Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LDM GROUP Investor Presentation
LDM GROUP Investor Presentation
Uploaded by
Janusz GossCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LDM GROUP Investor Presentation
LDM GROUP Investor Presentation
Uploaded by
Janusz GossCopyright:
Available Formats
23 23
Investment Strategy
Investment Strategy
and the Concept of
and the Concept of
Market Efficiency
Market Efficiency
LDM GROUP
LDM GROUP
Franklin Templeton Asset Group
Franklin Templeton Asset Group
24 24
Supply, Demand, and the
Supply, Demand, and the
Price of Real Estate Assets
Price of Real Estate Assets
Demand
Demand
Relationship between market
Relationship between market
price and the quantity of a good
price and the quantity of a good
or service that will be bought per
or service that will be bought per
time period, over the entire
time period, over the entire
range of possible prices
range of possible prices
For real estate assets, demand
For real estate assets, demand
is inversely related to their price
is inversely related to their price
25 25
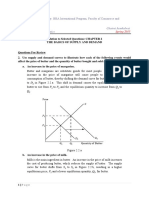
Figure 2.1
Figure 2.1
26 26
Supply, Demand, and the
Supply, Demand, and the
Price of Real Estate Assets
Price of Real Estate Assets
Demand Schedule
Demand Schedule
is the
is the
relationship between price and
relationship between price and
quantity;
quantity;
demand curve
demand curve
is the
is the
graphic form of the same
graphic form of the same
information
information
A specific demand schedule
A specific demand schedule
applies only to a defined
applies only to a defined
population vying for a particular
population vying for a particular
class of property
class of property
27 27
Supply, Demand, and the
Supply, Demand, and the
Price of Real Estate Assets
Price of Real Estate Assets
Shift in demand
Shift in demand
the entire
the entire
range of relationships between
range of relationships between
price and quantity demanded
price and quantity demanded
changes. Among determinants
changes. Among determinants
of location and shape of
of location and shape of
demand curves for real estate
demand curves for real estate
assets, and of changes in
assets, and of changes in
demand are:
demand are:
Number of prospective tenants
Number of prospective tenants
Changes in operating expenses
Changes in operating expenses
Yields available on other assets
Yields available on other assets
Technology
Technology
Tastes
Tastes
28 28
Figure 2.2
Figure 2.2
29 29
Supply, Demand, and the
Supply, Demand, and the
Price of Real Estate Assets
Price of Real Estate Assets
Example
Example
-
-
demand schedule
demand schedule
for downtown office space
for downtown office space
Price changes alter quantity
Price changes alter quantity
demanded
demanded
Decline in after
Decline in after
-
-
tax cash flow
tax cash flow
Market areas become relatively Market areas become relatively
more desirable, drop bidding for more desirable, drop bidding for
downtown property downtown property
Less downtown space purchased Less downtown space purchased
at each possible price per square at each possible price per square
foot foot
30 30
Figure 2.3
Figure 2.3
31 31
Supply, Demand, and the
Supply, Demand, and the
Price of Real Estate Assets
Price of Real Estate Assets
Relative Scarcity
Relative Scarcity
Property in abundance
Property in abundance
commands no substantial value
commands no substantial value
Supply is defined as the
Supply is defined as the
relationship between price and
relationship between price and
the quantity of a product
the quantity of a product
suppliers place on the market
suppliers place on the market
during a specified time period,
during a specified time period,
for all possible prices
for all possible prices
32 32
Supply, Demand, and the
Supply, Demand, and the
Price of Real Estate Assets
Price of Real Estate Assets
Supply function differs as
Supply function differs as
specified time period is
specified time period is
lengthened or shortened
lengthened or shortened
Short run
Short run
variations in the
variations in the
supply of real estate placed on
supply of real estate placed on
the market are an individuals
the market are an individuals
perceptions of the relationship
perceptions of the relationship
between market value and
between market value and
investment value
investment value
Long run
Long run
the supply curve of
the supply curve of
real estate is influenced by cost
real estate is influenced by cost
of construction
of construction
33 33
Supply, Demand, and the
Supply, Demand, and the
Price of Real Estate Assets
Price of Real Estate Assets
Quantity supplied
Quantity supplied
refers to
refers to
amount of product that will be
amount of product that will be
placed on the market per
placed on the market per
period of time at a specified
period of time at a specified
price
price
Supply
Supply
the relationship
the relationship
between price and quantity
between price and quantity
supplied over the entire range
supplied over the entire range
of possible prices
of possible prices
34 34
Supply, Demand, and the
Supply, Demand, and the
Price of Real Estate Assets
Price of Real Estate Assets
Equilibrium price
Equilibrium price
price at
price at
which there will be sufficient
which there will be sufficient
quantity of a product to satisfy
quantity of a product to satisfy
desires of all consumers at that
desires of all consumers at that
price, but with no surplus
price, but with no surplus
remaining on the market.
