Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conformations
Conformations
Uploaded by
rameshiit0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
225 views8 pagesThe document contains multiple choice questions about the conformations and relative stabilities of various organic molecules, including alkanes, cycloalkanes, and halogenated derivatives. It tests the examinee's understanding of topics such as: preferred conformations (axial vs equatorial substituents), relative energies of different rotational isomers, relationship between structure and conformation (cis/trans, geometric isomers). The answers provided indicate the most stable conformation for each structure.
Original Description:
alkanes
Original Title
conformations
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document contains multiple choice questions about the conformations and relative stabilities of various organic molecules, including alkanes, cycloalkanes, and halogenated derivatives. It tests the examinee's understanding of topics such as: preferred conformations (axial vs equatorial substituents), relative energies of different rotational isomers, relationship between structure and conformation (cis/trans, geometric isomers). The answers provided indicate the most stable conformation for each structure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
225 views8 pagesConformations
Conformations
Uploaded by
rameshiitThe document contains multiple choice questions about the conformations and relative stabilities of various organic molecules, including alkanes, cycloalkanes, and halogenated derivatives. It tests the examinee's understanding of topics such as: preferred conformations (axial vs equatorial substituents), relative energies of different rotational isomers, relationship between structure and conformation (cis/trans, geometric isomers). The answers provided indicate the most stable conformation for each structure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 8
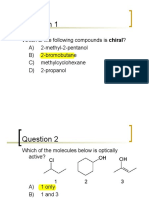
1.
The least stable conformation of butane is:
H H
3
C
H
H
H
H
3
C
H H
CH
3
H
CH
3 H
CH
3
H
H
H
H
H
3
C
CH
3
H
H
H
CH
3
H
H
CH
3
H
H
CH
3
I II III
IV V
H
A) I B) II C) III D) IV
E) V
2. The preferred conformation of cis -3-tert-butyl-1-methylcyclohexane is the one in which:
A) the tert-butyl group is axial and the methyl group is equatorial.
B) the methyl group is axial and the tert-butyl group is equatorial.
C) both groups are axial.
D) both groups are equatorial.
E) the molecule exists in a boat conformation.
3. What structure represents the most stable conformation of cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane?
H
H
3
C
H
CH
3
CH
3
H
H
H
3
C
H
CH
3
H
H
3
C
CH
3
H
CH
3
H
I II III
H
CH
3
H
H
3
C
V IV
A) I B) II C) III
D) IV
E) V
4. The most stable conformation of butane is:
H H
3
C
H
H
H
H
3
C
H H
CH
3
H
CH
3 H
CH
3
H
H
H
H
H
3
C
CH
3
H
H
H
CH
3
H
H
CH
3
H
H
CH
3
I II III
IV V
H
A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
CONFORMATIONS
5. The most stable conformation of 1,2-dibromoethane is:
H
Br H
H
Br
H
H Br
H
H
H
Br H H
Br
H
Br
H Br H
H
H
H
Br
Br H
H
H
Br
H
I II III
IV V
A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
6.
The most stable conformation of 2,3-dibromobutane, viewed through the C-2C-3 bond :
H
Br H
3
C
H
Br
H
3
C
H Br
CH
3
CH
3
H
Br H H
3
C
Br
CH
3
Br
H Br H
3
C
H
H
CH
3
Br
H H
3
C
Br
Br
H
H
3
C
I II III IV V
A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
7. The most stable conformation of 3-br omo-2-methylpentane, viewed through the
C-3C-4 bond (i.e., C-3 in the front, C-4 in the back):
Br H
CH(CH
3
)
2
H
CH
3
H
III
H
CH(CH
3
)
2
H
Br
CH
3 H
II
H Br
CH(CH
3
)
2
CH
3
H
H
I
CH(CH
3
)
2
Br
H
H
CH
3
H
IV
CH
3
H
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
H
Br
V
A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
8 . In the most stable conformation of cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane, the methyl groups are:
A) one axial, one equatorial.
B) both axial.
C) both equatorial.
D) alternating between being both axial and both equatorial.
