Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problems For Chapter 1 & 2 ANSWERS: 2xH 2 2xN 10 O 6
Problems For Chapter 1 & 2 ANSWERS: 2xH 2 2xN 10 O 6
Uploaded by
JibrilAttawarahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problems For Chapter 1 & 2 ANSWERS: 2xH 2 2xN 10 O 6
Problems For Chapter 1 & 2 ANSWERS: 2xH 2 2xN 10 O 6
Uploaded by
JibrilAttawarahCopyright:
Available Formats
Problems for Chapter 1 & 2 ANSWERS
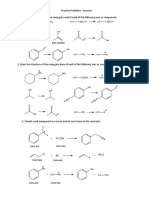
1. Draw an appropriate Lewis electron dot structure for the compound HONNH.
Valence electrons
2xH = 2
2xN = 10
O = 6
TOTAL = 18
H N N O H
2. Show the formal charge, if one exists, on each atom in the Lewis electron dot
structure at below:
HO
C
O
O
FC = 6-!/2(2) - 6 = -1
FC = 6-!/2(4) - 4 = O
FC = 4-!/2(8) - 0 = O
FC = 6-!/2(4) - 4 = )
3. Rewrite the structural formula, below, using a Kekule structure.
(CH
3
)
2
CHCH(CH
3
)CH=CHCH(OH)CH
3
C
CH
3
H
3
C
H
C
H
CH
3
C C
H H
C
H
O
CH
3
H
4. Show the three-dimensional structure for the compound, AlBr
3
. If the
compound has an overall dipole moment, show the direction of that dipole with
an arrow, +.
Br
Al
Br
Br
Trigonal Planar Shape
(flat, like a 3 bladed
propellar)
These two dipoles, have vectors which resolve into a
vector equal in magnitude to, but opposite direction to
the one pointing up...NO NET DIPOLE
5. Show the three-dimensional structure for the compound, NH
3
. If the compound
has an overall dipole moment, show the direction of that dipole with an arrow,
+.
H
N
H
H
NET DIPOLE
Pyramidal shape,
based on sp
3
nitrogen
6. Draw a Lewis dot structure for the following compounds, show formal charge
if any
a. CH
3
CH=O b. NH
4
+
N H H
H
H
C C O
H H
H
H
+1
7. Draw the Kekule structures for the above condensed structures.
H
C H
H
C
H
O
H
N H H
H
8. Draw the 3-D shape of each molecule, in question (6) above, about the
a. right carbon atom b. nitrogen
C O
H
CH
3
Trigonal Planar
H
N
H H
H
Tetrahedral
9. Name the 3-D shape of each molecule in question (6), about the:
a. right carbon atom b. nitrogen
Trigonal Planar Tetrahedral
10. Name the orbital hybridization for the compounds in question (6) above, about
the:
a. right carbon atom b. nitrogen
sp
2
sp
3
11. What will be the approximate bond angles in the molecules in question (6)
above, about the:
a. right carbon atom b. nitrogen
120 109
12. Carbon can exist in a trivalent state (three bonds) but neutral in charge. Predict
(show) the Lewis structure for such a carbon with all bonds to hydrogen.
H
C H
H
13. What orbital hybridization is likely for the carbon in the above species?
Remember that hybridized electrons are always paired (bonded or non-
bonded). Draw the carbon showing all orbitals.
H C
H
H
Carbon is sp
2
hybridized, with one p
orbital left for the unpaired electron
to reside in
14.Draw the Kekul structure for the skeletal drawing shown below.
C C
CH
3
CH
3
C C
H
H
H
H
H
H
CH
3
CH
3
H
C C
H
H
H
H
H
15.Draw the above compound in a condensed structure.
CH
3
CH
2
C[CH(CH
3
)
2
]C(CH
3
)
2
CH
2
CH
3
16. Show, with an arrow, the polar bonds and the direction of polarity in the
following molecules.
C C C C
O
CH
3
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
Cl
C C C C N
O H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
17. What will be the numerical value of the K
a
whose pK
a
is 4.2?
