Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aging-Causes and Prevention - A Review
Aging-Causes and Prevention - A Review
Uploaded by
Wwwanand111Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aging-Causes and Prevention - A Review
Aging-Causes and Prevention - A Review
Uploaded by
Wwwanand111Copyright:
Available Formats
Advances in Biological Research 8 (3): 127-130, 2014
ISSN 1992-006
IDOSI Publications, 2014
DOI: 10.5829/idosi.abr.2014.8.3.82412
Aging- Causes and Prevention A Review
Shubham Verma, Nitin Kumar, Rishabha Malviya,
Rupesh Dudhe and Pramod Kumar Sharma
Department of Pharmacy, School of Medical and Allied Sciences,
Galgotias University, Greater Noida, G. B. Nagar, U.P. India
Abstract: Aging is a process in which continuous failure of maintenance and repair mechanism occurs which
are very important for cellular homeostasis. Antioxidants and growth hormone regulators are used to decrease
the process of longevity or abnormal aging. Protandim and nuclear factor 2 (Nrf2) are used as super antioxidant
to minimise the oxidative stress in the body. Some aging syndromes are also there in which age of person
increases three times of its original age such as progeria. Progeria occurs due to gene changes in the body and
this disease does not have any cure and a person with this disease having a life of only 13-14 years.
Key words: Growth Hormones Insulin Growth Factor-1
Nuclear Factor-2
INTRODUCTION
Protandim
Reactive Oxygen Species
related change that decreases the number of native cells
and accumulation of sensitized cells [4]. Aging is a
concept that includes physical changes to our bodies,
psychological changes to our minds and social attributes
through adult life [5].
Now-a-days everyone wants to look younger and
attractive always, it is not possible to block our age but
you can decrease the process of aging. Aging can also be
recognised by the visual aspects of the body. Most of the
peoples are bothered about one common affair called age.
Aging occurs continuously without our approbation.
Aging is an intricate process characterised by the gradual
failure of maintenance and repair pathways important for
homeostasis of cell which results in progressive accretion
of unwanted macromolecules and organelles. The
accretion of these unwanted macromolecules and
organelles has harmful effects on cellular homeostasis and
cause hindrance with activity of functional molecules
which tends to subsequent dysfunction [1,2].
There are certain changes that are pernicious,
gradual and thus far irrevocable. Aging damage occur to
molecule to cell and to organs. The molecular damage
associated with aging may increasingly perturb normal
homeostasis and increase the susceptibility to disease
and disability.
Symptoms That Transpire with Aging Are Categorised
As:
Physical Aging: There are certain symptoms of Physical
aging which are as follows
Decrease in Physical strength, endurance and
flexibility.
Decline in the body organs.
Slower reflexes.
Decline in the senses.
Psychological Aging: DEMENTIA* is the major symptom
of Psychological aging in which sudden memory and
behavioural changes occurs.
D- Drugs Confusion between the drugs prescribed
by the doctor and the over the counter drugs.
E- Emotions especially depression, have a major
impact on memory but the persons suffering from
DEMENTIA do not complain about their memory
problems.
Symptoms of Aging: Aging changes are frequently
related with an increase in eventuality of mortality, but
this is not necessarily the case i.e., greying of hairs is a
symptom of aging but this does not increase eventuality
of mortality [3]. T cell populations having the most age
Corresponding Author:
Progeria
Shubham Verma, Department of Pharmacy, School of Medical and Allied Sciences,
Galgotias University, Greater Noida, G. B. Nagar, U.P. India.
127
Advan. Biol. Res., 8 (3): 127-130, 2014
Symptoms of Progeria: Typical symptoms of progeria are
growth insufficiency, wrinkled skin, loss of eye sight, hair
loss, cardiovascular diseases etc. the earliest symptoms
may include a localised scleroderma like skin condition, a
distinctive appearance i.e., small face, pinched nose and
shallow, recessed jaw are all characteristics of progeria
[10].
M- Medical problems, lack of fluid in the body
(dehydration) and lack of oxygen to the brain
(hypoxia) can commonly cause confusion and
disorientation.