E) None of the above
9. The most stable conformation of 3-br omo-2-methylpentane, viewed through the
C-2C-3 bond (i.e., C-2 in the front, C-3 in the back):
H
CH
2
CH
3
H
3
C
Br
CH
3 H
II
CH
3
H
CH
3
H
CH
3
Br
I
CH
3
H
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
H
Br
V
Br H
CH(CH
3
)
2
H
CH
3
H
III
CH
2
CH
3
Br
H
CH
3
CH
3
H
IV
A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
10. The most stable conformation of 2,3-dimethylpentane, viewed through the
C-2C-3 bond (i.e., C-2 in the front, C-3 in the back):
H
H H
3
C
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3 H
II
CH
3
H
CH
3
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
H
I
CH
3
H
CH
3
CH(CH
3
)
2
H
H
3
C
V
CH
3
H
CH(CH
3
)
2
CH
3
H
H
III
CH
3
H
CH
3
CH
3
H
H
3
CH
2
C
IV
A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
11. The most stable conformation of cis-1-tert-butyl-2-methylcyclohexane is the one in which:
A) the tert-butyl group is axial and the methyl group is equatorial.
B) the methyl group is axial and the tert-butyl group is equatorial.
C) both groups are axial.
D) both groups are equatorial.
E) the twist boat conformation is adopted.
12. The most stable conformation of trans-1-tert-butyl-2-methylcyclohexane is the one in which:
A) the tert-butyl group is axial and the methyl group is equatorial.
B) the methyl group is axial and the tert-butyl group is equatorial.
C) both groups are axial.
D) both groups are equatorial.
E) the molecule is in the half chair conformation.
13. The most stable conformation of trans-1-tert-butyl-3-methylcyclohexane is the one in which:
A) the tert-butyl group is axial and the methyl group is equatorial.
B) the methyl group is axial and the tert-butyl group is equatorial.
C) both groups are axial.
D) both groups are equatorial.
E) the twist boat conformation is adopted.
14. In the most stable conformation of cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane, the methyl groups are:
A) one axial, one equatorial.
B) both axial.
C) both equatorial.
D) alternating between being both axial and both equatorial.
E) None of the above
15. The most stable conformation for 1,2-ethanediol (ethylene glycol) is shown below. It is
the most stable conformation because:
OH H
H
H
OH
H
A) this corresponds to an anti conformation.
B) in general, gauche conformations possess the minimum energy.
C) it is stabilized by intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
D) it is a staggered conformation.
E) it has the highest energy of all the possibilities.
16. The graph below is a plot of the relative energies of the various conformations of:
0
o
60
o
120
o
180
o
240
o
300
o
360
o
R
e
l
a
t
i
v
e
e
n
e
r
g
y
Angle of rotation
A) Ethane
B) Propane
C) Chloroethane
D) 1-Chloropropane (C1-C2 rotation)
E) Butane (C1-C2 rotation)
17. The graph below is a plot of the relative energies of the various conformations of:
0
o
60
o
120
o
180
o
240
o
300
o
360
o
R
e
l
a
t
i
v
e
e
n
e
r
g
y
Angle of rotation
A) 2-chloropropane B) 1,3-dichloropropane
C) 2-methylpropane
D) Butane (C1-C2 rotation)
E) Butane (C2-C3 rotation)
18. Consider the graph below, which is a plot of the relative energies of the various
conformations of hexane, viewed through the C2-C3 bond. The conformations
corresponding to the 60
o
and 300
o
are:
0
o
60
o
120
o
180
o
240
o
300
o
360
o
R
e
l
a
t
i
v
e
e
n
e
r
g
y
Angle of rotation
A) Eclipsed B) Staggered, and gauche C) Staggered and anti
D) More stable than the conformation at 180
o
E) None of the above
19. Which conformation of trans-1-isopropyl-3-methylcyclohexane would be present in
greatest amount at equilibrium?
A) The conformation with the methyl group equatorial and the isopropyl group axial
B) The conformation with the methyl group axial and the isopropyl group equatorial
C) The conformation with both groups axial
D) The conformation with both groups equatorial
E) The twist boat conformation.
20. Consider the graph below, which is a plot of the relative energies of the various
conformations of 2,3-dimethylbutane, viewed through the C2-C3 bond. The
conformations corresponding to the 120
o
and 240
o
are:
0
o
60
o
120
o
180
o
240
o
300
o
360
o
R
e
l
a
t
i
v
e
e
n
e
r
g
y
Angle of rotation
A) Eclipsed, more stable than the conformation at 0
o
B) Eclipsed, more stable than the conformation at 180
o
C) Staggered, more stable than the conformation at 0
o
D) Staggered, less stable than the conformation at 180
o
E) Two of the above are true
21. Which conformation represents the most stable conformation of trans-1-bromo-4-
methylcyclohexane?
