Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CXC Mathematics Tutorial: Author: John Spencer MBA (Dist), M. SC, B. SC
CXC Mathematics Tutorial: Author: John Spencer MBA (Dist), M. SC, B. SC
Uploaded by
Perry SinCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Unrequited Feelings (B, Leslie) (Z-Library)Document149 pagesUnrequited Feelings (B, Leslie) (Z-Library)bekoenergysave100% (3)
- After Democracy Imagining Our Political Future Zizi PapacharissiDocument149 pagesAfter Democracy Imagining Our Political Future Zizi PapacharissiBrandon RojasNo ratings yet
- FP1 Jan 2022 MSDocument21 pagesFP1 Jan 2022 MSCalixto JaxonNo ratings yet
- Math Paper 3 Practice MSDocument47 pagesMath Paper 3 Practice MSRaahish KalariaNo ratings yet
- CS2 B Chapters 4 and 5 - Markov Jump Processes - QuestionsDocument3 pagesCS2 B Chapters 4 and 5 - Markov Jump Processes - QuestionsJames AsesNo ratings yet
- 2007 2008S6FinalPmath 1Document4 pages2007 2008S6FinalPmath 1api-3742735No ratings yet
- Sense Organ PDFDocument5 pagesSense Organ PDFPerry Sin75% (4)
- Jean-Luc Marion-Cartesian Questions - Method and Metaphysics-University of Chicago Press (1999) PDFDocument226 pagesJean-Luc Marion-Cartesian Questions - Method and Metaphysics-University of Chicago Press (1999) PDFJuan Pablo CotrinaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Tutorial On Sequences & SeriesDocument7 pages2nd Tutorial On Sequences & Seriestoh tim lamNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods: Written Examination 2Document29 pagesMathematical Methods: Written Examination 2Kevin NguyenNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Question Bank Maths LDocument60 pagesDifferentiation Question Bank Maths LUmair Khan MarwatNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics: (Final Exam Revision)Document4 pagesProbability and Statistics: (Final Exam Revision)PHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNNo ratings yet
- Explanation (Arithmetic and Geometric)Document7 pagesExplanation (Arithmetic and Geometric)Jemyr Ann NavarroNo ratings yet
- Statistical Modeling of Extreme Values PDFDocument28 pagesStatistical Modeling of Extreme Values PDFHassanRazaNo ratings yet
- المعادلات التفاضلية الاعتياديةDocument150 pagesالمعادلات التفاضلية الاعتياديةخيرالله عبد حسين محمدNo ratings yet
- Lehmann Scheffe PDFDocument7 pagesLehmann Scheffe PDFBarnita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Surds and Indices: I. Laws of Indices: I) A Xa A (A) A (Ab) A BDocument19 pagesSurds and Indices: I. Laws of Indices: I) A Xa A (A) A (Ab) A BArunachalam NarayananNo ratings yet
- 12 Area Under CurvesDocument28 pages12 Area Under CurvesNathan Ha100% (1)
- 16 Quiz Review Quadratic EquationsDocument21 pages16 Quiz Review Quadratic EquationsdevikaNo ratings yet
- Linear Control Systems Lecture # 8 Observability & Discrete-Time SystemsDocument25 pagesLinear Control Systems Lecture # 8 Observability & Discrete-Time SystemsRavi VermaNo ratings yet
- VCE Unit 1 Specialist Maths Bound ReferenceDocument17 pagesVCE Unit 1 Specialist Maths Bound ReferenceMikiNo ratings yet
- Implicit DifferentiationDocument2 pagesImplicit DifferentiationAlicia TerrazasNo ratings yet
- State SpaceDocument20 pagesState SpacepattanayaksuchiNo ratings yet
- Complex Number Exercise Book PDFDocument26 pagesComplex Number Exercise Book PDFRitik KumarNo ratings yet
- 23-24 Y12 IB Quiz 3Document15 pages23-24 Y12 IB Quiz 33414642747No ratings yet
- Roots of Complex NumbersDocument3 pagesRoots of Complex NumbersntimalsinaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets ALL PDFDocument34 pagesProblem Sets ALL PDFLeroy ChengNo ratings yet
- Module 15 Trigonomeertric FunctionsDocument32 pagesModule 15 Trigonomeertric Functionsbakaraz7523027No ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument1 pageQuadratic EquationEmyRaNo ratings yet
- The Miller-Rabin Randomized Primality TestDocument10 pagesThe Miller-Rabin Randomized Primality TestHung Nguyen0% (1)
- W s-1 Factorizing Algebraic ExpressionsDocument2 pagesW s-1 Factorizing Algebraic Expressionsapi-253679034No ratings yet
- Controllability and Observability of Linear Time Invariant SystemsDocument31 pagesControllability and Observability of Linear Time Invariant SystemsumeshNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Descriptive Statistics (10 Marks)Document4 pagesAssignment 1: Descriptive Statistics (10 Marks)Malik Faizan100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - DifferentiationDocument56 pagesChapter 4 - DifferentiationTOBY RANNo ratings yet
- Observers For Non-Linear SystemsDocument35 pagesObservers For Non-Linear SystemsdvnccbmacbtNo ratings yet
- Binomial TheoremDocument3 pagesBinomial TheoremKelvin LimNo ratings yet
- Rouche's TheoremDocument9 pagesRouche's TheoremJeoff Libo-onNo ratings yet
- 04 Jackknife PDFDocument22 pages04 Jackknife PDFuniversedrillNo ratings yet
- Set 2 Linear InequalitiesDocument3 pagesSet 2 Linear InequalitiesGee Zainurdin100% (1)
- Business Mathematics Application Calculus To Solve Business ProblemsDocument51 pagesBusiness Mathematics Application Calculus To Solve Business ProblemsEida HidayahNo ratings yet
- A2T Practice - Test - Chapter - 9 SolutionsDocument9 pagesA2T Practice - Test - Chapter - 9 SolutionsSheryn MalayaNo ratings yet
