Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Self Test
Self Test
Uploaded by
ray72roCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis With BEASTDocument262 pagesBayesian Evolutionary Analysis With BEASTFranco Santin100% (1)
- ERBAI (M-UE-29) : Two WhitesDocument1 pageERBAI (M-UE-29) : Two Whitesray72roNo ratings yet
- Pericardium Meridian PDFDocument1 pagePericardium Meridian PDFrinkyNo ratings yet
- Scriptieacu Jelena Kasteel ChronicmusculoskeletalpainDocument36 pagesScriptieacu Jelena Kasteel ChronicmusculoskeletalpainMontserrat100% (1)
- Yang Earth Joye Yap PDFDocument18 pagesYang Earth Joye Yap PDFSerenity Serenity100% (4)
- NS1881 EXAM PREP Flashcards - QuizletDocument3 pagesNS1881 EXAM PREP Flashcards - QuizletLaetitia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Protocol Hybridization Capture of Dna Libraries Using Xgen Lockdown Probes and Reagents Version 3Document16 pagesProtocol Hybridization Capture of Dna Libraries Using Xgen Lockdown Probes and Reagents Version 3Rodger12No ratings yet
- IB Biology Study NotesDocument134 pagesIB Biology Study Noteshdpham100% (25)
- The Gall Bladder Channel of Foot ShaoyangDocument6 pagesThe Gall Bladder Channel of Foot Shaoyangray72roNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy For Neurological Disorders (2) 2Document11 pagesPhysical Therapy For Neurological Disorders (2) 2Muskan AhujaNo ratings yet
- Lu 2Document1 pageLu 2ray72roNo ratings yet
- Acupressure Centre 2017-Khemka Delhi Noida Bhi Hai PDFDocument3 pagesAcupressure Centre 2017-Khemka Delhi Noida Bhi Hai PDFVinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Shiatsu and Acupressure Two Different and DistinctDocument8 pagesShiatsu and Acupressure Two Different and DistinctEmre YalçınNo ratings yet
- Pulse: Good Width at Medium Level, Regular, 78 BPM, Wiry On Right, Thin On LeftDocument11 pagesPulse: Good Width at Medium Level, Regular, 78 BPM, Wiry On Right, Thin On LeftHui YingNo ratings yet
- Dannangxue (M-Le-23) : Gallbladder PointDocument1 pageDannangxue (M-Le-23) : Gallbladder Pointray72roNo ratings yet
- Korean Medicine in Kazakhstan Ideas Prac PDFDocument33 pagesKorean Medicine in Kazakhstan Ideas Prac PDFAngel MalzoneNo ratings yet
- Spleen PiDocument39 pagesSpleen PiOmar Duran Castro100% (1)
- General Introduction To AcupointsDocument48 pagesGeneral Introduction To Acupointsjonan hemingted10No ratings yet
- AcupunctureDocument15 pagesAcupuncturezextorcNo ratings yet
- BNYS Colleges List - Updated On 14.11.20 EDITED NAVEEN GHDocument8 pagesBNYS Colleges List - Updated On 14.11.20 EDITED NAVEEN GHchinnu1235395No ratings yet
- The Pericardium Channel of Hand Jueyi NDocument5 pagesThe Pericardium Channel of Hand Jueyi Nray72roNo ratings yet
- Bell's Palsy: Submitted By: Twinkle Singh & Kinjalika VarmaDocument34 pagesBell's Palsy: Submitted By: Twinkle Singh & Kinjalika Varmatwinklestar1396No ratings yet
- Acupuncture: DR Kevin Hickey Shipley Health CentreDocument45 pagesAcupuncture: DR Kevin Hickey Shipley Health CentreAstrology KingNo ratings yet
- Biomagnetic Acupoint Therapy: Practice and TheoryDocument51 pagesBiomagnetic Acupoint Therapy: Practice and Theoryaculearn100% (1)
- Acupuncture and Moxibustion Techniques PDFDocument71 pagesAcupuncture and Moxibustion Techniques PDFJessé de Andrade100% (2)
- Acupoints Learning Module 2Document6 pagesAcupoints Learning Module 2Navneet Singh100% (1)
- Jizhong Du-6: Centre of The SpineDocument1 pageJizhong Du-6: Centre of The SpineBDI92No ratings yet
- Si 9Document1 pageSi 9ray72roNo ratings yet
- YNM Part 2 - ExplainDocument61 pagesYNM Part 2 - ExplainCHAKRADHARA RAO100% (1)
- Clinic Theater 2 - Class 4Document2 pagesClinic Theater 2 - Class 4drprasantNo ratings yet
- Sujok SongsDocument2 pagesSujok SongsprasadmvkNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Vision:: Based On The Concept of Energy Flow and The "Organs"Document50 pagesA Simplified Vision:: Based On The Concept of Energy Flow and The "Organs"dustysuloNo ratings yet
- Essence, Qi Blood and Body FluidsDocument35 pagesEssence, Qi Blood and Body FluidsNaya Pebriana100% (1)
- Intro To AyurvedaDocument53 pagesIntro To AyurvedarakeshNo ratings yet
- Cranio em InglesDocument39 pagesCranio em InglesbrunamontenegrooNo ratings yet
- 361 Standard and 48 Extra (1001 - 1048) Acupuncture PointsDocument12 pages361 Standard and 48 Extra (1001 - 1048) Acupuncture PointsKesavadev100% (1)
- Meridian Analysis Energy DeviceDocument4 pagesMeridian Analysis Energy Devicehistory APNo ratings yet
- Tianquan P-2: Heavenly SpringDocument1 pageTianquan P-2: Heavenly Springray72roNo ratings yet
- AcupuncturistDocument51 pagesAcupuncturistDrMohamed RifasNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Therapy QuestionnaireDocument8 pagesNutritional Therapy Questionnairezgray20No ratings yet
- Physiology of HealingDocument9 pagesPhysiology of Healingcarlos100% (9)
- Pattern DiagnosisDocument20 pagesPattern DiagnosisEdison HlmNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Regulation 1Document5 pagesAutonomic Regulation 1Darren StarwynnNo ratings yet
- 4 - Fire - Heart Manage & TreatmentDocument19 pages4 - Fire - Heart Manage & Treatmentpeter911xNo ratings yet
- Large Intestine LI 1Document11 pagesLarge Intestine LI 1Renugadevi DinakaranNo ratings yet
- Ayurveda Training CoursesDocument5 pagesAyurveda Training CoursesDrSandeep MadaanNo ratings yet
- 14 Governor VesselDocument54 pages14 Governor Vesselshamsorah100% (1)
- Pediatric Class Hand Out 2008Document33 pagesPediatric Class Hand Out 2008Ramesh Babu ManivannanNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Complementary and Self-Help Treatments For Anxiety DisordersDocument18 pagesEffectiveness of Complementary and Self-Help Treatments For Anxiety DisordersSoulyogaNo ratings yet
- Jue Yin Principle MeridianDocument17 pagesJue Yin Principle MeridianAnonymous 5IUoLwGSdNo ratings yet
- The Role of Cupping Therapy in Pain Management A LDocument19 pagesThe Role of Cupping Therapy in Pain Management A LMohitha Parla100% (1)
- Endophysics, Time, QuantumDocument16 pagesEndophysics, Time, QuantumRiccardo MantelliNo ratings yet
- On English Translation of Infant Tuina Points in Traditional Chinese MedicineDocument3 pagesOn English Translation of Infant Tuina Points in Traditional Chinese MedicineSam SonNo ratings yet
- Meridian MassageDocument20 pagesMeridian MassageTaichiaikidoka100% (1)
- 14 Point Acupresuusre & TCM Acupressure TheraphyDocument9 pages14 Point Acupresuusre & TCM Acupressure TheraphyNallaTMNo ratings yet
- 07 Caroline RadiceDocument7 pages07 Caroline Radicetigerstyle1No ratings yet
- Meditation Map1Document1 pageMeditation Map1koravNo ratings yet
- HEMME Approach Concepts and TehniquesDocument285 pagesHEMME Approach Concepts and TehniquesAlexandra AiftimieNo ratings yet
