Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nozzle FEA Calculation
Nozzle FEA Calculation
Uploaded by
berylqzCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pvelite OutputDocument44 pagesPvelite OutputRam MurtyNo ratings yet
- Solution: WE1 12 Nov 2008Document9 pagesSolution: WE1 12 Nov 2008aauppalNo ratings yet
- Crossover Area Calc For Floating HeadDocument2 pagesCrossover Area Calc For Floating HeadRitesh VishambhariNo ratings yet
- Design of Circular Flat Endplate With Stiffeners - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-TipsDocument2 pagesDesign of Circular Flat Endplate With Stiffeners - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-Tipsisrar khanNo ratings yet
- Design of Tooth Locked Quick Open Die Pressure VesselDocument4 pagesDesign of Tooth Locked Quick Open Die Pressure VesselSEP-PublisherNo ratings yet
- PV Elite 2015 Sp1 Licensee: SPLM Licensed User Filename: Untitled Nozzle Calcs.: N1 Nozl: 3 9:36am Dec 7,2018Document32 pagesPV Elite 2015 Sp1 Licensee: SPLM Licensed User Filename: Untitled Nozzle Calcs.: N1 Nozl: 3 9:36am Dec 7,2018Priyo Jati WahyonoNo ratings yet
- Lug On SkidDocument8 pagesLug On Skidmiteshpatel191No ratings yet
- PV Elite ResultDocument239 pagesPV Elite ResultChaitanya Sai TNo ratings yet
- PV Newsletter - Skirt Connections PDFDocument5 pagesPV Newsletter - Skirt Connections PDFDivyesh Patel100% (1)
- Lug SupportDocument2 pagesLug SupportSachin5586No ratings yet
- Nozzle Design CalculationDocument1 pageNozzle Design CalculationSachin55860% (1)
- Small Vertical Pressure Vessel Leg Support Design - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-Tips PDFDocument6 pagesSmall Vertical Pressure Vessel Leg Support Design - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-Tips PDFhussamammarNo ratings yet
- Skirt Design - For Small VesselsDocument7 pagesSkirt Design - For Small VesselsSakthi VelNo ratings yet
- Pressure VesselDocument46 pagesPressure VesselHaftamu HilufNo ratings yet
- Dennis R Moss 4th EditionDocument5 pagesDennis R Moss 4th Editionsenthil kumarNo ratings yet
- Help For P-V Elite PDFDocument39 pagesHelp For P-V Elite PDFTushar MangratiNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation: Fuel Gas Scrubber TAG NO: V-6011Document239 pagesDesign Calculation: Fuel Gas Scrubber TAG NO: V-6011Peja Jusoh100% (1)
- H H Optimum 0,2: Instructions For Using NomogramDocument4 pagesH H Optimum 0,2: Instructions For Using NomogrammithunjobsNo ratings yet
- Deaera DesignDocument13 pagesDeaera DesignBhanu K PrakashNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Check Top Head: Input ParametersDocument2 pagesNozzle Check Top Head: Input ParametersRaj Sharma100% (1)
- H200141 - Calculation of Basering Rev 0 PDFDocument9 pagesH200141 - Calculation of Basering Rev 0 PDFSani Adipura WinataNo ratings yet
- Final Weld Strength CalnsDocument5 pagesFinal Weld Strength CalnsamachmouchiNo ratings yet
- U-V-673 - Manual Flange and GussetDocument8 pagesU-V-673 - Manual Flange and GussetDarshan PanchalNo ratings yet
- STHE Design (Training Material)Document37 pagesSTHE Design (Training Material)Herman_ms2000100% (2)
- External Pressure CalculationsDocument40 pagesExternal Pressure Calculationsmisterdavi50% (2)
- Wind Seismic Calculation DataDocument8 pagesWind Seismic Calculation Dataaknauriyal2013No ratings yet
- SHELL THICKNESS CHECK-ASME Section VIIIDocument2 pagesSHELL THICKNESS CHECK-ASME Section VIIIskocogluNo ratings yet
- Girth Flange Load Calculation Using by FEA TechniquesDocument12 pagesGirth Flange Load Calculation Using by FEA TechniqueskingstonNo ratings yet
- Calculations For: Calculations No. Asme Viii Div 1 Ed 2019Document21 pagesCalculations For: Calculations No. Asme Viii Div 1 Ed 2019David Vanegas100% (1)
- Cover Pages For PV Elite VenvelDocument14 pagesCover Pages For PV Elite VenvelSakthi VelNo ratings yet
- Flange Pad CalcsDocument4 pagesFlange Pad CalcstomNo ratings yet
- Allowable Nozzle LoadsDocument7 pagesAllowable Nozzle LoadsSiva baalanNo ratings yet
- 003-Heat ExchangerDocument299 pages003-Heat ExchangerVijayshanker GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sample Design Calculation - Vessel Supported On LugsDocument11 pagesSample Design Calculation - Vessel Supported On Lugsandry4jc100% (1)
- Flat Plate - Roark & YoungDocument15 pagesFlat Plate - Roark & YoungPrasad Pingle0% (1)
- PV Elite Vessel Analysis Program HorizontalDocument55 pagesPV Elite Vessel Analysis Program HorizontalMarizta Perdani PutriNo ratings yet
- Coupling Calculations and Ug-32 Unstayed Head CalculationsDocument9 pagesCoupling Calculations and Ug-32 Unstayed Head CalculationsLcm TnlNo ratings yet
- Saddle Reaction Summary - For Empty CaseDocument12 pagesSaddle Reaction Summary - For Empty CasesridharNo ratings yet
- TUBESHEETDocument5 pagesTUBESHEETMehta MehulNo ratings yet
- Tailing LugDocument12 pagesTailing LuguvarajmecheriNo ratings yet
- 06745JS2 (7) - Strength Calculations of Module4 (IBR)Document23 pages06745JS2 (7) - Strength Calculations of Module4 (IBR)Pratik Ray Chaudhury100% (3)
- Compress CalculationDocument106 pagesCompress CalculationKrupal Patel100% (1)
- Design Calculation Sheet: H2So4 Neutralization TankDocument43 pagesDesign Calculation Sheet: H2So4 Neutralization TankEkki Petrus BubunNo ratings yet
- Design of Partition PlateDocument5 pagesDesign of Partition Platepippo2378793No ratings yet
- WRC 107 TipsDocument4 pagesWRC 107 Tipsyatin888No ratings yet
- External Nozzle Loads Nozzle To Shells: Type of Loading Symbol Formula UnitDocument1 pageExternal Nozzle Loads Nozzle To Shells: Type of Loading Symbol Formula UnitSachinNo ratings yet
- Sample FLG CalcDocument6 pagesSample FLG CalcameyyammaiNo ratings yet
- Narrow Face Flange - Slip On Hub TypeDocument17 pagesNarrow Face Flange - Slip On Hub TypeEng-CalculationsNo ratings yet
- FEA Check List For Expansion BellowDocument3 pagesFEA Check List For Expansion BellowRyan FisherNo ratings yet
- Saddle AnalysisDocument17 pagesSaddle AnalysisPEJU0007No ratings yet
- 10.1 Asme Viii A-13 Rectangular VesselDocument2 pages10.1 Asme Viii A-13 Rectangular Vesselpastyl100% (1)
- Ibr Calc GSRDocument4 pagesIbr Calc GSRAniket GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Top Pipe MomentDocument2 pagesTop Pipe Momentrsubramani100% (1)
- Nozzle TestDocument9 pagesNozzle TestDarshan PanchalNo ratings yet
- Graphical ResultsDocument11 pagesGraphical Resultshgag selimNo ratings yet
- Test ReportDocument18 pagesTest ReportBilel MahjoubNo ratings yet
- Quick PrintDocument2 pagesQuick PrintSimeon ArabovNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Loads AnalysisDocument110 pagesNozzle Loads Analysishgag selimNo ratings yet
- Quick PrintDocument2 pagesQuick PrintSimeon ArabovNo ratings yet
- Aaaa XXX BBB XXX CCC XXX DDD XXX FFF XXXDocument3 pagesAaaa XXX BBB XXX CCC XXX DDD XXX FFF XXXberylqzNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Tir-Rod StiffnessDocument1 pageCalculation of Tir-Rod StiffnessberylqzNo ratings yet
- As-NZS1170.5 Seismic CoefficientDocument2 pagesAs-NZS1170.5 Seismic CoefficientberylqzNo ratings yet
- Flat Rectangular Plate With Four Sides Fixed Under Uniform PressureDocument4 pagesFlat Rectangular Plate With Four Sides Fixed Under Uniform PressureberylqzNo ratings yet
- My Own Tips For Using Solidworks SimulationDocument2 pagesMy Own Tips For Using Solidworks SimulationberylqzNo ratings yet
- Perforated Plate PDFDocument6 pagesPerforated Plate PDFberylqzNo ratings yet
- Aspen HX Design ReportDocument78 pagesAspen HX Design ReportberylqzNo ratings yet
- O RingsDocument211 pagesO Ringsberylqz100% (2)
- AnswersDocument5 pagesAnswers22 shantanu kapadnisNo ratings yet
- Transport Mechanisms in CellsDocument4 pagesTransport Mechanisms in Cellsd_94No ratings yet
- CH 21 Bridge Works - Super Structure - SteelDocument21 pagesCH 21 Bridge Works - Super Structure - SteelSubhash SinhaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Properties HandbookDocument15 pagesPlastic Properties HandbookguilloteARGNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Lecture Notes - CHAPTER-3 STEAM GENERATOR: October 2014Document46 pagesPower Plant Lecture Notes - CHAPTER-3 STEAM GENERATOR: October 2014Lösky D. PinnockNo ratings yet
- 2002 AriDocument53 pages2002 AriMbarouk Shaame MbaroukNo ratings yet
- Semi-Centrifugal Casting: An Extensive Analysis: Technical ReportDocument10 pagesSemi-Centrifugal Casting: An Extensive Analysis: Technical ReportS. R. OvhalNo ratings yet
- Steam TablesDocument11 pagesSteam TablesARNOUXNo ratings yet
- Excel BasedDocument24 pagesExcel Basedelha e. maruquinNo ratings yet
- A Study On Some Durability Properties of Coconut Shell Aggregate ConcreteDocument13 pagesA Study On Some Durability Properties of Coconut Shell Aggregate ConcreteMa Victoria CaneteNo ratings yet
- Iqwq-Cpp-Grinv-00-0001 - 0Document24 pagesIqwq-Cpp-Grinv-00-0001 - 0வி.சுரேஷ் குமார்100% (1)
- Background of Titrino 702 Automatic TitratorDocument4 pagesBackground of Titrino 702 Automatic TitratorbuttamanatNo ratings yet
- Vol1i7x ECCC RecommandationsDocument21 pagesVol1i7x ECCC RecommandationsRami GhorbelNo ratings yet
- Mining: Supercritical Flow Critical Flow Subcritical FlowDocument3 pagesMining: Supercritical Flow Critical Flow Subcritical FlowBoonsita NammanaNo ratings yet
- ST Handout 3Document23 pagesST Handout 3SwagBeast SKJJNo ratings yet
- En Comparision TableDocument3 pagesEn Comparision TablenikhilnsbNo ratings yet
- Cosmoplast Upvc Drainage Pipes FittingsDocument34 pagesCosmoplast Upvc Drainage Pipes FittingsBahar AbdulqadirNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Sugarcane Bagasse AshDocument27 pagesPpt-Sugarcane Bagasse AshHegdeVenugopalNo ratings yet
- The Real Trick To Drying Ceramic Ware Is To Use A Method That Removes The Water From The Inside of The Ceramic As Fast As The Surface Water Is EvaporatedDocument55 pagesThe Real Trick To Drying Ceramic Ware Is To Use A Method That Removes The Water From The Inside of The Ceramic As Fast As The Surface Water Is EvaporatedMiguel OcampoNo ratings yet
- H2SDocument2 pagesH2Snsivasankar14No ratings yet
- Jurnal InternasionalDocument9 pagesJurnal InternasionalalninditaNo ratings yet
- 15 - Amines (New) PDFDocument25 pages15 - Amines (New) PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Rotacoat 330 Q-CTSDocument2 pagesRotacoat 330 Q-CTSkkkkrolikNo ratings yet
- FCD 450-10Document2 pagesFCD 450-10MohammedFaisalGirachNo ratings yet
- Class X Half Yearly Exam Syllabus 2019 20Document6 pagesClass X Half Yearly Exam Syllabus 2019 20RahulNo ratings yet
- National Fire Protection Association-GoogleDocument2 pagesNational Fire Protection Association-GooglesandeepNo ratings yet
- INDOKOTE Company Profile-4Document8 pagesINDOKOTE Company Profile-4AvijitSinghNo ratings yet
- Time Date I. Objectives: A. Content StandardsDocument5 pagesTime Date I. Objectives: A. Content StandardsRod ReyesNo ratings yet
- Product Catalog PDFDocument979 pagesProduct Catalog PDFa7mos0% (1)
Nozzle FEA Calculation
Nozzle FEA Calculation
Uploaded by
berylqzOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nozzle FEA Calculation
Nozzle FEA Calculation
Uploaded by
berylqzCopyright:
Available Formats
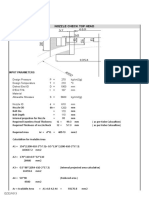
Model Notes (80 NB Shell, 32NB Nozzle)
Input Echo:
Model Type : Cylindrical Shell
Parent Outside Diameter : 88.900 mm.
