Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bevel Gear Model-3
Bevel Gear Model-3
Uploaded by
vijay_khandgeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bevel Gear Model-3
Bevel Gear Model-3
Uploaded by
vijay_khandgeCopyright:
Available Formats
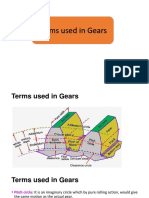
Pitch angle of pinion (gear) y (F) is the angle between an element of the pitch cone
and its axis.
Pitch apex beyond crossing point on the pinion (gear) G (Z) is the distance
between the pitch apex and the crossing point on a hypoid set.
Pitch diameter of pinion (gear) d (D) is the diameter of the pitch cone at the outside
of the blank.
Pitch, mean circular pm is the distance along the pitch circle at the mean cone distance
between corresponding profiles of adjacent teeth.
Pressure angle $ is the angle at the pitch point between the line of pressure which
is normal to the tooth surface and the plane tangent to the pitch surface. It is specified
at the mean cone distance.
Ratio, gear mG is the ratio of the number of gear teeth to the number of pinion
teeth.
Root angle of pinion (gear) JR (F/?) is the angle between an element of the root
cone and its axis.
Root apex beyond crossing point on the pinion (gear) GR (ZR) is the distance
between the root apex and the crossing point on a bevel or hypoid set.
Shaft angle S is the angle between the axes of the pinion shaft and the gear shaft.
Spiral angle \|/ is the angle between the tooth trace and an element of the pitch
cone. It is specified at the mean cone distance.
Spiral-bevel gear, left-hand is one in which the outer half of a tooth is inclined in
the counterclockwise direction from the axial plane through the midpoint of the
tooth, as viewed by an observer looking at the face of the gear.
Spiral-bevel gear, right-hand is one in which the outer half of a tooth is inclined in
the clockwise direction from the axial plane through the midpoint of the tooth, as
viewed by an observer looking at the face of the gear.
Tangential force Wt is the force applied to a gear tooth at the mean cone distance
in a direction tangent to the pitch cone and normal to a pitch-cone element.
Thickness of pinion (gear), mean circular t (T) is the length of arc on the pitch cone
between the two sides of the tooth at the mean cone distance.
Thickness of pinion (gear), mean normal chordal tnc (Tnc) is the chordal thickness
of the pinion tooth at the mean cone distance in a plane normal to the tooth trace.
34.2.3
Calculation Methods
Four methods of blank design are commonly used in the design of bevel and hypoid
gears:
1. Standard taper
2. Duplex taper
3. Uniform taper
4. Tilted root-line taper
Application Requirements
Bevel and hypoid gears are suitable for transmitting power between shafts at practically
any angle and speed. The load, speed, and special operating conditions must be
defined as the first step in designing a gear set for a specific application.