E- Eyes, ears and environmental changes also may
affect behavior.
N- Nutritional deficiency
T- Trauma or a head injury from any type of accident,
including a fall or a brain tumor, can cause confusion
and disorientation.
I- Infection, pneumonia or urinary tract infection, a
high fever, or syphilis can cause dementia.
A- Alcoholism, whether a recent or long-standing
problem, can cause temporary confusion and
disorientation or permanent brain damage.
Treatment: There is only a drug which focuses on
reducing complications and i.e., farnesyl tranferase
inhibitor called lanofarnib which is able to improve the
cardiovascular health and increase their weight gain but
there is no treatments have been proven effective to
symptoms of progeria.
Aging Due To Hormonal Change: Growth hormone (GH)
and insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1) plays a vital role in
normal growth and development in humans [11]. Normal
release of growth hormone in body is essential for aging
process but excess release of growth hormone and
concomitant increase in circulating IGF-1 levels by GH
producing adenoma causes in abnormal growth i.e., tissue
overgrowth, metabolic abnormalities such as diabetes and
hypertension [12,13].
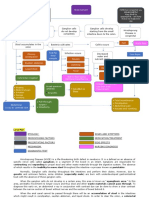
From this flow chart it is cleared that as growth
hormone increases, insulin growth factor and cellular
senescence also increases due to this anti oxidant enzyme
and insulin sensitivity of the body decreases. Thus these
are the main cause for the aging process of the body [14].
Social Aging: The symptoms of social aging are loss,
Grief and Bereavement [6,7].
The gradual decline in functional ability and muscle
strength is related to normal aging processes [8]. The rate
of aging varies from individual to individual and the age
of different organ system is different in same person.
Causes of Aging:
Intrinsic Aging: This type of aging is caused by the
internal defects in the human body system. Some time
there is some hormonal changes in the body and some
time there is unwanted changes in the genes of human
that will cause aging [9].
Fig. 1: Possible involvement of ROS-induced cellular
senescence in the regulation of lifespan.
Aging Due To Gene: A point mutation in the gene causes
aging syndromes like PROGERIA and WERNERS
SYNDROME. PROGERIA (Hutchinson Gilford progeria
syndrome) is extremely rare genetic disease. The first
symptoms manifest in infants and neonates. Cause of
progeria is identified by a point mutation at position 1824
of lamin A (LMNA) gene.
Extrinsic Aging: This type of aging is mainly caused by
the external environmental conditions. Most commonly
ultraviolet rays are responsible for the extrinsic aging
which results in cell damage and formation of free
radicals.
128
Advan. Biol. Res., 8 (3): 127-130, 2014
Aging Due To Ultra Violet Rays & Photo oxidation: Ultra
violet rays mostly produces free radicals in the body that
sometimes causes aberrant side reactions resulting in cell
damage and thus causes the mutation and affect the
cell cycle
and
causes symptoms of aging like
atherosclerosis.
It may also involve in Parkinsonism disease &
Alzheimer disease. UV commences a number of cellular
responses, including reactive oxygen species (ROS)
production within upper layer of the skin
and
middle layer of the skin i.e., epidermal and dermal cells.
The free radical theory of aging suggests that aging
results from the accretion of the oxidative damage over
time, which persuade to cellular dysfunction and
organism death. The epidermis becomes shrivel compared
to sun protected areas on the same individual. There are
some structural alterations found in the epidermis cell due
to ultraviolet rays which particularly corrode the
biochemical properties of the skin. A cutaneous aging
was found by the comparative studies between photo
exposed and photo protected areas in same individual
[15, 16].
CONCLUSION
As we have reviewed that the aging is the
process of progressive failure of functioning of parts in
the body which is important for cellular haemostasis.
