Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Yearly Plan SC Year 4
Yearly Plan SC Year 4
Uploaded by
ajibCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Catapult CalculationsDocument2 pagesCatapult Calculationsbridgetd14100% (4)
- Yearly Plan Science Year 4Document16 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 4Kom Mathi BalaNo ratings yet
- Science Yearly Plan 4 2011Document12 pagesScience Yearly Plan 4 2011Zulkhairi AbidinNo ratings yet
- First Term Science Year 5 Yearly Plan Themes A: Investigating Living ThingsDocument24 pagesFirst Term Science Year 5 Yearly Plan Themes A: Investigating Living ThingsXgeniusXNo ratings yet
- Yearlyplanning Science Year5Document6 pagesYearlyplanning Science Year5Satia KumarNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Yearly PlanDocument14 pagesScience 5 Yearly PlanSri GanggaNo ratings yet
- Jsu Pat SN Yr 4Document17 pagesJsu Pat SN Yr 4lennypowdziNo ratings yet
- Science Year 5 Yearly PlanDocument7 pagesScience Year 5 Yearly Plan惠鑫No ratings yet
- Theme: Investigating Living Things Learning Area Learning Objective Learning OutcomeDocument8 pagesTheme: Investigating Living Things Learning Area Learning Objective Learning OutcomewmpejonNo ratings yet
- TMK Yr2Document73 pagesTMK Yr2Rosnita Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Document7 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 5Aceley JainuddinNo ratings yet
- RPT Sains THN 5 - 2012Document9 pagesRPT Sains THN 5 - 2012zan75No ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Document5 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 5azmnqiinNo ratings yet
- Week Learning Area Learning Objectve Learnng Outcomes Scientfc Process Skills & Thinking SkillDocument7 pagesWeek Learning Area Learning Objectve Learnng Outcomes Scientfc Process Skills & Thinking SkillDinamaniYeogesNo ratings yet
- Year Four Science Scheme of Work: Semester IDocument9 pagesYear Four Science Scheme of Work: Semester IEzhilita EzhillNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Document7 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 5Burhan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Grade 5, Science CurriculumDocument3 pagesGrade 5, Science CurriculumJoel C. Yuvienco67% (3)
- Integrated ScienceDocument6 pagesIntegrated Scienceiteachclassroom100% (2)
- Borang Kontrak Latihan Murid: Nama Guru: Azah Afnan Shamsudin Mata Pelajaran: Sains Tahun: 4BDocument3 pagesBorang Kontrak Latihan Murid: Nama Guru: Azah Afnan Shamsudin Mata Pelajaran: Sains Tahun: 4Banon_314646649No ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Year 5 Science 2008Document5 pagesYearly Plan Year 5 Science 2008marccw2000No ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Science Year 5Document4 pagesScheme of Work Science Year 5murniNo ratings yet
- Kontrak Latihan Murid Tahun6Document2 pagesKontrak Latihan Murid Tahun6Sue Suemanie TicerNo ratings yet
- Science StandardsDocument2 pagesScience Standardsapi-369625583No ratings yet
- RPT SC Yr5 2011Document6 pagesRPT SC Yr5 2011gurlzmiuraNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Cambridge o Level BiologyDocument12 pagesSyllabus Cambridge o Level BiologyNisha AliyaNo ratings yet
- Engineering, Technology, and The Applications of Science: Standards Science Fusion National (2012) Grade 4Document9 pagesEngineering, Technology, and The Applications of Science: Standards Science Fusion National (2012) Grade 4IbrahimMohammedNo ratings yet
- Science Competencies For Grade 1Document5 pagesScience Competencies For Grade 1KAT DANTESNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Document5 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 5wawa2006No ratings yet
- 2021 3rd Science g8 em 1Document9 pages2021 3rd Science g8 em 1SumuduMPereraNo ratings yet
- Round 1Document25 pagesRound 1bakosua141No ratings yet
- Enabling and Enrichment Competencies For Science Melcs (Most Essential Learning Competencies)Document49 pagesEnabling and Enrichment Competencies For Science Melcs (Most Essential Learning Competencies)Zea May BiasNo ratings yet
- F2C3 - BiodiversityDocument11 pagesF2C3 - BiodiversitytankiuNo ratings yet
- Theme / Learning Area / Learning Objective EkstrapolationDocument21 pagesTheme / Learning Area / Learning Objective EkstrapolationMary Dorris JohnNo ratings yet
- Variety of Living Things and Their ClassificationDocument11 pagesVariety of Living Things and Their ClassificationAyuni100% (1)
- Yr5 Science Specification 2012Document17 pagesYr5 Science Specification 2012Norazura ZuraNo ratings yet
- Activitysheets5 2Document11 pagesActivitysheets5 2Benmar L. OrterasNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan 2011 Science Y5Document4 pagesYearly Plan 2011 Science Y5Mohd ZulkarnainNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER ONE: A View of Life: 1.1 How To Define LifeDocument60 pagesCHAPTER ONE: A View of Life: 1.1 How To Define LifeIngrid Dominique P. SanchezNo ratings yet
