Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 viewsAnswers and Explanations: (Moore, P 846)
Answers and Explanations: (Moore, P 846)
Uploaded by
SomiZafarThis document provides answers and explanations for 17 multiple choice questions about anatomical structures and features of the neurocranium and facial skeleton. It identifies the bones that make up the neurocranium and facial skeleton, the names and locations of various foramina and sutures, and the structures that pass through different openings in the skull. Key details are referenced from a textbook by Moore.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Peterson-Field Guide To The Mammals 3rdedDocument378 pagesPeterson-Field Guide To The Mammals 3rdedDon Chemo100% (7)
- Unit VIIIa Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesUnit VIIIa Lecture NotesSteve Sullivan100% (1)
- Cosmetic Otoplasty 2018 DBDocument11 pagesCosmetic Otoplasty 2018 DBcirugia plastica uisNo ratings yet
- (Moore, P 1016) .: 7: The Head and NeckDocument1 page(Moore, P 1016) .: 7: The Head and NeckSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- (Moore, P 846) .: Answers and Explanations: 1-39Document1 page(Moore, P 846) .: Answers and Explanations: 1-39SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Skull Base Embryology: A Multidisciplinary ReviewDocument10 pagesSkull Base Embryology: A Multidisciplinary ReviewJulio AbarzuaNo ratings yet
- Zafar 14 PDFDocument1 pageZafar 14 PDFSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Essay Solution On Space in The SkullDocument21 pagesEssay Solution On Space in The SkullEmmanuel IshiomaNo ratings yet
- Zafar 141Document1 pageZafar 141SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Head Lecture NotesDocument49 pagesHead Lecture Notesvipul51190No ratings yet
- Derivation of The Mammalian Skull Vault: Gillianm - Morriss-KayDocument9 pagesDerivation of The Mammalian Skull Vault: Gillianm - Morriss-KaygandhiayuNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Anterior Skull Base: 1.1.1 Cribriform Plate/Crista GalliDocument9 pages1.1 Anterior Skull Base: 1.1.1 Cribriform Plate/Crista GalliYhafapCezNo ratings yet
- Zafar 143Document1 pageZafar 143SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- SkullDocument11 pagesSkullGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Mgutknecht,+sdj Article 618Document13 pagesMgutknecht,+sdj Article 618Emanuela MironNo ratings yet
- The Head and Neck Q - ADocument4 pagesThe Head and Neck Q - Ahafsag307No ratings yet
- Lecture Note - Skull and Visceral SkeletonDocument4 pagesLecture Note - Skull and Visceral SkeletonLopez Manilyn CNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Cranial Base: SeminarDocument34 pagesGrowth and Development of Cranial Base: SeminarMNSNo ratings yet
- riccardo,+OP03845 IJAE 2019 2 176-181 20191122 0833Document6 pagesriccardo,+OP03845 IJAE 2019 2 176-181 20191122 0833researchnnnnNo ratings yet
- (Moore, P 486) .: 1: The BackDocument1 page(Moore, P 486) .: 1: The BackSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Eye & OrbitDocument21 pagesAnatomy of The Eye & OrbitKshitij ShukulNo ratings yet
- Skullbasefracturesand Theircomplications: Kristen L. Baugnon,, Patricia A. HudginsDocument27 pagesSkullbasefracturesand Theircomplications: Kristen L. Baugnon,, Patricia A. Hudginshenandwitafadilla28No ratings yet
- The Anterior and Middle Cranial BaseDocument30 pagesThe Anterior and Middle Cranial Basejuan valencia sotoNo ratings yet
- Basis CraniiDocument11 pagesBasis Craniicharlesy TNo ratings yet
- Concerning Viewing The Head in Norma LateralisDocument2 pagesConcerning Viewing The Head in Norma LateralisEdgar MandengNo ratings yet
- Senter 2003Document9 pagesSenter 2003J.D. NobleNo ratings yet
- Identification of The Cranium of W.A. Mozart: Forensic Science International, 41 (1989) 101 - 110 101Document11 pagesIdentification of The Cranium of W.A. Mozart: Forensic Science International, 41 (1989) 101 - 110 101massiminoNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Skull Author Department of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument17 pagesBones of The Skull Author Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeryمدونة الأحترافNo ratings yet
- Answers and Explanations: 109-156Document1 pageAnswers and Explanations: 109-156SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System NotesDocument7 pagesThe Skeletal System NotesPIOZRNo ratings yet
