Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test PDF
Test PDF
Uploaded by
bluegreen700Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test PDF
Test PDF
Uploaded by
bluegreen700Copyright:
Available Formats
test Starch Hydrolysis Gelatin
Liquefaction
X-ray film Catalase production
Purpose Detect bacteria that produce
-amylase
Detect bacteria
that produce
Gelatinase
Detect bacteria
that produce
Gelatinase
Detect bacteria that produce
Catalase
Principle In the presence of starch
iodine will form complex
with it purple or or black
color
Hydrolysis of starch - No
starch to react with iodine
clear zone after adding
iodine
Gelatin solid at a
temperature of
25
o
C or lower.
gelatinase
breaks up the
gelatin the
medium cannot
solidify at cold
temperatures
X-ray film is
coated with
gelatin emulsion.
gelatinase
breaks up the
gelatin on X-ray
clear zone on
x-ray film
Catalase hydrogen peroxide
into water and oxygen
bubbles
Media
contents
Nutrient Agar + starch Gelatin tube of 0.5 ml
saline.
Tube method : Nutrient Agar
Slide method : Add H2o2 Drop
Add the organism on it !
Media
type
Agar plate Gelatin Tube Liquid tube agar slant tube
Media
color
Black after adding iodine transparent --- Trasnparent
Reagents Iodine None X-ray film strip 3% Hydrogen peroxide
Results +ve clear zone after
adding iodine
-ve No clear zone , plate
remain black
After 30 days
+ve Reamain
liquid after
cooling
-be Become
sold after cooling
+ve clear
zone on x-ray
-ve no change
of X-ray film
+ve Gas bubbles
-ve No Bubbles
Examples +ve : Bacillus subtilis
-ve : E. Coli
+ve : Serratia, Pseudomonas, and
Vibrio
+ve : -ve :
Staphylococci Streptococci
Listeria
monocytogenes
beta
hemolytic
streptococci.
Neisseria
Bacillus Clostridium
Biochemical tests
test Coagulase Test MR-VP tests Oxidase Test Tryptophan
hydrolysis
Purpose Detect bacteria that
Have Coagulase
MR portion : Detect
bacteria that ferment
glucose to acidic products
VP portion : Detect
bacteria that ferment
glucose to acetoin
Detect bacteria that have
Cytochrome oxidase
Detect bacteria
that have
tryptophanase
Principle Plasma " contain
fibrinogen "
CoagulaseFibrinog
en
To fibrin clump
the plasma
MR portion :
Dextrose ferment to
acid products pH drop
below pH 5 methyl red
"indictor " turn red
VP portion : Dextrose
ferment to Acetoin Add
Barritt's reagents " alpha-
naphthol & potassium
hydroxide " red color
Cytochrome oxidase
O2 & reduced will be
oxidized to to form water
and oxidized cytochrome c.
cytochrome oxidase will
oxidase the test reagent
purple color
Tryptophan by
tryptophanase
indole and other
products
Indole + Kovac's
reagent red
color
test
contents
Test slide : plasma +
organism
Media : MR-VP Broth :
Liquid media contain
Dextrose
transfer the bacteria to the
filter paper Add oxidase
reagent Purple color
Media : Tryptone
broth "liquid
media contain
tryptophan "
Media type None Broth "liquid" None Broth "liquid"
Media
color
---- transparent ---- transparent
Reagents None MR portion : Methyl Red
VP portion : Barritt's
reagents
A: 5% Alpha-Naphthol
B: Potassium Hydroxide
oxidase test reagent :
(tetramethyl-p-
phenylenediamine
dihydrochloride or an
Oxidase Disk, p
aminodimethylaniline
Kovacs reagent
contains HCL ,
dimethylaminoben
zaldehyde, and
amyl alcohol
yellow in color.
Results +ve plasma
clumps
-ve No clumps
MR portion :
+ve Red color
-ve yellow color
VP portion :
+ve Red color
-ve copper in colo
+ve purple color
-ve No color change
+ve red/pink
layer "red ring "
-ve No Layer
Examples +ve :
Staphylococcus
aureus
-ve : the rest of
Staphylocci
MR +ve : E. Coli
MR ve : Enterobacter
VP +ve : Enterobacter
VP ve : E. Coli
+ve : many gram negative
and gram positive
-ve : Enterobacteriaceae
+ve : E. Coli
ve : Enterobacter
test Citrate Utilization
test
Urease Test Nitrate reduction Zinc test
Purpose Determine ability of
an organism to use
citrate as sole
carbon source.
