Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Treatment/ Infusion d5lr
Treatment/ Infusion d5lr
Uploaded by
jbespirituCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Nps Thesis DatabaseDocument5 pagesNps Thesis Databasekathymillerminneapolis100% (2)
- Work Practice Manual - Western PowerDocument751 pagesWork Practice Manual - Western Powerjeb13100% (1)
- Esprit 08Document32 pagesEsprit 08fanny100% (6)
- Review of Related Literature Term PaperDocument6 pagesReview of Related Literature Term PaperAllyana Julienne100% (6)
- Activity 4Document7 pagesActivity 4Mary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Wesleyan: College of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesDocument2 pagesWesleyan: College of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesShane Aileen AngelesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Emergency DrugsDocument6 pagesDrug Study Emergency DrugsJhessa Curie PitaganNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RopivacaineDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ropivacainerica sebabillonesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MsDocument10 pagesDrug Study MsAbie Jewel Joy RoqueNo ratings yet
- Docu - Tips Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDocu - Tips Drug StudyArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- Virtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsDocument7 pagesVirtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsEdgie FabreNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Document2 pagesDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- GENTIMICINDocument1 pageGENTIMICINVinzNo ratings yet
- VILLAMIN - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesVILLAMIN - Drug StudyAzizah VillaminNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY-Lidocaine RyreyDocument1 pageDRUG-STUDY-Lidocaine RyreyJanelle Cabida SupnadNo ratings yet
- Crisis Management .Document9 pagesCrisis Management .jeromeNo ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinJoi Danielle Tabares IsturisNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AzithromycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study AzithromycinYamete KudasaiNo ratings yet
- DUPHASTON Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDUPHASTON Drug StudyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Final Magnesium SulfateDocument3 pagesFinal Magnesium SulfateGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Celecoxib CelebrexDocument1 pageCelecoxib CelebrexBeverly Ann de LeonNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone, MetropololDocument7 pagesAzithromycin, Ceftriaxone, Metropolollei_odanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Loop DiureticDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Loop DiureticNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication: Department of Health, PhilippinesDocument35 pagesTherapeutic Communication: Department of Health, PhilippinesKeith Clarence BunaganNo ratings yet
- Drugs Mechanism of Action Nursing Responsibilities OMXDocument5 pagesDrugs Mechanism of Action Nursing Responsibilities OMXEmmanuelRodriguezNo ratings yet
- Aspirin Drug SummDocument2 pagesAspirin Drug SummWarren0% (1)
- Kremil S Drug StudyDocument1 pageKremil S Drug StudyDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyLorraine Tuesday BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drug StudyDocument3 pagesEmergency Drug StudyGrace Santos MirandaNo ratings yet
- PantoprazoleDocument1 pagePantoprazolehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- PROPYLTHIOURACILDocument35 pagesPROPYLTHIOURACILMagdy Ali ELsherbenyNo ratings yet
- Functional Health Pattern AssessmentDocument2 pagesFunctional Health Pattern AssessmentsuegegeNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY NaproxenDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY NaproxenMargarette Mae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Procreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableDocument9 pagesProcreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableShiela Mae GalisaNo ratings yet
- NCP Anemia LongDocument6 pagesNCP Anemia LongJudeLaxNo ratings yet