(You may use two different powers of ten as your answer.)
pKa = - Log Ka,
pKa = 4.2
Ka = 10
-4.2
= 0.00063
18 If a compound is 62.041% carbon and 10.412% hydrogen, what is its empirical
formula?
If there is 62.031% carbon and 10.412% hydrogen, there must be 27.547% oxygen
in sample.
In 100 g of sample there is: 62.041 g C, 10.412 g H and 27.547 g O.
In 100 g of sample there is: 62.041g/12.011 = 5.16 moles of Carbon,
10.412g/1.008 = 10.33 moles of Hydrogen
27.547g/15.999 = 1.72 moles of Oxygen
Molar ratio :C
5.16
, H
10.33
, O
1.72,
divide all by smallest ratio i.e. 1.72, formula becomes
C
3
H
6
O
19. Identify the acids and bases in the following equation.
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
O
+ CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
Li
+
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
3
CH
3
CH
2
CHCH
O
+
acid base conjugate base conjugate acid
20. The OH ion is the conjugate base of H
2
O. If water has a pKa of 15.7, which of
the following acids would be completely neutralized by NaOH? Circle them.
(Bold is correct answer)
Acid pKa
A 14
B 20
C 33
A-H +
-
OH A
-
+ H
2
O
B-H +
-
OH B
-
+ H
2
O
C-H +
-
OH C
-
+ H
2
O
pKa =14 pKa = 15.7
pKa = 15.7
pKa = 15.7
pKa =20
pKa =33
K
eq
K
eq
K
eq
K
eq
= 10
Pka(conj acid)
10
pKa (acid)
K
eq
= 10
1.7
K
eq
= 10
-4.3
K
eq
= 10
-17.3
21. Draw the following molecules in their three dimensional form and show, on the
structure, the following: (1) The polarity of each polar bond (>) and (2) The
overall polarity direction of the molecule (+>). If there is no molecular
dipole moment, circle the structure
CH
3
NH
2
BF
3
N
H
H
H
C
H
H
Net Dipole
B
F
F F
Dipole moments
Cancell
22. Compounds A and B, at right, have the same polar CN bond. However,
A has a dipole moment of 1.31 D while that of B is 2.11 D. Explain why B
has almost double the dipole moment of A. Illustrate your explination.
(Hint: Look at formal charges in structure B)
N
H
H
H
C
H
H
Net Dipole
N N N
H
C
H
H
Extremely large dipole
oriented toward negative charge
23. In each of the following chemical reactions, circle the acid and place an X
over the conjugate base.
CH
3
CH
2
OH + Na
+
CH
3
CH
3
CH
2
O
+
Na + CH
4
CH
3
CCH
2
CCH
3
+ NH
2
O O
CH
3
CCHCCH
3
+ NH
3
O O
AlCl
3
+ HCl AlCl
4
+ H
+
AlCl
3
+ NH
3
H
3
N
+
AlCl
3
X
X
X
Lewis Acid
24. Combustion analysis of an organic compound shows it to have 64.3% carbon
and 7.2% hydrogen. What is the emperical formula for the compound?
If there is 64.3% carbon and 7.2% hydrogen, there must be 28.5% oxygen in sample.
In 100 g of sample there is: 64.3 g C, 7.2 g H and 28.5 g O.
In 100 g of sample there is: 64.3g/12.011 = 5.35 moles of Carbon,
7.2g/1.008 = 7.14 moles of Hydrogen
28.5g/15.999 = 1.78 moles of Oxygen
Molar ratio :C
5.35
, H
7.14
, O
1.78,
divide all by smallest ratio i.e. 1.78, formula becomes C
3.00
H
4.01
O
C
3
H
4
O
25.Identify the Lewis acids and bases in the reactions of question (23).
