Professional Documents
Culture Documents
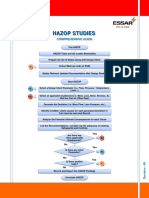
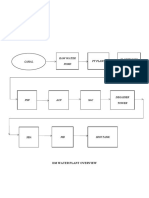
Hazop PDF
Hazop PDF
Uploaded by
Luiz Rubens Souza CantelliCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- IB Buisness Management Study GuideDocument127 pagesIB Buisness Management Study GuideJohnathan ChargaffNo ratings yet
- HAZOP HAZID Haliburton PDFDocument2 pagesHAZOP HAZID Haliburton PDFamirNo ratings yet
- HAZOPDocument34 pagesHAZOPMohammed100% (1)
- HAZOP ON Sulfuric Acid Transfer To Storage TankDocument6 pagesHAZOP ON Sulfuric Acid Transfer To Storage Tankram0% (1)
- Humber RefineryDocument2 pagesHumber RefineryRatna Paramitha SariNo ratings yet
- KAHLIDr Yehia45 PDFDocument36 pagesKAHLIDr Yehia45 PDFLuiz Rubens Souza CantelliNo ratings yet
- Produced Water Characteristics, Treatment and ReuseDocument18 pagesProduced Water Characteristics, Treatment and ReuseVIVIANA ANDREA GARCIA ROCHA100% (1)
- 0 0 25 Feb 2016 1108554031AnnexureManufacturing&EffluentTreatmentProcessDocument28 pages0 0 25 Feb 2016 1108554031AnnexureManufacturing&EffluentTreatmentProcessNeerav Indrajit GadhviNo ratings yet
- Urea Stripper ProcedureDocument6 pagesUrea Stripper ProcedureSoumitra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Hazard and Operability StudiesDocument8 pagesHazard and Operability Studiesangry_granNo ratings yet
- Method Statement - BenchmarkDocument15 pagesMethod Statement - BenchmarkStansilous Tatenda NyagomoNo ratings yet
- Qhse-Sop-054 Oil Spill PreventionDocument14 pagesQhse-Sop-054 Oil Spill PreventionJust AabNo ratings yet
- Molten Sulphur Rail Tank Car Loading and Unloading Operations Final With AppendicesDocument68 pagesMolten Sulphur Rail Tank Car Loading and Unloading Operations Final With AppendicesvlabdulazeemNo ratings yet
- Lifting & Rigging ProceduresDocument27 pagesLifting & Rigging ProceduresBrunoro DantasNo ratings yet
- Work Method Statement For Structure ErectionDocument12 pagesWork Method Statement For Structure ErectionMuhammad TeguhNo ratings yet
- IHC Beaver 600 C Cutter Suction DredgerDocument2 pagesIHC Beaver 600 C Cutter Suction DredgerHamada GadNo ratings yet
- ESIA WaadDocument463 pagesESIA WaadRRHH100% (3)
- Offshore Support Vessel & Marine Support Craft VettingDocument19 pagesOffshore Support Vessel & Marine Support Craft Vettingjk.jackycheokNo ratings yet
- Report On Student Iw Experience SchemeDocument9 pagesReport On Student Iw Experience SchemeifiokNo ratings yet
- 2013aicheammoniasafetysymposiumquestions AnswersDocument27 pages2013aicheammoniasafetysymposiumquestions AnswersRindeshNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure For HSDDocument3 pagesStandard Operating Procedure For HSDisjglfdskNo ratings yet
- Basic Introduction of Coal Handling SystemDocument7 pagesBasic Introduction of Coal Handling SystemHerman AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Lifting Plan of SpoolDocument1 pageLifting Plan of SpoolhazopengineerNo ratings yet
- Annex 17 - Induction Nawara ProjDocument18 pagesAnnex 17 - Induction Nawara ProjMajdiSahnounNo ratings yet
- 6.1.2 Gasification ReactorDocument2 pages6.1.2 Gasification ReactorShemzinhoNo ratings yet
- Mineralsfocus Issue 2015 SiemensDocument52 pagesMineralsfocus Issue 2015 SiemensmirkomakNo ratings yet
- HAZID HAZOP Project Brief PDFDocument15 pagesHAZID HAZOP Project Brief PDFAndi Ade Putra SiregarNo ratings yet
- Process Industry HAZOP Techniques & Applications and HAZOP Leader Training, Indonesia, JohnnyDocument9 pagesProcess Industry HAZOP Techniques & Applications and HAZOP Leader Training, Indonesia, JohnnyEko PoerwantoNo ratings yet
- Hazop ExampleDocument4 pagesHazop Exampledroffilcz27No ratings yet
- Useful Tips For A Successful HAZOP Study: Process Hazard Analysis TechniquesDocument10 pagesUseful Tips For A Successful HAZOP Study: Process Hazard Analysis TechniquesDesiree MolinaNo ratings yet
- IMCA-Event-2018-09-27 - Presentation 7 - Understanding Your Limits (Subsea7) PDFDocument21 pagesIMCA-Event-2018-09-27 - Presentation 7 - Understanding Your Limits (Subsea7) PDFsatrio aryoNo ratings yet
- Dibia Ifeanyichukwu Peter Updated CV (Resume)Document7 pagesDibia Ifeanyichukwu Peter Updated CV (Resume)wizzy basseyNo ratings yet
- Strategy For Extending The Useful Lifetime of A Wind TurbineDocument41 pagesStrategy For Extending The Useful Lifetime of A Wind TurbineRkantvyasNo ratings yet
- APPENDIX 4 Statement On Telescopic Spout Operation Fraser Surrey Docks DTCF AmendmentDocument8 pagesAPPENDIX 4 Statement On Telescopic Spout Operation Fraser Surrey Docks DTCF AmendmentRestuNo ratings yet
- Method Statement LuderitzDocument11 pagesMethod Statement LuderitzYoung R-j MafaraNo ratings yet
- NAWPPL-BIMS-NPPL-000-HS-PRO-00009 - C01 - Tagging & Isolation ProcedureDocument8 pagesNAWPPL-BIMS-NPPL-000-HS-PRO-00009 - C01 - Tagging & Isolation ProcedureMoaatazz NouisriNo ratings yet
- Plf-jms-031 - r0 - Jms of Lifting, Shifting, Stringing, Lowering-In and Transportation Using Excavator - SignedDocument85 pagesPlf-jms-031 - r0 - Jms of Lifting, Shifting, Stringing, Lowering-In and Transportation Using Excavator - SignedHafiz YunusNo ratings yet
- Safety Shower PDFDocument7 pagesSafety Shower PDFnaveen142No ratings yet
- Pipeline Risk Assessment and Environmental Consequence AnalysisDocument82 pagesPipeline Risk Assessment and Environmental Consequence Analysisnanking100% (1)
- Piper AlphaDocument6 pagesPiper AlphaAhmed Eldeeb100% (1)
- Common Hazards DescriptionsDocument2 pagesCommon Hazards Descriptionsasifniazi4No ratings yet
- Catastrophic Fire in Ammonia Plant Compressor RoomDocument10 pagesCatastrophic Fire in Ammonia Plant Compressor RoomRavi KasaudhanNo ratings yet
- A ESIA Yemen Section 3 Revision 1Document42 pagesA ESIA Yemen Section 3 Revision 1Denstar Ricardo SilalahiNo ratings yet
- NH3 RiskDocument59 pagesNH3 RiskDave CNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument19 pagesFinal ReportAbdul Azeez100% (1)
- G.I. 150.007 Radiation Radioactive ControlDocument8 pagesG.I. 150.007 Radiation Radioactive ControlbryanNo ratings yet
- Safe Practice For Vessel Positioning With Mooring Analysis (Orcaflex)Document19 pagesSafe Practice For Vessel Positioning With Mooring Analysis (Orcaflex)KhoironSyamdatuNo ratings yet
- Hazop Record Form: Condensate Lines From The Condensers To The Holding TankDocument3 pagesHazop Record Form: Condensate Lines From The Condensers To The Holding Tanksajni123No ratings yet
- HAZOP Studies GuideDocument4 pagesHAZOP Studies GuideMRITYUNJOY GUPTANo ratings yet
- Method Statement - Tower ErectionDocument2 pagesMethod Statement - Tower ErectionsoubhagyaNo ratings yet
- Manual: Procedure Titel: HSE-ManualDocument11 pagesManual: Procedure Titel: HSE-ManualGeetha_jagadish30No ratings yet