- Anatomie Os Mandibulaire J.ydbio.2004.08.046Document12 pagesAnatomie Os Mandibulaire J.ydbio.2004.08.046Free CoursesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The OrbitsDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Orbitslaljadeff12No ratings yet
- Oral Anatomy & Physiology TestDocument34 pagesOral Anatomy & Physiology TestEliza EllieNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System. SkullDocument24 pagesSkeletal System. SkullJessa BelleNo ratings yet
- Worksheet SkulllDocument6 pagesWorksheet SkulllJingle Capistrano TarucNo ratings yet
- Ear HubbardDocument3 pagesEar HubbardAashish SinghNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of The CochleaDocument4 pagesFunctional Anatomy of The CochleaEva SánchezNo ratings yet
- Human Ear: (Or Phono Receptor Organ)Document32 pagesHuman Ear: (Or Phono Receptor Organ)Sampada GautamNo ratings yet
- 1 M2XEmNdWyU0UgSsb6l-b1bJW4m4gPWADocument7 pages1 M2XEmNdWyU0UgSsb6l-b1bJW4m4gPWAmdikwamihlaliiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear DR Ahmed Mohammed Al AlwanDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Ear DR Ahmed Mohammed Al AlwanNashat SaadiNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of SkullDocument83 pagesFunctional Anatomy of SkullTaha Ahsan100% (1)
- The Bones in The Neurocranium: David Terfera Shereen Jegtvig Clinical Anatomy For DummiesDocument25 pagesThe Bones in The Neurocranium: David Terfera Shereen Jegtvig Clinical Anatomy For DummiesFrozen Pandora MahayaNo ratings yet
- The Axial Skeleton - 2Document158 pagesThe Axial Skeleton - 2Zaid HamdanNo ratings yet
- Moore 1987Document11 pagesMoore 1987ivansosnowNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See .: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument17 pagesFor Other Uses, See .: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchMichael FelicianoNo ratings yet
- The Human Ear - 1Document8 pagesThe Human Ear - 1jacques.duplessisNo ratings yet
- Embryology and Anatomy of The Earoperative Techniques in OtolaryngologyDocument23 pagesEmbryology and Anatomy of The Earoperative Techniques in OtolaryngologyAtrik PristicaNo ratings yet
- Notochord - WikipediaDocument22 pagesNotochord - WikipediaJagannath RaoNo ratings yet
- Exterior and Middle EarDocument26 pagesExterior and Middle EarAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 139 Anatomy of The Skull Base Temporal Bone External Ear and Middle Ear Larry G Duckert - CompressDocument12 pagesChapter 139 Anatomy of The Skull Base Temporal Bone External Ear and Middle Ear Larry G Duckert - CompressWudieNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing:Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorder.Document126 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing:Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorder.Minlik-alew Dejenie89% (18)
- 16meceebl S 20800330MDocument11 pages16meceebl S 20800330MGhanshyam YadavNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See .: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument72 pagesFor Other Uses, See .: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediavishalsidankarNo ratings yet
- Vi. Head and Neck MorphologyDocument4 pagesVi. Head and Neck MorphologyDewa Aix61No ratings yet
- The Skeletal System OutlineDocument11 pagesThe Skeletal System OutlinePIOZRNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Hearing and EarDocument10 pagesThe Physiology of Hearing and EarMustafam98No ratings yet
- Osta Lecture 4 Notes Online ENGLISH Base of Skull and BrainDocument36 pagesOsta Lecture 4 Notes Online ENGLISH Base of Skull and BrainslyfoxkittyNo ratings yet
- Radius and Ulna: PPP Jazlan Bin Mohamad (Posbasic Ortho 1/2018)Document17 pagesRadius and Ulna: PPP Jazlan Bin Mohamad (Posbasic Ortho 1/2018)Jazlan MohamadNo ratings yet
- Bones of The H&NDocument12 pagesBones of The H&Naminshafihassan902No ratings yet
- Head Neck Topical Papers 1Document5 pagesHead Neck Topical Papers 1Abdul AhadNo ratings yet
