Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mireia Pelaez. First Draft Consequences of Excessive Weight Gain During Pregnancy
Mireia Pelaez. First Draft Consequences of Excessive Weight Gain During Pregnancy
Uploaded by
bertabastionniCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- NCM 109 (OB) - 4.1 Nursing Care of The Postpartum ClientDocument9 pagesNCM 109 (OB) - 4.1 Nursing Care of The Postpartum ClientKristine Joyce Bongao BediaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Maternal Obesity On Maternal and Fetal Health: Anagement EviewDocument9 pagesThe Impact of Maternal Obesity On Maternal and Fetal Health: Anagement EviewlukmanyahyaNo ratings yet
- Impetigo FactsheetDocument2 pagesImpetigo FactsheetReza PahleviNo ratings yet
- 04.the Cleveland Clinic Intensive Review of Pediatrics 2nd EdDocument513 pages04.the Cleveland Clinic Intensive Review of Pediatrics 2nd EdSav GaNo ratings yet
- Consequences of Gestational and Pregestational Diabetes On Placental Function and Birth WeightDocument8 pagesConsequences of Gestational and Pregestational Diabetes On Placental Function and Birth WeightannisaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Macrosomia UptodateDocument22 pagesFetal Macrosomia UptodateWinny Roman AybarNo ratings yet
- Large For Gestational Age Newborn - UpToDateDocument17 pagesLarge For Gestational Age Newborn - UpToDateFernando Kamilo Ruiz ArévaloNo ratings yet
- Implications of Early Pregnancy Obesity On Maternal, Fetal and Neonatal Health PDFDocument7 pagesImplications of Early Pregnancy Obesity On Maternal, Fetal and Neonatal Health PDFAndhika Dimas ANo ratings yet
- Large For Gestational Age Is Used To Describe Newborn Babies Who Weigh More Than Usual ForDocument3 pagesLarge For Gestational Age Is Used To Describe Newborn Babies Who Weigh More Than Usual Forfaye kimNo ratings yet
- Final Research Paper - Maternal Risks OutcomesDocument12 pagesFinal Research Paper - Maternal Risks Outcomesapi-354198040No ratings yet
- Macrosomia Clinical Presentation History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDocument1 pageMacrosomia Clinical Presentation History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsRizka AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Review Article Gestational Diabetes: Risk Factors and Recent Advances in Its Genetics and TreatmentDocument13 pagesReview Article Gestational Diabetes: Risk Factors and Recent Advances in Its Genetics and TreatmentTeky WidyariniNo ratings yet
- Macrosomia Risk Factors and Labor Outcome Methal-A. Alrubae, Klood JaferDocument8 pagesMacrosomia Risk Factors and Labor Outcome Methal-A. Alrubae, Klood JaferKhuriyatun NadhifahNo ratings yet
- Fetal DistressDocument5 pagesFetal DistressRonnie Portillo Cruz100% (1)
- Infants of Women With Diabetes - UpToDateDocument28 pagesInfants of Women With Diabetes - UpToDateFernando Kamilo Ruiz ArévaloNo ratings yet
- Bjo0118 0578 PDFDocument11 pagesBjo0118 0578 PDFwe sagara dewiNo ratings yet
- Adverse Fetal Outcomes of Diabetic Pregnancy Diabetic FetopathyDocument21 pagesAdverse Fetal Outcomes of Diabetic Pregnancy Diabetic FetopathyMorad AlaboudNo ratings yet
- High Risk WomenDocument17 pagesHigh Risk WomenamitNo ratings yet
- ACOG Committee Opinion On Weight Gain in PregnancyDocument0 pagesACOG Committee Opinion On Weight Gain in PregnancyKevin MulyaNo ratings yet
- Risks-Of-Delivery-Related-To-The-Ff.-Factors 2Document7 pagesRisks-Of-Delivery-Related-To-The-Ff.-Factors 2daniloallauigan19No ratings yet
- Macrosomia, Big Fetus, LgaDocument18 pagesMacrosomia, Big Fetus, Lgamishka.dubtsovNo ratings yet
- GDM DhanaDocument169 pagesGDM Dhananaga maniNo ratings yet