- Korea ManopunturaDocument7 pagesKorea ManopunturaRicard Revuelto Orengo100% (1)
- Classical and Modern Theories of AcupunctureDocument11 pagesClassical and Modern Theories of AcupunctureAbhishek Dubey100% (1)
- Pathway: and Then Across The Face and Cheek To Connect With The Tissues Surrounding The EyeDocument9 pagesPathway: and Then Across The Face and Cheek To Connect With The Tissues Surrounding The EyeCarleta Stan100% (1)
- Abdomen Study Guide QuestionsDocument6 pagesAbdomen Study Guide QuestionsGuarina MolinaNo ratings yet
- The Spleen Channel of Foot TaiyinDocument6 pagesThe Spleen Channel of Foot Taiyinray72roNo ratings yet
- The Large Intestine Channel of Hand YangmingDocument6 pagesThe Large Intestine Channel of Hand Yangmingray72roNo ratings yet
- Atlas of High-Resolution Manometry, Impedance, and pH MonitoringFrom EverandAtlas of High-Resolution Manometry, Impedance, and pH MonitoringNo ratings yet
- DLR 2021 04 18 10 00Document3 pagesDLR 2021 04 18 10 00ray72roNo ratings yet
- Emotions Essential Oils 6th EnlightenDocument271 pagesEmotions Essential Oils 6th Enlightenray72roNo ratings yet
- DLR 2021 04 18 14 00Document3 pagesDLR 2021 04 18 14 00ray72roNo ratings yet
- Da Liu Ren: Hour Day Month Year SpiritsDocument2 pagesDa Liu Ren: Hour Day Month Year Spiritsray72roNo ratings yet
- DLR 2021 04 18 02 00Document3 pagesDLR 2021 04 18 02 00ray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 34Document3 pagesGB 34ray72roNo ratings yet
- DLR 2021 04 18 08 00Document3 pagesDLR 2021 04 18 08 00ray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 31Document2 pagesGB 31ray72roNo ratings yet
- Yi Notes PDFDocument19 pagesYi Notes PDFEe6803100% (2)
- Zhongdu Gb-32: Middle DitchDocument1 pageZhongdu Gb-32: Middle Ditchray72roNo ratings yet
- The Gall Bladder Channel of Foot ShaoyangDocument6 pagesThe Gall Bladder Channel of Foot Shaoyangray72roNo ratings yet
- Guangming Gb-37: Bright LightDocument2 pagesGuangming Gb-37: Bright Lightray72roNo ratings yet
- Zuqiaoyin Gb-44: Yin Portals of The FootDocument2 pagesZuqiaoyin Gb-44: Yin Portals of The Footray72roNo ratings yet
- Notes: Gall Bladder ChannelDocument1 pageNotes: Gall Bladder Channelray72roNo ratings yet
- Zulinqi Gb-41: Foot Governor of TearsDocument2 pagesZulinqi Gb-41: Foot Governor of Tearsray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 36Document1 pageGB 36ray72roNo ratings yet
- Toulinqi Gb-15: Gall Bladder Channel 1Document1 pageToulinqi Gb-15: Gall Bladder Channel 1ray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 20 PDFDocument2 pagesGB 20 PDFray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 22Document1 pageGB 22ray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 25Document2 pagesGB 25ray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 21 PDFDocument2 pagesGB 21 PDFray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 23 PDFDocument1 pageGB 23 PDFray72roNo ratings yet
- Naokong Gb-19: Gall Bladder Channel 1Document1 pageNaokong Gb-19: Gall Bladder Channel 1ray72roNo ratings yet
- Biomimetic Supramolecular Designs For Growth FactorsDocument14 pagesBiomimetic Supramolecular Designs For Growth FactorsMuhammad SuhaeriNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom - MnemonicsDocument24 pagesAnimal Kingdom - Mnemonicssinhatanvi40No ratings yet
- 月4 Unit 5 Video scriptsDocument2 pages月4 Unit 5 Video scriptsrikuto dokkyoNo ratings yet
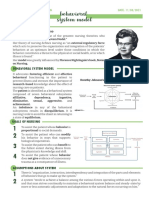
- Nursing Theory Johnson - Behavioral System ModelDocument3 pagesNursing Theory Johnson - Behavioral System ModelANGEL BIEN LEVERIZANo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional BiokimiaDocument12 pagesJurnal Internasional BiokimiaLaRa Tika Febriani0% (1)
- Meroplankton Part IDocument5 pagesMeroplankton Part IMuhammad Nur SaidNo ratings yet
- Bio 024 - Quiz Cfu Sas 3 (Answer Key)Document4 pagesBio 024 - Quiz Cfu Sas 3 (Answer Key)ELLE WOODSNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 1Document23 pagesPathfit 1Sep TemNo ratings yet
- Keswani 2019Document4 pagesKeswani 2019gyogi1989No ratings yet
- Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium Simulator Lab Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesHardy Weinberg Equilibrium Simulator Lab Lesson Planapi-359867350No ratings yet
- იმუნოს ზეპირი 1 1Document65 pagesიმუნოს ზეპირი 1 1Levani KartvelishviliNo ratings yet
- Botany Assignment MUHSIN K P - 872Document9 pagesBotany Assignment MUHSIN K P - 872muhsinNo ratings yet
- Functional Mri BookheimerDocument79 pagesFunctional Mri BookheimerPrasidha PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Scientific Evidence Vedantic Light EbookDocument302 pagesScientific Evidence Vedantic Light Ebookmaran s100% (2)
- Hussain et al_NEJM_2020Document13 pagesHussain et al_NEJM_2020zdmoorNo ratings yet
- Marine Biotechnology: An Overview: Narsinh L Thakur and Archana N ThakurDocument6 pagesMarine Biotechnology: An Overview: Narsinh L Thakur and Archana N ThakurPilar Saravia HuaringaNo ratings yet
- Wound Management in Diabetic Patients Focus On Diabetic FootDocument36 pagesWound Management in Diabetic Patients Focus On Diabetic FootHerry KongkoNo ratings yet
- Fluid & Elec DidacticsDocument64 pagesFluid & Elec DidacticsTonie AbabonNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Multidrug Resistance in Enterococci Isolates From Different Clinical Sources in Al-Diwaniyah CityDocument9 pagesPrevalence of Multidrug Resistance in Enterococci Isolates From Different Clinical Sources in Al-Diwaniyah CityCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Ponce, Angelica Christine P. Biochemistry/ N1A 2O2O21OO285 11/16/2O2ODocument5 pagesPonce, Angelica Christine P. Biochemistry/ N1A 2O2O21OO285 11/16/2O2OfallenNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 SOW 2023 24 (Updated Term 2 4)Document9 pagesGrade 10 SOW 2023 24 (Updated Term 2 4)Huseynov SardorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4Kate Wen GuanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - Medical Mycoloy - AspergillosisDocument17 pagesLecture 10 - Medical Mycoloy - AspergillosisXavier DharmaNo ratings yet
- DK All Codes.Document23 pagesDK All Codes.mdhd1467No ratings yet
- Aakash Botany Study Package 2 SolutionsDocument116 pagesAakash Botany Study Package 2 Solutionsrekim23414No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Biodiversity and The Healthy Society (Final Copy)Document156 pagesChapter 9 - Biodiversity and The Healthy Society (Final Copy)Josh DumalagNo ratings yet
Self Test
Self Test
Uploaded by
ray72roOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Self Test
Self Test
Uploaded by
ray72roCopyright:
Available Formats
SELF-TESTING MODULE QUESTIONS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
CHANNEL PATHWAYS GENERAL
QUESTIONS
1 Describe the difference between the internal and
the external pathways of the primary channels.