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 147 Through 151) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 pageDIRECTIONS (Questions 147 Through 151) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 157 Through 161) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 pageDIRECTIONS (Questions 157 Through 161) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 147Document1 pageZafar 147SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 13Document1 pageZafar 13SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- (Moore, P 846) .: Answers and Explanations: 1-39Document1 page(Moore, P 846) .: Answers and Explanations: 1-39SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Answers and Explanations: 109-156Document1 pageAnswers and Explanations: 109-156SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 152 Through 156) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 pageDIRECTIONS (Questions 152 Through 156) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- (Moore, P 1016) .: 7: The Head and NeckDocument1 page(Moore, P 1016) .: 7: The Head and NeckSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 141Document1 pageZafar 141SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- (Moore, P 486) .: 1: The BackDocument1 page(Moore, P 486) .: 1: The BackSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 143Document1 pageZafar 143SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 11Document1 pageZafar 11SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 162 Through 166) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 pageDIRECTIONS (Questions 162 Through 166) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 172 Through 176) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 pageDIRECTIONS (Questions 172 Through 176) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 14 PDFDocument1 pageZafar 14 PDFSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 182 Through 186) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 pageDIRECTIONS (Questions 182 Through 186) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 9Document1 pageZafar 9SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 10Document1 pageZafar 10SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 12Document1 pageZafar 12SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Answers, Explanations, and References: Zinsser's Microbiology. 20th Ed. Norwalk, Conn: AppleDocument1 pageAnswers, Explanations, and References: Zinsser's Microbiology. 20th Ed. Norwalk, Conn: AppleSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 2Document1 pageZafar 2SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- The Back: QuestionsDocument1 pageThe Back: QuestionsSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- One Best-Answer-Single Item QuestionDocument1 pageOne Best-Answer-Single Item QuestionSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument1 pageThis Page Intentionally Left BlankSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 4Document1 pageZafar 4SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Appleton & Lange Review of Anatomy, Sixth Edition: NoticeDocument1 pageAppleton & Lange Review of Anatomy, Sixth Edition: NoticeSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 149Document1 pageZafar 149SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Sedimentology Cabello Et Al 2018Document38 pagesSedimentology Cabello Et Al 2018María Alejandra BarajasNo ratings yet
- Merrimelia Field PDFDocument70 pagesMerrimelia Field PDFAhmad Farhan Farabi100% (1)
- Geologic Formation of The HimalayaDocument10 pagesGeologic Formation of The Himalayashanki0072015100% (1)
- Microfossils Description Paper: Palaeontology Practical: KalpanadekakalitaDocument32 pagesMicrofossils Description Paper: Palaeontology Practical: Kalpanadekakalitarikalave ramanNo ratings yet
- Biostratigraphy of Lower Cretaceous Microfossils From The Araripe Basin, Northeastern BrazilDocument12 pagesBiostratigraphy of Lower Cretaceous Microfossils From The Araripe Basin, Northeastern Braziljoão carlos CoimbraNo ratings yet
- PAPER - Shell Directions As A Tool in Palaeocurrent AnalysisDocument26 pagesPAPER - Shell Directions As A Tool in Palaeocurrent AnalysisResky ArdianNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift TheoryDocument19 pagesContinental Drift Theoryla vaniza100% (1)
- Phanerozoic Stratigraphic ColumnDocument1 pagePhanerozoic Stratigraphic ColumnSeptriandi ChanNo ratings yet
- 4) Mandibular Central and LateralDocument20 pages4) Mandibular Central and LateralZahra BaniameryanNo ratings yet
- Low-Sulphidation Epithermal SystemsDocument57 pagesLow-Sulphidation Epithermal SystemsGraciela CostaNo ratings yet
