Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter - 11: Quick Revision Notes Biotechnology - Principle and Processes Important Terms
Chapter - 11: Quick Revision Notes Biotechnology - Principle and Processes Important Terms
Uploaded by
Shaharukh NadafOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter - 11: Quick Revision Notes Biotechnology - Principle and Processes Important Terms
Chapter - 11: Quick Revision Notes Biotechnology - Principle and Processes Important Terms
Uploaded by
Shaharukh NadafCopyright:
Available Formats
Quick Revision
63
CHAPTER 11
Quick Revision Notes
BIOTECHNOLOGY - PRINCIPLE AND PROCESSES
Important Terms
1) Biotechnology The use of microorganisms, plants, animal cells or their enzymes to
produce products and processes useful to humans.
2) Genetic Engineering Techniques to alter the chemistry of genetic material, DNA and
RNA, to introduce these into host organisms and thus change the phenotype of the host
organism.
3) Gene Cloning Technique of obtaining identical copies of a particular DNA segment or
gene.
4) Plasmid- Autonomously replicating, circular, extra chromosomal DNA in a bacterial cell.
5) Recombinant DNA DNA formed from combining DNA sequences from two different
organisms.
6)
Palindromes Groups of letters that form the same word when read both forward and
backward. (Used for sequence of bases in this chapter)
7) Electroporation Technique by which holes are created in the plasma membrane of a
host cell to facilitate entry of a foreign DNA.
8) Gene therapy Technique of replacement or alteration of a defective gene responsible
for a hereditary disease.
9) Origin of replication Specific DNA sequence from where replication starts.
Two core techniques that gave rise to biotechnology are:
(a) Genetic Engineering
(b) Maintenance of sterile ambience in chemical engineering processes so that
growth of only desired cell takes place.
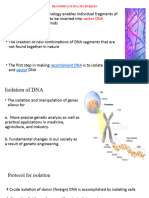
The construction of the first recombinant DNA was done by Stanley Cohen and
Herbert Boyer in 1972. They linked gene encoding antibiotic resistance to native
plasmid of Salmonella typhionurium.
Tools of Recombinant DNA Technology
(1) Restriction Endonuclease - These are called molecular scissors.
Each restriction endonuclease recognizes a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence.
When cut by the same restriction enzyme, the resultant DNA have the same kind of
sticky ends and these can be joined together using DNA ligases.
64
BiologyXII
Steps in formation of recombinant DNA by action of restriction endonuclease enzyme
EcoRI
Separation and isolation of DNA fragments is done by a technique known as gel
electrophoresis.
As DNA fragments are negatively charged, they can be separated by forcing them
to move towards the anode under an electric field through a matrix.
2) Cloning vectors To facilitate cloning into a vector, the following features are required:
(a) Origin of replication - The sequence from where replication starts.
(b) Selectable marker It helps in identifying and eliminating non-transformants and
selectively permitting the growth of transformants.
(c) Cloning sites To link the alien DNA, the vector needs to have very few preferably
single, recognition sites for the commonly used restriction enzymes.
E. coli cloning vector pBR322 showing restriction sites.
Quick Revision
65
(d) Vectors for cloning genes in plants and animals - Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a pathogen
of several dicot plants. It is able to deliver genes to transform eukaryotic cells. It is able
to pass a piece of DNA known as T-DNA to transform normal plant cells into a tumor and
direct these tumor cells to produce chemicals required by the pathogen.
Competent host
A host cell should be competent enough to take the DNA molecule for the transformation.
Following methods are used (i) Using divalent cations
(ii) Heat and cold treatment Cells can be incubated with rDNA on ice and then briefly
placed at 42o C and then putting them back on ice
(iii) Microinjection
(iv) Biolistics or gene gun.
Process of Recombinant DNA technology
(i) Isolation of genetic material Treating the bacterial cell or any other cell with enzymes
such as lysozyme for bacteria, cellulase for plant cell, chitinase for fungal cells. RNA to
be removed by treating with ribonuclease and finally DNA can be precipitated by treating
with chilled ethanol.
(ii) Use of restriction enzymes to cut DNA.
(iii) Amplification of gene using PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
66
BiologyXII
(iv) Insertion of Recombinant DNA into the host cell or organism.
(v) Obtaining the foreign gene product - If any protein encoding gene is expressed in a
heterologous host, it is called a recombinant protein.
Cells can be multiplied in a continuous culture system wherein used medium is
drained out from one side while fresh medium is added from the other.
To produce large quantities of products, bioreactors are used where 100-1000 litres
of culture can be processed.