- Name of The DrugDocument2 pagesName of The DrugSistine Rose LabajoNo ratings yet
- DioxelDocument1 pageDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- Rationale:: Drug MOA Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Implication AssessmentDocument3 pagesRationale:: Drug MOA Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Implication AssessmentTrishia Mae GallardoNo ratings yet
- Drug Benzocaine LozengeDocument1 pageDrug Benzocaine LozengeSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsMarie Kris Chua AbelleraNo ratings yet
- Salazar DsDocument4 pagesSalazar DsDjayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Case PresentationDocument5 pagesDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studymegreen GamingNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyTherese ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Serving Sterile GownDocument2 pagesServing Sterile GownGelo BallartaNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY (Calcium)Document3 pagesDRUG-STUDY (Calcium)NicholeGarcesCisnerosNo ratings yet
- EscitalopramDocument1 pageEscitalopramRicky Ramos Jr.No ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument8 pagesDRUG StudyLou-Lou HadaniNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEChezka Orton Swift BolintiamNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Clausii ErcefloraDocument1 pageBacillus Clausii ErcefloraCezhille BattadNo ratings yet
- CALCITRIOLDocument2 pagesCALCITRIOLdesshe09No ratings yet
- As Pi LetDocument7 pagesAs Pi Letianecunar100% (1)
- Atropine SulfateDocument1 pageAtropine SulfateTrishaaMayolNo ratings yet
- NCP CholeraDocument2 pagesNCP CholeraMichael Angelo Garcia RafananNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyIvan Matthew SuperioNo ratings yet
- Tablets: Tablets (Chewable) : Tablets (Extended-Release)Document1 pageTablets: Tablets (Chewable) : Tablets (Extended-Release)Melissa Marie CustodioNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolKay MirandaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNo ratings yet
- CU Task 11 RLE - Urinary Problems in Older Adults - GROUP2E 3Document7 pagesCU Task 11 RLE - Urinary Problems in Older Adults - GROUP2E 3FERMIL PASGALANo ratings yet
- F and E ReviewerDocument9 pagesF and E Revieweralifah.macabagoNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Bleeding: Late SignDocument12 pagesMinimizing Bleeding: Late SignMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- Aguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Nursing Care Plan On Problem-Based LearningDocument9 pagesAguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Nursing Care Plan On Problem-Based LearningSophia Kaye AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Elementary Logic Gates PDFDocument14 pagesElementary Logic Gates PDFGokaran ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Bengt B Broms Lateral Resistance of PileDocument43 pagesBengt B Broms Lateral Resistance of PileJerin LeenusNo ratings yet
- Flow Measuring System: ModelDocument2 pagesFlow Measuring System: ModelSAKDA MAPRADITKULNo ratings yet
- Magic Quadrant For E-Discovery SoftwareDocument15 pagesMagic Quadrant For E-Discovery SoftwaremanishsgNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ArchaeologyDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Archaeologytcs517090No ratings yet
- Reply Affirmation by Philip Karmel Regarding ESDC Motion For Change of VenueDocument8 pagesReply Affirmation by Philip Karmel Regarding ESDC Motion For Change of VenueNorman OderNo ratings yet
- Nuclear StructureDocument47 pagesNuclear StructureJohnNo ratings yet
- CODY Et Al v. TYLER PLACE, INC. - Document No. 19Document2 pagesCODY Et Al v. TYLER PLACE, INC. - Document No. 19Justia.comNo ratings yet
- 1.1 1 BPB-Cisco-CCNP-Switch-300-115-INTRODocument9 pages1.1 1 BPB-Cisco-CCNP-Switch-300-115-INTRONguyễnTiếnĐạtNo ratings yet
- WWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWDocument3 pagesWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWzoran0706No ratings yet
- Organisational Behaviour (Bba)Document39 pagesOrganisational Behaviour (Bba)Khushi NaharNo ratings yet
