Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
SHeenah Qo100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views1 pageThe patient was experiencing difficulty urinating, incontinence, dysuria, and grimacing with urination. Vital signs showed an elevated temperature. The nursing diagnosis was impaired urinary elimination related to increased urethral occlusion. The goals were for the patient and family to understand the condition and prevent urinary infection. Interventions included monitoring vitals, encouraging oral fluids and urination, and administering medications as prescribed to help recovery.
Original Description:
Nursing Care Plan
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe patient was experiencing difficulty urinating, incontinence, dysuria, and grimacing with urination. Vital signs showed an elevated temperature. The nursing diagnosis was impaired urinary elimination related to increased urethral occlusion. The goals were for the patient and family to understand the condition and prevent urinary infection. Interventions included monitoring vitals, encouraging oral fluids and urination, and administering medications as prescribed to help recovery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views1 pageNursing Care Plan
Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
SHeenah QoThe patient was experiencing difficulty urinating, incontinence, dysuria, and grimacing with urination. Vital signs showed an elevated temperature. The nursing diagnosis was impaired urinary elimination related to increased urethral occlusion. The goals were for the patient and family to understand the condition and prevent urinary infection. Interventions included monitoring vitals, encouraging oral fluids and urination, and administering medications as prescribed to help recovery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
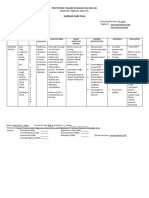
VIII.
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT
NURSING
DIANOSIS
OBJECTI VES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE
Subjective Cues:
The patient
verbalized
difficulty in
urinating.
Objective Cues:
(+)incontinence
(+) dysuria
(+) facial
grimacing upon
urination
With FBC to
UDB
Dyspnea with
exertion
Fatigue and
weakness
Vital Signs:
T: 35.2 C
P: 112 bpm
R: 25 cpm
BP: 120/68
mmHg
Impaired
urinary
elimination
related to
increase
urethral
occlusion
Short term goal:
After 8 hours of
holistic nursing
intervention, the
patient and S.O.
will be able to :
Verbalized
understanding
of condition
Participate in
measures to
correct or
compensate
for defects.
Demonstrate
behavior and
techniques to
prevent
urinary
infection.
I ndependent:
1. Monitor vital signs closely.
Observe for hypertension,
peripheral/ dependent
edema, and changes in
mentation. Maintain
accurate I &O.
2. Encourage oral fluids up to
3000 mL daily, within
cardiac tolerance,
if indicated.
3. Encourage patient to
void every2-4 hours and
when urge is noted.
4. Encourage
meticulous catheter
and perineal care.
Dependent:
1. Administer
medications as
prescribed.
1. Loss of kidney
function results in
decreased fluid
elimination and
accumulation of toxic
wastes may progress to
complete renal shutdown.
2. Increased circulating
fluid maintains
renal perfusion and
flushes kidneys, bladder,
and ureters of
sedimented bacteria.
Note: Initially, fluids may
be restricted to prevent
bladder distension until
adequate urinary flow is
reestablished.
3. May minimize over
distension of the bladder.
4. Reduces risk of
ascending infection
1. Pharmacologic regimen
helps in faster recovery.