- Week Theme Learning Area Learning Objectve Learnng Outcomes: Scientfc Process Skills & Thinking SkillDocument4 pagesWeek Theme Learning Area Learning Objectve Learnng Outcomes: Scientfc Process Skills & Thinking SkillThamil ArasiNo ratings yet
- Year Planner SC Yr 6Document8 pagesYear Planner SC Yr 6ccqwanNo ratings yet
- Science Competencies in 5th and 6th Grade With Table of SpecificationsDocument25 pagesScience Competencies in 5th and 6th Grade With Table of SpecificationsTerence Pelingon89% (18)
- Investigating Living Things LA: 1. Interaction Among Living ThingsDocument11 pagesInvestigating Living Things LA: 1. Interaction Among Living ThingsCikgunazrisksac BasirunNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan - Science Year 2Document10 pagesYearly Plan - Science Year 2siah.ameer5382No ratings yet
- LAS - Final Term - Eartrh and Life 2021-2022Document28 pagesLAS - Final Term - Eartrh and Life 2021-2022Az BacligNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologyiteachclassroom100% (2)
- Science Form 3 2016 Year Plan: SMK (L) Methodist Kuala LumpurDocument13 pagesScience Form 3 2016 Year Plan: SMK (L) Methodist Kuala LumpurkriizNo ratings yet
- Biology Syllabus For Secondary Schools Form I-IV in Tanzania, 2010 EditionDocument14 pagesBiology Syllabus For Secondary Schools Form I-IV in Tanzania, 2010 EditionhanspopeNo ratings yet
- Basic ScienceDocument8 pagesBasic SciencemetahelpcentermanagementNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan - Science Year 2Document9 pagesYearly Plan - Science Year 2Muhammad Azrieen SamsudinNo ratings yet
- WASSCE WAEC Integrated Science Syllabus PDFDocument24 pagesWASSCE WAEC Integrated Science Syllabus PDFKojo Yeboah Enchill100% (1)
- Which Snake Plant Is The Best Air Cleanser? (A Comparative of Snake Plants in Purifying The Polluted Air: Sansievera Plant vs. Aloe Vera Plant)Document16 pagesWhich Snake Plant Is The Best Air Cleanser? (A Comparative of Snake Plants in Purifying The Polluted Air: Sansievera Plant vs. Aloe Vera Plant)Phillip BernaldezNo ratings yet
- Biology Ecology Revision NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Ecology Revision NotesGeorge ArgyrouNo ratings yet
- Teacher Support Manual With Elective EnglishDocument260 pagesTeacher Support Manual With Elective EnglishVal CortesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan STD 6 ScienceDocument3 pagesLesson Plan STD 6 ScienceVijay ManogaranNo ratings yet
- Bank RPHDocument33 pagesBank RPHWAN NAZRINA BINTI WAN NAWAWI MoeNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 / Year 10 Biology Course Syllabus 2020-2021course Outline Term 1Document8 pagesGrade 9 / Year 10 Biology Course Syllabus 2020-2021course Outline Term 1CanioNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives 1. Animals Pupils Should LearnDocument6 pagesLearning Objectives 1. Animals Pupils Should LearnSeashellcrabNo ratings yet
- Practical Field Ecology: A Project GuideFrom EverandPractical Field Ecology: A Project GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Microbiology of AerosolsFrom EverandMicrobiology of AerosolsAnne-Marie DelortNo ratings yet
- Anggaran Bajet Hi-Tea BKGK 2018Document1 pageAnggaran Bajet Hi-Tea BKGK 2018ajibNo ratings yet
- Multiplication Crazy GridsDocument1 pageMultiplication Crazy Gridsajib0% (1)
- Group Lawatan KLCC 2014Document1 pageGroup Lawatan KLCC 2014ajibNo ratings yet
- Learning WalkDocument10 pagesLearning WalkajibNo ratings yet
- The Year 5/6 Science Quiz: Part TwoDocument42 pagesThe Year 5/6 Science Quiz: Part TwoajibNo ratings yet
- Simplify This Fractions Simplify This FractionsDocument1 pageSimplify This Fractions Simplify This FractionsajibNo ratings yet
- Thevenin and Norton EquivalentsDocument36 pagesThevenin and Norton EquivalentsJosé Guillermo De Chomón AranguenaNo ratings yet
- Measurements of Dielectric Constant of Solid Material (Leather Belt) at X-Band and Proposed Wearable AntennaDocument5 pagesMeasurements of Dielectric Constant of Solid Material (Leather Belt) at X-Band and Proposed Wearable AntennaIJMERNo ratings yet
- TechDaten Man 7SK85 V0750 enUSDocument180 pagesTechDaten Man 7SK85 V0750 enUSAnonymous dH3DIEtzNo ratings yet
- Basics of Medium-Voltage Wiring - SolarPro MagazineDocument18 pagesBasics of Medium-Voltage Wiring - SolarPro MagazinehariNo ratings yet
- RSO TestingDocument19 pagesRSO TestingAntonio DsfvsdcNo ratings yet
- 1 Ren APl HDocument350 pages1 Ren APl HKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Worksheet (AS)Document4 pagesWorksheet (AS)Mahad AsimNo ratings yet