- Obesity in Pregnancy - UPTO DATEComplications and Maternal Management - UpToDateDocument43 pagesObesity in Pregnancy - UPTO DATEComplications and Maternal Management - UpToDateCristinaCaprosNo ratings yet
- Fetal MacrosomiaDocument2 pagesFetal MacrosomiaReyniel Pablo ElumbaNo ratings yet
- Postterm Pregnancy - UpToDateDocument16 pagesPostterm Pregnancy - UpToDateCarlos Jeiner Díaz SilvaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic MaternlaDocument4 pagesDiabetic MaternlaAde Gustina SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter One PHDDocument55 pagesChapter One PHDL3mi DNo ratings yet
- Infants of Women With Diabetes - UpToDateDocument16 pagesInfants of Women With Diabetes - UpToDatethelesphol pascalNo ratings yet
- Gestational Weight GainDocument3 pagesGestational Weight GainainindyaNo ratings yet
- Being Macrosomic at Birth Is An Independent Predictor of Overweight in Children: Results From The IDEFICS StudyDocument9 pagesBeing Macrosomic at Birth Is An Independent Predictor of Overweight in Children: Results From The IDEFICS StudySayuri BenitesNo ratings yet
- Case Write UpDocument5 pagesCase Write UpAisyah Hamdan100% (1)
- Maternal Obesity 2Document13 pagesMaternal Obesity 2lalimdNo ratings yet
- Macrosmia and DMDocument4 pagesMacrosmia and DMAde Gustina SiahaanNo ratings yet
- The Macrosomic Fetus: A Challenge in Current Obstetrics: Tore HenriksenDocument12 pagesThe Macrosomic Fetus: A Challenge in Current Obstetrics: Tore HenriksenLNFNo ratings yet
- 02 003 ValsamakisDocument13 pages02 003 ValsamakisCostin VrabieNo ratings yet
- 15twin Pregnancy PDFDocument18 pages15twin Pregnancy PDFuouoNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Perinatal Maternal and Perinatal Outcome of Maternal Obesity Outcome of Maternal Obesity at RSCM in 2014-2019 at RSCM in 2014-2019Document1 pageMaternal and Perinatal Maternal and Perinatal Outcome of Maternal Obesity Outcome of Maternal Obesity at RSCM in 2014-2019 at RSCM in 2014-2019heidi leeNo ratings yet
- Jurnal MaternitasDocument10 pagesJurnal Maternitasasep saepulohNo ratings yet
- Distosia Ncbi (Ana)Document8 pagesDistosia Ncbi (Ana)Ni Wayan Ana PsNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Where Are We NowDocument7 pagesGestational Diabetes Mellitus Where Are We NowjohnturpoNo ratings yet
- Postterm Pregnancy - UpToDateDocument17 pagesPostterm Pregnancy - UpToDateJosé Abraham Amaya DuarteNo ratings yet
- FVVinObGyn 4 175 187 PDFDocument13 pagesFVVinObGyn 4 175 187 PDFSuhada AkmalNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive BiologyDocument6 pagesEuropean Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biologynova febrianiNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia 5Document10 pagesPreeclampsia 5FabiolaGodoyNo ratings yet
- The Implications of Obesity On Pregnancy Outcome 2015 Obstetrics Gynaecology Reproductive MedicineDocument4 pagesThe Implications of Obesity On Pregnancy Outcome 2015 Obstetrics Gynaecology Reproductive MedicineNora100% (1)
- Maternity Case StudyDocument31 pagesMaternity Case StudySyed Mohd Asri SabNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors and Outcomes of Fetal Macrosomia in A Tertiary Centre in Tanzania: A Case-Control StudyDocument8 pagesRisk Factors and Outcomes of Fetal Macrosomia in A Tertiary Centre in Tanzania: A Case-Control StudyMarianella Saravia LopezNo ratings yet
- Reading - Post Term Pregnancy PDFDocument9 pagesReading - Post Term Pregnancy PDFchn millamaNo ratings yet
- Maternal Pregnancy Weight Gain and The Risk of Placental AbruptionDocument9 pagesMaternal Pregnancy Weight Gain and The Risk of Placental AbruptionMuhammad Aulia KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Adverse Maternal Outcomes Associated With Fetal Macrosomia: What Are The Risk Factors Beyond Birthweight?Document6 pagesAdverse Maternal Outcomes Associated With Fetal Macrosomia: What Are The Risk Factors Beyond Birthweight?Khuriyatun NadhifahNo ratings yet
