 pagesProb5 37smartinreaky100% (1)
- Circuits 2nd EditionDocument2 pagesCircuits 2nd EditionmartinreakyNo ratings yet
- Prob5 51sDocument2 pagesProb5 51smartinreaky100% (1)