Professional Documents
Culture Documents
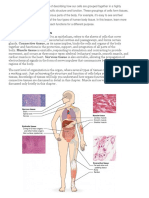
Muscle Tissue: The Muscular System
Muscle Tissue: The Muscular System
Uploaded by
amadi3ndessy1260Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Jyotish - Nakshatra Light PDFDocument123 pagesJyotish - Nakshatra Light PDFpradeepnagda100% (19)
- IUCAADocument11 pagesIUCAApragati vpkNo ratings yet
- (Robert E. Sheriff (Auth.) ) Seismic StratigraphyDocument234 pages(Robert E. Sheriff (Auth.) ) Seismic StratigraphyMuhammad FaddhilaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy - Lec. 2 - GR1Document9 pagesHuman Anatomy - Lec. 2 - GR1bmydwoybx482No ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy (Lec 7)Document32 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy (Lec 7)ehtshamulhaq06No ratings yet
- 01 Animal TissueDocument8 pages01 Animal TissueRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nselec TissueDocument6 pagesNselec TissueClaire funtilarNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Document3 pagesAnimal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Amor Panopio MagtibayNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TISSUE NOTESpdfDocument30 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TISSUE NOTESpdfYego EdwinNo ratings yet
- M 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument39 pagesM 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamarendrar87No ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument13 pagesAnimal TissuesYudatami TiaraNo ratings yet
- Different Body Tissues: By: Group 4Document25 pagesDifferent Body Tissues: By: Group 4Aisha Mae Cañete JawadNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Soft Tissue Mechanics The Soft Tissues of The Body:: Kripa's Notes.Document14 pagesUnit Iv Soft Tissue Mechanics The Soft Tissues of The Body:: Kripa's Notes.Kripa NNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues: Tissue Matrix MuscleDocument8 pagesBody Tissues: Tissue Matrix Muscle9. Hoàng Mai ChiNo ratings yet
- The Muscular TissueDocument23 pagesThe Muscular TissueMuhammad Salisu IliyasuNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueDocument6 pagesPlant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueBhoomika GoyalNo ratings yet
- Biology Lect1. Type of Tissue DR - Aida AlobaidiDocument22 pagesBiology Lect1. Type of Tissue DR - Aida AlobaidiYaqeen AlaidyNo ratings yet
- Tissues (Image) Description and LocationDocument10 pagesTissues (Image) Description and LocationJOHNNY YNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresDocument58 pagesLesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresPhoenixNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesJamesNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument17 pagesAnimal TissuesMuskan Shree100% (1)
- Present 1 - HistologyDocument59 pagesPresent 1 - HistologySultanNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثانية تشريح اسنان م 1Document26 pagesالمحاضرة الثانية تشريح اسنان م 1mfhrluvxxxNo ratings yet
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDocument74 pagesTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- Animal Tissues: What Is Tissue?Document8 pagesAnimal Tissues: What Is Tissue?DuaneNo ratings yet
- Daniela Fernanda Soto Lima TissuesDocument2 pagesDaniela Fernanda Soto Lima TissuesDaniela SotoNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument33 pagesTissuesAnonymous imF0MCd9UNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology LabDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Labشهد إياد0% (1)
- 3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015Document34 pages3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015yigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- Exercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreDocument9 pagesExercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreMaria MarmitaNo ratings yet
- HP I P2 Tissues and MembranesDocument38 pagesHP I P2 Tissues and MembranesNazir RabiuNo ratings yet
- TISSUESDocument12 pagesTISSUESMaria Stephanie LabutapNo ratings yet