2 Describe the general areas of the body covered
by the yin channels and the yang channels
respectively.
3 Where do the following groups of channels
begin and end?
a Three yin channels of the hand
b Three yang channels of the hand
c Three yang channels of the foot
d Three yin channels of the foot
4 How do the arm channels within the six
channel system relate anatomically to their
corresponding leg channel?
5 The superficial pathways of the twelve channels
complete three circuits of the body. Describe the
direction of the flow through this circuit, with
reference to areas of the body and yin and yang.
6 Give two characteristics that are specific to the
Sinew channels.
7 Which luo-connecting channels connect to internal
zangfu. Name the zangfu they connect to.
8 Which luo-connecting channels connect to sense
organs. Name the sense organs they connect to.
9 How are the luo-connecting channel pathways
similar to the primary channel pathways?
10 What are the functions of the luo-connecting
channels?
SELF-TESTING MODULE QUESTIONS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
LUNG CHANNEL
11 Most of the luo-connecting channels follow the
pathways of their primary channel. The Lung luo
is one of the exceptions to this. Where does it run?
12a Where does the Lung channel primary
channel originate?
12b What is the significance of this in terms of the
actions and indications of the Lung channel?
13 The Lung and Large Intestine are internally
and externally paired zangfu. How do various
portions of the Lung channel connect to the Large
Intestine?
14 Which significant part of the anatomy does the
Lung channel reach in its uppermost aspect?
15 Which of the Lung primary or secondary
channels reach this area?
LARGE INTESTINE CHANNEL
16 What is unusual about the Large Intestine
channel pathway when it reaches the face?
17 What is the significance of the branch of the Large
Intestine primary channel that descends to the leg?
18a At which sense organ does the Large Intestine
luo-connecting channel make connections with
several other channel pathways.
18b Name these connections.
19 Name another sense organ that the luo-
connecting channel connects to.
20a Describe two areas the Large Intestine sinew
channel runs to on the face.
20b Which other sinew channel does it pass close to
in this area?
SELF-TESTING MODULE QUESTIONS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
STOMACH CHANNEL
21a Which of the six channels is the Stomach
channel a part of and which is its paired channel?
21b Where do these two channels meet?
22 Where do the two branches of the Stomach
sinew channel terminate?
23 There are two branches of the Stomach primary
channel on the leg and foot. Describe their
pathways and significance?
24 Which channels/vessels does the Stomach
channel intersect with on the face?
25a Which group of channels meets at Quepen
ST-12?
25b Which channel is the exception to this?
SPLEEN CHANNEL
26a Which zangfu does the Spleen channel connect
to internally?
26b What relationship does the Spleen have to these
zangfu regarding the production of qi and blood?
27a What additional channel does the Spleen
channel system have, that the other channels do not?
27b What is its main area of influence?
27c Where does this channel originate?
28 What connections to other channels does the
Spleen channel make in the lower abdomen?
29 What connections to other channels/vessels does
the Spleen channel make in the mid-abdomen area?
30a What connection does the Spleen channel make
to other channels in the chest area?
30b What is the six channel pair relationship
between these two channels?
SELF-TESTING MODULE QUESTIONS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
HEART CHANNEL
31a Which three zangfu does the Heart primary
channel connect to?
31b What relationship does the Heart channel and
organ system have to each of these zangfu?
32a At which sense organ does the Heart primary
channel end?
32b Which other portions of the Heart channel
system also travel to this area?
33 Where does the Heart sinew channel
terminate?
34 Which other sinew channel does the Heart
sinew channel intersect?
35a Which sense organ is related to the Heart?
35b Which portion of the Heart channel system
connects here?
SMALL INTESTINE CHANNEL
36a The Small Intestine primary channel connects
with which two sense organs on the face?
36b Which other primary channels go to the same
two sense organs?
37 Which three zangfu does the Small Intestine
primary channel connect to?
38 What is the significance of the Small Intestine
primary channel branch that ends at the inner
canthus of the eye?
39a Which area of the body is represented by the
taiyang channel pair?
39b Describe how the Small Intestine channel
pathways reflect this.
40 Which channel does the Small Intestine primary
channel intersect in the chest and abdomen?
SELF-TESTING MODULE QUESTIONS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
BLADDER CHANNEL
41 Which two channels/vessels does the Bladder
channel intersect with on the head?
42 At which point on the Bladder channel does the
main channel separate into two branches and at
which point do they merge back together again?
43 Which two sense organs does the Bladder
primary channel connect with?
44 Which channel does the Bladder pathway
connect to in the buttock area?
45 What important Bladder channel connection
takes place at Baihui DU-20?
46 What is unusual about the Bladder luo-
connecting channel?
KIDNEY CHANNEL
47a Which zangfu does the internal pathway of the
Kidney channel connect to?
47b Describe the relationship between the Kidney
and each of these zangfu with reference to the
following:
i. five phase cycles.
ii. he physiological connection between these zangfu.
iii. yin and yang relationships
48a The Kidney channel closely follows which vessel
along its pathway up the abdomen?
48b What is the relationship between these two
channels/vessels?
49 Which significant anatomical area does the
Kidney sinew channel connect to in the lower
abdomen?
50 Where does the internal pathway of the Kidney
primary channel terminate?
SELF-TESTING MODULE QUESTIONS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
KIDNEY CHANNEL CONTINUED
51 The Kidneys are said to dominate the bones
and rule the lower back. Which channel pathway
connections reinforce these statements?
PERICARDIUM CHANNEL
52 How does the Pericardium channel connect to its
paired Sanjiao channel and fu?
53 What is the significance of the branch of the
Pericardium channel that arises at Laogong P8 and
travels to the tip of the ring finger?
54 Which two zang does the Pericardium luo-
connecting channel connect with?
55 Where does the Pericardium sinew channel
reach?
56 The Pericardium channel treats disorders of the
lateral costal region. Which of the Pericardium
channels has a particular influence over this area?
SELF-TESTING MODULE QUESTIONS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
SAN JIAO CHANNEL
57a The Sanjiao channel is linked to which
channel on the leg through the six channel pairing
and what is this channel pair called?
57b Which area of the body do these two channels
significantly influence?
58 Which two zangfu does the Sanjiao primary
channel connect to?
59 Which yang sinew channel does this sinew
channel connect with and where?
60 Which two sense organs does the Sanjiao sinew
channel connect to?
61 Which two channels does the Sanjiao primary
channel connect to on the head?
GALL BLADDER CHANNEL
62 Which two sense organs does the Gall Bladder
channel connect to?
63a Headaches related to the Gall Bladder manifest
at which aspect of the head?
63b Relate this to the Gall Bladder channel
pathways.
64 The Girdling vessel is closely linked to the Gall
Bladder channel. Explain this connection.
SELF-TESTING MODULE QUESTIONS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
LIVER CHANNEL
65 All the Liver channel pathways make a
significant connection with which anatomical
structure on the lower abdomen?
66a Which zangfu does the Liver channel connect
to through its internal pathway?
66b Describe the relationship the Liver has to
these zangfu?
67 Which sense organ connections does the Liver
primary channel make?
68a Which channel crosses the Liver channel in
its lower aspect?
68b How are these two zang related
physiologically?
THE GOVERNING VESSEL
69 Why are the Governing and Conception vessels
different to the other extraordinary vessels?
70 The primary pathway of the Governing vessel
passes along and through which significant
structures on its course?
