Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MPEG-1 Audio: 18-899 Special Topics in Signal Processing
MPEG-1 Audio: 18-899 Special Topics in Signal Processing
Uploaded by
Juan M. Córdova0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views10 pages1. The document discusses MPEG-1 Audio, the first high quality audio compression standard that could provide CD quality two-channel audio at 256 kbits/s.
2. It describes the key aspects of MPEG-1 Audio including psychoacoustics, subband coding, and its three layers (Layer I, II, and III) that provide increasing quality and compression ratios.
3. The document outlines the encoder and decoder block diagrams, how filterbanks and quantization are used, and new features of Layer III including MDCT, nonuniform quantization, and entropy coding.
Original Description:
Original Title
PGM-1.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document discusses MPEG-1 Audio, the first high quality audio compression standard that could provide CD quality two-channel audio at 256 kbits/s.
2. It describes the key aspects of MPEG-1 Audio including psychoacoustics, subband coding, and its three layers (Layer I, II, and III) that provide increasing quality and compression ratios.
3. The document outlines the encoder and decoder block diagrams, how filterbanks and quantization are used, and new features of Layer III including MDCT, nonuniform quantization, and entropy coding.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views10 pagesMPEG-1 Audio: 18-899 Special Topics in Signal Processing
MPEG-1 Audio: 18-899 Special Topics in Signal Processing
Uploaded by
Juan M. Córdova1. The document discusses MPEG-1 Audio, the first high quality audio compression standard that could provide CD quality two-channel audio at 256 kbits/s.
2. It describes the key aspects of MPEG-1 Audio including psychoacoustics, subband coding, and its three layers (Layer I, II, and III) that provide increasing quality and compression ratios.
3. The document outlines the encoder and decoder block diagrams, how filterbanks and quantization are used, and new features of Layer III including MDCT, nonuniform quantization, and entropy coding.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 10
1
Prof. Tsuhan Chen
tsuhan@ece.cmu.edu
18-899 Special Topics in Signal Processing
Multimedia Communications:
Coding, Systems, and Networking
Lecture 8
MPEG-1 Audio
2
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
MPEG-1 Audio
Outline
Background
Psychoacoustics
Subband coding
Layer I and II
Layer III
Frame structure and packetization
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
MPEG-1 Audio
ISO/IEC 11172-3 (1988~1991)
First high quality audio compression standard
CD quality two-channel audio at 256 kbits/s
CD: 44.1 kHz 16 bits 2 = 1.411 Mbits/s
Frequency
Band (Hz)
Sampling
Rate
Bits per
Sample
Raw Bitrate
Telephone
Speech
300~3400 8 8 64
Wideband
Speech
50~7000 16 8 128
Mediumband
Audio
10~11000 24 16 384
Wideband
Audio
10~22000 48 16 768
3
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
Quality Demonstration
MPEG-1 Audio (Layer II)
Stereo 44.1 kHz at 64 kbits/s
Stereo 44.1 kHz at 128 kbits/s
Stereo 44.1 kHz at 192 kbits/s
Stereo 44.1 kHz at 256 kbits/s
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
Psychoacoustics
Threshold in quiet
4
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
Frequency Masking
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
Temporal Masking
Post-Masking: 50~200ms
Also Pre-Masking (much shorter)
5
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
Encoder Block Diagram
mapping
quantizer
and
coding
frame
packing
psychoacoustic
model
PCM
audio samples
32, 44.1, 48 kHz
encoded
bitstream
11172-3
Encoder
ancillary data
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
Decoder Block Diagram
frame
unpacking
reconstruction
inverse
mapping
encoded
bits tream
PCM
audio samples
32, 44.1, 48 kHz
ancillary data
11172-3 Decoder
6
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
H
1
(z)
H
2
(z)
F
1
(z)
F
2
(z)
H
M
(z) F
M
(z)
M
M
M
M
M
M
Q
Q
Q
Analysis
Filterbank
Synthesis
Filterbank
Mapping: Subband Coding
Critical downsampling
Q should be based on signal-to-masking ratio (SMR)
Ears critical bands are not uniform, but logarithmic
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
Alias cancellation and perfect reconstruction
M
M
M
z
-1
z
-1
E(z) R(z)
M
M
M
z
z
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Polyphase Filterbank
7
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
Layers
Increasing complexity, delay, and quality
Layer I
~384 kbits/s for perceptually lossless quality (4:1)
Layer II
~192 kbits/s for perceptually lossless quality (8:1)
Layer III
~128 kbits/s for perceptually lossless quality (12:1)
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
Analysis
Filterbank
Scaler &
Quantizer
Mux
32
Masking
Threshold
Generator
Layer I and II Encoder
Dynamic
Bit
Allocator
FFT
Coder
8
Analysis
Filterbank
.