- Tissues (Notes)Document11 pagesTissues (Notes)Rezeil CaNo ratings yet
- The Four Types of Tissues: Epithelial Tissue, Also Referred To As Epithelium, Refers To The Sheets of Cells That CoverDocument9 pagesThe Four Types of Tissues: Epithelial Tissue, Also Referred To As Epithelium, Refers To The Sheets of Cells That CoveraudreyNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument10 pagesMuscle TissueHesbone AneneNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 1Document45 pagesAnimal Tissues 1sirajNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER V: Tissues: Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous TissueDocument10 pagesCHAPTER V: Tissues: Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous TissueAem TalNo ratings yet
- Human TissuesDocument7 pagesHuman Tissuesapi-269312030No ratings yet
- Human Body Tissues Power PointDocument60 pagesHuman Body Tissues Power PointMaxwell C Jay KafwaniNo ratings yet
- Cells: Skeletal Muscle Is A Form of Striated Muscle Tissue Existing Under Control of The SomaticDocument11 pagesCells: Skeletal Muscle Is A Form of Striated Muscle Tissue Existing Under Control of The SomaticbloodythornNo ratings yet
- Cds Day1Document15 pagesCds Day1Rajkamal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Histology Notes: Epithelial TissueDocument4 pagesHistology Notes: Epithelial TissueSteph AsideNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument45 pagesAnimal TissueAyesha YusopNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Examination of H&P 2,3,4,5,6Document8 pagesMicroscopic Examination of H&P 2,3,4,5,6sorrygoodthings98No ratings yet
- That Means That Underlying The Cells That Are The Cellular Component of The Epithelial TissueDocument3 pagesThat Means That Underlying The Cells That Are The Cellular Component of The Epithelial TissueDivine HernandezNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument3 pagesAnimal TissueAkmal MusyaffaNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues and Animal Tissues 1Document6 pagesPlant Tissues and Animal Tissues 1PawanNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 1. EpithelialDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissues 1. EpithelialRogeimar Claire MangomayaoNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 Zoology Tissues - Component of Cells With The Same Functions and Same Structural AdaptationDocument4 pagesBio 11 Zoology Tissues - Component of Cells With The Same Functions and Same Structural AdaptationJamaine VillacortaNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsDocument7 pagesActivity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsAryan Jovic DomingoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Group 5 PRESENTATIONDocument21 pagesAnatomy Group 5 PRESENTATIONambaig661No ratings yet
- Advanced Anatomy - Myofascial MeridiansDocument37 pagesAdvanced Anatomy - Myofascial MeridiansBioTaoQi100% (2)
- Tissues of Body: Chapter # 3Document20 pagesTissues of Body: Chapter # 3Mrym NbNo ratings yet
- 3 Week - TissuesDocument55 pages3 Week - TissuesGeevee Naganag Ventula100% (1)
- TissueDocument27 pagesTissueemilpauloquibilanNo ratings yet
- MODULe 3 AnaphysioDocument9 pagesMODULe 3 Anaphysiojoshua ordenaNo ratings yet
- Bio101Lab DiscussionW2Document16 pagesBio101Lab DiscussionW2iloveacuandtuinaNo ratings yet
- ?????????? ??????Document6 pages?????????? ??????DEBASISH MOHANTYNo ratings yet
- Specificatio N: Tissues: Epithelial: Simple (CuboidalDocument22 pagesSpecificatio N: Tissues: Epithelial: Simple (CuboidalFatma AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 6 Muscle TissueDocument10 pagesExercise No. 6 Muscle TissueRyan Aaron Cruz ParNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Body TissuesDocument10 pagesModule 5 - Body Tissues10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument16 pagesTissuesDiya sashiniNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper in ArkeoDocument2 pagesReaction Paper in ArkeoFraul Tadle100% (3)
- Prashan JyotishDocument15 pagesPrashan JyotishAnmohiey0% (1)