Thickness : 5.490 mm.
Fillet Along Shell : 5.000 mm.
Parent Properties:
Material DB # 1068318.
(See Output Reports for Allowables.)
Elastic Modulus (Amb) : 195100.0 MPa
Poissons Ratio : 0.300
Expansion Coefficient : 0.1707E-04 mm./mm./deg.
Weight Density : 0.0000E+00 N /cu.mm.(NOT USED)
Nozzle Outside Diameter : 42.100 mm.
Thickness : 3.680 mm.
Length : 150.000 mm.
Nozzle Weld Length : 5.000 mm.
Nozzle Tilt Angle : 0.000 deg.
Distance from Top : 0.000 mm.
Distance from Bottom : 500.000 mm.
Nozzle Properties
Material DB # 1064818.
(See Output Reports for Allowables.)
Elastic Modulus (Amb) : 195100.0 MPa
Poissons Ratio : 0.300
Expansion Coefficient : 0.1707E-04 mm./mm./deg.
Weight Density : 0.0000E+00 N /cu.mm. (NOT USED)
Design Operating Cycles : 7000.
Ambient Temperature (Deg.) : 21.10
The following temperatures have been specified for the analysis:
Nozzle Inside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Nozzle Outside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Vessel Inside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Vessel Outside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Nozzle Pressure : 2.800 MPa
Vessel Pressure : 2.800 MPa
User Defined Load Input Echo:
Loads are given at the Nozzle/Header Junction
Loads are defined in Local Coordinatesc
Forces( N ) Moments (N-m)
Load Case FX FY FZ MX MY MZ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OPER: 1200.0 1200.0 1200.0 350.0 350.0 350.0
FEA Model Loads:
These are the actual loads applied to the FEA model.
These are the User Defined Loads translated to the
end of the nozzle and reported in global coordinates.
Forces( N ) Moments (N-m)
Load Case FX FY FZ MX MY MZ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OPER: 1200.0 1200.0 1200.0 350.0 530.0 170.0
The "top" or "positive" end of this model is "free" in
the axial and translational directions.
Stresses ARE nodally AVERAGED.
Vessel Centerline Vector : 0.000 1.000 0.000
Nozzle Orientation Vector : 1.000 0.000 0.000
Table of Contents
Load Case Report
Inner and outer element temperatures are the same
throughout the model. No thermal ratcheting
calculations will be performed.
THE 8 LOAD CASES ANALYZED ARE:
1 SUSTAINED (Pr Only)
Sustained case run to satisfy local primary
membrane and bending stress limits.
/-------- Loads in Case 1
Pressure Case 1
2 Thermal ONLY
Thermal ONLY case run in the event expansion
stresses exceed the secondary stress allowable.
/-------- Loads in Case 2
Temperature Case 1
3 OPERATING (Fatigue Calc Performed)
Case run to compute the operating stresses used in
secondary, peak and range calculations as needed.
/-------- Loads in Case 3
Pressure Case 1
Temperature Case 1
Loads from (Operating)
4 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 4
Loads from (Axial)
5 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 5
Loads from (Inplane)
6 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 6
Loads from (Outplane)
7 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 7
Loads from (Torsion)
8 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 8
Pressure Case 1
Table of Contents
Solution Data
Maximum Solution Row Size = 870
Number of Nodes = 2112
Number of Elements = 696
Number of Solution Cases = 8
Summation of Loads per Case
Case # FX FY FZ
1 -528. 15309. 0.
2 0. 0. 0.
3 672. 16509. 1200.
4 353202. 0. 0.
5 0. 0. 0.
6 0. 0. 0.
7 0. 0. 0.
8 -528. 15309. 0.
Table of Contents
ASME Code Stress Output Plots
1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
2) Qb < SPS (SUS,Bending) Case 1
3) S1+S2+S3 < 4S (SUS,S1+S2+S3) Case 1
4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
8) Membrane < User (OPE,Membrane) Case 3
9) Bending < User (OPE,Bending) Case 3
10) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 4
11) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 5
12) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 6
13) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 7
14) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 8
Table of Contents
Region Data
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Cold Allowable ........... 138. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 133. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 237. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 795. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 23. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Branch Next to Header Weld
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 237. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 795. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 23. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Branch Transition
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 237. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 795. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 23. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Header away from Junction
Cold Allowable ........... 138. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 133. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 237. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 795. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 23. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.000
Branch away from Junction
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 237. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 795. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 90. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 23. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.000
Table of Contents
Stress Results - Notes
- Results in this analysis were generated using the finite
element solution method.
- Using post 07 ASME Section VIII Division 2
- Use Polished Bar fatigue curve.
- Ratio between Operating and Design Pressure = 0.9000000
Assume pressure increases all other stresses.
Use operating pressure for occasional load cases.
- Assume free end displacements of attached pipe are
secondary loads within limits of nozzle reinforcement.
- Use Equivalent Stress (Von Mises).
- S1+S2+S3 evaluation omitted from operating stress.
Include S1+S2+S3 evaluation in primary case evaluation.
Assume bending stress not local primary for S1+S2+S3.
Table of Contents
ASME Overstressed Areas
*** NO OVERSTRESSED NODES IN THIS MODEL ***
Table of Contents
Highest Primary Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
24 200 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
12%
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
15 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
9%
Branch Transition
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
14 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
8%
Header away from Junction
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
22 200 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
10%
Branch away from Junction
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
14 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
8%
Table of Contents
Highest Secondary Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
290 407 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
71%
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
312 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
92%
Branch Transition
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
193 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
57%
Header away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Inner) Load Case 3
106 407 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
26%
Branch away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
147 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
43%
Table of Contents
Highest Fatigue Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
196 0.007 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.406 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 944,526.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 339.2
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 317,661.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 73,796.
40% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 102,456.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 31,790.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.602
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.624
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
211 0.013 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.437 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 552,854.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 319,984.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 74,335.
43% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 103,205.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 18,610.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.783
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.561
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch Transition
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
130 0.002 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.270 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 4,505,958.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 1,368,181.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 317,841.
26% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 441,282.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 108,897.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 2.063
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.327
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Header away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Inner) Load Case 3
53 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.000
MPa 0.110 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 339.2
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 7,399,607.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 1,718,996.
11% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 2,386,610.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 644,618.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.330
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.752
Plot Reference:
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
Branch away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
73 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.000
MPa 0.152 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 3,121,431.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 725,137.
15% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 1,006,761.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 245,942.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 22.788
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.042
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Table of Contents
Stress Intensification Factors
Branch/Nozzle Sif Summary
Peak Primary Secondary
Axial : 3.289 1.835 4.873
Inplane : 1.144 0.926 1.695
Outplane: 1.934 1.097 2.866
Torsion : 0.816 0.985 1.209
Pressure: 0.879 1.069 1.303
The above stress intensification factors are to be used
in a beam-type analysis of the piping system. Inplane,
Outplane and Torsional sif's should be used with the
matching branch pipe whose diameter and thickness is given
below. The axial sif should be used to intensify the
axial stress in the branch pipe calculated by F/A. The
pressure sif should be used to intensify the nominal
pressure stress in the PARENT or HEADER, calculated
from PD/2T.
Pipe OD : 42.100 mm.
Pipe Thk: 3.680 mm.
Z approx: 4266.306 cu.mm.
Z exact : 3929.104 cu.mm.
B31.3 Branch Pressure i-factor = 2.490
Header Pressure i-factor = 1.759
The B31.3 pressure i-factors should be used with with
F/A, where F is the axial force due to pressure, and
A is the area of the pipe wall. This is equivalent to
finding the pressure stress from (ip)(PD/4T).
B31.3
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
1.916 Inplane
2.331 Outplane
1.000 Torsional
B31.1
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
2.407 Inplane
2.407 Outplane
2.407 Torsional
WRC 330
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
1.488 Inplane
1.624 Outplane
1.000 Torsional
Table of Contents
Allowable Loads
SECONDARY Maximum Conservative Realistic
Load Type (Range): Individual Simultaneous Simultaneous
Occuring Occuring Occuring
Axial Force ( N ) 30620. 9666. 14499.
Inplane Moment (mm. N ) 778910. 173873. 368839.
Outplane Moment (mm. N ) 460549. 102806. 218085.
Torsional Moment (mm. N ) 1091422. 344549. 516824.
Pressure (MPa ) 36.82 2.80 2.80
PRIMARY Maximum Conservative Realistic
Load Type: Individual Simultaneous Simultaneous
Occuring Occuring Occuring
Axial Force ( N ) 39515. 11979. 17969.
Inplane Moment (mm. N ) 692745. 149258. 316625.
Outplane Moment (mm. N ) 584368. 125267. 265732.
Torsional Moment (mm. N ) 651047. 197369. 296054.
Pressure (MPa ) 23.13 2.80 2.80
NOTES:
1) Maximum Individual Occuring Loads are the maximum
allowed values of the respective loads if all other
load components are zero, i.e. the listed axial force
may be applied if the inplane, outplane and torsional
moments, and the pressure are zero.
2) The Conservative Allowable Simultaneous loads are
the maximum loads that can be applied simultaneously.
A conservative stress combination equation is used
that typically produces stresses within 50-70% of the
allowable stress.
3) The Realistic Allowable Simultaneous loads are the
maximum loads that can be applied simultaneously. A
more realistic stress combination equation is used
based on experience at Paulin Research. Stresses are
typically produced within 80-105% of the allowable.
4) Secondary allowable loads are limits for expansion
and operating piping loads.
5) Primary allowable loads are limits for weight,
primary and sustained type piping loads.
Table of Contents
Flexibilities
The following stiffnesses should be used in a piping,
"beam-type" analysis of the intersection. The stiff-
nesses should be inserted at the surface of the
branch/header or nozzle/vessel junction. The general
characteristics used for the branch pipe should be:
Outside Diameter = 42.100 mm.
Wall Thickness = 3.680 mm.
Axial Translational Stiffness = 328869. N /mm.
Inplane Rotational Stiffness = 5227770. mm. N /deg
Outplane Rotational Stiffness = 2134740. mm. N /deg
Torsional Rotational Stiffness = 17393708. mm. N /deg
Intersection Flexibility Factors for
Branch/Nozzle :
Find axial stiffness: K = 3EI/(kd)^3 N /mm.
Find bending and torsional stiffnesses: K = EI/(kd) mm. N per radian.
The EI product is 0.16128E+11 N mm.^2
The value of (d) to use is: 38.420 mm..
The resulting bending stiffness is in units of force x length per radian.
Axial Flexibility Factor (k) = 1.374
Inplane Flexibility Factor (k) = 1.401
Outplane Flexibility Factor (k) = 3.432
Torsional Flexibility Factor (k) = 0.421
Model Notes (80NB Shell, 25NB nozzle)
Input Echo:
Model Type : Cylindrical Shell
Parent Outside Diameter : 88.900 mm.
Thickness : 5.490 mm.
Fillet Along Shell : 5.000 mm.
Parent Properties:
Material DB # 1068318.
(See Output Reports for Allowables.)
Elastic Modulus (Amb) : 195100.0 MPa
Poissons Ratio : 0.300
Expansion Coefficient : 0.1707E-04 mm./mm./deg.
Weight Density : 0.0000E+00 N /cu.mm.(NOT USED)
Nozzle Outside Diameter : 33.500 mm.
Thickness : 3.380 mm.
Length : 150.000 mm.
Nozzle Weld Length : 5.000 mm.
Nozzle Tilt Angle : 0.000 deg.
Distance from Top : 0.000 mm.
Distance from Bottom : 500.000 mm.
Nozzle Properties
Material DB # 1064818.
(See Output Reports for Allowables.)
Elastic Modulus (Amb) : 195100.0 MPa
Poissons Ratio : 0.300
Expansion Coefficient : 0.1707E-04 mm./mm./deg.
Weight Density : 0.0000E+00 N /cu.mm. (NOT USED)
Design Operating Cycles : 7000.
Ambient Temperature (Deg.) : 21.10
The following temperatures have been specified for the analysis:
Nozzle Inside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Nozzle Outside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Vessel Inside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Vessel Outside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Nozzle Pressure : 2.800 MPa
Vessel Pressure : 2.800 MPa
User Defined Load Input Echo:
Loads are given at the Nozzle/Header Junction
Loads are defined in Local Coordinatesc
Forces( N ) Moments (N-m)
Load Case FX FY FZ MX MY MZ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OPER: 1100.0 1100.0 1100.0 250.0 250.0 250.0
FEA Model Loads:
These are the actual loads applied to the FEA model.
These are the User Defined Loads translated to the
end of the nozzle and reported in global coordinates.