Due to this our appearance also decreases, as we aged
our body functioning decreases. There is one deadly
syndrome of the aging which occurs due to
mutation in 1824 position of LMNA gene, the
syndrome named as PROGERIA. Aging due to photo
oxidation is treated by using antioxidants. Now protandim
is used for the treatment of photo oxidation as a super anti
oxidant and nuclear factor-2 (NrF-2) also used as super
oxidant & it is the master regulator of the bodys aging
process.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors are highly thankful to Department of
Pharmacy, School of Medical and Allied Sciences,
Galgotias University, Greater Noida India for providing
library facility during literature survey.
Conflict of Interest: Authors have no conflict of
interest.
Treatment: Use of the antioxidant is the most successful
treatment. Now-a-days Protandim & nuclear factor 2
(NrF2) are used as super antioxidant. Protandim is
patented dietary supplement that has five herbs with
antioxidant properties and increase bodys natural
antioxidant protection by inducing two protective
enzymes i.e., superoxide dismutase (SOD) & catalase
(CAT).
REFERENCES
1.
Gelino, S. and M. Hansen, 2012. Autophagy- An
Emerging Anti Aging Mechanism. J Clin Exp Pathol.,
84: 1-12.
2. Rajawat, Y.S. and I. Bossis, 2008. Autophagy in and
in neurodegenerative disorders, hormones. J. Clin.
Exp. Pathol., 7: 46-61.
3. Kaul, S. and R. Wadhwa, 2003. Aging of cells in and
outside the body. Netherland, Kluwer Academic
Publisher.
4. Athari, S.S., 2013. Immune Response Shifting of
Asthma in Aging. Middle-East Journal of Scientific
Research, IDOSI Publications., 13(4): 489-498.
5. Abdullah,
O.C., M.S.Y. Abdullah
and
A.M.M. Al-Merbawi, 2013. Ageing Population in
Developed Counties: A Study of Process and
Phenomena. Middle-East Journal of Scientific
Research, IDOSI Publications., 17(2): 219-225.
6. Anderson and P. Gayle, 1989. A fresh look at
assessing the elderly. Academic Journal., 52: 28-39.
7. Dubin, S., 1992. The physiologic changes of aging.
Orthop Nurs., 11(3): 45-50.
Composition of Protandim:
Milk thistles (silybum marianum) extract (225mg).
Bacopa (bacopa monniera) extract (150mg).
Aswagandha (withania somnifera) root (150mg).
Green tea (camellia sinensis) extract (75mg).
Turmeric (curcuma longa) extract (75 mg).
Nuclear factor-2 (NrF2) stimulates the Superoxide
dismutase (SOD) and fights oxidative stress and help to
regulate at peak efficiency.
Nuclear factor-2 (NrF2) is the protein messenger that
binds itself to the DNA. It is the master regulator of the
bodys aging process and fight against oxidative stress.
It communes with the cells & instructing them to do what
they were design to do.
129
Advan. Biol. Res., 8 (3): 127-130, 2014
8.
Teimoori, A., M.R. Kordi, S. Choobine and B. Heidari,
2009. The Effects of Aging on Muscle Strength and
Functional Ability of Healthy Iranian Males. World
Journal of Sport Sciences. IDOSI Publications.,
2(4): 261-265.
9. Lauker, R.M., 1995. Cutaneous aging: chronologic
versus photoaging. Photodamage., 1: 123-125.
10. Merideth, M.A. and L.B. Gordon, 2008. Phenotype
and course of Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome.
N. Engl. J. Med., 358: 592-604.
11. Lupu, F. and J.D. Terwilliger, 2001. Roles of growth
hormones and insulin growth factor 1 in mouse
postnatal growth. Dev. Biol., 229: 141-162.
12. Leroith, D. and S. Yakar, 2007. Mechanism of disease,
metabolic effects of growth hormones and insulin
growth factor 1. Nat Cli Pract Endocrinal Metlab.,
3: 302-310.
13. Oliveira, C.R., R. Salvatori and R.A. MeneguzMoreno, 2009. Adipokine Profile and urinary albubin
excretion in isolated growth hormone deficiency. J
Clin Endocrinol., 161: 837-844.
