Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 Marks (Questions & Answers) : Geared Coupling Power Supply
2 Marks (Questions & Answers) : Geared Coupling Power Supply
Uploaded by
pugazhendira0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
101 views5 pagesThis document contains questions and answers related to electric drives. It defines drive and electric drive, lists examples of prime movers like IC engines and electric motors. It outlines some advantages of electric drives such as wide power range and speed/torque control. Examples of electric drives include fans, pumps, conveyors and locomotives. Typical elements are identified as the power supply, motor, coupling and mechanical load. Drive systems can be electric, electromechanical, or mechanical. Factors that influence electric drive choice include power/speed needs, efficiency, cost and load characteristics. Load equalization and different braking methods like regenerative, dynamic and plugging are also described.
Original Description:
Much useful to engineering graduates in the stream of EEE
Original Title
21
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains questions and answers related to electric drives. It defines drive and electric drive, lists examples of prime movers like IC engines and electric motors. It outlines some advantages of electric drives such as wide power range and speed/torque control. Examples of electric drives include fans, pumps, conveyors and locomotives. Typical elements are identified as the power supply, motor, coupling and mechanical load. Drive systems can be electric, electromechanical, or mechanical. Factors that influence electric drive choice include power/speed needs, efficiency, cost and load characteristics. Load equalization and different braking methods like regenerative, dynamic and plugging are also described.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
101 views5 pages2 Marks (Questions & Answers) : Geared Coupling Power Supply
2 Marks (Questions & Answers) : Geared Coupling Power Supply
Uploaded by
pugazhendiraThis document contains questions and answers related to electric drives. It defines drive and electric drive, lists examples of prime movers like IC engines and electric motors. It outlines some advantages of electric drives such as wide power range and speed/torque control. Examples of electric drives include fans, pumps, conveyors and locomotives. Typical elements are identified as the power supply, motor, coupling and mechanical load. Drive systems can be electric, electromechanical, or mechanical. Factors that influence electric drive choice include power/speed needs, efficiency, cost and load characteristics. Load equalization and different braking methods like regenerative, dynamic and plugging are also described.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
2 marks (Questions & Answers)
1.
Define Drive and Electric Drive.
Drive: A combination of prime mover, transmission equipment and
mechanical working load is called a drive
Electric drive: An Electric Drive can be defined as an
electromechanical device for converting electrical energy to
mechanical energy to impart motion to different machines and
mechanisms for various kinds of process control.
2.
List out some examples of prime movers.
I.C Engines, Steam engine, Turbine or electric motors.
3. List out some advantages of electric drives.
i.
ii.
iii.
Availability of electric drives over a wide range of power a few
watts to mega watts.
Ability to provide a wide range of torques over wide range of
speeds.
Electric motors are available in a variety of design in order to
make them compatible to any type of load.
4. Give some examples of Electric Drives.
i.
ii.
iii.
iv.
Driving fans, ventilators, compressors and pumps.
Lifting goods by hoists and cranes.
Imparting motion to conveyors in factories, mines and
warehouses
Running excavators & escalators, electric locomotives trains,
cars trolley buses, lifts & drum winders etc.
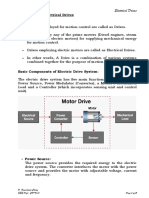
5. What are the Typical elements of an Electric Drive?
Power Supply
Speed & Torque
Control
Motor
Geared
Coupling
Mechanical Laod
6. What are the types Drive systems?
Electric Drives
Electromechanical Drives
Mechanical Drives
Hydraulic drives.
7. What are the factors that influence the choice of electrical
drives?
1. Shaft power & speed
11. Speed range
2. Power range
12. Efficiency
3. Starting torque
13.
Influence on the supply
network
4. Maintenance
5. Total purchase cost
6. Influence on power supply
7. Availability
8. Nature of electric supply
9. Types of drive
10.Service cost
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
Special competence
Cost of energy losses
Environment
Accessibility
Nature of load
Electrical Characteristics
Service capacity & rating
.
8.
What is meant by load equalization?
In the method of load Equalization intentionally the motor inertia
is increased by adding a flywheel on the motor shaft, if the motor is not
to be reversed. For effectiveness of the flywheel, the motor should have a
prominent drooping characteristic so that on load there is a considerable
speed drop.