.
.
12 12 12
Layer I
Layer II
Block-Based Coding
12 samples for Layer I, 36 samples for Layer II
Block companding: Each block normalized by scalefactor
For Layer II, up to 3 scalefactors, with 2-bit scalefactor select
Each block receives one bit allocation
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
Analysis
Filterbank
Scaler &
Quantizer
Mux
Layer III Encoder
FFT
MDCT
Huffman
Coding
Masking
Threshold
Generator
Coding
6 or 18
with overlap
9
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
New Features in Layer III
Modified DCT (MDCT)
DCT with overlap
Long/short window switching
Short for better temporal resolution (to prevent pre-echoes)
Long for better frequency resolution
Nonuniform quantization
Entropy coding
Run-length and Huffman coding
Bit reservoir (buffer)
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
Side Info Subband Sanples Header Info Aux Data
Frame Structure
Header info: Sync bits, system info, CRC (cyclic
redundancy code)
Side info: bit allocation, scalefactor, (and scalefactor select
for Layer II and III)
Subband samples: 32 12 for Layer I, 32 36 for Layer II
and III
Packetization: 4-byte header, 184-byte payload
10
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
Stereo Redundancy Coding
Four modes: mono, stereo, dual with two separate
channel, joint stereo
In joint stereo mode
Human stereo perception > 2kHz is based on envelope
Intensity stereo coding > 2kHz
Encode (L + R)
Assign independent left- and right- scalefactors
Layer III supports (L+R) and (LR) coding
18-899/Spring 1998/Chen
References
Peter Noll, MPEG digital audio coding, IEEE Signal
Processing Magazine, Sept. 1997, pp. 59-81
D. Pan, A tutorial on MPEG/Audio compression,
IEEE Trans. on Multimedia, vol. 2, no. 2, 1995, pp.
60-74
You might also like
- PCM, PDH and SDHDocument58 pagesPCM, PDH and SDHAbdul Wahab67% (3)
- Replacing A Failed Boot Disk (HP-UX 11.23)Document3 pagesReplacing A Failed Boot Disk (HP-UX 11.23)Mohammad ArefNo ratings yet
- Kaeser CompDocument34 pagesKaeser CompJose LunaNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Using C, 2e Reema TharejaDocument30 pagesData Structures Using C, 2e Reema TharejaSatyaki SarkarNo ratings yet
- Change Capture Stage - Lookup StageDocument10 pagesChange Capture Stage - Lookup Stagevin_hiworldNo ratings yet
- MPEG Audio: Multimedia Communications: Coding, Systems, and NetworkingDocument15 pagesMPEG Audio: Multimedia Communications: Coding, Systems, and Networkingluigi-porritiello-uni-6951No ratings yet
- ضغط الصوتDocument31 pagesضغط الصوتNoor MohmadNo ratings yet
- Time Division TDMDocument10 pagesTime Division TDMPawan VaskarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Audio Coding (Aac)Document33 pagesAdvanced Audio Coding (Aac)sirhanshafahath8415No ratings yet
- PDH SDH Presentation 1Document67 pagesPDH SDH Presentation 1Mhamad Dannawi100% (1)
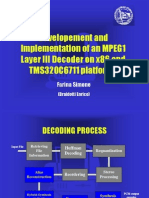
- Developement and Implementation of An MPEG1 Layer III Decoder On x86 and TMS320C6711 PlatformsDocument17 pagesDevelopement and Implementation of An MPEG1 Layer III Decoder On x86 and TMS320C6711 PlatformsAlexander NevidimovNo ratings yet
- Study and Comparison of AC3, AAC and HE-AAC Audio Codecs: EE5359 Multimedia Processing ProjectDocument28 pagesStudy and Comparison of AC3, AAC and HE-AAC Audio Codecs: EE5359 Multimedia Processing ProjectSurekha SundarrNo ratings yet