The most commonly used bioreactors are of stirring type.
a) Simple stirred-tank bioreactor
b) Sparged stirred-tank bioreactor through which sterile air bubbles are
sparged
Downstream processing are processes which include separation and purification of
the product before it is ready for marketing as finished product.
You might also like
- Hematology SOPsDocument99 pagesHematology SOPssalamon2t100% (2)
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument80 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologyRaizza Mae CorderoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Chapter 9: Biotechnology and Recombinant DNADocument37 pagesMicrobiology Chapter 9: Biotechnology and Recombinant DNAHarinder BajwaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY XII Study Material 2022-23 Chapter Wise PrepDocument29 pagesBIOLOGY XII Study Material 2022-23 Chapter Wise PrepashwinkumarcoimatoreNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument38 pagesGenetic EngineeringNaila Izzaty KarimahNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principle & Process PyqDocument14 pagesBiotechnology Principle & Process PyqSoumya Ranjan NaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter-11 BiotechnologyDocument7 pagesChapter-11 BiotechnologyJay RoyNo ratings yet
- L5 MLB 110 Recombinant Dna TechniquesDocument15 pagesL5 MLB 110 Recombinant Dna Techniquesmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Rajkumar Biology Unit - 9 by RajatDocument12 pagesRajkumar Biology Unit - 9 by RajatprasannandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Biology Xii PyqDocument20 pagesChapter - Biology Xii PyqSiva selviNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology NotesDocument18 pagesBiotechnology NotesAmmar ZahidNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology: Principles and ProcessesDocument3 pagesBiotechnology: Principles and ProcessesRishi Rao ANo ratings yet
- Recombinant DnaDocument3 pagesRecombinant DnaleicatapangNo ratings yet
- Notebook Q & ADocument11 pagesNotebook Q & Aumamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and Processes Revision Notes Cbse Class 12 BiologyDocument7 pagesBiotechnology Principles and Processes Revision Notes Cbse Class 12 Biologyak9268509No ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering and RDNA TechnologyDocument83 pagesGenetic Engineering and RDNA TechnologyvaldezjesebyNo ratings yet
- Notes CH-11 Biotechnology and Its PrinciplesDocument6 pagesNotes CH-11 Biotechnology and Its Principles16739No ratings yet
- Biotechnology I (Lecture Note)Document8 pagesBiotechnology I (Lecture Note)Pranav ShinojNo ratings yet
- 3 Recombinant DNA Technology IntroductionDocument43 pages3 Recombinant DNA Technology IntroductionSamarth TalatiNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XII Botany CH 11 Minhad NewDocument4 pagesHsslive XII Botany CH 11 Minhad NewAKUULLLNo ratings yet
- GCMBDocument5 pagesGCMBHarshita SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-11-Practice Biology Class 12Document19 pagesChapter-11-Practice Biology Class 12geethaNo ratings yet
- Contents:: Project Report 1. Introduction To Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument15 pagesContents:: Project Report 1. Introduction To Recombinant DNA TechnologyShivraj GundayyaNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument21 pagesBio ProjectabhayNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesDocument15 pagesBiotechnology Principles and Processesloxif49565No ratings yet
- 11 - Biotechnology Principles AssignDocument8 pages11 - Biotechnology Principles AssignLohitha ANo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Gene Technology & ApplicationsDocument6 pagesChapter 20 Gene Technology & ApplicationsIrish Jem BantolinoNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument28 pagesFinalapi-19783425No ratings yet
- Unit 9Document12 pagesUnit 9Rohan sharmaNo ratings yet
- c01-02 (A)Document36 pagesc01-02 (A)Lucas BarbosaNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument62 pagesGeneticsDeriq MaorenzNo ratings yet
- Recombinant Dna Tech SaswatDocument8 pagesRecombinant Dna Tech SaswatSaswat Anurag RoutNo ratings yet