- Branches of Architectural AcousticsDocument26 pagesBranches of Architectural AcousticsGanie MhooreNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase-Inductionmotor With Squirrel Cage Rotor: P U F I N MDocument1 pageThree-Phase-Inductionmotor With Squirrel Cage Rotor: P U F I N MveemandalNo ratings yet
- Stokes' and Newton's Viscous DragDocument7 pagesStokes' and Newton's Viscous DragL V SatyavathiNo ratings yet
- Break It Apart Technical ReportDocument9 pagesBreak It Apart Technical Reportapi-347850579No ratings yet
- Differentiating Circuit and Integrating Circuit - Electronics PostDocument5 pagesDifferentiating Circuit and Integrating Circuit - Electronics Postmishba kNo ratings yet
- Sample Training MatrixDocument4 pagesSample Training MatrixTeckii MSOfficeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document10 pagesUnit 1lg481476114No ratings yet
- MHD PropulsionDocument10 pagesMHD PropulsionAbdullah BölekNo ratings yet
- Civil-Vi-Hydraulic Structures and Irrigation Design-Drawin (10CV65) - Notes PDFDocument93 pagesCivil-Vi-Hydraulic Structures and Irrigation Design-Drawin (10CV65) - Notes PDFRavi Kumar85% (27)
- Manual Metal Arc Welding or Shielded Metal Arc WeldingDocument19 pagesManual Metal Arc Welding or Shielded Metal Arc WeldingLâm ThanhNo ratings yet
- Lecture Antenna MiniaturizationDocument34 pagesLecture Antenna MiniaturizationJuhi GargNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Electricity Magnetism & SemiconductorsDocument38 pagesUnit 2 Electricity Magnetism & SemiconductorsBharat JadhavNo ratings yet
- Engg Mechanics Question Bank UNIT-1Document10 pagesEngg Mechanics Question Bank UNIT-1Thiyagarajan GurusamyNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Structures (Methods of Joints and Sections)Document53 pagesStructures (Methods of Joints and Sections)Edreno Olpino Jr.100% (1)
- PDFDocument250 pagesPDFMarvellousNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Current Electricity Part 1Document20 pagesChapter 16 - Current Electricity Part 1api-275374056No ratings yet
- EE Lab#08 Group#04Document11 pagesEE Lab#08 Group#04Maida IrshadNo ratings yet
- IPC Digital Coulombmeter ExperimentsDocument9 pagesIPC Digital Coulombmeter Experimentslev76No ratings yet
- Technical and Vocational Education Faculty: Engineering Education Department (JPK)Document27 pagesTechnical and Vocational Education Faculty: Engineering Education Department (JPK)Farahnasuhaa JamilNo ratings yet
- Chtest8 SolutionDocument9 pagesChtest8 SolutionMaulitaNo ratings yet
- SACE Isomax PDFDocument28 pagesSACE Isomax PDFdwiyanto73No ratings yet
Yearly Plan SC Year 4
Yearly Plan SC Year 4
Uploaded by
ajibOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Yearly Plan SC Year 4
Yearly Plan SC Year 4
Uploaded by
ajibCopyright:
Available Formats
http://www.skmaklagam.
com
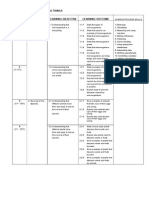
YEARLY PLAN SCIENCE YEAR 4
WEEK
THEMES
LEARNING
AREA
1.Investigating 1.0 Living things
have basic
Living Things
needs
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
SCIENCE
PROCESS SKILLS
1.1 Understanding 1.1.1 identify the basic needs
that humans have of humans
basic needs
1.1.2 give reasons why
humans need food, water, air
and shelter
observing,
predicting
making
inferences
communicating
1.2 Understanding
that animals have
basic needs
1.2.1 identify the basic needs
of animals
1.2.2 give reasons why animals
need food, water, air and
shelter
describe types of shelters for
animals
observing,
making
inferences,
communicating
1.3 Understanding
that plants have
basic needs
1.3.1 identify the basic needs
of plants
observing,
making
inferences,
communicating,
predicting, using
time relationship
http://www.skmaklagam.com
2.0 Living things
undergo life
process
2.1 Analysing life
processes in
humans
2.1.1 explain that humans
breathe
2.1.2 describe what inhale is
2.1.3 describe what exhale is
2.1.4 differentiate the air that
we inhale and the air that we
exhale
observing,
communicating,
1.Investigating 2.0 Living things
undergo life
Living Things
processes
2.1 Analysing life
processes in
humans
2.1.5 state that humans use
lungs to breathe
2.1.6 identify the passage of
air during breathing
2.1.7 conclude that not all
individuals have the same
rate of breathing
observing,
communicating,
measuring and
using numbers
2.1.8 state that humans
excrete and defecate
2.1.9 state the products of
human excretion
2.1.11 give reasons why
humans need to excrete and
defecate
observing,
communicating,
making
inferences
http://www.skmaklagam.com
2.2 Being aware
that certain
behaviour can
disturb life
processes
2.2 Being aware
that certain
behaviour can
disturb life
processes
2.1.12 state that humans
respond to stimuli
2.1.13 give reasons why
humans respond to stimuli
2.1.14 state that humans
reproduce