CH
3
CH
2
OH + Na
+
CH
3
CH
3
CH
2
O
+
Na + CH
4
CH
3
CCH
2
CCH
3
+ NH
2
O O
CH
3
CCHCCH
3
+ NH
3
O O
AlCl
3
+ HCl AlCl
4
+ H
+
AlCl
3
+ NH
3
H
3
N
+
AlCl
3
Lewis Acid
Lewis acids are electron acceptors
Lewis Acid
Lewis Acid
Lewis Acid
Lewis bbases are electron donors
Lewis Base
Lewis Base
Lewis Base
Lewis Base
26.How can you explain the fact that the O-H bond in methanol(CH
3
-OH) is more
acidic than the C-H bonds.
Compare the conjugate bases which are formed when methanol (CH3-OH) acts
as an acid by breaking either the O-H or C-H bond:
H CH
3
O CH
3
O + H
+
Negative charge resides
on more electronegative
oxygen atom.
HOH
2
C H
HOH
2
C + H
+
Negative charge resides
on less electronegative
carbon atom.
The conjugate base with the negative charge on the oxygen is more stable
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms Focused Approach 3rd Edition Thomas R Gilbert Rein V Kirss Stacey Lowery Bretz Natalie FosterDocument37 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms Focused Approach 3rd Edition Thomas R Gilbert Rein V Kirss Stacey Lowery Bretz Natalie FosterChristianGonzalezsrybm100% (87)
- Electronic Configuration of ElementsDocument3 pagesElectronic Configuration of ElementsVeeresh Ananda Butti88% (17)
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Chapter 1 Org ChemDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Org ChemBheaBylRiveraNo ratings yet
- CH1O3 Questions PDFDocument52 pagesCH1O3 Questions PDFPrince T MashandaNo ratings yet
- 1 AllDocument18 pages1 AllMarcos ViníciusNo ratings yet
- 26 Petrucci10e CSMDocument44 pages26 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNo ratings yet
- CHM 1321 Assignment #2 - : AnswersDocument11 pagesCHM 1321 Assignment #2 - : AnswersSara YuenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ExrecicesDocument24 pagesChapter 2 Exrecicespaulinhagraebin100% (4)
- Assignment 7 and Practice Third Exam Solutions: C N S C N SDocument6 pagesAssignment 7 and Practice Third Exam Solutions: C N S C N SJoshua OndiegiNo ratings yet
- Ch1 2 3 ExercisesDocument11 pagesCh1 2 3 ExercisesMancini100% (1)
- 2,5-Dimethylheptane: Condensed Structural Formula (6 Points)Document4 pages2,5-Dimethylheptane: Condensed Structural Formula (6 Points)Andra AlNo ratings yet
- Bansal Classes Organic Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEEDocument477 pagesBansal Classes Organic Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEEAditya Kavuluri40% (5)
- Soln 2023 ChemDocument15 pagesSoln 2023 ChemSpaztick 10No ratings yet
- Kvs Sample Paper Chemistry Page 2 - 6Document5 pagesKvs Sample Paper Chemistry Page 2 - 6Rohan BaghelNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 Structure and BondingDocument19 pagesLab 01 Structure and BondingynottripNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document47 pagesChap 2h2300147No ratings yet
- BR BR BR: O-Bromotuloene P-Bromotuloene M-BromotuloeneDocument46 pagesBR BR BR: O-Bromotuloene P-Bromotuloene M-Bromotuloenejan100% (1)
- Ujian Pengukuhan 2 - SoalanDocument5 pagesUjian Pengukuhan 2 - SoalanDee -AdilaNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document15 pagesChap 2h2300021No ratings yet
- Chemistry 22: Some Notes On Chapter 10 Reactions: Y Y Y YDocument6 pagesChemistry 22: Some Notes On Chapter 10 Reactions: Y Y Y Yhairey947594No ratings yet
- Long Exam 1Document8 pagesLong Exam 1Allan DNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 AssignDocument7 pagesChap 1 AssignJianqi NiHao ChenNo ratings yet
- Aromatic It yDocument33 pagesAromatic It yHaris ANo ratings yet