- ChronostratChart2017 02NLDutchDocument1 pageChronostratChart2017 02NLDutchDafne Ramírez MendozaNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals Webquest 3Document4 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquest 3api-264090670No ratings yet
- Eolian EnvironmentDocument16 pagesEolian EnvironmentJobit ParapatNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Rough DraftDocument2 pagesResearch Proposal Rough Draftapi-306885462No ratings yet
- Vedantu Best Notes OrgDocument24 pagesVedantu Best Notes Orggaurav bhanotNo ratings yet
- Natural History 2916 New yDocument716 pagesNatural History 2916 New yacademo misirNo ratings yet
- Notes For Zoology - Page 5 - CSS ForumsDocument13 pagesNotes For Zoology - Page 5 - CSS ForumsTahirMobeen0% (1)
- TocDocument58 pagesTocrafaelNo ratings yet
- Story of Noah Scripture ReferenceDocument5 pagesStory of Noah Scripture ReferenceboetabradNo ratings yet
- Human EvolutionDocument10 pagesHuman EvolutionVenn Bacus Rabadon0% (1)
- Stratigraphic Chronological Chart History-of-the-Earth-posterDocument1 pageStratigraphic Chronological Chart History-of-the-Earth-posterUdit KumarNo ratings yet
- The Marine Biology of Spongebob SquarepantsDocument13 pagesThe Marine Biology of Spongebob Squarepants022072No ratings yet
- CH 25Document17 pagesCH 25Nesya JanesyaNo ratings yet
- Big IV BorneoDocument165 pagesBig IV BorneoRutami Shine100% (1)
- Human Evolution ChecklistDocument2 pagesHuman Evolution Checklistapi-324166624No ratings yet
- Timeline (From Big Bang To Imperial Persia)Document1 pageTimeline (From Big Bang To Imperial Persia)Sougata PurkayasthaNo ratings yet
- Villamil-1998-Chronology Relative Sea Level History and A New Sequence Stratigraphic Model For Basinal Cretaceous Facies of ColombiaDocument56 pagesVillamil-1998-Chronology Relative Sea Level History and A New Sequence Stratigraphic Model For Basinal Cretaceous Facies of ColombiaAlejandra PazNo ratings yet
- Geoheritage in Europe and Its Conservation - RomaniaDocument10 pagesGeoheritage in Europe and Its Conservation - RomaniaAlexandru AndrasanuNo ratings yet
- Basin Development and Tectonic History of The Llanos Basin. Cooper 36Document7 pagesBasin Development and Tectonic History of The Llanos Basin. Cooper 36Carlos Andres RojasNo ratings yet
Answers and Explanations: (Moore, P 846)
Answers and Explanations: (Moore, P 846)
Uploaded by
SomiZafar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 pageThis document provides answers and explanations for 17 multiple choice questions about anatomical structures and features of the neurocranium and facial skeleton. It identifies the bones that make up the neurocranium and facial skeleton, the names and locations of various foramina and sutures, and the structures that pass through different openings in the skull. Key details are referenced from a textbook by Moore.
Original Description:
usmle
Original Title
zafar 139
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides answers and explanations for 17 multiple choice questions about anatomical structures and features of the neurocranium and facial skeleton. It identifies the bones that make up the neurocranium and facial skeleton, the names and locations of various foramina and sutures, and the structures that pass through different openings in the skull. Key details are referenced from a textbook by Moore.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 pageAnswers and Explanations: (Moore, P 846)
Answers and Explanations: (Moore, P 846)
Uploaded by
SomiZafarThis document provides answers and explanations for 17 multiple choice questions about anatomical structures and features of the neurocranium and facial skeleton. It identifies the bones that make up the neurocranium and facial skeleton, the names and locations of various foramina and sutures, and the structures that pass through different openings in the skull. Key details are referenced from a textbook by Moore.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Answers and Explanations
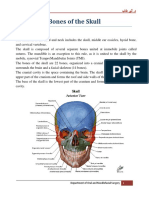
1. (A) The bones of the neurocranium include the
frontal bone, paired parietal bones, paired tem-
poral bones, the occipital bone, the sphenoid
bone, and the ethmoid bone (Moore, p 832).
2. (C) The bones of the facial skeleton (viscerocra-
nium or splanchnocranium) include the vomer,
the mandible, inferior nasal conchae, the pala-
tine bones, the zygomatic bones, the maxillae,
the nasal bones, and the lacrimal bones (Moore,
p 832).