9.List the different types of electrical drives.
1)dc drives
2)ac drives
10.Mention the parts of electrical drives.
1) Electrical motors and load.
2) Power modulator
3) Sources
4) Control unit
5) Sensing unit
11. What is meant by regenerative braking?
Regenerative braking occurs when the motor speed exceeds the
synchronous speed. In this case the IM runs as the induction m\c is
converting the mechanical power into electrical power which is
delivered back to the electrical system. This method of braking is
known as regenerative braking.
12. What is meant by dynamic braking?
Dynamic braking of electric motors occurs when the energy stored in the
rotating mass is dissipated in an electrical resistance. This requires a
motor to operate as a gen. to convert the stored energy into electrical.
13. What is meant by plugging?
It is one method of braking of IM. When phase sequence of supply of the
motor running at the speed is reversed by interchanging connections of
any two phases of stator with respect to supply terminals, operation
shifts from motoring to plugging region.
14.What are the methods of operation of electric drives?
Steady state
acceleration including starting
deceleration including starting
15. Define four quadrant operation.
The motor operates in two mode: motoring and braking. In
motoring, it converts electrical energy into mechanical energy
which supports its motion. In braking, it works as a generator,
converting mathematical energy into electrical energy and thus
opposes the motion. Motor can provide motoring and braking
operations for both forward and reverse directions.
16. What is meant by mechanical characteristics?
The curve is drawn between speed and torque. This characteristic is
called mechanical characteristics.
Write down the equation governing motor load dynamics.
Te TL J
d
d
or Te TL J
dt
dt
COMPONENTS OF LOAD TORQUE
Friction
Windage
Torque required to do the mechanical work
Types of load torques
Passive torque
Active torque
Passive torque
oppose the motion.
Ex.. Friction torque
Active torque
Load torque is constant
Retain its sign always.
Ex.. Force of gravity
You might also like
- Drilling FormulasDocument87 pagesDrilling Formulaswhydowelove89% (9)
- Unit I V 2 Mark Question Answer 16 Mark QuestionsDocument23 pagesUnit I V 2 Mark Question Answer 16 Mark QuestionspugazhendiraNo ratings yet
- Panimalar Engineering Collge: Department of Mechanical Engineering Ii Year / Iii SemesterDocument32 pagesPanimalar Engineering Collge: Department of Mechanical Engineering Ii Year / Iii SemestersivaNo ratings yet
- EE1351 Solid State DrivesDocument25 pagesEE1351 Solid State DrivesGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- EDCDocument178 pagesEDCAjay Kavi100% (1)
- Lecture-9: Load Equalization and Two Mark QuestionsDocument6 pagesLecture-9: Load Equalization and Two Mark QuestionsTimoNo ratings yet
- PSD 2 MarkDocument30 pagesPSD 2 MarkKarthik KandellaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines and Drives/Electrical Drives and Control Third Semester Mechanical Engineering 2 Marks (Questions & Answers)Document7 pagesElectrical Machines and Drives/Electrical Drives and Control Third Semester Mechanical Engineering 2 Marks (Questions & Answers)Joseph HarindranathNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine and DrivesDocument18 pagesElectrical Machine and DrivesNEERAJ27TRIPATHINo ratings yet
- Electrical Drives and Control EE1213Document18 pagesElectrical Drives and Control EE1213ViswanathanBalajiNo ratings yet
- M Group: Electrical Drives and Control - EE 1213Document18 pagesM Group: Electrical Drives and Control - EE 1213scribdm100% (3)