- Joe JOE 18 0670Document19 pagesJoe JOE 18 0670Braulio Lugo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes MellitusJheryck Sabadao100% (1)
- Constitutional Macrosomia - A Case ReportDocument3 pagesConstitutional Macrosomia - A Case ReportIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Res Lounge Infant of Diabetic MotherDocument19 pagesRes Lounge Infant of Diabetic MotherYong Kui ChooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4muhammadosama0121No ratings yet
- Bmi PregnancyDocument11 pagesBmi PregnancyLilik AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Maternal Obesity, Length of Gestation, Risk of Postdates Pregnancy and Spontaneous Onset of Labour at TermDocument6 pagesMaternal Obesity, Length of Gestation, Risk of Postdates Pregnancy and Spontaneous Onset of Labour at TermEdita Janet Yupanqui FlorianoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes in PregnancyDocument15 pagesDiabetes in PregnancyRazi MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Distress SGDDocument24 pagesFetal Distress SGDLyca Mae AurelioNo ratings yet
- Winter, Spring, Summer or Fall Temporal Patterns in Placenta-Mediated Pregnancy Complications-An Exploratory AnalysisDocument8 pagesWinter, Spring, Summer or Fall Temporal Patterns in Placenta-Mediated Pregnancy Complications-An Exploratory AnalysisTushar RameshNo ratings yet
- Assignment ON Identification, Classification & Nursing Management of High Risk NewbornDocument18 pagesAssignment ON Identification, Classification & Nursing Management of High Risk NewbornSanthosh.S.U100% (1)
- Lacson JournalDocument2 pagesLacson JournalBerlon LacsonNo ratings yet
- BFCR (12) 11 Standards For The Communication of Critical, Urgent and Unexpected Significant Radiological Findings, Second EditionDocument21 pagesBFCR (12) 11 Standards For The Communication of Critical, Urgent and Unexpected Significant Radiological Findings, Second Editionpjwaugh2No ratings yet
- Minnesota Fall School Planning Guide - Minnesota Department of HealthDocument16 pagesMinnesota Fall School Planning Guide - Minnesota Department of HealthPatch Minnesota100% (1)
- MedicalDevices Orthopaedics 2021Document45 pagesMedicalDevices Orthopaedics 2021Пламена ПетроваNo ratings yet
- Bu Widy - Ginjal (Patofisiologi & Penatalaksanaan GGK)Document40 pagesBu Widy - Ginjal (Patofisiologi & Penatalaksanaan GGK)Ravinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Vascular Surgery Notes: DR H LouwrensDocument41 pagesVascular Surgery Notes: DR H LouwrensbiancaNo ratings yet
- Sedation in Pediatric Dentistry: January 2019Document8 pagesSedation in Pediatric Dentistry: January 2019Ina Vetrila100% (1)
- Diagnosis and Treatment PlanningDocument66 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment PlanningVincent SerNo ratings yet
- New Defmition Medicine: 'Neo-Islamic Medicine'Document2 pagesNew Defmition Medicine: 'Neo-Islamic Medicine'Meity ElvinaNo ratings yet
- Vi Psa Pres Common Eye Conditions Aug10 3.08.29 PMDocument58 pagesVi Psa Pres Common Eye Conditions Aug10 3.08.29 PMSarthak KabiNo ratings yet
- Resume of KareokegrlDocument4 pagesResume of Kareokegrlapi-23967126No ratings yet
- Lab AboDocument5 pagesLab Aboclower112No ratings yet
- O&G OSCE by MaddyDocument287 pagesO&G OSCE by MaddyNariska Cooper100% (1)
- C1 Progress Test 2Document5 pagesC1 Progress Test 2Angie LaNo ratings yet
- Doh Ao 2008-0008-ADocument2 pagesDoh Ao 2008-0008-AvanceNo ratings yet
- Chennai HospitalsDocument6 pagesChennai HospitalsGp MishraNo ratings yet
