Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Automatic Gain Control Spatial Aliasing: Gscas 1 Gscas 2
Automatic Gain Control Spatial Aliasing: Gscas 1 Gscas 2
Uploaded by
somplatOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Automatic Gain Control Spatial Aliasing: Gscas 1 Gscas 2
Automatic Gain Control Spatial Aliasing: Gscas 1 Gscas 2
Uploaded by
somplatCopyright:
Available Formats
1
GSCAS 1
Automatic Gain Control
GSCAS 2
Spatial Aliasing
GSCAS 3 GSCAS 4
Reflection Data
GSCAS 5
Seismic Section
Seismic reflection data
Offset sources
Recorded by several receivers offset from each source
Seismic section (unmigrated time section)
Combined data of many shots
Presented as if a source and a receiver in the same position GSCAS 6
Acquisition (1): Geophones
2
GSCAS 7
Basics of Reflection Time
receiver to source the from
distance horizontal X
2
intercept axis - T t
receiver to interface, to
source, the from time travel T
1
0
0
f
2
1
2
2
0
=
=
=
=
+ =
V
h
t
V
X
t T
f
GSCAS 8
Source-Receiver Design: Common Midpoint Method
GSCAS 9
Reflection Data Processing (1): Shot
Gather
GSCAS 10
Reflection Data Processing (2):
CMP Gather
GSCAS 11
Reflection Data Processing (3):
Normal Moveout Correction and Stack
GSCAS 12
Processing Details (5) Statics Corrections
3
GSCAS 13
Basics of Reflection Time
receiver to source the from
distance horizontal X
2
intercept axis - T t
receiver to interface, to
source, the from time travel T
1
0
0
f
2
1
2
2
0
=
=
=
=
+ =
V
h
t
V
X
t T
f
GSCAS 14
Normal Moveout Correction
0 2
1
2
2
0 0
t
V
X
t t T T
x x
+ = =
GSCAS 15
Velocity Spectrum
A velocity spectrum is a graph showing the power of
signals arriving at different two way vertical travel
time over a spectrum of velocities.
GSCAS 16
GSCAS 17
Processing Details (1) Gather
GSCAS 18
Processing Details (2) Velocity Analysis
4
GSCAS 19
Processing Details (3) NMO Correction
GSCAS 20
Processing Details (4) Mute
GSCAS 21
Migration
GSCAS 22
Anticline
GSCAS 23
An Example of Anticline
GSCAS 24
Syncline
5
GSCAS 25
Finite - Difference method of wave- equation migration
GSCAS 26
GSCAS 27
Migration Algorithms
Finite-difference solutions methods
Exploding Reflectors/Huygens secondary source
principle
Downward continuation/wavefield extrapolation
Frequency-wavenumber implementation
Stolt mapping
Integral solution of to the scalar wave equation
Diffraction summation
Kirchhoff migration
GSCAS 28
Exploding Reflector Model
GSCAS 29 GSCAS 30
Huygens Principle
Beach Barrier Example
6
GSCAS 31 GSCAS 32
GSCAS 33
Horizontal Resolution
GSCAS 34
Scalar wave equation
2
2
2
2 2
2 2 2
2 2
2
2 2
2 2 2 2 2
2
2 2 2
2 2
1
( , , ) 0
( , , ) ( , , )
( , , ) ( , , ) 0
( , , ) ( , 0, )
2
1 1
4
( , , ) 2
1
4
x
x
i t ik x
x x
x x x
i k z
c
x x
x x
z x
x x
P x z t
x z c
P x z t P k z e d dk
P k z k P k z
z c
P k z P k e
c k v k
k k
c c v
P k z v k
i
z v
| |
+ =
|
\ .
=
| |
+ =
|
\ .