- II ME NRP B SS 27. Biotechnology-Principles and Processes, Biotechnology - ApplicationsDocument8 pagesII ME NRP B SS 27. Biotechnology-Principles and Processes, Biotechnology - ApplicationsAmit RavindhraNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles & ProcessesDocument3 pagesBiotechnology Principles & ProcessesKambaska Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 and 2 BGE - IntroDocument81 pagesLecture 1 and 2 BGE - Introaishah1997No ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument13 pagesBiotechnologyranvir madaviNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesDocument9 pagesBiotechnology Principles and Processes228 S.Vignesh 10No ratings yet
- CH 11 Biotechnology Principle & ProcessDocument12 pagesCH 11 Biotechnology Principle & ProcessAksharaNo ratings yet
- Dna Recombinant TechnologyDocument20 pagesDna Recombinant TechnologyJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- Cloning and Re Comb in Ant DnaDocument38 pagesCloning and Re Comb in Ant DnaMak ItiNo ratings yet
- Aula BMol 2Document35 pagesAula BMol 2Diogo MadalenoNo ratings yet
- 14th WeekDocument21 pages14th WeekMoonHoLeeNo ratings yet
- Biology: Board - Cbse Class - Xii Topic - Principles and ProcessesDocument7 pagesBiology: Board - Cbse Class - Xii Topic - Principles and ProcessesAkshat JainNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 PCR and DNA TechnologyDocument22 pagesWEEK 4 PCR and DNA TechnologyotaibynaifNo ratings yet
- Dr. V. P. Wankhade: Vidyabharti College of Pharmacy, AmravatiDocument31 pagesDr. V. P. Wankhade: Vidyabharti College of Pharmacy, AmravatiNikita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Notes-1Document6 pagesBiotechnology Notes-1Exporting WarriorNo ratings yet
- Bio TechnologyDocument51 pagesBio Technologylalithadithya85No ratings yet
- BiotechDocument5 pagesBiotechkaiaNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document101 pagesCH 08dolt2111No ratings yet
- Add A Little Bit of Body TextDocument9 pagesAdd A Little Bit of Body Textaayushparmar361No ratings yet
- Describe The Natural Function of Restriction Enzymes (RE)Document9 pagesDescribe The Natural Function of Restriction Enzymes (RE)Liling CassiopeiaNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Technology - OurvleDocument30 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology - Ourvledpkf6dj725No ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Fall BUC PDFDocument36 pagesMolecular Biology Fall BUC PDFThe Egy NerdNo ratings yet
- BioDocument11 pagesBioLalein VillodresNo ratings yet
- 08 Lec.8 Dr. Sddiq Recombinant DNA 20200414030255 PDFDocument7 pages08 Lec.8 Dr. Sddiq Recombinant DNA 20200414030255 PDFحسن الأسديNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principle and Processes PowerNotes 4Document2 pagesBiotechnology Principle and Processes PowerNotes 4Dreamsach Gaming100% (1)
- rDNA PDFDocument11 pagesrDNA PDFbroken reedNo ratings yet
- Ch3 NotesDocument52 pagesCh3 NotesMahesh ShirsatNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesDocument43 pagesBiotechnology Principles and ProcessesAnushka LimbuNo ratings yet
- Recombinant Dna Technology-A Perforated InsightDocument40 pagesRecombinant Dna Technology-A Perforated InsightBobby Arguilles PaboresNo ratings yet
- Novapdf: Unfiled Notes Page 1Document4 pagesNovapdf: Unfiled Notes Page 1Shaharukh NadafNo ratings yet
- Core Java API: I/ODocument13 pagesCore Java API: I/OShaharukh NadafNo ratings yet
- Wednesday, January 14, 2015 2:12 PM: NovapdfDocument3 pagesWednesday, January 14, 2015 2:12 PM: NovapdfShaharukh NadafNo ratings yet
- M15 - XMLDocument36 pagesM15 - XMLShaharukh NadafNo ratings yet
- M18 - Case StudyDocument32 pagesM18 - Case StudyShaharukh NadafNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering An Overview: Ranjit Raman Team Coordinator E-Gov, C-DAC, PuneDocument37 pagesSoftware Engineering An Overview: Ranjit Raman Team Coordinator E-Gov, C-DAC, PuneShaharukh NadafNo ratings yet
- CAT TEP0512 SolutionsDocument7 pagesCAT TEP0512 Solutionsapi-26456455No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Spring FrameworkDocument19 pagesIntroduction To The Spring FrameworkShaharukh NadafNo ratings yet
- Webwork in Action: An Introduction To WebworkDocument26 pagesWebwork in Action: An Introduction To WebworkShaharukh NadafNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 13: Quick Revision Notes Organisms and Population Important TermsDocument5 pagesChapter - 13: Quick Revision Notes Organisms and Population Important TermsShaharukh NadafNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12: Quick Revision Notes Biotechnology and Its Applications Important TermsDocument3 pagesChapter - 12: Quick Revision Notes Biotechnology and Its Applications Important TermsShaharukh NadafNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Quick Revision Notes Human Reproduction Important TermsDocument7 pagesChapter - 3: Quick Revision Notes Human Reproduction Important TermsShaharukh NadafNo ratings yet