remaining on the market.
Quantity demanded and
Quantity demanded and
quantity supplied meet at the
quantity supplied meet at the
point where the supply and
point where the supply and
demand functions intersect.
demand functions intersect.
35 35
Figure 2.4
Figure 2.4
36 36
Figure 2.5
Figure 2.5
37 37
Figure 2.6
Figure 2.6
38 38
Market Efficiency and
Market Efficiency and
Profit Opportunities
Profit Opportunities
Markets
Markets
institutional
institutional
arrangements or mechanisms
arrangements or mechanisms
whereby buyers and sellers are
whereby buyers and sellers are
brought into contact with each
brought into contact with each
other. There are not
other. There are not
necessarily physical entities or
necessarily physical entities or
geographical location
geographical location
39 39
Market Efficiency and
Market Efficiency and
Profit Opportunities
Profit Opportunities
Markets
Markets
commonality of
commonality of
product
product
Owner
Owner
-
-
occupant market
occupant market
Renter
Renter
-
-
occupant market
occupant market
Multifamily investment
Multifamily investment
Nonresidential market
Nonresidential market
40 40
Figure 2.7
Figure 2.7
41 41
Market Efficiency and
Market Efficiency and
Profit Opportunities
Profit Opportunities
Range of Markets
Range of Markets
In an
In an
atomistic market,
atomistic market,
each
each
participant is so insignificant
participant is so insignificant
relative to the size of the total
relative to the size of the total
market that he has no
market that he has no
perceptible effect on price, Every
perceptible effect on price, Every
buyer can purchase as much as
buyer can purchase as much as
desired, every seller can sell as
desired, every seller can sell as
much as desired.
much as desired.
In an
In an
absolute monopoly
absolute monopoly
, there
, there
is only one supplier or a good or
is only one supplier or a good or
service for which there are not
service for which there are not
reasonably acceptable
reasonably acceptable
substitutes
substitutes
42 42
Figure 2.8
Figure 2.8
43 43
Market Efficiency and
Market Efficiency and
Profit Opportunities
Profit Opportunities
Price Searchers and Market
Price Searchers and Market
Efficiency
Efficiency
In an
In an
efficient market
efficient market
,
,
information is transmitted quickly
information is transmitted quickly
and without cost, eliminating
and without cost, eliminating
above average profit
above average profit
Time required for information to
Time required for information to
be reflected in price is a
be reflected in price is a
measure of market efficiency
measure of market efficiency
In less efficient market,
In less efficient market,
information is scarce and costly;
information is scarce and costly;
greater degree of price
greater degree of price
searching
searching
44 44
Market Efficiency and
Market Efficiency and
Profit Opportunities
Profit Opportunities
Sources of Market Inefficiency
Sources of Market Inefficiency
Information costly and difficult to
Information costly and difficult to
obtain; comparison shopping
obtain; comparison shopping
expensive and time consuming
expensive and time consuming
High transaction costs prohibit
High transaction costs prohibit
portfolio adjustment
portfolio adjustment
No two properties exactly alike
No two properties exactly alike
45 45
Strategy Implications
Strategy Implications
In atomistic markets,
In atomistic markets,
economic
economic
rent
rent
will be rare and short
will be rare and short
-
-
lived
lived
Less efficient the market,
Less efficient the market,
