Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ALKOHOL
ALKOHOL
Uploaded by
roslin12Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Perc Kimia K3 2019Document6 pagesPerc Kimia K3 2019donutNo ratings yet
- Modul PDP Ting 5 Sebatian Karbon 2016Document31 pagesModul PDP Ting 5 Sebatian Karbon 2016Rohana AsranNo ratings yet
- Modul 3 Sebatian Karbon Alcohol Tingkatan 5Document8 pagesModul 3 Sebatian Karbon Alcohol Tingkatan 5NoorAzlizaAbdullahNo ratings yet
- ALKANADocument25 pagesALKANAroslin12No ratings yet
- Modul PDP Ting 5 Sebatian Karbon 2016Document31 pagesModul PDP Ting 5 Sebatian Karbon 2016Atiqah LIaNo ratings yet
- Cakna Kimia 2 2017Document5 pagesCakna Kimia 2 2017Farhalina NaziraNo ratings yet
- F5 C2 BM 2013Document19 pagesF5 C2 BM 2013nurulakmal mohd kamalNo ratings yet
- 9 Bahan Buatan Dalam IndustriDocument13 pages9 Bahan Buatan Dalam Industrifadhlinam0% (1)
- 7-SOAL LATIHAN Kimia Organik-BiokimiaDocument2 pages7-SOAL LATIHAN Kimia Organik-BiokimiaVincent Vetter100% (1)
- Assignment Pengenalan Kimia OrganikDocument8 pagesAssignment Pengenalan Kimia OrganikLiza RahmatNo ratings yet
- TOPIK 7 & 8 - Alhehid, Keton. Asid Karboksilik, Ester Dan AmidaDocument12 pagesTOPIK 7 & 8 - Alhehid, Keton. Asid Karboksilik, Ester Dan AmidaMohd Nazri100% (1)
- Perc Kimia K3 2019Document6 pagesPerc Kimia K3 2019donutNo ratings yet
- Bab2 Sebatian KarbonDocument19 pagesBab2 Sebatian Karbonameerul_hazeeqNo ratings yet
- BAB 2 - Sebatian KarbonDocument126 pagesBAB 2 - Sebatian KarbonadimanokNo ratings yet
- Ulangkaji Pra SPM 2013Document175 pagesUlangkaji Pra SPM 2013Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Pep Awal Tahun F5 2015Document20 pagesPep Awal Tahun F5 2015Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Kimia F4 US1 2017Document5 pagesKimia F4 US1 2017Reneelda HassanNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 Sebatian KarbonDocument13 pagesBab 4 Sebatian KarbonNur Ardellaa100% (1)
- Sebatian KarbonnnnnDocument8 pagesSebatian KarbonnnnnDiya DaniaNo ratings yet
- KimiaDocument5 pagesKimialieaNo ratings yet
- Kimia Bab 7Document14 pagesKimia Bab 7Izyan Marissa MarissaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylik AsidDocument4 pagesCarboxylik AsidAq Nadzrul LarhNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 t5 Sebatian Karbon (Murid)Document13 pagesBab 4 t5 Sebatian Karbon (Murid)Saffiyah AdamNo ratings yet
- KelantanDocument15 pagesKelantanBryanLeeChienYungNo ratings yet
- Topik 6-AlkoholDocument36 pagesTopik 6-AlkoholREMIEYNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal BabDocument7 pagesLatihan Soal BabDian Adelia PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Peperiksaan Progresif PDPR Kimia k2 t5 SMK Sandong JayaDocument18 pagesPeperiksaan Progresif PDPR Kimia k2 t5 SMK Sandong JayaNIK NORASHRAH BT CHE MAT MoeNo ratings yet
- F5 S1 Tuisyen Kimia Muafakat SoalanDocument7 pagesF5 S1 Tuisyen Kimia Muafakat Soalanqlysyen tasyaNo ratings yet
- Sifat Fizik Dan Sifat Kimia Asid BesDocument5 pagesSifat Fizik Dan Sifat Kimia Asid Besdee zackNo ratings yet
- Sce 3103 Praktikal 3Document10 pagesSce 3103 Praktikal 3Siti Atiqah Md FahmeNo ratings yet