- Project Risk Analysis and Management: Mini GuideDocument20 pagesProject Risk Analysis and Management: Mini GuideIuliana AronNo ratings yet
- Merrill CroweDocument7 pagesMerrill CroweAlejandro ClavijoNo ratings yet
- Spec of Bitumen TankDocument9 pagesSpec of Bitumen Tanknswain76No ratings yet
- Bulk Material HandlingDocument5 pagesBulk Material HandlingPrasenjit BhuiyaNo ratings yet
- Workpack TEMANA ShutdownDocument23 pagesWorkpack TEMANA Shutdownhitm357No ratings yet
- HazCom With GhsDocument33 pagesHazCom With GhsAnonymous iI88LtNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid Manufacturing ProcessDocument7 pagesNitric Acid Manufacturing ProcessLenin PrabhuNo ratings yet
- TOS HA LONG PIPE LAY Spec (Updated 30 12 19)Document3 pagesTOS HA LONG PIPE LAY Spec (Updated 30 12 19)Mr. DNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Horizontal Tray Erection.Document5 pagesMethod Statement For Horizontal Tray Erection.soubhagyaNo ratings yet
- Apron Feeder Data SheetDocument1 pageApron Feeder Data SheetPat AuffretNo ratings yet
- Hazop LEADER TrainingDocument2 pagesHazop LEADER Trainingbaaziz2015No ratings yet
- ANCOLD Response Combined MinDocument33 pagesANCOLD Response Combined MinPCYM GEOTECNIANo ratings yet
- Management of DredgedExcavated SedimentDocument17 pagesManagement of DredgedExcavated SedimentMan Ho LamNo ratings yet
- 062-063 Passive Samplers - ULTRA Passive SamplersDocument2 pages062-063 Passive Samplers - ULTRA Passive SamplersLuiz Rubens Souza CantelliNo ratings yet
- MSD Prevention Toolbox PartC English in Depth Risk Assessment FinalDocument49 pagesMSD Prevention Toolbox PartC English in Depth Risk Assessment FinalLuiz Rubens Souza CantelliNo ratings yet
- Fact Shett - OSHADocument2 pagesFact Shett - OSHALuiz Rubens Souza CantelliNo ratings yet
- HEM Silver Ion Steriliser SIS B40-R1Document1 pageHEM Silver Ion Steriliser SIS B40-R1kyle wetherillNo ratings yet
- DM PlantDocument8 pagesDM PlantSandeep TanwarNo ratings yet
- Bhopal WTP PDFDocument75 pagesBhopal WTP PDFAnonymous hMech04fiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Water Treatment Questions of The Day 1-2-20Document19 pagesIndustrial Water Treatment Questions of The Day 1-2-20AkashTripathiNo ratings yet
- The Study of The Design of Production Systems of Purified Water For The Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument19 pagesThe Study of The Design of Production Systems of Purified Water For The Pharmaceutical IndustryAndreaVargasNo ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument34 pagesWater TreatmentJessa Dynn Agraviador Velarde100% (1)
- Water SupplyDocument67 pagesWater SupplyHusnina FakhiraNo ratings yet
- HCL Corrosion Under ControlDocument4 pagesHCL Corrosion Under ControlNXVNNo ratings yet
- Swimming Pool Risk Management Plan GuideDocument24 pagesSwimming Pool Risk Management Plan GuideAbdulmalekNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument7 pagesWaste Water TreatmentBusi_SeleshoNo ratings yet
- Intership Report 2023 1Document51 pagesIntership Report 2023 1Jyotirmoy MahataNo ratings yet
- 1Document15 pages1dalton2004No ratings yet
- Portable Water PurificationDocument9 pagesPortable Water PurificationAnonymous V5UYBUMaNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in Waste Water TreatmentDocument12 pagesNanotechnology in Waste Water TreatmentLubna Amreen100% (1)
- OCY751-Waste Water TreatmentDocument13 pagesOCY751-Waste Water Treatmentsureshvkumar80% (5)
- InfoCell Water Purifier v2207 FADocument22 pagesInfoCell Water Purifier v2207 FAIbnu TalibNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Control of Biofouling in Industrial Water Systems PDFDocument14 pagesThe Chemical Control of Biofouling in Industrial Water Systems PDFsyarifuddinNo ratings yet
- Laporan PKLDocument42 pagesLaporan PKLRaya Fernanda AriantoNo ratings yet
- 649108.dekanic WASTEWATERDocument60 pages649108.dekanic WASTEWATERharshadNo ratings yet
- Physical, Chemical and Biological Characteristics of WastewaterDocument27 pagesPhysical, Chemical and Biological Characteristics of WastewaterRushed AlamaNo ratings yet
- Training Need Assesment SurveyDocument178 pagesTraining Need Assesment SurveyquebellaNo ratings yet
- Reporting ME 01Document84 pagesReporting ME 01Diane Fe CajaroNo ratings yet
- Thermax WWS BrochureDocument6 pagesThermax WWS BrochureAquasoul CoNo ratings yet
- Assg Ecw 567 Mac Jul 22 PDFDocument2 pagesAssg Ecw 567 Mac Jul 22 PDFNUR NABIHAH AZMI AZRINNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Desal 2006 09 007 PDFDocument6 pages10 1016@j Desal 2006 09 007 PDFMimi TanNo ratings yet
- Vws Oil GasDocument8 pagesVws Oil GasFabricio TrosarelloNo ratings yet
- Water and Waste Water EngineeringDocument8 pagesWater and Waste Water EngineeringOlateju AgboolaNo ratings yet
Hazop PDF
Hazop PDF
Uploaded by
Luiz Rubens Souza CantelliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hazop PDF
Hazop PDF
Uploaded by
Luiz Rubens Souza CantelliCopyright:
Available Formats
Agreement No.
CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-1 October 2004
9. HAZARD TO LIFE
9.1 Introduction
9.1.1 This Section investigates the issue of Hazard to Life associated with chlorine, which is used as
the major disinfection agent in Siu Ho Wan WTW. With reference to the Section 3.7 of the
EIA Study Brief, chlorine hazards during construction phase and operation phase will be
investigated. For hazards during construction phase, the additional hazards initiated by
construction activities will be identified by systematic method (i.e. Hazard and Operability
(HAZOP) Study). For operation phase, hazards associated with chlorine will be assessed if
and only if there is an increase of storage and on-site transport of chlorine.
9.2 Rationale of the HAZOP Study
9.2.1 According to Section 1.2 (i) of the EIA Study Brief, the Project comprises, inter alias, the
extension of Siu Ho Wan WTW from the capacity of 150,000 m
3
/day to 300,000 m
3
/day, with
an option for further uprating to 350,000 m
3
/day. Based on a review update on the ultimate
water demand at this stage, the extension work would only comprise of uprating to 300,000
m
3
/day. No further uprating to the capacity of 350,000 m
3
/day is required for this Project.
9.2.2 For the investigation study under the agreement, options selection for the appropriate water
treatment process has been conducted by the Consultants. The recommended water treatment
process consists of the following:
- Removal of odour by pre-ozonation;
- Pre-treatment of manganese by potassium permanganate;
- Sedimentation by installation of tube settlers in clarifiers;
- Primary disinfection by intermediate ozonation;
- Filtration by installation of dual media filters (GAC media and fine sand);
- Post chlorination for residual chlorine requirement.