- Astrology and Vastu ShastraDocument3 pagesAstrology and Vastu ShastrasssmouNo ratings yet
- Superposition NotesDocument23 pagesSuperposition NoteshaelstoneNo ratings yet
- Geological Society of America Citation StyleDocument4 pagesGeological Society of America Citation Style146256No ratings yet
- Gravitation Notes: MHT-CETDocument15 pagesGravitation Notes: MHT-CETSachin67% (6)
- Chapter Five Class 9thDocument11 pagesChapter Five Class 9thAliNo ratings yet
- 0806 Synthetic BiologyDocument36 pages0806 Synthetic BiologyArjun ArjunNo ratings yet
- Good Phrases That Describe EmotionsDocument9 pagesGood Phrases That Describe EmotionsKevin Lim100% (2)
- WITSML - Lithology - Object - Usage - Guide - 1.1revisions Version 2 PDFDocument41 pagesWITSML - Lithology - Object - Usage - Guide - 1.1revisions Version 2 PDFBarrett BoucherNo ratings yet
- Microscope TeacherNotesDocument4 pagesMicroscope TeacherNotesJulie GerberNo ratings yet
- Hermelín Et Al 2015 - Landscapes - Landforms - CDocument232 pagesHermelín Et Al 2015 - Landscapes - Landforms - CSandra Paola Mendoza OrtizNo ratings yet
- Soil La MaDocument126 pagesSoil La MaDr. Subash ThanappanNo ratings yet
- QTR 2 Module 2 Plant and Animal CellsDocument16 pagesQTR 2 Module 2 Plant and Animal CellsNick Bantolo100% (7)
- Chapter 13 - The Peripheral Nervous System and Reflex ActivityDocument53 pagesChapter 13 - The Peripheral Nervous System and Reflex Activityramadan100% (1)
- Els DLP q2 GeneticsDocument11 pagesEls DLP q2 GeneticsIrish John GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- Sensory Systems Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesSensory Systems Lecture Notesdevilstrill1605100% (1)
- The A.P.R.O. Bulletin Mar-Apr 1972Document9 pagesThe A.P.R.O. Bulletin Mar-Apr 1972Nicholas VolosinNo ratings yet
- Sulawesi Tectonic PlateDocument20 pagesSulawesi Tectonic PlateElgi Zacky ZachryNo ratings yet
- Astrological Degrees and Fixed Stars PDFDocument14 pagesAstrological Degrees and Fixed Stars PDFMia Bukovsky100% (11)
- Sinkholes and Subsidence in South AfricaDocument34 pagesSinkholes and Subsidence in South AfricaZé Guilherme100% (1)
- Part 4 Transport in Plants Lesson 4Document10 pagesPart 4 Transport in Plants Lesson 4Kajana Sivarasa ShenthanNo ratings yet
- BenitoiteDocument13 pagesBenitoiteZoltánSáfárNo ratings yet
- PHD - Integrated Slope Channel Depositional ModelsDocument13 pagesPHD - Integrated Slope Channel Depositional Modelsomoba solaNo ratings yet
- Late Cretaceous Stratigraphy of The Upper Magdalena Basin in The Payandwhaparral Segment (Western Girardot Sub-Basin), ColombiaDocument17 pagesLate Cretaceous Stratigraphy of The Upper Magdalena Basin in The Payandwhaparral Segment (Western Girardot Sub-Basin), ColombiaOscar LugoNo ratings yet
- The Class MammaliaDocument5 pagesThe Class MammaliaMohammad Raza RizviNo ratings yet
Muscle Tissue: The Muscular System
Muscle Tissue: The Muscular System
Uploaded by
amadi3ndessy1260Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Muscle Tissue: The Muscular System
Muscle Tissue: The Muscular System
Uploaded by
amadi3ndessy1260Copyright:
Available Formats
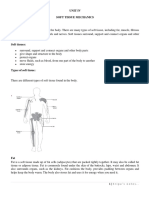
Muscle tissue
Muscle tissue consists of highly specialized cells, which provides motion, maintenance of posture and
heat production. Classification of muscles is made by structure and function.
Muscle tissues are grouped in to skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle tissue.
Skeletal muscle tissue are attached to bones, it is voluntary, cylindrical, multinucleated &
striated
Cardiac muscle tissue: It forms the wall of the heart; it is involuntary, uni-nucleated and
striated.
Smooth muscle tissue: located in the wall of hallow internal structure like Blood vessels,
stomach, intestine,and urinary bladder. It is involuntary and non-striated.
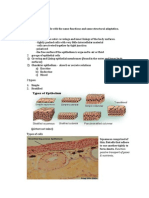
Membranes
Membranes are thin pliable layers of epithelial and/or connective tissue. They line body cavities, cover
surfaces,connect, or separate regions, structures and organs of the
body. The three kinds of membranes are
i.
mucous,
ii.
serous
iii.
synovial.
