Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiratory Pharmacology For Asthma
Respiratory Pharmacology For Asthma
Uploaded by
kman0722Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Respiratory Tract PharmacologyDocument68 pagesRespiratory Tract PharmacologyRohaan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Making Sense of ProprioceptionDocument10 pagesMaking Sense of Proprioceptionjuanito1979No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Reading AssignmentDocument39 pagesChapter 1 Reading Assignmentkman07220% (1)
- Board Prep-COMLEX Level 1 ResourcesDocument37 pagesBoard Prep-COMLEX Level 1 Resourceskman0722100% (1)
- ACOG PRACTICE BULLETIN 203chronic Hypertension in Pregnancy2019Document25 pagesACOG PRACTICE BULLETIN 203chronic Hypertension in Pregnancy2019ange100% (1)
- (3 Volume Set) Zelah Pengilley-Scott-Brown's Otorhinolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery-CRC Press (2008)Document4 pages(3 Volume Set) Zelah Pengilley-Scott-Brown's Otorhinolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery-CRC Press (2008)Dede Fatmawati0% (1)
- Athma, COPD and Cough AgentsDocument71 pagesAthma, COPD and Cough AgentsBriana NdayisabaNo ratings yet
- 2&3-Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDocument58 pages2&3-Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDKishan SethNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDocument71 pagesDrugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDShabnam Binte AlamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4, 5 - Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDocument57 pagesLecture 4, 5 - Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDBalakrishnan Thangaraj100% (1)
- All DrugsDocument482 pagesAll DrugsJessica IbañezNo ratings yet
- Antiasthamatics Cology - (Yash Vardhan Sharma)Document50 pagesAntiasthamatics Cology - (Yash Vardhan Sharma)YASH VARDHAN SHARMANo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 - Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma L0 COPD - EditedDocument42 pagesLecture 14 - Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma L0 COPD - EditedAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Asthma COPDDocument55 pagesDrugs Used in Asthma COPDNitikaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PharmacologyDocument89 pagesRespiratory PharmacologyEka PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Adrenergic Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesDrugs Affecting The Adrenergic Nervous SystemJah SuNo ratings yet
- Bronchodilators and Other Respiratory AgentsDocument61 pagesBronchodilators and Other Respiratory Agentsone_nd_onlyuNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Drugs: BronchodilatorsDocument16 pagesRespiratory System Drugs: Bronchodilatorsngoto88No ratings yet
- PNS Drugs, Veterinary Use.Document6 pagesPNS Drugs, Veterinary Use.rqu3l0% (1)
- Asthma 2020Document44 pagesAsthma 2020Mehdy ElghaeiNo ratings yet
- Antiasthamatic DrugsDocument72 pagesAntiasthamatic DrugsDeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System AgentsDocument120 pagesAutonomic Nervous System Agentscoosa liquors100% (1)
- Antiasthmatic DrugsDocument36 pagesAntiasthmatic DrugsJannah ZahraaNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument3 pagesPharmacologyMohd Afiq AizuddinNo ratings yet
- Dr. Elly Nurus Sakinah 2010Document23 pagesDr. Elly Nurus Sakinah 2010udunk adhinkNo ratings yet
- Drug ClassesDocument73 pagesDrug Classesloglesb1100% (1)
- Respiratory NotesDocument6 pagesRespiratory Notesapi-324425075No ratings yet
- Antiasthma and Cough MedicineDocument47 pagesAntiasthma and Cough MedicineYordanos EshetuNo ratings yet
- GIT Dr. Jahangir Kaboutari Assistant Professor of Pharmacology Faulty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Shahrekord. Shahrekord. IranDocument110 pagesGIT Dr. Jahangir Kaboutari Assistant Professor of Pharmacology Faulty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Shahrekord. Shahrekord. IranUrsula HilleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document5 pagesLecture 6Grafu Andreea AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument27 pagesRespiratory SystemSowndariyaNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic DrugsDocument2 pagesAdrenergic DrugsSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System AgentsDocument14 pagesAutonomic Nervous System AgentsRhenier S. Ilado100% (1)