A basic load and a suitable factor encompassing protection from intermittent
overloads, desired life, and safety are determined from
1. The power rating of the prime mover, its overload potential, and the uniformity
of its output torque
2. The normal output loading, peak loads and their duration, and the possibility of
stalling or severe loading at infrequent intervals
3. Inertia loads arising from acceleration or deceleration
You might also like
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics 4th Edition Knight Test BankDocument26 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics 4th Edition Knight Test BankDianaMartinygrb100% (48)
- Analytical Gear Inspection Symbols and Interpretation of Charts PDFDocument10 pagesAnalytical Gear Inspection Symbols and Interpretation of Charts PDFniloblue67% (3)
- Gear NomenclatureDocument41 pagesGear NomenclatureViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Bevel Gear Model-2Document1 pageBevel Gear Model-2vijay_khandgeNo ratings yet
- Gear and FormulaDocument7 pagesGear and FormulahrsreenathNo ratings yet
- Kom Gear TerminologyDocument3 pagesKom Gear Terminologydhilip_sacetNo ratings yet
- Gear Definitions and FormulasDocument8 pagesGear Definitions and FormulasSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Gear TerminologyDocument11 pagesGear TerminologyGoutam AcharjeeNo ratings yet
- Gear LecturDocument50 pagesGear LecturMuralikrishnan GM100% (1)
- Gear Terms and DefinitionsDocument5 pagesGear Terms and DefinitionsAaron_Liu_1555No ratings yet
- Involute Gear and Spline SoftwareDocument9 pagesInvolute Gear and Spline Softwaresumeetsaini88No ratings yet
- Module IV: Gears and Gear TrainsDocument38 pagesModule IV: Gears and Gear TrainsSuraj VinayNo ratings yet
- Gears AppendixDocument7 pagesGears AppendixPratik ThapaNo ratings yet
- 202003291623595791prince Singh Spur GearDocument10 pages202003291623595791prince Singh Spur GearDARPAN BHARDWAJNo ratings yet
- Gear TerminologyDocument42 pagesGear Terminologyyair Enrique Romero OspinoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer para Sa WednesdayDocument4 pagesReviewer para Sa WednesdayRyza MartizanoNo ratings yet
- KDM UNIT-2 Gears - Gear TrainsDocument11 pagesKDM UNIT-2 Gears - Gear TrainsAchyuth KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Gear, Contact Ratio, InterferenceDocument52 pagesGroup 1 Gear, Contact Ratio, InterferenceAnthony FajardoNo ratings yet
- Line of Action or Pressure Line: The Force, Which The Driving Tooth Exerts at Point of Contact of The TwoDocument2 pagesLine of Action or Pressure Line: The Force, Which The Driving Tooth Exerts at Point of Contact of The TwoMari MuthuNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument8 pagesGearsKevin JoeNo ratings yet
- Gear Geometry & Profile TheoryDocument24 pagesGear Geometry & Profile Theoryansh1983100% (2)
- Gear Terminology: What Is Gear Module?Document5 pagesGear Terminology: What Is Gear Module?Rabia ZulqarnainNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of GearsDocument7 pagesNomenclature of GearsAamir RazaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Spur Gear - A Gearwheel With Teeth Projecting Parallel To The Wheel's Axis. Nomenclature of Spur GearDocument6 pagesDefinition of Spur Gear - A Gearwheel With Teeth Projecting Parallel To The Wheel's Axis. Nomenclature of Spur GearMichael Angelo ComediaNo ratings yet
- Terminology SpurDocument3 pagesTerminology SpurNimish Pande100% (1)
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument41 pagesIlovepdf MergedTim DrakeNo ratings yet
- Gears TerminologyDocument10 pagesGears TerminologyJawad Ullah100% (2)
- GearsDocument70 pagesGearsJayesh NayakantiNo ratings yet
- Design of GearsDocument94 pagesDesign of Gears60-Hafiz Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Ephrem Zeleke: Prepared byDocument44 pagesEphrem Zeleke: Prepared bysamuel mechNo ratings yet