2.1.15 predict what will
happen if humans do not
reproduce
observing,
communicating,
making
inferences,
predicting
2.2.1 give examples of habits
that bring harm to human life
processes
2.2.2 state the effects of
smoking on lungs
observing,
communicating
2.2.3 explain that taking drugs
and alcohol can delay a
persons response to stimuli
2.2.4 participate in a
campaign to discourage
smoking, drugs taking and
alcohol drinking among their
peers
http://www.skmaklagam.com
1.Investigating 2.0 Living things
undergo life
Living Things
processes
2.3 Analysing the
life processes in
animals
10
11
1.Investigating 2.0 Living things
undergo life
Living Things
2.4 Understanding
the life processes
4
2.3.1 state that animals
excrete
2.3.2 state that animals
defecate
2.3.3 give reasons why animals
need to excrete and
defecate
2.3.4 state that animals
breathe
2.3.5 identify the breathing
organs for certain animals
2.3.6 state that breathing
organs for different types of
animals may be different
observing,
making
inferences,
communicating,
2.3.7 state animals reproduce
2.3.8 state that some animals
give birth and some lay eggs
2.3.9 classify animals
according to the way they
reproduce
2.3.10 describe the life cycles
of different animals
2.2.11 state that animals may
have different life cycles
observing,
classifying
communicating,
using space time
relationship
2.4.1 state that plants respond
to stimuli
observing,
communicating,
http://www.skmaklagam.com
processes
in plants
2.4.2 identify the part of plant
that responds to water
2.4.3 identify the part of plant
that responds to gravity
2.4.4 identify the part of plant
that responds to sunlight
2.4.5 identify the part of plant
that responds to touch
12
13
3.0 Animals
and plants
protect
themselves
3.1 Understanding
that animals have
specific
characteristics
and behaviour to
protect
themselves from
danger
2.4.6 state that plants
reproduce
2.4.7 explain why plants need
to reproduce
2.4.8 predict what will happen
to the world if plants do not
produce
2.4.9 explain the various ways
plants reproduce
observing,
making
inferences,
predicting
communicating
3.1.1 identify special
characteristics of animals that
protect them from danger
3.1.2 identify special
behaviour of animals that
protect them from danger
3.1.3 describe how the special
characteristics and behaviour
of animals help to protect
them from danger
observing,
communicating,
interpreting data
http://www.skmaklagam.com
14
15
16
1.Investigating 3.0 Animals
and plants
Living Things
protect
themselves
3.2 Understanding
that animals have
specific
characteristics
and behaviour to
protect
themselves from
extreme weather
3.2.1 identify specific
characteristics and behaviour
of animals that protect them
from very hot or cold weather
3.2.2 describe how specific
characteristics and behaviour
of animals help to protect
them from very hot or cold
weather
observing,
interpreting
data,
communicating
3.3 Understanding
that animals have
specific
characteristics
and behaviour to
enable them to
survive
3.3.1 recognise the need for
animals to protect themselves
from enemies and extreme
weather
3.3.2 make a model of an
imaginary animal that can
survive both extreme weather
and enemies
3.3.3 give reasons why models
are built in such ways
observing,
making
inferences,
communicating
3.4 Understanding
that plants have
specific
characteristics to
protect
themselves from
3.4.1 identify the specific
characteristics of plants that
protect them from enemies
3.4.2 describe how the
specific characteristics of
plants help to protect them
observing,
communicating
interpreting data
http://www.skmaklagam.com
17
1.Investigating 3.0 Animals
and plants
Living Things
protect
themselves
enemies
from enemies
3.5 Understanding
that plants have
specific
characteristics to
protect
themselves from
dry region and
strong wind
3.5.1 give example of plants
found in very dry region
3.5.2 identify specific
characteristics of plants that
protect them from excessive
loss of water
3.5.3 describe how specific
characteristics of plants help
them to survive in dry region
observing,
communicating
interpreting data
3.5.4 give examples of plants
found in strong wind area
3.5.5 identify specific
characteristics of plants that
protect them from strong
winds
3.5.6 describe how specific
characteristics of plants help
them to survive in strong winds
observing
communicating
interpreting data
1.1.1 state the different ways
to measure length
1.1.2 state the standard unit
for length in the metric system
1.1.3 choose the appropriate
measuring tools to measure
observing,
measuring and
using numbers,
communicating,
using space-time
relationship,
18
19
2.
Investigating
Force and
Energy
1.0
Measurement
1.1 Understanding
the measurement
of length
http://www.skmaklagam.com
20
21
2.