- Chemistry Final ExamDocument4 pagesChemistry Final ExamIpshita pathakNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Chang 10th Edition 4Document1 pageChemistry - Chang 10th Edition 4Ayman MurrarNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry-JeeDocument33 pagesOrganic Chemistry-JeeRamesh Babu GarlapatiNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee Model Test - 3:: Paper - I: Time: 3 Hrs Max. Marks: 240 Ii YearDocument8 pagesIit Jee Model Test - 3:: Paper - I: Time: 3 Hrs Max. Marks: 240 Ii YearSayan Kumar KhanNo ratings yet
- Oganic Cem PDFDocument2 pagesOganic Cem PDFaulaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesHalimaNo ratings yet
- KTESP SEM 1 TRIAL 2017 With AnswerDocument7 pagesKTESP SEM 1 TRIAL 2017 With AnswerShima SenseiiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 - Organic Chemistry Important Questions 2022-23Document15 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 - Organic Chemistry Important Questions 2022-23Divye DasNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document8 pagesProblem Set 2Katrina Louise GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Structure and Bonding:Acids and BasesDocument12 pagesChapter 1-Structure and Bonding:Acids and BasesANTON JOSHUA G. LAPINIGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document18 pagesChapter 10Khaled NaseerNo ratings yet
- CHM 1321 Assignment 4 AnswersDocument12 pagesCHM 1321 Assignment 4 AnswersSara YuenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic PrinciplesDocument29 pagesChapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic PrinciplesYash PlayNo ratings yet
- Combined OrganicDocument82 pagesCombined OrganicSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones For IitjeeDocument65 pagesAldehydes and Ketones For Iitjeevarundhall1994No ratings yet
- Quiz1 1ANSDocument1 pageQuiz1 1ANSabubakarabubakarbah563No ratings yet
- Work Book (Phase - IV) : SubjectiveDocument21 pagesWork Book (Phase - IV) : SubjectiveAshwani Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Chem52 Su13 PracticeExam1ADocument11 pagesChem52 Su13 PracticeExam1Aamarka01No ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 PDFDocument2 pagesProblem Set 1 PDFLouisNo ratings yet
- ReactionsDocument5 pagesReactionsYeKwon Patrick HuhNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry H2 Questions MCQDocument15 pagesOrganic Chemistry H2 Questions MCQkitonium100% (1)
- OrganicDocument6 pagesOrganicTrent SwordsNo ratings yet
- STPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Paper 1 (SMJK Sam Tet Ipoh)Document9 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Paper 1 (SMJK Sam Tet Ipoh)sherry_christyNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Estructura MolecularDocument4 pagesEjercicios Estructura MolecularDANNANo ratings yet
- Putting Together Organic Molecules: Death Taxes andDocument31 pagesPutting Together Organic Molecules: Death Taxes andIvan BuljanNo ratings yet
- NTU CB1117 Tutorial 1Document3 pagesNTU CB1117 Tutorial 1cassidychandidiNo ratings yet
- CHM 1321 Assignment 1 Answers: CN H H H H HDocument10 pagesCHM 1321 Assignment 1 Answers: CN H H H H HSara YuenNo ratings yet
- Final Exam KeyDocument12 pagesFinal Exam KeykitthiNo ratings yet
- Allen Allen330Document192 pagesAllen Allen330Fatimah Ali AfrozNo ratings yet
- The Problem Set of The Four Rounds: ProblemsDocument29 pagesThe Problem Set of The Four Rounds: ProblemsMinh TieuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Orgnic ChemistryDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Orgnic ChemistryladybugNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Uop Merox Process: G. A. DziabisDocument13 pagesUop Merox Process: G. A. Dziabisespectrox07No ratings yet
- Catalogo Weston 2016Document55 pagesCatalogo Weston 2016daxmeNo ratings yet
- Soalan No 9 PPT Ting 4 3023Document6 pagesSoalan No 9 PPT Ting 4 3023Asma ZainalNo ratings yet