- Colons-Semicolons-And-Commas 15874 0Document5 pagesColons-Semicolons-And-Commas 15874 0OPS PMLCNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Cases Chapter 3Document53 pagesOblicon Cases Chapter 3Yasser AureadaNo ratings yet
- Anthro Chapter Wise Previous QuestionsDocument15 pagesAnthro Chapter Wise Previous Questionsfiza shameemNo ratings yet
- Sociology Essay Nature Vs NurtureDocument1 pageSociology Essay Nature Vs NurtureFarhana JaidiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document61 pagesChapter 6asmelash gideyNo ratings yet
- Ultra320 Scsi UmDocument70 pagesUltra320 Scsi UmChandan SharmaNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. L-15088 January 31, 1961 Toribia Fontanilla Pacio, Santiago Pacio, Esperanza Pacio, and Rosario PacioDocument8 pagesG.R. No. L-15088 January 31, 1961 Toribia Fontanilla Pacio, Santiago Pacio, Esperanza Pacio, and Rosario PaciojojoNo ratings yet
- SHS Academic Reading and Writing Week 3Document14 pagesSHS Academic Reading and Writing Week 3Sir Ryan ZNo ratings yet
- History of CostumeDocument108 pagesHistory of CostumeMichi87% (15)
- Ford Foundation Annual Report 2005Document197 pagesFord Foundation Annual Report 2005kalyanaraman7No ratings yet
- CD MneumonicDocument9 pagesCD Mneumonicgaa5No ratings yet
- Philippine Pop Culture and New Media: Memeology 101: Group 2Document7 pagesPhilippine Pop Culture and New Media: Memeology 101: Group 2Jacob HurstNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) C++ Programming Program Design Including Data Structures 8th Edition Malik Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument24 pages(Download PDF) C++ Programming Program Design Including Data Structures 8th Edition Malik Solutions Manual Full Chapterwasihawwa100% (7)
- Tensile Test Lap ReportDocument11 pagesTensile Test Lap ReportApostrophe Fareez ImprezzaNo ratings yet
- Cps CpsDocument20 pagesCps Cpsapi-545617234No ratings yet
Treatment/ Infusion d5lr
Treatment/ Infusion d5lr
Uploaded by
jbespirituOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Treatment/ Infusion d5lr
Treatment/ Infusion d5lr
Uploaded by
jbespirituCopyright:
Available Formats
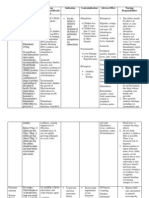
TREATMENT/ CLASSIFICATION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
INFUSION
D5LR Hypertonic Replacement therapy • Renal failure 1. Never stop hypertonic solutions abruptly.
Solution particularly in • Liver dysfunction 2. Don’t give concentrated solutions I.M. or
extracellular fluid • Diabetes Mellitus subcutaneously.
deficit accompanied • Lactic acidosis 3. Monitor glucose level carefully.
by acidosis • Alkalosis 4. Check vital signs frequently. Report adverse
Hyperkalemia reactions.
5. Monitor fluid intake and output and weight
carefully. Watch closely for signs and symptoms of
fluid overload.
6. Monitor patient for signs of mental confusion
D5W Isotonic solution used to supply water 1.Patients at risk for increased I.C.P. 1. Do not administer quantity in excess of that
and calories to the 2. Patients who have an acute required to keep vein open or administer
body neurological dysfunction. appropriate dose of medication.
3. Hypovolemic states. 2. Do not use solution if outdated, cloudy or the
4. Patients at risk for third-space fluid seal is not intact, as with all IV solutions.
shifts. 3. Monitor E.C.G. continuously.
5. Elevated blood glucose 4. Monitor blood pressure, pulse rate and
concentrations. respiratory rate frequently.
6. heart problems (e.g., congestive
heart failure), 7.kidney problems,
fluid balance problems (e.g.,
hypovolemia),
8.low levels of potassium
(hypokalemia)
9.vitamin B deficiencies
10.swelling (edema).
D5NM Hypertonic • Maintenance • Contraindicated in patient in 1. Never stop hypertonic solutions abruptly.
Solution of fluid and diabetic coma while glucose level 2. Don’t give concentrated solutions I.M. or
electrolytes. remains excessively high. subcutaneously.
Maintenance therapy • Use cautiously in patients 3. Monitor glucose level carefully.
for major surgical with cardiac or pulmonary disease, 4. Check vital signs frequently. Report adverse
procedures, burns, hypertension, renal insufficiency, reactions.
colostomies, etc. urinary obstruction, or hypovolemia 5. Monitor fluid intake and output and weight
carefully. Watch closely for signs and symptoms of
fluid overload.