Investigating
Force and
Energy
1.0
Measurement
length
1.1.4 measure length using the
correct technique
1.1.5 record lengths in metric
system
defining
operationally
1.2 Understanding
how to calculate
area
1.2.1 compare a square and
a rectangle and guess which
object has a bigger area
1.2.2 carry out a test to
confirm their guesses
1.2.3 state that area = length
width
1.2.4 state the standard unit
for area in the metric system
1.2.5 calculate the area of a
given shape in metric system
observing,
measuring and
using numbers,
communicating,
using space-time
relationship,
defining
operationally
1.3 Understanding
how to measure
the volume of
solid
1.3.1 compare a cube and a
cuboid and
guess which object has a
bigger volume
1.2.2 carry out a test to
confirm their guesses
1.2.3 state that volume =
length width height
1.2.4 state the standard unit
for volume in the metric
system
observing,
measuring and
using numbers,
communicating,
using space-time
relationship,
defining
operationally
http://www.skmaklagam.com
1.2.5 calculate the volumes of
cubes and cuboids based on
the measurements taken in
metric system
22
1.4 Understanding
how to measure
volume of liquid
1.4.1 state the different ways
to measure the volume of a
liquid
1.4.2 state the standard unit
for volume of liquids in the
metric system
1.4.3 choose the appropriate
measuring tools to measure
the volume of a liquid
observing,
measuring and
using numbers,
communicating,
using space-time
relationship,
defining
operationally
1.4.4 measure the volume of a
liquid using the correct
technique
1.4.5 record the volume
measured in metric system
23
2.
Investigating
Force and
Energy
1.0
Measurement
1.2 Understanding
how to measure
mass
1.4.1 state ways tool
measuring mass
1.4.2 state the standard unit
for mass in the metric system
1.4.3 measure the mass of an
object using the correct
technique
1.4.5 record the measurement
observing,
measuring and
using numbers,
communicating,
using space-time
relationship,
defining
operationally
http://www.skmaklagam.com
using metric system
24
25
2.
Investigating
Force and
Energy
1.0
Measurement
1.6 Understanding
how to measure
time
1.6.1 identify different ways to
measure time
1.6.2 state that processes that
repeat uniformly can be used
to measure time
1.6.3 state the standard unit
for time in the metric standard
1.6.4 identify tools for
measuring time
1.6.5 measure time using
appropriate tools
1.6.6 record the time
measured in metric system
observing,
measuring and
using numbers,
communicating,
using space-time
relationship,
defining
operationally
1.7 Realising the
importance of
using standard
units
1.7.1 choose and use the
appropriate tools to measure
the volumes of liquids and
masses of the ingredient in a
recipe
1.7.2 give reasons for any
differences in the dough
prepare by pupils using the
given recipe
1.7.3 conclude the need for
observing,
making
inferences,
measuring and
using numbers,
using space-time
relationship,
communicating
10
http://www.skmaklagam.com
using standard unit
26
3.
Investigating
materials
1.0 Properties
of materials
1.1 Understanding
the properties of
materials
27
11
1.1.1 classify objects into
groups according to the
materials they are made
1.1.2 identify materials that
conduct electricity
1.1.3 identify materials that
conduct heat
1.1.4 identify materials that
float on water
1.1.5 identify materials that
absorb water
1.1.6 identify materials that
can be stretched
1.1.7 identify materials that
allow light to pass through
( station activity )
observing,
classifying,
making
inferences,
predicting,
communicating,
defining
operationally,
1.1.8 state what a conductor
is
1.1.9 state what an insulator is
1.1.10 make a generalisation
that a good conductor of
heat is also a good conductor
of electricity
observing,
making
inferences,
predicting,
communicating
http://www.skmaklagam.com
28
3.
Investigating
materials
1.0 Properties
of materials
1.1 Understanding
the properties of
materials
observing,
1.1.11 classify materials based classifying,
communicating,
on their abilities to allow light
interpreting
to pass through
1.1.12 state what a
data,
making
transparent material is
1.1.13 state what a translucent inferences,
predicting
material is
1.1.14 state what an opaque
material is
1.1.15 list uses of transparent,
translucent and opaque
materials
29
1.2 Applying the
knowledge of
properties of
materials in
everyday life
1.2.1 suggest ways to keep
things cold
1.2.2 suggest ways to keep
things cold
1.2.3 design an effective way
to keep things hot or to keep
things cold
observing,
communicating,
30
1.3 Synthesising
the knowledge
about uses of
materials based
on their properties
1.3.1 list objects and the
materials that they are made
of
1.3.2 give reasons why
particular materials are used
to make objects
1.3.3 state that materials are
chosen to make an object
observing,
making
inferences,
predicting,
communicating
12
http://www.skmaklagam.com
based on their properties
1.3.4 design an object for a
specific purpose and give
reasons why certain materials
are used to make it
1.4 Knowing the
importance of
reuse, reduce and
recycle of
materials
31
3.
Investigating
materials
32
1.0 Properties
of materials
1.4.1 give examples of natural
materials
1.4.2 give examples of manmade materials
1.4 Knowing the
importance of
reuse, reduce and
recycle of
materials
1.4.3 state that man-made
materials come from natural
materials
1.4.4 give reasons why
materials need to be
conserved
1.4.5 practise reusing,
reducing and recycling to
conserve materials
1.5 Understanding
that some
materials can rust
1.5.1 differentiate between a
rusty object and a non rusty
object
1.5.2 identify objects that can
rust
1.5.3 conclude that objects
made from iron can rust
1.5.4 design a fair test to find
13
observing,
communicating
observing
making
inferences
communicating
observing
communicating
experimenting
( all science
process skills
http://www.skmaklagam.com
33
34
35
4.