- Foct 2 Advanced Fiber Optics TrainerDocument1 pageFoct 2 Advanced Fiber Optics TrainerAmish TankariyaNo ratings yet
- Cdma Tdma FdmaDocument87 pagesCdma Tdma FdmaShivlal Yadav100% (1)
- New Trends in Wireless Communication Technology: (With Suitable Multiple Access)Document87 pagesNew Trends in Wireless Communication Technology: (With Suitable Multiple Access)Manoj ShuklaNo ratings yet
- MM Ise 2002 Solns PDFDocument16 pagesMM Ise 2002 Solns PDFAHMED ALANINo ratings yet
- Optical Amplifiers and NetworksDocument45 pagesOptical Amplifiers and NetworksDr Ravi Kumar A VNo ratings yet
- Multimedia I (Audio/Video Data) : CS423, Fall 2007 Klara Nahrstedt/Sam KingDocument28 pagesMultimedia I (Audio/Video Data) : CS423, Fall 2007 Klara Nahrstedt/Sam Kinglizhi0007No ratings yet
- Digital Speech ProcessingDocument18 pagesDigital Speech ProcessingMohamedKadryNo ratings yet
- Voice Digitization and Voice/Data Integration: TCOM 370Document7 pagesVoice Digitization and Voice/Data Integration: TCOM 370saidur183No ratings yet
- 1.digital Signal HierarchyDocument21 pages1.digital Signal HierarchymumerbuttNo ratings yet
- Transmission SystemDocument25 pagesTransmission SystemRama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 32 NMDocument18 pages32 NMAshwini MalladNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Digital Modulation) - Review: Pulses - PAM, PWM, PPM Binary - Ask, FSK, PSK, BPSK, DBPSK, PCM, QamDocument7 pagesChapter 4 (Digital Modulation) - Review: Pulses - PAM, PWM, PPM Binary - Ask, FSK, PSK, BPSK, DBPSK, PCM, QamMuhamad FuadNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Communications: Coding, Systems, and Networking: Prof. Tsuhan ChenDocument17 pagesMultimedia Communications: Coding, Systems, and Networking: Prof. Tsuhan ChenwawmwiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 10310Document2 pagesExercise 10310Najwa IshakNo ratings yet
- GSM System EssentialsDocument45 pagesGSM System EssentialsDavidDavidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 Digital Modulation Techniques Like BPSK, MSK, QPSK and QamDocument6 pagesLesson 9 Digital Modulation Techniques Like BPSK, MSK, QPSK and QamChandni RaoNo ratings yet
- Unit I.1Document13 pagesUnit I.1cool21johnNo ratings yet
- Capacity and ModulasiDocument20 pagesCapacity and ModulasiRizka Nurhasanah0% (1)
- 06 Multiple Access TechniqueDocument23 pages06 Multiple Access TechniqueBijoy SahaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Phone Systems: Li-Hsing Yen National University of KaohsiungDocument22 pagesCellular Phone Systems: Li-Hsing Yen National University of KaohsiungVictor Arkaprava DharNo ratings yet
- Audio Coding: Basics and State of The ArtDocument6 pagesAudio Coding: Basics and State of The ArtAu Belchez ZamudioNo ratings yet
- Audio Coding: Basics and State of The ArtDocument6 pagesAudio Coding: Basics and State of The ArtAu Belchez ZamudioNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Chapter 11Document5 pagesDigital Communication Chapter 11MIsh GomezNo ratings yet
- ESE680: Wireless Sensor Networks: Prof. Rahul MangharamDocument73 pagesESE680: Wireless Sensor Networks: Prof. Rahul MangharamArivazhagan ChinnamadhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter (2) (The Physical Layer)Document50 pagesChapter (2) (The Physical Layer)Ahmed SalehNo ratings yet