- 1819 Chemistry 2Document11 pages1819 Chemistry 2Qhai HayreenNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Kimia SPMDocument20 pagesPaper 2 Kimia SPMZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- 3-Smile-Plus Two Chemistry QP Set-BDocument9 pages3-Smile-Plus Two Chemistry QP Set-BMo RazNo ratings yet
- 2.3 - Formatif 3Document21 pages2.3 - Formatif 3Khairul HakiminNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2 Kimia F4 ESimulasi2Document22 pagesKertas 2 Kimia F4 ESimulasi2MONA WATI BINTI ROMELI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- TOPIK 6-Alkohol, Etr Dan Amina 2Document36 pagesTOPIK 6-Alkohol, Etr Dan Amina 2Mohd NazriNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikal 3 Etanol1Document19 pagesLaporan Praktikal 3 Etanol1FT Geeyah TahirNo ratings yet
- Praktikal 3Document8 pagesPraktikal 3Hamidah JamaludinNo ratings yet
- 2020 - Modul 1latih Tubi Soalan SPMDocument41 pages2020 - Modul 1latih Tubi Soalan SPMwansuhailyNo ratings yet
- Ujian Bulanan Sains Tingkatan 5Document15 pagesUjian Bulanan Sains Tingkatan 5Nurul Zahira Md Isa100% (2)
- k2 f4 BC KIMIADocument12 pagesk2 f4 BC KIMIAAzalida Md YusofNo ratings yet
- Merancang Eks SEBATIAN KARBONDocument2 pagesMerancang Eks SEBATIAN KARBONSiti HafidahNo ratings yet
- p1 Oti 1 TG 5 Chemistry 2011Document34 pagesp1 Oti 1 TG 5 Chemistry 2011Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Sem 1Document46 pagesAlcohol Sem 1Tharsini SalyamNo ratings yet
- PPC SPM 2023 K2 BHGN A No 1-4Document13 pagesPPC SPM 2023 K2 BHGN A No 1-4NORHEDAYAH BINTI MOHD JANI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Ujian 1 Kimia Ting 4 SubjektifDocument10 pagesUjian 1 Kimia Ting 4 Subjektifmaznah omarNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document16 pagesPaper 2noor hidayah MustafaNo ratings yet
- SPM Kimia Kimia k2 Set2Document13 pagesSPM Kimia Kimia k2 Set2api-3841296100% (1)
- Latihan Prestasi Bab 6Document2 pagesLatihan Prestasi Bab 6akmarfadzilNo ratings yet
- Asid Dan BesDocument5 pagesAsid Dan BesArbayana AmbranNo ratings yet
- Modul Kecemerlangan Sains KSSM 2021 OktoberDocument21 pagesModul Kecemerlangan Sains KSSM 2021 OktoberMd ShaifudinNo ratings yet
- Pecutan Akhir Sains K2BDocument22 pagesPecutan Akhir Sains K2BNURASHIDAH BINTI A. GHANI MoeNo ratings yet
- Soklan Kimia 2Document26 pagesSoklan Kimia 2NIK NORASHRAH BT CHE MAT MoeNo ratings yet
- Praktikal 3Document13 pagesPraktikal 3suadtitanNo ratings yet
- KimiaDocument2 pagesKimiaRendo.stack qwerty123No ratings yet
ALKOHOL
ALKOHOL
Uploaded by
roslin12Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ALKOHOL
ALKOHOL
Uploaded by
roslin12Copyright:
Available Formats
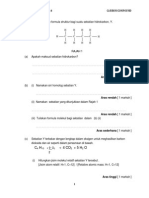
1
ALKOHOL
(a) Isikan tempat kosong dengan memilih jawapan yang sesuai daripada kotak di bawah.
i) Alkohol ialah salah satu daripada siri homolog dengan kumpulan berfungsi ..
ii) Formula am bagi alkohol ialah .
iii) Takat lebur alkohol .. daripada alkana dan alkena disebabkan kehadiran
.
iv) Ini kerana kumpulan berfungsinya membentuk ikatan hidrogen yang .. daripada
ikatan antara molekul alkohol.
v) Metanol, etanol dan propanol larut dalam air. Keterlarutan alkohol yang lain menurun dengan bertambahnya
.
vi) Penamaan sebatian alkohol adalah sama seperti ..... . C1 dinomborkan dari karbon yang paling dekat
dengan kumpulan berfungsi.
vii) Alkohol digunakan sebagai bahan api, ........., dalam perubatan, dalam pembuatan .