CH
3
Br
Br
CH
3
CH
3
Br
Br
H
3
C
Br
CH
3
I II III
IV V
A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
22. Which of the following can be described as cis isomers?
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
Cl
CH
3
Br
HO
CH
3
HO
Br
F
I II III IV V
A) I
B) II, V C) III, IV
D) I, III and IV
E) None of the above are cis isomers.
23. The least stable conformation of cyclohexane is the:
A) boat.
B) twist boat. C) chair. D) half-chair.
E) twist chair.
24. Which of the following can be described as trans isomers?
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
Cl
CH
3
Br
HO
CH
3
HO
Br
F
I II III IV V
E) None are trans isomers.
25. Which of the following will have the same energy after undergoing ring flip?
CH
2
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
Cl
CH
3
OH
HO
CH
3
HO
Br
F
I II III IV V
A) I
B) II, V C) III, IV
D) I, III and IV
A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
26. The twist boat conformation is the preferred conformation for this compound.
A) cis-1,4-Di-tert-butylcyclohexane
B) trans-1,4-Di-tert-butylcyclohexane
C) cis-1,3-Di-tert-butylcyclohexane
D) trans-1,2-Di-tert-butylcyclohexane
27. The structures
CH
3
H
CH
3
H
CH
3
H CH
3
H
represent:
A) a single compound.
B) Geometricalisomers. C) meso forms.
D) diastereomers.
E) conformational isomers.
28. cis-1,3-Dibromocyclohexane is represented by structure(s):
Br
H H
Br
Br
H
H
Br
H
Br
H
Br
I II III
A) I B) II C) III D) II and III
E) I and II
1: B 2: D 3: B
4: C 5: C 6: C 7: A
8: A
9: E 10: D
11: B 12: D 13: B 14: A 15: C
16:D
17: E 18: B 19: B 20: A
21: A
22: B
23: D
24: C
25: E 26: A
27: A 28: A
30. Draw the bond-line structural formula corresponding to the most stable conformation of
the following substance: trans-1-bromo-3-(1-methylpropyl)cyclohexane
30:
Br
31. Draw the Newman projection formula for the gauche conformation of the C2-C3 bond
in pentane.
31:
H H
CH
3
H
CH
2
CH
3 H
32. Draw the Newman projection formula for the most stable conformation of the C2-C3
bond in 3-methylpentane.
32:
H H
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
CH
3 H
29. What is the relationship between alcohols I and II?
H
CH
3
OH
H
H
CH
3
H
OH
I II
A) different conformations of the same compound. B) constitutional isomers.
C) enantiomers.
D) diastereomers.
E) identical.
29: D
You might also like
- Biologically Important Molecules: Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic AcidsDocument9 pagesBiologically Important Molecules: Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic AcidsJim Goetz100% (2)
- Manufacturing Processes For Engineering MaterialsDocument10 pagesManufacturing Processes For Engineering Materialsrmsamy125% (37)
- Practice Exam ChemDocument10 pagesPractice Exam Chemabhijit.salvekarNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryDocument9 pagesOxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryTarun Lfc Gerrard100% (1)
- NMR 1Document3 pagesNMR 1amitNo ratings yet
- Exercise With Ans FinalDocument24 pagesExercise With Ans Finald anjilappa25% (4)
- PMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIFrom EverandPMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Ch1 2 3 ExercisesDocument11 pagesCh1 2 3 ExercisesMancini100% (1)
- Stereochemistry QustionsDocument43 pagesStereochemistry QustionsSwaraj Paul100% (1)
- Chapter 15Document27 pagesChapter 15anastark100% (6)
- Stereochemistry 22Document21 pagesStereochemistry 22Ahmed SideegNo ratings yet
- Coordination MCQDocument11 pagesCoordination MCQSubhasish Sau100% (2)
- Stereo Chemistry QuestionsDocument19 pagesStereo Chemistry QuestionsfritzNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2 Practice Exam 1Document15 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2 Practice Exam 1KaybidoNo ratings yet
- Some Important Organic Information by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument2 pagesSome Important Organic Information by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry83% (6)
- CSIR UGC NET Model Question Papers Chemical SciencesDocument32 pagesCSIR UGC NET Model Question Papers Chemical SciencesShiksha PortalNo ratings yet