- Oft2 Optical Fiber Communication Optical Fiber Communication Optical Fiber Communication Optical Fiber Communication Optical Fiber CommunicationDocument4 pagesOft2 Optical Fiber Communication Optical Fiber Communication Optical Fiber Communication Optical Fiber Communication Optical Fiber CommunicationRashed IslamNo ratings yet
- Dolby AC3 Audio Codec and MPEG-2 Advanced Audio Coding: Recommended byDocument4 pagesDolby AC3 Audio Codec and MPEG-2 Advanced Audio Coding: Recommended byJorge Luis PomachaguaNo ratings yet
- DC-module 1 - NotesDocument69 pagesDC-module 1 - Notescobad87435No ratings yet
- Digital Transmission Fundamentals 04Document35 pagesDigital Transmission Fundamentals 04IhsanNo ratings yet
- Vienna LTE-A System Level Simulator v2.0 Q3-2018 List of FeaturesDocument3 pagesVienna LTE-A System Level Simulator v2.0 Q3-2018 List of FeaturesD Harish KumarNo ratings yet
- T1 and The T Carrier SystemDocument15 pagesT1 and The T Carrier SystemDhiraj KaushalNo ratings yet
- 1155dBTE 504Document13 pages1155dBTE 504Shubham AgrawalNo ratings yet
- CSE820 Week 2 - Introduction: Rich Enbody (Based Loosely On Slides by David Patterson)Document21 pagesCSE820 Week 2 - Introduction: Rich Enbody (Based Loosely On Slides by David Patterson)kbkkrNo ratings yet
- Training Module On Transmission Network and Testing Concep 1Document638 pagesTraining Module On Transmission Network and Testing Concep 1kltowerNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication and Computing (ICT 3272) Ofdm MimoDocument25 pagesWireless Communication and Computing (ICT 3272) Ofdm Mimobaidnirvana8No ratings yet
- MP3 FormatDocument25 pagesMP3 FormatNalluri H C GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document49 pagesChapter 6sahil_saini298No ratings yet
- Fundamental of SDH TechnologyDocument467 pagesFundamental of SDH TechnologyNishad Patil100% (1)
- Presentation On SDH Vs SS7Document59 pagesPresentation On SDH Vs SS7lvsaruNo ratings yet
- PDH SDH PresentationDocument67 pagesPDH SDH PresentationDanish Ahmed100% (3)
- AacDocument27 pagesAacramakrishnamullapudiNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics Transmission System (FOTS) inDocument24 pagesFiber Optics Transmission System (FOTS) inkovid321100% (2)
- Student TDM DPCM DM QDocument1 pageStudent TDM DPCM DM Qmoath farrajNo ratings yet
- DC Tutorial Sheet 1Document2 pagesDC Tutorial Sheet 1Sabir SankhlaNo ratings yet
- ch3 TotDocument2 pagesch3 Tot190148sandipNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processor Evolution Over The Last 30 Years PDFDocument79 pagesDigital Signal Processor Evolution Over The Last 30 Years PDFFrancois Charlot100% (1)
- Huff Man 1Document4 pagesHuff Man 1Gaurav PantNo ratings yet
- Transmission Is The Act of Transporting Information From One Location To Another Via A SignalDocument55 pagesTransmission Is The Act of Transporting Information From One Location To Another Via A SignalDeepesh TrivediNo ratings yet
- Data Communication: By:Eng - Alaa I.HaniyDocument8 pagesData Communication: By:Eng - Alaa I.Haniypömo cNo ratings yet
- Non-Linearities in Passive RFID Systems: Third Harmonic Concept and ApplicationsFrom EverandNon-Linearities in Passive RFID Systems: Third Harmonic Concept and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Radio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDFrom EverandRadio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDNo ratings yet