You might also like
- Administrative and Clinical Procedures For The Canadian Health Professional 5th Edition - Valerie ThompsonDocument662 pagesAdministrative and Clinical Procedures For The Canadian Health Professional 5th Edition - Valerie Thompsonbooksandco88100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy NCPDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan For Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy NCPderic88% (8)
- Patriarca, Janna Mae H. Nursing Care Plan Client: Mr. YingDocument1 pagePatriarca, Janna Mae H. Nursing Care Plan Client: Mr. Yingjanna mae patriarca100% (2)
- CERT+Basic Unit+1+Instructor+Guide EnglishDocument56 pagesCERT+Basic Unit+1+Instructor+Guide EnglishBrandon OlsenNo ratings yet
- Apollos HeartDocument296 pagesApollos HeartCaissa PenaNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis ADocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis APravesh Verma100% (1)
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDocument2 pagesRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJoy Callo100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Isabel Barredo Del MundoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPhaniehaehae100% (1)
- Actual Nursing Care Plan 2Document16 pagesActual Nursing Care Plan 2Alyanna Evangelista100% (2)
- 3 Nursing Care Plan Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pages3 Nursing Care Plan Diabetes MellitusAnnisa Silvera II50% (2)
- NCP - Fluid Volume ExcessDocument2 pagesNCP - Fluid Volume ExcessIngrid Sasha Fong100% (4)
- Iii. Nursing Care PlansDocument13 pagesIii. Nursing Care PlansLharra Cagulada-Postrano100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNo ratings yet
- NCP GbsDocument2 pagesNCP GbsJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- NCP BPHDocument8 pagesNCP BPHjyaba0% (1)
- Hepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesHepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- NCP Pre EclampsiaDocument2 pagesNCP Pre EclampsiaFarrah Grace Birowa0% (1)
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- NCP pAlPITATIONSDocument3 pagesNCP pAlPITATIONSHazel PalomaresNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresNo ratings yet
- NCP Epidural HemDocument32 pagesNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- NCP PancreatitisDocument2 pagesNCP PancreatitisJeanelle Generoso100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlansanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- NCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesNCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeNica RespondoNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationDocument2 pagesAnxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationmonaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ConstipationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan ConstipationGio Baduria100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- NCP PryllDocument6 pagesNCP PryllpjcolitaNo ratings yet
- Thyroidectomy NCPDocument1 pageThyroidectomy NCPkzbreakerrNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Altered Urinary Elimination Related To Perineal Edema and Decreased Bladder Tone From Fetal Head Pressure During Birth.Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Altered Urinary Elimination Related To Perineal Edema and Decreased Bladder Tone From Fetal Head Pressure During Birth.Angel Angeles Pitogo Jr.100% (1)
- NCP and DStudyDocument8 pagesNCP and DStudyJessica Rosan Hewald ManapatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan CYSTITISDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan CYSTITIS@ngelo0% (1)
- Uti NCPDocument1 pageUti NCPAngelique Vinoya100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument2 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationMatty-b AskalaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sleep PatternDocument2 pagesDisturbed Sleep PatternROxanne S. RendonNo ratings yet
- NCP Template ObDocument7 pagesNCP Template ObMae CeaesarNo ratings yet
- NCP Fluid Vol Excess AgnDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid Vol Excess AgnArbie JacintoNo ratings yet
- NCP ConstipationDocument3 pagesNCP ConstipationKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN of CoughDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN of Coughrhizalyn1383% (6)
- Multiple MyelomaDocument2 pagesMultiple MyelomaKolin JandocNo ratings yet
- Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1Document8 pagesRisk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1kint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Renal FailureMark Jason Rabadan100% (1)
- Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDocument11 pagesNormal Spontaneous DeliveryAyah GarciaNo ratings yet
- NCP AnemiaDocument2 pagesNCP AnemiaAriaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To InjuryDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Related To InjuryErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCP PDFDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCP PDFFARAH MAE MEDINA100% (2)
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Uremic SyndromeDocument11 pagesNursing Care of Uremic Syndromeyoedha_banditozz50% (2)
- NCP Urinary Tract InfectionDocument4 pagesNCP Urinary Tract InfectiondollythesheepNo ratings yet
- Uti NCPDocument3 pagesUti NCPHamdy Pagilit Dimaporo0% (1)
- Drug Study 2Document7 pagesDrug Study 2Jediale CarcelerNo ratings yet
- Ms Flash CardsDocument15 pagesMs Flash CardsMia MalazoNo ratings yet
- NCP RHDocument3 pagesNCP RHMariquita Buenafe57% (7)
- VIII. Nursing Care PlanDocument12 pagesVIII. Nursing Care PlanNefre Dayap DarrocaNo ratings yet
- NCP Group4Document15 pagesNCP Group4justinbrillo28No ratings yet
- Med Surg ReviewDocument6 pagesMed Surg ReviewSabhi Sandhu75% (4)
- Cross-Match TestDocument2 pagesCross-Match TestSaman HarsNo ratings yet
- Body Composition Lab Report-CompleteDocument4 pagesBody Composition Lab Report-CompleteEmmae ThaleenNo ratings yet
- Lplpo Poskeskel 2021Document6 pagesLplpo Poskeskel 2021Michel Caesar Analta MichelNo ratings yet
- Bruckman - Gaven ChristopherDocument2 pagesBruckman - Gaven Christophergbruckman08No ratings yet
- Contact Us Career: PharmaceuticalsDocument3 pagesContact Us Career: PharmaceuticalsPoogle111No ratings yet
- FHP ResearchDocument61 pagesFHP ResearchPooja DaveNo ratings yet
- A Study of The Umbilical Cord Length and Foetal Outcome .Document10 pagesA Study of The Umbilical Cord Length and Foetal Outcome .webster mumaNo ratings yet
- Ky PosisDocument26 pagesKy PosisUsama TahirNo ratings yet
- Daftar Nama Obat - ObatanDocument2 pagesDaftar Nama Obat - ObatanhimerlyaestheticclinicNo ratings yet
- Harvard White Paper BB August 2019Document9 pagesHarvard White Paper BB August 2019simona pisuNo ratings yet
- SCPTraining Calendar FY22Document43 pagesSCPTraining Calendar FY22deviNo ratings yet
- Diagnosa Lidah - AyurvedicDocument2 pagesDiagnosa Lidah - AyurvedicteukuawyNo ratings yet
- Johns Hopkins DKA Clinical PathwayDocument31 pagesJohns Hopkins DKA Clinical PathwayPatricia Denise Tome MagisaNo ratings yet
- LifeShare PPT PresentationDocument12 pagesLifeShare PPT PresentationEriccaNo ratings yet
- The End of Gray Hair: Ex-Uhuru Escort Now A Quarry WorkerDocument6 pagesThe End of Gray Hair: Ex-Uhuru Escort Now A Quarry WorkerKaranja GitauNo ratings yet
- Leader's Guide Summer Camp 2023Document132 pagesLeader's Guide Summer Camp 2023Jonathan ReevesNo ratings yet
- Prosthesis: Uganeswary VenugopalDocument14 pagesProsthesis: Uganeswary VenugopalUganeswary VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Cook Guia Referencia Aorta Ai-D38186-En-F - Ia - 1509975852846Document140 pagesCook Guia Referencia Aorta Ai-D38186-En-F - Ia - 1509975852846Alejandro MarzucoNo ratings yet
- A Glimpse To A Human Person: Who Am I?: Front PageDocument17 pagesA Glimpse To A Human Person: Who Am I?: Front PageGabrielle May LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- Linay, Maria Jennylyn A Ppar Q Standard and Data PrivacyDocument3 pagesLinay, Maria Jennylyn A Ppar Q Standard and Data PrivacyJEN LINAYNo ratings yet
- CRMC PGS Module - Output 2 2Document29 pagesCRMC PGS Module - Output 2 2MJNo ratings yet
- The Roots of Education Are Bitter, But The Fruit Is Sweet.Document9 pagesThe Roots of Education Are Bitter, But The Fruit Is Sweet.Nhật Thiên Trương HoàngNo ratings yet
- Adult CPR: Assessor Say CaregiverDocument3 pagesAdult CPR: Assessor Say CaregiverSandeeNo ratings yet
- Movement Competency Training Module No. 1Document3 pagesMovement Competency Training Module No. 1Jhon Keneth NamiasNo ratings yet
- The Fault Tree Analysis of Infectious Medical Waste Management PDFDocument9 pagesThe Fault Tree Analysis of Infectious Medical Waste Management PDFNataša PetrovićNo ratings yet
- Resume Business Presentation Specialist (Trainee) BengaluruDocument1 pageResume Business Presentation Specialist (Trainee) BengaluruDakshesh SoodNo ratings yet
- Remote Therapeutic Monitoring For 2022: Barbara Frances Kho, RN MANDocument12 pagesRemote Therapeutic Monitoring For 2022: Barbara Frances Kho, RN MANBFKHONo ratings yet