Mucous membranes (mucosa) lines body cavity that opens directly to the exterior. It is an epithelial layer.
Mucous membranes line the entire gastro intestine, respiratory excretory and reproductive tracts and constitute a
lining layer of epithelium. The connective tissue layer of mucous membrane is lamina propra.To prevent dry out
and to trap particles mucous membranes secret mucous.
Serous membrane / serosa: contains loose connective tissue covered by a layer of mesothelium. It lines body
cavity that does not open directly to the exterior. Covers the organs that lie within the cavity. Serosa is
composed of parietal layer (pertaining to be outer) and visceral layer
(pertaining to be near to the organ). Pleura and pericardium are serous membrane that line thoracic and heart
cavity respectively. The epithelial layer of a serious membrane secret a lubricating fluid called serious fluid. The
fluid allows organs to glide one another easily.
Synovial membrane: Unlike to other membranes this membrane does not contain epithelium. Therefore, it is not
epithelial membrane. It lines the cavities of the freely movable joints. Like serious membrane it lines structures
that do not open to the exterior. Synovial membranes secret synovial fluid that lubricate articular cartilage at the
ends of bones as they move at joints.
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
Chapter Objectives
At the end of this chapter, the student should be able to:
- List the general characteristics and functions of skeletal muscle tissue.
- Describe the structure of a muscle
- Describe the connective tissue components of skeletal muscles
- Briefly describe how muscles contract
- List the substances needed in muscle contraction and describe the function of each
- Differentiate between isotonic and isometric contractions
- Define the following terms: origin, insertion, synergist,antagonist, and prime mover
- Define the different bases employed in naming skeletal muscles Identify the principal skeletal Muscle in
different regions of the body by name, action, and innervations.
You might also like
- Jyotish - Nakshatra Light PDFDocument123 pagesJyotish - Nakshatra Light PDFpradeepnagda100% (19)
- IUCAADocument11 pagesIUCAApragati vpkNo ratings yet
- (Robert E. Sheriff (Auth.) ) Seismic StratigraphyDocument234 pages(Robert E. Sheriff (Auth.) ) Seismic StratigraphyMuhammad FaddhilaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy - Lec. 2 - GR1Document9 pagesHuman Anatomy - Lec. 2 - GR1bmydwoybx482No ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy (Lec 7)Document32 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy (Lec 7)ehtshamulhaq06No ratings yet
- 01 Animal TissueDocument8 pages01 Animal TissueRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nselec TissueDocument6 pagesNselec TissueClaire funtilarNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Document3 pagesAnimal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Amor Panopio MagtibayNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TISSUE NOTESpdfDocument30 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TISSUE NOTESpdfYego EdwinNo ratings yet
- M 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument39 pagesM 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamarendrar87No ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument13 pagesAnimal TissuesYudatami TiaraNo ratings yet
- Different Body Tissues: By: Group 4Document25 pagesDifferent Body Tissues: By: Group 4Aisha Mae Cañete JawadNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Soft Tissue Mechanics The Soft Tissues of The Body:: Kripa's Notes.Document14 pagesUnit Iv Soft Tissue Mechanics The Soft Tissues of The Body:: Kripa's Notes.Kripa NNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues: Tissue Matrix MuscleDocument8 pagesBody Tissues: Tissue Matrix Muscle9. Hoàng Mai ChiNo ratings yet
- The Muscular TissueDocument23 pagesThe Muscular TissueMuhammad Salisu IliyasuNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueDocument6 pagesPlant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueBhoomika GoyalNo ratings yet
- Biology Lect1. Type of Tissue DR - Aida AlobaidiDocument22 pagesBiology Lect1. Type of Tissue DR - Aida AlobaidiYaqeen AlaidyNo ratings yet
- Tissues (Image) Description and LocationDocument10 pagesTissues (Image) Description and LocationJOHNNY YNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresDocument58 pagesLesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresPhoenixNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesJamesNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument17 pagesAnimal TissuesMuskan Shree100% (1)
- Present 1 - HistologyDocument59 pagesPresent 1 - HistologySultanNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثانية تشريح اسنان م 1Document26 pagesالمحاضرة الثانية تشريح اسنان م 1mfhrluvxxxNo ratings yet
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDocument74 pagesTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- Animal Tissues: What Is Tissue?Document8 pagesAnimal Tissues: What Is Tissue?DuaneNo ratings yet
- Daniela Fernanda Soto Lima TissuesDocument2 pagesDaniela Fernanda Soto Lima TissuesDaniela SotoNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument33 pagesTissuesAnonymous imF0MCd9UNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology LabDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Labشهد إياد0% (1)
- 3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015Document34 pages3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015yigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- Exercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreDocument9 pagesExercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreMaria MarmitaNo ratings yet
- HP I P2 Tissues and MembranesDocument38 pagesHP I P2 Tissues and MembranesNazir RabiuNo ratings yet
- TISSUESDocument12 pagesTISSUESMaria Stephanie LabutapNo ratings yet
- Tissues (Notes)Document11 pagesTissues (Notes)Rezeil CaNo ratings yet
- The Four Types of Tissues: Epithelial Tissue, Also Referred To As Epithelium, Refers To The Sheets of Cells That CoverDocument9 pagesThe Four Types of Tissues: Epithelial Tissue, Also Referred To As Epithelium, Refers To The Sheets of Cells That CoveraudreyNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument10 pagesMuscle TissueHesbone AneneNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 1Document45 pagesAnimal Tissues 1sirajNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER V: Tissues: Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous TissueDocument10 pagesCHAPTER V: Tissues: Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous TissueAem TalNo ratings yet
- Human TissuesDocument7 pagesHuman Tissuesapi-269312030No ratings yet
- Human Body Tissues Power PointDocument60 pagesHuman Body Tissues Power PointMaxwell C Jay KafwaniNo ratings yet
- Cells: Skeletal Muscle Is A Form of Striated Muscle Tissue Existing Under Control of The SomaticDocument11 pagesCells: Skeletal Muscle Is A Form of Striated Muscle Tissue Existing Under Control of The SomaticbloodythornNo ratings yet
- Cds Day1Document15 pagesCds Day1Rajkamal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Histology Notes: Epithelial TissueDocument4 pagesHistology Notes: Epithelial TissueSteph AsideNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument45 pagesAnimal TissueAyesha YusopNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Examination of H&P 2,3,4,5,6Document8 pagesMicroscopic Examination of H&P 2,3,4,5,6sorrygoodthings98No ratings yet
- That Means That Underlying The Cells That Are The Cellular Component of The Epithelial TissueDocument3 pagesThat Means That Underlying The Cells That Are The Cellular Component of The Epithelial TissueDivine HernandezNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument3 pagesAnimal TissueAkmal MusyaffaNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues and Animal Tissues 1Document6 pagesPlant Tissues and Animal Tissues 1PawanNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 1. EpithelialDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissues 1. EpithelialRogeimar Claire MangomayaoNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 Zoology Tissues - Component of Cells With The Same Functions and Same Structural AdaptationDocument4 pagesBio 11 Zoology Tissues - Component of Cells With The Same Functions and Same Structural AdaptationJamaine VillacortaNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsDocument7 pagesActivity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsAryan Jovic DomingoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Group 5 PRESENTATIONDocument21 pagesAnatomy Group 5 PRESENTATIONambaig661No ratings yet