- Djmit Mogar Anand: Prepared byDocument19 pagesDjmit Mogar Anand: Prepared byDhruv UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii Tom Part IiDocument12 pagesUnit-Ii Tom Part Iigourav708680No ratings yet
- Gearthread 120918023938 Phpapp01Document50 pagesGearthread 120918023938 Phpapp01Bakkiya RajNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Gears and Gear TrainsDocument27 pagesKinematics of Gears and Gear TrainsAbdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 GearsDocument73 pagesModule 4 GearsDheeraj PNo ratings yet
- Gears Nomenclature: by Feedback by Comments 1 MahekDocument20 pagesGears Nomenclature: by Feedback by Comments 1 MahekSujai BaskarNo ratings yet
- Gears Nomenclature: by Feedback by Comments 1 MahekDocument20 pagesGears Nomenclature: by Feedback by Comments 1 MahekSujai BaskarNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines (Mom)Document73 pagesMechanics of Machines (Mom)Steve ChaurasiyaNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument45 pagesGearsSomendra Brijesh Pandey100% (1)
- Gears PDFDocument45 pagesGears PDFSanmukh ShindeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Information: Spur GearsDocument6 pagesEngineering Information: Spur GearsLuis MarcosNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements-II (MEPC-306) : Prepared By: DR Saurabh Kango Assistant Professor NIT JalandharDocument21 pagesDesign of Machine Elements-II (MEPC-306) : Prepared By: DR Saurabh Kango Assistant Professor NIT JalandharGAURAV YADAVNo ratings yet
- List of Gear NomenclatureDocument26 pagesList of Gear Nomenclatureyair Enrique Romero OspinoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PDF File SPUR GEARSDocument6 pagesModule 3 PDF File SPUR GEARSAdolfo KayeNo ratings yet
- Gears, Splines, and Serrations: Unit 24Document8 pagesGears, Splines, and Serrations: Unit 24Satish Dhandole100% (1)
- Introduction To Mechanisms: 7 GearsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Mechanisms: 7 GearsDezert EagleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Gears and Gear TrainsDocument93 pagesChapter 4-Gears and Gear TrainssahilrajpootasusNo ratings yet
- Spur GearDocument73 pagesSpur GearhaymanotNo ratings yet
- Gears: Looking For GATE Preparation Material? Join & Get Here Now!Document8 pagesGears: Looking For GATE Preparation Material? Join & Get Here Now!Akash SoniNo ratings yet
- DME AllDocument36 pagesDME AllBashu Dev SanjelNo ratings yet
- Gear TerminologyDocument21 pagesGear TerminologyAns ahmed100% (1)
- DMS PPTDocument116 pagesDMS PPTAyush BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Gear MeasurementDocument12 pagesGear MeasurementCobra BabaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No (6) Spur Gear Terms and ConceptsDocument3 pagesExperiment No (6) Spur Gear Terms and ConceptsHayfa SalihNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanisms: 7 GearsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Mechanisms: 7 GearsgauravthamanNo ratings yet
- List of Gear NomenclatureDocument23 pagesList of Gear NomenclatureSyed Wajih Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Spur and Gear Trains KOM PDFDocument18 pagesSpur and Gear Trains KOM PDFSam prabhakarNo ratings yet
- Helicalgear 170104101849Document9 pagesHelicalgear 170104101849ChiragSMishra0% (1)
- Conjugate Tooth-1-2 PDFDocument8 pagesConjugate Tooth-1-2 PDFHarshavardhan Kutal100% (1)
- Pitch Diameter, DDocument2 pagesPitch Diameter, DAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Gear Design BookDocument3 pagesGear Design Bookvijay_khandge100% (1)
- Involute Inspection Methods and Interpretation of Inspection ResultsDocument7 pagesInvolute Inspection Methods and Interpretation of Inspection Resultsvijay_khandgeNo ratings yet
- SymmetryDocument1 pageSymmetryvijay_khandgeNo ratings yet
- Vehicle CalDocument1 pageVehicle Calvijay_khandgeNo ratings yet
- Bevel Gear Modelling Formula:-:) Is The Angle Between Elements of The Root Cone and Pitch ConeDocument1 pageBevel Gear Modelling Formula:-:) Is The Angle Between Elements of The Root Cone and Pitch Conevijay_khandgeNo ratings yet