=
= = =
2
( , , )
x
P k z
GSCAS 35 GSCAS 36
0 ) , (
1
) , (
2
2
2
2
= t r U
t c
t r U
) ( ) ( ) , , (
1
) , , (
2
2
2
2
r r t t r r G
t c
t r r G =
Kirchhoff integral
0 ) , ( ) , (
2 2
= + r U k r U
) ( ) , , ( ) , , (
2 2
r r r r G k r r G = +
7
GSCAS 37 GSCAS 38
Kirchhoff integral
R
c R i
z y x G
FS
4
) / exp(
) , , , ( =
2
2
1
1
4
) / exp(
4
) / exp(
) , , , (
R
c R i
R
c R i
z y x G
=
| |
(
=
n
U
G
n
G
U dS U G G U r dV
0
2 2
) (
(
=
n
U
G
n
G
U dS r r r U r dV
0
) ( ) , ( ) (
GSCAS 39
Kirchhoff integral
U(r,) =
1
4
dS
0
[G(r
0
, r,)
U(r
0
,)
n
U(r
0
,)
G(r
0
, r,)
n
]
U(r, ) is a scalar field recorded along a surface S
o
,
S
0
encompasses the volume of interest,
G(r
0
,r, ) is the Greens function for a medium with equivalent velocity
structure,
r
0
is location along the surface,
r is location anywhere in the propagation space,
n is the normal direction to the surface, positive outward, and is angular
frequency.
G(r
0
, r,) = A(r
0
, r)exp(i(r
0
, r))
U(r,) =
1
2
dS
0
U(r
0
,)[
A
n
e
i
+ iA
n
]
You might also like
- Control Systems Formula SheetDocument12 pagesControl Systems Formula SheetliamhrNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Tutorial 28 Disk Brake Friction SimuleonDocument10 pagesAbaqus Tutorial 28 Disk Brake Friction Simuleongurpinder Singh DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Rock Physics: Jack P. DvorkinDocument15 pagesRock Physics: Jack P. DvorkinZULFAKHRIBINZAKARIANo ratings yet
- Solution Manual - Control Systems by GopalDocument0 pagesSolution Manual - Control Systems by Gopalsaggu199185% (27)
- Solution Stabilization: For FSI and 6DOF With FluentDocument34 pagesSolution Stabilization: For FSI and 6DOF With FluentMasterAlbus3dNo ratings yet
- Solutions For Problem Set For Ch. 23Document12 pagesSolutions For Problem Set For Ch. 23ZbiggNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument21 pagesCircular MotionManthan Sharma100% (4)
- M2V104 FS 01eDocument23 pagesM2V104 FS 01eLewis BryanNo ratings yet
- Solutions Chap 6Document16 pagesSolutions Chap 6john_playdaNo ratings yet
- Vector Analysis Formulas (Electromagnetic Fields)Document2 pagesVector Analysis Formulas (Electromagnetic Fields)Quý HoàngNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Equation Sheet: Last NameDocument1 pageAnalog Electronics Equation Sheet: Last NameRadoslawNo ratings yet
- Vector Operator Identities: D DF F D DP PDocument8 pagesVector Operator Identities: D DF F D DP PAshvin GraceNo ratings yet
- Fre Sers Sws Moving SensorsDocument24 pagesFre Sers Sws Moving SensorshenrydclNo ratings yet
- Nyquist I Bode ZadaciDocument29 pagesNyquist I Bode ZadaciNikola HardiNo ratings yet
- VectoresDocument6 pagesVectoresSantiago KarabasogluNo ratings yet
- Metode RombergDocument37 pagesMetode RombergBhidaraNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios DinamicaDocument11 pagesEjercicios DinamicaNicolas Alejandro Herrera RomeroNo ratings yet
- Black Hole Lecture NotesDocument28 pagesBlack Hole Lecture NotesMaitraya BatmancharyyaNo ratings yet
- Gauss-Bonnet Gravity With Scalar Field in Four DimensionsDocument10 pagesGauss-Bonnet Gravity With Scalar Field in Four DimensionsRuriNo ratings yet
- Intro To GPSDocument62 pagesIntro To GPSlimpkid666No ratings yet
- IIT JEE - Mains Model Test Paper - 1 (Physics, Chemistry, Maths) - SolutionsDocument10 pagesIIT JEE - Mains Model Test Paper - 1 (Physics, Chemistry, Maths) - Solutionsstudysteps.inNo ratings yet
- Solution For Chapter 24Document8 pagesSolution For Chapter 24Sveti JeronimNo ratings yet
- The Frecuency-Response Design Method: Universidad Politecnica SalesianaDocument28 pagesThe Frecuency-Response Design Method: Universidad Politecnica SalesianaFabiola ChachaNo ratings yet