- NMR SpectrosDocument29 pagesNMR Spectroshareesh13h100% (1)
- Stereochemistry Basic Concepts Useful Notes For StudentsDocument26 pagesStereochemistry Basic Concepts Useful Notes For StudentsReddappaNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Cmpds AnskeyDocument6 pagesAromatic Cmpds AnskeyAaron LeeNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Chem 206: Fall Term, 2005, David A. EvansDocument22 pagesWelcome To Chem 206: Fall Term, 2005, David A. EvanseraborNo ratings yet
- Amines MCQDocument3 pagesAmines MCQaleena'No ratings yet
- ICSE Chemistry Board Paper19 PDFDocument9 pagesICSE Chemistry Board Paper19 PDFPrajakta DigheNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 32-235 Practice Questions For Exam #2: 2. Consider The SDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry 32-235 Practice Questions For Exam #2: 2. Consider The Ssweta KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Hydrocarbon (Q.B.) (MSC)Document14 pagesAromatic Hydrocarbon (Q.B.) (MSC)Raj ModiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Organic Chemistry SolomonDocument6 pagesChapter 9 Organic Chemistry SolomonSukhi Sohal0% (1)
- Organic Chemistry TestDocument1 pageOrganic Chemistry Testron971No ratings yet
- Module8 PDFDocument40 pagesModule8 PDFFaizan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Difficult Questions On Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesDifficult Questions On Organic Chemistrytarunbirbanga100% (1)
- Test1 Goc & Poc Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument3 pagesTest1 Goc & Poc Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry100% (1)
- General Organic Chemistry For IITDocument21 pagesGeneral Organic Chemistry For IITParas Thakur83% (6)
- Chem52 Su13 PracticeExam1ADocument11 pagesChem52 Su13 PracticeExam1Aamarka01No ratings yet
- Question Bank Class Xii (Chemistry) Unit 5: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument21 pagesQuestion Bank Class Xii (Chemistry) Unit 5: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Multiple Choice QuestionsSahilNo ratings yet
- Alcohols TestDocument2 pagesAlcohols TestAboahmed AliNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument16 pagesIsomerismAnusmita MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Amines Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen NEET Chemistry MCQs 6Document2 pagesAmines Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen NEET Chemistry MCQs 62003vinay50% (2)
- Chem 1040 Final Exam ReviewDocument8 pagesChem 1040 Final Exam ReviewUzair AliNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compound & MatallurgyDocument118 pagesCoordination Compound & MatallurgyMD MoonNo ratings yet
- Alcohols & EtherDocument18 pagesAlcohols & EtherRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Infrared Lecture 1Document49 pagesInfrared Lecture 1anthonyNo ratings yet
- Midterm II Key Chem 2312-003 F '12Document7 pagesMidterm II Key Chem 2312-003 F '12acb4039No ratings yet
- NMR HandoutDocument23 pagesNMR HandoutVirendra Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDocument11 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrosilias1973No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IIDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry IIRoberto SIlvaNo ratings yet
- Qoii0708 CO 17 TIFDocument34 pagesQoii0708 CO 17 TIFLovely Joysweet100% (2)
- Chapter 20 & 21 - Wade - NDDocument93 pagesChapter 20 & 21 - Wade - NDyonggyeNo ratings yet
- Chem Academy: Chemical BondingDocument4 pagesChem Academy: Chemical BondingEmraan EmmiNo ratings yet
- Questions Chapter 1-10 PDFDocument107 pagesQuestions Chapter 1-10 PDFrashidNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument22 pagesIsomerismShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- QOI0809 AlkenesDocument30 pagesQOI0809 Alkenesmtucker17No ratings yet
- Reaksi SN-1, SN-2, E-1, Dan E-2.Document64 pagesReaksi SN-1, SN-2, E-1, Dan E-2.Annik QurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Answer: (A) and (B)Document18 pagesAnswer: (A) and (B)Germaine Manangan100% (1)