- Permutations and CombinationsDocument48 pagesPermutations and CombinationsAnonymous auSpiAmZvnNo ratings yet
- Polynomial and Rational FunctionsDocument11 pagesPolynomial and Rational Functionsoana_brincoveanuNo ratings yet
- Maths3 PDFDocument5 pagesMaths3 PDFKunal KaranNo ratings yet
- BCS 012 MathsDocument431 pagesBCS 012 Mathssomeone someoneNo ratings yet
- 9 13 2016 1 1 1 Solving Puzzles in TeamsDocument2 pages9 13 2016 1 1 1 Solving Puzzles in Teamsapi-327140356No ratings yet
- IB Mathematics AA HL Questionbank - FunctionsDocument76 pagesIB Mathematics AA HL Questionbank - FunctionsMatias LandiNo ratings yet
- Logistics Regression ExerciseDocument2 pagesLogistics Regression ExerciseLakshmi NairNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: by Solomon BatiDocument59 pagesChapter Two: by Solomon BatiUsmaan GammachuuNo ratings yet
- Properties of Curves Worksheet Easy Problems 1Document9 pagesProperties of Curves Worksheet Easy Problems 1V NagarjunaNo ratings yet
- E7 Ordinary Differential Equation New - 0Document28 pagesE7 Ordinary Differential Equation New - 0Mor DepRzNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometry DoneDocument4 pagesInverse Trigonometry Donesourabh rajNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods Paper - 2013Document7 pagesNumerical Methods Paper - 2013Sourav PandaNo ratings yet
- MTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 5 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 2.6 To 3.5 Except 3.3Document10 pagesMTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 5 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 2.6 To 3.5 Except 3.3Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Discrete Math Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesDiscrete Math Exam QuestionsSandeep SajuNo ratings yet
- Binomial ExpansionsDocument5 pagesBinomial ExpansionsShafiqueDeshongNo ratings yet
- Final 2002F: InterpolationDocument3 pagesFinal 2002F: InterpolationmakrsnakminesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Koopman Operator Theory of Dynamical SystemsDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Koopman Operator Theory of Dynamical SystemsJimiao ZhangNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: CambridgeDocument8 pages9709 Mathematics: CambridgeanzaaariNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory Problems PDFDocument11 pagesProbability Theory Problems PDFPaun MihaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document23 pagesChapter 1Philimon TajemNo ratings yet
- I.S.F.D y T. #103: Profesorado de Técnicos Prof: Martín MellerDocument11 pagesI.S.F.D y T. #103: Profesorado de Técnicos Prof: Martín MellerAriel LeucipoNo ratings yet
- Summary On Relation FunctionDocument4 pagesSummary On Relation FunctionKenville JackNo ratings yet
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Course Outline: Course Title: Linear Algebra Course Code: EDME3201 (ME32A) Level: 3 Semester: 3 Credits: 3Document3 pagesCourse Outline: Course Title: Linear Algebra Course Code: EDME3201 (ME32A) Level: 3 Semester: 3 Credits: 3Perry SinNo ratings yet
- 3850 - Mathematics - Stage - 1 - Question - Paper - Set 1 PDFDocument19 pages3850 - Mathematics - Stage - 1 - Question - Paper - Set 1 PDFPerry Sin100% (1)
- 2004 Csec Chem Paper 01Document10 pages2004 Csec Chem Paper 01Perry SinNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorem Booklet PDFDocument16 pagesCircle Theorem Booklet PDFPerry Sin100% (1)
- Full Maths SbaDocument9 pagesFull Maths SbaPerry Sin86% (22)
- 7B ReproductionDocument31 pages7B ReproductionPerry Sin50% (2)
- Lesson Plan September 24 To 28Document19 pagesLesson Plan September 24 To 28Perry SinNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System PDFDocument3 pagesThe Nervous System PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- 3850 Mathematics Stage 1 Marking Guide Set 1Document1 page3850 Mathematics Stage 1 Marking Guide Set 1Perry SinNo ratings yet
- White Blood Cells (WBC) PDFDocument3 pagesWhite Blood Cells (WBC) PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Types of Neurons PDFDocument2 pagesTypes of Neurons PDFPerry Sin100% (2)
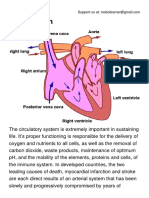
- The Circulatory System PDFDocument4 pagesThe Circulatory System PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Positive and Negative Feedback PDFDocument3 pagesPositive and Negative Feedback PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Cell Division PDFDocument8 pagesMitosis Cell Division PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- The Menstrual Cycle PDFDocument6 pagesThe Menstrual Cycle PDFPerry Sin100% (2)
- Male Reproductive System PDFDocument4 pagesMale Reproductive System PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction PDFDocument4 pagesSexual Reproduction PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Skin PDFDocument3 pagesSkin PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Life Hacks SpeechDocument1 pageLife Hacks SpeechKate EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- BHO - His Secret Agent Pretend Wife (Book 1)Document183 pagesBHO - His Secret Agent Pretend Wife (Book 1)Mae ZyzaleNo ratings yet
- BBM Business Ethics Assignment (FEB2020)Document10 pagesBBM Business Ethics Assignment (FEB2020)marwaNo ratings yet
- The Art of ChessDocument518 pagesThe Art of ChessSophie Germain100% (1)