- Indian Herbs & DetailsDocument11 pagesIndian Herbs & Detailsjai2allNo ratings yet
- DRM Tool For StudentsDocument6 pagesDRM Tool For StudentsTricia PrestozaNo ratings yet
- Running Head: 1: PolypharmacyDocument3 pagesRunning Head: 1: PolypharmacyjosephNo ratings yet
- A Lens To Understand Sanitation Workers and Their Health Status in IndiaDocument3 pagesA Lens To Understand Sanitation Workers and Their Health Status in IndiaRejesh BoseNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryDocument2 pagesJournal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationChamelli RobinNo ratings yet
- Components of The CBCDocument8 pagesComponents of The CBCapi-236078478No ratings yet
- 15025.201530: Practical Nursing Leadership - NURS-250-0NEDocument4 pages15025.201530: Practical Nursing Leadership - NURS-250-0NEapi-283978039No ratings yet
- StrokeDocument4 pagesStrokeAyuni SallehNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Massage TherapyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Massage TherapysalimhillNo ratings yet
- Check - List - Form - No - 2 - Registration of Imported - MedicinesDocument1 pageCheck - List - Form - No - 2 - Registration of Imported - Medicines박지원No ratings yet
- Personal Injury Ire FormDocument2 pagesPersonal Injury Ire FormBioVeda Health and Wellness CentersNo ratings yet
Mireia Pelaez. First Draft Consequences of Excessive Weight Gain During Pregnancy
Mireia Pelaez. First Draft Consequences of Excessive Weight Gain During Pregnancy
Uploaded by
bertabastionniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mireia Pelaez. First Draft Consequences of Excessive Weight Gain During Pregnancy
Mireia Pelaez. First Draft Consequences of Excessive Weight Gain During Pregnancy
Uploaded by
bertabastionniCopyright:
Available Formats
Mireia Pelaez.
First draft
CONSEQUENCES OF EXCESSIVE WEIGHT GAIN DURING PREGNANCY
During pregnancy, all body systems are modified in order to allow an optimum
enviroment for the developing embryo. One of these adaptations is the weight gain. A
gain within 9 and 14 kg are considered as a normal gain rate, however, higher rates are
founded in developed countries. Studies have shown that when women exceed the
recommendations given by The Institute of Medicine (recommendations that take into
acount pre-pregnancy body mass index) are at higher risk of suffering problems such us
gestational diabetes, gestate macrosomic fetus and having cesarean delivery (Asbee et
al., 2009; Polley, Wing and Sims 2002).
Gestational diabetes could be defined as every type of diabetes diagnosed for the first
time during pregnancy (Stafne, Salvensen, Romundstad, Stuge and Morkved2012). The
prevalence of this condition is about 5%, of pregnancies although differences could be
found between countries (Dempsey et al., 2004). The consequences of gestational
diabetes for mother and baby are very similar to those derivated of excessive weight
gain. This risks could be gathered into three groups: (i) risks during pregnancy and
delivery, such us excessive weight gain, preeclamspsia and cesarean delivery, (ii)
mother long-term risks, like obesity, diabetes type II or cardiovascular disease and (iii)
baby short-term and child long-term risks, for example, increased perinatal morbility,
obesity and glucose intolerance, 45% higher probability of developing diabetes type II,
macrosomia and brachial plexus damage and to a lesser extent, jaundice, respiratory
stress, hypocalcemia, higher rate of fetal malformation and perinatal mortality (Marshall
y Carpenter, 2007). Therefore, it could be sugested that gestacional diabetes is a
transitory condition that might lead metabolic disfunctions in long-term.