- Drugs Used To Treat Asthma 2010Document48 pagesDrugs Used To Treat Asthma 2010nk999999No ratings yet
- Bronchodilators and Other Respiratory DrugsDocument44 pagesBronchodilators and Other Respiratory DrugsastriedamaliaamanatNo ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument37 pagesASTHMAGian Carlo RabagoNo ratings yet
- Asthma and Anti-Asthmatic DrugsDocument26 pagesAsthma and Anti-Asthmatic DrugsHonour JamesNo ratings yet
- Status Asthmaticus DR Divya JainDocument45 pagesStatus Asthmaticus DR Divya JainParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- Drugs Effecting Respiratory System (MSCN)Document63 pagesDrugs Effecting Respiratory System (MSCN)Irshad SahilNo ratings yet
- Pharma ChartsDocument33 pagesPharma ChartsNooreen Hussain100% (1)
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument46 pagesBronchial AsthmaKhor Kee GuanNo ratings yet
- Obat SimpatomimetikDocument42 pagesObat SimpatomimetiknatinlalaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology RCR1 RespiratoryDocument10 pagesPharmacology RCR1 RespiratoryeamcrawleyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Agents.2015Document75 pagesRespiratory Agents.2015sarwatNo ratings yet
- Drug Acting in Respiratory SystemDocument30 pagesDrug Acting in Respiratory SystemYunita WidyastutiNo ratings yet
- NEONATAL MedicationDocument10 pagesNEONATAL Medicationfalodun miracleNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Pharmacology: - Pharmacotherapy of Bronchial AsthmaDocument47 pagesRespiratory Pharmacology: - Pharmacotherapy of Bronchial AsthmaKadye DersoNo ratings yet
- ANS PharmacologyDocument24 pagesANS PharmacologySOMOSCONo ratings yet
- Epinephrine: Drug Site of Action Effect Use Adverse EffectsDocument12 pagesEpinephrine: Drug Site of Action Effect Use Adverse EffectsChristina SantosNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used For Bronchial AsthmaDocument81 pagesDrugs Used For Bronchial AsthmaJinTaoNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia: Russell D. Briggs, M.D. Francis B. Quinn, M.D. February 2, 2000Document68 pagesAnesthesia: Russell D. Briggs, M.D. Francis B. Quinn, M.D. February 2, 2000Shravan TuragaNo ratings yet
- Antiadrenergic Drugs - DrdhritiDocument35 pagesAntiadrenergic Drugs - DrdhritiDr. Dhriti Kumar BrahmaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument35 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemAyat KhalilNo ratings yet
- Onchial AsthmaDocument13 pagesOnchial Asthmaram krishna100% (1)
- Definition of Bronchial AsthmaDocument49 pagesDefinition of Bronchial AsthmaVikas GoyalNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Pharmacology Histamines: Autocoids. Greek For "Self Remedy"Document4 pagesRespiratory Pharmacology Histamines: Autocoids. Greek For "Self Remedy"jchyeung20No ratings yet
- 6 Asthma and Copd HandoutDocument10 pages6 Asthma and Copd HandoutMd Sakil AminNo ratings yet
- ASTHMA AND COPD PharmacologyDocument42 pagesASTHMA AND COPD Pharmacologycarla osbourneNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]From EverandBasic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- THE BUTEYKO METHOD (Translated): The secret of controlled breathing for health, well-being and vitalityFrom EverandTHE BUTEYKO METHOD (Translated): The secret of controlled breathing for health, well-being and vitalityNo ratings yet
- I1949 8357 7 2 230 PDFDocument4 pagesI1949 8357 7 2 230 PDFkman0722No ratings yet
- Physician Care ManagerDocument3 pagesPhysician Care Managerkman0722No ratings yet
- TABLE 254-11 - Converting From Parenteral To Oral AnticoagulanDocument2 pagesTABLE 254-11 - Converting From Parenteral To Oral Anticoagulankman0722No ratings yet
- Educational Summary Report 10454Document6 pagesEducational Summary Report 10454kman0722No ratings yet