- Concepts of Time in Post-War - PreviewDocument22 pagesConcepts of Time in Post-War - Preview方科惠No ratings yet
- Sally R. Munt - Cultural Studies and The Working Class (2000)Document254 pagesSally R. Munt - Cultural Studies and The Working Class (2000)josipavancasa100% (1)
- The Difference Between Educational Management and Educational Leadership and The Importance of Educational ResponsibilityDocument16 pagesThe Difference Between Educational Management and Educational Leadership and The Importance of Educational ResponsibilityKhalidJaferNo ratings yet
- Why Chinese Mothers Are SuperiorDocument1 pageWhy Chinese Mothers Are SuperiorBeyonce NorcioNo ratings yet
- Presence: An Exploration of Profound Change in People, Organizations and SocietyDocument8 pagesPresence: An Exploration of Profound Change in People, Organizations and SocietyPaul SchumannNo ratings yet
- Chordplay - The Chords of Death PDFDocument3 pagesChordplay - The Chords of Death PDFstorminsteNo ratings yet
- Rudolf Otto and The Concept of The NuminousDocument24 pagesRudolf Otto and The Concept of The NuminousRanjitDevGoswamiNo ratings yet
- Structuralism and SemioticsDocument31 pagesStructuralism and SemioticsSelegance Fortes100% (1)
- Daftar Peserta UkgDocument23 pagesDaftar Peserta UkgLatifahNo ratings yet
- Pronumele Şi Adjectivul Pronominal Demonstrativ În Limba Română Actuală Şi În Limba Arabă Modernă Standard - O Abordare CONTRASTIVĂ The Demonstrative Pronoun and The Demonstrative P..Document11 pagesPronumele Şi Adjectivul Pronominal Demonstrativ În Limba Română Actuală Şi În Limba Arabă Modernă Standard - O Abordare CONTRASTIVĂ The Demonstrative Pronoun and The Demonstrative P..Elena NancuNo ratings yet
- Thomas HobbesDocument23 pagesThomas HobbesImti LemturNo ratings yet
- Romantic America (Anglo American Literature)Document13 pagesRomantic America (Anglo American Literature)Elmer Pajarito BelarminoNo ratings yet
- The Life Cycle Completed (Erikson, Erik Homburger Erikson, Joan Mowat)Document122 pagesThe Life Cycle Completed (Erikson, Erik Homburger Erikson, Joan Mowat)Gustavo Ribeiro100% (1)
- 《道德经》中英对照 (林语堂)Document34 pages《道德经》中英对照 (林语堂)Jiajia LiNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Analysis of Paul Bowles's The Sheltering Sky.'Document20 pagesCognitive Analysis of Paul Bowles's The Sheltering Sky.'Alfred NgNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalysis in Modern Health PracticeDocument9 pagesPsychoanalysis in Modern Health PracticeMauroNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesThe Goat CyranicalNo ratings yet
- Takamatsu QuotesDocument3 pagesTakamatsu Quotespinkmedia100% (1)
- The Effect of Attitude and Religiosity On Tax Compliant Intention Moderated by The Utilization of e FilingDocument12 pagesThe Effect of Attitude and Religiosity On Tax Compliant Intention Moderated by The Utilization of e FilingHerry SugiantoNo ratings yet
- The Goal of Happiness: A Summary of Nicomachean Ethics: Tweet AristotleDocument6 pagesThe Goal of Happiness: A Summary of Nicomachean Ethics: Tweet AristotleCarla ConchaNo ratings yet
- Meditation Very Very EasyDocument52 pagesMeditation Very Very Easyrk singhNo ratings yet
- Jay's Recommended Structure For IELTS Writing Task-2Document2 pagesJay's Recommended Structure For IELTS Writing Task-2Khushraj SinghNo ratings yet
- The Litany (W20 Version)Document4 pagesThe Litany (W20 Version)J Halstead100% (1)
CXC Mathematics Tutorial: Author: John Spencer MBA (Dist), M. SC, B. SC
CXC Mathematics Tutorial: Author: John Spencer MBA (Dist), M. SC, B. SC
Uploaded by
Perry SinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CXC Mathematics Tutorial: Author: John Spencer MBA (Dist), M. SC, B. SC
CXC Mathematics Tutorial: Author: John Spencer MBA (Dist), M. SC, B. SC
Uploaded by
Perry SinCopyright:
Available Formats
Omega Omega Education Unit
cxcDirect Institute
CXC MATHEMATICS
Tutorial
Functions & Relations
Author: John Spencer MBA (Dist), M. Sc, B. Sc.
ormer Senior !ecturer and "ead o# Section$ Uni%ersit& o# 'echno(og& $ )amaica
ormer !ecturer * )ohn Dona(dson 'echnica( Institute $ 'rinidad
A(( rights reser%ed. +o ,art o# this document must -e re,roduced stored in a retrie%a(
s&stem, or transmitted in an& #orm or -& an& means, e(ectronic, mechanica(, ,hotoco,&ing,
recording or other.ise, .ithout the ,rior .ritten ,ermission o# the author.
/0/Direct Institute
Emai(: admin1cxcDirect.org
2e-site: ....cxcDirect.org
Math c(u- : htt,:33cxc(in4.56.#orumer.com3
'e(e,hone: 789 :9;$<885, 789 :9<$9=>;
irst ,rinted Octo-er <66;
cxcDirect Institute
cxcDirect Institute $ 789 :9;$<885
Emai(: admin1cxcdirect.org .e-site: ....cxcdirect.org Math c(u- : htt,:33cxc(in4.56.#orumer.com3 <
cxcDirect Institute
unctions ? @e(ations
/onsider t.o sets o# in#ormation .here the e(ements in
one set can -e (in4ed or has a connection to the
e(ements in the other set o# in#ormation.
Mathematica((& .e can sa& that a re(ation exist -et.een
the t.o sets.
Some exam,(es are :
A Menu items and ,rices.
A +ames and ages o# students in a c(ass
A Boo4s and their (ocation in a (i-rar&
A +ames and ,hone num-ers in a director&
A In,ut and out,ut e(ements o# #unctions
Each e(ement is the in,ut set B ca((ed the Domain, is
,aired or ma,,ed to one or more e(ements in the other
set ca((ed the @ange. 'his ,airing or ma,,ing is done
-ased on a s,eci#ic ru(e.