Detect bacteria that
have urease
bacteria that have nitrate
reductase , so it can utilize
organic compounds as
sources of carbon and use
nitrate as a terminal
electron acceptor during
anaerobic respiration.
Distinguish between
bacteria didn't utilize
nitrate or that
reduced nitrite
further to ammonia or
molecular nitrogen
- Done after nitrate
test if it was
negative -
Principle Metabolize citrate
& utilize ammonium
relaes ammonia
increasing the pH
Bromthymol blue
"indicator " turns
from green to blue
Urease convert
urea ammonia,
CO2, and water
ammonia increase pH
phenol red" pH
indicator " change
from red to bright pink
"
nitrate reductase reduce
nitrate to nitrite add
Sulfanic acid and
naphthylamine red color
No color change : either
bacteria didn't utilize nitrate
or it reduced nitrite further
to ammonia or molecular
nitrogen
-- use zinc to distinguish it -
If nitrate wasn't
reduced :
Zinc reduce nitrate
to nitrite the
Sulfanic acid and
naphthylamine that
were added in the
nitrate test change
to red color
If nitrate was further
reduced : no color
change
test
contents
Simmons Citrate
Agar : contains
sodium citrate
(carbon source),
ammonium ion ,
PH indicator
bromthymol Blue
Media :
urea slant agar :
contain urea + agar
pH indicator phenol
red
Nitrate broth containing
0.5% potassium nitrate
Nitrat test
Media type Agar slant tube Broth "liquid" Broth "liquid" Broth "liquid"
Media
color
Green
Yellow
Transparent Transparent
Reagents None None Reagent A (Sulfanic acid) and
reagent B (naphthylamine)
Zinc powder
Results +ve blue
-ve green
+ve bright pink
color
+ve red color
-ve No color change
+ve red color
-ve No color
change
-ve media remain
yellow
Examples +ve : Enterobacter
ve : E. Coli
+ve Proteus
+ve : Escherichia coli
Klebsiella pneumonia
Morganella morganii and
Proteus mirabilis
+ve complete : (full
reduction ): Pseudomonas
aeruginosa must use zinc
to prove that NO color
change !!!!!
-ve : Acinetobacter
Staphylococcus epidermidis
+ve : Acinetobacter
Staphylococcus
epidermidis
ve : Pseudomonas
aeruginosa
test Motility test SIM agar
Purpose Detect motile bacteria 1-Determine ability of an
organism to produce H2S
2- Determine the abilitry to
produce Indole
3- Determine motility
Principle Stab quickly a tube of
semi solid media if
motile, there will be
growth going out
away from the stab
line, and test is
positive
If bacteria is not
motile, there will only
be growth along the
stab line.
Media contain Cysteine and
sodium thiosulfate
bacteria metabolized these
amino acids Produce H2S
ferrous sulfate "
indicator" react with H2S
black color
If motile the entire tube
become black
If non motile black
pericipitate only around the
stab line
To test For indole add
Kovac's reagent red color
test
contents
Semi solid media
contains tryptose,
sodium chloride, agar,
and a color indicator
"tetrazolium chloride"
SIM media : sulfur
containing amino acid
"cysteine, sodium
thiosulfate" ,
ferrous sulfate"indicator"
Media
type
Semi solid Agar semisolid
Media Transparent Transparent
Differential and selective Media
color
Reagents None Kovac's reagent
Results +ve = Motile : growth
going out away from
the stab line
-ve = Non Motile =
growth along the stab
line
H2S and motile the whole
tube become black
H2S and non motile black
around stab line
Non H2S No color change
After addition of Kovac's
Indole +ve : +ve red/pink
layer "red ring "
-ve No Layer
Examples +ve : Salmonella
Proteus
-ve : Klebsilla
H2S and motile:
Salmonella
Proteus
H2S and non motile :
Citrobacter
Non H2S and non motile :
Klebsiella
test Mannitol Salt Agar
(MSA)
Eosin Methylene Blue
Agar
MacConkey Agar Blood agar
Purpose 1-Allow growth of
staphylococci
2- Differentiate
between
Staphylococcus
aureus & other
staphylococci
1-allow growth of Gram-
negative bacteria.
2- Differentiate between of
Gram-negative
"Enterobactericae"
1-allow growth of
Gram-negative bacteria.