Investigating
The Earth and
the Universe
1.0 The Solar
System
out what factors cause rusting
by deciding what to keep the
same, what to change and
what to observe
1.5.5 carry out the test and
record the observations
used)
1.6 Understanding
that rusting can
be prevented
1.6.1 state the different ways
to prevent objects from rusting
11.6.2 explain how these ways
can prevent rusting
1.6.3 explain why it is
necessary to prevent rusting
observing,
communicating,
interpreting
data,
defining
operationally,
making
inferences
1.1Understanding
the Solar System
1.1.1 list the constituents of the
Solar system
1.1.2 list the planets in the
Solar System
in a sequence
1.1.3 state that planets move
around the Sun
observing
communicating
1.2 Understanding
the relative size
and the distance
between the
1.1.1 state the size of the Sun
relative to the size of the Earth
1.1.2 state the size of the Earth
relative to the size of the
observing
communicating
14
http://www.skmaklagam.com
36
37
5.
Investigating
Technology
1.0 Technology
Earth, the Moon
and the Sun
Moon
1.1.3 state the relative
distance from the Earth to the
Sun compared to the relative
distance from the Earth to the
Moon
1.3 Appreciating
the perfect
placement of the
planet Earth in the
Solar System
1.3.1 state why certain planets
are not conducive for living
things
1.3.2 predict what will happen
if the Earth is placed much
nearer or farther from the Sun
1.3.3 conclude that the Earth
is the only planet in the Solar
System that has living things
observing
communicating
predicting
making
inferences
1.1 Understanding
the importance of
technology in
everyday life
1.1.1 state that there are
limitations to humans abilities
to do things
1.1.2 identify devices used to
overcome humans limitations
1.1.3 relate how certain
devices are used to
overcome humans limitations
observing
communicating
15
http://www.skmaklagam.com
38
1.2 Understanding
the development
of technology
1.2.1 give examples of
development of technology
1.2.2 recognise the needs to
innovate or invent devices for
the betterment of mankind
observing
communicating
39
1.3 Synthesising
how technology
can be used to
solve problem
1.3.1 identify problems they
encounter in their daily life
1.3.1 generate ideas to solve
the problems identified
1.3.3 design a device to solve
the problem identified
1.3.4 demonstrate how the
device invented can be used
to solve the problem identified
1..4.1 state that technology
has advantages and
disadvantages
1.4.2 conclude that
technology can benefit
mankind if used wisely
observing
communicating
40
1.4 Analysing that
technology can
benefit mankind if
used wisely
16
observing
communicating
You might also like
- Catapult CalculationsDocument2 pagesCatapult Calculationsbridgetd14100% (4)
- Yearly Plan Science Year 4Document16 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 4Kom Mathi BalaNo ratings yet
- Science Yearly Plan 4 2011Document12 pagesScience Yearly Plan 4 2011Zulkhairi AbidinNo ratings yet
- First Term Science Year 5 Yearly Plan Themes A: Investigating Living ThingsDocument24 pagesFirst Term Science Year 5 Yearly Plan Themes A: Investigating Living ThingsXgeniusXNo ratings yet
- Yearlyplanning Science Year5Document6 pagesYearlyplanning Science Year5Satia KumarNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Yearly PlanDocument14 pagesScience 5 Yearly PlanSri GanggaNo ratings yet
- Jsu Pat SN Yr 4Document17 pagesJsu Pat SN Yr 4lennypowdziNo ratings yet
- Science Year 5 Yearly PlanDocument7 pagesScience Year 5 Yearly Plan惠鑫No ratings yet
- Theme: Investigating Living Things Learning Area Learning Objective Learning OutcomeDocument8 pagesTheme: Investigating Living Things Learning Area Learning Objective Learning OutcomewmpejonNo ratings yet
- TMK Yr2Document73 pagesTMK Yr2Rosnita Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Document7 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 5Aceley JainuddinNo ratings yet
- RPT Sains THN 5 - 2012Document9 pagesRPT Sains THN 5 - 2012zan75No ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Document5 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 5azmnqiinNo ratings yet
- Week Learning Area Learning Objectve Learnng Outcomes Scientfc Process Skills & Thinking SkillDocument7 pagesWeek Learning Area Learning Objectve Learnng Outcomes Scientfc Process Skills & Thinking SkillDinamaniYeogesNo ratings yet
- Year Four Science Scheme of Work: Semester IDocument9 pagesYear Four Science Scheme of Work: Semester IEzhilita EzhillNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Document7 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 5Burhan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Grade 5, Science CurriculumDocument3 pagesGrade 5, Science CurriculumJoel C. Yuvienco67% (3)
- Integrated ScienceDocument6 pagesIntegrated Scienceiteachclassroom100% (2)