'he domain e(ement x is sometimes said to -e ma,,ed
unto the range e(ement.
x 5x=
'his notation is ca((ed a ma,,ing notation and is used
to descri-e the s,eci#ic ru(e used to ma, x unto 5x+1.
2e can a(so de#ine x as an in,ut %aria-(e and & as the
out,ut so that:
y = 5x + 1
or the a-o%e eCuation, the re(ation -et.een x and & #or
%a(ues o# x -et.een $< and D< is sho.n in the ta-(e
-e(o..
Each %a(ue o# x resu(ts in an out,ut & -ased on a
specific rule o# y = 5x+1.
'he (ast ro. o# the ta-(e, sho.s the (x, y) ,airs. +ote
that the ,airs are ordered, .hich is to sa& that x is
s,eci#ied as the #irst e(ement in the ,air, and y as the
(ast e(ement. B& ordering the ,airs, .e can easi(& sho.
the re(ation on a gra,h.
cxcDirect Institute $ 789 :9;$<885
Emai(: admin1cxcdirect.org .e-site: ....cxcdirect.org Math c(u- : htt,:33cxc(in4.56.#orumer.com3 >
A relation can be defined as
set of ordered pairs where each pair
has a specific rule of assin!ent"
x -2 -1 0 1 2
5x -10 -5 0 5 10
+1 1 1 1 1 1
y
-9 -4 1 6 11
( x, y ) ( -2, -9 ) ( -1, -4 ) ( 0, 1 ) ( 1, 6 ) ( 2, 11 )
cxcDirect Institute
T#pes of relations$
%ne to %ne Relation
I# each %a(ue o# x ma,s to onl# one %a(ue o# & then .e
ha%e a one to one re(ation.
Man# to one Relation
"ere .e see a case .here !ore than one
in,ut %a(ue x, ma,s to the same out,ut &.
Exam,(e: x E =.:= and x E $ =.:= -oth ma, to the
same out,ut & E <.
'his is an exam,(e o# a !an# to one re(ation.
%ne to Man# Relation
"ere .e see a case .here one in,ut %a(ue x, ma,s to
more than one out %a(ues o# &.
Exam,(e: x E :, ma,s to t.o ,ossi-(e out,uts:
& E <, or & E $ <.
'his is an exam,(e o# a one to !an# re(ation.
Man# to Man# Relation
"ere .e ha%e the case .here x is ,aired .ith one or
more e(ement in &, and a(so & is ,aired .ith one or
more e(ement in x gi%ing rise to a !an# to !an#
re(ation.
cxcDirect Institute $ 789 :9;$<885
Emai(: admin1cxcdirect.org .e-site: ....cxcdirect.org Math c(u- : htt,:33cxc(in4.56.#orumer.com3 :
& E x
<
1
2
3
4
5
11
22
33
34
45
y = x + 1
cxcDirect Institute
Functions
A function is a special type of relation.
2e de#ine a #unction as a re(ation .here each e(ement
in the in,ut set ma,s to one and onl# one ele!ent in
the out,ut set.
rom the three re(ations discussed ear(ier, .e can see
that the one to one re(ation and the man& to one
re(ation are #unctions. "o.e%er, in the one to man&
re(ation, an e(ement in the in,ut set can -e ma,,ed to
more than one out,ut e(ement, so the one to man&
re(ation is not a #unction.
An example of a function is the exchange rate between the
Canadian dollar and the US dollar
A sim,(e test #or a #unction is ca((ed a &ertical line test.
I# a %ertica( (ine cuts a gra,h at more that one ,oint,
then it is +ot a #unction.
+ot a #unction
'or(in with Functions
2e can %isua(iFe the #unction f re(ating t.o %aria-(es x
and y as a bloc( diara! as sho.n -e(o..
"ere x represents the do!ain e(ements a(so ca((ed the
independent &ariable or the input to the #unction
-(oc4.
Simi(ar(& y re,resents the rane ele!ents, a(so ca((ed
the dependent &ariable or in this case, the output.
So: y = f(x)
.here: f(x is ,ronounced: B f o# xG
n!b
f (6) means that &ou su-stitute x .ith 6 in #(x)
E)a!ple$ *"+
,i&en f(x) = x
2
- 4x +5-
2hat is the %a(ue o#:
a) f (6)
-) f ($ =)
c) f (>3<)
d) (>x)
e) f (= * x)
#) f (a)
Solution:
a) f(6) E (6)
<
* :(6) D 5 E 5
-) f($=) E ($=)
<
* :($=) D 5 E =6
c) f(>3<) E (>3<)
<
* :(>3<) D 5 E 53:
d) f("x # ("x
$
% &("x + 5 # 'x
$
% 1$x + 5
e f(1( x # (1( x
$
% &(1( x + 5
#(1( x(1(x % &(1(x + 5
#1 %x %x + x
$
( & +&x + 5
# x
$
+ $x+$
f f(a # a
$
% &a + 5
Exercise: 5.2
I# f (x) E <x
<
D :x * ; :
#ind:
a) f (<)
-) f ($ <)
c) f (=3<)
d) f (5x)
e) f (: $ x)
cxcDirect Institute $ 789 :9;$<885
Emai(: admin1cxcdirect.org .e-site: ....cxcdirect.org Math c(u- : htt,:33cxc(in4.56.#orumer.com3 5
f x y = f(x)
cxcDirect Institute
Composite Functions
)f the input to a function f, is another function g, then
the output combination of the two functions is called a
composite function!
'his can -e %isua(iFed using the -(oc4 diagram -e(o..