6. Monitor patient for signs of mental confusion
You might also like
- Nps Thesis DatabaseDocument5 pagesNps Thesis Databasekathymillerminneapolis100% (2)
- Work Practice Manual - Western PowerDocument751 pagesWork Practice Manual - Western Powerjeb13100% (1)
- Esprit 08Document32 pagesEsprit 08fanny100% (6)
- Review of Related Literature Term PaperDocument6 pagesReview of Related Literature Term PaperAllyana Julienne100% (6)
- Activity 4Document7 pagesActivity 4Mary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Wesleyan: College of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesDocument2 pagesWesleyan: College of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesShane Aileen AngelesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Emergency DrugsDocument6 pagesDrug Study Emergency DrugsJhessa Curie PitaganNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RopivacaineDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ropivacainerica sebabillonesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MsDocument10 pagesDrug Study MsAbie Jewel Joy RoqueNo ratings yet
- Docu - Tips Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDocu - Tips Drug StudyArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- Virtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsDocument7 pagesVirtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsEdgie FabreNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Document2 pagesDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- GENTIMICINDocument1 pageGENTIMICINVinzNo ratings yet
- VILLAMIN - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesVILLAMIN - Drug StudyAzizah VillaminNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY-Lidocaine RyreyDocument1 pageDRUG-STUDY-Lidocaine RyreyJanelle Cabida SupnadNo ratings yet
- Crisis Management .Document9 pagesCrisis Management .jeromeNo ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinJoi Danielle Tabares IsturisNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AzithromycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study AzithromycinYamete KudasaiNo ratings yet
- DUPHASTON Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDUPHASTON Drug StudyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Final Magnesium SulfateDocument3 pagesFinal Magnesium SulfateGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Celecoxib CelebrexDocument1 pageCelecoxib CelebrexBeverly Ann de LeonNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone, MetropololDocument7 pagesAzithromycin, Ceftriaxone, Metropolollei_odanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Loop DiureticDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Loop DiureticNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication: Department of Health, PhilippinesDocument35 pagesTherapeutic Communication: Department of Health, PhilippinesKeith Clarence BunaganNo ratings yet
- Drugs Mechanism of Action Nursing Responsibilities OMXDocument5 pagesDrugs Mechanism of Action Nursing Responsibilities OMXEmmanuelRodriguezNo ratings yet
- Aspirin Drug SummDocument2 pagesAspirin Drug SummWarren0% (1)
- Kremil S Drug StudyDocument1 pageKremil S Drug StudyDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyLorraine Tuesday BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drug StudyDocument3 pagesEmergency Drug StudyGrace Santos MirandaNo ratings yet
- PantoprazoleDocument1 pagePantoprazolehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- PROPYLTHIOURACILDocument35 pagesPROPYLTHIOURACILMagdy Ali ELsherbenyNo ratings yet
- Functional Health Pattern AssessmentDocument2 pagesFunctional Health Pattern AssessmentsuegegeNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY NaproxenDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY NaproxenMargarette Mae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Procreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableDocument9 pagesProcreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableShiela Mae GalisaNo ratings yet
- NCP Anemia LongDocument6 pagesNCP Anemia LongJudeLaxNo ratings yet
- Name of The DrugDocument2 pagesName of The DrugSistine Rose LabajoNo ratings yet
- DioxelDocument1 pageDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- Rationale:: Drug MOA Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Implication AssessmentDocument3 pagesRationale:: Drug MOA Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Implication AssessmentTrishia Mae GallardoNo ratings yet
- Drug Benzocaine LozengeDocument1 pageDrug Benzocaine LozengeSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsMarie Kris Chua AbelleraNo ratings yet
- Salazar DsDocument4 pagesSalazar DsDjayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Case PresentationDocument5 pagesDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studymegreen GamingNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyTherese ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Serving Sterile GownDocument2 pagesServing Sterile GownGelo BallartaNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY (Calcium)Document3 pagesDRUG-STUDY (Calcium)NicholeGarcesCisnerosNo ratings yet