- Uptodate Access GuideDocument20 pagesUptodate Access Guidekman0722No ratings yet
- Postpartum HemorrhageDocument7 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhagekman0722No ratings yet
- 003 PDFDocument28 pages003 PDFkman0722No ratings yet
- 004 PDFDocument24 pages004 PDFkman0722No ratings yet
- 005 PDFDocument31 pages005 PDFkman0722No ratings yet
- 006 PDFDocument26 pages006 PDFkman0722No ratings yet
- Career Choices PDFDocument1 pageCareer Choices PDFkman0722No ratings yet
- Medicare & Home Health CareDocument32 pagesMedicare & Home Health Carekman0722No ratings yet
- Relationship Maintenance and Dissolution: Christopher R. Agnew and Laura E. VanderdriftDocument24 pagesRelationship Maintenance and Dissolution: Christopher R. Agnew and Laura E. Vanderdriftkman0722No ratings yet
- Enhancing PCP Specialist CommunicationDocument21 pagesEnhancing PCP Specialist Communicationkman0722100% (1)
- Name: NIM: Class:: Medical InstrumentsDocument9 pagesName: NIM: Class:: Medical InstrumentsNessyaa SyahnaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 2Document0 pagesJurnal 2Seftiana SaftariNo ratings yet
- Bone Healing and Non UnionsDocument50 pagesBone Healing and Non UnionsFelicia BockNo ratings yet
- Ortho - Prostho RelationshipDocument40 pagesOrtho - Prostho RelationshipAshis Biswas100% (1)
- General Dentist Qualifying Examination Blueprint (Nature & Contents of The Test)Document2 pagesGeneral Dentist Qualifying Examination Blueprint (Nature & Contents of The Test)ShifzNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 14 Pain Assessment Sheet Worksheet 14 Pain Assessment SheetDocument18 pagesWorksheet 14 Pain Assessment Sheet Worksheet 14 Pain Assessment SheetSinta Mul16No ratings yet
- Peripheral Intervention: Ardhiana KasabaDocument36 pagesPeripheral Intervention: Ardhiana KasabaFitri ShabrinaNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine Programs ListDocument96 pagesFamily Medicine Programs ListNilay BhattNo ratings yet
- Uniform ESRD Transient Hemodialysis FormDocument3 pagesUniform ESRD Transient Hemodialysis FormacqueNo ratings yet
- Nle MCN Road To SuccessDocument59 pagesNle MCN Road To SuccessKaye PatanindagatNo ratings yet
- Articulo Hipoxia BDocument11 pagesArticulo Hipoxia BAlgy Emiro Vergara MendozaNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of High Risk Neonates DrLawHN PDFDocument45 pagesAssessment and Management of High Risk Neonates DrLawHN PDFShiva KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Thoracic Outlet SyndromeDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Thoracic Outlet SyndromeDony Astika WigunaNo ratings yet
- Seattle Children's - 2009 Community Benefit ReportDocument32 pagesSeattle Children's - 2009 Community Benefit ReportJeneen CoydanNo ratings yet
- Birth Plan WebDocument3 pagesBirth Plan WebSarah BoyeNo ratings yet
- Bedpans and UrinalsDocument4 pagesBedpans and UrinalsCham De Leon50% (4)
- Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesDaftar PustakaInggrid RahletsNo ratings yet
- 6 SbarDocument11 pages6 Sbarsathish kumarNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Values Case Study 2Document3 pagesArterial Blood Gas Values Case Study 2julissaNo ratings yet
- (NLM) Nursing Specialization PPT True (Am)Document120 pages(NLM) Nursing Specialization PPT True (Am)kimchi girlNo ratings yet
- Wrights Stain Diff Quick Manual MethDocument7 pagesWrights Stain Diff Quick Manual MethJose CisnerosNo ratings yet
- Musculosleketal Risk Assesment Among Nurses in Pateint Manual Handling in Hospital Wards - A Cross Sectional StudyDocument10 pagesMusculosleketal Risk Assesment Among Nurses in Pateint Manual Handling in Hospital Wards - A Cross Sectional StudyCureusNo ratings yet
- GEHealthcare Brochure - Reusable Temperature Probes PDFDocument4 pagesGEHealthcare Brochure - Reusable Temperature Probes PDFHomeroPerezNo ratings yet
- Txcindia - Gov.in - Report On Medical TextilesDocument66 pagesTxcindia - Gov.in - Report On Medical TextilesPARMAR14107735No ratings yet
- Crisis Trauma: WWW - Eastzonemedico.co M WWW - Eastzonemedico.inDocument14 pagesCrisis Trauma: WWW - Eastzonemedico.co M WWW - Eastzonemedico.inswipetoplay32No ratings yet