- Anon - Naval Research Laboratory Plasma Formulary - NRL - 2009Document73 pagesAnon - Naval Research Laboratory Plasma Formulary - NRL - 2009Aditya ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- SM ch11Document45 pagesSM ch11charlesbrachNo ratings yet
- 4 More About Trigonometric Functions (I) : OAD, We HaveDocument21 pages4 More About Trigonometric Functions (I) : OAD, We HaveVincent LauNo ratings yet
- Calculate Distance and Bearing Between Latitude Longitude PointsDocument31 pagesCalculate Distance and Bearing Between Latitude Longitude PointsyuritabascoNo ratings yet
- Techniques - ESPDocument116 pagesTechniques - ESPjayapandis83No ratings yet
- Formulario: L Ogica Matem AticaDocument8 pagesFormulario: L Ogica Matem AticaDiana Carolina DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Asymptotic Limits and Sum Rules For Gauge Field PropagatorsDocument11 pagesAsymptotic Limits and Sum Rules For Gauge Field PropagatorsYeimy Vivar LobosNo ratings yet
- Sphere Tor UsDocument1 pageSphere Tor UsaamnaahNo ratings yet
- May 2002 Solution (Mathematics, Surveying, and Transportation Engineering)Document30 pagesMay 2002 Solution (Mathematics, Surveying, and Transportation Engineering)CinderellatheartNo ratings yet
- Moran 7ed Therm Eq SP11 - RMDocument6 pagesMoran 7ed Therm Eq SP11 - RMNathan AndersenNo ratings yet
- Filtering: 7.1 (A) The Error Is Orthogonal To The DataDocument7 pagesFiltering: 7.1 (A) The Error Is Orthogonal To The DataSudipta GhoshNo ratings yet
- R/ CosaDocument11 pagesR/ CosaSantiago dewitNo ratings yet
- 2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - NJC P1 SolutionDocument13 pages2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - NJC P1 Solutioncherylhzy0% (4)
- Notes Design Process PDFDocument11 pagesNotes Design Process PDFanhNo ratings yet
- 3AE Exercises Chap 1 Freq Resp Solutions Aug10Document3 pages3AE Exercises Chap 1 Freq Resp Solutions Aug10Aluwani KhomolaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2019 Physics January Attempt Shift - 1 (10th January, 2019) PDFDocument19 pagesJEE Main 2019 Physics January Attempt Shift - 1 (10th January, 2019) PDFResonance Eduventures92% (37)
- Chapter 4XDocument96 pagesChapter 4XAndrei FirteNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Their GraphsDocument5 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions and Their Graphssanjeev100% (1)
- TalkDocument74 pagesTalkapi-238805532No ratings yet
- DESIGN OF MACHINERY - Problem 4-18gDocument2 pagesDESIGN OF MACHINERY - Problem 4-18gGiordano VieiraNo ratings yet
- Formula ListDocument5 pagesFormula ListAritra MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Lagrangian FormulationDocument7 pagesLagrangian FormulationFer Moncada100% (1)
- AP SolnDocument4 pagesAP SolnSajad VmNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry - NCERT Solutions For Class 10 MathematicsDocument18 pagesTrigonometry - NCERT Solutions For Class 10 MathematicsAayat QureshiNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Jee Main 2016 (Code H) : PhysicsDocument11 pagesSolutions of Jee Main 2016 (Code H) : PhysicsTobiramaNo ratings yet
- Calculate Distance, Bearing and More Between Latitude-Longitude PointsDocument24 pagesCalculate Distance, Bearing and More Between Latitude-Longitude PointsDoy Doy ArifNo ratings yet
- Mohr Circle & Buckling Task ExampleDocument7 pagesMohr Circle & Buckling Task ExampleMuhammad Akbar FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Formulario: L Ogica Matem AticaDocument10 pagesFormulario: L Ogica Matem AticaDaniel ChuquipomaNo ratings yet
- cHAPTER 7 SOULUTIONSDocument35 pagescHAPTER 7 SOULUTIONScharlottedwnNo ratings yet
- Inverse Kinematics-Geometric+AlgebraicDocument22 pagesInverse Kinematics-Geometric+AlgebraicPradyumna Keshari NahakNo ratings yet
- Geometry of Radiation: Plane Angle Solid Angle Differential Solid AngleDocument1 pageGeometry of Radiation: Plane Angle Solid Angle Differential Solid Angle1anoopishereNo ratings yet