- A Review On Preparation, Characterization, Properties and ApplicationsDocument20 pagesA Review On Preparation, Characterization, Properties and ApplicationsAnonymous ND2SsqkXCeNo ratings yet
- Effect of Type of Acid Used in Direct Acidification Procedures On Moisture, Firmness, and Calcium Levels of CheeseDocument4 pagesEffect of Type of Acid Used in Direct Acidification Procedures On Moisture, Firmness, and Calcium Levels of CheesemanushaNo ratings yet
- Câu Hỏi Thi FinalDocument12 pagesCâu Hỏi Thi FinalDuy Do MinhNo ratings yet
- A Wheel Used For Cutting, Grinding, or Finishing Metal or Other Objects, and Typically Made of Abrasive Particles Bonded TogetherDocument4 pagesA Wheel Used For Cutting, Grinding, or Finishing Metal or Other Objects, and Typically Made of Abrasive Particles Bonded TogetherSofyan HadiNo ratings yet
- TDS Salcare SC96Document4 pagesTDS Salcare SC96Carmen LinaresNo ratings yet
- State of The Art Review On Efficacy of Xanthan Gum and Guar Gum Inclusion On The Engineering Behavior of SoilsDocument14 pagesState of The Art Review On Efficacy of Xanthan Gum and Guar Gum Inclusion On The Engineering Behavior of SoilsvydehiNo ratings yet
- High Pressure System Boiler Water Chemical Dosing Calculations (Coal F - Industrial Professionals - CheresourcesDocument3 pagesHigh Pressure System Boiler Water Chemical Dosing Calculations (Coal F - Industrial Professionals - Cheresourcescepong89No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document16 pagesChapter 7alyalaswad4445No ratings yet
- Single Step Synthesis of Strigolactone Analogues From Cy 2011 Bioorganic MDocument6 pagesSingle Step Synthesis of Strigolactone Analogues From Cy 2011 Bioorganic MRigotti BrNo ratings yet
- 12 ElicheDocument11 pages12 ElicheAli SherNo ratings yet
- 8 Redox Reactions: SolutionsDocument22 pages8 Redox Reactions: SolutionsAnil AggaarwalNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation and Its CompositionDocument22 pagesUrine Formation and Its CompositionZahidKhanNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Lecture 3 Angular Overlap: I. Ligand Field Theory and Square Planar ComplexesDocument16 pagesCH 10 Lecture 3 Angular Overlap: I. Ligand Field Theory and Square Planar ComplexesIsrael PobleteNo ratings yet
- Xii Chemistry Holiday HWDocument3 pagesXii Chemistry Holiday HWtwinkleparmar0064No ratings yet
- Piezoresistive Sensors 11-4-2011Document21 pagesPiezoresistive Sensors 11-4-2011Dan HoovlerNo ratings yet
- Mister-Fix Non Shrinkage 410VGMDocument2 pagesMister-Fix Non Shrinkage 410VGMIsrael ExporterNo ratings yet
- Eastman™ DP SolventDocument2 pagesEastman™ DP SolventRajNo ratings yet
- Bonding Structure and Periodicity Assessed HW MsDocument10 pagesBonding Structure and Periodicity Assessed HW MsKizzy Anne Boatswain CarbonNo ratings yet
- MetablosimDocument17 pagesMetablosimM IrfanNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergerticsDocument24 pagesChemical EnergerticsAnotidaishe ChakanetsaNo ratings yet
- Metodos Cuantificar Alteracion HidrotermalDocument27 pagesMetodos Cuantificar Alteracion HidrotermalIrvingNo ratings yet
- Nanomaterials and Their Applications in Healthcare: Sangeeta N. KaleDocument54 pagesNanomaterials and Their Applications in Healthcare: Sangeeta N. Kalepriyaibt6269No ratings yet
- Topic 4 Intermolecular ForcesDocument2 pagesTopic 4 Intermolecular ForcesNgoc TranNo ratings yet
- JEE MAIN AND ADVANCED Chapterwise PYQ Chemistry Prabhat Publication PDFDocument413 pagesJEE MAIN AND ADVANCED Chapterwise PYQ Chemistry Prabhat Publication PDFk p rathour100% (4)
- Caffeine Determination by HPLCDocument3 pagesCaffeine Determination by HPLCnga_yan0% (1)
- High Performance Thin Layer ChromatographyDocument42 pagesHigh Performance Thin Layer ChromatographySadhan PadhiNo ratings yet