Mireia Pelaez. First draft
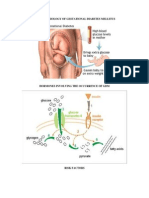
The second consequence of excessive weight gain during pregnancy is macrosomia.
The considered normal range of newborn weight is between 2 500 g and 4 000 g. Babies
with weight equal or above 4 000 g are considered as macrosomic babies. This situation
places the newborn at a high risk of suffering obesity and diabetes type II in the
adulthood (Mottola et al., 2010). Besides, macrosomia could produce complications in
the courso of labor, such us pelvic floor lacerations, the need of episiotomy or the need
of an instrumental delivery. Altough macrosomia is conditioned by diferent factors like
parents genetics, women with excesive weight gain during pregnancy and/or gestacional
diabetes are more likely to gestate macrosomic babies.
Referring the thrid consequence, an excessive weight gain during pregancy could also
increase the rate of cesarean delivery. It consists on the extraction of the baby, placenta
and membranes through the abdominal wall by surgery. This intervention has several
associated risks. Enumerating some short-term risks for the mother, could be
highlighted more pain after delivery and longer hospitalization and recovery periods. In
the long-term risks, authors find more pain, scar adhesion and perinatal complications in
subsequented pregnancies. Women who had several cesarean sections, are at higher risk
of hemorrhage because of the development of placenta accreta (deep attachment of the
placenta throug the uterine walls). There are also other risks of cesarean delivery related
with the newborn: higer incidence of respiratory disease and a reduction on the suction
reflex (O'Shea, Klebanoff y Signore, 2010; Silver, 2010).
In conclusion, women with excessive weight gain during pregnancy are at higher risk of
suffering gestational diabetes, gestate macrosomic babies and having cesarea delivery.
Studies have shown that the aforementioned conditions are linked with short and long-
term consequences for both, the mother and the child, so the development of programs
to prevent the excessive weight gain during pregnancy are warranted.
You might also like
- NCM 109 (OB) - 4.1 Nursing Care of The Postpartum ClientDocument9 pagesNCM 109 (OB) - 4.1 Nursing Care of The Postpartum ClientKristine Joyce Bongao BediaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Maternal Obesity On Maternal and Fetal Health: Anagement EviewDocument9 pagesThe Impact of Maternal Obesity On Maternal and Fetal Health: Anagement EviewlukmanyahyaNo ratings yet
- Impetigo FactsheetDocument2 pagesImpetigo FactsheetReza PahleviNo ratings yet
- 04.the Cleveland Clinic Intensive Review of Pediatrics 2nd EdDocument513 pages04.the Cleveland Clinic Intensive Review of Pediatrics 2nd EdSav GaNo ratings yet
- Consequences of Gestational and Pregestational Diabetes On Placental Function and Birth WeightDocument8 pagesConsequences of Gestational and Pregestational Diabetes On Placental Function and Birth WeightannisaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Macrosomia UptodateDocument22 pagesFetal Macrosomia UptodateWinny Roman AybarNo ratings yet
- Large For Gestational Age Newborn - UpToDateDocument17 pagesLarge For Gestational Age Newborn - UpToDateFernando Kamilo Ruiz ArévaloNo ratings yet
- Implications of Early Pregnancy Obesity On Maternal, Fetal and Neonatal Health PDFDocument7 pagesImplications of Early Pregnancy Obesity On Maternal, Fetal and Neonatal Health PDFAndhika Dimas ANo ratings yet