14. Bartke, A., 2011. Growth hormone, insulin and aging;
The benefits of endocrinal defects. Exp Gerontol.,
46: 108-111.
15. Ames, B.N., 1980. Endogenous oxidative DNA
damage, aging & cancer: free Radic. Res. Commun.,
7: 121-128.
16. Nelson, K. Sally, Bose, K. Swapon, Grunwald,
K. Gary, P. Myhill, McCord and M. Joe, 2006. Free
Radical Biology and Medicine., 40(1): 341-347.
130
You might also like
- Interpretation Financial Statements PDFDocument134 pagesInterpretation Financial Statements PDFWwwanand111No ratings yet
- Comparative Animal Physiology: Philip C. WithersDocument7 pagesComparative Animal Physiology: Philip C. WithersWwwanand111No ratings yet
- Metatonin & Pineal GlandDocument107 pagesMetatonin & Pineal GlandSoman100% (2)
- CytokinesDocument3 pagesCytokinesMohanad JawadNo ratings yet
- The Science and Technology of Growing Young: How to Look Younger, Live Longer, and Feel Your Best with New Breakthroughs in Anti-Aging ScienceFrom EverandThe Science and Technology of Growing Young: How to Look Younger, Live Longer, and Feel Your Best with New Breakthroughs in Anti-Aging ScienceNo ratings yet
- Ageing The Emerging Area of Bio Gerontology A ReviewDocument13 pagesAgeing The Emerging Area of Bio Gerontology A ReviewAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Anti-Aging Medicine: Balvant P. AroraDocument4 pagesAnti-Aging Medicine: Balvant P. AroraSimoneNo ratings yet
- Theories of AgingDocument5 pagesTheories of AgingDawah Bockarie AmaduNo ratings yet
- Natural Medicines - AgingDocument6 pagesNatural Medicines - AgingRebeccaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Shayma'a Jamal Ahmed Prof. Genetic Engineering & BiotechnologyDocument32 pagesDr. Shayma'a Jamal Ahmed Prof. Genetic Engineering & BiotechnologyMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Defying Age: The Ultimate Guide to Living a Long and Healthy LifeFrom EverandDefying Age: The Ultimate Guide to Living a Long and Healthy LifeNo ratings yet
- Artikel 1-Review Nutrasetikal Untuk LansiaDocument10 pagesArtikel 1-Review Nutrasetikal Untuk LansiaMade DesmantaNo ratings yet
- Nano Greens Phyto Nut AgingDocument4 pagesNano Greens Phyto Nut AgingWwwanand111No ratings yet
- Nutrients: Nutrition Can Help DNA Repair in The Case of AgingDocument20 pagesNutrients: Nutrition Can Help DNA Repair in The Case of AgingAlvin HabaraNo ratings yet
- Brain Aging and Regeneration After InjuriesDocument16 pagesBrain Aging and Regeneration After InjuriesProsen21No ratings yet
- 2020-Biochem-Activity-18 - BIOCHEMISTRY OF AGINGDocument6 pages2020-Biochem-Activity-18 - BIOCHEMISTRY OF AGINGGabrielle John HernaezNo ratings yet
- Seatwork No. 2.3 - Activity B (Page 50) 1. Using Steroids and Recreational DrugsDocument3 pagesSeatwork No. 2.3 - Activity B (Page 50) 1. Using Steroids and Recreational DrugsJaroushie FlynnNo ratings yet
- Mecanisme AntiagingDocument12 pagesMecanisme AntiagingSonia CaruntuNo ratings yet
- Pathology LO1&2 NotesDocument4 pagesPathology LO1&2 NotesT .AlainNo ratings yet
- Photo AgingDocument39 pagesPhoto AgingIrene EvelynNo ratings yet
- Basic of Geriatrics and Internal Medicine For PhysiotherapistDocument128 pagesBasic of Geriatrics and Internal Medicine For PhysiotherapistDoha EbedNo ratings yet
- Biomolecular Mechanism of Antioxidant Activity On Aging ProcessDocument13 pagesBiomolecular Mechanism of Antioxidant Activity On Aging ProcessShofi Nur AidahNo ratings yet
- Cell InjuryDocument33 pagesCell Injurywizborrlyzo006No ratings yet