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument29 pagesAldehydes and KetonesJiya singhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Alkene ReactivityDocument23 pagesChapter 8 - Alkene ReactivitySimran DhunnaNo ratings yet
- Caieee04fisica PDFDocument15 pagesCaieee04fisica PDFRafaelNo ratings yet
- HaloalkanesDocument13 pagesHaloalkanesChingYan TanNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alkenes: CC HX C HX C Markovnikov's OrientationDocument8 pagesReactions of Alkenes: CC HX C HX C Markovnikov's OrientationMarc RitzNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry MCQs - Questions - Paper 1Document7 pagesSurface Chemistry MCQs - Questions - Paper 1krishna prasad ghantaNo ratings yet
- Conformation Practice QuestionDocument5 pagesConformation Practice Questionkunalpandya92No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 7th Edition Carey Test BankDocument15 pagesOrganic Chemistry 7th Edition Carey Test BankEunice Cheslock100% (34)
- Organic Chemistry 7th Edition Carey Test Bank download pdf full chapterDocument39 pagesOrganic Chemistry 7th Edition Carey Test Bank download pdf full chapterloranereigo100% (1)
- Iwaste Hardness PDFDocument5 pagesIwaste Hardness PDFOnyx XynoNo ratings yet
- C.T - 1 (2023-24) CL-12 ChemDocument1 pageC.T - 1 (2023-24) CL-12 ChemShrutiveda SarkarNo ratings yet
- Gas Lift in Heavy Oil ManuscriptDocument9 pagesGas Lift in Heavy Oil Manuscriptmahmoud korieshNo ratings yet
- CNC ToolingDocument3 pagesCNC Toolingkranthi142434No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Higher Tier Paper 2Document32 pagesChemistry: Higher Tier Paper 2Mohamad HabbalNo ratings yet
- 5b Mole Conversions WorksheetDocument3 pages5b Mole Conversions Worksheetapi-369690183100% (1)
- Polymers Based Type of Monomer Involved in The Structure: Homopolymer and CopolymerDocument5 pagesPolymers Based Type of Monomer Involved in The Structure: Homopolymer and CopolymerFlorelyn GocotanoNo ratings yet
- The Potential of Organometallic Complexes in Medicinal Chemistry PDFDocument8 pagesThe Potential of Organometallic Complexes in Medicinal Chemistry PDFArijit dasguptaNo ratings yet
- The Consep AcaciaDocument7 pagesThe Consep AcaciaPrincess Ruwarashe Courteney MunyoroNo ratings yet
- Copy (2) of ASTM - A90A 90M PDFDocument4 pagesCopy (2) of ASTM - A90A 90M PDFVenreplast PueblaNo ratings yet
- F321 CalculationsDocument21 pagesF321 CalculationsDoc_CrocNo ratings yet
- CCUS Chap - 6 030521Document18 pagesCCUS Chap - 6 030521Ali AltowilibNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 CBSE Hots Chemistry XII 2009Document9 pagesUnit 13 CBSE Hots Chemistry XII 2009kartikey jainNo ratings yet
- Review Paper - Hydrogen Embrittlement in Coated Steel Fasteners - Brahimi-2006Document37 pagesReview Paper - Hydrogen Embrittlement in Coated Steel Fasteners - Brahimi-2006Son NguyenNo ratings yet
- Iso 6634 1982Document8 pagesIso 6634 1982odota deoNo ratings yet
- Engineering ChemistryDocument293 pagesEngineering ChemistrySun Tzu67% (3)
- General Organic and Biological Chemistry 2Nd Edition Frost Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesGeneral Organic and Biological Chemistry 2Nd Edition Frost Test Bank Full Chapter PDFBradMartiniczn100% (13)
- Titanium.: Chemical PropertiesDocument3 pagesTitanium.: Chemical PropertiesIna TamayoNo ratings yet
- Sure ND IranDocument15 pagesSure ND IranB. Srini VasanNo ratings yet
- Is 1786 2008Document22 pagesIs 1786 2008Jeevan Kumar ShettyNo ratings yet
- AISI 1018 Mild Low Carbon Steel PDFDocument3 pagesAISI 1018 Mild Low Carbon Steel PDFSandip JawalkarNo ratings yet
- WTPCDocument13 pagesWTPCsauyingNo ratings yet
- Acs Iecr 0c05041rtyDocument25 pagesAcs Iecr 0c05041rtyAmir HassanNo ratings yet
- Approval Ballast eDocument7 pagesApproval Ballast eAbd ZouhierNo ratings yet
- Metakaolin ClayDocument3 pagesMetakaolin ClayMineral Processing SucofindoNo ratings yet
- Claus Plants Prove FlexibleDocument3 pagesClaus Plants Prove Flexiblebakhtiari_afNo ratings yet
- 02 WholeDocument333 pages02 WholeKatherine Camacho ZorogastúaNo ratings yet
- A Green Chemistry Approach To Mercury ControlDocument7 pagesA Green Chemistry Approach To Mercury ControlDennis Daniel Condori EspilcoNo ratings yet