2- Differentiate
between Gram-
negative "
Detect bacteria that
produce enzymes
hemolysins (exotoxin)
that act on the red
cells
Principle high salt
concentration inhibits
the growth of most
bacteria other than
staphylococci
Staphylococcus
aureus ferment
ferments the mannitol
acid lower pH
changes the
indicator "phenol red "
from red to yellow
contains methylene blue and
eosin inhibit the growth
of Gram-positive
contains lactose & sucrose
Lactose and sucrose
fermenters dark metallic
green colonies " E. coli "
Only Lactose fermenters
pink colonies "Enterobacter"
Non-fermenters produce
no color and take the color
contains bile salts and
crystal violet inhibit
the growth of Gram-
positive
Lactose fermenters
Pink colonies
" E. coli , Enterobacter "
Non-fermenters
produce no color and
take the color of the
media "only growth" -
Beta hemolysis:
Enzymes lyse the
blood cells completely,
producing a clear area
around the colony.
Alpha hemolysis:
Incomplete hemolysis
produces a greenish
discoloration around
the colony.
Gamma hemolysis: No
effect on the red cells.
of the media " Salmonella " Salmonella
Media
contents
Mannitol
7.5% sodium chloride
phenol red "indicator
"
methylene blue
eosin
bile salts and crystal
violet
Nutrient agar + 5%
sheep blood
Media
type
Agar plate Agar plate Agar plate Agar plate
Media
color
Results S. aureus
- growth + color
change from red to
yellow
Other staphylococci
-only growth , color
remain red
Other bacteria
No growth or color
change
dark metallic green colonies
Lactose and sucrose " E.
coli
&
K. pneumonia"Mucoid "
pink colonies lactose only
" Enterobacter"
No color change , only
growth Non-fermenters
" Salmonella"
pink colonies
lactose " E. coli ,
Enterobacter , K.
pneumonia"Mucoid "
No color change , only
growth
Non-fermenters
" Salmonella"
Clear zone beta
hemolysis
Greenish discoloration
alpha hemolysis
No effect gamma
hemolysis
You might also like
- Biochemical Test of BacteriaDocument33 pagesBiochemical Test of Bacteriaaziskf100% (2)
- UrinalysisDocument43 pagesUrinalysisJames Knowell80% (5)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- CASCO Phil. Chemical. v. Gimenez Case DigestDocument1 pageCASCO Phil. Chemical. v. Gimenez Case Digestrebeccajordan550% (2)
- Feasibility Study Report of Fertilizer Plant in Mozambique-Toyo EngineeringDocument129 pagesFeasibility Study Report of Fertilizer Plant in Mozambique-Toyo EngineeringRRHH50% (4)
- Biochemical Tests: Laboratory ObjectivesDocument24 pagesBiochemical Tests: Laboratory ObjectivesIsak Isak IsakNo ratings yet
- Media Biochemical TestsDocument24 pagesMedia Biochemical TestsSudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Media & Biochemical Tests: Laboratory ObjectivesDocument36 pagesMedia & Biochemical Tests: Laboratory ObjectivesHiba Abu-jumahNo ratings yet
- Media&Biochemica TestsDocument25 pagesMedia&Biochemica TestsMansoor KhalidNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Microbiology: Biochemical Tests, Immunoassays and Molecular DiagnosticsDocument62 pagesDiagnostic Microbiology: Biochemical Tests, Immunoassays and Molecular DiagnosticsBryan de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Media Biochemical TestsDocument36 pagesMedia Biochemical TestsIsmail Bazly ZarirNo ratings yet
- Biochemical - TestsDocument5 pagesBiochemical - TestsMohsen Haleem100% (1)
- ENTEROBACTERIACEAEDocument81 pagesENTEROBACTERIACEAEAyessa VillacorteNo ratings yet
- Lab 8Document28 pagesLab 8Mustafa A. DawoodNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests: I. Carbohydrate FermentationDocument5 pagesBiochemical Tests: I. Carbohydrate FermentationMelody Jane PardilloNo ratings yet
- Biochemical TestDocument25 pagesBiochemical TestBiswajit DharuaNo ratings yet
- EnterobacteriaceaeDocument20 pagesEnterobacteriaceaeNarayani MathivananNo ratings yet
- Bichemichal Tests Dr. Orass MadhiDocument29 pagesBichemichal Tests Dr. Orass Madhiwissam salimNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Test of BacteriaDocument33 pagesBiochemical Test of BacteriaGuna SheelaNo ratings yet