3. (A) When the frontal suture persists, it is
known as the metopic suture (Moore, p 834).
4. (B) The external occipital protuberance is also
known as the inion (Moore, p 839).
5. (A) Lambda is the point on the calvaria at the
junction of the sagittal and lambdoid sutures
(Moore, p 842).
6. (C) The vertex is the superior point of the neu-
rocranium in the midline (Moore, p 842).
7. (E) The foramen magnum is in the posterior
cranial fossa (Moore, p 846).
8. (A) The foramen cecum is located in the ante-
rior cranial fossa (Moore, p 846).
9. (E) The anterior and posterior ethmoidal fora-
mina transmit anterior and posterior ethmoidal
arteries and nerves, not emissary veins (Moore,
p 846).
10. (B) The superior orbital ssure transmits the
ophthalmic veins, ophthalmic division of the
trigeminal nerve, oculomotor nerve, trochlear
nerve, abducens nerve, and sympathetic bers
(Moore, p 846).
11. (B) The foramen ovale transmits the accessory
meningeal artery. The foramen spinosum trans-
mits the middle meningeal artery. The groove
of the greater petrosal nerve transmits the
petrosal branch of the middle meningeal artery.
The jugular foramen transmits the meningeal
branches of the ascending pharyngeal and oc-
cipital arteries. The mastoid foramen transmits
the meningeal branch of the occipital artery
(Moore, p 846).
12. (A) The foramina in the cribriform plate trans-
mit axons of olfactory cells in the olfactory epi-
thelium (Moore, p 846).
13. (D) The optic canals transmit the optic nerves
and the ophthalmic arteries (Moore, p 846).
14. (A) The foramen rotundum transmits the max-
illary division of the trigeminal nerve (Moore,
p 846).
15. (A) The foramen spinosum transmits the men-
ingeal branch of the mandibular division of the
trigeminal nerve (Moore, p 846).
16. (E) The foramen magnum transmits the me-
dulla and meninges, vertebral arteries, spinal
roots of the accessory nerve, dural veins, and the
anterior and posterior spinal arteries (Moore,
p 846).
17. (E) The jugular foramen transmits the glos-
sopharyngeal nerve, vagus nerve, accessory
132
0523-07 Chap 7 07/15/02 15:35 Page 132
You might also like
- Peterson-Field Guide To The Mammals 3rdedDocument378 pagesPeterson-Field Guide To The Mammals 3rdedDon Chemo100% (7)
- Unit VIIIa Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesUnit VIIIa Lecture NotesSteve Sullivan100% (1)
- Cosmetic Otoplasty 2018 DBDocument11 pagesCosmetic Otoplasty 2018 DBcirugia plastica uisNo ratings yet
- (Moore, P 1016) .: 7: The Head and NeckDocument1 page(Moore, P 1016) .: 7: The Head and NeckSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- (Moore, P 846) .: Answers and Explanations: 1-39Document1 page(Moore, P 846) .: Answers and Explanations: 1-39SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Skull Base Embryology: A Multidisciplinary ReviewDocument10 pagesSkull Base Embryology: A Multidisciplinary ReviewJulio AbarzuaNo ratings yet
- Zafar 14 PDFDocument1 pageZafar 14 PDFSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Essay Solution On Space in The SkullDocument21 pagesEssay Solution On Space in The SkullEmmanuel IshiomaNo ratings yet
- Zafar 141Document1 pageZafar 141SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Head Lecture NotesDocument49 pagesHead Lecture Notesvipul51190No ratings yet
- Derivation of The Mammalian Skull Vault: Gillianm - Morriss-KayDocument9 pagesDerivation of The Mammalian Skull Vault: Gillianm - Morriss-KaygandhiayuNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Anterior Skull Base: 1.1.1 Cribriform Plate/Crista GalliDocument9 pages1.1 Anterior Skull Base: 1.1.1 Cribriform Plate/Crista GalliYhafapCezNo ratings yet
- Zafar 143Document1 pageZafar 143SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- SkullDocument11 pagesSkullGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Mgutknecht,+sdj Article 618Document13 pagesMgutknecht,+sdj Article 618Emanuela MironNo ratings yet
- The Head and Neck Q - ADocument4 pagesThe Head and Neck Q - Ahafsag307No ratings yet
- Lecture Note - Skull and Visceral SkeletonDocument4 pagesLecture Note - Skull and Visceral SkeletonLopez Manilyn CNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Cranial Base: SeminarDocument34 pagesGrowth and Development of Cranial Base: SeminarMNSNo ratings yet