- SMLE Sections With Mastery Level Aug 2020Document22 pagesSMLE Sections With Mastery Level Aug 2020aslyNo ratings yet
- Critical Care NursingDocument5 pagesCritical Care NursingMK BelitungNo ratings yet
Respiratory Pharmacology For Asthma
Respiratory Pharmacology For Asthma
Uploaded by
kman0722Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Respiratory Pharmacology For Asthma
Respiratory Pharmacology For Asthma
Uploaded by
kman0722Copyright:
Available Formats
Respiratory Pharmacology for Asthma
P
a
t
h
o
p
h
y
s
i
o
l
o
g
y
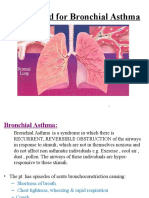
Bronchial Asthma
-Airway inflammation
-Bronchial Hyperreactivity
allergens, chemicals, Exercise, NSAIDS, infection
Symptoms
Chest tightness, bronchoconstriciton, secretions,
cought, wheeze, > decreased FEV1
Autopsy Histology
Epithelial Sloughing
Hypertrophy/hyperplasia airway SM
Airway thickness by inflammation, edema
mucous gland hypertrophy, hypersecretionmucous
plugginghyperinflation
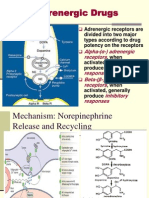
Regulation of Bronchial Smooth Muscle
Resting tone sm. muscle affected by vagal (PNS)
innervation
* irritants cause vagal reflex-ACh
bronchoconstriction/increased mucous,
mast cell release
No sympathetic innervation, noninnervated beta2
receptors present
* activated by circulating catecholamines
bronchodilation mast cell release
increase ciliary activity (via cAMP)
Nonadrenergic/noncholinergic mediators from
sensory C fibers
* release substance P (increase mucous/permeability)
* release neurokinin A (spasmogen)
Asthma Attack
Early or immediate phase EAR
* bronchoconstriction due to preformed
mast cell mediator release
* Decreased FEV1
Late Phase LAR
* occurs in 50 % of adult asthmatic
* due to progressive inflammatory and allergic reaction
-Infiltration of Th2release cytokines
- Eosinophils-epithelial damage
*continued release of mediators and activation of C receptors
* Decreased FEV1
Reliever Drugs-Bronchodilator action plus effects on mucous production, cilia, mast cell mediator release
Drug Mechanism Pharm Use Adverse
M
e
t
h
y
l
x
a
n
t
h
i
n
e
s
Theophylline
Inhibits Phosphodiesterase thus cAMP
by its degradation
Blocks adenosine receptor
Slower onset/less potency than drugs
es skeletal muscle contractility/
muscle fatigue
mucociliary clearance
GI
CNS stimulation (seizures)
Cardiac stimulation (arrhythmias)
Aminophylline
H2O soluble salt form (of theophylline)
for IV admin
N
o
n
-
s
e
l
e
c
t
i
v
e
S
y
m
p
a
t
h
o
m
i
m
e
t
i
c
s
Epinephrine
Not selective for Beta2
OTC available but not recommended:
-short duration of axn
-B1 HR
Acute asthmatic emergency: admin SC
, -1 activity (tachycardia, arrhythmias)
Not used
Isproterenol
Not selective for beta2
Onset of action: 2 to 5 min
Dosing: up to 6 xs daily
OTC available but not recommended:
-short duration of axn
-B1 HR
-1 activity (arrhythmia)
Not used
Drug Mechanism Pharm Use Adverse
S
y
m
p
a
t
h
o
m
i
m
e
t
i
c
s
S
e
l
e
c
t
i
v
e
B
e
t
a
2
A
g
o
n
i
s
t
s
(
S
H
O
R
T
A
C
T
I
N
G
)
Albuterol
(SABA)
Racemic mixture: S & R enantiomers
Bind beta2 receptors- rate of cAMP
synthesis by adenyl cyclase
relax airway smooth muscle
inhibit release of bronchoconstrictor
mediators from mast cells
Additional possible actions:
inhibit microvascular leakage
increase mucociliary transport by ing
ciliary activity
Onset of axn (via inhalation)
-initial = < 5 min
-max effect = 10-15 min
Duration of axn (via inhalation): 3 to 4 hr
Dosing: Q4-6h
Only agents immediately effective in
EAR/Acute Asthma attacks
Aerosol inhalation [preferred]
Selective -2 drugs [preferred]
S-albuterol may cause paradoxical
bronchospasm by Ca in smooth muscle
PO (same as terbutaline):
-skeletal muscle tremor
-nervousness
-weakness
-peripheral vasodilation dose related
Levalbuterol
(SABA)
R enantiomer (which binds -2 receptor
100xs > S)
Formulation:
-avail as inhalation soln via neb
Causes slightly less cardiac stimulation
(than albuterol)
Terbutaline
(SABA)
Acute asthmatic emergencies: admin SC
PO (same as albuterol):
-skeletal muscle tremor
-nervousness
-weakness