- Aging & Health: Widayanti - DR., M.KesDocument32 pagesAging & Health: Widayanti - DR., M.Kesanon_852191021No ratings yet
- Unlock The Secrets To A Sharper Mind 2430Document11 pagesUnlock The Secrets To A Sharper Mind 2430Eva MNo ratings yet
- Pharma NutritionDocument36 pagesPharma NutritionАлександр КолядаNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Exploration of Gene, CellularDocument21 pagesA Comprehensive Exploration of Gene, Cellularvanessa_werbickyNo ratings yet
- Skin AntioksidanDocument8 pagesSkin AntioksidanAngga SuryaNo ratings yet
- Phytochemicals A Promising Alternative For The Prevention of 3mr8x2c8Document35 pagesPhytochemicals A Promising Alternative For The Prevention of 3mr8x2c8NatanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Applications BookshelfDocument35 pagesPathophysiology Applications Bookshelfmorgan bigelow100% (2)
- Introd, Disease, Cell Injury & Cell DeathDocument53 pagesIntrod, Disease, Cell Injury & Cell DeathSintya Anggraeni SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Maria Blasco Article June2013-The Hallmarks of AgingDocument24 pagesMaria Blasco Article June2013-The Hallmarks of AgingDavid CrossNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Research PaperDocument6 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Research Paperntjjkmrhf100% (1)
- Cellular Aging - CorrectedDocument78 pagesCellular Aging - Correctedtravis efraimNo ratings yet
- Bhumika VageriyaDocument28 pagesBhumika Vageriyaalive computerNo ratings yet
- Alz Review 2016Document18 pagesAlz Review 2016Ligia Rojas de PautaNo ratings yet
- Fatin 2019Document14 pagesFatin 2019Luis Gonzalo Sequeda CNo ratings yet
- Cell Injury Ist Year 1Document19 pagesCell Injury Ist Year 1khurramchoudhary05No ratings yet
- Bioinformatic Analysis of Selected Natural Compounds For Antidiabetic PotentialDocument12 pagesBioinformatic Analysis of Selected Natural Compounds For Antidiabetic PotentialEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Husson AgeingDocument36 pagesHusson Ageinghusson_ameenNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Biology of Ageing and Role of Dietary AntioxidantsDocument14 pagesReview Article: Biology of Ageing and Role of Dietary AntioxidantsMedicina EncantadaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Aging 2022Document12 pagesTheories of Aging 2022Lara Victoria DuenasNo ratings yet
- Geriatric NursingDocument64 pagesGeriatric NursingMark Elben100% (2)
- 1024-Article Text-2679-1-10-20180929Document4 pages1024-Article Text-2679-1-10-20180929Life LineNo ratings yet
- 1 Patho IntroDocument77 pages1 Patho IntroDominic DizonNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Ageing AssignmentDocument9 pagesBiochemistry of Ageing Assignmentkalejaiye johnNo ratings yet
- 10 3390@nu13072273Document20 pages10 3390@nu13072273hjerkovic4444No ratings yet
- Genetics of LongevityDocument28 pagesGenetics of LongevityMariana ValdespinoNo ratings yet
- The Errors in Cell Cycle: Angelica Rose Y. Remonde Grade 11-MoscoviumDocument3 pagesThe Errors in Cell Cycle: Angelica Rose Y. Remonde Grade 11-Moscoviumange the frettyNo ratings yet
- Concept of IllnessDocument12 pagesConcept of IllnesscarltumlosNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0028390813003195 MainDocument24 pages1 s2.0 S0028390813003195 MainOanaNo ratings yet
- Ijerph 15 01083Document12 pagesIjerph 15 01083princess Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Herbal Formulation Considerations For Autoimmune DisordersDocument26 pagesHerbal Formulation Considerations For Autoimmune Disordershitesh mendirattaNo ratings yet