+ote that the in,ut to the #unction f is g(x), so the
out,ut .i(( -e f.g(x)/. So -& ,utting g(x) into #(x),
the resu(ting com,osite #unction is y = f (g(x)) .hich
can -e .ritten as fg(x).
'his is ,ronounced Bf of g of xG.
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
E)a!ple$ *"0
,i&en f (x) E <x D = and g(x) E x
<
$ =
.hat is the %a(ue o#:
a f g(x
b gf(x
c fg(*
d fg((1
e gf((1
Solution$
a) f(x # $x+1 and g(x # x
<
* =
so fg(x) + put g into f
# $(x
<
* =) D =
# $x
<
* < D =
i.e. f g(x E $x
$
% 1
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
b) now gf(x) + put f(x into g
# ($x + 1
$
( 1
# ($x + 1 ($x + 1 % 1
# &x
$
+ $x +$x+ 1 % 1
#&x
$
+ &x
so: gf(x) = 4(x
2
+ x)
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
no. f g(x E $x
$
% 1 ( obtained from (a abo-e
(c fg(* # $(*
$
% 1
# ( 1
(d fg((1 #$((1
$
% 1
# $(1 % 1 # 1
e gf(x #&(x
$
+ x !! obtained from (b
so gf((1 # &(((1
$
+ ((1
# &(1 + ((1
# *
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
E)ercise$ *"1
I# f (x) E <x $ =,
g(x) E >x D <, and h(x) E 5x,
.hat is the %a(ue o#:
a) fg(x)
-) fh(x)
c) gh(x)
d) gfh(x)
e) ghf(x)
cxcDirect Institute $ 789 :9;$<885
Emai(: admin1cxcdirect.org .e-site: ....cxcdirect.org Math c(u- : htt,:33cxc(in4.56.#orumer.com3 9
g x g(x) y = f( g(x) ) f
cxcDirect Institute
In&erse of a Function
'he in&erse o# a #unction is another #unction that
re%erses the o,eration o# the origina( #unction.
Mathematica((& .e sa& that a #unction is the in%erse o#
another #unction i#:
f
=
f x=x
2here f
(1
(x is de#ined as the in%erse o# f(x
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
The steps to find f
-1
(x) are$
=. Introduce a ne. %aria-(e & E #(x)
<. Interchange x and &
>. 'rans,ose the eCuation to ma4e & the su-Iect
:. 'he ne. resu(t #or & is no. the in%erse
#unction f
(1
(x
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
E)a!ple *"01$ Alebraic !anipulation
Ji%en f x=>x= K #ind f
=
x
Solution$
step 1 define. y # f(x
y # "x % 1
step $ )nterchange x and y
x # "y(1
step " /a0e y the sub1ect
y=
x=
>
step & replace y with f
-1
(x)
f
(1
(x#
x=
>
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
E)a!ple *"03$
Ji%en f x=
5x
<
> K #ind f
-1
(x)
Solution$
let y=
5x
<
>
then x=
5&
<
> interchange x and y
ma4e & the su-Iect:
x>=
5&
<
y=
< x >
5
replace y with f
-1
(x)
f
-1
(x) =
< x>
5
E)ercise$ *"4
ind the in%erse o# the #o((o.ing #unctions:
i) f x=x=
ii)
f x= x =
=
>
iii) f x=x
<
<x hint: #irst, com,(ete the sCuare
cxcDirect Institute $ 789 :9;$<885
Emai(: admin1cxcdirect.org .e-site: ....cxcdirect.org Math c(u- : htt,:33cxc(in4.56.#orumer.com3 8
cxcDirect Institute
In&erse of a co!posite function
E)a!ple *"1
Ji%en f x=
x=
x <
K and g x=x
<
ind:
=. f
=
g x
<. fg
=
x
>. f
=
g
=
x
:. 2hat is the %a(ue o# x #or .hich #(x) is unde#ined
So(ution:
f
=
g x ,ut g x into f
=
x
First- we need to find$ f
=
x
(et y= f x y=
x=
x<
Interchange x and & x=
y=
y<
Ma4e & the su-Iect:
x y<=y=
<xxy=y =
<x+==yxy
<x+==y (=x)
y=
<x+=
=x
replace & .ith f
=
( x)
gi%es: f
=
( x) E
<x+=
=x
no. .e must ,ut g ( x) into f
=
( x)
f
=
g ( x) E
<x
<
+=
=x
<
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
<. 'o #ind: ( fg)
=
( x)
'his reCuires t.o ste,s:
ste,=: ,ut g into # to get fg ( x)
ste,<: #ind the in%erse o# fg ( x)
Step+$
fg ( x) E f ( x)=
x
<
=
x
<
+<
.. ... g into #
Step0$ Find the in&erse$
(et: y=
x
<
=
x
<
+<
x=
y
<
=
y
<
+<
Interchange x and & :
x y
<
<=y
<
=
Ma4e & the su-Iect:
<x==y
<
=x
y
<
=
<x=
=x
y=
<x=
=x
re,(ace & .ith fg
=
x
fg
=
x E
<x=
=x
1"
f
=
g
=
x
in%erse o# g into the in%erse o# f
in%erse o# g E g
=
x E x
in%erse o# # E f
=
x E
<x=
=x
so : f
=
g
=
x E
< x=
=x
3" f ( x) is unde#ined #or %a(ues o# x .hich ma4es the
denominator E 6.
i# x E $ < , then #(x) is unde#ined
HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
E)ercise *"5 Ji%en:
f : x >x += K g : x <x and h : x x=
Find
i) gf
=
x K fgh
=
x
ii) sho. that gf
=
x = f
=
g
=
x
iii) gf
=
= K fgh
=
=8
cxcDirect Institute $ 789 :9;$<885
Emai(: admin1cxcdirect.org .e-site: ....cxcdirect.org Math c(u- : htt,:33cxc(in4.56.#orumer.com3 7
cxcDirect Institute
6sin the in&erse function to sol&e e7uations"
E)a!ple *"*
=. So(%e the eCuation -e(o. using the in%erse #unction:
5x<
x:
=;
<. 2hat is the %a(ue o# x #or .hich the #unction E 6
>. 2hat is the %a(ue o# x #or .hich the #unction is
unde#ined
8ote$ if f x=; 9 then x = f
=
;
:roof$
Ji%en$ f(x # '
then: f
=
f x= f
=
! ; ..mu(ti,(& -oth sides -& #
$=
(x)
-ut: f
=
f x=x
x = f
=
;
'his means that the so(ution x, is #ound su-stituting the %a(ue ; in
the in%erse o# the #unction.