71 The Governing vessel pathways travel along the
posterior aspect of the body. One of the secondary
pathways ascends along the anterior aspect.
Describe the significance of this pathway?
72 What is the difference between the primary
pathway of the Conception vessel and the second
branch of the Governing vessel?
73 Which group of channels meets at Dazhui DU-14?
SELF-TESTING MODULE QUESTIONS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
CONCEPTION VESSEL
74a Where does the Conception vessel originate in
men?
74b Where does the Conception vessel originate in
women?
75 Which two sense organs does the Conception
vessel connect to?
76 Li Shi-zhen says: The Conception and
Governing vessels are like midnight and midday,
they are the polar axis of the body. Explain this
statement with reference to the Conception vessel.
77 Jiuwei REN-15, the luo-connecting point of the
Conception vessel, descends the qi and unbinds
the chest. How do these actions relate to the Luo
channel pathway?
DIVERGENT CHANNELS
78 List the functions of the divergent channels.
79 Explain how the yang divergent channels assist
the yin divergent and primary channels to circulate
to yang areas of the body.
EXTRAORDINARY VESSELS
80 What are the functions of the extraordinary
vessels?
81 Which of the extraordinary vessels originate in
the lower abdomen?
82 Differentiate the main areas of influence (not the
pathways) of the Yin Linking vessel and the Yang
Linking vessel.
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
1 Describe the difference between the internal and
the external pathways of the primary channels.
The internal pathways connect to the channels
related zangfu and its internally/externally
related zangfu e.g. the Lung channel connects
internally to the Lung zang and Large Intestine fu.
The internal pathway of a channel may also
connect to other zangfu.
The external pathway of a channel is where the
acupuncture points are located.
REF PAGE 14
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
2 Describe the general areas of the body covered
by the yin channels and the yang channels
respectively.
The yin channels traverse the inner surface of the
limbs, the abdomen and the chest.
The yang channels traverse the outer surface of
the limbs and travel to the head, and with the
exception of the Stomach channel, the back.
REF: P. 13
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
3 Where do the following groups of channels
begin and end?
a Three yin channels of the hand
Begin on the chest and end on the inner
aspect of the hand
b Three yang channels of the hand
Begin on the hand and end on the
head.
c Three yang channels of the foot
Begin on the face and end on the outer
surface of the foot.
d Three yin channels of the foot
Begin on the foot and end on the chest
or flanks.
REF: P. 14
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
4 How do the arm channels within the six
channel system relate anatomically to their
corresponding leg channel?
Lung taiyin:
Anterior portion of the inside of the arm
Spleen taiyin:
Anterior portion of the inside of the leg
Pericardium jueyin:
Middle portion of the inside of the arm
Liver jueyin:
Middle portion of the inside of the leg
Heart shaoyin:
Posterior portion of the inside of the arm
Kidney shaoyin:
Posterior portion of the inside of the leg
Large Intestine yangming:
Anterior portion of the outside of the arm
Stomach yangming:
Anterior portion of the outside of the leg
Sanjiao shaoyang:
Middle portion of the outside of the arm
Gall Bladder shaoyang:
Middle portion of the outside of the leg
Small Intestine taiyang:
Posterior portion of the outside of the arm
Bladder taiyang:
Posterior portion of the outside of the leg
REF: p. 15
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
5 The superficial pathways of the twelve channels
complete three circuits of the body. Describe the
direction of the flow through this circuit, with
reference to areas of the body and yin and yang.
Chest to hand (downwards), to face (upwards), to
foot (downwards), to chest (upwards) travelling
from yin to yang and back again.
REF: p. 14
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
6 Give two characteristics that are specific to the
Sinew channels.
i. Circulate only on the periphery of the body.
ii. Do not penetrate to the zangfu.
iii. Are more superficial and follow the lines of
major muscles and muscle groups, tendons,
ligaments etc.
iv. All originate at the extremities and ascend to
the head and trunk.
REF: p. 26
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
7 Which luo-connecting channels connect to internal
zangfu. Name the zangfu they connect to.
Spleen Stomach and intestines
Heart Heart
Pericardium Pericardium and Heart
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
8 Which luo-connecting channels connect to sense
organs. Name the sense organs they connect to.
Large Intestine teeth and ear
Heart base of tongue and eye
REF: p. 26
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
9 How are the luo-connecting channel pathways
similar to the primary channel pathways?
i. They make connections from their internally-
externally paired channel; ii. They usually
continue to follow their primary channel
pathways.
REF: p. 26
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
10 What are the functions of the luo- connecting
channels?
They strengthen the connection between the
internally-externally paired channel and zangfu.
REF: p. 26 See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
11 Most of the luo-connecting channels follow the
pathways of their primary channel. The Lung luo
is one of the exceptions to this. Where does it run?
From Lieque LU-7, it travels into the palm of the
hand and spreads through the thenar eminence.
REF: p. 74 See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
12a Where does the Lung channel primary
channel originate?
A: In the middle jiao, in the region of the Stomach.
12b What is the significance of this in terms of the
actions and indications of the Lung channel?
A: Many of the Lung channel points treat
disorders of the Stomach such as nausea and
vomiting.
REF: p.75
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
13 The Lung and Large Intestine are internally and
externally paired zangfu. How do various portions of
the Lung channel connect to the Large Intestine?
i. The deep pathway of the Lung primary channel
descends to connect with the Large Intestine fu.
ii. A branch of the Lung primary channel from
Lieque LU-7 links with the Large Intestine
channel at Shangyang LI-1.
iii. The Lung luo-connectng channel connects with
the Large Intestine channel.
iv. The Lung divergent channel disperses in the
Large Intestine.
REF: p. 73 75.
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
14 Which significant part of the anatomy does the
Lung channel reach in its uppermost aspect?
The throat
REF PAGE 73
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
15 Which of the Lung primary or secondary
channels reach this area?
The internal pathway of the Lung primary
channel and the Lung divergent channel.
REF: p.73, 74
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
16 What is unusual about the Large Intestine
channel pathway when it reaches the face?
The channel crosses over from one side of the
body to the other at the nose.
REF: p. 95-96
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
17 What is the significance of the branch of the
Large Intestine primary channel that descends to
the leg?
It descends to the lower he-sea point of the Large
Intestine channel at Shangjuxu ST-37.
REF: p.95 See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
18a At which sense organ does the Large
Intestine luo-connecting channel make
connections with several other channel
pathways.
A: The ear.
18b Name these connections.
The Stomach, Small Intestine, Gall Bladder &
Sanjiao channels.
REF: p.96 See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
19 Name another sense organ that the luo-
connecting channel connects to.
The mouth: the luo-connecting channel goes to the
teeth.
REF: p.97
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
20a Describe two areas the Large Intestine sinew
channel runs to on the face.
A: The main channel crosses the temple to the
corner of the forehead and crosses over the top of
the head to the mandible on the opposite side; a
branch ascends across the cheek to bind at the
side of the nose.
20b Which other sinew channel does it pass close
to in this area?
A: The Small Intestine sinew channel.
REF: p. 98.
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
21a Which of the six channels is the Stomach
channel a part of and which is its paired channel?
A: Yangming; paired with the Large Intestine
channel.
21b Where do these two channels meet?
A: At the side of the nose at Yingxiang LI-20 the
start of the Stomach channel.
REF: p. 125,129 See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
22 Where do the two branches of the Stomach
sinew channel terminate?
Around the eyes and in front of the ears.
ref page 128
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
23 There are two branches of the Stomach primary
channel on the leg and foot. Describe their
pathways and significance?
One branch separates at Chongyang ST-42 and
terminates at the big toe at Yinbai SP-1. The
Spleen channel follows the Stomach channel in
the circuit of qi circulation.