Forces( N ) Moments (N-m)
Load Case FX FY FZ MX MY MZ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OPER: 1100.0 1100.0 1100.0 250.0 415.0 85.0
The "top" or "positive" end of this model is "free" in
the axial and translational directions.
Stresses ARE nodally AVERAGED.
Vessel Centerline Vector : 0.000 1.000 0.000
Nozzle Orientation Vector : 1.000 0.000 0.000
Table of Contents
Load Case Report
Inner and outer element temperatures are the same
throughout the model. No thermal ratcheting
calculations will be performed.
THE 8 LOAD CASES ANALYZED ARE:
1 SUSTAINED (Pr Only)
Sustained case run to satisfy local primary
membrane and bending stress limits.
/-------- Loads in Case 1
Pressure Case 1
2 Thermal ONLY
Thermal ONLY case run in the event expansion
stresses exceed the secondary stress allowable.
/-------- Loads in Case 2
Temperature Case 1
3 OPERATING (Fatigue Calc Performed)
Case run to compute the operating stresses used in
secondary, peak and range calculations as needed.
/-------- Loads in Case 3
Pressure Case 1
Temperature Case 1
Loads from (Operating)
4 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 4
Loads from (Axial)
5 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 5
Loads from (Inplane)
6 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 6
Loads from (Outplane)
7 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 7
Loads from (Torsion)
8 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 8
Pressure Case 1
Table of Contents
Solution Data
Maximum Solution Row Size = 870
Number of Nodes = 2256
Number of Elements = 744
Number of Solution Cases = 8
Summation of Loads per Case
Case # FX FY FZ
1 -455. 15299. 0.
2 0. 0. 0.
3 645. 16399. 1100.
4 205408. 0. 0.
5 0. 0. 0.
6 0. 0. 0.
7 0. 0. 0.
8 -455. 15299. 0.
Table of Contents
ASME Code Stress Output Plots
1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
2) Qb < SPS (SUS,Bending) Case 1
3) S1+S2+S3 < 4S (SUS,S1+S2+S3) Case 1
4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
8) Membrane < User (OPE,Membrane) Case 3
9) Bending < User (OPE,Bending) Case 3
10) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 4
11) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 5
12) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 6
13) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 7
14) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 8
Table of Contents
Region Data
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Cold Allowable ........... 138. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 133. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 337. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 642. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 23. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.380 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Branch Next to Header Weld
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 337. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 642. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 23. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.380 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Branch Transition
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 337. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 642. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 23. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.380 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Header away from Junction
Cold Allowable ........... 138. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 133. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 337. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 642. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 23. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.380 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.000
Branch away from Junction
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 337. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 23. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 642. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 94. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 23. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.380 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.000
Table of Contents
Stress Results - Notes
- Results in this analysis were generated using the finite
element solution method.
- Using post 07 ASME Section VIII Division 2
- Use Polished Bar fatigue curve.
- Ratio between Operating and Design Pressure = 0.9000000
Assume pressure increases all other stresses.
Use operating pressure for occasional load cases.
- Assume free end displacements of attached pipe are
secondary loads within limits of nozzle reinforcement.
- Use Equivalent Stress (Von Mises).
- S1+S2+S3 evaluation omitted from operating stress.
Include S1+S2+S3 evaluation in primary case evaluation.
Assume bending stress not local primary for S1+S2+S3.
Table of Contents
ASME Overstressed Areas
*** NO OVERSTRESSED NODES IN THIS MODEL ***
Table of Contents
Highest Primary Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
22 200 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
11%
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
11 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
6%
Branch Transition
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
12 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
7%
Header away from Junction
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
20 200 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
10%
Branch away from Junction
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
12 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
7%
Table of Contents
Highest Secondary Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
286 407 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
70%
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
322 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
95%
Branch Transition
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
254 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
75%
Header away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Inner) Load Case 3
100 407 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
24%
Branch away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
182 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
54%
Table of Contents
Highest Fatigue Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
193 0.007 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.400 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1,026,306.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 339.2
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 335,511.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 77,942.
40% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 108,213.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 33,329.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.561
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.640
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
218 0.016 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.452 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 446,366.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 302,511.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 70,276.
45% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 97,570.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 15,731.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.920
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.521
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch Transition
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
172 0.005 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.356 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1,503,594.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 609,573.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 141,609.
35% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 196,607.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 47,359.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 2.060
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.327
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Header away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Inner) Load Case 3
50 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.000
MPa 0.103 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 339.2
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 9,028,427.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 2,097,386.
10% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 2,911,956.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 783,499.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.349
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.741
Plot Reference:
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
Branch away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
91 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.000
MPa 0.189 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 1,680,991.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 390,510.
18% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 542,173.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 128,176.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 15.094
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.062
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Table of Contents
Stress Intensification Factors
Branch/Nozzle Sif Summary
Peak Primary Secondary
Axial : 2.772 1.656 4.107
Inplane : 1.048 0.911 1.553
Outplane: 1.480 0.921 2.192
Torsion : 0.764 0.919 1.131
Pressure: 0.799 0.980 1.184
The above stress intensification factors are to be used
in a beam-type analysis of the piping system. Inplane,
Outplane and Torsional sif's should be used with the
matching branch pipe whose diameter and thickness is given
below. The axial sif should be used to intensify the
axial stress in the branch pipe calculated by F/A. The
pressure sif should be used to intensify the nominal
pressure stress in the PARENT or HEADER, calculated
from PD/2T.
Pipe OD : 33.500 mm.
Pipe Thk: 3.380 mm.
Z approx: 2408.331 cu.mm.
Z exact : 2192.609 cu.mm.
B31.3 Branch Pressure i-factor = 2.611
Header Pressure i-factor = 1.598
The B31.3 pressure i-factors should be used with with
F/A, where F is the axial force due to pressure, and
A is the area of the pipe wall. This is equivalent to
finding the pressure stress from (ip)(PD/4T).
B31.3
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
1.760 Inplane
2.141 Outplane
1.000 Torsional
B31.1
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
1.928 Inplane
1.928 Outplane
1.928 Torsional
WRC 330
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
1.314 Inplane
1.500 Outplane
1.000 Torsional
Table of Contents
Allowable Loads
SECONDARY Maximum Conservative Realistic
Load Type (Range): Individual Simultaneous Simultaneous
Occuring Occuring Occuring
Axial Force ( N ) 26161. 8332. 12498.
Inplane Moment (mm. N ) 474306. 106818. 226594.
Outplane Moment (mm. N ) 336002. 75670. 160521.
Torsional Moment (mm. N ) 651026. 207347. 311020.
Pressure (MPa ) 42.47 2.80 2.80
PRIMARY Maximum Conservative Realistic
Load Type: Individual Simultaneous Simultaneous
Occuring Occuring Occuring
Axial Force ( N ) 31517. 9772. 14659.
Inplane Moment (mm. N ) 392661. 85818. 182047.
Outplane Moment (mm. N ) 388545. 84939. 180183.
Torsional Moment (mm. N ) 389298. 120709. 181064.
Pressure (MPa ) 25.22 2.80 2.80
NOTES:
1) Maximum Individual Occuring Loads are the maximum
allowed values of the respective loads if all other
load components are zero, i.e. the listed axial force
may be applied if the inplane, outplane and torsional
moments, and the pressure are zero.
2) The Conservative Allowable Simultaneous loads are
the maximum loads that can be applied simultaneously.
A conservative stress combination equation is used
that typically produces stresses within 50-70% of the
allowable stress.
3) The Realistic Allowable Simultaneous loads are the
maximum loads that can be applied simultaneously. A
more realistic stress combination equation is used
based on experience at Paulin Research. Stresses are
typically produced within 80-105% of the allowable.
4) Secondary allowable loads are limits for expansion
and operating piping loads.
5) Primary allowable loads are limits for weight,
primary and sustained type piping loads.
Table of Contents
Flexibilities
The following stiffnesses should be used in a piping,
"beam-type" analysis of the intersection. The stiff-
nesses should be inserted at the surface of the
branch/header or nozzle/vessel junction. The general
characteristics used for the branch pipe should be:
Outside Diameter = 33.500 mm.
Wall Thickness = 3.380 mm.
Axial Translational Stiffness = 252619. N /mm.
Inplane Rotational Stiffness = 3489170. mm. N /deg
Outplane Rotational Stiffness = 1513391. mm. N /deg
Torsional Rotational Stiffness = 15530895. mm. N /deg
Intersection Flexibility Factors for
Branch/Nozzle :
Find axial stiffness: K = 3EI/(kd)^3 N /mm.
Find bending and torsional stiffnesses: K = EI/(kd) mm. N per radian.
The EI product is 0.71616E+10 N mm.^2
The value of (d) to use is: 30.120 mm..
The resulting bending stiffness is in units of force x length per radian.
Axial Flexibility Factor (k) = 1.460
Inplane Flexibility Factor (k) = 1.189
Outplane Flexibility Factor (k) = 2.742
Torsional Flexibility Factor (k) = 0.267
Model Notes
Input Echo:
Model Type : Cylindrical Shell
Parent Outside Diameter : 114.300 mm.
Thickness : 6.020 mm.
Fillet Along Shell : 5.000 mm.
Parent Properties:
Material DB # 1085918.
(See Output Reports for Allowables.)
Elastic Modulus (Amb) : 195100.0 MPa
Poissons Ratio : 0.300
Expansion Coefficient : 0.1740E-04 mm./mm./deg.
Weight Density : 0.0000E+00 N /cu.mm.(NOT USED)
Nozzle Outside Diameter : 60.300 mm.
Thickness : 5.540 mm.
Length : 150.000 mm.
Nozzle Weld Length : 5.000 mm.
Nozzle Tilt Angle : 0.000 deg.
Distance from Top : 0.000 mm.
Distance from Bottom : 500.000 mm.
Nozzle Properties
Material DB # 1068318.
(See Output Reports for Allowables.)
Elastic Modulus (Amb) : 195100.0 MPa
Poissons Ratio : 0.300
Expansion Coefficient : 0.1740E-04 mm./mm./deg.
Weight Density : 0.0000E+00 N /cu.mm. (NOT USED)
Design Operating Cycles : 7000.
Ambient Temperature (Deg.) : 21.10
The following temperatures have been specified for the analysis:
Nozzle Inside Temperature : 250.00 deg.
Nozzle Outside Temperature : 250.00 deg.
Vessel Inside Temperature : 250.00 deg.
Vessel Outside Temperature : 250.00 deg.
Nozzle Pressure : 2.800 MPa
Vessel Pressure : 2.800 MPa
User Defined Load Input Echo:
Loads are given at the Nozzle/Header Junction
Loads are defined in Local Coordinatesc
Forces( N ) Moments (N-m)
Load Case FX FY FZ MX MY MZ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OPER: 1700.0 1700.0 1700.0 650.0 650.0 650.0
FEA Model Loads:
These are the actual loads applied to the FEA model.
These are the User Defined Loads translated to the
end of the nozzle and reported in global coordinates.
Forces( N ) Moments (N-m)
Load Case FX FY FZ MX MY MZ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OPER: 1700.0 1700.0 1700.0 650.0 905.0 395.0
The "top" or "positive" end of this model is "free" in
the axial and translational directions.
Stresses ARE nodally AVERAGED.
Vessel Centerline Vector : 0.000 1.000 0.000
Nozzle Orientation Vector : 1.000 0.000 0.000
Table of Contents
Load Case Report
Inner and outer element temperatures are the same
throughout the model. No thermal ratcheting
calculations will be performed.
THE 8 LOAD CASES ANALYZED ARE:
1 SUSTAINED (Pr Only)
Sustained case run to satisfy local primary
membrane and bending stress limits.
/-------- Loads in Case 1
Pressure Case 1
2 Thermal ONLY
Thermal ONLY case run in the event expansion
stresses exceed the secondary stress allowable.
/-------- Loads in Case 2
Temperature Case 1
3 OPERATING (Fatigue Calc Performed)
Case run to compute the operating stresses used in
secondary, peak and range calculations as needed.
/-------- Loads in Case 3
Pressure Case 1
Temperature Case 1
Loads from (Operating)
4 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 4
Loads from (Axial)
5 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 5
Loads from (Inplane)
6 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 6
Loads from (Outplane)
7 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 7
Loads from (Torsion)
8 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 8
Pressure Case 1
Table of Contents
Solution Data
Maximum Solution Row Size = 1296
Number of Nodes = 3076
Number of Elements = 1012
Number of Solution Cases = 8
Summation of Loads per Case
Case # FX FY FZ
1 -1294. 25806. 0.
2 0. 0. 0.
3 406. 27507. 1700.
4 1090827. 0. 0.
5 0. 0. 0.
6 0. 0. 0.
7 0. 0. 0.
8 -1294. 25806. 0.