- Why Do People Age ChemDocument8 pagesWhy Do People Age ChemKarlo SpotifyNo ratings yet
- Satkynbai Tentishev Memorial Asian Medical Institute: By: Dr. Aminov ShamilDocument53 pagesSatkynbai Tentishev Memorial Asian Medical Institute: By: Dr. Aminov ShamilBorigam Aravind PatelNo ratings yet
- 2018 Introduction To The PathophysiologyDocument25 pages2018 Introduction To The PathophysiologyzekoNo ratings yet
- Intervention in Human Cycle: Possibility of Age ReversingDocument6 pagesIntervention in Human Cycle: Possibility of Age ReversingJagdish MalavNo ratings yet
- 19 Theory of Aging ProcessDocument110 pages19 Theory of Aging ProcessVhandy Ramadhan100% (3)
- Side Subjects of 1st Year Mbbs Modular ExamDocument214 pagesSide Subjects of 1st Year Mbbs Modular ExamRAHEEL khattakNo ratings yet
- Anti Aging TechnologiiesDocument13 pagesAnti Aging TechnologiiesZohaib SarwarNo ratings yet
- Biology of Aging and FrailtyDocument11 pagesBiology of Aging and FrailtyJay DNo ratings yet
- Gerontological NursingDocument91 pagesGerontological Nursingrinkai13100% (10)
- Biochemistry of Ageing.Document52 pagesBiochemistry of Ageing.deva_baraskar88% (8)
- DM Clinical & Interventional Physiology INI SS July 2023Document14 pagesDM Clinical & Interventional Physiology INI SS July 2023Wwwanand111No ratings yet
- Semester I1Document8 pagesSemester I1Wwwanand111No ratings yet
- IndexingDocument2 pagesIndexingWwwanand111No ratings yet
- Arterial PulseDocument2 pagesArterial PulseWwwanand111No ratings yet
- Nano Greens Phyto Nut AgingDocument4 pagesNano Greens Phyto Nut AgingWwwanand111No ratings yet
- 5b9b97c22adf4 - Final Faculty Advt. Sep 2018Document21 pages5b9b97c22adf4 - Final Faculty Advt. Sep 2018Wwwanand111No ratings yet
- That One Privacy Guy's VPN Comparison ChartDocument50 pagesThat One Privacy Guy's VPN Comparison ChartWwwanand111No ratings yet
- The Evolution of Eyes: Michael F. LandDocument30 pagesThe Evolution of Eyes: Michael F. LandWwwanand111No ratings yet
- Book Review-Evolutions WitnessDocument2 pagesBook Review-Evolutions WitnessWwwanand111No ratings yet
- Temperature: Click For UpdatesDocument6 pagesTemperature: Click For UpdatesWwwanand111No ratings yet
- Deyo 1992Document6 pagesDeyo 1992Wwwanand111No ratings yet
- Human Evolution: Mader: Biology 8th EdDocument24 pagesHuman Evolution: Mader: Biology 8th EdWwwanand111No ratings yet
- Body Imaging 09082012 1333Document19 pagesBody Imaging 09082012 1333Wwwanand111No ratings yet
- Eye Evolution Jan13figs 2Document10 pagesEye Evolution Jan13figs 2Wwwanand111No ratings yet
- 10575Document4 pages10575Wwwanand111No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Chemistry: Dr. Herat D. Soni Assistant Professor Rural Medical College LoniDocument117 pagesCarbohydrate Chemistry: Dr. Herat D. Soni Assistant Professor Rural Medical College LoniWwwanand111No ratings yet
- Color VisionDocument6 pagesColor VisionWwwanand111No ratings yet
- Development and Evolution of Eyes and Photoreceptors: From Cyanobacteria To HumansDocument2 pagesDevelopment and Evolution of Eyes and Photoreceptors: From Cyanobacteria To HumansWwwanand111No ratings yet
- 7th Grade Microscope Exam ReviewDocument34 pages7th Grade Microscope Exam ReviewWwwanand111100% (1)
- Syllabus: Maharashtra University of Health Sciences, NashikDocument6 pagesSyllabus: Maharashtra University of Health Sciences, NashikWwwanand111No ratings yet
- Course in Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative MedicineDocument1 pageCourse in Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative MedicineWwwanand111No ratings yet