Another branch separates at Zusanli ST-36 and
terminates at the end of the middle toe. No other
channel ends at this phalanx.
REF : p. 125 126, p. 15
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
24 Which channels/vessels does the Stomach
channel intersect with on the face?
The Large Intestine channel at Yingxiang LI-20,
The Governing vessel at Shenting DU-24, and
Renzhong DU-26,
The Conception vessel at Chengjiang REN-24,
The Gall Bladder channel at Shangguan GB-3,
Hanyan GB-4, Xuanlu GB-5, and Xuanli GB-6,
The Bladder channel at Jingming BL-1.
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
25a Which group of channels meets at Quepen
ST-12?
A: The yang primary channels.
25b Which channel is the exception to this?
A: The Bladder channel is the only yang channel
that does not meet at this point.
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
26a Which zangfu does the Spleen channel
connect to internally?
A: The Spleen, Stomach and Heart.
26b What relationship does the Spleen have to
these zangfu regarding the production of qi and
blood?
A: The Spleen and Stomach are involved in the
transportation and transformation of the liquid
and solid products of digestion after the Stomach
has rotted and ripened the digestate. The Spleen
controls blood and dominates the first stage of its
formation and holding. The Heart is involved in
the final stages of production of blood and
governs blood.
REF: p. 177 181; p. 211; See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
27a What additional channel does the Spleen
channel system have, that the other channels do
not?
A: The great luo-connecting channel.
27b What is its main area of influence?
A: It spreads through the chest and lateral costal
region.
27c Where does this channel originate?
A: Dabao SP-21.
REF: 179 See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
28 What connections to other channels does the
Spleen channel make in the lower abdomen?
It connects with the Conception vessel at Zhongji
REN-3 and Guanyuan REN-4.
ref. page 177
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
29 What connections to other channels/vessels
does the Spleen channel make in the mid-
abdomen area?
The Conception vessel at Xiawan REN-10, the
Liver channel at Qimen LIV-14, and the Gall
Bladder channel at Riyue GB-24.
ref. page 177 See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
30a What connection does the Spleen channel
make to other channels in the chest area?
A: It connects with the Lung channel at Zhongfu
LU-1.
ref. page 177
30b What is the six channel pair relationship
between these two channels?
A: Together they form the taiyin channel.
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
31a Which three zangfu does the Heart primary
channel connect to?
A: The Heart, Lung and Small Intestine.
31b What relationship does the Heart channel and
organ system have to each of these zangfu?
The Heart channel links to its own zang.
The Heart and Lung are both in the upper jiao;
the Heart channel crosses over the Lung area in
the torso; the Heart and Lung are closely related
through the production of qi and blood. The
gathering qi is closely related to the functions of
the Heart and Lung.
The Heart andSmall Intestine are internally
externally related channel pairs.
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
32a At which sense organ does the Heart primary
channel end?
A: The eye.
32b Which other portions of the Heart channel
system also travel to this area?
A: The Heart luo-connecting channel and the
Heart divergent channel.
REF: 210 See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
33 Where does the Heart sinew channel terminate?
The umbilicus.
REF: p. 211
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
34 Which other sinew channel does the Heart
sinew channel intersect?
The Lung sinew channel.
REF: p. 211 See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
35a Which sense organ is related to the Heart?
A: The tongue.
35b Which portion of the Heart channel system
connects here?
A: The luo-connecting channel connects with the
root of the tongue.
REF: p. 210-211
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
36a The Small Intestine primary channel connects
with which two sense organs on the face?
A: The ears and the eyes.
36b Which other primary channels go to the same
two sense organs?
A: The Sanjiao, Bladder and Gall Bladder
channels. The Stomach channel passes close to the
ear.
REF: p. 227-228, p.387-388, p.417-418, p.125-126
See reference See reference
See reference See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
37 Which three zangfu does the Small Intestine
primary channel connect to?
The Small Intestine, Heart and Stomach.
REF: p. 227-228
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
38 What is the significance of the Small Intestine
primary channel branch that ends at the inner
canthus of the eye?
It meets with Jingming BL-1 here which is the
start of the Bladder channel. Together the Small
Intestine and Bladder channels form the taiyang
channel. The Bladder channel follows the Small
Intestine channel in the circulation of qi cycle.
REF: p. 227 228, p.15
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
39a Which area of the body is represented by the
taiyang channel pair?
A: The most yang area: the posterior aspect of the
body.
39b Describe how the Small Intestine channel
pathways reflect this.
A: The Small Intestine primary channel zigzags
around the scapula area on the upper back. The
Small Intestine sinew channel surrounds the
scapula.
REF: p. 227-228, p. 28
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
40 Which channel does the Small Intestine
primary channel intersect in the chest and
abdomen?
The Conception vessel at Shanzhong REN-17,
Shangwan REN-13 and Zhongwan REN-12.
REF: p. 227 228
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
41 Which two channels/vessels does the Bladder
channel intersect with on the head?
The Gall Bladder channel and the Governing
vessel.
REF: p. 251 252
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
42 At which point on the Bladder channel does the
main channel separate into two branches and at
which point do they merge back together again?
Tianzhu BL-10 and Weizhong BL-40.
REF: p. 251 252
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
43 Which two sense organs does the Bladder
primary channel connect with?
The eye (where the primary channel begins) and
the ears (the internal pathway of the Bladder
channel circulates the ears).
REF: p. 251 252
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
44 Which channel does the Bladder pathway
connect to in the buttock area?
The Gall Bladder channel at Huantiao GB-30.
REF: p. 251 - 252
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
45 What important Bladder channel connection
takes place at Baihui DU-20?
The Bladder channel runs internally to the brain.
REF: p. 251-252
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
46 What is unusual about the Bladder luo-
connecting channel?
It connects with the Kidney channel, but has no
pathway that follows the primary channel in
either direction.
REF: 253
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
47a Which zangfu does the internal pathway of
the Kidney channel connect to?
A: The Kidney, Bladder, Lung, Liver and Heart.
47b Describe the relationship between the Kidney
and each of these zangfu with reference to the
following:
i. five phase cycles.
ii. the physiological connection between these
zangfu.
iii. yin and yang relationships
Kidney/Bladder
i. internal external paired channels/zangfu - both
pertain to water.
ii. both involved in water metabolism.
iii.yin-yang paired channels.
Kidney/Lung
i. Metal (Lung) is the mother of water (Kidney).
ii.both are involved in qi and fluid metabolism.
iii.The Kidney in the lower jiao (yin area) is the
bottomost zang and the root of yin in the body.
The Lung in the upper jiao (yang area) is the
"canopy" or "lid".
Kidney Heart
i. Water (Kidney) controls Fire (Heart).
ii. Kidney water controls Heart fire.
iii.Kidney water (yin) below controls Heart fire
(yang) above.
Kidney Liver
i. Water (Kidney) is the mother of wood (Liver).
ii. Kidney yin nourishes Liver yin;
iii. Kidney yin nourishes Liver yin to keep Liver
yang under control.
REF: p. 331-332
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
48a The Kidney channel closely follows which
vessel along its pathway up the abdomen?
A: The Conception vessel.
48b What is the relationship between these two
channels/vessels?
A: The Kidney channel is the root of original yin
and yang of the body and is the foundation of the
Conception vessel.
REF: p. 331-335
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
49 Which significant anatomical area does the
Kidney sinew channel connect to in the lower
abdomen?
The genitals.
REF: p. 334
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
50 Where does the internal pathway of the Kidney
primary channel terminate?
The root of the tongue.
REF: p. 331-332
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
51 The Kidneys are said to dominate the bones
and rule the lower back. Which channel pathway
connections reinforce these statements?