- Advanced Anatomy - Myofascial MeridiansDocument37 pagesAdvanced Anatomy - Myofascial MeridiansBioTaoQi100% (2)
- Tissues of Body: Chapter # 3Document20 pagesTissues of Body: Chapter # 3Mrym NbNo ratings yet
- 3 Week - TissuesDocument55 pages3 Week - TissuesGeevee Naganag Ventula100% (1)
- TissueDocument27 pagesTissueemilpauloquibilanNo ratings yet
- MODULe 3 AnaphysioDocument9 pagesMODULe 3 Anaphysiojoshua ordenaNo ratings yet
- Bio101Lab DiscussionW2Document16 pagesBio101Lab DiscussionW2iloveacuandtuinaNo ratings yet
- ?????????? ??????Document6 pages?????????? ??????DEBASISH MOHANTYNo ratings yet
- Specificatio N: Tissues: Epithelial: Simple (CuboidalDocument22 pagesSpecificatio N: Tissues: Epithelial: Simple (CuboidalFatma AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 6 Muscle TissueDocument10 pagesExercise No. 6 Muscle TissueRyan Aaron Cruz ParNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Body TissuesDocument10 pagesModule 5 - Body Tissues10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument16 pagesTissuesDiya sashiniNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper in ArkeoDocument2 pagesReaction Paper in ArkeoFraul Tadle100% (3)
- Prashan JyotishDocument15 pagesPrashan JyotishAnmohiey0% (1)
- Astrology and Vastu ShastraDocument3 pagesAstrology and Vastu ShastrasssmouNo ratings yet
- Superposition NotesDocument23 pagesSuperposition NoteshaelstoneNo ratings yet
- Geological Society of America Citation StyleDocument4 pagesGeological Society of America Citation Style146256No ratings yet
- Gravitation Notes: MHT-CETDocument15 pagesGravitation Notes: MHT-CETSachin67% (6)
- Chapter Five Class 9thDocument11 pagesChapter Five Class 9thAliNo ratings yet
- 0806 Synthetic BiologyDocument36 pages0806 Synthetic BiologyArjun ArjunNo ratings yet
- Good Phrases That Describe EmotionsDocument9 pagesGood Phrases That Describe EmotionsKevin Lim100% (2)
- WITSML - Lithology - Object - Usage - Guide - 1.1revisions Version 2 PDFDocument41 pagesWITSML - Lithology - Object - Usage - Guide - 1.1revisions Version 2 PDFBarrett BoucherNo ratings yet
- Microscope TeacherNotesDocument4 pagesMicroscope TeacherNotesJulie GerberNo ratings yet
- Hermelín Et Al 2015 - Landscapes - Landforms - CDocument232 pagesHermelín Et Al 2015 - Landscapes - Landforms - CSandra Paola Mendoza OrtizNo ratings yet
- Soil La MaDocument126 pagesSoil La MaDr. Subash ThanappanNo ratings yet
- QTR 2 Module 2 Plant and Animal CellsDocument16 pagesQTR 2 Module 2 Plant and Animal CellsNick Bantolo100% (7)
- Chapter 13 - The Peripheral Nervous System and Reflex ActivityDocument53 pagesChapter 13 - The Peripheral Nervous System and Reflex Activityramadan100% (1)
- Els DLP q2 GeneticsDocument11 pagesEls DLP q2 GeneticsIrish John GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- Sensory Systems Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesSensory Systems Lecture Notesdevilstrill1605100% (1)
- The A.P.R.O. Bulletin Mar-Apr 1972Document9 pagesThe A.P.R.O. Bulletin Mar-Apr 1972Nicholas VolosinNo ratings yet
- Sulawesi Tectonic PlateDocument20 pagesSulawesi Tectonic PlateElgi Zacky ZachryNo ratings yet
- Astrological Degrees and Fixed Stars PDFDocument14 pagesAstrological Degrees and Fixed Stars PDFMia Bukovsky100% (11)
- Sinkholes and Subsidence in South AfricaDocument34 pagesSinkholes and Subsidence in South AfricaZé Guilherme100% (1)
- Part 4 Transport in Plants Lesson 4Document10 pagesPart 4 Transport in Plants Lesson 4Kajana Sivarasa ShenthanNo ratings yet
- BenitoiteDocument13 pagesBenitoiteZoltánSáfárNo ratings yet
- PHD - Integrated Slope Channel Depositional ModelsDocument13 pagesPHD - Integrated Slope Channel Depositional Modelsomoba solaNo ratings yet
- Late Cretaceous Stratigraphy of The Upper Magdalena Basin in The Payandwhaparral Segment (Western Girardot Sub-Basin), ColombiaDocument17 pagesLate Cretaceous Stratigraphy of The Upper Magdalena Basin in The Payandwhaparral Segment (Western Girardot Sub-Basin), ColombiaOscar LugoNo ratings yet
- The Class MammaliaDocument5 pagesThe Class MammaliaMohammad Raza RizviNo ratings yet