- Adhiparasakthi College of Engineering: Ee2352 - Solid State DrivesDocument23 pagesAdhiparasakthi College of Engineering: Ee2352 - Solid State DrivesSidali ChaibNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Question BankDocument13 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Question Bankl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Kongu Engineering College, PerunduraiDocument23 pagesKongu Engineering College, PerunduraiSingh VelNo ratings yet
- Electrical Drives:: Unit - I Drive CharacteristicsDocument22 pagesElectrical Drives:: Unit - I Drive CharacteristicsJegan8586100% (1)
- Solid State Drives Ee2352 SSD NotesDocument19 pagesSolid State Drives Ee2352 SSD NotesGooge ReviewerNo ratings yet
- Study Protection 2537Document118 pagesStudy Protection 2537todayinfo42No ratings yet
- EEE259 ELECTRICAL - DRIVES - AND - CONTROLS QB and AnswerDocument20 pagesEEE259 ELECTRICAL - DRIVES - AND - CONTROLS QB and AnswerMuniyasamyNo ratings yet
- Bule Hora University Department of Ece Eceg 4222 Power Electronics & Electric DrivesDocument14 pagesBule Hora University Department of Ece Eceg 4222 Power Electronics & Electric DrivesBilisuma DamiteNo ratings yet
- DC DrivesDocument10 pagesDC DrivesEuoshy HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Electric Drives and Converters Feeding Electric MotorsDocument11 pagesChapter 3: Electric Drives and Converters Feeding Electric MotorsSelemon AssefaNo ratings yet
- III-EEE-2-mark-NEW-2019Document128 pagesIII-EEE-2-mark-NEW-2019PrabuNo ratings yet
- Unit I Ee6351Document23 pagesUnit I Ee6351karthiNo ratings yet
- Solid State Drives 2 MarksDocument9 pagesSolid State Drives 2 MarksskrtamilNo ratings yet
- Ee6009 PeresDocument89 pagesEe6009 PeresparthibanNo ratings yet
- Eee-Vii-Industrial Drives and Applications (10ee74) - SolutionDocument54 pagesEee-Vii-Industrial Drives and Applications (10ee74) - SolutionAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electric DrivesDocument67 pagesAdvanced Electric DrivesrashmisbhumbareNo ratings yet
- Electrical DrivesDocument194 pagesElectrical DrivesKITSAO SAMUELNo ratings yet
- PSD DIGITAL NOTES-word CDocument177 pagesPSD DIGITAL NOTES-word CMarupakaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Electrical DrivesDocument16 pagesUnit 4 Electrical DrivesVaishnavi BharatiNo ratings yet
- CIA - I Question Bank With Answers SOLID STATE DRIVESDocument4 pagesCIA - I Question Bank With Answers SOLID STATE DRIVESdeepakraghavanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Electric Drives: Subject Name: Electric Drives Class: 4 Year/ VII SemesterDocument35 pagesCharacteristics of Electric Drives: Subject Name: Electric Drives Class: 4 Year/ VII SemesterBabbu DograNo ratings yet
- Solid State DrivesDocument81 pagesSolid State DrivesjedidiahsuleymanNo ratings yet
- IDA Notes by Balaji RamakrishnaDocument71 pagesIDA Notes by Balaji RamakrishnaPkNo ratings yet
- See 1306Document153 pagesSee 1306Mogaka LucasNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument32 pagesQuestion BankBhuvaneshNo ratings yet
- Solid State Drives 2 Marks and 16Document34 pagesSolid State Drives 2 Marks and 16Dhamu DharanNo ratings yet
- Electric Drives: Subject Code: EEE11 Credit: 3: 0: 0Document28 pagesElectric Drives: Subject Code: EEE11 Credit: 3: 0: 0Harsh ThamkeNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Electrical Energy: Chapter 2: Electric Drives L-2-1Document23 pagesUtilization of Electrical Energy: Chapter 2: Electric Drives L-2-1Frozen BoyNo ratings yet
- MECH - THIRD SEMESTER - 2 MARK AND 13 MARK QUESTION BANK - by LearnEngineering - inDocument204 pagesMECH - THIRD SEMESTER - 2 MARK AND 13 MARK QUESTION BANK - by LearnEngineering - inVishnu VaradhanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Drives & Control-100 Two Marks With AnswerDocument10 pagesElectrical Drives & Control-100 Two Marks With Answerarivurp86% (7)