-peripheral vasodilation dose related
S
y
m
p
a
t
h
o
m
i
m
e
t
i
c
s
S
e
l
e
c
t
i
v
e
B
e
t
a
2
A
g
o
n
i
s
t
s
L
O
N
G
A
C
T
I
N
G
Salmeterol
(LABA)
Formulations:
-salmeterol +/- fluticasone (Advair)
Onset of action: 10 to 20 min
Duration of axn: 12 hrs
-long duration blocks both early & late
asthmatic response when used
chronically
Dosing: Q12h
Due to its slow onset:
-prophylactic control (esp. nocturnal
attacks)
DO NOT USE for acute attacks
FDA Warning (2003): small, but
significant asthma-related deaths
Formoterol
(LABA)
Faster onset of axn
Duration of axn: 12 hrs
-long duration blocks both early and late
asthmatic response when used
chronically
*NOTE: B-Agonist Chronic Tx Concerns
-tolerance: tachyphylaxis, receptor
down-regulation, peak effect,
duration of axn
-rebound bronchoconstriction
-worsening asthma symptoms
- bronchial hyperreactivity
A
n
t
i
m
u
s
c
a
r
i
n
i
c
s
Ipratropium
Block ACh receptors in airway
NOTE: ACh is released form Vagus nerve
endings and results in contraction of
smooth muscle and ed secretion of
mucus
-----------
Blocks muscarinic receptor
sputum volume w/o viscosity
Claimed not to inhibit mucociliary
clearance
Onset (slow): 1-2 hrs
-NOT for emergencies
Duration (modest bronchodilator): 4-6 h
Asthma
-usually combined with beta-2 drug in
asthma (ipratropium + albuterol)
Respiratory dryness
Irritation
Cough
Tiotropium (Spiriva)
Onset (slow)
Duration of axn: 24 hrs
Formulation: PO inhalation (dry powder)
COPD
-LA anticholinergic bronchodilator
Controller Drugs: Anti-inflammatory
Drug Mechanism Pharm Use Adverse
C
o
r
t
i
c
o
s
t
e
r
o
i
d
s
Specific:
Beclomethasone
Budesonide
Ciclesonide
Flunisolide
Fluticasone
Mometasone
Triamcinolone
Inhibit expression of genes for many
inflammatory proteins via intracellular
receptor activation
Stabilize mast cells
synthesis of PGs/leukotrienes
Immunosuppressive ( WBCs/
eosinophils/IgE Ab production)
PO/IV for acute conditions
Aerosol (inhalation):
-dysphonia
-oropharyngeal candidiasis
M
a
s
t
C
e
l
l
S
t
a
b
i
l
i
z
e
r
s
Cromolyn/
Nedocromil
Inhibit antigen-induced release of
mediators from sensitized mast cells
Inhibits sensory nerve reflexes
Inhibits activation of membrane Cl
channels to dec Ca activation
Long term use lessens EAR and LAR
Lessens response to EIA/cold air/
allergens
Formulation:
-nebulizer/aerosol spray
Asthma (prophylactic use) NOT a
bronchodilator
Allergic rhinitis (nasal spray)
Food allergy in GI tract (PO soln)
Local irritation (eyes, nose)
Bronchospasm/cough/wheezing
Bad taste
HA/dizziness
L
e
u
k
o
t
r
i
e
n
e
I
n
h
i
b
i
t
o
r
s
(
A
n
t
i
-
L
e
u
k
o
t
r
i
e
n
e
s
)
Zafirlukast
Antagonism of the LTD4 receptor binding
Leukotriene receptor (cysLT1)
antagonists; NOTE: cysLT1 is the receptor
1 for LTD4
NOTE:
-LTC4, LTD4 are potent inflammatory
mediators synthesized by mast cells
-LTB4 is a potent neutrophil
chemoattractant
Activity begins w/1
st
dose
-requires days weeks for full effect
Drug Ix:
-inhibits P450 enzymes (2C9- phenytoin,
warfarin) and (3A4)
Prophylactic/chronic control asthma
Used to reduce/control chronic
inflammation of asthma AND-
Allow reduction of reliever/steroid drug
dosages
Aspirin-induced asthma
GI (n/v)
HA/dizziness
LFTs
Myalgia/back pain
Infection
Note: Rare eosinophilic vasculitis/
granuloma formation, Churg-Strauss
syndrome, observed w/this drug class
Montelukast (Singulair)
**STAR DRUG***
More specific cys-LT1 blocker (esp. LTD4)
Drug Ix: none significant to date
HA/dizziness
Rash
GI
Nasal/ear/throat/resp congestion/infxns
M
o
A
b
Omalizumab
Humanized MoAb binds circulating IgE
Prevents IgE binding on mast cells
Admin: SC Q3-4 weeks based on body wt
and serum IgE level
Peak serum conc.: 7-8 days
t : 26 days
Moderate-severe persistent asthma
uncontrolled by inhaled steroids
Annual cost: $10-12,000
Injection-site rxns
Risk anaphylaxis/anaphylactoid rxn
You might also like
- Respiratory Tract PharmacologyDocument68 pagesRespiratory Tract PharmacologyRohaan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Making Sense of ProprioceptionDocument10 pagesMaking Sense of Proprioceptionjuanito1979No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Reading AssignmentDocument39 pagesChapter 1 Reading Assignmentkman07220% (1)