9.2.3 In the original water treatment process, chlorine was proposed for oxidation of impurities and
disinfection. The allowable storage of chlorine in the existing Siu Ho Wan WTW compound
at a capacity of up to 73 tonnes which was endorsed by Co-ordinating Committee on
Land-Use Planning and Control relating to Potentially Hazardous Installations (CCPHI) on
30.5.1992 during the Stage I WTW, has already duly taken into account future extension of
the WTW up to 300 MLD i.e. 300,000 m
3
/day.
9.2.4 The recommended water treatment process as endorsed by WSD in February 2004 adopts
"ozone" for primary disinfection with the addition of potassium permanganate to remove
manganese and BAC filter to remove ammonia for the Siu Ho Wan WTW extension. As such,
no chlorine would be required for the proposed water treatment process under normal
condition except for post chlorination. Chlorine dose would not exceed the designed dosing
capacity of the WTW as defined in the Steering Group Report on Hazard Assessment,
Planning Study and Action Plan endorsed by CCPHI in May 1992. Hence, there will be no
increase of storage and on-site transport of chlorine to that of the allowable storage capacity
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-2 October 2004
for the Siu Ho Wan WTW. As a result, the hazard assessment for the operation phase is not
required in the EIA stage and only a HAZOP study was conducted in this EIA study.
9.3 Risk Guidelines
9.3.1 As stipulated in Annex 4 of the Technical Memorandum on Environmental Impact
Assessment Process (EIAO-TM), the societal risk guidelines for acceptable risk levels has
included the ALARP region, which required that risk within ALARP region should be
mitigated to As Low As Reasonably Practicable. In comparing with the CCPHI Interim
Guideline for Acceptable Societal Risk (IRG) adopted for the Hazard Assessment, no
ALARP region was adopted for that study. In reviewing the societal risk associated with the
water treatment works assessed in the Hazard Assessment, some of the scenarios, with the
assumptions of implementing several mitigation measures, would lie within one to two orders
of magnitude below the IRG, which is the ALARP region of the societal risk guideline
stipulated in the TM.
9.3.2 Referring to the recommendations from the Hazard Assessment, it concluded that any risk
within two orders of magnitude of the IRG should be mitigated as low as reasonably practical.
Also, it mentioned that any risk at two orders of magnitude below the IRG may, in ALARP
terms, be considered negligible. Therefore, the Hazard Assessment noted it is unlikely that
any further mitigation measures for the works may be justified and the site may be considered
suitable from the perspective of public safety.
9.3.3 The Hazard Assessment also concluded that the site selected for the WTW was suitable in
terms of the Interim Risk Guidelines with the implementation of the following risk mitigation
measures:
Use reinforced concrete panels in the construction of the chlorine drum store
Adopt Route 2 (transport liquid chlorine by sea to Refuse Transfer Station (RTS) near
the WTW at Siu Ho Wan and the remaining short distance to the plant by road) as the
primary chlorine transportation route
Restrict the chlorine delivery using the seawall at or near the RTS at Siu Ho Wan to the
weekend or only transport of up to 12 drums by sea to the RTS seawall at any one time
with only 26 deliveries per year
Prohibit overnight chlorine drums storage at the seawall
Institute a 30m cordon around the chlorine unloading point during deliveries and
temporary storage within a secure area surrounded by a steel barrier
9.3.4 The Hazard Assessment also recommended a 1000 metre radius centred on (excluding land
50m in altitude above) the Chlorine Building as Consultation Zone for Siu Ho Wan WTW.
Moreover, land-use restrictions at Areas 7, 9 and 10 in the Recommended Outline
Development Plan (RODP) for the North Lantau Development were recommended in the
Hazard Assessment to ensure the compliance of Interim Risk Guidelines.
9.3.5 As confirmed with WSD on the implementation of mitigation measures stated in Section 9.3.3,
the establishment of consultation zone for Siu Ho Wan WTW and the implementation of
land-use restrictions in Section 9.3.4 with no change in land-use for the restricted areas, the
societal risk associated with the Siu Ho Wan WTW would have been no change from that
previously assessed in the Hazard Assessment.
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-3 October 2004
9.4 Approach of HAZOP Study
9.4.1 The HAZOP Study was carried out in several stages:
Define the scope of the Study
Select the HAZOP Study Team
Prepare for the HAZOP Study Meeting
Execute HAZOP Study Meeting
Report the Study Results
Define the scope of the Study
9.4.2 The scope of the Study is in line with the EIA Study Brief, which is:
i) Identify additional hazards initiated by construction activities which may increase the
risk of chlorine accidents during storage, handling, transport
ii) Recommend risk mitigation measures for implementation during construction phase
Select the HAZOP Study Team
9.4.3 The team members were selected in a manner that could ensure the Study Team would have
sufficient knowledge of the following items:
a) Design of the existing and future extended Siu Ho Wan WTW
b) Daily operation of the existing Siu Ho Wan WTW
c) Maintenance and repair works at existing Siu Ho Wan WTW
d) Chemical properties of chemicals/compounds involved in operation and extension
work of Siu Ho Wan WTW
e) Safety issues encountered at the existing Siu Ho Wan WTW and future extension
works
f) Environmental issues encountered in future Siu Ho Wan WTW extension works
Prepare for the HAZOP Study Meeting
9.4.4 The preparation work prior to the HAZOP Study Meeting involved:
Collect useful information
Information collected prior to the Study Meeting included the followings:
Locations of the chlorine storage area and chlorine pipework
Chlorine delivery procedures and travel route of Chlorine Delivery Truck on site
Chlorine handling and emergency procedures
Possible construction activities and corresponding plants/equipment involved
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) of chemicals and material encountered/to be
encountered during the Water Treatment Works operation and extension construction
activities
Convert the collected information into a suitable form
In order to provide concise and easy-understanding information to the Study Team
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-4 October 2004
members, the collected information were converted into layout plan and summary table.
Plan the Study Meeting sequence
Prior to the Study Meeting, a Study Meeting sequence was prepared to ensure the Study
Meeting could proceed smoothly and systematically. During the preparative work, it was
planned that the Study Meeting would be conducted in a construction activity-based
sequence. That is, all the possible extension construction activities and plants/equipment
involved would be discussed in turn to identify possible hazards and mitigation measures.
Arrange Study Meeting
After necessary information was obtained and Study Meeting sequence was planned, all the
Study Team members were invited to attend the Study Meeting. In the meantime, obtained
information (in form of layout plan and summary table) and Study Meeting sequence were
sent to the Study Team members for their preparation before the meeting.
Execute HAZOP Study Meeting
One HAZOP Study Meeting session was carried out on 5 February 2004. Representatives
from WSD, M&E and MEMCL participated in the Study Meeting. The items discussed
were recorded during the Study Meeting.
Report the Study Results
Key findings in the Study including causes of the hazard initiating events and the
corresponding mitigation measures are presented in the following paragraphs.
9.5 Description of Site Conditions and Possible Construction Activities
9.5.1 The Siu Ho Wan WTW is located in Area 4 on the Siu Ho Wan Layout Plan No.L/I-SHW/1,
with area about 5.8ha. For the HAZOP Study, locations of chlorine-related facilities and
travel route of chlorine delivery truck in the existing Siu Ho Wan WTW compound are of
interest. A layout plan showing locations of Chlorine Building, chlorine pipeworks and
chlorine delivery truck travel route is given in Figure 9.1.
9.5.2 Description of the Project has been given in Section 2. As agreed in the HAZOP Study
Meeting, only construction activities inside the Siu Ho Wan WTW compound were discussed
in the HAZOP Study because construction works outside the Siu Ho Wan WTW compound
were considered unlikely to initiate additional hazards related to chlorine. The construction
activities and corresponding plants/equipment discussed in the Study Meeting were listed in
Table 9.1.