- riccardo,+OP03845 IJAE 2019 2 176-181 20191122 0833Document6 pagesriccardo,+OP03845 IJAE 2019 2 176-181 20191122 0833researchnnnnNo ratings yet
- (Moore, P 486) .: 1: The BackDocument1 page(Moore, P 486) .: 1: The BackSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Eye & OrbitDocument21 pagesAnatomy of The Eye & OrbitKshitij ShukulNo ratings yet
- Skullbasefracturesand Theircomplications: Kristen L. Baugnon,, Patricia A. HudginsDocument27 pagesSkullbasefracturesand Theircomplications: Kristen L. Baugnon,, Patricia A. Hudginshenandwitafadilla28No ratings yet
- The Anterior and Middle Cranial BaseDocument30 pagesThe Anterior and Middle Cranial Basejuan valencia sotoNo ratings yet
- Basis CraniiDocument11 pagesBasis Craniicharlesy TNo ratings yet
- Concerning Viewing The Head in Norma LateralisDocument2 pagesConcerning Viewing The Head in Norma LateralisEdgar MandengNo ratings yet
- Senter 2003Document9 pagesSenter 2003J.D. NobleNo ratings yet
- Identification of The Cranium of W.A. Mozart: Forensic Science International, 41 (1989) 101 - 110 101Document11 pagesIdentification of The Cranium of W.A. Mozart: Forensic Science International, 41 (1989) 101 - 110 101massiminoNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Skull Author Department of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument17 pagesBones of The Skull Author Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeryمدونة الأحترافNo ratings yet
- Answers and Explanations: 109-156Document1 pageAnswers and Explanations: 109-156SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System NotesDocument7 pagesThe Skeletal System NotesPIOZRNo ratings yet
- Anatomie Os Mandibulaire J.ydbio.2004.08.046Document12 pagesAnatomie Os Mandibulaire J.ydbio.2004.08.046Free CoursesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The OrbitsDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Orbitslaljadeff12No ratings yet
- Oral Anatomy & Physiology TestDocument34 pagesOral Anatomy & Physiology TestEliza EllieNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System. SkullDocument24 pagesSkeletal System. SkullJessa BelleNo ratings yet
- Worksheet SkulllDocument6 pagesWorksheet SkulllJingle Capistrano TarucNo ratings yet
- Ear HubbardDocument3 pagesEar HubbardAashish SinghNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of The CochleaDocument4 pagesFunctional Anatomy of The CochleaEva SánchezNo ratings yet
- Human Ear: (Or Phono Receptor Organ)Document32 pagesHuman Ear: (Or Phono Receptor Organ)Sampada GautamNo ratings yet
- 1 M2XEmNdWyU0UgSsb6l-b1bJW4m4gPWADocument7 pages1 M2XEmNdWyU0UgSsb6l-b1bJW4m4gPWAmdikwamihlaliiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear DR Ahmed Mohammed Al AlwanDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Ear DR Ahmed Mohammed Al AlwanNashat SaadiNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of SkullDocument83 pagesFunctional Anatomy of SkullTaha Ahsan100% (1)
- The Bones in The Neurocranium: David Terfera Shereen Jegtvig Clinical Anatomy For DummiesDocument25 pagesThe Bones in The Neurocranium: David Terfera Shereen Jegtvig Clinical Anatomy For DummiesFrozen Pandora MahayaNo ratings yet
- The Axial Skeleton - 2Document158 pagesThe Axial Skeleton - 2Zaid HamdanNo ratings yet
- Moore 1987Document11 pagesMoore 1987ivansosnowNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See .: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument17 pagesFor Other Uses, See .: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchMichael FelicianoNo ratings yet
- The Human Ear - 1Document8 pagesThe Human Ear - 1jacques.duplessisNo ratings yet
- Embryology and Anatomy of The Earoperative Techniques in OtolaryngologyDocument23 pagesEmbryology and Anatomy of The Earoperative Techniques in OtolaryngologyAtrik PristicaNo ratings yet
- Notochord - WikipediaDocument22 pagesNotochord - WikipediaJagannath RaoNo ratings yet