- Large For Gestational Age Is Used To Describe Newborn Babies Who Weigh More Than Usual ForDocument3 pagesLarge For Gestational Age Is Used To Describe Newborn Babies Who Weigh More Than Usual Forfaye kimNo ratings yet
- Final Research Paper - Maternal Risks OutcomesDocument12 pagesFinal Research Paper - Maternal Risks Outcomesapi-354198040No ratings yet
- Macrosomia Clinical Presentation History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDocument1 pageMacrosomia Clinical Presentation History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsRizka AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Review Article Gestational Diabetes: Risk Factors and Recent Advances in Its Genetics and TreatmentDocument13 pagesReview Article Gestational Diabetes: Risk Factors and Recent Advances in Its Genetics and TreatmentTeky WidyariniNo ratings yet
- Macrosomia Risk Factors and Labor Outcome Methal-A. Alrubae, Klood JaferDocument8 pagesMacrosomia Risk Factors and Labor Outcome Methal-A. Alrubae, Klood JaferKhuriyatun NadhifahNo ratings yet
- Fetal DistressDocument5 pagesFetal DistressRonnie Portillo Cruz100% (1)
- Infants of Women With Diabetes - UpToDateDocument28 pagesInfants of Women With Diabetes - UpToDateFernando Kamilo Ruiz ArévaloNo ratings yet
- Bjo0118 0578 PDFDocument11 pagesBjo0118 0578 PDFwe sagara dewiNo ratings yet
- Adverse Fetal Outcomes of Diabetic Pregnancy Diabetic FetopathyDocument21 pagesAdverse Fetal Outcomes of Diabetic Pregnancy Diabetic FetopathyMorad AlaboudNo ratings yet
- High Risk WomenDocument17 pagesHigh Risk WomenamitNo ratings yet
- ACOG Committee Opinion On Weight Gain in PregnancyDocument0 pagesACOG Committee Opinion On Weight Gain in PregnancyKevin MulyaNo ratings yet
- Risks-Of-Delivery-Related-To-The-Ff.-Factors 2Document7 pagesRisks-Of-Delivery-Related-To-The-Ff.-Factors 2daniloallauigan19No ratings yet
- Macrosomia, Big Fetus, LgaDocument18 pagesMacrosomia, Big Fetus, Lgamishka.dubtsovNo ratings yet
- GDM DhanaDocument169 pagesGDM Dhananaga maniNo ratings yet
- Obesity in Pregnancy - UPTO DATEComplications and Maternal Management - UpToDateDocument43 pagesObesity in Pregnancy - UPTO DATEComplications and Maternal Management - UpToDateCristinaCaprosNo ratings yet
- Fetal MacrosomiaDocument2 pagesFetal MacrosomiaReyniel Pablo ElumbaNo ratings yet
- Postterm Pregnancy - UpToDateDocument16 pagesPostterm Pregnancy - UpToDateCarlos Jeiner Díaz SilvaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic MaternlaDocument4 pagesDiabetic MaternlaAde Gustina SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter One PHDDocument55 pagesChapter One PHDL3mi DNo ratings yet
- Infants of Women With Diabetes - UpToDateDocument16 pagesInfants of Women With Diabetes - UpToDatethelesphol pascalNo ratings yet
- Gestational Weight GainDocument3 pagesGestational Weight GainainindyaNo ratings yet
- Being Macrosomic at Birth Is An Independent Predictor of Overweight in Children: Results From The IDEFICS StudyDocument9 pagesBeing Macrosomic at Birth Is An Independent Predictor of Overweight in Children: Results From The IDEFICS StudySayuri BenitesNo ratings yet
- Case Write UpDocument5 pagesCase Write UpAisyah Hamdan100% (1)
- Maternal Obesity 2Document13 pagesMaternal Obesity 2lalimdNo ratings yet
- Macrosmia and DMDocument4 pagesMacrosmia and DMAde Gustina SiahaanNo ratings yet
- The Macrosomic Fetus: A Challenge in Current Obstetrics: Tore HenriksenDocument12 pagesThe Macrosomic Fetus: A Challenge in Current Obstetrics: Tore HenriksenLNFNo ratings yet
- 02 003 ValsamakisDocument13 pages02 003 ValsamakisCostin VrabieNo ratings yet