- Bevel Gear Model-2Document1 pageBevel Gear Model-2vijay_khandgeNo ratings yet
- Housing Influences On Churning Losses in Geared TransmissionsDocument6 pagesHousing Influences On Churning Losses in Geared TransmissionsSaipriya BalakumarNo ratings yet
- Bevel Gear Design & CalculationDocument1 pageBevel Gear Design & Calculationvijay_khandgeNo ratings yet
- Auto Transmission Engg - Duty CycleDocument2 pagesAuto Transmission Engg - Duty Cyclevijay_khandgeNo ratings yet
- CastingDocument3 pagesCastingvijay_khandgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Jacobain - From Khatib - Introduction To RoboticsDocument44 pagesChapter 4 - Jacobain - From Khatib - Introduction To RoboticskpnskNo ratings yet
- CATIA Kinematics: 3DEXPERIENCE® R2019xDocument47 pagesCATIA Kinematics: 3DEXPERIENCE® R2019xGadhireddy Ashokkumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Kinematics in 1 DDocument12 pagesWeek 2 Kinematics in 1 DKA R LANo ratings yet
- Yildiz Tech Univ Mech Eng Dept ERASMUS Descriptive Information PackageDocument24 pagesYildiz Tech Univ Mech Eng Dept ERASMUS Descriptive Information PackageAlper AltenNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0094114X22000106 MainDocument18 pages1 s2.0 S0094114X22000106 MainKaviraj SenguntharNo ratings yet
- Wave HydrodynamicsDocument344 pagesWave HydrodynamicsSathishSrsNo ratings yet
- Manual TransmissionDocument60 pagesManual Transmissionʞǝǝs Uǝ ƎpıɥNo ratings yet
- 6-Speed Manual Gearbox 02S PDFDocument206 pages6-Speed Manual Gearbox 02S PDFWalter Mazibuko100% (2)
- Phy130 Textbook College PhysicsDocument2 pagesPhy130 Textbook College PhysicsHisyammudin RoslanNo ratings yet
- Transmicion R1600Document31 pagesTransmicion R1600Anonymous SxvgPDoEpNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Model of Three Wheeled Mobile RobotDocument13 pagesKinematic Model of Three Wheeled Mobile RobotHiển TyNo ratings yet
- Aakash 02 - Description of Motion in One DimensionDocument8 pagesAakash 02 - Description of Motion in One DimensionAshish RanjanNo ratings yet
- 220-16 G GearboxDocument120 pages220-16 G GearboxBadia MudhishNo ratings yet
- Compliant MechanismsDocument18 pagesCompliant MechanismsSelim DoğanNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Epicyclic Gear TrainsDocument40 pagesSynthesis of Epicyclic Gear TrainsAshok DargarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Concepts in RoboticsDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Concepts in Roboticsharikiran3285No ratings yet
- Advanced Kinematics and Dynamics of MachineryDocument8 pagesAdvanced Kinematics and Dynamics of MachineryIbmWasuserNo ratings yet
- Cinematica ParticulaDocument20 pagesCinematica ParticulaGeovanny OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Honda Civic (96-98) Transmission Service Manual PDFDocument286 pagesHonda Civic (96-98) Transmission Service Manual PDFAnderson Lodi100% (1)
- ME 563 HOMEWORK # 1 (Solutions) Fall 2010: PROBLEM 1: (40%)Document11 pagesME 563 HOMEWORK # 1 (Solutions) Fall 2010: PROBLEM 1: (40%)M Willy TarmidziNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document5 pagesSheet 2Mahmoud salahNo ratings yet
- How Backlash Affects GearsDocument15 pagesHow Backlash Affects GearsMohammad Ali TaghdiriNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of A Robotic ArmDocument5 pagesDesign and Development of A Robotic ArmAdvitiya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Gyroscopic Effect (Theory of Machines E-Note 10122015 030631AM)Document18 pagesGyroscopic Effect (Theory of Machines E-Note 10122015 030631AM)Vasudev GuptaNo ratings yet
- PS Phy chp.1 5Document6 pagesPS Phy chp.1 5Shivang GuptaNo ratings yet
- Shimano Tiagra Ti16 (2003)Document1 pageShimano Tiagra Ti16 (2003)Wk NgNo ratings yet
- RoboticsDocument32 pagesRoboticsAsh5367No ratings yet
- Sat PhysicsDocument327 pagesSat PhysicsVenki GovindNo ratings yet
- Binder1 PDFDocument28 pagesBinder1 PDFAdnan KhaldunNo ratings yet