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-5 October 2004
Table 9.1 Construction Activities and Corresponding Plants/equipment Discussed in HAZOP Study Meeting
Extension Work Component Construction Activity Group Construction Activity Plant/equipment
material Involved
A1. Site clearance and site formation 1. Excavation
2. Removing debris
1. Backhoe
2. Bulldozer
3. Dump truck
A2. Access road construction 1. Excavation
2. Removing debris
3. Paving road
1. Backhoe
2. Dump truck
A3. Electricity generation and supply 1. Generate electricity
2. Preparing electricity supply facilities
and connecting electricity
transmission wire
1. Generator
A4. Site personnel, plants and
equipment mobilization
1. Mobilizing personnel, equipment and
plants by vehicles and crane
1. Site vehicle
2. Crane lorry
3. Mobile crane
A5. Material/Waste storage 1. Storing/stockpiling of material/waste
2. Material/waste delivery
1. Truck
2. Crane lorry
A6. Operations related to fire 1. Cooking by on-site personnel
2. Welding
1. Welding machines
2. Catering equipment
3. Liquid/gas fuel
A. General Site Activities
A7. Chemicals/fuel storage 1. Chemicals/fuel storage
2. Transporting chemicals/fuel
1. Chemicals/fuel
delivery vehicle
2. Crane lorry
B1. Temporary works for temporary
earth retaining structure, bulk
excavation, piling and foundation
work
1. Excavation
2. Piling works
3. Concrete slab demolition
4. Transporting large objects and
equipment
1. Backhoe
2. Oscillator
3. Pneumatic breaker
4. Roller
5. Air compressor
6. Tower crane
7. Dump truck
B. Stage II Extension
Construction of Laboratory
Extension
B2. Form work erection and rebar
refixing
1. Fixing steel
2. Mobilization of pile of steel by crane
3. Welding
1. Welding machine
2. Mobile crane
3. Tower crane
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-6 October 2004
Extension Work Component Construction Activity Group Construction Activity Plant/equipment
material Involved
B3. Concreting 1. Mixing concrete
2. Pour concrete into structure
1. Concrete mixer
2. Crane lorry
3. Tower Crane
4. Backhoe
5. Vibrator
B4. Column and Roof 1. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Mobile crane
B5. Brickwork and finishing 1. Welding
2. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Backhoe
2. Mobile crane
3. Welding machine
B6. E&M installation 1. Welding
2. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Mobile crane
2. Backhoe
3. Welding machine
B. Stage II Extension
Construction of Laboratory
Extension
B7. Landscaping Work 1. Excavation for soft landscape works
implementation
2. Tree plantation for soft landscape
works
1. Backhoe
2. Crane lorry
C1. Temporary works for temporary
earth retaining structure, bulk
excavation, piling and foundation
work
1. Excavation
2. Piling works
3. Concrete slab demolition
4. Transporting large objects and
equipment
1. Backhoe
2. Oscillator
3. Pneumatic breaker
4. Roller
5. Air compressor
6. Tower crane
7. Dump truck
C2. Form work erection and rebar
refixing
1. Fixing steel
2. Mobilization of pile of steel by crane
3. Welding
1. Welding machine
2. Mobile crane
3. Tower crane
C3. Concreting 1. Mixing concrete
2. Pour concrete into structure
1. Concrete mixer
2. Crane lorry
3. Tower Crane
4. Backhoe
5. Vibrator
C. Stage II Extension-
Construction of Sludge
Thickener and Washwater
Tank
C4. Column and Roof 1. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Mobile crane
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-7 October 2004
Extension Work Component Construction Activity Group Construction Activity Plant/equipment
material Involved
C5. Brickwork and finishing 1. Welding
2. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Backhoe
2. Mobile crane
3. Welding machine
C6. E&M installation 1. Welding
2. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Mobile crane
2. Backhoe
3. Welding machine
C. Stage II Extension-
Construction Sludge
Thickener and Washwater
Tank
C7. Landscaping Work 1. Excavation for soft landscape works
implementation
2. Tree plantation for soft landscape
works
1. Backhoe
2. Crane lorry
D1. Temporary works for temporary
earth retaining structure, bulk
excavation, piling and foundation
work
1. Excavation
2. Piling works
3. Transporting large objects and
equipment
1. Backhoe
2. Oscillator
3. Pneumatic breaker
4. Roller
5. Air compressor
6. Tower crane
D2. Form work erection and rebar
refixing
1. Fixing steel
2. Mobilization of pile of steel by crane
3. Welding
1. Welding machine
2. Mobile crane
3. Tower crane
D3. Concreting 1. Mixing concrete
2. Pour concrete into structure
1. Concrete mixer
2. Crane lorry
3. Tower Crane
4. Backhoe
5. Vibrator
D4. Column and Roof 1. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Mobile crane
D5. Brickwork and finishing 1. Welding
2. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Backhoe
2. Mobile crane
3. Welding machine
D. Stage II Extension
Construction of
Pre-treatment Contact
Chambers, Rapid Mix
Chambers, Flocculation
Tanks, Sedimentation
Basins, Intermediate Ozone
Tank and BAC Filters
D6. E&M installation 1. Welding
2. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Mobile crane
2. Backhoe
3. Welding machine
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-8 October 2004
Extension Work Component Construction Activity Group Construction Activity Plant/equipment
material Involved
D. Stage II Extension
Construction of
Pre-treatment Contact
Chambers, Rapid Mix
Chambers, Flocculation
Tanks, Sedimentation
Basins, Intermediate Ozone
Tank and BAC Filters
D7. Landscaping Work 1. Excavation for soft landscape works
implementation
2. Tree plantation for soft landscape
works
1. Backhoe
2. Crane lorry
E1. Temporary works for temporary
earth retaining structure, bulk
excavation, piling and foundation
work
1. Excavation
2. Concrete slab demolition
3. Transporting large objects and
equipment
1. Backhoe
2. Oscillator
3. Pneumatic breaker
4. Roller
5. Air compressor
6. Tower crane
7. Dump truck
E2. Form work erection and rebar
refixing
1. Fixing steel
2. Mobilization of pile of steel by crane
3. Welding
1. Welding machine
2. Mobile crane
E3. Concreting 1. Mixing concrete
2. Pour concrete into structure
1. Concrete mixer
2. Crane lorry
3. Backhoe
4. Vibrator
E4. Brickwork and finishing 1. Welding
2. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Backhoe
2. Mobile crane
3. Welding machine
E5. E&M installation 1. Welding
2. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Mobile crane
2. Backhoe
3. Welding machine
E. Stage II Extension
Construction of Lime
Saturators
E6. Landscaping Work 1. Excavation for soft landscape works
implementation
2. Tree plantation for soft landscape
works
1. Backhoe
2. Crane lorry
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-9 October 2004
Extension Work Component Construction Activity Group Construction Activity Plant/equipment
material Involved
F. Stage II Extension
Installation of one additional
Filter Press
F1. E&M installation 1. Welding
2. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Mobile crane
2. Backhoe
3. Welding machine
G1. Form work erection and rebar
refixing
1. Fixing steel
2. Mobilization of pile of steel by crane
3. Welding
1. Welding machine
2. Mobile crane
3. Tower crane
G2. Concreting 1. Mixing concrete
2. Pour concrete into structure
1. Concrete mixer
2. Crane lorry
3. Backhoe
4. Vibrator
G3. Column and roof 1. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Mobile crane
G4. Brickwork and finishing 1. Welding
2. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Backhoe
2. Mobile crane
3. Welding machine
G5. E&M installation 1. Welding
2. Transferring large objects and
equipment
1. Mobile crane
2. Backhoe
3. Welding machine
G. Stage II Extension-
Construction of Ozonation
Building/ Facilities
G6. Landscaping work 1. Excavation for soft landscape works
implementation
2. Tree plantation for soft landscape
works
1. Backhoe
2. Crane lorry
H. Stage II Extension
Construction of Pipeline
Extension
H1. Pipeline laying 1. Excavation
2. Transferring pipeline
3. Connecting extended pipework
4. Welding
1. Backhoe
2. Crane lorry
3. Welding machine
I. Stage II Extension Testing
and Commissioning of
Chlorine-related Extension
Installation
I1. Testing and Commissioning 1. Check the reliability of the equipment
2. Purge the gaseous nitrogen through
the extended pipework
3. Inject chlorinated water into the
contact tank
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-10 October 2004
Extension Work Component Construction Activity Group Construction Activity Plant/equipment
material Involved
J. Stage II Extension Testing
and Commissioning of
Ozone-related Installation
J1. Testing and Commissioning 1. Check the reliability of the equipment
2. Purge the gaseous nitrogen through
the extended pipework
3. Inject ozone into the contact tank
K. Stage I Modification
Installation of Pumps for Siu
Ho Wan Raw Water and
Fresh Water Pumping
Station
K1. E&M installation 1. Retrofitting water pump with higher
capacity, including installation of
additional pumps and replacement of
existing pumps
1. Crane lorry
2. Welding machine
L1. Demolition work 1. Demolition of concrete slab of
existing facilities
2. Removing debris
1. Pneumatic breaker
2. Dump truck
L. Stage I Modification
Converting one
Sedimentation Basin into an
Intermediate Ozone Contact
Tank
L2. Retrofitting works and E&M
works
1. Transferring large objects and
equipment
2. Retrofitting the ozone contact tank
equipment
3. Welding
1. Crane lorry
2. Backhoe
3. Welding machine
M1. Demolition Work 1. Demolition of concrete slab of
existing facilities
2. Removing debris
1. Pneumatic breaker
2. Dump truck
M. Stage I Modification
Retrofitting of Lamella
Settlers in the
Sedimentation Basins
M2. E&M installation 1. Retrofitting lamella settlers
2. Welding
1. Crane lorry
2. Tower crane
3. Welding machine
N. Stage I Modification
Installation of Equipment
for Alum Sludge Holding
Tanks Nos. 3 & 4 inside
Chemical Storage Building
N1. E&M installation 1. Provision of equipment for alum
sludge holding tanks
2. Welding
1. Crane lorry
2. Welding machine
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-11 October 2004
9.6 HAZOP Study
9.6.1 A HAZOP Study is the method for identifying hazards and problems which prevent efficient
operation. It is a technique that provides opportunities for people to let their imaginations go
free and think of all possible ways in which hazards or operation problem might arise.