- Borang Kontrak Latihan Murid: Nama Guru: Azah Afnan Shamsudin Mata Pelajaran: Sains Tahun: 4BDocument3 pagesBorang Kontrak Latihan Murid: Nama Guru: Azah Afnan Shamsudin Mata Pelajaran: Sains Tahun: 4Banon_314646649No ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Year 5 Science 2008Document5 pagesYearly Plan Year 5 Science 2008marccw2000No ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Science Year 5Document4 pagesScheme of Work Science Year 5murniNo ratings yet
- Kontrak Latihan Murid Tahun6Document2 pagesKontrak Latihan Murid Tahun6Sue Suemanie TicerNo ratings yet
- Science StandardsDocument2 pagesScience Standardsapi-369625583No ratings yet
- RPT SC Yr5 2011Document6 pagesRPT SC Yr5 2011gurlzmiuraNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Cambridge o Level BiologyDocument12 pagesSyllabus Cambridge o Level BiologyNisha AliyaNo ratings yet
- Engineering, Technology, and The Applications of Science: Standards Science Fusion National (2012) Grade 4Document9 pagesEngineering, Technology, and The Applications of Science: Standards Science Fusion National (2012) Grade 4IbrahimMohammedNo ratings yet
- Science Competencies For Grade 1Document5 pagesScience Competencies For Grade 1KAT DANTESNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Document5 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 5wawa2006No ratings yet
- 2021 3rd Science g8 em 1Document9 pages2021 3rd Science g8 em 1SumuduMPereraNo ratings yet
- Round 1Document25 pagesRound 1bakosua141No ratings yet
- Enabling and Enrichment Competencies For Science Melcs (Most Essential Learning Competencies)Document49 pagesEnabling and Enrichment Competencies For Science Melcs (Most Essential Learning Competencies)Zea May BiasNo ratings yet
- F2C3 - BiodiversityDocument11 pagesF2C3 - BiodiversitytankiuNo ratings yet
- Theme / Learning Area / Learning Objective EkstrapolationDocument21 pagesTheme / Learning Area / Learning Objective EkstrapolationMary Dorris JohnNo ratings yet
- Variety of Living Things and Their ClassificationDocument11 pagesVariety of Living Things and Their ClassificationAyuni100% (1)
- Yr5 Science Specification 2012Document17 pagesYr5 Science Specification 2012Norazura ZuraNo ratings yet
- Activitysheets5 2Document11 pagesActivitysheets5 2Benmar L. OrterasNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan 2011 Science Y5Document4 pagesYearly Plan 2011 Science Y5Mohd ZulkarnainNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER ONE: A View of Life: 1.1 How To Define LifeDocument60 pagesCHAPTER ONE: A View of Life: 1.1 How To Define LifeIngrid Dominique P. SanchezNo ratings yet
- Week Theme Learning Area Learning Objectve Learnng Outcomes: Scientfc Process Skills & Thinking SkillDocument4 pagesWeek Theme Learning Area Learning Objectve Learnng Outcomes: Scientfc Process Skills & Thinking SkillThamil ArasiNo ratings yet
- Year Planner SC Yr 6Document8 pagesYear Planner SC Yr 6ccqwanNo ratings yet
- Science Competencies in 5th and 6th Grade With Table of SpecificationsDocument25 pagesScience Competencies in 5th and 6th Grade With Table of SpecificationsTerence Pelingon89% (18)
- Investigating Living Things LA: 1. Interaction Among Living ThingsDocument11 pagesInvestigating Living Things LA: 1. Interaction Among Living ThingsCikgunazrisksac BasirunNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan - Science Year 2Document10 pagesYearly Plan - Science Year 2siah.ameer5382No ratings yet
- LAS - Final Term - Eartrh and Life 2021-2022Document28 pagesLAS - Final Term - Eartrh and Life 2021-2022Az BacligNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologyiteachclassroom100% (2)
- Science Form 3 2016 Year Plan: SMK (L) Methodist Kuala LumpurDocument13 pagesScience Form 3 2016 Year Plan: SMK (L) Methodist Kuala LumpurkriizNo ratings yet
- Biology Syllabus For Secondary Schools Form I-IV in Tanzania, 2010 EditionDocument14 pagesBiology Syllabus For Secondary Schools Form I-IV in Tanzania, 2010 EditionhanspopeNo ratings yet
- Basic ScienceDocument8 pagesBasic SciencemetahelpcentermanagementNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan - Science Year 2Document9 pagesYearly Plan - Science Year 2Muhammad Azrieen SamsudinNo ratings yet
- WASSCE WAEC Integrated Science Syllabus PDFDocument24 pagesWASSCE WAEC Integrated Science Syllabus PDFKojo Yeboah Enchill100% (1)
- Which Snake Plant Is The Best Air Cleanser? (A Comparative of Snake Plants in Purifying The Polluted Air: Sansievera Plant vs. Aloe Vera Plant)Document16 pagesWhich Snake Plant Is The Best Air Cleanser? (A Comparative of Snake Plants in Purifying The Polluted Air: Sansievera Plant vs. Aloe Vera Plant)Phillip BernaldezNo ratings yet
- Biology Ecology Revision NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Ecology Revision NotesGeorge ArgyrouNo ratings yet