The internal pathway of the Kidney primary
channel threads through the spine. A branch of
the Kidney luo-connecting channel travels
posteriorly to and spreads into the lumbar
vertebrae. Te Kidney sinew channel travels
internally to the spinal vertebrae and ascends the
inner aspect of the spine.
REF: p. 331 335
See reference
See reference
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
52 How does the Pericardium channel connect to
its paired Sanjiao channel and fu?
The Pericardium primary channel descends
through the upper, middle and lower jiao in the
abdomen. The Pericardium divergent channel
also descends through the three jiaos. A branch of
the divergent channel ascends across the throat
and emerges behind the ear to converge with the
San Jiao channel.
REF: 367-368
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
53 What is the significance of the branch of the
Pericardium channel that arises at Laogong P8
and travels to the tip of the ring finger?
The Sanjiao channel begins on this finger, though
the Pericardium channel runs to the radial side
and the Sanjiao channel begins on the ulnar side.
The change of polarity from yin to yang takes
place at the extremities.
REF: p. 367, p. 15
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
54 Which two zang does the Pericardium luo-
connecting channel connect with?
The Pericardium & Heart.
REF: p. 368
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
55 Where does the Pericardium sinew channel
reach?
It enters the chest below the axilla, disperses in the
chest and binds at the diaphragm.
REF: p. 369
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
56 The Pericardium channel treats disorders of the
lateral costal region. Which of the Pericardium
channels has a particular influence over this area?
The Pericardium sinew channel disperses over the
anterior and posterior ribs
REF: p. 369-70
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
57a The Sanjiao channel is linked to which channel
on the leg through the six channel pairing and
what is this channel pair called?
A: The Gall Bladder channel: shaoyang channel.
57b Which area of the body do these two channels
significantly influence?
A: The sides of the body and head.
REF: p. 387-390 See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
58 Which two zangfu does the Sanjiao primary
channel connect to?
The Sanjiao and Pericardium.
REF: p. 387-289
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
59 Which yang sinew channel does the Sanjiao
sinew channel connect with and where?
The Small intestine sinew channel in the neck.
REF: p.389
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
60 Which two sense organs does the Sanjiao sinew
channel connect to?
The ears and the eyes.
REF: p. 387-388
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
61 Which two channels does the Sanjiao primary
channel connect to on the head?
The Gall Bladder and Small Intestine channels.
REF: 387-388
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
62 Which two sense organs does the Gall Bladder
channel connect to?
The eyes and the ears.
ref page 417
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
63a Headaches related to the Gall Bladder
manifest at which aspect of the head?
A: The side of the head and temples.
63b Relate this to the Gall Bladder channel
pathways.
A: The channel crosses back and forth over the
side of the head, the area of the shaoyang channel.
Hanyan GB-4 to Qubin GB-7 at the temples.
Shuaigu GB-8 to Wangu GB-12 behind the ear.
Benshen GB-13 to Toulinqi GB-15 at the forehead
above the eyes.
Toulinqi GB-15 to Fengchi GB- 20 in the parietal
region.
REF: p. 417 421
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
64 The Girdling vessel is closely linked to the Gall
Bladder channel. Explain this connection.
The Girdling vessel only passes through three
acupuncture points all of which are on the Gall
Bladder channel: Daimai GB-26, Wushu GB-27
and Weidao GB-28. The confluent point of the
Girdling vessel is Zulinqi GB-41.
REF: p. 421
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
65 All the Liver channel pathways make a
significant connection with which anatomical
structure on the lower abdomen?
The genitals.
REF: p. 469-471
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
66a Which zangfu does the Liver channel connect
to through its internal pathway?
A: The Liver, Gall Bladder, Stomach (curves
around it), and Lung.
REF: p. 469
66b Describe the relationship the Liver has to
these zangfu?
A: The Liver and Gall Bladder are entrusted with
the ministerial fire and their stagnant qi readily
transforms to fire. Liver pathology frequently
manifests along the course of the Gall Bladder
channel. The Liver assists in the descent of
Stomach and Lung qi.
REF: p. 421, p. 472
See reference
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
67 Which sense organ connections does the Liver
primary channel make?
It enircles the lips, nasopharynx and eyes.
REF: p. 469
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
68a Which channel crosses the Liver channel in
its lower aspect?
A: The Spleen.
68b How are these two zang related
physiologically?
A: The Liver stores the blood, the Spleen controls
the blood dominating the first stage of its
formation and holding it in its proper place.
REF: p. 472, p. 181
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
69 Why are the Governing and Conception vessels
different to the other extraordinary vessels?
They have their own acupuncture points.
REF: p. 531
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
70 The primary pathway of the Governing vessel
passes along and through which significant
structures on its course?
The spine and the brain.
REF: p. 529, 531
See reference
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
71 The Governing vessel pathways travel along
the posterior aspect of the body. One of the
secondary pathways ascends along the anterior
aspect. Describe the significance of this pathway?
This pathway closely resembles that of the
Conception vessel.
REF: p. 530-531
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
72 What is the difference between the primary
pathway of the Conception vessel and the second
branch of the Governing vessel?
The second branch of the Governing vessel passes
through the Heart; the Conception vessel does
not.
REF: p. 495, 530
See reference
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
73 Which group of channels meets at Dazhui DU-
14?
It is the meeting point of the Governing vessel
with the six yang channels of the hand and foot.
The Governing vessel is known as the sea of the
yang channels.
REF. p.545
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
74a Where does the Conception vessel originate in
men?
A: The lower abdomen.
74b Where does the Conception vessel originate in
women?
A: The uterus.
REF: p.495
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
75 Which two sense organs does the Conception
vessel connect to?
The eyes and the mouth.
REF: p. 495 496
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
76 Li Shi-zhen says: The Conception and
Governing vessels are like midnight and midday,
they are the polar axis of the body. Explain this
statement with reference to the Conception vessel.
Both the Conception and Governing vessels
originate in the lower abdomen. The primary
channel of the Conception vessel ascends along
the anterior midline, yin aspect of the body. The
Governing vessel primary channel ascends along
the posterior midline, yang aspect. The
Conception vessel also has a branch that ascends
along the back, whilst a branch of the Governing
vessel ascends the anterior midline of the body.
REF: p. 496
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
77 Jiuwei REN-15, the luo-connecting point of the
Conception vessel, descends the qi and unbinds
the chest. How do these actions relate to the Luo
channel pathway?
The luo-connecting channel disperses and spreads
down the abdomen from this point. One of the
main actions of Jiuwei REN-15 is to regulate
stagnation of qi and blood in the Heart region,
giving rise to oppression and pain.
REF: p. 496, 516 See reference
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
78 List the functions of the divergent channels.
i. They strengthen the yin-yang relationship
between the internally-externally paired channels
and zangfu.
ii. They distribute qi and blood to the head and
face
iii. They integrate areas of the body not supplied
or interconnected by the primary channels.
iv. They help explain the clinical action of some
commonly-used acupuncture points.
REF: p. 16-17
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
79 Explain how the yang divergent channels assist
the yin divergent and primary channels to
circulate to yang areas of the body.
Apart from the Heart and the Liver channels, the
yin primary channels do not go to the head and
face. The link with the yang divergent and
primary channels enables the other four yin
channels to make a connection at the top of the
body.
REF: p.16
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
80 What are the functions of the extraordinary
vessels?
i. They act as reservoirs.
ii. They link the twelve primary channels.
iii. They protect the body.
REF: p.17-18
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
81 Which of the extraordinary vessels originate in
the lower abdomen?
The Penetrating, Conception and Governing
vessels.
REF: p..19,495, 529-530,
See reference
See reference
See reference
SELF-TESTING MODULE ANSWERS
Combinations Index Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
CONTENTS
82 Differentiate the main areas of influence (not
the pathways) of the Yin Linking vessel and the
Yang Linking vessel.