Table of Contents
ASME Code Stress Output Plots
1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
2) Qb < SPS (SUS,Bending) Case 1
3) S1+S2+S3 < 4S (SUS,S1+S2+S3) Case 1
4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
8) Membrane < User (OPE,Membrane) Case 3
9) Bending < User (OPE,Bending) Case 3
10) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 4
11) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 5
12) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 6
13) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 7
14) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 8
Table of Contents
Region Data
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Cold Allowable ........... 138. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 250 deg .. 122. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 27. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 134. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 27. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 1145. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 27. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 5.540 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Branch Next to Header Weld
Cold Allowable ........... 138. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 250 deg .. 126. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 27. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 134. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 27. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 1145. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 27. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 5.540 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Branch Transition
Cold Allowable ........... 138. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 250 deg .. 126. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 27. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 134. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 27. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 1145. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 27. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 5.540 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Header away from Junction
Cold Allowable ........... 138. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 250 deg .. 122. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 27. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 134. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 27. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 1145. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 27. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 5.540 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.000
Branch away from Junction
Cold Allowable ........... 138. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 250 deg .. 126. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 27. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 134. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 27. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 1145. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 27. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 5.540 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.000
Table of Contents
Stress Results - Notes
- Results in this analysis were generated using the finite
element solution method.
- Using post 07 ASME Section VIII Division 2
- Use Polished Bar fatigue curve.
- Ratio between Operating and Design Pressure = 0.9000000
Assume pressure increases all other stresses.
Use operating pressure for occasional load cases.
- Assume free end displacements of attached pipe are
secondary loads within limits of nozzle reinforcement.
- Use Equivalent Stress (Von Mises).
- S1+S2+S3 evaluation omitted from operating stress.
Include S1+S2+S3 evaluation in primary case evaluation.
Assume bending stress not local primary for S1+S2+S3.
Table of Contents
ASME Overstressed Areas
*** NO OVERSTRESSED NODES IN THIS MODEL ***
Table of Contents
Highest Primary Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
31 182 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
17%
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
20 189 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
10%
Branch Transition
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
14 189 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
7%
Header away from Junction
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
24 182 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
13%
Branch away from Junction
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
14 189 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
7%
Table of Contents
Highest Secondary Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
313 389 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
80%
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
258 395 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
65%
Branch Transition
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
115 395 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
29%
Header away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Inner) Load Case 3
107 389 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
27%
Branch away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Inner) Load Case 3
94 395 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
23%
Table of Contents
Highest Fatigue Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
211 0.013 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.438 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 542,806.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 324.4
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 237,731.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 55,227.
43% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 76,676.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 25,335.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.544
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.648
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
174 0.005 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.361 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1,433,146.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.5
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 446,978.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 103,837.
36% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 144,165.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 45,313.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.674
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.597
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch Transition
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
78 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.161 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.5
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 5,160,248.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 1,198,772.
16% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 1,664,344.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 510,190.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 1.897
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.345
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Header away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Inner) Load Case 3
53 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.000
MPa 0.111 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 324.4
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 6,838,555.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 1,588,658.
11% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 2,205,652.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 640,861.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.362
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.734
Plot Reference:
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
Branch away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Inner) Load Case 3
47 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.000
MPa 0.098 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.5
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 9,393,385.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 2,182,169.
9% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 3,029,666.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 929,255.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 14.331
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.065
Plot Reference:
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
Table of Contents
Stress Intensification Factors
Branch/Nozzle Sif Summary
Peak Primary Secondary
Axial : 4.530 2.243 6.711
Inplane : 1.383 1.316 2.049
Outplane: 3.047 1.370 4.513
Torsion : 0.901 0.982 1.334
Pressure: 0.951 1.171 1.409
The above stress intensification factors are to be used
in a beam-type analysis of the piping system. Inplane,
Outplane and Torsional sif's should be used with the
matching branch pipe whose diameter and thickness is given
below. The axial sif should be used to intensify the
axial stress in the branch pipe calculated by F/A. The
pressure sif should be used to intensify the nominal
pressure stress in the PARENT or HEADER, calculated
from PD/2T.
Pipe OD : 60.300 mm.
Pipe Thk: 5.540 mm.
Z approx: 13047.465 cu.mm.
Z exact : 11970.017 cu.mm.
B31.3 Branch Pressure i-factor = 3.318
Header Pressure i-factor = 1.902
The B31.3 pressure i-factors should be used with with
F/A, where F is the axial force due to pressure, and
A is the area of the pipe wall. This is equivalent to
finding the pressure stress from (ip)(PD/4T).
B31.3
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
2.916 Inplane
3.582 Outplane
1.000 Torsional
B31.1
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
3.582 Inplane
3.582 Outplane
3.582 Torsional
WRC 330
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
2.309 Inplane
2.602 Outplane
1.316 Torsional
Table of Contents
Allowable Loads
SECONDARY Maximum Conservative Realistic
Load Type (Range): Individual Simultaneous Simultaneous
Occuring Occuring Occuring
Axial Force ( N ) 56160. 17639. 26459.
Inplane Moment (mm. N ) 2310468. 508404. 1078488.
Outplane Moment (mm. N ) 1032534. 224472. 476178.
Torsional Moment (mm. N ) 3547619. 1114283. 1671424.
Pressure (MPa ) 29.11 2.80 2.80
PRIMARY Maximum Conservative Realistic
Load Type: Individual Simultaneous Simultaneous
Occuring Occuring Occuring
Axial Force ( N ) 80128. 23038. 34557.
Inplane Moment (mm. N ) 1659555. 324434. 688228.
Outplane Moment (mm. N ) 1647272. 346564. 735173.
Torsional Moment (mm. N ) 2259663. 624731. 937096.
Pressure (MPa ) 16.41 2.80 2.80
NOTES:
1) Maximum Individual Occuring Loads are the maximum
allowed values of the respective loads if all other
load components are zero, i.e. the listed axial force
may be applied if the inplane, outplane and torsional
moments, and the pressure are zero.
2) The Conservative Allowable Simultaneous loads are
the maximum loads that can be applied simultaneously.
A conservative stress combination equation is used
that typically produces stresses within 50-70% of the
allowable stress.
3) The Realistic Allowable Simultaneous loads are the
maximum loads that can be applied simultaneously. A
more realistic stress combination equation is used
based on experience at Paulin Research. Stresses are
typically produced within 80-105% of the allowable.
4) Secondary allowable loads are limits for expansion
and operating piping loads.
5) Primary allowable loads are limits for weight,
primary and sustained type piping loads.
Table of Contents
Flexibilities
The following stiffnesses should be used in a piping,
"beam-type" analysis of the intersection. The stiff-
nesses should be inserted at the surface of the
branch/header or nozzle/vessel junction. The general
characteristics used for the branch pipe should be:
Outside Diameter = 60.300 mm.
Wall Thickness = 5.540 mm.
Axial Translational Stiffness = 332999. N /mm.
Inplane Rotational Stiffness = 9792365. mm. N /deg
Outplane Rotational Stiffness = 3616443. mm. N /deg
Torsional Rotational Stiffness = 30174178. mm. N /deg
Intersection Flexibility Factors for
Branch/Nozzle :
Find axial stiffness: K = 3EI/(kd)^3 N /mm.
Find bending and torsional stiffnesses: K = EI/(kd) mm. N per radian.
The EI product is 0.70375E+11 N mm.^2
The value of (d) to use is: 54.760 mm..
The resulting bending stiffness is in units of force x length per radian.
Axial Flexibility Factor (k) = 1.569
Inplane Flexibility Factor (k) = 2.291
Outplane Flexibility Factor (k) = 6.202
Torsional Flexibility Factor (k) = 0.743
Model Notes
Input Echo:
Model Type : Cylindrical Shell
Parent Outside Diameter : 168.300 mm.
Thickness : 7.110 mm.
Fillet Along Shell : 5.000 mm.
Parent Properties:
Material DB # 1064818.
(See Output Reports for Allowables.)
Elastic Modulus (Amb) : 195100.0 MPa
Poissons Ratio : 0.300
Expansion Coefficient : 0.1730E-04 mm./mm./deg.
Weight Density : 0.0000E+00 N /cu.mm.(NOT USED)
Nozzle Outside Diameter : 88.900 mm.
Thickness : 5.490 mm.
Length : 150.000 mm.
Nozzle Weld Length : 5.000 mm.
Nozzle Tilt Angle : 0.000 deg.
Distance from Top : 0.000 mm.
Distance from Bottom : 500.000 mm.
Nozzle Properties
Material DB # 1064818.
(See Output Reports for Allowables.)
Elastic Modulus (Amb) : 195100.0 MPa
Poissons Ratio : 0.300
Expansion Coefficient : 0.1730E-04 mm./mm./deg.
Weight Density : 0.0000E+00 N /cu.mm. (NOT USED)
Design Operating Cycles : 7000.
Ambient Temperature (Deg.) : 21.10
The following temperatures have been specified for the analysis:
Nozzle Inside Temperature : 235.00 deg.
Nozzle Outside Temperature : 235.00 deg.
Vessel Inside Temperature : 235.00 deg.
Vessel Outside Temperature : 235.00 deg.
Nozzle Pressure : 2.800 MPa
Vessel Pressure : 2.800 MPa
User Defined Load Input Echo:
Loads are given at the Nozzle/Header Junction
Loads are defined in Local Coordinatesc
Forces( N ) Moments (N-m)
Load Case FX FY FZ MX MY MZ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OPER: 2700.0 2700.0 2700.0 1000.0 1000.0 1000.0
FEA Model Loads:
These are the actual loads applied to the FEA model.
These are the User Defined Loads translated to the
end of the nozzle and reported in global coordinates.
Forces( N ) Moments (N-m)
Load Case FX FY FZ MX MY MZ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OPER: 2700.0 2700.0 2700.0 1000.0 1405.0 595.0
The "top" or "positive" end of this model is "free" in
the axial and translational directions.
Stresses ARE nodally AVERAGED.
Vessel Centerline Vector : 0.000 1.000 0.000
Nozzle Orientation Vector : 1.000 0.000 0.000
Table of Contents
Load Case Report
Inner and outer element temperatures are the same
throughout the model. No thermal ratcheting
calculations will be performed.
THE 8 LOAD CASES ANALYZED ARE:
1 SUSTAINED (Pr Only)
Sustained case run to satisfy local primary
membrane and bending stress limits.
/-------- Loads in Case 1
Pressure Case 1
2 Thermal ONLY
Thermal ONLY case run in the event expansion
stresses exceed the secondary stress allowable.
/-------- Loads in Case 2
Temperature Case 1
3 OPERATING (Fatigue Calc Performed)
Case run to compute the operating stresses used in
secondary, peak and range calculations as needed.
/-------- Loads in Case 3
Pressure Case 1
Temperature Case 1
Loads from (Operating)
4 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 4
Loads from (Axial)
5 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 5
Loads from (Inplane)
6 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 6
Loads from (Outplane)
7 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 7
Loads from (Torsion)
8 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 8
Pressure Case 1
Table of Contents
Solution Data
Maximum Solution Row Size = 1164
Number of Nodes = 2764
Number of Elements = 908
Number of Solution Cases = 8
Summation of Loads per Case
Case # FX FY FZ
1 -2027. 57168. 0.
2 0. 0. 0.
3 673. 59868. 2700.
4 2349565. 0. 0.
5 0. 0. 0.
6 0. 0. 0.
7 0. 0. 0.
8 -2027. 57168. 0.
Table of Contents
ASME Code Stress Output Plots
1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
2) Qb < SPS (SUS,Bending) Case 1
3) S1+S2+S3 < 4S (SUS,S1+S2+S3) Case 1
4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
8) Membrane < User (OPE,Membrane) Case 3
9) Bending < User (OPE,Bending) Case 3
10) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 4
11) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 5
12) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 6
13) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 7
14) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 8
Table of Contents
Region Data
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 235 deg .. 105. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 1633. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 33. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 5.490 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Branch Next to Header Weld
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 235 deg .. 105. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 1633. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 33. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 5.490 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Branch Transition
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 235 deg .. 105. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 1633. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 33. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 5.490 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Header away from Junction
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 235 deg .. 105. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 1633. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 33. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 5.490 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.000
Branch away from Junction
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 235 deg .. 105. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 91. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 1633. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 83. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 33. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 5.490 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.000
Table of Contents
Stress Results - Notes
- Results in this analysis were generated using the finite
element solution method.
- Using post 07 ASME Section VIII Division 2
- Use Polished Bar fatigue curve.
- Ratio between Operating and Design Pressure = 0.9000000
Assume pressure increases all other stresses.
Use operating pressure for occasional load cases.
- Assume free end displacements of attached pipe are
secondary loads within limits of nozzle reinforcement.
- Use Equivalent Stress (Von Mises).
- S1+S2+S3 evaluation omitted from operating stress.
Include S1+S2+S3 evaluation in primary case evaluation.
Assume bending stress not local primary for S1+S2+S3.
Table of Contents
ASME Overstressed Areas
*** NO OVERSTRESSED NODES IN THIS MODEL ***
Table of Contents
Highest Primary Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
47 157 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
29%
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
39 157 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
24%
Branch Transition
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
22 157 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
13%
Header away from Junction
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
33 157 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
20%
Branch away from Junction
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
22 157 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
14%
Table of Contents
Highest Secondary Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
238 330 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
72%
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
246 330 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
74%
Branch Transition
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
86 330 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
26%
Header away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
95 330 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
28%
Branch away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Inner) Load Case 3
79 330 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
23%
Table of Contents
Highest Fatigue Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
160 0.004 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.333 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1,869,714.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 275.0
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 500,365.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 116,239.
33% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 161,384.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 57,872.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.534
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.652
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
166 0.004 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.344 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1,683,686.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 275.0
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 538,848.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 125,179.
34% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 173,796.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 52,553.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.560
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.641
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch Transition
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
58 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.121 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 275.0
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 13,044,634.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 3,030,384.
12% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 4,207,306.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 1,208,851.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 1.181
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.459
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Header away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
48 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.000
MPa 0.099 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 275.0
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 8,456,431.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 1,964,506.
9% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 2,727,469.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 903,240.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.889
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.529
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Inner) Load Case 3
39 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.000
MPa 0.082 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 275.0
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 16,800,968.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 3,903,014.
8% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 5,418,844.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 1,602,801.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 4.413
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.185
Plot Reference:
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
Table of Contents
Stress Intensification Factors
Branch/Nozzle Sif Summary
Peak Primary Secondary
Axial : 5.172 2.413 7.663
Inplane : 1.761 1.426 2.608
Outplane: 3.838 1.805 5.686
Torsion : 0.838 1.050 1.242
Pressure: 1.110 1.409 1.644
The above stress intensification factors are to be used
in a beam-type analysis of the piping system. Inplane,
Outplane and Torsional sif's should be used with the
matching branch pipe whose diameter and thickness is given
below. The axial sif should be used to intensify the
axial stress in the branch pipe calculated by F/A. The
pressure sif should be used to intensify the nominal
pressure stress in the PARENT or HEADER, calculated
from PD/2T.
Pipe OD : 88.900 mm.
Pipe Thk: 5.490 mm.
Z approx: 29998.402 cu.mm.
Z exact : 28267.791 cu.mm.
B31.3 Branch Pressure i-factor = 3.244
Header Pressure i-factor = 2.219
The B31.3 pressure i-factors should be used with with
F/A, where F is the axial force due to pressure, and
A is the area of the pipe wall. This is equivalent to
finding the pressure stress from (ip)(PD/4T).
B31.3
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
2.823 Inplane
3.507 Outplane
1.000 Torsional
B31.1
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
3.507 Inplane
3.507 Outplane
3.507 Torsional
WRC 330
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
2.345 Inplane
2.663 Outplane
1.378 Torsional
Table of Contents
Allowable Loads
SECONDARY Maximum Conservative Realistic
Load Type (Range): Individual Simultaneous Simultaneous
Occuring Occuring Occuring
Axial Force ( N ) 61951. 18468. 27702.
Inplane Moment (mm. N ) 3576334. 753856. 1599170.
Outplane Moment (mm. N ) 1640552. 345812. 733578.
Torsional Moment (mm. N ) 7512132. 2239384. 3359075.
Pressure (MPa ) 16.96 2.80 2.80
PRIMARY Maximum Conservative Realistic
Load Type: Individual Simultaneous Simultaneous
Occuring Occuring Occuring
Axial Force ( N ) 93768. 23567. 35351.
Inplane Moment (mm. N ) 3116851. 516572. 1095815.
Outplane Moment (mm. N ) 2462808. 437692. 928484.
Torsional Moment (mm. N ) 4231704. 991848. 1487772.
Pressure (MPa ) 9.43 2.80 2.80
NOTES:
1) Maximum Individual Occuring Loads are the maximum
allowed values of the respective loads if all other
load components are zero, i.e. the listed axial force
may be applied if the inplane, outplane and torsional
moments, and the pressure are zero.
2) The Conservative Allowable Simultaneous loads are
the maximum loads that can be applied simultaneously.
A conservative stress combination equation is used
that typically produces stresses within 50-70% of the
allowable stress.
3) The Realistic Allowable Simultaneous loads are the
maximum loads that can be applied simultaneously. A
more realistic stress combination equation is used
based on experience at Paulin Research. Stresses are
typically produced within 80-105% of the allowable.
4) Secondary allowable loads are limits for expansion
and operating piping loads.
5) Primary allowable loads are limits for weight,
primary and sustained type piping loads.
Table of Contents
Flexibilities
The following stiffnesses should be used in a piping,
"beam-type" analysis of the intersection. The stiff-
nesses should be inserted at the surface of the
branch/header or nozzle/vessel junction. The general
characteristics used for the branch pipe should be:
Outside Diameter = 88.900 mm.
Wall Thickness = 5.490 mm.
Axial Translational Stiffness = 355901. N /mm.
Inplane Rotational Stiffness = 20446666. mm. N /deg
Outplane Rotational Stiffness = 7338696. mm. N /deg
Torsional Rotational Stiffness = 67436208. mm. N /deg
Intersection Flexibility Factors for
Branch/Nozzle :
Find axial stiffness: K = 3EI/(kd)^3 N /mm.
Find bending and torsional stiffnesses: K = EI/(kd) mm. N per radian.
The EI product is 0.24502E+12 N mm.^2
The value of (d) to use is: 83.410 mm..
The resulting bending stiffness is in units of force x length per radian.
Axial Flexibility Factor (k) = 1.527
Inplane Flexibility Factor (k) = 2.507
Outplane Flexibility Factor (k) = 6.986
Torsional Flexibility Factor (k) = 0.760
Model Notes
Input Echo:
Model Type : Cylindrical Shell
Parent Outside Diameter : 168.300 mm.
Thickness : 7.110 mm.
Fillet Along Shell : 5.000 mm.
Parent Properties:
Material DB # 1064818.
(See Output Reports for Allowables.)
Elastic Modulus (Amb) : 195100.0 MPa
Poissons Ratio : 0.300
Expansion Coefficient : 0.1730E-04 mm./mm./deg.
Weight Density : 0.0000E+00 N /cu.mm.(NOT USED)
Nozzle Outside Diameter : 48.300 mm.
Thickness : 3.680 mm.
Length : 150.000 mm.
Nozzle Weld Length : 5.000 mm.
Nozzle Tilt Angle : 0.000 deg.
Distance from Top : 0.000 mm.
Distance from Bottom : 500.000 mm.
Nozzle Properties
Material DB # 1064818.
(See Output Reports for Allowables.)
Elastic Modulus (Amb) : 195100.0 MPa
Poissons Ratio : 0.300
Expansion Coefficient : 0.1730E-04 mm./mm./deg.
Weight Density : 0.0000E+00 N /cu.mm. (NOT USED)
Design Operating Cycles : 7000.
Ambient Temperature (Deg.) : 21.10
The following temperatures have been specified for the analysis:
Nozzle Inside Temperature : 235.00 deg.
Nozzle Outside Temperature : 235.00 deg.
Vessel Inside Temperature : 235.00 deg.
Vessel Outside Temperature : 235.00 deg.
Nozzle Pressure : 2.800 MPa
Vessel Pressure : 2.800 MPa
User Defined Load Input Echo:
Loads are given at the Nozzle/Header Junction
Loads are defined in Local Coordinatesc
Forces( N ) Moments (N-m)
Load Case FX FY FZ MX MY MZ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OPER: 1250.0 1250.0 1250.0 450.0 450.0 450.0
FEA Model Loads:
These are the actual loads applied to the FEA model.
These are the User Defined Loads translated to the
end of the nozzle and reported in global coordinates.
Forces( N ) Moments (N-m)
Load Case FX FY FZ MX MY MZ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OPER: 1250.0 1250.0 1250.0 450.0 637.5 262.5
The "top" or "positive" end of this model is "free" in
the axial and translational directions.
Stresses ARE nodally AVERAGED.
Vessel Centerline Vector : 0.000 1.000 0.000
Nozzle Orientation Vector : 1.000 0.000 0.000
Table of Contents
Load Case Report
Inner and outer element temperatures are the same
throughout the model. No thermal ratcheting
calculations will be performed.
THE 8 LOAD CASES ANALYZED ARE:
1 SUSTAINED (Pr Only)
Sustained case run to satisfy local primary
membrane and bending stress limits.
/-------- Loads in Case 1
Pressure Case 1
2 Thermal ONLY
Thermal ONLY case run in the event expansion
stresses exceed the secondary stress allowable.
/-------- Loads in Case 2
Temperature Case 1
3 OPERATING (Fatigue Calc Performed)
Case run to compute the operating stresses used in
secondary, peak and range calculations as needed.
/-------- Loads in Case 3
Pressure Case 1
Temperature Case 1
Loads from (Operating)
4 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 4
Loads from (Axial)
5 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 5
Loads from (Inplane)
6 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 6
Loads from (Outplane)
7 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 7
Loads from (Torsion)
8 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 8
Pressure Case 1
Table of Contents
Solution Data
Maximum Solution Row Size = 1062
Number of Nodes = 2124
Number of Elements = 700
Number of Solution Cases = 8
Summation of Loads per Case
Case # FX FY FZ
1 -737. 57132. 0.
2 0. 0. 0.
3 513. 58382. 1250.
4 464894. 0. 0.
5 0. 0. 0.
6 0. 0. 0.
7 0. 0. 0.
8 -737. 57132. 0.
Table of Contents
ASME Code Stress Output Plots
1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
2) Qb < SPS (SUS,Bending) Case 1
3) S1+S2+S3 < 4S (SUS,S1+S2+S3) Case 1
4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
8) Membrane < User (OPE,Membrane) Case 3
9) Bending < User (OPE,Bending) Case 3
10) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 4
11) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 5
12) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 6
13) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 7
14) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 8
Table of Contents
Region Data
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 235 deg .. 105. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 219. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 901. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 33. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Branch Next to Header Weld
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 235 deg .. 105. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 219. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 901. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 33. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Branch Transition
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 235 deg .. 105. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 219. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 901. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 33. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Header away from Junction
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 235 deg .. 105. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 219. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 901. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 33. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.000
Branch away from Junction
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 235 deg .. 105. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 219. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 33. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 901. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 33. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.000
Table of Contents
Stress Results - Notes
- Results in this analysis were generated using the finite
element solution method.
- Using post 07 ASME Section VIII Division 2
- Use Polished Bar fatigue curve.
- Ratio between Operating and Design Pressure = 0.9000000
Assume pressure increases all other stresses.
Use operating pressure for occasional load cases.
- Assume free end displacements of attached pipe are
secondary loads within limits of nozzle reinforcement.
- Use Equivalent Stress (Von Mises).
- S1+S2+S3 evaluation omitted from operating stress.
Include S1+S2+S3 evaluation in primary case evaluation.
Assume bending stress not local primary for S1+S2+S3.
Table of Contents
ASME Overstressed Areas
*** NO OVERSTRESSED NODES IN THIS MODEL ***
Table of Contents
Highest Primary Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
38 157 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
23%
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
20 157 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
12%
Branch Transition
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
17 157 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
10%
Header away from Junction
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
29 157 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
18%
Branch away from Junction
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
17 157 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
10%
Table of Contents
Highest Secondary Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
250 330 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
75%
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
328 330 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
99%
Branch Transition
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
176 330 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
53%
Header away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Inner) Load Case 3
95 330 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
28%
Branch away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Inner) Load Case 3
141 330 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
42%
Table of Contents
Highest Fatigue Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
169 0.004 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.350 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1,584,247.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 275.0
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 423,810.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 98,455.
35% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 136,692.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 49,691.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.527
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.655
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
221 0.017 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.459 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 404,473.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 275.0
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 279,620.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 64,958.
45% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 90,186.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 14,093.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.700
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.588
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch Transition
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
119 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.247 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 44,591,824.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 275.0
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 1,801,502.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 418,505.
24% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 581,042.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 141,886.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 2.109
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.322
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Header away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Inner) Load Case 3
48 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.000
MPa 0.099 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 275.0
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 8,256,199.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 1,917,990.
9% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 2,662,888.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 906,728.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.710
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.585
Plot Reference:
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
Branch away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Inner) Load Case 3
70 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.000
MPa 0.146 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 275.0
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 3,549,409.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 824,560.
14% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 1,144,798.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 277,628.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 10.165
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.090
Plot Reference:
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
Table of Contents
Stress Intensification Factors
Branch/Nozzle Sif Summary
Peak Primary Secondary
Axial : 3.628 2.086 5.375
Inplane : 1.373 0.936 2.034
Outplane: 2.088 1.163 3.093
Torsion : 0.737 0.924 1.092
Pressure: 0.914 1.135 1.354
The above stress intensification factors are to be used
in a beam-type analysis of the piping system. Inplane,
Outplane and Torsional sif's should be used with the
matching branch pipe whose diameter and thickness is given
below. The axial sif should be used to intensify the
axial stress in the branch pipe calculated by F/A. The
pressure sif should be used to intensify the nominal
pressure stress in the PARENT or HEADER, calculated
from PD/2T.
Pipe OD : 48.300 mm.
Pipe Thk: 3.680 mm.
Z approx: 5754.353 cu.mm.
Z exact : 5352.084 cu.mm.
B31.3 Branch Pressure i-factor = 3.297
Header Pressure i-factor = 1.828
The B31.3 pressure i-factors should be used with with
F/A, where F is the axial force due to pressure, and
A is the area of the pipe wall. This is equivalent to
finding the pressure stress from (ip)(PD/4T).