Solution$
(et f x=
5x<
x:
Two steps are needed to sol&e$
Ste,= #ind the in%erse o# the #unction
Ste,< su-stitute the %a(ue ;
Step+. (#ind the in%erse * a(ge-raic method)
!et y=
5x<
x:
Interchange x and & x=
5&<
y:
Ma4e & the su-Iect:
xy:x=5&<
:x<=y 5x
y=
:x<
5x
f
=
x=
:x <
5x
Step2:
substitute 9 into the inverse function
: ;<
5;
;
>7
:
;
;.5
<. or the #unction to -e <ero the numerator must
-e Fero.
5x % <=6
x=</5
>. or the #unction to -e undefined, the
denominator must -e Fero.
x:=6 or .hen x= :
E)ercise *"=
gi%en h x=
8x=
x >
2hat is %a(ue o# x #or .hich the #unction:
=) is eCua( to Fero
<) is unde#ined
Use the in%erse #unction method to so(%e the eCuation
8x=
x >
=7
Answers
E)ercise$ *"0
a #2, b # ( ', c # ( 3!5
d # 5*x
$
+ $*x % '
e # $x
$
( $*x + "'
Acti&it#$ *"1
a # 3x+", b#1*x(1
e# 15x+$, d # "*x ( 1, e # "*x(1"
Acti&it#$ *"4
i) =x
<
ii) x
>
= iii) =x=
Acti&it#$ *"5
gf
=
x=
x <
9
K
fgh
=
x=
x8
9
gf
=
===/ < fgh
=
=8=5/ >
Acti&it#$ *"=
h
=
x=
>x=
8x
h
=
7=<5 K
h x=6 i# x E =38K h x is unde#ined i# x E $>
cxcDirect Institute $ 789 :9;$<885
Emai(: admin1cxcdirect.org .e-site: ....cxcdirect.org Math c(u- : htt,:33cxc(in4.56.#orumer.com3 ;
You might also like
- Unrequited Feelings (B, Leslie) (Z-Library)Document149 pagesUnrequited Feelings (B, Leslie) (Z-Library)bekoenergysave100% (3)
- After Democracy Imagining Our Political Future Zizi PapacharissiDocument149 pagesAfter Democracy Imagining Our Political Future Zizi PapacharissiBrandon RojasNo ratings yet
- FP1 Jan 2022 MSDocument21 pagesFP1 Jan 2022 MSCalixto JaxonNo ratings yet
- Math Paper 3 Practice MSDocument47 pagesMath Paper 3 Practice MSRaahish KalariaNo ratings yet
- CS2 B Chapters 4 and 5 - Markov Jump Processes - QuestionsDocument3 pagesCS2 B Chapters 4 and 5 - Markov Jump Processes - QuestionsJames AsesNo ratings yet
- 2007 2008S6FinalPmath 1Document4 pages2007 2008S6FinalPmath 1api-3742735No ratings yet
- Sense Organ PDFDocument5 pagesSense Organ PDFPerry Sin75% (4)
- Jean-Luc Marion-Cartesian Questions - Method and Metaphysics-University of Chicago Press (1999) PDFDocument226 pagesJean-Luc Marion-Cartesian Questions - Method and Metaphysics-University of Chicago Press (1999) PDFJuan Pablo CotrinaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Tutorial On Sequences & SeriesDocument7 pages2nd Tutorial On Sequences & Seriestoh tim lamNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods: Written Examination 2Document29 pagesMathematical Methods: Written Examination 2Kevin NguyenNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Question Bank Maths LDocument60 pagesDifferentiation Question Bank Maths LUmair Khan MarwatNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics: (Final Exam Revision)Document4 pagesProbability and Statistics: (Final Exam Revision)PHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNNo ratings yet
- Explanation (Arithmetic and Geometric)Document7 pagesExplanation (Arithmetic and Geometric)Jemyr Ann NavarroNo ratings yet
- Statistical Modeling of Extreme Values PDFDocument28 pagesStatistical Modeling of Extreme Values PDFHassanRazaNo ratings yet
- المعادلات التفاضلية الاعتياديةDocument150 pagesالمعادلات التفاضلية الاعتياديةخيرالله عبد حسين محمدNo ratings yet
- Lehmann Scheffe PDFDocument7 pagesLehmann Scheffe PDFBarnita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Surds and Indices: I. Laws of Indices: I) A Xa A (A) A (Ab) A BDocument19 pagesSurds and Indices: I. Laws of Indices: I) A Xa A (A) A (Ab) A BArunachalam NarayananNo ratings yet
- 12 Area Under CurvesDocument28 pages12 Area Under CurvesNathan Ha100% (1)
- 16 Quiz Review Quadratic EquationsDocument21 pages16 Quiz Review Quadratic EquationsdevikaNo ratings yet
- Linear Control Systems Lecture # 8 Observability & Discrete-Time SystemsDocument25 pagesLinear Control Systems Lecture # 8 Observability & Discrete-Time SystemsRavi VermaNo ratings yet
- VCE Unit 1 Specialist Maths Bound ReferenceDocument17 pagesVCE Unit 1 Specialist Maths Bound ReferenceMikiNo ratings yet
- Implicit DifferentiationDocument2 pagesImplicit DifferentiationAlicia TerrazasNo ratings yet
- State SpaceDocument20 pagesState SpacepattanayaksuchiNo ratings yet
- Complex Number Exercise Book PDFDocument26 pagesComplex Number Exercise Book PDFRitik KumarNo ratings yet
- 23-24 Y12 IB Quiz 3Document15 pages23-24 Y12 IB Quiz 33414642747No ratings yet
- Roots of Complex NumbersDocument3 pagesRoots of Complex NumbersntimalsinaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets ALL PDFDocument34 pagesProblem Sets ALL PDFLeroy ChengNo ratings yet
- Module 15 Trigonomeertric FunctionsDocument32 pagesModule 15 Trigonomeertric Functionsbakaraz7523027No ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument1 pageQuadratic EquationEmyRaNo ratings yet
- The Miller-Rabin Randomized Primality TestDocument10 pagesThe Miller-Rabin Randomized Primality TestHung Nguyen0% (1)
- W s-1 Factorizing Algebraic ExpressionsDocument2 pagesW s-1 Factorizing Algebraic Expressionsapi-253679034No ratings yet