- 15twin Pregnancy PDFDocument18 pages15twin Pregnancy PDFuouoNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Perinatal Maternal and Perinatal Outcome of Maternal Obesity Outcome of Maternal Obesity at RSCM in 2014-2019 at RSCM in 2014-2019Document1 pageMaternal and Perinatal Maternal and Perinatal Outcome of Maternal Obesity Outcome of Maternal Obesity at RSCM in 2014-2019 at RSCM in 2014-2019heidi leeNo ratings yet
- Jurnal MaternitasDocument10 pagesJurnal Maternitasasep saepulohNo ratings yet
- Distosia Ncbi (Ana)Document8 pagesDistosia Ncbi (Ana)Ni Wayan Ana PsNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Where Are We NowDocument7 pagesGestational Diabetes Mellitus Where Are We NowjohnturpoNo ratings yet
- Postterm Pregnancy - UpToDateDocument17 pagesPostterm Pregnancy - UpToDateJosé Abraham Amaya DuarteNo ratings yet
- FVVinObGyn 4 175 187 PDFDocument13 pagesFVVinObGyn 4 175 187 PDFSuhada AkmalNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive BiologyDocument6 pagesEuropean Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biologynova febrianiNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia 5Document10 pagesPreeclampsia 5FabiolaGodoyNo ratings yet
- The Implications of Obesity On Pregnancy Outcome 2015 Obstetrics Gynaecology Reproductive MedicineDocument4 pagesThe Implications of Obesity On Pregnancy Outcome 2015 Obstetrics Gynaecology Reproductive MedicineNora100% (1)
- Maternity Case StudyDocument31 pagesMaternity Case StudySyed Mohd Asri SabNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors and Outcomes of Fetal Macrosomia in A Tertiary Centre in Tanzania: A Case-Control StudyDocument8 pagesRisk Factors and Outcomes of Fetal Macrosomia in A Tertiary Centre in Tanzania: A Case-Control StudyMarianella Saravia LopezNo ratings yet
- Reading - Post Term Pregnancy PDFDocument9 pagesReading - Post Term Pregnancy PDFchn millamaNo ratings yet
- Maternal Pregnancy Weight Gain and The Risk of Placental AbruptionDocument9 pagesMaternal Pregnancy Weight Gain and The Risk of Placental AbruptionMuhammad Aulia KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Adverse Maternal Outcomes Associated With Fetal Macrosomia: What Are The Risk Factors Beyond Birthweight?Document6 pagesAdverse Maternal Outcomes Associated With Fetal Macrosomia: What Are The Risk Factors Beyond Birthweight?Khuriyatun NadhifahNo ratings yet
- Joe JOE 18 0670Document19 pagesJoe JOE 18 0670Braulio Lugo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes MellitusJheryck Sabadao100% (1)
- Constitutional Macrosomia - A Case ReportDocument3 pagesConstitutional Macrosomia - A Case ReportIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Res Lounge Infant of Diabetic MotherDocument19 pagesRes Lounge Infant of Diabetic MotherYong Kui ChooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4muhammadosama0121No ratings yet
- Bmi PregnancyDocument11 pagesBmi PregnancyLilik AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Maternal Obesity, Length of Gestation, Risk of Postdates Pregnancy and Spontaneous Onset of Labour at TermDocument6 pagesMaternal Obesity, Length of Gestation, Risk of Postdates Pregnancy and Spontaneous Onset of Labour at TermEdita Janet Yupanqui FlorianoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes in PregnancyDocument15 pagesDiabetes in PregnancyRazi MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Distress SGDDocument24 pagesFetal Distress SGDLyca Mae AurelioNo ratings yet
- Winter, Spring, Summer or Fall Temporal Patterns in Placenta-Mediated Pregnancy Complications-An Exploratory AnalysisDocument8 pagesWinter, Spring, Summer or Fall Temporal Patterns in Placenta-Mediated Pregnancy Complications-An Exploratory AnalysisTushar RameshNo ratings yet