B31.3
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
1.892 Inplane
2.351 Outplane
1.000 Torsional
B31.1
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
1.904 Inplane
1.904 Outplane
1.904 Torsional
WRC 330
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
1.463 Inplane
1.500 Outplane
1.000 Torsional
Table of Contents
Allowable Loads
SECONDARY Maximum Conservative Realistic
Load Type (Range): Individual Simultaneous Simultaneous
Occuring Occuring Occuring
Axial Force ( N ) 31667. 9804. 14706.
Inplane Moment (mm. N ) 868281. 190079. 403219.
Outplane Moment (mm. N ) 570983. 124997. 265158.
Torsional Moment (mm. N ) 1617004. 500612. 750918.
Pressure (MPa ) 20.59 2.80 2.80
PRIMARY Maximum Conservative Realistic
Load Type: Individual Simultaneous Simultaneous
Occuring Occuring Occuring
Axial Force ( N ) 38890. 11305. 16957.
Inplane Moment (mm. N ) 899466. 189511. 402014.
Outplane Moment (mm. N ) 723724. 148755. 315556.
Torsional Moment (mm. N ) 911104. 264838. 397257.
Pressure (MPa ) 11.70 2.80 2.80
NOTES:
1) Maximum Individual Occuring Loads are the maximum
allowed values of the respective loads if all other
load components are zero, i.e. the listed axial force
may be applied if the inplane, outplane and torsional
moments, and the pressure are zero.
2) The Conservative Allowable Simultaneous loads are
the maximum loads that can be applied simultaneously.
A conservative stress combination equation is used
that typically produces stresses within 50-70% of the
allowable stress.
3) The Realistic Allowable Simultaneous loads are the
maximum loads that can be applied simultaneously. A
more realistic stress combination equation is used
based on experience at Paulin Research. Stresses are
typically produced within 80-105% of the allowable.
4) Secondary allowable loads are limits for expansion
and operating piping loads.
5) Primary allowable loads are limits for weight,
primary and sustained type piping loads.
Table of Contents
Flexibilities
The following stiffnesses should be used in a piping,
"beam-type" analysis of the intersection. The stiff-
nesses should be inserted at the surface of the
branch/header or nozzle/vessel junction. The general
characteristics used for the branch pipe should be:
Outside Diameter = 48.300 mm.
Wall Thickness = 3.680 mm.
Axial Translational Stiffness = 174252. N /mm.
Inplane Rotational Stiffness = 5729783. mm. N /deg
Outplane Rotational Stiffness = 2501572. mm. N /deg
Torsional Rotational Stiffness = 41353168. mm. N /deg
Intersection Flexibility Factors for
Branch/Nozzle :
Find axial stiffness: K = 3EI/(kd)^3 N /mm.
Find bending and torsional stiffnesses: K = EI/(kd) mm. N per radian.
The EI product is 0.25204E+11 N mm.^2
The value of (d) to use is: 44.620 mm..
The resulting bending stiffness is in units of force x length per radian.
Axial Flexibility Factor (k) = 1.697
Inplane Flexibility Factor (k) = 1.721
Outplane Flexibility Factor (k) = 3.941
Torsional Flexibility Factor (k) = 0.238
Model Notes
Input Echo:
Model Type : Cylindrical Shell
Parent Outside Diameter : 219.100 mm.
Thickness : 8.180 mm.
Fillet Along Shell : 5.000 mm.
Parent Properties:
Material DB # 1064818.
(See Output Reports for Allowables.)
Elastic Modulus (Amb) : 195100.0 MPa
Poissons Ratio : 0.300
Expansion Coefficient : 0.1707E-04 mm./mm./deg.
Weight Density : 0.0000E+00 N /cu.mm.(NOT USED)
Nozzle Outside Diameter : 48.300 mm.
Thickness : 3.680 mm.
Length : 150.000 mm.
Nozzle Weld Length : 5.000 mm.
Nozzle Tilt Angle : 0.000 deg.
Distance from Top : 0.000 mm.
Distance from Bottom : 500.000 mm.
Nozzle Properties
Material DB # 1064818.
(See Output Reports for Allowables.)
Elastic Modulus (Amb) : 195100.0 MPa
Poissons Ratio : 0.300
Expansion Coefficient : 0.1707E-04 mm./mm./deg.
Weight Density : 0.0000E+00 N /cu.mm. (NOT USED)
Design Operating Cycles : 7000.
Ambient Temperature (Deg.) : 21.10
The following temperatures have been specified for the analysis:
Nozzle Inside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Nozzle Outside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Vessel Inside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Vessel Outside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Nozzle Pressure : 2.800 MPa
Vessel Pressure : 2.800 MPa
User Defined Load Input Echo:
Loads are given at the Nozzle/Header Junction
Loads are defined in Local Coordinatesc
Forces( N ) Moments (N-m)
Load Case FX FY FZ MX MY MZ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OPER: 1250.0 1250.0 1250.0 450.0 450.0 450.0
FEA Model Loads:
These are the actual loads applied to the FEA model.
These are the User Defined Loads translated to the
end of the nozzle and reported in global coordinates.
Forces( N ) Moments (N-m)
Load Case FX FY FZ MX MY MZ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OPER: 1250.0 1250.0 1250.0 450.0 637.5 262.5
The "top" or "positive" end of this model is "free" in
the axial and translational directions.
Stresses ARE nodally AVERAGED.
Vessel Centerline Vector : 0.000 1.000 0.000
Nozzle Orientation Vector : 1.000 0.000 0.000
Table of Contents
Load Case Report
Inner and outer element temperatures are the same
throughout the model. No thermal ratcheting
calculations will be performed.
THE 8 LOAD CASES ANALYZED ARE:
1 SUSTAINED (Pr Only)
Sustained case run to satisfy local primary
membrane and bending stress limits.
/-------- Loads in Case 1
Pressure Case 1
2 Thermal ONLY
Thermal ONLY case run in the event expansion
stresses exceed the secondary stress allowable.
/-------- Loads in Case 2
Temperature Case 1
3 OPERATING (Fatigue Calc Performed)
Case run to compute the operating stresses used in
secondary, peak and range calculations as needed.
/-------- Loads in Case 3
Pressure Case 1
Temperature Case 1
Loads from (Operating)
4 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 4
Loads from (Axial)
5 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 5
Loads from (Inplane)
6 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 6
Loads from (Outplane)
7 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 7
Loads from (Torsion)
8 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 8
Pressure Case 1
Table of Contents
Solution Data
Maximum Solution Row Size = 954
Number of Nodes = 2280
Number of Elements = 752
Number of Solution Cases = 8
Summation of Loads per Case
Case # FX FY FZ
1 -713. 97830. 0.
2 0. 0. 0.
3 537. 99080. 1250.
4 464894. 0. 0.
5 0. 0. 0.
6 0. 0. 0.
7 0. 0. 0.
8 -713. 97830. 0.
Table of Contents
ASME Code Stress Output Plots
1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
2) Qb < SPS (SUS,Bending) Case 1
3) S1+S2+S3 < 4S (SUS,S1+S2+S3) Case 1
4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
8) Membrane < User (OPE,Membrane) Case 3
9) Bending < User (OPE,Bending) Case 3
10) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 4
11) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 5
12) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 6
13) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 7
14) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 8
Table of Contents
Region Data
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 227. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 901. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 37. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Branch Next to Header Weld
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 227. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 901. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 37. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Branch Transition
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 227. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 901. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 37. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Header away from Junction
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 227. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 901. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 37. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.000
Branch away from Junction
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 227. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 901. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 37. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 3.680 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.000
Table of Contents
Stress Results - Notes
- Results in this analysis were generated using the finite
element solution method.
- Using post 07 ASME Section VIII Division 2
- Use Polished Bar fatigue curve.
- Ratio between Operating and Design Pressure = 0.9000000
Assume pressure increases all other stresses.
Use operating pressure for occasional load cases.
- Assume free end displacements of attached pipe are
secondary loads within limits of nozzle reinforcement.
- Use Equivalent Stress (Von Mises).
- S1+S2+S3 evaluation omitted from operating stress.
Include S1+S2+S3 evaluation in primary case evaluation.
Assume bending stress not local primary for S1+S2+S3.
Table of Contents
ASME Overstressed Areas
*** NO OVERSTRESSED NODES IN THIS MODEL ***
Table of Contents
Highest Primary Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
42 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
25%
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
21 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
12%
Branch Transition
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
17 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
10%
Header away from Junction
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
33 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
20%
Branch away from Junction
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
17 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
10%
Table of Contents
Highest Secondary Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
214 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
63%
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
311 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
92%
Branch Transition
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
177 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
52%
Header away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Inner) Load Case 3
84 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
24%
Branch away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Inner) Load Case 3
139 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
41%
Table of Contents
Highest Fatigue Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
144 0.002 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.300 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 2,871,453.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 622,818.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 144,686.
29% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 200,879.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 79,368.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.548
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.646
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
210 0.012 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.435 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 575,400.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 328,657.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 76,350.
43% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 106,002.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 19,187.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.742
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.574
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch Transition
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
119 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.247 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 42,211,248.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 1,792,345.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 416,378.
24% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 578,088.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 141,158.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 2.091
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.323
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Header away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Inner) Load Case 3
42 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.000
MPa 0.087 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 10,937,369.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 2,540,848.
8% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 3,527,647.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 1,322,599.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.903
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.525
Plot Reference:
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
Branch away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Inner) Load Case 3
69 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.000
MPa 0.144 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 3,735,257.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 867,734.
14% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 1,204,740.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 291,685.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 11.422
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.081
Plot Reference:
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
Table of Contents
Stress Intensification Factors
Branch/Nozzle Sif Summary
Peak Primary Secondary
Axial : 3.367 1.977 4.988
Inplane : 1.415 0.939 2.096
Outplane: 1.933 1.101 2.864
Torsion : 0.704 0.895 1.043
Pressure: 0.914 1.123 1.354
The above stress intensification factors are to be used
in a beam-type analysis of the piping system. Inplane,
Outplane and Torsional sif's should be used with the
matching branch pipe whose diameter and thickness is given
below. The axial sif should be used to intensify the
axial stress in the branch pipe calculated by F/A. The
pressure sif should be used to intensify the nominal
pressure stress in the PARENT or HEADER, calculated
from PD/2T.
Pipe OD : 48.300 mm.
Pipe Thk: 3.680 mm.
Z approx: 5754.353 cu.mm.
Z exact : 5352.084 cu.mm.
B31.3 Branch Pressure i-factor = 3.731
Header Pressure i-factor = 1.828
The B31.3 pressure i-factors should be used with with
F/A, where F is the axial force due to pressure, and
A is the area of the pipe wall. This is equivalent to
finding the pressure stress from (ip)(PD/4T).
B31.3
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
1.782 Inplane
2.226 Outplane
1.000 Torsional
B31.1
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
1.577 Inplane
1.577 Outplane
1.577 Torsional
WRC 330
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
1.378 Inplane
1.500 Outplane
1.000 Torsional
Table of Contents
Allowable Loads
SECONDARY Maximum Conservative Realistic
Load Type (Range): Individual Simultaneous Simultaneous
Occuring Occuring Occuring
Axial Force ( N ) 34741. 10735. 16102.
Inplane Moment (mm. N ) 857685. 187402. 397539.
Outplane Moment (mm. N ) 627669. 137144. 290926.
Torsional Moment (mm. N ) 1724463. 532862. 799293.
Pressure (MPa ) 18.52 2.80 2.80
PRIMARY Maximum Conservative Realistic
Load Type: Individual Simultaneous Simultaneous
Occuring Occuring Occuring
Axial Force ( N ) 42580. 12404. 18606.
Inplane Moment (mm. N ) 929788. 196830. 417540.
Outplane Moment (mm. N ) 793530. 163458. 346747.
Torsional Moment (mm. N ) 976456. 284453. 426680.
Pressure (MPa ) 10.85 2.80 2.80
NOTES:
1) Maximum Individual Occuring Loads are the maximum
allowed values of the respective loads if all other
load components are zero, i.e. the listed axial force
may be applied if the inplane, outplane and torsional
moments, and the pressure are zero.
2) The Conservative Allowable Simultaneous loads are
the maximum loads that can be applied simultaneously.
A conservative stress combination equation is used
that typically produces stresses within 50-70% of the
allowable stress.
3) The Realistic Allowable Simultaneous loads are the
maximum loads that can be applied simultaneously. A
more realistic stress combination equation is used
based on experience at Paulin Research. Stresses are
typically produced within 80-105% of the allowable.
4) Secondary allowable loads are limits for expansion
and operating piping loads.
5) Primary allowable loads are limits for weight,
primary and sustained type piping loads.
Table of Contents
Flexibilities
The following stiffnesses should be used in a piping,
"beam-type" analysis of the intersection. The stiff-
nesses should be inserted at the surface of the
branch/header or nozzle/vessel junction. The general
characteristics used for the branch pipe should be:
Outside Diameter = 48.300 mm.
Wall Thickness = 3.680 mm.
Axial Translational Stiffness = 173696. N /mm.
Inplane Rotational Stiffness = 5831014. mm. N /deg
Outplane Rotational Stiffness = 2877526. mm. N /deg
Torsional Rotational Stiffness = 56653088. mm. N /deg
Intersection Flexibility Factors for
Branch/Nozzle :
Find axial stiffness: K = 3EI/(kd)^3 N /mm.
Find bending and torsional stiffnesses: K = EI/(kd) mm. N per radian.
The EI product is 0.25204E+11 N mm.^2
The value of (d) to use is: 44.620 mm..
The resulting bending stiffness is in units of force x length per radian.
Axial Flexibility Factor (k) = 1.698
Inplane Flexibility Factor (k) = 1.691
Outplane Flexibility Factor (k) = 3.426
Torsional Flexibility Factor (k) = 0.174
Model Notes
Input Echo:
Model Type : Cylindrical Shell
Parent Outside Diameter : 219.100 mm.
Thickness : 8.180 mm.
Fillet Along Shell : 5.000 mm.
Parent Properties:
Material DB # 1064818.
(See Output Reports for Allowables.)
Elastic Modulus (Amb) : 195100.0 MPa
Poissons Ratio : 0.300
Expansion Coefficient : 0.1707E-04 mm./mm./deg.
Weight Density : 0.0000E+00 N /cu.mm.(NOT USED)
Nozzle Outside Diameter : 114.300 mm.
Thickness : 6.020 mm.
Length : 150.000 mm.
Nozzle Weld Length : 5.000 mm.
Nozzle Tilt Angle : 0.000 deg.
Distance from Top : 0.000 mm.
Distance from Bottom : 500.000 mm.
Nozzle Properties
Material DB # 1064818.
(See Output Reports for Allowables.)
Elastic Modulus (Amb) : 195100.0 MPa
Poissons Ratio : 0.300
Expansion Coefficient : 0.1707E-04 mm./mm./deg.
Weight Density : 0.0000E+00 N /cu.mm. (NOT USED)
Design Operating Cycles : 7000.
Ambient Temperature (Deg.) : 21.10
The following temperatures have been specified for the analysis:
Nozzle Inside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Nozzle Outside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Vessel Inside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Vessel Outside Temperature : 200.00 deg.
Nozzle Pressure : 2.800 MPa
Vessel Pressure : 2.800 MPa
User Defined Load Input Echo:
Loads are given at the Nozzle/Header Junction
Loads are defined in Local Coordinatesc
Forces( N ) Moments (N-m)
Load Case FX FY FZ MX MY MZ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OPER: 4700.0 4700.0 4700.0 1700.0 1700.0 1700.0
FEA Model Loads:
These are the actual loads applied to the FEA model.
These are the User Defined Loads translated to the
end of the nozzle and reported in global coordinates.
Forces( N ) Moments (N-m)
Load Case FX FY FZ MX MY MZ
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OPER: 4700.0 4700.0 4700.0 1700.0 2405.0 995.0
The "top" or "positive" end of this model is "free" in
the axial and translational directions.
Stresses ARE nodally AVERAGED.
Vessel Centerline Vector : 0.000 1.000 0.000
Nozzle Orientation Vector : 1.000 0.000 0.000
Table of Contents
Load Case Report
Inner and outer element temperatures are the same
throughout the model. No thermal ratcheting
calculations will be performed.
THE 8 LOAD CASES ANALYZED ARE:
1 SUSTAINED (Pr Only)
Sustained case run to satisfy local primary
membrane and bending stress limits.
/-------- Loads in Case 1
Pressure Case 1
2 Thermal ONLY
Thermal ONLY case run in the event expansion
stresses exceed the secondary stress allowable.
/-------- Loads in Case 2
Temperature Case 1
3 OPERATING (Fatigue Calc Performed)
Case run to compute the operating stresses used in
secondary, peak and range calculations as needed.
/-------- Loads in Case 3
Pressure Case 1
Temperature Case 1
Loads from (Operating)
4 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 4
Loads from (Axial)
5 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 5
Loads from (Inplane)
6 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 6
Loads from (Outplane)
7 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 7
Loads from (Torsion)
8 Program Generated -- Force Only
Case run to compute sif's and flexibilities.
/-------- Loads in Case 8
Pressure Case 1
Table of Contents
Solution Data
Maximum Solution Row Size = 1164
Number of Nodes = 2764
Number of Elements = 908
Number of Solution Cases = 8
Summation of Loads per Case
Case # FX FY FZ
1 -2926. 97867. 0.
2 0. 0. 0.
3 1774. 102567. 4700.
4 4258930. 0. 0.
5 0. 0. 0.
6 0. 0. 0.
7 0. 0. 0.
8 -2926. 97867. 0.
Table of Contents
ASME Code Stress Output Plots
1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
2) Qb < SPS (SUS,Bending) Case 1
3) S1+S2+S3 < 4S (SUS,S1+S2+S3) Case 1
4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
8) Membrane < User (OPE,Membrane) Case 3
9) Bending < User (OPE,Bending) Case 3
10) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 4
11) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 5
12) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 6
13) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 7
14) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (SIF,Outside) Case 8
Table of Contents
Region Data
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 2080. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 37. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 6.020 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Branch Next to Header Weld
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 2080. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 37. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 6.020 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Branch Transition
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 2080. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 37. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 6.020 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.350
Header away from Junction
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 2080. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 37. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 6.020 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.000
Branch away from Junction
Cold Allowable ........... 115. MPa
Hot Allowable @ 200 deg .. 109. MPa
Case 1
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 0. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 3
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 87. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 37. MPa
Case 4
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 2080. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 5
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 6
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 7
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 81. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Case 8
Nominal Stress (M/Z) ... 37. MPa
Pressure Stress (Pd/2t) .. 0. MPa
Smallest Thickness ....... 6.020 mm.
Stress Concentration ..... 1.000
Table of Contents
Stress Results - Notes
- Results in this analysis were generated using the finite
element solution method.
- Using post 07 ASME Section VIII Division 2
- Use Polished Bar fatigue curve.
- Ratio between Operating and Design Pressure = 0.9000000
Assume pressure increases all other stresses.
Use operating pressure for occasional load cases.
- Assume free end displacements of attached pipe are
secondary loads within limits of nozzle reinforcement.
- Use Equivalent Stress (Von Mises).
- S1+S2+S3 evaluation omitted from operating stress.
Include S1+S2+S3 evaluation in primary case evaluation.
Assume bending stress not local primary for S1+S2+S3.
Table of Contents
ASME Overstressed Areas
*** NO OVERSTRESSED NODES IN THIS MODEL ***
Table of Contents
Highest Primary Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
61 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
37%
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
54 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
33%
Branch Transition
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
26 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
15%
Header away from Junction
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
37 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
22%
Branch away from Junction
Pl (1.5)(S) Primary Membrane Load Case 1
28 163 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 1) Pl < (1.5)(S) (SUS,Membrane) Case 1
16%
Table of Contents
Highest Secondary Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
235 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
69%
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
275 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
81%
Branch Transition
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
81 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
24%
Header away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Outer) Load Case 3
93 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 5) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Outside) Case 3
27%
Branch away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q SPS Primary+Secondary (Inner) Load Case 3
81 336 Plot Reference:
MPa MPa 4) Pl+Pb+Q < SPS (OPE,Inside) Case 3
24%
Table of Contents
Highest Fatigue Stress Ratios
Header Next to Nozzle Weld
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
159 0.004 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.329 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1,940,222.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 472,109.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 109,675.
32% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 152,270.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 59,877.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.511
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.662
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch Next to Header Weld
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
185 0.006 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.384 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1,170,180.
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 359,849.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 83,596.
38% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 116,063.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 37,604.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 0.556
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.642
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch Transition
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
54 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.350
MPa 0.113 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 15,281,600.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 3,550,051.
11% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 4,928,799.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 1,482,921.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 1.031
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.492
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Header away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Outer) Load Case 3
46 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.000
MPa 0.096 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 7,971,528.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 1,851,858.
9% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 2,571,072.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 974,049.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 1.318
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.431
Plot Reference:
7) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Outside) Case 3
Branch away from Junction
Pl+Pb+Q+F Damage Ratio Primary+Secondary+Peak (Inner) Load Case 3
41 0.000 Life Stress Concentration Factor = 1.000
MPa 0.084 Stress Strain Concentration Factor = 1.000
Cycles Allowed for this Stress = 1.0000E11
Allowable "B31" Fatigue Stress Allowable = 279.9
482.0 Markl Fatigue Stress Allowable = 329.8
MPa WRC 474 Mean Cycles to Failure = 14,308,282.
WRC 474 99% Probability Cycles = 3,323,940.
8% WRC 474 95% Probability Cycles = 4,614,873.
BS5500 Allowed Cycles(Curve F) = 1,451,158.
Membrane-to-Bending Ratio = 2.844
Bending-to-PL+PB+Q Ratio = 0.260
Plot Reference:
6) Pl+Pb+Q+F < Sa (EXP,Inside) Case 3
Table of Contents
Stress Intensification Factors
Branch/Nozzle Sif Summary
Peak Primary Secondary
Axial : 5.257 2.347 7.789
Inplane : 1.998 1.467 2.960
Outplane: 4.498 2.011 6.663
Torsion : 0.785 1.058 1.163
Pressure: 1.240 1.622 1.837
The above stress intensification factors are to be used
in a beam-type analysis of the piping system. Inplane,
Outplane and Torsional sif's should be used with the
matching branch pipe whose diameter and thickness is given
below. The axial sif should be used to intensify the
axial stress in the branch pipe calculated by F/A. The
pressure sif should be used to intensify the nominal
pressure stress in the PARENT or HEADER, calculated
from PD/2T.
Pipe OD : 114.300 mm.
Pipe Thk: 6.020 mm.
Z approx: 55434.809 cu.mm.
Z exact : 52677.469 cu.mm.
B31.3 Branch Pressure i-factor = 3.498
Header Pressure i-factor = 2.479
The B31.3 pressure i-factors should be used with with
F/A, where F is the axial force due to pressure, and
A is the area of the pipe wall. This is equivalent to
finding the pressure stress from (ip)(PD/4T).
B31.3
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
2.915 Inplane
3.642 Outplane
1.000 Torsional
B31.1
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
3.642 Inplane
3.642 Outplane
3.642 Torsional
WRC 330
Peak Stress Sif .... 0.000 Axial
2.456 Inplane
2.781 Outplane
1.428 Torsional
Table of Contents
Allowable Loads
SECONDARY Maximum Conservative Realistic
Load Type (Range): Individual Simultaneous Simultaneous
Occuring Occuring Occuring
Axial Force ( N ) 88321. 25438. 38158.
Inplane Moment (mm. N ) 5978765. 1217646. 2583018.
Outplane Moment (mm. N ) 2655692. 540863. 1147344.
Torsional Moment (mm. N ) 15219008. 4345610. 6518416.
Pressure (MPa ) 13.66 2.80 2.80
PRIMARY Maximum Conservative Realistic
Load Type: Individual Simultaneous Simultaneous
Occuring Occuring Occuring
Axial Force ( N ) 142428. 31772. 47657.
Inplane Moment (mm. N ) 5858600. 866289. 1837676.
Outplane Moment (mm. N ) 4275120. 674335. 1430481.
Torsional Moment (mm. N ) 8126936. 1699459. 2549188.
Pressure (MPa ) 7.51 2.80 2.80
NOTES:
1) Maximum Individual Occuring Loads are the maximum
allowed values of the respective loads if all other
load components are zero, i.e. the listed axial force
may be applied if the inplane, outplane and torsional
moments, and the pressure are zero.
2) The Conservative Allowable Simultaneous loads are
the maximum loads that can be applied simultaneously.
A conservative stress combination equation is used
that typically produces stresses within 50-70% of the
allowable stress.
3) The Realistic Allowable Simultaneous loads are the
maximum loads that can be applied simultaneously. A
more realistic stress combination equation is used
based on experience at Paulin Research. Stresses are
typically produced within 80-105% of the allowable.
4) Secondary allowable loads are limits for expansion
and operating piping loads.
5) Primary allowable loads are limits for weight,
primary and sustained type piping loads.
Table of Contents
Flexibilities
The following stiffnesses should be used in a piping,
"beam-type" analysis of the intersection. The stiff-
nesses should be inserted at the surface of the
branch/header or nozzle/vessel junction. The general
characteristics used for the branch pipe should be:
Outside Diameter = 114.300 mm.
Wall Thickness = 6.020 mm.
Axial Translational Stiffness = 458288. N /mm.
Inplane Rotational Stiffness = 35116940. mm. N /deg
Outplane Rotational Stiffness = 13162779. mm. N /deg
Torsional Rotational Stiffness = 126992016. mm. N /deg
Intersection Flexibility Factors for
Branch/Nozzle :
Find axial stiffness: K = 3EI/(kd)^3 N /mm.
Find bending and torsional stiffnesses: K = EI/(kd) mm. N per radian.
The EI product is 0.58705E+12 N mm.^2
The value of (d) to use is: 108.280 mm..
The resulting bending stiffness is in units of force x length per radian.