- Controllability and Observability of Linear Time Invariant SystemsDocument31 pagesControllability and Observability of Linear Time Invariant SystemsumeshNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Descriptive Statistics (10 Marks)Document4 pagesAssignment 1: Descriptive Statistics (10 Marks)Malik Faizan100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - DifferentiationDocument56 pagesChapter 4 - DifferentiationTOBY RANNo ratings yet
- Observers For Non-Linear SystemsDocument35 pagesObservers For Non-Linear SystemsdvnccbmacbtNo ratings yet
- Binomial TheoremDocument3 pagesBinomial TheoremKelvin LimNo ratings yet
- Rouche's TheoremDocument9 pagesRouche's TheoremJeoff Libo-onNo ratings yet
- 04 Jackknife PDFDocument22 pages04 Jackknife PDFuniversedrillNo ratings yet
- Set 2 Linear InequalitiesDocument3 pagesSet 2 Linear InequalitiesGee Zainurdin100% (1)
- Business Mathematics Application Calculus To Solve Business ProblemsDocument51 pagesBusiness Mathematics Application Calculus To Solve Business ProblemsEida HidayahNo ratings yet
- A2T Practice - Test - Chapter - 9 SolutionsDocument9 pagesA2T Practice - Test - Chapter - 9 SolutionsSheryn MalayaNo ratings yet
- Permutations and CombinationsDocument48 pagesPermutations and CombinationsAnonymous auSpiAmZvnNo ratings yet
- Polynomial and Rational FunctionsDocument11 pagesPolynomial and Rational Functionsoana_brincoveanuNo ratings yet
- Maths3 PDFDocument5 pagesMaths3 PDFKunal KaranNo ratings yet
- BCS 012 MathsDocument431 pagesBCS 012 Mathssomeone someoneNo ratings yet
- 9 13 2016 1 1 1 Solving Puzzles in TeamsDocument2 pages9 13 2016 1 1 1 Solving Puzzles in Teamsapi-327140356No ratings yet
- IB Mathematics AA HL Questionbank - FunctionsDocument76 pagesIB Mathematics AA HL Questionbank - FunctionsMatias LandiNo ratings yet
- Logistics Regression ExerciseDocument2 pagesLogistics Regression ExerciseLakshmi NairNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: by Solomon BatiDocument59 pagesChapter Two: by Solomon BatiUsmaan GammachuuNo ratings yet
- Properties of Curves Worksheet Easy Problems 1Document9 pagesProperties of Curves Worksheet Easy Problems 1V NagarjunaNo ratings yet
- E7 Ordinary Differential Equation New - 0Document28 pagesE7 Ordinary Differential Equation New - 0Mor DepRzNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometry DoneDocument4 pagesInverse Trigonometry Donesourabh rajNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods Paper - 2013Document7 pagesNumerical Methods Paper - 2013Sourav PandaNo ratings yet
- MTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 5 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 2.6 To 3.5 Except 3.3Document10 pagesMTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 5 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 2.6 To 3.5 Except 3.3Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Discrete Math Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesDiscrete Math Exam QuestionsSandeep SajuNo ratings yet
- Binomial ExpansionsDocument5 pagesBinomial ExpansionsShafiqueDeshongNo ratings yet
- Final 2002F: InterpolationDocument3 pagesFinal 2002F: InterpolationmakrsnakminesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Koopman Operator Theory of Dynamical SystemsDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Koopman Operator Theory of Dynamical SystemsJimiao ZhangNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: CambridgeDocument8 pages9709 Mathematics: CambridgeanzaaariNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory Problems PDFDocument11 pagesProbability Theory Problems PDFPaun MihaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document23 pagesChapter 1Philimon TajemNo ratings yet
- I.S.F.D y T. #103: Profesorado de Técnicos Prof: Martín MellerDocument11 pagesI.S.F.D y T. #103: Profesorado de Técnicos Prof: Martín MellerAriel LeucipoNo ratings yet
- Summary On Relation FunctionDocument4 pagesSummary On Relation FunctionKenville JackNo ratings yet
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Course Outline: Course Title: Linear Algebra Course Code: EDME3201 (ME32A) Level: 3 Semester: 3 Credits: 3Document3 pagesCourse Outline: Course Title: Linear Algebra Course Code: EDME3201 (ME32A) Level: 3 Semester: 3 Credits: 3Perry SinNo ratings yet
- 3850 - Mathematics - Stage - 1 - Question - Paper - Set 1 PDFDocument19 pages3850 - Mathematics - Stage - 1 - Question - Paper - Set 1 PDFPerry Sin100% (1)
- 2004 Csec Chem Paper 01Document10 pages2004 Csec Chem Paper 01Perry SinNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorem Booklet PDFDocument16 pagesCircle Theorem Booklet PDFPerry Sin100% (1)
- Full Maths SbaDocument9 pagesFull Maths SbaPerry Sin86% (22)
- 7B ReproductionDocument31 pages7B ReproductionPerry Sin50% (2)