- Exterior and Middle EarDocument26 pagesExterior and Middle EarAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 139 Anatomy of The Skull Base Temporal Bone External Ear and Middle Ear Larry G Duckert - CompressDocument12 pagesChapter 139 Anatomy of The Skull Base Temporal Bone External Ear and Middle Ear Larry G Duckert - CompressWudieNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing:Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorder.Document126 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing:Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorder.Minlik-alew Dejenie89% (18)
- 16meceebl S 20800330MDocument11 pages16meceebl S 20800330MGhanshyam YadavNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See .: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument72 pagesFor Other Uses, See .: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediavishalsidankarNo ratings yet
- Vi. Head and Neck MorphologyDocument4 pagesVi. Head and Neck MorphologyDewa Aix61No ratings yet
- The Skeletal System OutlineDocument11 pagesThe Skeletal System OutlinePIOZRNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Hearing and EarDocument10 pagesThe Physiology of Hearing and EarMustafam98No ratings yet
- Osta Lecture 4 Notes Online ENGLISH Base of Skull and BrainDocument36 pagesOsta Lecture 4 Notes Online ENGLISH Base of Skull and BrainslyfoxkittyNo ratings yet
- Radius and Ulna: PPP Jazlan Bin Mohamad (Posbasic Ortho 1/2018)Document17 pagesRadius and Ulna: PPP Jazlan Bin Mohamad (Posbasic Ortho 1/2018)Jazlan MohamadNo ratings yet
- Bones of The H&NDocument12 pagesBones of The H&Naminshafihassan902No ratings yet
- Head Neck Topical Papers 1Document5 pagesHead Neck Topical Papers 1Abdul AhadNo ratings yet
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 147 Through 151) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 pageDIRECTIONS (Questions 147 Through 151) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 157 Through 161) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 pageDIRECTIONS (Questions 157 Through 161) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 147Document1 pageZafar 147SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 13Document1 pageZafar 13SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- (Moore, P 846) .: Answers and Explanations: 1-39Document1 page(Moore, P 846) .: Answers and Explanations: 1-39SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Answers and Explanations: 109-156Document1 pageAnswers and Explanations: 109-156SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 152 Through 156) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 pageDIRECTIONS (Questions 152 Through 156) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- (Moore, P 1016) .: 7: The Head and NeckDocument1 page(Moore, P 1016) .: 7: The Head and NeckSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 141Document1 pageZafar 141SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- (Moore, P 486) .: 1: The BackDocument1 page(Moore, P 486) .: 1: The BackSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 143Document1 pageZafar 143SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 11Document1 pageZafar 11SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 162 Through 166) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 pageDIRECTIONS (Questions 162 Through 166) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 172 Through 176) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 pageDIRECTIONS (Questions 172 Through 176) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 14 PDFDocument1 pageZafar 14 PDFSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 182 Through 186) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 pageDIRECTIONS (Questions 182 Through 186) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 9Document1 pageZafar 9SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 10Document1 pageZafar 10SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 12Document1 pageZafar 12SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Answers, Explanations, and References: Zinsser's Microbiology. 20th Ed. Norwalk, Conn: AppleDocument1 pageAnswers, Explanations, and References: Zinsser's Microbiology. 20th Ed. Norwalk, Conn: AppleSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 2Document1 pageZafar 2SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- The Back: QuestionsDocument1 pageThe Back: QuestionsSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- One Best-Answer-Single Item QuestionDocument1 pageOne Best-Answer-Single Item QuestionSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument1 pageThis Page Intentionally Left BlankSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 4Document1 pageZafar 4SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Appleton & Lange Review of Anatomy, Sixth Edition: NoticeDocument1 pageAppleton & Lange Review of Anatomy, Sixth Edition: NoticeSomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Zafar 149Document1 pageZafar 149SomiZafarNo ratings yet