- Solutionmanual13!15!150303094029 Conversion Gate01Document18 pagesSolutionmanual13!15!150303094029 Conversion Gate01Ritu Raj RamanNo ratings yet
- Sweet Baby Dresses in Crochet: 4 Dresses in Sizes Newborn to 24 Months, with Matching AccessoriesFrom EverandSweet Baby Dresses in Crochet: 4 Dresses in Sizes Newborn to 24 Months, with Matching AccessoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Scattering Theory for Automorphic Functions. (AM-87), Volume 87From EverandScattering Theory for Automorphic Functions. (AM-87), Volume 87No ratings yet
- Uniform Circular Motion Problems With AnswersDocument28 pagesUniform Circular Motion Problems With AnswersElmer VillegasNo ratings yet
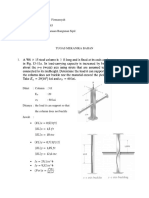
- Analysis of Indeterminate Structures by Force MethodDocument17 pagesAnalysis of Indeterminate Structures by Force Methodatish k100% (2)
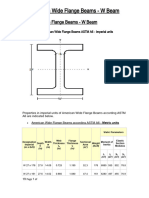
- American Wide Flange BeamsDocument19 pagesAmerican Wide Flange BeamsYakdhan YaseenNo ratings yet
- Cap 2Document110 pagesCap 2AdautozanataNo ratings yet
- Js200 Travel Gearbox New TypeDocument3 pagesJs200 Travel Gearbox New TypeManuel felipe PalmaNo ratings yet
- 28.3 Physica UG Question Paper Pattern of 5 & 6 Sem PDFDocument41 pages28.3 Physica UG Question Paper Pattern of 5 & 6 Sem PDFthomasgunaseelanNo ratings yet
- Group-2 ChE-135 Post Lab Experiment-2Document18 pagesGroup-2 ChE-135 Post Lab Experiment-2Rievelyn MartusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document15 pagesChapter 10JeromeNo ratings yet
- Soil Temperature and Heat Flow: CE/ENVE 320 - Vadose Zone Hydrology/Soil Physics Spring 2004Document37 pagesSoil Temperature and Heat Flow: CE/ENVE 320 - Vadose Zone Hydrology/Soil Physics Spring 2004shubanaNo ratings yet
- HookeDocument6 pagesHookeTitus KaselaNo ratings yet
- Newton's First LawDocument4 pagesNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Newton and The Mechanical Philosophy PDFDocument19 pagesNewton and The Mechanical Philosophy PDFdavid199415No ratings yet
- RAM Connection FoundationDocument17 pagesRAM Connection FoundationNguyễn Duy QuangNo ratings yet
- Comunicaciones Satelitales 2da Edicion Timothy Pratt, Charles W. Bostian, Jeremy E. AllnuttDocument143 pagesComunicaciones Satelitales 2da Edicion Timothy Pratt, Charles W. Bostian, Jeremy E. AllnuttAlfa Group0% (1)
- Introduction To Heat Transfer - S. K. Som PDFDocument570 pagesIntroduction To Heat Transfer - S. K. Som PDFMoinak Sarkar100% (2)
- Emc 2Document7 pagesEmc 2avanomminerNo ratings yet
- IS 456 - 2000 NotesDocument3 pagesIS 456 - 2000 Notesatulya kumar0% (2)
- Effective Laminate Thickness For The Design of Laminated GlassDocument5 pagesEffective Laminate Thickness For The Design of Laminated GlassLaurence SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Keieiie TQMCorrelation DesignDocument5 pagesKeieiie TQMCorrelation DesignJeth Verdejo RiveroNo ratings yet
- 2015 SP 12 Physics 08Document3 pages2015 SP 12 Physics 08maruthinmdcNo ratings yet
- ExpPhys BookformatDocument134 pagesExpPhys Bookformatcamelrider123No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PDFDocument25 pagesChapter 5 PDFShiva NandamNo ratings yet
- Review Test - 2Document16 pagesReview Test - 2vishal110085100% (2)
- Thermodynamic NotesDocument51 pagesThermodynamic NotesAnand MurugananthamNo ratings yet
- Review of The Performance of High Strength Steels Used OffshoreDocument130 pagesReview of The Performance of High Strength Steels Used OffshoreElias Kapa100% (1)
- Ion Scattering TechniquesDocument27 pagesIon Scattering TechniquesAmjed AL-KAHTEEBNo ratings yet
- Hartnell GovernorDocument3 pagesHartnell GovernorSoham DasNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument2 pagesQuestion BankKetan SonbawaneNo ratings yet