- Teacher Support Manual With Elective EnglishDocument260 pagesTeacher Support Manual With Elective EnglishVal CortesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan STD 6 ScienceDocument3 pagesLesson Plan STD 6 ScienceVijay ManogaranNo ratings yet
- Bank RPHDocument33 pagesBank RPHWAN NAZRINA BINTI WAN NAWAWI MoeNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 / Year 10 Biology Course Syllabus 2020-2021course Outline Term 1Document8 pagesGrade 9 / Year 10 Biology Course Syllabus 2020-2021course Outline Term 1CanioNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives 1. Animals Pupils Should LearnDocument6 pagesLearning Objectives 1. Animals Pupils Should LearnSeashellcrabNo ratings yet
- Practical Field Ecology: A Project GuideFrom EverandPractical Field Ecology: A Project GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Microbiology of AerosolsFrom EverandMicrobiology of AerosolsAnne-Marie DelortNo ratings yet
- Anggaran Bajet Hi-Tea BKGK 2018Document1 pageAnggaran Bajet Hi-Tea BKGK 2018ajibNo ratings yet
- Multiplication Crazy GridsDocument1 pageMultiplication Crazy Gridsajib0% (1)
- Group Lawatan KLCC 2014Document1 pageGroup Lawatan KLCC 2014ajibNo ratings yet
- Learning WalkDocument10 pagesLearning WalkajibNo ratings yet
- The Year 5/6 Science Quiz: Part TwoDocument42 pagesThe Year 5/6 Science Quiz: Part TwoajibNo ratings yet
- Simplify This Fractions Simplify This FractionsDocument1 pageSimplify This Fractions Simplify This FractionsajibNo ratings yet
- Thevenin and Norton EquivalentsDocument36 pagesThevenin and Norton EquivalentsJosé Guillermo De Chomón AranguenaNo ratings yet
- Measurements of Dielectric Constant of Solid Material (Leather Belt) at X-Band and Proposed Wearable AntennaDocument5 pagesMeasurements of Dielectric Constant of Solid Material (Leather Belt) at X-Band and Proposed Wearable AntennaIJMERNo ratings yet
- TechDaten Man 7SK85 V0750 enUSDocument180 pagesTechDaten Man 7SK85 V0750 enUSAnonymous dH3DIEtzNo ratings yet
- Basics of Medium-Voltage Wiring - SolarPro MagazineDocument18 pagesBasics of Medium-Voltage Wiring - SolarPro MagazinehariNo ratings yet
- RSO TestingDocument19 pagesRSO TestingAntonio DsfvsdcNo ratings yet
- 1 Ren APl HDocument350 pages1 Ren APl HKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Worksheet (AS)Document4 pagesWorksheet (AS)Mahad AsimNo ratings yet
- Branches of Architectural AcousticsDocument26 pagesBranches of Architectural AcousticsGanie MhooreNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase-Inductionmotor With Squirrel Cage Rotor: P U F I N MDocument1 pageThree-Phase-Inductionmotor With Squirrel Cage Rotor: P U F I N MveemandalNo ratings yet
- Stokes' and Newton's Viscous DragDocument7 pagesStokes' and Newton's Viscous DragL V SatyavathiNo ratings yet
- Break It Apart Technical ReportDocument9 pagesBreak It Apart Technical Reportapi-347850579No ratings yet
- Differentiating Circuit and Integrating Circuit - Electronics PostDocument5 pagesDifferentiating Circuit and Integrating Circuit - Electronics Postmishba kNo ratings yet
- Sample Training MatrixDocument4 pagesSample Training MatrixTeckii MSOfficeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document10 pagesUnit 1lg481476114No ratings yet
- MHD PropulsionDocument10 pagesMHD PropulsionAbdullah BölekNo ratings yet
- Civil-Vi-Hydraulic Structures and Irrigation Design-Drawin (10CV65) - Notes PDFDocument93 pagesCivil-Vi-Hydraulic Structures and Irrigation Design-Drawin (10CV65) - Notes PDFRavi Kumar85% (27)
- Manual Metal Arc Welding or Shielded Metal Arc WeldingDocument19 pagesManual Metal Arc Welding or Shielded Metal Arc WeldingLâm ThanhNo ratings yet
- Lecture Antenna MiniaturizationDocument34 pagesLecture Antenna MiniaturizationJuhi GargNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Electricity Magnetism & SemiconductorsDocument38 pagesUnit 2 Electricity Magnetism & SemiconductorsBharat JadhavNo ratings yet
- Engg Mechanics Question Bank UNIT-1Document10 pagesEngg Mechanics Question Bank UNIT-1Thiyagarajan GurusamyNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Structures (Methods of Joints and Sections)Document53 pagesStructures (Methods of Joints and Sections)Edreno Olpino Jr.100% (1)
- PDFDocument250 pagesPDFMarvellousNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Current Electricity Part 1Document20 pagesChapter 16 - Current Electricity Part 1api-275374056No ratings yet
- EE Lab#08 Group#04Document11 pagesEE Lab#08 Group#04Maida IrshadNo ratings yet
- IPC Digital Coulombmeter ExperimentsDocument9 pagesIPC Digital Coulombmeter Experimentslev76No ratings yet
- Technical and Vocational Education Faculty: Engineering Education Department (JPK)Document27 pagesTechnical and Vocational Education Faculty: Engineering Education Department (JPK)Farahnasuhaa JamilNo ratings yet
- Chtest8 SolutionDocument9 pagesChtest8 SolutionMaulitaNo ratings yet
- SACE Isomax PDFDocument28 pagesSACE Isomax PDFdwiyanto73No ratings yet