- Operation ManualDocument2 pagesOperation ManualJuan M. CórdovaNo ratings yet
- MRX525Document2 pagesMRX525Juan M. CórdovaNo ratings yet
- LD04 ch14 PDFDocument42 pagesLD04 ch14 PDFJuan M. CórdovaNo ratings yet
- Manual Soundraft Si ExpressionDocument76 pagesManual Soundraft Si ExpressionJuan M. CórdovaNo ratings yet
- Week 4.3 - MongoDB Deep Dive, AssignmentsDocument25 pagesWeek 4.3 - MongoDB Deep Dive, Assignmentspersonalsuraj69No ratings yet
- Data Management TURBANDocument39 pagesData Management TURBANArwie H. FernandoNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument14 pagesProject ReportKavita Pahadiya PGI20CA020No ratings yet
- KVS Jaipur CS 2ND Pre Board Term 2Document4 pagesKVS Jaipur CS 2ND Pre Board Term 2Sohan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Dit 111 Computer Applications QUESTION PAPER APR 2014Document3 pagesDit 111 Computer Applications QUESTION PAPER APR 2014Silas WafulaNo ratings yet
- NetBackup9.x EEB GuideDocument54 pagesNetBackup9.x EEB Guide黃國峯No ratings yet
- Data Analysis by N VivoDocument40 pagesData Analysis by N VivohakimNo ratings yet
- 6 - Log ShippingDocument11 pages6 - Log Shippingshridharb1177No ratings yet
- 14 2510-3946-2-PBDocument12 pages14 2510-3946-2-PBsriNo ratings yet
- TLE ICT 10 - Network Topologies - Activity SheetDocument7 pagesTLE ICT 10 - Network Topologies - Activity SheetGioSanBuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- D 06 Uservol 1Document533 pagesD 06 Uservol 1gblackweNo ratings yet
- String - What Is The Difference Between Char S and Char - S in C - Stack OverflowDocument5 pagesString - What Is The Difference Between Char S and Char - S in C - Stack OverflowtuyenndvttNo ratings yet
- Firebase ErrorDocument16 pagesFirebase ErrorrafelaptopNo ratings yet
- System Material 3Document10 pagesSystem Material 3Suhas V100% (1)
- PT. Sentra Studia Indonesia (SSI)Document36 pagesPT. Sentra Studia Indonesia (SSI)dimasNo ratings yet
- OopDocument9 pagesOopMohit MalghadeNo ratings yet
- Database Design DocumentDocument22 pagesDatabase Design DocumentOSCAR ALBERTO CHUMPITAZ PERALTANo ratings yet
- Dell Storage For HPC With Intel Enterprise Edition For LustreDocument27 pagesDell Storage For HPC With Intel Enterprise Edition For LustredhillaprNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Characterizing The Existing InternetworkDocument3 pagesChapter 3: Characterizing The Existing InternetworkKatherineNo ratings yet
- VPNDocument4 pagesVPNmohdevrajNo ratings yet
- Osf Unit 3 PDFDocument16 pagesOsf Unit 3 PDFRaRaRaNo ratings yet
- ErrDocument1 pageErrJose Carlos Perumundo CordovezNo ratings yet
- Router Serial Point To Point Connection HDLC, PPP With PAP and CHAPDocument5 pagesRouter Serial Point To Point Connection HDLC, PPP With PAP and CHAPSriharshitha DeepalaNo ratings yet
- HT48R30A-1/HT48C30-1 I/O Type 8-Bit MCU: Technical DocumentDocument40 pagesHT48R30A-1/HT48C30-1 I/O Type 8-Bit MCU: Technical DocumentPablo Jose Barreto RamosNo ratings yet
- AVCS User Guide For JRC ECDISDocument34 pagesAVCS User Guide For JRC ECDISardipangulihi100% (1)
- Compiler Construction: The Symbol TableDocument31 pagesCompiler Construction: The Symbol TableyekoyetigabuNo ratings yet