- Valores Calibrador PDFDocument66 pagesValores Calibrador PDFJoseCardonaNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document5 pagesTask 1Fajar SidikNo ratings yet
- NematodesDocument12 pagesNematodesAntonette ApaniNo ratings yet
- HemostasisDocument5 pagesHemostasisPadmavathi C100% (1)
- Basic and Applied Concepts of Blood Banking and Transfusion Practices 3rd Edition Blaney Test BankDocument8 pagesBasic and Applied Concepts of Blood Banking and Transfusion Practices 3rd Edition Blaney Test BankRyanAdamsfont100% (9)
- MEIOSIS WorksheetDocument8 pagesMEIOSIS WorksheetEliseo PamandananNo ratings yet
- 10th ScienceDocument310 pages10th ScienceAbishek BachanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 Reading 1 Resistance To AntibioticsDocument2 pagesExercise 5 Reading 1 Resistance To AntibioticsAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Guide ScriptDocument3 pagesResearch Proposal Guide ScriptShiela Joy Valdez AradoNo ratings yet
- Inflammation in Atrial Fibrillation: Yutao Guo, MDR, Gregory Y. H. Lip, MD, Stavros Apostolakis, MD, P DDocument8 pagesInflammation in Atrial Fibrillation: Yutao Guo, MDR, Gregory Y. H. Lip, MD, Stavros Apostolakis, MD, P DIbrahim HaidarNo ratings yet
- Corynebacterium DiphtheriaeDocument14 pagesCorynebacterium DiphtheriaeNoyal JosephNo ratings yet
- Genetic Lab NotebookDocument11 pagesGenetic Lab NotebookKevin Chen100% (1)
- MENINGITISDocument5 pagesMENINGITISapi-3822433100% (1)
- Enzyme Promiscuity in Earthworm Serine Protease: Substrate Versatility and Therapeutic PotentialDocument8 pagesEnzyme Promiscuity in Earthworm Serine Protease: Substrate Versatility and Therapeutic PotentialKhánh HuyềnNo ratings yet
- Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) : Exploring its implications in infectious diseasesDocument16 pagesInterferon-gamma (IFN-γ) : Exploring its implications in infectious diseasesBella LifindraNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Answer 1Document4 pagesExercises: Answer 1MOHD RASHIDNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Performance of Sysmex XN-3100 Automated Hematology Analyzer Regarding The Sysmex XE-2100 and Microscopic ExaminationDocument9 pagesEvaluation of The Performance of Sysmex XN-3100 Automated Hematology Analyzer Regarding The Sysmex XE-2100 and Microscopic ExaminationbalkisNo ratings yet
- Jama Gandhi 2022 SC 220007 1669761091.38561 PDFDocument22 pagesJama Gandhi 2022 SC 220007 1669761091.38561 PDFNelson GoulartNo ratings yet
- Ch5 GeneticsDocument63 pagesCh5 GeneticsleartaNo ratings yet
- HAP Lab Quiz (Midterm)Document11 pagesHAP Lab Quiz (Midterm)shane.erica.penitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cell BiologyDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Cell BiologyEllemrac GageloniaNo ratings yet
- 1 OnlineDocument6 pages1 Onlineanalisaapil312No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part 1 Blood Collection: Terry Kotrla, MS, MT (ASCP) MLAB 2431 ImmunohematologyDocument21 pagesUnit 1 Part 1 Blood Collection: Terry Kotrla, MS, MT (ASCP) MLAB 2431 ImmunohematologyleomillmendiolaNo ratings yet
- Lecture COPEG Qns (Last Lect)Document8 pagesLecture COPEG Qns (Last Lect)Wesley TanNo ratings yet
- Examkrackers Lecture 2 Section QuestionsDocument3 pagesExamkrackers Lecture 2 Section QuestionsAyodejiES1No ratings yet
- Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument55 pagesMicrobiology and ParasitologyJade BuriNo ratings yet
- WES WGS Brochure Pages V2.1eng Web 20201019Document16 pagesWES WGS Brochure Pages V2.1eng Web 20201019drumerNo ratings yet
- Blood: Blood Transports Everything That Must Be Carried From One Place To Another, Such AsDocument71 pagesBlood: Blood Transports Everything That Must Be Carried From One Place To Another, Such AsAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Principle and Techniques of Immunohistochemistry A Review PDFDocument7 pagesPrinciple and Techniques of Immunohistochemistry A Review PDFMohammed R.HusseinNo ratings yet