- Board Prep-COMLEX Level 1 ResourcesDocument37 pagesBoard Prep-COMLEX Level 1 Resourceskman0722100% (1)
- ACOG PRACTICE BULLETIN 203chronic Hypertension in Pregnancy2019Document25 pagesACOG PRACTICE BULLETIN 203chronic Hypertension in Pregnancy2019ange100% (1)
- (3 Volume Set) Zelah Pengilley-Scott-Brown's Otorhinolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery-CRC Press (2008)Document4 pages(3 Volume Set) Zelah Pengilley-Scott-Brown's Otorhinolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery-CRC Press (2008)Dede Fatmawati0% (1)
- Athma, COPD and Cough AgentsDocument71 pagesAthma, COPD and Cough AgentsBriana NdayisabaNo ratings yet
- 2&3-Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDocument58 pages2&3-Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDKishan SethNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDocument71 pagesDrugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDShabnam Binte AlamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4, 5 - Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDocument57 pagesLecture 4, 5 - Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDBalakrishnan Thangaraj100% (1)
- All DrugsDocument482 pagesAll DrugsJessica IbañezNo ratings yet
- Antiasthamatics Cology - (Yash Vardhan Sharma)Document50 pagesAntiasthamatics Cology - (Yash Vardhan Sharma)YASH VARDHAN SHARMANo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 - Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma L0 COPD - EditedDocument42 pagesLecture 14 - Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma L0 COPD - EditedAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Asthma COPDDocument55 pagesDrugs Used in Asthma COPDNitikaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PharmacologyDocument89 pagesRespiratory PharmacologyEka PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Adrenergic Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesDrugs Affecting The Adrenergic Nervous SystemJah SuNo ratings yet
- Bronchodilators and Other Respiratory AgentsDocument61 pagesBronchodilators and Other Respiratory Agentsone_nd_onlyuNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Drugs: BronchodilatorsDocument16 pagesRespiratory System Drugs: Bronchodilatorsngoto88No ratings yet
- PNS Drugs, Veterinary Use.Document6 pagesPNS Drugs, Veterinary Use.rqu3l0% (1)
- Asthma 2020Document44 pagesAsthma 2020Mehdy ElghaeiNo ratings yet
- Antiasthamatic DrugsDocument72 pagesAntiasthamatic DrugsDeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System AgentsDocument120 pagesAutonomic Nervous System Agentscoosa liquors100% (1)
- Antiasthmatic DrugsDocument36 pagesAntiasthmatic DrugsJannah ZahraaNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument3 pagesPharmacologyMohd Afiq AizuddinNo ratings yet
- Dr. Elly Nurus Sakinah 2010Document23 pagesDr. Elly Nurus Sakinah 2010udunk adhinkNo ratings yet
- Drug ClassesDocument73 pagesDrug Classesloglesb1100% (1)
- Respiratory NotesDocument6 pagesRespiratory Notesapi-324425075No ratings yet
- Antiasthma and Cough MedicineDocument47 pagesAntiasthma and Cough MedicineYordanos EshetuNo ratings yet
- GIT Dr. Jahangir Kaboutari Assistant Professor of Pharmacology Faulty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Shahrekord. Shahrekord. IranDocument110 pagesGIT Dr. Jahangir Kaboutari Assistant Professor of Pharmacology Faulty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Shahrekord. Shahrekord. IranUrsula HilleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document5 pagesLecture 6Grafu Andreea AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument27 pagesRespiratory SystemSowndariyaNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic DrugsDocument2 pagesAdrenergic DrugsSunshine_Bacla_4275No ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System AgentsDocument14 pagesAutonomic Nervous System AgentsRhenier S. Ilado100% (1)
- Drugs Used To Treat Asthma 2010Document48 pagesDrugs Used To Treat Asthma 2010nk999999No ratings yet
