Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trends in Training
Trends in Training
Uploaded by
bansalradhey0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views3 pagesThe document discusses different training methods and technologies used for employee development programs. It describes two main training methods: knowledge-based methods which focus on exposing trainees to concepts and fundamentals through lectures and seminars; and experiential methods which emphasize group processes and attitudinal training provided on-the-job. It also lists newer technologies being used for training, including web-conferencing, social networks, podcasts, blogs, wikis and virtual worlds, to reduce costs and increase access to learning. These technologies allow sharing of knowledge and resources before, during and after training events.
Original Description:
TRENDS IN TRAINING
Original Title
04. Trends in Training
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different training methods and technologies used for employee development programs. It describes two main training methods: knowledge-based methods which focus on exposing trainees to concepts and fundamentals through lectures and seminars; and experiential methods which emphasize group processes and attitudinal training provided on-the-job. It also lists newer technologies being used for training, including web-conferencing, social networks, podcasts, blogs, wikis and virtual worlds, to reduce costs and increase access to learning. These technologies allow sharing of knowledge and resources before, during and after training events.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views3 pagesTrends in Training
Trends in Training
Uploaded by
bansalradheyThe document discusses different training methods and technologies used for employee development programs. It describes two main training methods: knowledge-based methods which focus on exposing trainees to concepts and fundamentals through lectures and seminars; and experiential methods which emphasize group processes and attitudinal training provided on-the-job. It also lists newer technologies being used for training, including web-conferencing, social networks, podcasts, blogs, wikis and virtual worlds, to reduce costs and increase access to learning. These technologies allow sharing of knowledge and resources before, during and after training events.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
5
Knowledge Based Methods
In this technique, trainees are exposed to
concepts and theories, basic principles,
and pure and applied knowledge in any
subject area.
The main aim is to make trainees aware
of the fundamentals.
The examples of this method are
lectures, seminars, workshops, films and
training, group discussions, etc.
Experiential Methods
In this technique, the main focus is on
achieving through group processes and
dynamics.
Attitudinal training helps an individual to
better understand self, group behavior
and personal interaction.
This helps an individual to understand the
problems of human relationship in a work
situation.
This training is provided on-the-job by
the workers immediate supervisors.
The success of this method depends on
following facts:
The supervisor must be a good
teacher.
He should be given incentives
and time for carrying out the
training programmes.
They should know the training needs of the
trainees.
Need and Importance of Management
Development
Management development is the
development of management over and
above its science and theory, of its
practice and application in organizations,
corporations and institutions, alike in
relation to the organization and manager,
so as continuously to re-equip both to
fulfill their purposes more effectively and
in harmony with each other, and both
with the environment in which they
function and have their being and hope
to thrive upon and grow.
---- Dr. B.K. Madan
Executive development is defined as
improving an individuals managerial
effectiveness through a planned process
of learning.
The change in an individual should occur
in following areas:
Knowledge change
Attitude change
Behavior change
Performance change
End results
The success of executive development depends
on the following factors:
Trainees personal characteristics like
intelligence and motivation.
His actual learning efforts
These two variables are affected by the following
factors:
Formal organization
Leadership climate
Cultural factors
Organizations perform management
development to achieve the following results:
Improve technical performance.
Improve supervision and leadership.
Improve inter-departmental cooperation
Find an individuals weaknesses.
Attract good people.
Encourage promotion from within
policies.
Make sure that the qualifications of key
personnel become better known.
Create reserves in management ranks.
Make an organization more flexible by
making its members more resourceful
and multipurpose.
Improve organizational structure.
Encourage junior executives to do better
work.
Evaluation of Training
6
Training evaluation is done to
Judge the ability of the participants to
perform the jobs for which they were
trained.
Find defects or faults in training provided.
Find whether the trainee requires any
extra training.
Find the training requirements of the
participants to the meet job
requirements.
There are four basic categories of outcomes that
can be measured:
Reaction: It is evaluating the trainees
reaction to the programme.
Learning: It is finding whether the trainee
learnt the principles, skills and facts
taught by the trainer.
Behavior: Whether the trainees on-the-
job behavior changed after training.
Results: What results have been achieved
after training.
Training fails due to the following reasons:
The benefits of training are not clear to
the top management.
The top management does not give
reward to the supervisors for conducting
training.
The top management does not
systematically perform the tasks of
planning and budgeting.
The middle management does not get
proper incentive from top management
and hence does not account for training
in production scheduling.