- EscitalopramDocument1 pageEscitalopramRicky Ramos Jr.No ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument8 pagesDRUG StudyLou-Lou HadaniNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEChezka Orton Swift BolintiamNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Clausii ErcefloraDocument1 pageBacillus Clausii ErcefloraCezhille BattadNo ratings yet
- CALCITRIOLDocument2 pagesCALCITRIOLdesshe09No ratings yet
- As Pi LetDocument7 pagesAs Pi Letianecunar100% (1)
- Atropine SulfateDocument1 pageAtropine SulfateTrishaaMayolNo ratings yet
- NCP CholeraDocument2 pagesNCP CholeraMichael Angelo Garcia RafananNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyIvan Matthew SuperioNo ratings yet
- Tablets: Tablets (Chewable) : Tablets (Extended-Release)Document1 pageTablets: Tablets (Chewable) : Tablets (Extended-Release)Melissa Marie CustodioNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolKay MirandaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNo ratings yet
- CU Task 11 RLE - Urinary Problems in Older Adults - GROUP2E 3Document7 pagesCU Task 11 RLE - Urinary Problems in Older Adults - GROUP2E 3FERMIL PASGALANo ratings yet
- F and E ReviewerDocument9 pagesF and E Revieweralifah.macabagoNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Bleeding: Late SignDocument12 pagesMinimizing Bleeding: Late SignMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- Aguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Nursing Care Plan On Problem-Based LearningDocument9 pagesAguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Nursing Care Plan On Problem-Based LearningSophia Kaye AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Elementary Logic Gates PDFDocument14 pagesElementary Logic Gates PDFGokaran ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Bengt B Broms Lateral Resistance of PileDocument43 pagesBengt B Broms Lateral Resistance of PileJerin LeenusNo ratings yet
- Flow Measuring System: ModelDocument2 pagesFlow Measuring System: ModelSAKDA MAPRADITKULNo ratings yet
- Magic Quadrant For E-Discovery SoftwareDocument15 pagesMagic Quadrant For E-Discovery SoftwaremanishsgNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ArchaeologyDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Archaeologytcs517090No ratings yet
- Reply Affirmation by Philip Karmel Regarding ESDC Motion For Change of VenueDocument8 pagesReply Affirmation by Philip Karmel Regarding ESDC Motion For Change of VenueNorman OderNo ratings yet
- Nuclear StructureDocument47 pagesNuclear StructureJohnNo ratings yet
- CODY Et Al v. TYLER PLACE, INC. - Document No. 19Document2 pagesCODY Et Al v. TYLER PLACE, INC. - Document No. 19Justia.comNo ratings yet
- 1.1 1 BPB-Cisco-CCNP-Switch-300-115-INTRODocument9 pages1.1 1 BPB-Cisco-CCNP-Switch-300-115-INTRONguyễnTiếnĐạtNo ratings yet
- WWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWDocument3 pagesWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWzoran0706No ratings yet
- Organisational Behaviour (Bba)Document39 pagesOrganisational Behaviour (Bba)Khushi NaharNo ratings yet
- Colons-Semicolons-And-Commas 15874 0Document5 pagesColons-Semicolons-And-Commas 15874 0OPS PMLCNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Cases Chapter 3Document53 pagesOblicon Cases Chapter 3Yasser AureadaNo ratings yet
- Anthro Chapter Wise Previous QuestionsDocument15 pagesAnthro Chapter Wise Previous Questionsfiza shameemNo ratings yet
- Sociology Essay Nature Vs NurtureDocument1 pageSociology Essay Nature Vs NurtureFarhana JaidiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document61 pagesChapter 6asmelash gideyNo ratings yet
- Ultra320 Scsi UmDocument70 pagesUltra320 Scsi UmChandan SharmaNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. L-15088 January 31, 1961 Toribia Fontanilla Pacio, Santiago Pacio, Esperanza Pacio, and Rosario PacioDocument8 pagesG.R. No. L-15088 January 31, 1961 Toribia Fontanilla Pacio, Santiago Pacio, Esperanza Pacio, and Rosario PaciojojoNo ratings yet
- SHS Academic Reading and Writing Week 3Document14 pagesSHS Academic Reading and Writing Week 3Sir Ryan ZNo ratings yet
- History of CostumeDocument108 pagesHistory of CostumeMichi87% (15)
- Ford Foundation Annual Report 2005Document197 pagesFord Foundation Annual Report 2005kalyanaraman7No ratings yet
- CD MneumonicDocument9 pagesCD Mneumonicgaa5No ratings yet
- Philippine Pop Culture and New Media: Memeology 101: Group 2Document7 pagesPhilippine Pop Culture and New Media: Memeology 101: Group 2Jacob HurstNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) C++ Programming Program Design Including Data Structures 8th Edition Malik Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument24 pages(Download PDF) C++ Programming Program Design Including Data Structures 8th Edition Malik Solutions Manual Full Chapterwasihawwa100% (7)
- Tensile Test Lap ReportDocument11 pagesTensile Test Lap ReportApostrophe Fareez ImprezzaNo ratings yet
- Cps CpsDocument20 pagesCps Cpsapi-545617234No ratings yet