Moreover, it is done in a systematic way in order to reduce the chance that something is
missed. During the Study, each component of the Project (construction activity and
corresponding plant/equipment in this case) and each sort of hazard is considered in turn. The
Study is conducted by a team so that the team members can stimulate each other and build
upon ideas from each other.
Methodology
9.6.2 The basic concept of this HAZOP Study, is to take full description of the expected
construction activities by a summary table (as shown in Table 9.1) and an extension layout
plan (as shown in Figure 9.1), then to question every construction activity and its
corresponding plants/equipment to discover what deviation
1
from the intention
2
of the
activities can occur and what their causes
3
and consequences
4
would be. This is executed
systematically by applying suitable guidewords, which can assist prompt thinking about what
might go wrong.
9.6.3 In the Study Meeting, all construction activities (and corresponding plants/equipment) were
discussed in turn with the procedures listed as follows:
1. Explain the intention of the construction activity (and corresponding plants/equipment)
to be discussed
2. Identify possible deviations of the construction activity (and corresponding
plants/equipment) being discussed. The possible deviations were detected by
systematic application of guidewords
3. Spot possible causes of the identified deviations
4. Evaluate the possible consequences due to the deviation identified
5. Recommend possible mitigation measures to avoid the occurrence of the deviations
6. Identify the responsible parties to implement the recommended mitigation measures
7. Record the findings and recommendation during the discussion
HAZOP Study Execution
9.6.4 One session of the Study Meeting was conducted. The Study Meeting was conducted in the
following sequence:
1. Clarified the scope and objectives of this HAZOP Study, which were stated in the EIA
Study Brief to the Study Team
2. Explained the definition of hazard to be identified, methodology and procedure of
the HAZOP Study to the Study Team
9.1.1
1
The departures from the intention of construction activity
2
How the particular activity is intended to execute
3
The reasons why, and how, the deviations could occur
4
The results that follow from the occurrence of a deviation
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-12 October 2004
3. Presented each process of the proposed extension works to the Study Team
4. Finalized the possible construction activities (and corresponding plants/equipment) to
be discussed in the Study
5. Discussed each possible construction activity in turn with procedure listed in Section
9.4.3
6. The Study Meeting ended after all possible construction activity were discussed
9.7 Findings and Recommendations
9.7.1 As mentioned in Section 9.4.4, the followings were identified or recommended during the
HAZOP Study:
Causes of possible deviations
Hazardous scenarios which could lead to chlorine leakage/release (i.e. consequence)
Mitigation measures to avoid occurrence of deviations and corresponding responsible
parties
9.7.2 The aim of the HAZOP Study is to identify additional chlorine hazards during construction
and mitigate them as far as possible. It is considered that each of the identified hazardous
scenarios could cause personnel injury or fatality including WSD staff and construction
workers on site. In order to mitigate the possible hazards identified, all the mitigation
measures identified by the HAZOP team and suggested by FSD are to be incorporated in the
construction contract to ensure their implementation.
9.7.3 As suggested by EPD, a summary description of interface between construction activity and
the Chlorine Building is given in Table 9.2. It should be noted that most of the activities
presented in the Table below could cause hazard to the Chlorine Building if they are operated
at an inappropriate location (i.e. too close to the Chlorine Building). Ensuring the activities to
be implemented at appropriate location would be an effective mitigation measure.
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-13 October 2004
Table 9.2 Interface between Construction Activities and the Chlorine Building
Construction Activity/ Plant Interface
Excavation near Chlorine Building Too much excavation may lead to structural damage of
Chlorine Building
Piling Works Too much vibration may lead to structural damage of Chlorine
Building
Demolition of concrete slab of
existing facilities by pneumatic
breaker
Inappropriate method of demolition may cause damage to
chlorine dosing pipework, which causes chlorine leakage.
Backhoe
Bulldozer
Dump truck
Site Vehicle
Crane lorry
Mobile crane
Roller
Tower Crane
Construction plant/equipment crashes into Chlorine Building/
overturn; may cause structural damage
Preparing electricity supply
facilities and connecting electricity
transmission wire in Chlorine
Building
Accidents initiated by electricity supply facilities installed
inside/adjacent to Chlorine Building could cause damage to
the chlorine-related installation
Generator, air compressor Fire/explosion of generator may cause structural damage to
the Chlorine Building
Mobilizing personnel Construction workers enter Chlorine Building without
supervision; may cause damage to chlorine-related facilities
Mobilizing construction equipment/
plant
Construction equipment/ plant being mobilized causes impact
on Chlorine Building; may cause structural damage to
Chlorine Building
Storing/stockpiling of
material/waste near Chlorine
Building
Fire accidents involving stored flammable waste near
Chlorine Building impose fire hazard to Chlorine Building
Cooking by on-site personnel near
Chlorine Building
Accidents involving fuels used in cooking causes fire hazard
to Chlorine Building
Welding near Chlorine Building Accidents involving fuels used in welding and sparks
produced during the operation cause fire hazard to Chlorine
Building
Chemicals/fuel storage near
Chlorine Building
Fire of chemicals/fuel stored may impose fire hazard to the
Chlorine Building
Transferring pile of steel/ large
objects and equipment
Inappropriate transferring operation could cause impact on
Chlorine Building; may cause structural damage
Tree plantation for soft landscape
works
Roots of planted trees (with unknown extent of roots) near
Chlorine Building may cause structural damage
9.7.4 The above items identified during the HAZOP Study were summarized in Tables 9.3 9.5 as
shown below. Appendix 9.1 summarized the mitigation measures to be incorporated in the
construction contract.