- Docs For Topic 16Document8 pagesDocs For Topic 16JaneNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 BacteDocument7 pagesLec 3 BacteMitchee ZialcitaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab QuipperDocument4 pagesBiochem Lab QuipperJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Microbiology LABDocument8 pagesMicrobiology LABLazurdyNo ratings yet
- Biochem TestsDocument27 pagesBiochem TestsSteph VeeNo ratings yet
- MCB 180 Exercise 5 FULL REPORTDocument9 pagesMCB 180 Exercise 5 FULL REPORTkpfernandico.metslogisticsNo ratings yet
- Biochemical: ReactionsDocument62 pagesBiochemical: ReactionsIsaacJ22No ratings yet
- LAB 12 Biochemical Tests 2 2nd 2020-2021Document19 pagesLAB 12 Biochemical Tests 2 2nd 2020-2021Deena Hajj QasemNo ratings yet
- Biochemical TestingDocument10 pagesBiochemical TestingKatrina Mae MedinaNo ratings yet
- E. Coli and K. PneumoniaDocument26 pagesE. Coli and K. PneumoniamryamNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests IMViCDocument3 pagesBiochemical Tests IMViCSayyeda SumaiyahNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests: Shafie Abdulkadir HassanDocument29 pagesBiochemical Tests: Shafie Abdulkadir HassanShafici CqadirNo ratings yet
- Identification of An Unknown Organism #22 Nathan Cain Microbiology 201 Wed. 11 O'clock LabDocument6 pagesIdentification of An Unknown Organism #22 Nathan Cain Microbiology 201 Wed. 11 O'clock LablagbenektelseNo ratings yet
- Bacte TestDocument10 pagesBacte TestRiondalionNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Quality Control Sterilization and Disinfection ModuleDocument23 pagesLesson 3 Quality Control Sterilization and Disinfection ModuleTinNo ratings yet
- 10.biochemical Tests For Identification of BacteriaDocument20 pages10.biochemical Tests For Identification of BacteriatafaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical TestDocument8 pagesBiochemical Testsd.danapriya sd.priyaNo ratings yet
- Thi Lab FmaDocument15 pagesThi Lab FmaThuỳ TrangNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Biochemical TestsDocument45 pagesMiscellaneous Biochemical TestsDale Daniel Macarandan SisonNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Text Documenthari krishnaa athotaNo ratings yet
- Catalase TestDocument12 pagesCatalase Testshiva121294No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Biochemical Activity, Session 2ADocument16 pagesChapter 9 Biochemical Activity, Session 2AJoshua ZeelanderNo ratings yet
- Biochemical CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesBiochemical CharacteristicsVeishnavi RavikumarNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiochem Lab ReviewerJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests: Nitrate Reduction TestDocument5 pagesBiochemical Tests: Nitrate Reduction TestAnandNo ratings yet
- Urine TestDocument104 pagesUrine Testdustpops100% (1)
- Biochemical Tests Enterobacteria IdentificationDocument10 pagesBiochemical Tests Enterobacteria IdentificationArleen MatincaNo ratings yet
- PK Urine Practicum 1 KBK Sem 6 2016 ManualDocument38 pagesPK Urine Practicum 1 KBK Sem 6 2016 Manualanindita fauziahNo ratings yet
- Enterobacteriaceae BiochemialDocument15 pagesEnterobacteriaceae BiochemialRigel L. Licmoan0% (1)
- IMVICDocument20 pagesIMVICFenny Aulia Sugiana100% (1)
- Biochemical Tests FinalDocument30 pagesBiochemical Tests Finalahmed.mo.22555417No ratings yet
- Postlab Report - RevisedDocument90 pagesPostlab Report - Revisedjustine_baquiran100% (1)
- Gram Negative Bacill1Document6 pagesGram Negative Bacill1IAN GABRIELLE MERCADO CUYNONo ratings yet
- Identification of Pseudomonas SPDocument20 pagesIdentification of Pseudomonas SPUttam Kr Patra100% (4)
- Enterobacteriaceae: Biochemical ReactionsDocument20 pagesEnterobacteriaceae: Biochemical Reactionslindaprihastiwi100% (1)
- Isolation and Identification of Enteric OrganismsDocument7 pagesIsolation and Identification of Enteric OrganismsCzarina Charmaine DiwaNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Aureus - Pseudomonas Putida - Klebsiella OxytocaDocument4 pagesStaphylococcus Aureus - Pseudomonas Putida - Klebsiella OxytocaJeanette RiosNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Detection of Coliforms and Fecal Coliforms in FoodsDocument45 pagesIsolation and Detection of Coliforms and Fecal Coliforms in FoodsArianne ManuelNo ratings yet