- Assignment ON Identification, Classification & Nursing Management of High Risk NewbornDocument18 pagesAssignment ON Identification, Classification & Nursing Management of High Risk NewbornSanthosh.S.U100% (1)
- Lacson JournalDocument2 pagesLacson JournalBerlon LacsonNo ratings yet
- BFCR (12) 11 Standards For The Communication of Critical, Urgent and Unexpected Significant Radiological Findings, Second EditionDocument21 pagesBFCR (12) 11 Standards For The Communication of Critical, Urgent and Unexpected Significant Radiological Findings, Second Editionpjwaugh2No ratings yet
- Minnesota Fall School Planning Guide - Minnesota Department of HealthDocument16 pagesMinnesota Fall School Planning Guide - Minnesota Department of HealthPatch Minnesota100% (1)
- MedicalDevices Orthopaedics 2021Document45 pagesMedicalDevices Orthopaedics 2021Пламена ПетроваNo ratings yet
- Bu Widy - Ginjal (Patofisiologi & Penatalaksanaan GGK)Document40 pagesBu Widy - Ginjal (Patofisiologi & Penatalaksanaan GGK)Ravinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Vascular Surgery Notes: DR H LouwrensDocument41 pagesVascular Surgery Notes: DR H LouwrensbiancaNo ratings yet
- Sedation in Pediatric Dentistry: January 2019Document8 pagesSedation in Pediatric Dentistry: January 2019Ina Vetrila100% (1)
- Diagnosis and Treatment PlanningDocument66 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment PlanningVincent SerNo ratings yet
- New Defmition Medicine: 'Neo-Islamic Medicine'Document2 pagesNew Defmition Medicine: 'Neo-Islamic Medicine'Meity ElvinaNo ratings yet
- Vi Psa Pres Common Eye Conditions Aug10 3.08.29 PMDocument58 pagesVi Psa Pres Common Eye Conditions Aug10 3.08.29 PMSarthak KabiNo ratings yet
- Resume of KareokegrlDocument4 pagesResume of Kareokegrlapi-23967126No ratings yet
- Lab AboDocument5 pagesLab Aboclower112No ratings yet
- O&G OSCE by MaddyDocument287 pagesO&G OSCE by MaddyNariska Cooper100% (1)
- C1 Progress Test 2Document5 pagesC1 Progress Test 2Angie LaNo ratings yet
- Doh Ao 2008-0008-ADocument2 pagesDoh Ao 2008-0008-AvanceNo ratings yet
- Chennai HospitalsDocument6 pagesChennai HospitalsGp MishraNo ratings yet
- Indian Herbs & DetailsDocument11 pagesIndian Herbs & Detailsjai2allNo ratings yet
- DRM Tool For StudentsDocument6 pagesDRM Tool For StudentsTricia PrestozaNo ratings yet
- Running Head: 1: PolypharmacyDocument3 pagesRunning Head: 1: PolypharmacyjosephNo ratings yet
- A Lens To Understand Sanitation Workers and Their Health Status in IndiaDocument3 pagesA Lens To Understand Sanitation Workers and Their Health Status in IndiaRejesh BoseNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryDocument2 pagesJournal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationChamelli RobinNo ratings yet
- Components of The CBCDocument8 pagesComponents of The CBCapi-236078478No ratings yet
- 15025.201530: Practical Nursing Leadership - NURS-250-0NEDocument4 pages15025.201530: Practical Nursing Leadership - NURS-250-0NEapi-283978039No ratings yet
- StrokeDocument4 pagesStrokeAyuni SallehNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Massage TherapyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Massage TherapysalimhillNo ratings yet
- Check - List - Form - No - 2 - Registration of Imported - MedicinesDocument1 pageCheck - List - Form - No - 2 - Registration of Imported - Medicines박지원No ratings yet
- Personal Injury Ire FormDocument2 pagesPersonal Injury Ire FormBioVeda Health and Wellness CentersNo ratings yet