The Yin Linking vessel dominates the interior of
the body and the Yang Linking vessel dominates
the exterior of the body.
REF: p. 17 See reference
You might also like
- Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis With BEASTDocument262 pagesBayesian Evolutionary Analysis With BEASTFranco Santin100% (1)
- ERBAI (M-UE-29) : Two WhitesDocument1 pageERBAI (M-UE-29) : Two Whitesray72roNo ratings yet
- Pericardium Meridian PDFDocument1 pagePericardium Meridian PDFrinkyNo ratings yet
- Scriptieacu Jelena Kasteel ChronicmusculoskeletalpainDocument36 pagesScriptieacu Jelena Kasteel ChronicmusculoskeletalpainMontserrat100% (1)
- Yang Earth Joye Yap PDFDocument18 pagesYang Earth Joye Yap PDFSerenity Serenity100% (4)
- NS1881 EXAM PREP Flashcards - QuizletDocument3 pagesNS1881 EXAM PREP Flashcards - QuizletLaetitia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Protocol Hybridization Capture of Dna Libraries Using Xgen Lockdown Probes and Reagents Version 3Document16 pagesProtocol Hybridization Capture of Dna Libraries Using Xgen Lockdown Probes and Reagents Version 3Rodger12No ratings yet
- IB Biology Study NotesDocument134 pagesIB Biology Study Noteshdpham100% (25)
- The Gall Bladder Channel of Foot ShaoyangDocument6 pagesThe Gall Bladder Channel of Foot Shaoyangray72roNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy For Neurological Disorders (2) 2Document11 pagesPhysical Therapy For Neurological Disorders (2) 2Muskan AhujaNo ratings yet
- Lu 2Document1 pageLu 2ray72roNo ratings yet
- Acupressure Centre 2017-Khemka Delhi Noida Bhi Hai PDFDocument3 pagesAcupressure Centre 2017-Khemka Delhi Noida Bhi Hai PDFVinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Shiatsu and Acupressure Two Different and DistinctDocument8 pagesShiatsu and Acupressure Two Different and DistinctEmre YalçınNo ratings yet
- Pulse: Good Width at Medium Level, Regular, 78 BPM, Wiry On Right, Thin On LeftDocument11 pagesPulse: Good Width at Medium Level, Regular, 78 BPM, Wiry On Right, Thin On LeftHui YingNo ratings yet
- Dannangxue (M-Le-23) : Gallbladder PointDocument1 pageDannangxue (M-Le-23) : Gallbladder Pointray72roNo ratings yet
- Korean Medicine in Kazakhstan Ideas Prac PDFDocument33 pagesKorean Medicine in Kazakhstan Ideas Prac PDFAngel MalzoneNo ratings yet
- Spleen PiDocument39 pagesSpleen PiOmar Duran Castro100% (1)
- General Introduction To AcupointsDocument48 pagesGeneral Introduction To Acupointsjonan hemingted10No ratings yet
- AcupunctureDocument15 pagesAcupuncturezextorcNo ratings yet
- BNYS Colleges List - Updated On 14.11.20 EDITED NAVEEN GHDocument8 pagesBNYS Colleges List - Updated On 14.11.20 EDITED NAVEEN GHchinnu1235395No ratings yet
- The Pericardium Channel of Hand Jueyi NDocument5 pagesThe Pericardium Channel of Hand Jueyi Nray72roNo ratings yet
- Bell's Palsy: Submitted By: Twinkle Singh & Kinjalika VarmaDocument34 pagesBell's Palsy: Submitted By: Twinkle Singh & Kinjalika Varmatwinklestar1396No ratings yet
- Acupuncture: DR Kevin Hickey Shipley Health CentreDocument45 pagesAcupuncture: DR Kevin Hickey Shipley Health CentreAstrology KingNo ratings yet
- Biomagnetic Acupoint Therapy: Practice and TheoryDocument51 pagesBiomagnetic Acupoint Therapy: Practice and Theoryaculearn100% (1)
- Acupuncture and Moxibustion Techniques PDFDocument71 pagesAcupuncture and Moxibustion Techniques PDFJessé de Andrade100% (2)
- Acupoints Learning Module 2Document6 pagesAcupoints Learning Module 2Navneet Singh100% (1)
- Jizhong Du-6: Centre of The SpineDocument1 pageJizhong Du-6: Centre of The SpineBDI92No ratings yet
- Si 9Document1 pageSi 9ray72roNo ratings yet
- YNM Part 2 - ExplainDocument61 pagesYNM Part 2 - ExplainCHAKRADHARA RAO100% (1)
- Clinic Theater 2 - Class 4Document2 pagesClinic Theater 2 - Class 4drprasantNo ratings yet
- Sujok SongsDocument2 pagesSujok SongsprasadmvkNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Vision:: Based On The Concept of Energy Flow and The "Organs"Document50 pagesA Simplified Vision:: Based On The Concept of Energy Flow and The "Organs"dustysuloNo ratings yet
- Essence, Qi Blood and Body FluidsDocument35 pagesEssence, Qi Blood and Body FluidsNaya Pebriana100% (1)
- Intro To AyurvedaDocument53 pagesIntro To AyurvedarakeshNo ratings yet
- Cranio em InglesDocument39 pagesCranio em InglesbrunamontenegrooNo ratings yet
- 361 Standard and 48 Extra (1001 - 1048) Acupuncture PointsDocument12 pages361 Standard and 48 Extra (1001 - 1048) Acupuncture PointsKesavadev100% (1)
- Meridian Analysis Energy DeviceDocument4 pagesMeridian Analysis Energy Devicehistory APNo ratings yet
- Tianquan P-2: Heavenly SpringDocument1 pageTianquan P-2: Heavenly Springray72roNo ratings yet
- AcupuncturistDocument51 pagesAcupuncturistDrMohamed RifasNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Therapy QuestionnaireDocument8 pagesNutritional Therapy Questionnairezgray20No ratings yet
- Physiology of HealingDocument9 pagesPhysiology of Healingcarlos100% (9)
- Pattern DiagnosisDocument20 pagesPattern DiagnosisEdison HlmNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Regulation 1Document5 pagesAutonomic Regulation 1Darren StarwynnNo ratings yet
- 4 - Fire - Heart Manage & TreatmentDocument19 pages4 - Fire - Heart Manage & Treatmentpeter911xNo ratings yet
- Large Intestine LI 1Document11 pagesLarge Intestine LI 1Renugadevi DinakaranNo ratings yet
- Ayurveda Training CoursesDocument5 pagesAyurveda Training CoursesDrSandeep MadaanNo ratings yet
- 14 Governor VesselDocument54 pages14 Governor Vesselshamsorah100% (1)
- Pediatric Class Hand Out 2008Document33 pagesPediatric Class Hand Out 2008Ramesh Babu ManivannanNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Complementary and Self-Help Treatments For Anxiety DisordersDocument18 pagesEffectiveness of Complementary and Self-Help Treatments For Anxiety DisordersSoulyogaNo ratings yet
- Jue Yin Principle MeridianDocument17 pagesJue Yin Principle MeridianAnonymous 5IUoLwGSdNo ratings yet
- The Role of Cupping Therapy in Pain Management A LDocument19 pagesThe Role of Cupping Therapy in Pain Management A LMohitha Parla100% (1)
- Endophysics, Time, QuantumDocument16 pagesEndophysics, Time, QuantumRiccardo MantelliNo ratings yet
- On English Translation of Infant Tuina Points in Traditional Chinese MedicineDocument3 pagesOn English Translation of Infant Tuina Points in Traditional Chinese MedicineSam SonNo ratings yet
- Meridian MassageDocument20 pagesMeridian MassageTaichiaikidoka100% (1)
- 14 Point Acupresuusre & TCM Acupressure TheraphyDocument9 pages14 Point Acupresuusre & TCM Acupressure TheraphyNallaTMNo ratings yet
- 07 Caroline RadiceDocument7 pages07 Caroline Radicetigerstyle1No ratings yet