longer the adjustment process
longer the adjustment process
takes
takes
46 46
Figure 2.9
Figure 2.9
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- (12335) BM533 CbeDocument18 pages(12335) BM533 CbeMahbubur Rahman100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- EC1002 Commentary 2017Document40 pagesEC1002 Commentary 2017Sophia Garner100% (1)
- W17 MIC Problem Set 9 (With Solutions)Document4 pagesW17 MIC Problem Set 9 (With Solutions)Bowen ZhanNo ratings yet
- Barometric and Dominant Price LeadershipDocument14 pagesBarometric and Dominant Price LeadershipDA50% (4)
- CH 1 Introduction To Agricultural EconomicsDocument34 pagesCH 1 Introduction To Agricultural Economicsdinesh100% (4)
- Solutions To Chapter 2Document9 pagesSolutions To Chapter 2Alma Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Notes ECO162Document13 pagesNotes ECO162Nur HanisahNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Maize MarketingDocument128 pagesA Guide To Maize MarketingRoberto GarciaNo ratings yet
- Supply, Demand, and Equilibrium Assessment Questions - MRU (With Answers)Document13 pagesSupply, Demand, and Equilibrium Assessment Questions - MRU (With Answers)Jimmy RoblesNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 33 ECO121Document55 pagesChapter - 33 ECO121Le Pham Khanh Ha (K17 HCM)No ratings yet
- Market EquilibriumDocument7 pagesMarket Equilibriumunicornsarecoolasice100% (2)
- HS20001 Economics ES 2016Document2 pagesHS20001 Economics ES 2016Vivek MarwadeNo ratings yet
- Homework - 8 Answer KeyDocument6 pagesHomework - 8 Answer KeyMaríaNo ratings yet
- 3.E Demand and Supply (Exercises)Document9 pages3.E Demand and Supply (Exercises)adusa1No ratings yet
- Theory of Demand and Supply: Dr. Lê Thanh HàDocument109 pagesTheory of Demand and Supply: Dr. Lê Thanh HàHanh LeNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics 8th Edition Samuelson Solutions ManualDocument18 pagesManagerial Economics 8th Edition Samuelson Solutions ManualNormaEdwardsgcnr100% (32)
- 0455 s04 QP 1Document16 pages0455 s04 QP 1Elle PhoebeNo ratings yet
- Public Finance and TaxationDocument14 pagesPublic Finance and Taxationnegussie birieNo ratings yet
- Chap. 5 Perfect Comp.Document9 pagesChap. 5 Perfect Comp.amanuelNo ratings yet
- Economic SystemsDocument6 pagesEconomic SystemsKarma AkabaneNo ratings yet
- Economics Study MaterialDocument100 pagesEconomics Study MaterialVigneshraj VigneshrajNo ratings yet
- Economics ALevel 2018 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyDocument31 pagesEconomics ALevel 2018 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Mixed Economic SystemDocument26 pagesMixed Economic SystemFazra FarookNo ratings yet
- Revision Test - Ii STD - Xii (Economics) : Seventh Day Adventist Higher Secondary SchoolDocument7 pagesRevision Test - Ii STD - Xii (Economics) : Seventh Day Adventist Higher Secondary SchoolbhavyaNo ratings yet
- Textbook in Economics For Class XIIDocument8 pagesTextbook in Economics For Class XIIAnushka VashishthaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics - 2020-22 - RevisedDocument3 pagesManagerial Economics - 2020-22 - RevisedVedant HingeNo ratings yet
- NSS Exploring Economics 3 (Second Edition) : Consolidation WorksheetsDocument20 pagesNSS Exploring Economics 3 (Second Edition) : Consolidation WorksheetsSelina LeungNo ratings yet
- New SyllabusDocument7 pagesNew SyllabusApong LkrNo ratings yet
- Law On Supply and Demand ExamDocument6 pagesLaw On Supply and Demand ExamSharah Del T. TudeNo ratings yet