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-14 October 2004
Table 9.3 Summary of Identified Possible Deviation Causes
Category Identified Possible Deviation Causes
Lack of monitoring and
investigation
Lack of monitoring of the construction activities
Lack of investigation on the consequence of construction
activities to chlorine-related facilities
Poor chemicals/waste/material
management and storage
Accumulation of stacked debris
Too much material stockpiled
Too much chemicals/fuel stored
Chemicals/waste/material stored at inappropriate locations
Fire accidents involving flammable waste/fuels/chemicals
Poor maintenance or installation
of plant/equipment
Poor maintenance of equipment
Damage of equipment undetected
Malfunction of brake of vehicles
Insecure plant/equipment installation (e.g. counter weight
of tower crane)
Inappropriate location of
construction activity
Construction activity on travelling route of Chlorine
Delivery Truck
Construction activity too close to Chlorine Building
Construction activity too close to chlorine-related facilities
Excavation takes place at locations which underground
chlorine pipeworks are installed
Inappropriate equipment
operation
Operator unable to properly manipulate the equipment
Equipment overloaded
Speed of vehicle is too high
Conflict to chlorine delivery
operation
Equipment/vehicle is idle or working near/along the
Chlorine Delivery Truck traveling route
The chlorine delivery operation and chemicals/fuel
delivery operation are conducted on site simultaneously
Miscellaneous Too high vibration intensity caused by piling works
Construction workers are not aware about the locations
accommodating chlorine-related facilities
Plantation of trees with unknown extent of roots
Extended chlorine pipework connection work commences
before chlorine is isolated in existing facilities
Table 9.4 Summary of Hazardous Scenarios leading to Chlorine Leakage/release
Identified Hazardous Scenarios
Structural damage to Chlorine Building
Damage to chlorine dosing facilities
Damage to Chlorine pipeworks
Obstruct Chlorine Delivery Truck access
route; could cause accident of the vehicle
Cause Chlorine Delivery Truck unsuitable for
driving; could cause accident of the vehicle
Vehicle/equipment crashes to Chlorine
Delivery Truck, or vice versa
Fire hazard to chlorine related-facilities
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-15 October 2004
Table 9.5 Summary of Mitigation Measures to Avoid Occurrence of Deviations and
Corresponding Responsible Parties
Category Mitigation Measures Identified Parties Responsible
Monitoring
and Inspection
Monitor the excavation activity to avoid excavation to the
wrong depth (too much excavation)
Conduct monitoring to ensure the stability of building during
construction phase
Inspection and supervision to ensure operation of equipment
properly
Inspection of excavation progress near Chlorine Building and
Chemical Storage Building
Contractor
Contractor
Safety Officer
(Contractor)/ Contractor
Safety Officer
(Contractor)/ Contractor
Management Waste Management
Ensure good C&D waste management
Provide on-site sorting of debris to avoid excessive debris
accumulation
Provide temporary storage for debris at appropriate location
Ensure flammable waste is stored at appropriate/designated
location
Traffic Management
Maintain access roads as a freeway
Provide sufficient maintenance of the
vehicle/generator/equipment
Set a speed limit for site vehicle
Propose a designated route for site vehicles, avoid site vehicle
using travelling route of the Chlorine Delivery Truck
Provide adequate fire fighting equipment at the storage area
Provide clear road signs for site vehicles
Install hump on the access roads to reduce the speed of site
vehicles
Provide crash barrier to protect the Chlorine Building and the
Chemical Storage Building
No parking on access road, or proper parking area designated
for dump trucks
Chemicals/material Management
Ensure good management of material delivery to avoid
excessive material stock on site
Avoid incompatible chemicals storing together; provide
separate storage locations for different chemicals which are
incompatible to each other
Provide appropriate labels according to Dangerous Goods
Ordinance
Follow Fire Services Departments requirement for
flammable waste storage
Keep the amount of flammable waste stored in a minimum
level
Ensure adequate separation distance between each flammable
material storage area
No stockpile of material near the Chlorine Building and the
access road is allowed
Construction Activity/personnel Management
Personnel
Ensure sufficient guarding at Siu Ho Wan WTW to provide
sufficient access control
Provide clear indication of rooms accommodating
chlorine-related facilities and their hazards
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
WSD/ Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
WSD/ Contractor
WSD/ Contractor
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-16 October 2004
Category Mitigation Measures Identified Parties Responsible
Activity
Propose a communication system between operator of Siu Ho
Wan WTW and the Contractor on the date of chlorine delivery
to the WTW
Prepare a safety plan to avoid any electricity supply facilities
located inside/adjacent to the Chlorine Building
Propose a Permit -to-move system for large equipment/plant
movement:
Contractor provides WSD a list indicating the number
and type of equipment/plant to be mobilized,
equipment/plant movement route and mobilization
methodology
A risk assessment is conducted by Safety Officer
(Contractor)
No equipment/plant movement should be allowed before
approval from WSD/Safety Officer is obtained
The Permit shall rest rict the time period that
equipment/plant can be mobilized
Supervision of permitted work by Safety Representatives
from Contractor
Follow WSDs Permit -to-work System for extended
chlorine pipework connection
No connection work can commence before approval from
WSD is obtained
Supervision of permitted works by the Contractors Safety
Representative
No blasting operation on site is allowed
Define restricted zone for the equipment (i.e. keep the
equipment from the Chlorine Building at a safe distance). The
extent of the restricted zone would be determined by the size
of the equipment
Restrict excavation along travelling route of the Chlorine
Delivery Truck
Limit the reach of the tower crane used
Ensure generators are placed at a safe distance from Chlorine
Building
Provide indication/sign for chlorine pipeworks
Provide method statement with protective measures for the
chlorine dosing pipeworks (and other facilities)
Avoid welding operation inside buildings installed with
chlorine pipeworks
If welding is unavoidable, Hot -work permit system should
be applied for welding operation inside buildings installed
with chlorine pipeworks:
No welding work is allowed before approval from WSD is
obtained
Provide supervision to the operations inside buildings
installed with chlorine pipeworks by the Safety
Representative from Contractor
Landscaping Work Management
Avoid plantation of deep root trees near buildings, especially
Chlorine Building
WSD/ Contractor
Contractor
WSD/ Safety Officer
(Contractor)/ Contractor
WSD/ Safety
Representative
(Contractor)/ Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
WSD/ Safety
Representative
(Contractor)/ Contractor
Contractor
Investigation Investigate the lateral support of buildings/excavation to
ensure proposed extent of excavation would not affect
building stability
Locate chlorine pipeworks before execute excavation
Engineer/ Contractor
Contractor
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-17 October 2004
Category Mitigation Measures Identified Parties Responsible
Training
Provide adequate training to equipment operator; implement a
license system that only competent persons could operate the
equipment
Provide adequate training to construction workers on the
rooms accommodating chlorine-related facilities and their
associated hazards
Provide adequate training to construction workers on the
nature and hazards of chlorine, safety precautions and
emergency measures for leakage of chlorine from drums,
piping or installations.
Contractor
Contractor
Contractor
Other Recommendations
9.7.5 The Study Team identified a number of measures during the meeting, which are not directly
associated with additional chlorine hazard discussed above. However, they are considered as
appropriate measures to be implemented during the construction stage. These measures are
presented as follows:
i) To maintain all access roads of fire engine/FSD vehicles/ambulance as a freeway because
Fire Services/Rescue personnel may approach the location of chlorine leakage from different
directions, which depends on the wind direction. No equipment/plants and site vehicle is
allowed to park on the access roads. The Contractor should take the responsibility to
implement this mitigation measure.
ii) Some emissions could initiate chlorine leak/smoke detector alarm (i.e. cause false alarm),
which severely affects the operation of the Water Treatment Works, those emissions are listed
as follows:
Dust from site clearance and excavation work
Smoke from welding work
Fuel vapour from electricity generation
Exhaust gas from construction equipment and vehicles
Chemicals such as bitumen, paints, organic solvent etc.