Off-the-job training sometimes teaches
techniques or methods which are not
practically implemented in the
organization.
Trainers provide limited counseling and
consulting services.
Leveraging New Technologies for
Employee Development Programs
Rapid advances in technology have transformed the
workplace and changed the way we learn by impacting
the interpersonal communication and collaboration.
Many agencies have started implementing different
technologies into their learning and development
programs, using these tools to cut training costs, reduce
carbon footprint, and increase continual learning
outside the classroom. Below are examples of newer
technologies that agencies have integrated into their
employee development programs. Also listed are Web
2.0 tools, which allow learners to share knowledge and
best practices in a wiki, blog, or discussion forum, and
form networks through social network sites. Instead of
just reading static material, users of Web 2.0 tools have
the opportunity to create and modify content directly
onto these pages.
1. Web-conferencing: a method to allow instructors
to conduct live meetings, trainings, and
presentations via the Internet. Web-conferences
allow participants opportunities to ask questions
and participate in polls. Common examples of
web-conferencing tools are Webex, Adobe
Connect, Goto Meeting and Live Meeting
2. Social Network/ Community of Practice: An
online group of people who develop friendships,
find professional connections, share interests, and
gather knowledge and information. These
communities are formed online through social
sites. Learning and development programs can
utilize these networks to link course participants
before and after a training event to share
knowledge and ideas regarding the course.
Instructors and participants provide links to
articles, webinars, and on-the-job examples
before, during, and after a training event.
3. Podcast: a type of online media delivery allowing
users to download files via a feed onto a computer
and MP3 player. Podcasts allow learners to
access trainings at different times depending on
workload and availability. Instructors create
course podcasts for learners to download and
listen on their MP3 player, mobile phone, and
laptop.
4. Blog: website which allows an author to share
opinions, reflections, and discuss topics in the
form of online journals. Learning and development
programs can incorporate blogs to provide
supplemental course information and updates on
course materials. Participants can discuss the
course in this space.
7
5. Micro-blogs: a popular tool to share knowledge
and resources with one another. Instructors can
incorporate microblogs to create a community
around a course or an activity. Instructors also
can post tips, assignments, and other information
pertaining to the course. Course participants can
summarize information learned during and after
courses. Participants at conferences are using
microblogs to informally exchange information
learned from conference sessions. Common
microblogs are Twitter and Yammer.
6. Integrated Collaboration Environment or
Collaborative Workspace: a virtual environment
where teams may work on projects and share
information. Project teams can access a shared
workspace where they upload files and share
them with one another. Common examples are
Sharepoint, Google Apps, Google Docs, Zoho and
Moodle.
7. People may also establish shared spaces to learn
from one another either formally or informally. For
example, individuals from different agencies
involved in training and development may create a
workspace to share ideas, experiences, and
resources to develop a supervisory training
program.
8. Wiki: a website allowing users to create and edit
content on any number of interlinked web pages
via a web browser. This method is used in
learning and development programs to promote
collaborative learning and information sharing.
Instructors and participants use wikis to create
reading lists. Course participants use wikis to for
team projects. Organizations use wikis to post
internal processes, publish reference guides, and
capture best practices. Note: This website is a
wiki, and can be edited by a number of people
within OPM.
9. Social Bookmarks: a system allowing users to
collect and store bookmarks online, tag with key
words and share those bookmarks and tags with
others. This type of tool allows course instructors
develop course reading lists. Course participants
supplement course material by subscribing to a
particular tag or keyword that relates to the
course.
10. Media Sharing: an online environment which
allows users to search for photos, videos and/or
other media for uses in (among others)
presentations, learning materials and coursework.
Users publish content to a larger audience.
Instructors can record workshops and upload
them to an online social network. Common media
sharing tools are Flickr, Google+, and Youtube.
11. Virtual World: a simulated environment where
users can interact with one another and create
objects through an onscreen avatar. This type of
environment allows course participants to attend
live workshops and conferences in a virtual
classroom or conference space. Participants are
able to interact with each other in much the same
way as attending a real workshop or conference.
Course project teams can meet and collaborate in
a virtual space. Organizations have developed
courses using a virtual environment to conduct
simulations of various situations including disaster
preparedness or medical emergencies. Common
virtual worlds include Second Life, Protosphere,
and Forterra.
12. Authoring Tools or Instructional
Tools: software packages instructional designers
use to create and package content to end users.
Authoring tools are commonly used to create e-
learning modules. They are written to conform to
international standards such as Shareable
Content Object Reference Model (SCORM).