- Microbiology ReviewerDocument8 pagesMicrobiology ReviewerSteph Vee100% (7)
- Microbiolal TestingDocument8 pagesMicrobiolal Testingmalakst200No ratings yet
- Practical Manual of Analytical ChemistryFrom EverandPractical Manual of Analytical ChemistryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterFrom EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNo ratings yet
- Ammonia PresentationDocument37 pagesAmmonia Presentationch0906851002100% (1)
- Ts of Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Justicia Carnea On The Kidney Function Parameters in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Albino Wistar RatsDocument39 pagesTs of Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Justicia Carnea On The Kidney Function Parameters in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Albino Wistar RatsNwigwe Promise ChukwuebukaNo ratings yet
- 9701 w02 QP 2Document12 pages9701 w02 QP 2Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Some Facts About Urea Stripper by Prem BDocument12 pagesSome Facts About Urea Stripper by Prem Bdanil mahaNo ratings yet
- Biocementation and BiocementsDocument30 pagesBiocementation and BiocementscarloscarinelliNo ratings yet
- Worksheet ANSWER KEY Chapter 7 BIO-CLASSDocument13 pagesWorksheet ANSWER KEY Chapter 7 BIO-CLASSUCL SportsNo ratings yet
- Azolla & Soya Hulls-Substitutes For Urea in Coir Pith Composting PDFDocument1 pageAzolla & Soya Hulls-Substitutes For Urea in Coir Pith Composting PDFarunkumarbNo ratings yet
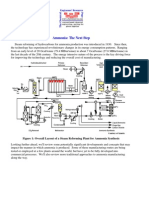
- Ammonia The Next StepDocument11 pagesAmmonia The Next StepmuralleroNo ratings yet
- Blowing Agents For RubberDocument32 pagesBlowing Agents For RubberNontawatNo ratings yet
- 3Document8 pages3sriram bharathNo ratings yet
- Simply Safer - . .: Wahlco U2A® Urea To Ammonia SystemDocument6 pagesSimply Safer - . .: Wahlco U2A® Urea To Ammonia SystemkangsungjinNo ratings yet
- Preparation of ReagentsDocument4 pagesPreparation of ReagentskvictoNo ratings yet
- Cause of Damage and Repair of Reformed Gas Firetube Boiler: Zeng Zhong Quan Mark A. HoldermanDocument11 pagesCause of Damage and Repair of Reformed Gas Firetube Boiler: Zeng Zhong Quan Mark A. Holdermanvaratharajan g rNo ratings yet
- Procedure For The Preparation of Blood AgarDocument3 pagesProcedure For The Preparation of Blood AgarSam Florenstein MontenegroNo ratings yet
- UrineDocument41 pagesUrineWahab KhaniNo ratings yet
- UreaDocument1 pageUreaDesiNo ratings yet
- How To Make The Most Of: Carbon DioxideDocument3 pagesHow To Make The Most Of: Carbon Dioxidetorta1No ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 11 Non Protein Nitrogen PDFDocument5 pagesEXPERIMENT 11 Non Protein Nitrogen PDFmkNo ratings yet
- Fertilizers and PesticidesDocument28 pagesFertilizers and PesticidesPukhrajNo ratings yet
- Bosch-Meiser Urea Process, 1922Document7 pagesBosch-Meiser Urea Process, 1922Wow WowNo ratings yet
- Yayo Urea Fertilizer Project 511 Dayswed 6/11/14 Wed 1/27/16 0 DaysDocument3 pagesYayo Urea Fertilizer Project 511 Dayswed 6/11/14 Wed 1/27/16 0 DaysAnonymous 7ZYHilDNo ratings yet
- Urea Feeding Recommendations For RuminantsDocument2 pagesUrea Feeding Recommendations For RuminantsVet Ameer HamzaNo ratings yet
- Deamination of Amino Acids - The Urea CycleDocument4 pagesDeamination of Amino Acids - The Urea CycleLei ぱんがにばん100% (1)
- CV Shabbir Ahmed DarDocument3 pagesCV Shabbir Ahmed DarFederico SeniorNo ratings yet
- tmp9250 TMPDocument8 pagestmp9250 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Industry in The PhilippinesDocument49 pagesFertilizer Industry in The PhilippinesmojakovichNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Pre-U: CHEMISTRY 9791/02Document20 pagesCambridge Pre-U: CHEMISTRY 9791/02laksh bissoondialNo ratings yet
- Nano Ureathe Philosophyof FutureDocument9 pagesNano Ureathe Philosophyof FutureMuhammad Iqbal ChandioNo ratings yet