- Part-B Unit-1: 1. Explain About Different Types of Load and Load Characteristics? (April/May 2019)Document52 pagesPart-B Unit-1: 1. Explain About Different Types of Load and Load Characteristics? (April/May 2019)VAHAB KHANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: IntroductionDocument118 pagesChapter 1: Introductionrizwan_adilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document4 pagesChapter 6Indu SusmiNo ratings yet
- Enercon Homework 4Document19 pagesEnercon Homework 4Ezekiel Brizuela100% (4)
- 04493430Document7 pages04493430Krishna KarthikNo ratings yet
- Part Ii: Electrical Drives Chapter TenDocument37 pagesPart Ii: Electrical Drives Chapter TenDawit Shimeles TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Rejinpaul App From PlaystoreDocument24 pagesRejinpaul App From Playstorepriya dharshiniNo ratings yet
- Adesh Edc Ut1Document6 pagesAdesh Edc Ut1harshshelke 123No ratings yet
- Power Electronics and EDDocument45 pagesPower Electronics and EDtefe yabatuNo ratings yet
- MJET Engg. CollegeDocument74 pagesMJET Engg. CollegePiyush AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Electrical DrivesDocument204 pagesElectrical DrivesRuchiNo ratings yet
- Bhs Inggris Electric MotorsDocument4 pagesBhs Inggris Electric MotorsHindra Aditya FamudjiNo ratings yet
- Ee6601 SSD PDFDocument21 pagesEe6601 SSD PDFRohithNo ratings yet
- ED - Notes Inroduction To Electric Drives-0Document8 pagesED - Notes Inroduction To Electric Drives-0Manideep ManiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseFrom EverandPower Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
- Electric Powertrain: Energy Systems, Power Electronics and Drives for Hybrid, Electric and Fuel Cell VehiclesFrom EverandElectric Powertrain: Energy Systems, Power Electronics and Drives for Hybrid, Electric and Fuel Cell VehiclesNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Electric Drives for Traction ApplicationsFrom EverandPower Electronics and Electric Drives for Traction ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Generation and Transmission of Electric Power: Lecture Notes of the Generation and Transmission of Electric Power CourseFrom EverandGeneration and Transmission of Electric Power: Lecture Notes of the Generation and Transmission of Electric Power CourseNo ratings yet
- DC DC ConverterDocument25 pagesDC DC ConverterpugazhendiraNo ratings yet
- Lecture #9 Control Engineering Review Slides: Reference: Textbook by Phillips and HaborDocument35 pagesLecture #9 Control Engineering Review Slides: Reference: Textbook by Phillips and HaborpugazhendiraNo ratings yet
- Unit I V 2 Mark Question Answer 16 Mark QuestionsDocument23 pagesUnit I V 2 Mark Question Answer 16 Mark QuestionspugazhendiraNo ratings yet
- EE6005 Power Quality Sem ViiiDocument2 pagesEE6005 Power Quality Sem ViiipugazhendiraNo ratings yet
- What Are The Three Types of Speed ControlDocument5 pagesWhat Are The Three Types of Speed ControlpugazhendiraNo ratings yet
- EE 1351 Solid State Drives UNIT 1 - Drive CharacteristicsDocument1 pageEE 1351 Solid State Drives UNIT 1 - Drive CharacteristicspugazhendiraNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor.Document172 pagesStepper Motor.pugazhendira50% (2)
- Cri 1Document20 pagesCri 1pugazhendiraNo ratings yet
- Power Supply NotesDocument48 pagesPower Supply NotespugazhendiraNo ratings yet
- Voltage Level ShiftingDocument5 pagesVoltage Level ShiftingpugazhendiraNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Sets and Fuzzy LogicDocument67 pagesFuzzy Sets and Fuzzy LogicpugazhendiraNo ratings yet
- EE2301 Power Electronics SyllabusDocument1 pageEE2301 Power Electronics SyllabuspugazhendiraNo ratings yet
- Static, Linear and Finite Element Analysis of Pressure VesselDocument8 pagesStatic, Linear and Finite Element Analysis of Pressure VesselAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2015-2016 (L-4, T-1) - Che PDFDocument52 pages2015-2016 (L-4, T-1) - Che PDFMahmud Rahman BizoyNo ratings yet