Contractor should implement mitigation measures to avoid occurrence of false alarm by
the following mitigation measures:
Provide dust suppression measures such as covering the dusty material
Implement Hot -work Permit system and provide sufficient ventilation during
welding operation to avoid accumulation of smoke
Place the generators away from the chlorine leak/smoke detector alarms
Park the construction equipment and vehicles away from the Chlorine Building
Notify WSD prior to the use of chemical compounds and provide sufficient ventilation
during operation involving chemicals
iii) An emergency plan should be proposed to ensure appropriate and quick response of site
staff to evacuate safely in case of chlorine leakage events, the emergency plan should include
the following items/objectives:
Provide a system for logging in-out record of all site staff, which could assist
immediate investigation and rescue in a chlorine leak incident when required
Ensure construction workers be familiar with chlorine alarm system (e.g. proper
training)
Propose construction workers to participate regular joint chlorine leak drill arranged
by WSD, and inform local fire stations in advance.
Agreement No. CE 75/2002 (WS)
EIA Report Report Extension of Siu Ho Wan Water Treatment Works - Investigation
Metcalf & Eddy Ltd. 9-18 October 2004
Propose alternative assembly point(s) for construction workers in case of chlorine
leakage event
The measures above should be included in the Safety Plan and emergency plan for the
extension of Siu Ho Wan WTW. It would be the responsibility of the Contractor for the safety
plan and emergency plan preparation. Copies of the safety and emergency plans shall be
provided to local fire stations for information. During the construction stage, the Contractor
and staff of SHW WTW shall brief local fire stations for the implementation of safety and
emergency plans.
9.7.6 A number of recommendations were suggested by FSD, which are also considered
appropriate to be implemented during the construction stage. These measures are presented as
follows:
i) For the storage, conveyance and use of potassium permanganate, nitrogen and other
substances giving inflammable vapour during the construction stage, the Contractor
should follow the requirements stipulated in Dangerous Goods Ordinance and its
subsidiary regulations
ii) For the storage and conveyance of chemical waste, the Contractor should follow
EPDs requirement
iii) Any vegetation near the Chlorine Building or work site should be trimmed to prevent
the spread of fire
iv) Sufficient number of fire extinguishers should be provided
You might also like
- IB Buisness Management Study GuideDocument127 pagesIB Buisness Management Study GuideJohnathan ChargaffNo ratings yet
- HAZOP HAZID Haliburton PDFDocument2 pagesHAZOP HAZID Haliburton PDFamirNo ratings yet
- HAZOPDocument34 pagesHAZOPMohammed100% (1)
- HAZOP ON Sulfuric Acid Transfer To Storage TankDocument6 pagesHAZOP ON Sulfuric Acid Transfer To Storage Tankram0% (1)
- Humber RefineryDocument2 pagesHumber RefineryRatna Paramitha SariNo ratings yet
- KAHLIDr Yehia45 PDFDocument36 pagesKAHLIDr Yehia45 PDFLuiz Rubens Souza CantelliNo ratings yet
- Produced Water Characteristics, Treatment and ReuseDocument18 pagesProduced Water Characteristics, Treatment and ReuseVIVIANA ANDREA GARCIA ROCHA100% (1)
- 0 0 25 Feb 2016 1108554031AnnexureManufacturing&EffluentTreatmentProcessDocument28 pages0 0 25 Feb 2016 1108554031AnnexureManufacturing&EffluentTreatmentProcessNeerav Indrajit GadhviNo ratings yet
- Urea Stripper ProcedureDocument6 pagesUrea Stripper ProcedureSoumitra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Hazard and Operability StudiesDocument8 pagesHazard and Operability Studiesangry_granNo ratings yet
- Method Statement - BenchmarkDocument15 pagesMethod Statement - BenchmarkStansilous Tatenda NyagomoNo ratings yet
- Qhse-Sop-054 Oil Spill PreventionDocument14 pagesQhse-Sop-054 Oil Spill PreventionJust AabNo ratings yet
- Molten Sulphur Rail Tank Car Loading and Unloading Operations Final With AppendicesDocument68 pagesMolten Sulphur Rail Tank Car Loading and Unloading Operations Final With AppendicesvlabdulazeemNo ratings yet
- Lifting & Rigging ProceduresDocument27 pagesLifting & Rigging ProceduresBrunoro DantasNo ratings yet
- Work Method Statement For Structure ErectionDocument12 pagesWork Method Statement For Structure ErectionMuhammad TeguhNo ratings yet
- IHC Beaver 600 C Cutter Suction DredgerDocument2 pagesIHC Beaver 600 C Cutter Suction DredgerHamada GadNo ratings yet
- ESIA WaadDocument463 pagesESIA WaadRRHH100% (3)
- Offshore Support Vessel & Marine Support Craft VettingDocument19 pagesOffshore Support Vessel & Marine Support Craft Vettingjk.jackycheokNo ratings yet
- Report On Student Iw Experience SchemeDocument9 pagesReport On Student Iw Experience SchemeifiokNo ratings yet
- 2013aicheammoniasafetysymposiumquestions AnswersDocument27 pages2013aicheammoniasafetysymposiumquestions AnswersRindeshNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure For HSDDocument3 pagesStandard Operating Procedure For HSDisjglfdskNo ratings yet
- Basic Introduction of Coal Handling SystemDocument7 pagesBasic Introduction of Coal Handling SystemHerman AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Lifting Plan of SpoolDocument1 pageLifting Plan of SpoolhazopengineerNo ratings yet
- Annex 17 - Induction Nawara ProjDocument18 pagesAnnex 17 - Induction Nawara ProjMajdiSahnounNo ratings yet
- 6.1.2 Gasification ReactorDocument2 pages6.1.2 Gasification ReactorShemzinhoNo ratings yet
- Mineralsfocus Issue 2015 SiemensDocument52 pagesMineralsfocus Issue 2015 SiemensmirkomakNo ratings yet
- HAZID HAZOP Project Brief PDFDocument15 pagesHAZID HAZOP Project Brief PDFAndi Ade Putra SiregarNo ratings yet
- Process Industry HAZOP Techniques & Applications and HAZOP Leader Training, Indonesia, JohnnyDocument9 pagesProcess Industry HAZOP Techniques & Applications and HAZOP Leader Training, Indonesia, JohnnyEko PoerwantoNo ratings yet
- Hazop ExampleDocument4 pagesHazop Exampledroffilcz27No ratings yet
- Useful Tips For A Successful HAZOP Study: Process Hazard Analysis TechniquesDocument10 pagesUseful Tips For A Successful HAZOP Study: Process Hazard Analysis TechniquesDesiree MolinaNo ratings yet
- IMCA-Event-2018-09-27 - Presentation 7 - Understanding Your Limits (Subsea7) PDFDocument21 pagesIMCA-Event-2018-09-27 - Presentation 7 - Understanding Your Limits (Subsea7) PDFsatrio aryoNo ratings yet
- Dibia Ifeanyichukwu Peter Updated CV (Resume)Document7 pagesDibia Ifeanyichukwu Peter Updated CV (Resume)wizzy basseyNo ratings yet
- Strategy For Extending The Useful Lifetime of A Wind TurbineDocument41 pagesStrategy For Extending The Useful Lifetime of A Wind TurbineRkantvyasNo ratings yet
- APPENDIX 4 Statement On Telescopic Spout Operation Fraser Surrey Docks DTCF AmendmentDocument8 pagesAPPENDIX 4 Statement On Telescopic Spout Operation Fraser Surrey Docks DTCF AmendmentRestuNo ratings yet