Dan sebagai komponen utama dalam minuman beralkohol.
viii) Alkohol ialah sebatian ...
(b) Lengkapkan jadual di bawah.
i) Nama :
ii) Nama:
iii) Nama:
iv) Formula struktur
Name : Propan-2-ol
v) Formula struktur
Name : Butan-1-ol
vi) Formula struktur
Name : Pentan-2,3-diol
(c) Lukiskan struktur formula dan namakan semua isomer bagi
(i) propanol (C3H7OH)
Hidroksil bukan hidrokarbon alkena pelarut lebih tinggi
kosmetik lebih kuat jisim molekul -OH CnH2n+1OH
2
(ii) butanol (C4H9OH)
(d) Rumuskan sifat fizikal etanol dalam jadual di bawah.
Sifat fizikal Penerangan
Keadaan fizikal pada suhu bilik
Bau dan warna
Kelarutan dalam air
kemeruapan
Takat didih
(e) Etanol boleh disediakan dengan dua cara, penapaian dan penghidratan.
1. Dalam proses penapaian,
(i) Apakah fungsi yis?
...............
.........................
(ii) Tuliskan persamaan kimia yang menunjukkan proses penapaian.
..............................................................................................
3
(iii) Nyatakan suhu, mangkin dan keadaan lain yang diperlukan untuk proses penapaian.
..................................................................................
.
(iv) Nyatakan keburukan proses ini.
....................................................................................
..
2. Proses penghidratan melibatkan penghidratan etena. Etena diperoleh daripada ydration process involves
hydration of ethene. Ethene is obtained from the
cracking of petroleum fractions.
(i) Write the chemical equation for hydration process.
..
(ii) State the temperature, pressure and catalyst needed for hydration process.
(f) Lengkapkan jadual berikut.
1 The Products of Combustion of ethanol
In excess oxygen:
In limited oxygen :
2 The products of Oxidation reaction of alcohol with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution or acidified
potassium manganate (VII) solution
Oxidation of ethanol
Oxidation of propanol
3 Dehydration of alcohol.
Draw and label the set of apparatus to show the dehydration process of propanol.
(g) State True or False for every statement below.
1 Ethanol is an alcoholic drinks
2 Ethanol acts as a depressant on central nervous system.
3 Alcoholic drinks only slow down physical activity, not affect
mental activity.
4
4 Alcoholism create social problems for the family and society.
5 Methanol is a very toxic chemical and can cause permanent
blindness when consumed
6 Alcohol is not addictive
7 Long- term excessive consumption of alcohol drinks
can cause chronic liver disease and brain damage.
8 Because of alcohol is miscible with water, it cannot be used as
a solvent in toiletries.
9 Alcohol is one of the raw materials in manufacture of explosive
10 Alcohol is an antiseptic
F CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
Learning outcomes
You should be able to :
state the general formula of carboxylic acids,
identify the functional group of carboxylic acids,
list the names and molecular formulae of the first four members of carboxylic acid,
draw structural formulae of the first four members of carboxylic acid and name them
using the IUPAC nomenclature,
describe the preparation of ethanoic acid in the laboratory,
state the physical properties of carboxylic acids,
state the chemical reactions of ethanoic acids with other chemicals,
predict the chemical properties for other members of carboxylic acid,
explain with example the uses of carboxylic acids in everyday life
Activity 13
(a) Complete the diagram below.
Functional group :
CARBOXYLIC
ACIDS
Uses :
a
b
c
d ..
Ethanoic acid normally
prepared by
of an alcohol
names end with
Physical properties
a ..
b ..
c
d ..
General formula:
5
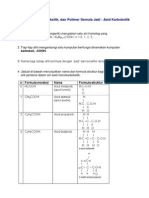
(b) Draw the structural formula of
Methanoic acid
Ethanoic acid
Propanoic acid Butanoic acid
2-methylbutanoic acid
Methyl propanoic acid
( c) A carboxylic acid, X has an empirical formula CH2O. Experimental determination
shows that it has a molar mass of about 59 g mol
-1
(i) What is the general formula of carboxylic acid?
(ii) Calculate the molecular formula of X
[ Relative atomic mass : H, 1 ; C, 12 ; O, 16 ]
(iii) Draw the structural formula of X and give name.
Activity 14
a) Figure shows a series of conversion starting from ethene to ethyl ethanoate.
I
Ethene Ethanol
Ethanoic acid
II
6
Based on the figure above, state
Reaction I :
Reaction II :
b) Draw the set up of apparatus to prepare ethanoic acid .in laboratory
Write the chemical reaction that involve.
c) Write the observation of every test for ethanoic acid below.
Test Observation Inference
1 a. Ethanoic acid + metal
carbonate
b. Gas released + lime water
2 a. Ethanoic acid + magnesium
b. Gas given off + lighted
splinter
3
Ethanoic acid +
copper (II)oxide
7
4 Glacial ethanoic acid + ethanol +
concentrated sulphuric acid + heat
Then the boiling contents are poured
into a beaker half filled with water.
.
G ESTER
Learning outcomes:
You should be able to:
state the general formula of esters
identify the functional group of esters
List the names and molecular formulae of simple esters.
Draw structural formulae of simple esters and name them using the IUPAC nomenclature,
Describe the preparation of ester in the laboratory,
State the physical properties of ethyl ethanoate.
Predict the ester produced from the esterification reaction.
Write equations for the esterification reactions,
state the natural sources of ester, state the uses of ester in everyday life.
Activity 15
(a) Name the following esters and give the alcohols and carboxylic acids required to synthesise
the esters name.
b) Draw the structural formula for the compound form in the reaction between alchol and carboxylic acid
Formula Name Carboxylic acid Alcohol
Example :HCOOC2H5
Ethyl methanoate Methanoic acid Ethanol
a) CH3 COOCH3
b) CH3 COOC3H7
c) C2H5 COOCH3
d) C3 H7COOC3H7
8
below.
(i) methanol and propanoic acid
(ii) ethanol + butanoic acid
(iii) propan-1-ol + ethanoic acid
Activity 16
(a) Complete the diagram below
b) Write the fruit flavour for each of the ester below
(i) n-pentyl ethanoate : .
(ii) Octyl ethanoate : .
(iii) Ethyl butanoate : .
Order in homologous series
ESTERS
Ester is a ..
organic compound
contain ,
and
.
The general formula is
the functional
group is COO- or
. group
the name of an ester consists of two words.
The first word originates from.,
the second is from the ..
All of them end with ..
product of an .
reaction between a carboxylic
acid and an alcohol.
The of flowers and
fruits is due to the presence
of esters
uses of ester,
a) ..
b) ..
c)
d)
Physical properties
1
2.
3.
4.
5.
9
Learning outcomes:
You should be able to :
describe the systematic approach in naming members of homologous series.
describe the order in the physical and chemical properties in homologous series.
Activity 17
a) Name the homologous series for
(i) Butan-1-ol : ..
(ii) Compound P : .
(iii) Compound R :
(iv) Compound S : ..
b) Write the molecular formula of
(i) compound P : ..
(ii) compound Q :
(iii) compound R : ..
(iv) compound S : .
H FATS
Learning outcomes:
You should be able to:
State what oils are
State what fats are
State the importance of oils and fats for body processes
State the sources of oils and fats
List the uses of oils and fats
State the differences between oils and fats
Identify structural formulae for fat molecules of certain fatty acids
State what saturated fats are
State what unsaturated fats are
Compare and contrast between saturated and unsaturated fats
Describe the effects of eating food high in fats on health
Describe the industrial extraction of palm oil
Justify the use of palm oil in the food production
Butan-1-ol
C
4
H
9
OH
Compound P
Porcelain chips
II
III
Hydrogen
chloride
Compound Q
I
Acidified potassium
dichromate(VI) solution
Compound R
ethanol
Compound S
IV
10
Activity 18
(I) Fill in the blank by choosing the correct answer from the table below.
ester solid heart
attack
hydrogenation harden stroke carbon high blood
pressure
margerine
saturated, ester
link
lipid trigleycerides Chlorofom liquid glycerol energy fatty acid
a) Fats , oils and waxes are from a large family of organic compound called ...
b) They are natural ..
c) They are product of the reaction between . and
d) Fats are usually found in animal and they are .while oil is fat from plant
and also from animal but they are at room condition.
e) Fatty acids are long straight-chain containing between 12 to 18 atoms per
molecule.
f) A molecule of glycerol may combine with one, two or three fatty acid to form a monoester, diester or trimester.
A Molecule of water is eliminated when a fatty acid joins to the glycerol molecule and the resulting bond
formed is called an (-COO-).
g) Most fats and oils are .
h) As a group, oil and fats tend to dissolve in organic solvents such as .
i) Fats are an important source of for our body.
j) fats may cause cholesterol to deposit on the blood vessels and making them .. .
This can lead to , .and ..
k) Unsaturated fats can be converted to saturated fats by a process called .
l) is made by hydrogenating some of the carbon-carbon double bond in vegetable oil.
(II) Compare fats and oils
Comparison Oils Fats
Source
Melting point
o
C < 20 / lower > 20 / higher
Physical state at room temperature
Cholesterol content
Examples Peanut oil, soybean oil Butter , lard
Molecular structure
(III) Write the Similarities of fats and oils
In terms of Similarities
Molecular formula
Type of compound
Type of bond
.
Activity 19
11
a) Complete the flow chart below to show the Extraction Process of Palm Oil.
b) State 5 benefits of palm oil compared to other vegetable oils
i) .
ii)
iii) ..
iv) .
v) .
I NATURAL RUBBER
Learning outcomes:
You should be able to :
List examples of natural polymers and their monomers,
Draw the structural formula of natural rubber,
State the properties of natural rubber,
State the uses of natural rubber
Describe the coagulation process of latex
Describe the method used to prevent latex from coagulating,
Describe the vulcanization of rubber,
Describe how the presence of sulphur atoms changes the properties of vulcanised rubber,
Compare and contrast the properties of vulcanised and unvulcanised natural rubber.
Oil palm fruit bunches
Stripping
Pressing
The fresh fruit bunches are sterilized ia large
pressure vessels at 140
o
C for 60-90 min.
The heat from the steam kills fungus and
bacteria
Breaking down the oil-bearing cells. Crush
the palm oil fruits
The mixture is filtered to remove solid or
coarse fibre and allow to settle in an a large
clarification tank. The oil is skimmed off and
dried in a vacuum drier.
12
Activity 20
a) Give explanation for every situation below:
i) Latex coagulate slowly when it is exposed to the air.
ii) When 20 cm
3
latex is added with 5cm
3
methanoic acid, latex coagulate rapidly.
iii) When 5 cm
3
ammonia solution is added to latex, latex does not coagulate.
b) Compare the unvulcanized and vulcanised rubber in the table below.
Aspect Unvulcanised rubber Vulcanised rubber
Structure
Oxidation
Resistance of heat
Strength
Elasticity
ACTIVITY 21
1 Base on the diagram above,
(a) Name the product formed in step I.
(b) (i) State the reagents needed for step II.
(ii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction in step II.
(c) (i) Name the type of reaction occurring in step III.
.
(ii) A catalyst is needed for the reaction in step III. Name the catalyst.
13
(d) (i) Describe briefly how to carry out the reaction in step IV.
.
(ii) What do you expect to observe when the reaction in step IV is carried out?
(e) Draw the possible structural formulae of C3H7OH formed in step V.
(f) (i) Name the type of reaction occurring in step VI.
.
(ii) Give one use for ( C3H6)n formed in step VI.
.
(g) Compare and explain the sootiness of C3H6 and C3H8 when each of these
hydrocarbons is burnt in excess air.
[Relative atomic mass: H = 1; C = 12) [4]
2 Diagram below shows the molecular formulae of 4 carbon compounds.
(a) Write the general formula of the homologous series of compound B.
..
(b) State the functional group of compound A and compound D
Compound A : ..
Compound D : ..
(c) Compound B shows isomerism. Draw the structural formula of all isomers of compound B.
(d) Compound D and compound C react in the presence of the concentrated sulphuric acid.
(i) Name the product formed from the reaction.
.
(ii) State one special characteristic of the product formed.
.
(e) Compound A burns in excess oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
(i) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
.................................................................................................................
C
4
H
8
C
2
H
5
COO
H
C
4
H
9
OH
C
4
H
10
A B C D
14
(ii) 11.2 g of compound A burns in excess oxygen, calculate number of carbon dioxide molecules
formed.
[Relative atomic mass C = 12, O = 16 and
Avogadro number = 6.02 x 10
23
]
You might also like
- Perc Kimia K3 2019Document6 pagesPerc Kimia K3 2019donutNo ratings yet
- Modul PDP Ting 5 Sebatian Karbon 2016Document31 pagesModul PDP Ting 5 Sebatian Karbon 2016Rohana AsranNo ratings yet
- Modul 3 Sebatian Karbon Alcohol Tingkatan 5Document8 pagesModul 3 Sebatian Karbon Alcohol Tingkatan 5NoorAzlizaAbdullahNo ratings yet
- ALKANADocument25 pagesALKANAroslin12No ratings yet
- Modul PDP Ting 5 Sebatian Karbon 2016Document31 pagesModul PDP Ting 5 Sebatian Karbon 2016Atiqah LIaNo ratings yet
- Cakna Kimia 2 2017Document5 pagesCakna Kimia 2 2017Farhalina NaziraNo ratings yet
- F5 C2 BM 2013Document19 pagesF5 C2 BM 2013nurulakmal mohd kamalNo ratings yet
- 9 Bahan Buatan Dalam IndustriDocument13 pages9 Bahan Buatan Dalam Industrifadhlinam0% (1)
- 7-SOAL LATIHAN Kimia Organik-BiokimiaDocument2 pages7-SOAL LATIHAN Kimia Organik-BiokimiaVincent Vetter100% (1)
- Assignment Pengenalan Kimia OrganikDocument8 pagesAssignment Pengenalan Kimia OrganikLiza RahmatNo ratings yet
- TOPIK 7 & 8 - Alhehid, Keton. Asid Karboksilik, Ester Dan AmidaDocument12 pagesTOPIK 7 & 8 - Alhehid, Keton. Asid Karboksilik, Ester Dan AmidaMohd Nazri100% (1)
- Perc Kimia K3 2019Document6 pagesPerc Kimia K3 2019donutNo ratings yet
- Bab2 Sebatian KarbonDocument19 pagesBab2 Sebatian Karbonameerul_hazeeqNo ratings yet
- BAB 2 - Sebatian KarbonDocument126 pagesBAB 2 - Sebatian KarbonadimanokNo ratings yet
- Ulangkaji Pra SPM 2013Document175 pagesUlangkaji Pra SPM 2013Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Pep Awal Tahun F5 2015Document20 pagesPep Awal Tahun F5 2015Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Kimia F4 US1 2017Document5 pagesKimia F4 US1 2017Reneelda HassanNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 Sebatian KarbonDocument13 pagesBab 4 Sebatian KarbonNur Ardellaa100% (1)
- Sebatian KarbonnnnnDocument8 pagesSebatian KarbonnnnnDiya DaniaNo ratings yet
- KimiaDocument5 pagesKimialieaNo ratings yet
- Kimia Bab 7Document14 pagesKimia Bab 7Izyan Marissa MarissaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylik AsidDocument4 pagesCarboxylik AsidAq Nadzrul LarhNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 t5 Sebatian Karbon (Murid)Document13 pagesBab 4 t5 Sebatian Karbon (Murid)Saffiyah AdamNo ratings yet
- KelantanDocument15 pagesKelantanBryanLeeChienYungNo ratings yet
- Topik 6-AlkoholDocument36 pagesTopik 6-AlkoholREMIEYNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal BabDocument7 pagesLatihan Soal BabDian Adelia PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Peperiksaan Progresif PDPR Kimia k2 t5 SMK Sandong JayaDocument18 pagesPeperiksaan Progresif PDPR Kimia k2 t5 SMK Sandong JayaNIK NORASHRAH BT CHE MAT MoeNo ratings yet
- F5 S1 Tuisyen Kimia Muafakat SoalanDocument7 pagesF5 S1 Tuisyen Kimia Muafakat Soalanqlysyen tasyaNo ratings yet
- Sifat Fizik Dan Sifat Kimia Asid BesDocument5 pagesSifat Fizik Dan Sifat Kimia Asid Besdee zackNo ratings yet
- Sce 3103 Praktikal 3Document10 pagesSce 3103 Praktikal 3Siti Atiqah Md FahmeNo ratings yet
- 1819 Chemistry 2Document11 pages1819 Chemistry 2Qhai HayreenNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Kimia SPMDocument20 pagesPaper 2 Kimia SPMZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- 3-Smile-Plus Two Chemistry QP Set-BDocument9 pages3-Smile-Plus Two Chemistry QP Set-BMo RazNo ratings yet
- 2.3 - Formatif 3Document21 pages2.3 - Formatif 3Khairul HakiminNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2 Kimia F4 ESimulasi2Document22 pagesKertas 2 Kimia F4 ESimulasi2MONA WATI BINTI ROMELI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- TOPIK 6-Alkohol, Etr Dan Amina 2Document36 pagesTOPIK 6-Alkohol, Etr Dan Amina 2Mohd NazriNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikal 3 Etanol1Document19 pagesLaporan Praktikal 3 Etanol1FT Geeyah TahirNo ratings yet
- Praktikal 3Document8 pagesPraktikal 3Hamidah JamaludinNo ratings yet
- 2020 - Modul 1latih Tubi Soalan SPMDocument41 pages2020 - Modul 1latih Tubi Soalan SPMwansuhailyNo ratings yet
- Ujian Bulanan Sains Tingkatan 5Document15 pagesUjian Bulanan Sains Tingkatan 5Nurul Zahira Md Isa100% (2)
- k2 f4 BC KIMIADocument12 pagesk2 f4 BC KIMIAAzalida Md YusofNo ratings yet
- Merancang Eks SEBATIAN KARBONDocument2 pagesMerancang Eks SEBATIAN KARBONSiti HafidahNo ratings yet
- p1 Oti 1 TG 5 Chemistry 2011Document34 pagesp1 Oti 1 TG 5 Chemistry 2011Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Sem 1Document46 pagesAlcohol Sem 1Tharsini SalyamNo ratings yet
- PPC SPM 2023 K2 BHGN A No 1-4Document13 pagesPPC SPM 2023 K2 BHGN A No 1-4NORHEDAYAH BINTI MOHD JANI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Ujian 1 Kimia Ting 4 SubjektifDocument10 pagesUjian 1 Kimia Ting 4 Subjektifmaznah omarNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document16 pagesPaper 2noor hidayah MustafaNo ratings yet
- SPM Kimia Kimia k2 Set2Document13 pagesSPM Kimia Kimia k2 Set2api-3841296100% (1)
- Latihan Prestasi Bab 6Document2 pagesLatihan Prestasi Bab 6akmarfadzilNo ratings yet
- Asid Dan BesDocument5 pagesAsid Dan BesArbayana AmbranNo ratings yet
- Modul Kecemerlangan Sains KSSM 2021 OktoberDocument21 pagesModul Kecemerlangan Sains KSSM 2021 OktoberMd ShaifudinNo ratings yet
- Pecutan Akhir Sains K2BDocument22 pagesPecutan Akhir Sains K2BNURASHIDAH BINTI A. GHANI MoeNo ratings yet
- Soklan Kimia 2Document26 pagesSoklan Kimia 2NIK NORASHRAH BT CHE MAT MoeNo ratings yet
- Praktikal 3Document13 pagesPraktikal 3suadtitanNo ratings yet
- KimiaDocument2 pagesKimiaRendo.stack qwerty123No ratings yet