- Meditation Map1Document1 pageMeditation Map1koravNo ratings yet
- HEMME Approach Concepts and TehniquesDocument285 pagesHEMME Approach Concepts and TehniquesAlexandra AiftimieNo ratings yet
- Korea ManopunturaDocument7 pagesKorea ManopunturaRicard Revuelto Orengo100% (1)
- Classical and Modern Theories of AcupunctureDocument11 pagesClassical and Modern Theories of AcupunctureAbhishek Dubey100% (1)
- Pathway: and Then Across The Face and Cheek To Connect With The Tissues Surrounding The EyeDocument9 pagesPathway: and Then Across The Face and Cheek To Connect With The Tissues Surrounding The EyeCarleta Stan100% (1)
- Abdomen Study Guide QuestionsDocument6 pagesAbdomen Study Guide QuestionsGuarina MolinaNo ratings yet
- The Spleen Channel of Foot TaiyinDocument6 pagesThe Spleen Channel of Foot Taiyinray72roNo ratings yet
- The Large Intestine Channel of Hand YangmingDocument6 pagesThe Large Intestine Channel of Hand Yangmingray72roNo ratings yet
- Atlas of High-Resolution Manometry, Impedance, and pH MonitoringFrom EverandAtlas of High-Resolution Manometry, Impedance, and pH MonitoringNo ratings yet
- DLR 2021 04 18 10 00Document3 pagesDLR 2021 04 18 10 00ray72roNo ratings yet
- Emotions Essential Oils 6th EnlightenDocument271 pagesEmotions Essential Oils 6th Enlightenray72roNo ratings yet
- DLR 2021 04 18 14 00Document3 pagesDLR 2021 04 18 14 00ray72roNo ratings yet
- Da Liu Ren: Hour Day Month Year SpiritsDocument2 pagesDa Liu Ren: Hour Day Month Year Spiritsray72roNo ratings yet
- DLR 2021 04 18 02 00Document3 pagesDLR 2021 04 18 02 00ray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 34Document3 pagesGB 34ray72roNo ratings yet
- DLR 2021 04 18 08 00Document3 pagesDLR 2021 04 18 08 00ray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 31Document2 pagesGB 31ray72roNo ratings yet
- Yi Notes PDFDocument19 pagesYi Notes PDFEe6803100% (2)
- Zhongdu Gb-32: Middle DitchDocument1 pageZhongdu Gb-32: Middle Ditchray72roNo ratings yet
- The Gall Bladder Channel of Foot ShaoyangDocument6 pagesThe Gall Bladder Channel of Foot Shaoyangray72roNo ratings yet
- Guangming Gb-37: Bright LightDocument2 pagesGuangming Gb-37: Bright Lightray72roNo ratings yet
- Zuqiaoyin Gb-44: Yin Portals of The FootDocument2 pagesZuqiaoyin Gb-44: Yin Portals of The Footray72roNo ratings yet
- Notes: Gall Bladder ChannelDocument1 pageNotes: Gall Bladder Channelray72roNo ratings yet
- Zulinqi Gb-41: Foot Governor of TearsDocument2 pagesZulinqi Gb-41: Foot Governor of Tearsray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 36Document1 pageGB 36ray72roNo ratings yet
- Toulinqi Gb-15: Gall Bladder Channel 1Document1 pageToulinqi Gb-15: Gall Bladder Channel 1ray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 20 PDFDocument2 pagesGB 20 PDFray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 22Document1 pageGB 22ray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 25Document2 pagesGB 25ray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 21 PDFDocument2 pagesGB 21 PDFray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 23 PDFDocument1 pageGB 23 PDFray72roNo ratings yet
- Naokong Gb-19: Gall Bladder Channel 1Document1 pageNaokong Gb-19: Gall Bladder Channel 1ray72roNo ratings yet
- Biomimetic Supramolecular Designs For Growth FactorsDocument14 pagesBiomimetic Supramolecular Designs For Growth FactorsMuhammad SuhaeriNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom - MnemonicsDocument24 pagesAnimal Kingdom - Mnemonicssinhatanvi40No ratings yet
- 月4 Unit 5 Video scriptsDocument2 pages月4 Unit 5 Video scriptsrikuto dokkyoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theory Johnson - Behavioral System ModelDocument3 pagesNursing Theory Johnson - Behavioral System ModelANGEL BIEN LEVERIZANo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional BiokimiaDocument12 pagesJurnal Internasional BiokimiaLaRa Tika Febriani0% (1)
- Meroplankton Part IDocument5 pagesMeroplankton Part IMuhammad Nur SaidNo ratings yet
- Bio 024 - Quiz Cfu Sas 3 (Answer Key)Document4 pagesBio 024 - Quiz Cfu Sas 3 (Answer Key)ELLE WOODSNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 1Document23 pagesPathfit 1Sep TemNo ratings yet
- Keswani 2019Document4 pagesKeswani 2019gyogi1989No ratings yet
- Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium Simulator Lab Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesHardy Weinberg Equilibrium Simulator Lab Lesson Planapi-359867350No ratings yet
- იმუნოს ზეპირი 1 1Document65 pagesიმუნოს ზეპირი 1 1Levani KartvelishviliNo ratings yet
- Botany Assignment MUHSIN K P - 872Document9 pagesBotany Assignment MUHSIN K P - 872muhsinNo ratings yet
- Functional Mri BookheimerDocument79 pagesFunctional Mri BookheimerPrasidha PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Scientific Evidence Vedantic Light EbookDocument302 pagesScientific Evidence Vedantic Light Ebookmaran s100% (2)
- Hussain et al_NEJM_2020Document13 pagesHussain et al_NEJM_2020zdmoorNo ratings yet
- Marine Biotechnology: An Overview: Narsinh L Thakur and Archana N ThakurDocument6 pagesMarine Biotechnology: An Overview: Narsinh L Thakur and Archana N ThakurPilar Saravia HuaringaNo ratings yet
- Wound Management in Diabetic Patients Focus On Diabetic FootDocument36 pagesWound Management in Diabetic Patients Focus On Diabetic FootHerry KongkoNo ratings yet
- Fluid & Elec DidacticsDocument64 pagesFluid & Elec DidacticsTonie AbabonNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Multidrug Resistance in Enterococci Isolates From Different Clinical Sources in Al-Diwaniyah CityDocument9 pagesPrevalence of Multidrug Resistance in Enterococci Isolates From Different Clinical Sources in Al-Diwaniyah CityCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Ponce, Angelica Christine P. Biochemistry/ N1A 2O2O21OO285 11/16/2O2ODocument5 pagesPonce, Angelica Christine P. Biochemistry/ N1A 2O2O21OO285 11/16/2O2OfallenNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 SOW 2023 24 (Updated Term 2 4)Document9 pagesGrade 10 SOW 2023 24 (Updated Term 2 4)Huseynov SardorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4Kate Wen GuanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - Medical Mycoloy - AspergillosisDocument17 pagesLecture 10 - Medical Mycoloy - AspergillosisXavier DharmaNo ratings yet
- DK All Codes.Document23 pagesDK All Codes.mdhd1467No ratings yet
- Aakash Botany Study Package 2 SolutionsDocument116 pagesAakash Botany Study Package 2 Solutionsrekim23414No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Biodiversity and The Healthy Society (Final Copy)Document156 pagesChapter 9 - Biodiversity and The Healthy Society (Final Copy)Josh DumalagNo ratings yet