- Method Statement LuderitzDocument11 pagesMethod Statement LuderitzYoung R-j MafaraNo ratings yet
- NAWPPL-BIMS-NPPL-000-HS-PRO-00009 - C01 - Tagging & Isolation ProcedureDocument8 pagesNAWPPL-BIMS-NPPL-000-HS-PRO-00009 - C01 - Tagging & Isolation ProcedureMoaatazz NouisriNo ratings yet
- Plf-jms-031 - r0 - Jms of Lifting, Shifting, Stringing, Lowering-In and Transportation Using Excavator - SignedDocument85 pagesPlf-jms-031 - r0 - Jms of Lifting, Shifting, Stringing, Lowering-In and Transportation Using Excavator - SignedHafiz YunusNo ratings yet
- Safety Shower PDFDocument7 pagesSafety Shower PDFnaveen142No ratings yet
- Pipeline Risk Assessment and Environmental Consequence AnalysisDocument82 pagesPipeline Risk Assessment and Environmental Consequence Analysisnanking100% (1)
- Piper AlphaDocument6 pagesPiper AlphaAhmed Eldeeb100% (1)
- Common Hazards DescriptionsDocument2 pagesCommon Hazards Descriptionsasifniazi4No ratings yet
- Catastrophic Fire in Ammonia Plant Compressor RoomDocument10 pagesCatastrophic Fire in Ammonia Plant Compressor RoomRavi KasaudhanNo ratings yet
- A ESIA Yemen Section 3 Revision 1Document42 pagesA ESIA Yemen Section 3 Revision 1Denstar Ricardo SilalahiNo ratings yet
- NH3 RiskDocument59 pagesNH3 RiskDave CNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument19 pagesFinal ReportAbdul Azeez100% (1)
- G.I. 150.007 Radiation Radioactive ControlDocument8 pagesG.I. 150.007 Radiation Radioactive ControlbryanNo ratings yet
- Safe Practice For Vessel Positioning With Mooring Analysis (Orcaflex)Document19 pagesSafe Practice For Vessel Positioning With Mooring Analysis (Orcaflex)KhoironSyamdatuNo ratings yet
- Hazop Record Form: Condensate Lines From The Condensers To The Holding TankDocument3 pagesHazop Record Form: Condensate Lines From The Condensers To The Holding Tanksajni123No ratings yet
- HAZOP Studies GuideDocument4 pagesHAZOP Studies GuideMRITYUNJOY GUPTANo ratings yet
- Method Statement - Tower ErectionDocument2 pagesMethod Statement - Tower ErectionsoubhagyaNo ratings yet
- Manual: Procedure Titel: HSE-ManualDocument11 pagesManual: Procedure Titel: HSE-ManualGeetha_jagadish30No ratings yet
- Project Risk Analysis and Management: Mini GuideDocument20 pagesProject Risk Analysis and Management: Mini GuideIuliana AronNo ratings yet
- Merrill CroweDocument7 pagesMerrill CroweAlejandro ClavijoNo ratings yet
- Spec of Bitumen TankDocument9 pagesSpec of Bitumen Tanknswain76No ratings yet
- Bulk Material HandlingDocument5 pagesBulk Material HandlingPrasenjit BhuiyaNo ratings yet
- Workpack TEMANA ShutdownDocument23 pagesWorkpack TEMANA Shutdownhitm357No ratings yet
- HazCom With GhsDocument33 pagesHazCom With GhsAnonymous iI88LtNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid Manufacturing ProcessDocument7 pagesNitric Acid Manufacturing ProcessLenin PrabhuNo ratings yet
- TOS HA LONG PIPE LAY Spec (Updated 30 12 19)Document3 pagesTOS HA LONG PIPE LAY Spec (Updated 30 12 19)Mr. DNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Horizontal Tray Erection.Document5 pagesMethod Statement For Horizontal Tray Erection.soubhagyaNo ratings yet
- Apron Feeder Data SheetDocument1 pageApron Feeder Data SheetPat AuffretNo ratings yet
- Hazop LEADER TrainingDocument2 pagesHazop LEADER Trainingbaaziz2015No ratings yet
- ANCOLD Response Combined MinDocument33 pagesANCOLD Response Combined MinPCYM GEOTECNIANo ratings yet
- Management of DredgedExcavated SedimentDocument17 pagesManagement of DredgedExcavated SedimentMan Ho LamNo ratings yet
- 062-063 Passive Samplers - ULTRA Passive SamplersDocument2 pages062-063 Passive Samplers - ULTRA Passive SamplersLuiz Rubens Souza CantelliNo ratings yet
- MSD Prevention Toolbox PartC English in Depth Risk Assessment FinalDocument49 pagesMSD Prevention Toolbox PartC English in Depth Risk Assessment FinalLuiz Rubens Souza CantelliNo ratings yet
- Fact Shett - OSHADocument2 pagesFact Shett - OSHALuiz Rubens Souza CantelliNo ratings yet
- HEM Silver Ion Steriliser SIS B40-R1Document1 pageHEM Silver Ion Steriliser SIS B40-R1kyle wetherillNo ratings yet
- DM PlantDocument8 pagesDM PlantSandeep TanwarNo ratings yet
- Bhopal WTP PDFDocument75 pagesBhopal WTP PDFAnonymous hMech04fiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Water Treatment Questions of The Day 1-2-20Document19 pagesIndustrial Water Treatment Questions of The Day 1-2-20AkashTripathiNo ratings yet
- The Study of The Design of Production Systems of Purified Water For The Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument19 pagesThe Study of The Design of Production Systems of Purified Water For The Pharmaceutical IndustryAndreaVargasNo ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument34 pagesWater TreatmentJessa Dynn Agraviador Velarde100% (1)
- Water SupplyDocument67 pagesWater SupplyHusnina FakhiraNo ratings yet
- HCL Corrosion Under ControlDocument4 pagesHCL Corrosion Under ControlNXVNNo ratings yet
- Swimming Pool Risk Management Plan GuideDocument24 pagesSwimming Pool Risk Management Plan GuideAbdulmalekNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument7 pagesWaste Water TreatmentBusi_SeleshoNo ratings yet
- Intership Report 2023 1Document51 pagesIntership Report 2023 1Jyotirmoy MahataNo ratings yet
- 1Document15 pages1dalton2004No ratings yet
- Portable Water PurificationDocument9 pagesPortable Water PurificationAnonymous V5UYBUMaNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in Waste Water TreatmentDocument12 pagesNanotechnology in Waste Water TreatmentLubna Amreen100% (1)
- OCY751-Waste Water TreatmentDocument13 pagesOCY751-Waste Water Treatmentsureshvkumar80% (5)
- InfoCell Water Purifier v2207 FADocument22 pagesInfoCell Water Purifier v2207 FAIbnu TalibNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Control of Biofouling in Industrial Water Systems PDFDocument14 pagesThe Chemical Control of Biofouling in Industrial Water Systems PDFsyarifuddinNo ratings yet
- Laporan PKLDocument42 pagesLaporan PKLRaya Fernanda AriantoNo ratings yet
- 649108.dekanic WASTEWATERDocument60 pages649108.dekanic WASTEWATERharshadNo ratings yet
- Physical, Chemical and Biological Characteristics of WastewaterDocument27 pagesPhysical, Chemical and Biological Characteristics of WastewaterRushed AlamaNo ratings yet
- Training Need Assesment SurveyDocument178 pagesTraining Need Assesment SurveyquebellaNo ratings yet
- Reporting ME 01Document84 pagesReporting ME 01Diane Fe CajaroNo ratings yet
- Thermax WWS BrochureDocument6 pagesThermax WWS BrochureAquasoul CoNo ratings yet
- Assg Ecw 567 Mac Jul 22 PDFDocument2 pagesAssg Ecw 567 Mac Jul 22 PDFNUR NABIHAH AZMI AZRINNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Desal 2006 09 007 PDFDocument6 pages10 1016@j Desal 2006 09 007 PDFMimi TanNo ratings yet
- Vws Oil GasDocument8 pagesVws Oil GasFabricio TrosarelloNo ratings yet
- Water and Waste Water EngineeringDocument8 pagesWater and Waste Water EngineeringOlateju AgboolaNo ratings yet