These tools allow for Common authoring tools are
Adobe Captivate, Adobe Flash, and Articulate.
13. Mobile Learning (M-learning): Mobile Learning
focuses on learning across contexts and locations
by the means of mobile devices (e.g. laptops, cell
phones, personal digital assistants, MP3 players,
smartphones, game devices, tablet PCs, and e-
books). M-learning devices are used to access
online courses and resources and can also foster
collaboration among individuals, conduct
assessments and evaluations, provide access to
performance support, and capture evidence of a
learning activity.
You might also like
- UEE Electrotechnology Release 2.0 CVIGDocument79 pagesUEE Electrotechnology Release 2.0 CVIGResa PramuditaNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Developing Instructional Materials For The Interpersonal DomainDocument4 pagesStrategies For Developing Instructional Materials For The Interpersonal Domaindcgalarion3946No ratings yet
- E-Learning Tender DocumentDocument13 pagesE-Learning Tender DocumentGabriel MullarkeyNo ratings yet
- Course Plan Worksheet: Part I: Audience and CourseDocument16 pagesCourse Plan Worksheet: Part I: Audience and CourseNan Ketpura-ChingNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - CREAT WPS OfficeDocument10 pagesLESSON 3 - CREAT WPS OfficeRaiza NufableNo ratings yet
- 3 High-Fidelity PrototypeDocument11 pages3 High-Fidelity Prototypeapi-281891656No ratings yet
- Facilitate and Manage StudentsDocument6 pagesFacilitate and Manage StudentsIrma Estela Marie EstebanNo ratings yet
- Learner Instruction HandbookDocument11 pagesLearner Instruction HandbookSachin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Systematic Design For MOOCs Captstone ProjectDocument19 pagesSystematic Design For MOOCs Captstone ProjectRomel AlfecheNo ratings yet
- Moodle 3.x Teaching Techniques - Third Edition - Sample ChapterDocument23 pagesMoodle 3.x Teaching Techniques - Third Edition - Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document8 pagesChapter 3Omkar Pradeep Khanvilkar100% (1)
- Cpe101 NotesDocument1 pageCpe101 NotesOmar SabanNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document5 pagesActivity 3LoveNo ratings yet
- How To Design An Effective E-Learning Course For Medical EducationDocument30 pagesHow To Design An Effective E-Learning Course For Medical EducationrianNo ratings yet
- Tech Port OverviewDocument4 pagesTech Port OverviewElissa Paige CheatwoodNo ratings yet
- FtrainingmanuelDocument14 pagesFtrainingmanuelapi-266517510No ratings yet
- Edutopia Onlinelearning Mastering Online Discussion Board Facilitation PDFDocument15 pagesEdutopia Onlinelearning Mastering Online Discussion Board Facilitation PDFPrateek LoganiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document3 pagesChapter 11omar anwarNo ratings yet
- My ReportDocument6 pagesMy ReportantoNo ratings yet
- Technology AnalysisDocument5 pagesTechnology Analysisapi-571991627No ratings yet
- METHOD OF MANAGEMENT DEVELOPMENTssignment Merin MissDocument7 pagesMETHOD OF MANAGEMENT DEVELOPMENTssignment Merin MissAnonymous VP5OJCNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Blended LearningDocument38 pagesFundamentals of Blended LearningRinny Banggur100% (2)
- Siimplified Module 6Document5 pagesSiimplified Module 6Dimple BolotaoloNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Blended LearningDocument38 pagesFundamentals of Blended LearningGatot SandyNo ratings yet
- Changing ELearning Dynamics in The Enterprise To User-Generated Content v7Document13 pagesChanging ELearning Dynamics in The Enterprise To User-Generated Content v7Julia OliveiraNo ratings yet
- It Skill WorkshopDocument4 pagesIt Skill Workshopchie yooNo ratings yet
- Managing Social Media: Management of Internet Information Sources and Services (Imc 407)Document22 pagesManaging Social Media: Management of Internet Information Sources and Services (Imc 407)syuhadaNo ratings yet