- Bronchodilators and Other Respiratory DrugsDocument44 pagesBronchodilators and Other Respiratory DrugsastriedamaliaamanatNo ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument37 pagesASTHMAGian Carlo RabagoNo ratings yet
- Asthma and Anti-Asthmatic DrugsDocument26 pagesAsthma and Anti-Asthmatic DrugsHonour JamesNo ratings yet
- Status Asthmaticus DR Divya JainDocument45 pagesStatus Asthmaticus DR Divya JainParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- Drugs Effecting Respiratory System (MSCN)Document63 pagesDrugs Effecting Respiratory System (MSCN)Irshad SahilNo ratings yet
- Pharma ChartsDocument33 pagesPharma ChartsNooreen Hussain100% (1)
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument46 pagesBronchial AsthmaKhor Kee GuanNo ratings yet
- Obat SimpatomimetikDocument42 pagesObat SimpatomimetiknatinlalaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology RCR1 RespiratoryDocument10 pagesPharmacology RCR1 RespiratoryeamcrawleyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Agents.2015Document75 pagesRespiratory Agents.2015sarwatNo ratings yet
- Drug Acting in Respiratory SystemDocument30 pagesDrug Acting in Respiratory SystemYunita WidyastutiNo ratings yet
- NEONATAL MedicationDocument10 pagesNEONATAL Medicationfalodun miracleNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Pharmacology: - Pharmacotherapy of Bronchial AsthmaDocument47 pagesRespiratory Pharmacology: - Pharmacotherapy of Bronchial AsthmaKadye DersoNo ratings yet
- ANS PharmacologyDocument24 pagesANS PharmacologySOMOSCONo ratings yet
- Epinephrine: Drug Site of Action Effect Use Adverse EffectsDocument12 pagesEpinephrine: Drug Site of Action Effect Use Adverse EffectsChristina SantosNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used For Bronchial AsthmaDocument81 pagesDrugs Used For Bronchial AsthmaJinTaoNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia: Russell D. Briggs, M.D. Francis B. Quinn, M.D. February 2, 2000Document68 pagesAnesthesia: Russell D. Briggs, M.D. Francis B. Quinn, M.D. February 2, 2000Shravan TuragaNo ratings yet
- Antiadrenergic Drugs - DrdhritiDocument35 pagesAntiadrenergic Drugs - DrdhritiDr. Dhriti Kumar BrahmaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument35 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemAyat KhalilNo ratings yet
- Onchial AsthmaDocument13 pagesOnchial Asthmaram krishna100% (1)
- Definition of Bronchial AsthmaDocument49 pagesDefinition of Bronchial AsthmaVikas GoyalNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Pharmacology Histamines: Autocoids. Greek For "Self Remedy"Document4 pagesRespiratory Pharmacology Histamines: Autocoids. Greek For "Self Remedy"jchyeung20No ratings yet
- 6 Asthma and Copd HandoutDocument10 pages6 Asthma and Copd HandoutMd Sakil AminNo ratings yet
- ASTHMA AND COPD PharmacologyDocument42 pagesASTHMA AND COPD Pharmacologycarla osbourneNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]From EverandBasic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- THE BUTEYKO METHOD (Translated): The secret of controlled breathing for health, well-being and vitalityFrom EverandTHE BUTEYKO METHOD (Translated): The secret of controlled breathing for health, well-being and vitalityNo ratings yet
- I1949 8357 7 2 230 PDFDocument4 pagesI1949 8357 7 2 230 PDFkman0722No ratings yet
- Physician Care ManagerDocument3 pagesPhysician Care Managerkman0722No ratings yet
- TABLE 254-11 - Converting From Parenteral To Oral AnticoagulanDocument2 pagesTABLE 254-11 - Converting From Parenteral To Oral Anticoagulankman0722No ratings yet
- Educational Summary Report 10454Document6 pagesEducational Summary Report 10454kman0722No ratings yet
- Uptodate Access GuideDocument20 pagesUptodate Access Guidekman0722No ratings yet
- Postpartum HemorrhageDocument7 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhagekman0722No ratings yet
- 003 PDFDocument28 pages003 PDFkman0722No ratings yet
- 004 PDFDocument24 pages004 PDFkman0722No ratings yet
- 005 PDFDocument31 pages005 PDFkman0722No ratings yet
- 006 PDFDocument26 pages006 PDFkman0722No ratings yet
- Career Choices PDFDocument1 pageCareer Choices PDFkman0722No ratings yet
- Medicare & Home Health CareDocument32 pagesMedicare & Home Health Carekman0722No ratings yet
- Relationship Maintenance and Dissolution: Christopher R. Agnew and Laura E. VanderdriftDocument24 pagesRelationship Maintenance and Dissolution: Christopher R. Agnew and Laura E. Vanderdriftkman0722No ratings yet
- Enhancing PCP Specialist CommunicationDocument21 pagesEnhancing PCP Specialist Communicationkman0722100% (1)
- Name: NIM: Class:: Medical InstrumentsDocument9 pagesName: NIM: Class:: Medical InstrumentsNessyaa SyahnaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 2Document0 pagesJurnal 2Seftiana SaftariNo ratings yet
- Bone Healing and Non UnionsDocument50 pagesBone Healing and Non UnionsFelicia BockNo ratings yet
- Ortho - Prostho RelationshipDocument40 pagesOrtho - Prostho RelationshipAshis Biswas100% (1)
- General Dentist Qualifying Examination Blueprint (Nature & Contents of The Test)Document2 pagesGeneral Dentist Qualifying Examination Blueprint (Nature & Contents of The Test)ShifzNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 14 Pain Assessment Sheet Worksheet 14 Pain Assessment SheetDocument18 pagesWorksheet 14 Pain Assessment Sheet Worksheet 14 Pain Assessment SheetSinta Mul16No ratings yet
- Peripheral Intervention: Ardhiana KasabaDocument36 pagesPeripheral Intervention: Ardhiana KasabaFitri ShabrinaNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine Programs ListDocument96 pagesFamily Medicine Programs ListNilay BhattNo ratings yet
- Uniform ESRD Transient Hemodialysis FormDocument3 pagesUniform ESRD Transient Hemodialysis FormacqueNo ratings yet
- Nle MCN Road To SuccessDocument59 pagesNle MCN Road To SuccessKaye PatanindagatNo ratings yet
- Articulo Hipoxia BDocument11 pagesArticulo Hipoxia BAlgy Emiro Vergara MendozaNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of High Risk Neonates DrLawHN PDFDocument45 pagesAssessment and Management of High Risk Neonates DrLawHN PDFShiva KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Thoracic Outlet SyndromeDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Thoracic Outlet SyndromeDony Astika WigunaNo ratings yet
- Seattle Children's - 2009 Community Benefit ReportDocument32 pagesSeattle Children's - 2009 Community Benefit ReportJeneen CoydanNo ratings yet
- Birth Plan WebDocument3 pagesBirth Plan WebSarah BoyeNo ratings yet
- Bedpans and UrinalsDocument4 pagesBedpans and UrinalsCham De Leon50% (4)
- Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesDaftar PustakaInggrid RahletsNo ratings yet
- 6 SbarDocument11 pages6 Sbarsathish kumarNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Values Case Study 2Document3 pagesArterial Blood Gas Values Case Study 2julissaNo ratings yet
- (NLM) Nursing Specialization PPT True (Am)Document120 pages(NLM) Nursing Specialization PPT True (Am)kimchi girlNo ratings yet
- Wrights Stain Diff Quick Manual MethDocument7 pagesWrights Stain Diff Quick Manual MethJose CisnerosNo ratings yet
- Musculosleketal Risk Assesment Among Nurses in Pateint Manual Handling in Hospital Wards - A Cross Sectional StudyDocument10 pagesMusculosleketal Risk Assesment Among Nurses in Pateint Manual Handling in Hospital Wards - A Cross Sectional StudyCureusNo ratings yet
- GEHealthcare Brochure - Reusable Temperature Probes PDFDocument4 pagesGEHealthcare Brochure - Reusable Temperature Probes PDFHomeroPerezNo ratings yet
- Txcindia - Gov.in - Report On Medical TextilesDocument66 pagesTxcindia - Gov.in - Report On Medical TextilesPARMAR14107735No ratings yet
- Crisis Trauma: WWW - Eastzonemedico.co M WWW - Eastzonemedico.inDocument14 pagesCrisis Trauma: WWW - Eastzonemedico.co M WWW - Eastzonemedico.inswipetoplay32No ratings yet
- SMLE Sections With Mastery Level Aug 2020Document22 pagesSMLE Sections With Mastery Level Aug 2020aslyNo ratings yet
- Critical Care NursingDocument5 pagesCritical Care NursingMK BelitungNo ratings yet






















































![Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/475660044/149x198/2c7fc45015/1691161640?v=1)