- Sedimentology Cabello Et Al 2018Document38 pagesSedimentology Cabello Et Al 2018María Alejandra BarajasNo ratings yet
- Merrimelia Field PDFDocument70 pagesMerrimelia Field PDFAhmad Farhan Farabi100% (1)
- Geologic Formation of The HimalayaDocument10 pagesGeologic Formation of The Himalayashanki0072015100% (1)
- Microfossils Description Paper: Palaeontology Practical: KalpanadekakalitaDocument32 pagesMicrofossils Description Paper: Palaeontology Practical: Kalpanadekakalitarikalave ramanNo ratings yet
- Biostratigraphy of Lower Cretaceous Microfossils From The Araripe Basin, Northeastern BrazilDocument12 pagesBiostratigraphy of Lower Cretaceous Microfossils From The Araripe Basin, Northeastern Braziljoão carlos CoimbraNo ratings yet
- PAPER - Shell Directions As A Tool in Palaeocurrent AnalysisDocument26 pagesPAPER - Shell Directions As A Tool in Palaeocurrent AnalysisResky ArdianNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift TheoryDocument19 pagesContinental Drift Theoryla vaniza100% (1)
- Phanerozoic Stratigraphic ColumnDocument1 pagePhanerozoic Stratigraphic ColumnSeptriandi ChanNo ratings yet
- 4) Mandibular Central and LateralDocument20 pages4) Mandibular Central and LateralZahra BaniameryanNo ratings yet
- Low-Sulphidation Epithermal SystemsDocument57 pagesLow-Sulphidation Epithermal SystemsGraciela CostaNo ratings yet
- ChronostratChart2017 02NLDutchDocument1 pageChronostratChart2017 02NLDutchDafne Ramírez MendozaNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals Webquest 3Document4 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquest 3api-264090670No ratings yet
- Eolian EnvironmentDocument16 pagesEolian EnvironmentJobit ParapatNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Rough DraftDocument2 pagesResearch Proposal Rough Draftapi-306885462No ratings yet
- Vedantu Best Notes OrgDocument24 pagesVedantu Best Notes Orggaurav bhanotNo ratings yet
- Natural History 2916 New yDocument716 pagesNatural History 2916 New yacademo misirNo ratings yet
- Notes For Zoology - Page 5 - CSS ForumsDocument13 pagesNotes For Zoology - Page 5 - CSS ForumsTahirMobeen0% (1)
- TocDocument58 pagesTocrafaelNo ratings yet
- Story of Noah Scripture ReferenceDocument5 pagesStory of Noah Scripture ReferenceboetabradNo ratings yet
- Human EvolutionDocument10 pagesHuman EvolutionVenn Bacus Rabadon0% (1)
- Stratigraphic Chronological Chart History-of-the-Earth-posterDocument1 pageStratigraphic Chronological Chart History-of-the-Earth-posterUdit KumarNo ratings yet
- The Marine Biology of Spongebob SquarepantsDocument13 pagesThe Marine Biology of Spongebob Squarepants022072No ratings yet
- CH 25Document17 pagesCH 25Nesya JanesyaNo ratings yet
- Big IV BorneoDocument165 pagesBig IV BorneoRutami Shine100% (1)
- Human Evolution ChecklistDocument2 pagesHuman Evolution Checklistapi-324166624No ratings yet
- Timeline (From Big Bang To Imperial Persia)Document1 pageTimeline (From Big Bang To Imperial Persia)Sougata PurkayasthaNo ratings yet
- Villamil-1998-Chronology Relative Sea Level History and A New Sequence Stratigraphic Model For Basinal Cretaceous Facies of ColombiaDocument56 pagesVillamil-1998-Chronology Relative Sea Level History and A New Sequence Stratigraphic Model For Basinal Cretaceous Facies of ColombiaAlejandra PazNo ratings yet
- Geoheritage in Europe and Its Conservation - RomaniaDocument10 pagesGeoheritage in Europe and Its Conservation - RomaniaAlexandru AndrasanuNo ratings yet
- Basin Development and Tectonic History of The Llanos Basin. Cooper 36Document7 pagesBasin Development and Tectonic History of The Llanos Basin. Cooper 36Carlos Andres RojasNo ratings yet