- Part Iv - Managing and Evaluating Learning Activities: Implementation Development Evaluation Design AnalisysDocument28 pagesPart Iv - Managing and Evaluating Learning Activities: Implementation Development Evaluation Design AnalisysliviuadrianromascanuNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Learning Best Practices 2Document3 pagesSynchronous Learning Best Practices 2api-240613392No ratings yet
- Blended Learning in English Language Teaching: Course Design and Implementation Edited by Brian Tomlinson and Claire WhittakerDocument66 pagesBlended Learning in English Language Teaching: Course Design and Implementation Edited by Brian Tomlinson and Claire WhittakerMassy2020No ratings yet
- Empowerment Technologies Q2 Module 6Document40 pagesEmpowerment Technologies Q2 Module 6ginaNo ratings yet
- Etec 510 - Curriculum User DraftDocument9 pagesEtec 510 - Curriculum User Draftapi-247699970No ratings yet
- Thalente DlaminiDocument7 pagesThalente Dlaminimosisidineo28No ratings yet
- Ellohe Melat Technical ProposalDocument6 pagesEllohe Melat Technical Proposalkasyas ketemaNo ratings yet
- MSC Applied Elearning Assignment Cover SheetDocument9 pagesMSC Applied Elearning Assignment Cover SheetmkseeryNo ratings yet
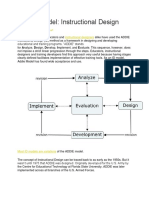
- ADDIE ModelDocument12 pagesADDIE ModelMel Bautista DomingoNo ratings yet
- Staff Development UBD Stage 3 Lesson PlanningDocument4 pagesStaff Development UBD Stage 3 Lesson Planningdebra_scott_6No ratings yet
- Addie Model of Instructional DesignDocument8 pagesAddie Model of Instructional Designfariez79No ratings yet
- Inbound 2765309805015172669Document3 pagesInbound 2765309805015172669Roselle Luzano GalugaNo ratings yet
- Cur 532 Signature Assignment PaperDocument13 pagesCur 532 Signature Assignment Paperapi-372005043No ratings yet
- Formato de Ideas ClaveDocument12 pagesFormato de Ideas ClaveJorge AranaNo ratings yet
- Unit Four MMG4008Document12 pagesUnit Four MMG4008Adarsh YadavNo ratings yet
- The ADDIE ModelDocument14 pagesThe ADDIE ModelPaul De Las Alas100% (1)
- AnswerDocument10 pagesAnswermikko ibiasNo ratings yet
- Text 2Document2 pagesText 2jmugisha193No ratings yet
- Workbook For Helping Teachers To LearnDocument18 pagesWorkbook For Helping Teachers To LearnhikmatyhNo ratings yet
- Choosing The Right Elearning MethodsDocument6 pagesChoosing The Right Elearning MethodsNoemie LongcayanaNo ratings yet
- Techno-Pedagogic Content Knowledge Analysis - EnglishDocument15 pagesTechno-Pedagogic Content Knowledge Analysis - EnglishDhanyaNo ratings yet
- Addie ModelDocument11 pagesAddie ModelPanis RyanNo ratings yet
- ADDIE Model: Instructional DesignDocument10 pagesADDIE Model: Instructional DesignJames ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document36 pagesChapter 4Fi FaNo ratings yet
- Hackathon Problems - MOSTDocument5 pagesHackathon Problems - MOSTdarknightdarknarNo ratings yet
- Workbook For Focus On Professional DevelopmentDocument19 pagesWorkbook For Focus On Professional DevelopmentroshiemurugisNo ratings yet
- Effective Online Instruction Depends On Learning Experiences That Are Appropriately Designed and Facilitated by Knowledgeable EducatorsDocument50 pagesEffective Online Instruction Depends On Learning Experiences That Are Appropriately Designed and Facilitated by Knowledgeable EducatorsMarynel ZaragosaNo ratings yet
- PRACTICUMDocument6 pagesPRACTICUMMeljune Sala PomentoNo ratings yet
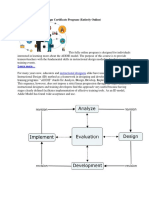
- ADDIE Instructional Design Certificate ProgramDocument12 pagesADDIE Instructional Design Certificate ProgramJoeManikNo ratings yet
- TTL 2: MATH Lesson 1Document6 pagesTTL 2: MATH Lesson 1Efraem CelesteNo ratings yet
- Model Addie 5Document7 pagesModel Addie 5Egan-Ash ArijenanNo ratings yet
- E Learning - What's It All About?Document6 pagesE Learning - What's It All About?Jeremy FrancisNo ratings yet
- ICAL 2012 Presentation SlideDocument15 pagesICAL 2012 Presentation SlideShaffika SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- ABCs of e-Learning (Review and Analysis of Broadbent's Book)From EverandABCs of e-Learning (Review and Analysis of Broadbent's Book)No ratings yet