- Lesson Plan September 24 To 28Document19 pagesLesson Plan September 24 To 28Perry SinNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System PDFDocument3 pagesThe Nervous System PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- 3850 Mathematics Stage 1 Marking Guide Set 1Document1 page3850 Mathematics Stage 1 Marking Guide Set 1Perry SinNo ratings yet
- White Blood Cells (WBC) PDFDocument3 pagesWhite Blood Cells (WBC) PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Types of Neurons PDFDocument2 pagesTypes of Neurons PDFPerry Sin100% (2)
- The Circulatory System PDFDocument4 pagesThe Circulatory System PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Positive and Negative Feedback PDFDocument3 pagesPositive and Negative Feedback PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Cell Division PDFDocument8 pagesMitosis Cell Division PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- The Menstrual Cycle PDFDocument6 pagesThe Menstrual Cycle PDFPerry Sin100% (2)
- Male Reproductive System PDFDocument4 pagesMale Reproductive System PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction PDFDocument4 pagesSexual Reproduction PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Skin PDFDocument3 pagesSkin PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Life Hacks SpeechDocument1 pageLife Hacks SpeechKate EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- BHO - His Secret Agent Pretend Wife (Book 1)Document183 pagesBHO - His Secret Agent Pretend Wife (Book 1)Mae ZyzaleNo ratings yet
- BBM Business Ethics Assignment (FEB2020)Document10 pagesBBM Business Ethics Assignment (FEB2020)marwaNo ratings yet
- The Art of ChessDocument518 pagesThe Art of ChessSophie Germain100% (1)
- Concepts of Time in Post-War - PreviewDocument22 pagesConcepts of Time in Post-War - Preview方科惠No ratings yet
- Sally R. Munt - Cultural Studies and The Working Class (2000)Document254 pagesSally R. Munt - Cultural Studies and The Working Class (2000)josipavancasa100% (1)
- The Difference Between Educational Management and Educational Leadership and The Importance of Educational ResponsibilityDocument16 pagesThe Difference Between Educational Management and Educational Leadership and The Importance of Educational ResponsibilityKhalidJaferNo ratings yet
- Why Chinese Mothers Are SuperiorDocument1 pageWhy Chinese Mothers Are SuperiorBeyonce NorcioNo ratings yet
- Presence: An Exploration of Profound Change in People, Organizations and SocietyDocument8 pagesPresence: An Exploration of Profound Change in People, Organizations and SocietyPaul SchumannNo ratings yet
- Chordplay - The Chords of Death PDFDocument3 pagesChordplay - The Chords of Death PDFstorminsteNo ratings yet
- Rudolf Otto and The Concept of The NuminousDocument24 pagesRudolf Otto and The Concept of The NuminousRanjitDevGoswamiNo ratings yet
- Structuralism and SemioticsDocument31 pagesStructuralism and SemioticsSelegance Fortes100% (1)
- Daftar Peserta UkgDocument23 pagesDaftar Peserta UkgLatifahNo ratings yet
- Pronumele Şi Adjectivul Pronominal Demonstrativ În Limba Română Actuală Şi În Limba Arabă Modernă Standard - O Abordare CONTRASTIVĂ The Demonstrative Pronoun and The Demonstrative P..Document11 pagesPronumele Şi Adjectivul Pronominal Demonstrativ În Limba Română Actuală Şi În Limba Arabă Modernă Standard - O Abordare CONTRASTIVĂ The Demonstrative Pronoun and The Demonstrative P..Elena NancuNo ratings yet
- Thomas HobbesDocument23 pagesThomas HobbesImti LemturNo ratings yet
- Romantic America (Anglo American Literature)Document13 pagesRomantic America (Anglo American Literature)Elmer Pajarito BelarminoNo ratings yet
- The Life Cycle Completed (Erikson, Erik Homburger Erikson, Joan Mowat)Document122 pagesThe Life Cycle Completed (Erikson, Erik Homburger Erikson, Joan Mowat)Gustavo Ribeiro100% (1)
- 《道德经》中英对照 (林语堂)Document34 pages《道德经》中英对照 (林语堂)Jiajia LiNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Analysis of Paul Bowles's The Sheltering Sky.'Document20 pagesCognitive Analysis of Paul Bowles's The Sheltering Sky.'Alfred NgNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalysis in Modern Health PracticeDocument9 pagesPsychoanalysis in Modern Health PracticeMauroNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesThe Goat CyranicalNo ratings yet
- Takamatsu QuotesDocument3 pagesTakamatsu Quotespinkmedia100% (1)
- The Effect of Attitude and Religiosity On Tax Compliant Intention Moderated by The Utilization of e FilingDocument12 pagesThe Effect of Attitude and Religiosity On Tax Compliant Intention Moderated by The Utilization of e FilingHerry SugiantoNo ratings yet
- The Goal of Happiness: A Summary of Nicomachean Ethics: Tweet AristotleDocument6 pagesThe Goal of Happiness: A Summary of Nicomachean Ethics: Tweet AristotleCarla ConchaNo ratings yet
- Meditation Very Very EasyDocument52 pagesMeditation Very Very Easyrk singhNo ratings yet
- Jay's Recommended Structure For IELTS Writing Task-2Document2 pagesJay's Recommended Structure For IELTS Writing Task-2Khushraj SinghNo ratings yet
- The Litany (W20 Version)Document4 pagesThe Litany (W20 Version)J Halstead100% (1)