Axial Flexibility Factor (k) = 1.446
Inplane Flexibility Factor (k) = 2.695
Outplane Flexibility Factor (k) = 7.189
Torsional Flexibility Factor (k) = 0.745
You might also like
- Pvelite OutputDocument44 pagesPvelite OutputRam MurtyNo ratings yet
- Solution: WE1 12 Nov 2008Document9 pagesSolution: WE1 12 Nov 2008aauppalNo ratings yet
- Crossover Area Calc For Floating HeadDocument2 pagesCrossover Area Calc For Floating HeadRitesh VishambhariNo ratings yet
- Design of Circular Flat Endplate With Stiffeners - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-TipsDocument2 pagesDesign of Circular Flat Endplate With Stiffeners - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-Tipsisrar khanNo ratings yet
- Design of Tooth Locked Quick Open Die Pressure VesselDocument4 pagesDesign of Tooth Locked Quick Open Die Pressure VesselSEP-PublisherNo ratings yet
- PV Elite 2015 Sp1 Licensee: SPLM Licensed User Filename: Untitled Nozzle Calcs.: N1 Nozl: 3 9:36am Dec 7,2018Document32 pagesPV Elite 2015 Sp1 Licensee: SPLM Licensed User Filename: Untitled Nozzle Calcs.: N1 Nozl: 3 9:36am Dec 7,2018Priyo Jati WahyonoNo ratings yet
- Lug On SkidDocument8 pagesLug On Skidmiteshpatel191No ratings yet
- PV Elite ResultDocument239 pagesPV Elite ResultChaitanya Sai TNo ratings yet
- PV Newsletter - Skirt Connections PDFDocument5 pagesPV Newsletter - Skirt Connections PDFDivyesh Patel100% (1)
- Lug SupportDocument2 pagesLug SupportSachin5586No ratings yet
- Nozzle Design CalculationDocument1 pageNozzle Design CalculationSachin55860% (1)
- Small Vertical Pressure Vessel Leg Support Design - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-Tips PDFDocument6 pagesSmall Vertical Pressure Vessel Leg Support Design - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-Tips PDFhussamammarNo ratings yet
- Skirt Design - For Small VesselsDocument7 pagesSkirt Design - For Small VesselsSakthi VelNo ratings yet
- Pressure VesselDocument46 pagesPressure VesselHaftamu HilufNo ratings yet
- Dennis R Moss 4th EditionDocument5 pagesDennis R Moss 4th Editionsenthil kumarNo ratings yet
- Help For P-V Elite PDFDocument39 pagesHelp For P-V Elite PDFTushar MangratiNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation: Fuel Gas Scrubber TAG NO: V-6011Document239 pagesDesign Calculation: Fuel Gas Scrubber TAG NO: V-6011Peja Jusoh100% (1)
- H H Optimum 0,2: Instructions For Using NomogramDocument4 pagesH H Optimum 0,2: Instructions For Using NomogrammithunjobsNo ratings yet
- Deaera DesignDocument13 pagesDeaera DesignBhanu K PrakashNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Check Top Head: Input ParametersDocument2 pagesNozzle Check Top Head: Input ParametersRaj Sharma100% (1)
- H200141 - Calculation of Basering Rev 0 PDFDocument9 pagesH200141 - Calculation of Basering Rev 0 PDFSani Adipura WinataNo ratings yet
- Final Weld Strength CalnsDocument5 pagesFinal Weld Strength CalnsamachmouchiNo ratings yet
- U-V-673 - Manual Flange and GussetDocument8 pagesU-V-673 - Manual Flange and GussetDarshan PanchalNo ratings yet
- STHE Design (Training Material)Document37 pagesSTHE Design (Training Material)Herman_ms2000100% (2)
- External Pressure CalculationsDocument40 pagesExternal Pressure Calculationsmisterdavi50% (2)
- Wind Seismic Calculation DataDocument8 pagesWind Seismic Calculation Dataaknauriyal2013No ratings yet
- SHELL THICKNESS CHECK-ASME Section VIIIDocument2 pagesSHELL THICKNESS CHECK-ASME Section VIIIskocogluNo ratings yet
- Girth Flange Load Calculation Using by FEA TechniquesDocument12 pagesGirth Flange Load Calculation Using by FEA TechniqueskingstonNo ratings yet
- Calculations For: Calculations No. Asme Viii Div 1 Ed 2019Document21 pagesCalculations For: Calculations No. Asme Viii Div 1 Ed 2019David Vanegas100% (1)
- Cover Pages For PV Elite VenvelDocument14 pagesCover Pages For PV Elite VenvelSakthi VelNo ratings yet
- Flange Pad CalcsDocument4 pagesFlange Pad CalcstomNo ratings yet
- Allowable Nozzle LoadsDocument7 pagesAllowable Nozzle LoadsSiva baalanNo ratings yet
- 003-Heat ExchangerDocument299 pages003-Heat ExchangerVijayshanker GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sample Design Calculation - Vessel Supported On LugsDocument11 pagesSample Design Calculation - Vessel Supported On Lugsandry4jc100% (1)
- Flat Plate - Roark & YoungDocument15 pagesFlat Plate - Roark & YoungPrasad Pingle0% (1)
- PV Elite Vessel Analysis Program HorizontalDocument55 pagesPV Elite Vessel Analysis Program HorizontalMarizta Perdani PutriNo ratings yet
- Coupling Calculations and Ug-32 Unstayed Head CalculationsDocument9 pagesCoupling Calculations and Ug-32 Unstayed Head CalculationsLcm TnlNo ratings yet
- Saddle Reaction Summary - For Empty CaseDocument12 pagesSaddle Reaction Summary - For Empty CasesridharNo ratings yet
- TUBESHEETDocument5 pagesTUBESHEETMehta MehulNo ratings yet
- Tailing LugDocument12 pagesTailing LuguvarajmecheriNo ratings yet
- 06745JS2 (7) - Strength Calculations of Module4 (IBR)Document23 pages06745JS2 (7) - Strength Calculations of Module4 (IBR)Pratik Ray Chaudhury100% (3)
- Compress CalculationDocument106 pagesCompress CalculationKrupal Patel100% (1)
- Design Calculation Sheet: H2So4 Neutralization TankDocument43 pagesDesign Calculation Sheet: H2So4 Neutralization TankEkki Petrus BubunNo ratings yet
- Design of Partition PlateDocument5 pagesDesign of Partition Platepippo2378793No ratings yet
- WRC 107 TipsDocument4 pagesWRC 107 Tipsyatin888No ratings yet
- External Nozzle Loads Nozzle To Shells: Type of Loading Symbol Formula UnitDocument1 pageExternal Nozzle Loads Nozzle To Shells: Type of Loading Symbol Formula UnitSachinNo ratings yet
- Sample FLG CalcDocument6 pagesSample FLG CalcameyyammaiNo ratings yet
- Narrow Face Flange - Slip On Hub TypeDocument17 pagesNarrow Face Flange - Slip On Hub TypeEng-CalculationsNo ratings yet
- FEA Check List For Expansion BellowDocument3 pagesFEA Check List For Expansion BellowRyan FisherNo ratings yet
- Saddle AnalysisDocument17 pagesSaddle AnalysisPEJU0007No ratings yet
- 10.1 Asme Viii A-13 Rectangular VesselDocument2 pages10.1 Asme Viii A-13 Rectangular Vesselpastyl100% (1)
- Ibr Calc GSRDocument4 pagesIbr Calc GSRAniket GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Top Pipe MomentDocument2 pagesTop Pipe Momentrsubramani100% (1)
- Nozzle TestDocument9 pagesNozzle TestDarshan PanchalNo ratings yet
- Graphical ResultsDocument11 pagesGraphical Resultshgag selimNo ratings yet
- Test ReportDocument18 pagesTest ReportBilel MahjoubNo ratings yet
- Quick PrintDocument2 pagesQuick PrintSimeon ArabovNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Loads AnalysisDocument110 pagesNozzle Loads Analysishgag selimNo ratings yet
- Quick PrintDocument2 pagesQuick PrintSimeon ArabovNo ratings yet
- Aaaa XXX BBB XXX CCC XXX DDD XXX FFF XXXDocument3 pagesAaaa XXX BBB XXX CCC XXX DDD XXX FFF XXXberylqzNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Tir-Rod StiffnessDocument1 pageCalculation of Tir-Rod StiffnessberylqzNo ratings yet
- As-NZS1170.5 Seismic CoefficientDocument2 pagesAs-NZS1170.5 Seismic CoefficientberylqzNo ratings yet
- Flat Rectangular Plate With Four Sides Fixed Under Uniform PressureDocument4 pagesFlat Rectangular Plate With Four Sides Fixed Under Uniform PressureberylqzNo ratings yet
- My Own Tips For Using Solidworks SimulationDocument2 pagesMy Own Tips For Using Solidworks SimulationberylqzNo ratings yet
- Perforated Plate PDFDocument6 pagesPerforated Plate PDFberylqzNo ratings yet
- Aspen HX Design ReportDocument78 pagesAspen HX Design ReportberylqzNo ratings yet
- O RingsDocument211 pagesO Ringsberylqz100% (2)
- AnswersDocument5 pagesAnswers22 shantanu kapadnisNo ratings yet
- Transport Mechanisms in CellsDocument4 pagesTransport Mechanisms in Cellsd_94No ratings yet
- CH 21 Bridge Works - Super Structure - SteelDocument21 pagesCH 21 Bridge Works - Super Structure - SteelSubhash SinhaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Properties HandbookDocument15 pagesPlastic Properties HandbookguilloteARGNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Lecture Notes - CHAPTER-3 STEAM GENERATOR: October 2014Document46 pagesPower Plant Lecture Notes - CHAPTER-3 STEAM GENERATOR: October 2014Lösky D. PinnockNo ratings yet
- 2002 AriDocument53 pages2002 AriMbarouk Shaame MbaroukNo ratings yet
- Semi-Centrifugal Casting: An Extensive Analysis: Technical ReportDocument10 pagesSemi-Centrifugal Casting: An Extensive Analysis: Technical ReportS. R. OvhalNo ratings yet
- Steam TablesDocument11 pagesSteam TablesARNOUXNo ratings yet
- Excel BasedDocument24 pagesExcel Basedelha e. maruquinNo ratings yet
- A Study On Some Durability Properties of Coconut Shell Aggregate ConcreteDocument13 pagesA Study On Some Durability Properties of Coconut Shell Aggregate ConcreteMa Victoria CaneteNo ratings yet
- Iqwq-Cpp-Grinv-00-0001 - 0Document24 pagesIqwq-Cpp-Grinv-00-0001 - 0வி.சுரேஷ் குமார்100% (1)
- Background of Titrino 702 Automatic TitratorDocument4 pagesBackground of Titrino 702 Automatic TitratorbuttamanatNo ratings yet
- Vol1i7x ECCC RecommandationsDocument21 pagesVol1i7x ECCC RecommandationsRami GhorbelNo ratings yet
- Mining: Supercritical Flow Critical Flow Subcritical FlowDocument3 pagesMining: Supercritical Flow Critical Flow Subcritical FlowBoonsita NammanaNo ratings yet
- ST Handout 3Document23 pagesST Handout 3SwagBeast SKJJNo ratings yet
- En Comparision TableDocument3 pagesEn Comparision TablenikhilnsbNo ratings yet
- Cosmoplast Upvc Drainage Pipes FittingsDocument34 pagesCosmoplast Upvc Drainage Pipes FittingsBahar AbdulqadirNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Sugarcane Bagasse AshDocument27 pagesPpt-Sugarcane Bagasse AshHegdeVenugopalNo ratings yet
- The Real Trick To Drying Ceramic Ware Is To Use A Method That Removes The Water From The Inside of The Ceramic As Fast As The Surface Water Is EvaporatedDocument55 pagesThe Real Trick To Drying Ceramic Ware Is To Use A Method That Removes The Water From The Inside of The Ceramic As Fast As The Surface Water Is EvaporatedMiguel OcampoNo ratings yet
- H2SDocument2 pagesH2Snsivasankar14No ratings yet
- Jurnal InternasionalDocument9 pagesJurnal InternasionalalninditaNo ratings yet
- 15 - Amines (New) PDFDocument25 pages15 - Amines (New) PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Rotacoat 330 Q-CTSDocument2 pagesRotacoat 330 Q-CTSkkkkrolikNo ratings yet
- FCD 450-10Document2 pagesFCD 450-10MohammedFaisalGirachNo ratings yet
- Class X Half Yearly Exam Syllabus 2019 20Document6 pagesClass X Half Yearly Exam Syllabus 2019 20RahulNo ratings yet
- National Fire Protection Association-GoogleDocument2 pagesNational Fire Protection Association-GooglesandeepNo ratings yet
- INDOKOTE Company Profile-4Document8 pagesINDOKOTE Company Profile-4AvijitSinghNo ratings yet
- Time Date I. Objectives: A. Content StandardsDocument5 pagesTime Date I. Objectives: A. Content StandardsRod ReyesNo ratings yet
- Product Catalog PDFDocument979 pagesProduct Catalog PDFa7mos0% (1)