- Chapter-6: Training AND Developing EmployeesDocument21 pagesChapter-6: Training AND Developing EmployeesMd. Golam Rabby RifatNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task 3 - BSBHRM512 HandoutDocument28 pagesAssessment Task 3 - BSBHRM512 HandoutAna Paula VianaNo ratings yet
- Literasi Bahasa Inggris 001Document7 pagesLiterasi Bahasa Inggris 001Ikhwan FauziNo ratings yet
- Industry Profile: Vega Auto Accessories Private LTDDocument57 pagesIndustry Profile: Vega Auto Accessories Private LTDSanjay SmartNo ratings yet
- By Order of The Secretary of The Air Force Air Force Instruction 11-2F-16, 19 JANUARY 2007 Flying Operations F-16 - Pilot TrainingDocument85 pagesBy Order of The Secretary of The Air Force Air Force Instruction 11-2F-16, 19 JANUARY 2007 Flying Operations F-16 - Pilot TrainingJacob MillerNo ratings yet
- Infantry Basic Officer Leader's Course Leader SmartbookDocument106 pagesInfantry Basic Officer Leader's Course Leader SmartbookDustin Miner100% (4)
- SWOT Analysis Template For Technology Planning Needs AssessmentDocument12 pagesSWOT Analysis Template For Technology Planning Needs Assessmentapi-290597914No ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis of KissanDocument16 pagesSWOT Analysis of KissanRajath m GogiNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Opportunities of College Students TDocument8 pagesChallenges and Opportunities of College Students THa Phuong AnhNo ratings yet
- UBLDocument41 pagesUBLShoaib AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Training and DevelopmentDocument39 pagesChapter 7 - Training and DevelopmentMoshmi MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Peat ChreeDocument11 pagesPeat ChreeAbdii DhufeeraNo ratings yet
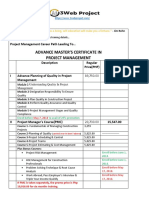
- Advance Master Certificate in Project ManagementDocument5 pagesAdvance Master Certificate in Project ManagementNewton GalileoNo ratings yet
- Introductory Human Resource ManagementDocument15 pagesIntroductory Human Resource ManagementCharmynJiaMin100% (1)
- 06electrical - Electronic PDFDocument159 pages06electrical - Electronic PDFMohd Sanusi IsmailNo ratings yet
- Alfred MwendwaDocument44 pagesAlfred MwendwaCarol SoiNo ratings yet
- PGDHRM - CurrDocument5 pagesPGDHRM - CurrHawa SinghNo ratings yet
- PHRI Mod 5 PDFDocument81 pagesPHRI Mod 5 PDFmostey mosteyNo ratings yet
- TR - Automotive Body Painting Finishing NC IIDocument94 pagesTR - Automotive Body Painting Finishing NC IIAljon BalanagNo ratings yet
- Analysing Workplace Oral Communication Needs in English Among IT GraduatesDocument11 pagesAnalysing Workplace Oral Communication Needs in English Among IT Graduatesmaram123No ratings yet
- Soto Gómez, Pérez Gómez Et Al - Action Research Through Lesson Study For The Reconstruction of Teacher's Practical KnowledgeDocument17 pagesSoto Gómez, Pérez Gómez Et Al - Action Research Through Lesson Study For The Reconstruction of Teacher's Practical KnowledgeGustavo LeyesNo ratings yet
- SOP First Aid TrainingDocument4 pagesSOP First Aid TrainingshreyasNo ratings yet
- 2009 Catalog: Credentials Matter!Document108 pages2009 Catalog: Credentials Matter!Jorge Rodriguez GNo ratings yet
- The Art of Occult Translation - IGOS - International Guild of Occult SciencesDocument29 pagesThe Art of Occult Translation - IGOS - International Guild of Occult SciencesInternational Guild of Occult Sciences - College and Research Society100% (1)
- The Risk Reduction Process Utilizing A Hierarchy of ControlsDocument11 pagesThe Risk Reduction Process Utilizing A Hierarchy of ControlsZélia OrnelasNo ratings yet
- TG - Provide F&B Services - Final PDFDocument254 pagesTG - Provide F&B Services - Final PDFIonut Stoica75% (4)
- CHED Application FormDocument8 pagesCHED Application FormMa. Gemille NopradaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Training On Employee PerformanceDocument4 pagesThe Effect of Training On Employee PerformanceChiyin LeoNo ratings yet
- MJ Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesMJ Interview QuestionsS1626No ratings yet