- Homework2 - KIM224E - 2020 Inorganic Chemistry 2Document4 pagesHomework2 - KIM224E - 2020 Inorganic Chemistry 2irembasar2000No ratings yet
- Delsu Current Science Post Utme Past QuestionDocument216 pagesDelsu Current Science Post Utme Past Question76xzv4kk5vNo ratings yet
- BD52XXG/FVE Series BD53XXG/FVE Series: Voltage Detector Ic With Adjustable Delay TimeDocument5 pagesBD52XXG/FVE Series BD53XXG/FVE Series: Voltage Detector Ic With Adjustable Delay Timemartin sembinelliNo ratings yet
- ITF Bulls Eye BatchDocument4 pagesITF Bulls Eye BatchDecoded 1 Mr unknownNo ratings yet
- RPA113-Structural-Rod-Catalogue-2.0 RONSTANDocument32 pagesRPA113-Structural-Rod-Catalogue-2.0 RONSTANadhithyaNo ratings yet
- Posalux Multifor 10-14-22-25Document10 pagesPosalux Multifor 10-14-22-25Mojtaba GholamiNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument1 pageProblem SolvingDarren Ezra AliagaNo ratings yet
- DESIGN OF COLD STORAGE FACILITY FOR Anthurium Sp. IN BENGUET PROVINCE, PHILIPPINESDocument13 pagesDESIGN OF COLD STORAGE FACILITY FOR Anthurium Sp. IN BENGUET PROVINCE, PHILIPPINESKimberly OrtizNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Led4 InstruccionesDocument5 pagesHyundai Led4 InstruccionesEncep ZaenalNo ratings yet
- Toptherm Wall-Mounted Cooling Unit Blue E Total Cooling Output 0.50 - 0.75 KW - SK 3361.500Document4 pagesToptherm Wall-Mounted Cooling Unit Blue E Total Cooling Output 0.50 - 0.75 KW - SK 3361.500andri putrantoNo ratings yet
- Assign 233 SDocument5 pagesAssign 233 SMzhfr IzzatNo ratings yet
- Particle Like Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation: Yudhiakto PramudyaDocument53 pagesParticle Like Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation: Yudhiakto PramudyaMengharu BiruNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Conceptual Physical Science 6th Edition All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Conceptual Physical Science 6th Edition All Chapterhergyyilou100% (7)
- Англо-русский и Русско-английский Нефтегазопромысловый Словарь - English-Russian and Russian-English Dictionary on Oil and Gas (PDFDrive)Document853 pagesАнгло-русский и Русско-английский Нефтегазопромысловый Словарь - English-Russian and Russian-English Dictionary on Oil and Gas (PDFDrive)Рифгат МирзаевNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Spring 2012Document57 pagesLecture 7 - Spring 2012yuy caNo ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in Chemistry Project Space ChemistryDocument22 pagesFdocuments - in Chemistry Project Space ChemistryLip UtNo ratings yet
- Air To Water Heat Pump LabDocument4 pagesAir To Water Heat Pump Labgamers meniaNo ratings yet
- Technical Speci Cation: Product SpecificationDocument2 pagesTechnical Speci Cation: Product SpecificationMiguel GarzaNo ratings yet
- Electrodynamics Advanced Level QB PhysicsDocument28 pagesElectrodynamics Advanced Level QB Physicsaboutk748No ratings yet
- The Design and Construction of Electric Arc Welding MachineDocument14 pagesThe Design and Construction of Electric Arc Welding Machinemichael gorgeNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion - Quesiton BankDocument5 pagesProjectile Motion - Quesiton BankSaήjaγKsNo ratings yet
- UPS Battery Size & Runtime Calculations - PHD PowerhouseDocument3 pagesUPS Battery Size & Runtime Calculations - PHD PowerhousedarlingtonNo ratings yet
- 18cdna44 - Basic Ship TheoryDocument15 pages18cdna44 - Basic Ship TheoryDeepak PooranachandranNo ratings yet
- NS BERO 2001 Chapter 4 Part2Document61 pagesNS BERO 2001 Chapter 4 Part2Pablo RosasNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Energy: Physics 20 Unit C: Energy and WorkDocument10 pagesConservation of Energy: Physics 20 Unit C: Energy and WorkUnzal FatehullahNo ratings yet
- Generating Light From LemonDocument12 pagesGenerating Light From LemonShalom AbebawNo ratings yet
- X-Calibur ManualDocument175 pagesX-Calibur ManualanalisissNo ratings yet