- DASC20010Document2 pagesDASC20010Wwwanand111No ratings yet
- RMRC Blegaum PostsDocument5 pagesRMRC Blegaum PostsWwwanand111No ratings yet
- Bicentennial ManDocument2 pagesBicentennial ManBubbles InojalesNo ratings yet
- Griskevisius Replication Poster 002Document1 pageGriskevisius Replication Poster 002api-383582002No ratings yet
- The Andromedan Compendium - 7bDocument10 pagesThe Andromedan Compendium - 7bAnonymous XSNBQQ4yNo ratings yet
- 9700 s11 QP 22Document16 pages9700 s11 QP 22Ahmed Kaleem Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Dna Rna No VirusDocument4 pagesStudy Guide Dna Rna No VirusLara AlbeeshyNo ratings yet
- Yeast Pop. LabDocument3 pagesYeast Pop. Labtanu96tp5952No ratings yet
- Mudras For Awakening Chakras 19Document93 pagesMudras For Awakening Chakras 19NiravMakwanaNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Mid Term PaperDocument6 pages10 Science Mid Term PaperAnishika100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Nervous SystemDocument85 pagesAnatomy of The Nervous SystemjoelNo ratings yet
- Seed Production Technologyof Wheatand BarleyDocument33 pagesSeed Production Technologyof Wheatand BarleyAlemayehu TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Johnson Et Al.2006. Felidae Phylogeny PDFDocument6 pagesJohnson Et Al.2006. Felidae Phylogeny PDFNydia JGNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Guava 1Document16 pagesEffectiveness of Guava 1Arellano Reyson100% (1)
- Determination of Yield of Silver Nanoparticles Using Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)Document2 pagesDetermination of Yield of Silver Nanoparticles Using Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)Afrah MNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus 2004Document9 pagesHypothalamus 2004Deepak MainiNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Photosynthesis and Energy FlowDocument4 pagesBioenergetics Photosynthesis and Energy Flowvin ocangNo ratings yet
- (E12) GM Food-VocabDocument2 pages(E12) GM Food-VocabAlexandru Marius100% (1)
- Biology Paper 6 November October 2008 IGCSE Question Paper QPDocument12 pagesBiology Paper 6 November October 2008 IGCSE Question Paper QPStevo4975% (4)
- In Vitro Gas Measuring Techniques Review HohenheimDocument21 pagesIn Vitro Gas Measuring Techniques Review HohenheimHelio LimaNo ratings yet
- Stomata Lab 2023Document4 pagesStomata Lab 2023api-711256385No ratings yet
- Tugas Kelompok Perenc PendDocument32 pagesTugas Kelompok Perenc PendEko WidodoNo ratings yet
- 04 Evolution StrategiesDocument30 pages04 Evolution StrategiesAditya Gururaja Rao KarnamNo ratings yet
- Scientific Aspects in Ramcharit ManasDocument52 pagesScientific Aspects in Ramcharit ManasRam Kumar Kuril100% (9)
- Class 9 TissueDocument10 pagesClass 9 Tissuekhatridheeraj657No ratings yet
- Science Magazine 5694 2004-10-08 PDFDocument89 pagesScience Magazine 5694 2004-10-08 PDFTân ChipNo ratings yet
- Ra 7586 - Nipas ActDocument10 pagesRa 7586 - Nipas ActggbadayosNo ratings yet
- HUMAN BEHAVIOR AND VICTIMOLOGY Autosaved AutosavedDocument55 pagesHUMAN BEHAVIOR AND VICTIMOLOGY Autosaved AutosavedJodmainel LeradoNo ratings yet
- Biology and Physiology of Saline PlantsDocument32 pagesBiology and Physiology of Saline PlantsNguyễn Lê Quốc ThiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology-Ng Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiology-Ng Hirschsprung DiseaseJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet