Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Four Types of Repetition JO
Four Types of Repetition JO
Uploaded by
Muhammad FikriCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pattern & Isometries AND Fibonacci Sequence & Golden RatioDocument11 pagesPattern & Isometries AND Fibonacci Sequence & Golden Ratiokirsten ching100% (1)
- 4 Types of Symmetry in The PlaneDocument5 pages4 Types of Symmetry in The PlaneRohit MaldeNo ratings yet
- 878 Chapter 14 Partial DerivativesDocument14 pages878 Chapter 14 Partial DerivativesdannisaackNo ratings yet
- Dayanand Wandre Sept 2016 Estimation and Cost AnalystDocument4 pagesDayanand Wandre Sept 2016 Estimation and Cost AnalystVIJETA YADAVNo ratings yet
- Library Management SystemDocument58 pagesLibrary Management SystemPurushottam Choudhary100% (9)
- Mathematics in The Modern World Chapter 8Document26 pagesMathematics in The Modern World Chapter 8dreih MadrigNo ratings yet
- Frieze PaperDocument6 pagesFrieze PaperbelluomoNo ratings yet
- Final ModuleDocument5 pagesFinal ModuledatumanongnormalahNo ratings yet
- MMW Module 2C IsometriesDocument7 pagesMMW Module 2C Isometrieselmer.platiljrNo ratings yet
- 5.mathematics of Symmetry Part 2 For StudentsDocument22 pages5.mathematics of Symmetry Part 2 For StudentsPrincess SingNo ratings yet
- Mit18 900s23 Lec1Document5 pagesMit18 900s23 Lec1Htike HtikeNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of Symmetry in The PlaneDocument5 pages4 Types of Symmetry in The PlaneDent KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- The Four Type of Symmetry in The PlaneDocument4 pagesThe Four Type of Symmetry in The PlaneHimansu MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- Frieze Symmetries: ThereDocument2 pagesFrieze Symmetries: ThereTiffany GeluzNo ratings yet
- m208 3 Section 5Document11 pagesm208 3 Section 5pigcowdog100% (1)
- Redelmeier's AlgorithmDocument13 pagesRedelmeier's Algorithmluis lopezNo ratings yet
- Lecture#6Document14 pagesLecture#6tokaliabdelrahman05No ratings yet
- Transformations: Wjec MathematicsDocument20 pagesTransformations: Wjec MathematicsEff0% (1)
- Gec104 Module 3Document5 pagesGec104 Module 3MicsjadeCastillo100% (1)
- Drawing Polygons: Loops and Arrays: 5.1. The Repeat LoopDocument8 pagesDrawing Polygons: Loops and Arrays: 5.1. The Repeat LooplaoraculoNo ratings yet
- Geometry Crns 12-13 4th Nine WeeksDocument15 pagesGeometry Crns 12-13 4th Nine Weeksapi-201428071No ratings yet
- Symmetric Patterns: The Nature of Mathematics and Mathematics in NatureDocument23 pagesSymmetric Patterns: The Nature of Mathematics and Mathematics in NaturejennaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical TransformationsDocument15 pagesGeometrical Transformationswahyupreneur92No ratings yet
- Cohen A. Group Theory For Maths, Physics and Chemistry Students 2002Document91 pagesCohen A. Group Theory For Maths, Physics and Chemistry Students 2002Thongkool CtpNo ratings yet
- Symmetric Fractals: Seeking Sangaku Ramanujan, Hardy, and OnoDocument5 pagesSymmetric Fractals: Seeking Sangaku Ramanujan, Hardy, and Onoياسر عوض اللّهNo ratings yet
- 2.10 Rearranging Formulas 1: I V R R V IDocument2 pages2.10 Rearranging Formulas 1: I V R R V ISam LankaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Ug Module 4Document2 pagesModule 3 Ug Module 4Ellorvie Carcueva SandoyNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 TransformationDocument28 pagesTOPIC 2 Transformationjonathanmaithya9No ratings yet
- Frieze PatternsDocument7 pagesFrieze PatternsAndRos Chin Yong KeatNo ratings yet
- Airline Tickets: Unit SquareDocument1 pageAirline Tickets: Unit SquareCarol LizardoNo ratings yet
- Geometric Design 1Document61 pagesGeometric Design 1Kaius VezirNo ratings yet
- Geometry Book-Chapter 5.2Document6 pagesGeometry Book-Chapter 5.2alternativoNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument28 pagesFormulasA CNo ratings yet
- Graph of Tangent and CotangentDocument13 pagesGraph of Tangent and CotangentlpuelearningNo ratings yet
- The Derivatives of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument29 pagesThe Derivatives of Trigonometric FunctionsM Arifin RasdhakimNo ratings yet
- Taylor PolynomialDocument22 pagesTaylor Polynomialjakharviru009No ratings yet
- Formulae and TranspositionDocument8 pagesFormulae and TranspositiontitserNo ratings yet
- Lesson Presentation Warm Up: Holt Algebra 1 Holt Algebra 1Document22 pagesLesson Presentation Warm Up: Holt Algebra 1 Holt Algebra 1Puvaneswary SegharanNo ratings yet
- The Mathematics of Patterns and SymmetriesDocument22 pagesThe Mathematics of Patterns and SymmetriesED PradoNo ratings yet
- Theorem (Sum of Degrees of Vertices Theorem)Document17 pagesTheorem (Sum of Degrees of Vertices Theorem)Harsh RajNo ratings yet
- Mock AcetDocument100 pagesMock AcetKasumi ChanNo ratings yet
- Frieze PatternsDocument9 pagesFrieze Patternstaziaboy_91No ratings yet
- WS 3Document12 pagesWS 3Christian LerrickNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 25: Frieze PatternsDocument4 pagesWorksheet 25: Frieze PatternsMayaNo ratings yet
- Geometric Transformations 23-24Document47 pagesGeometric Transformations 23-24Jose Arturo Gonzalez GomezNo ratings yet
- MPM2D - Unit 7 Notes Solutions ThurnerDocument12 pagesMPM2D - Unit 7 Notes Solutions ThurnerAndre-Malique DavisNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of The Planarity Condition of Grötzsch's TheoremDocument10 pagesAn Investigation of The Planarity Condition of Grötzsch's TheoremEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Greenwood Tejay TransformationsDocument2 pagesGreenwood Tejay Transformationsapi-316353237No ratings yet
- Lecture#3Document19 pagesLecture#3ahmedessamaee654No ratings yet
- Tesselations Video Notes 1Document3 pagesTesselations Video Notes 1api-264764674No ratings yet
- What Is Differentiation?: Rate of Change of The Distance Compared To The Time. The Slope Is Positive All TheDocument14 pagesWhat Is Differentiation?: Rate of Change of The Distance Compared To The Time. The Slope Is Positive All TheWuey MeiiNo ratings yet
- Three-Octave Scales: ObjectivesDocument1 pageThree-Octave Scales: ObjectivesVictor ChangNo ratings yet
- Partial DerivativesDocument5 pagesPartial DerivativeshussainboiNo ratings yet
- TrigratiosanysizeDocument8 pagesTrigratiosanysizeDaiszyBarakaNo ratings yet
- Translation - Reflections - Rotations - Glide ReflectionsDocument24 pagesTranslation - Reflections - Rotations - Glide ReflectionsMat KingNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument27 pagesUntitledErjohn OcaNo ratings yet
- Wallpaper GroupDocument30 pagesWallpaper GroupCallMe NumberSixteenNo ratings yet
- Drum PDFDocument13 pagesDrum PDFAntonio Almenara LópezNo ratings yet
- Frieze Groups PDFDocument6 pagesFrieze Groups PDFanon_164463578No ratings yet
- Vectors Exercises - PrintDocument6 pagesVectors Exercises - PrintMuhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Answer ALL The QuestionsDocument2 pagesInstruction: Answer ALL The QuestionsMuhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- 7 Amalgamation PDFDocument8 pages7 Amalgamation PDFMuhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- Panofsky ATH701 1Document9 pagesPanofsky ATH701 1Muhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- Translation Rotation Reflection 1 - TZQTQ PDFDocument2 pagesTranslation Rotation Reflection 1 - TZQTQ PDFMuhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- FemaleDocument72 pagesFemaleMuhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- Bio L 2281 Experiment 6Document8 pagesBio L 2281 Experiment 6karyanNo ratings yet
- Itr 22-23 PDFDocument1 pageItr 22-23 PDFPixel computerNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Pumps: Reliable & Long-LastingDocument2 pagesWastewater Pumps: Reliable & Long-LastingMina IskanderNo ratings yet
- EDA VHDL SimulationDocument19 pagesEDA VHDL SimulationYQ WNo ratings yet
- Stock 2014 DiopsDocument770 pagesStock 2014 DiopsHoàng Minh HuyềnNo ratings yet
- AdvBiomedRes61134-4368627 120806Document11 pagesAdvBiomedRes61134-4368627 120806dzaky fadhilNo ratings yet
- Microsoft-Case StudyDocument26 pagesMicrosoft-Case StudyHiten GuptaNo ratings yet
- DejectionDocument6 pagesDejectionMani Kandan100% (1)
- IcrmnDocument26 pagesIcrmnAbhishek ThakurNo ratings yet
- Biological Conservation: Policy AnalysisDocument8 pagesBiological Conservation: Policy AnalysisEmilio Lecaros BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.2 - Material HandlingDocument23 pagesUnit 3.2 - Material Handlinglamao123No ratings yet
- 7 25 12 0204 62337 242 Pages 61901 26405 ROA From RMC To 2JDC CR12-1262-3049796 (Appeal From Municipal's Court) Digitized Ocr A9 DigitizedDocument242 pages7 25 12 0204 62337 242 Pages 61901 26405 ROA From RMC To 2JDC CR12-1262-3049796 (Appeal From Municipal's Court) Digitized Ocr A9 DigitizedNevadaGadflyNo ratings yet
- PLANTILLA de Animales para PresentaciónDocument53 pagesPLANTILLA de Animales para PresentaciónoliNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 News Clips Unit OutlineDocument6 pagesGrade 10 News Clips Unit Outlineapi-245846103No ratings yet
- Devoir de Synthèse N°1 Collège Pilote - Anglais - 7ème (2015-2016) Mme Saadaoui Nesrya PDFDocument5 pagesDevoir de Synthèse N°1 Collège Pilote - Anglais - 7ème (2015-2016) Mme Saadaoui Nesrya PDFmethnani chaimaNo ratings yet
- Drought in Bangladesh and Its Adaptive Measures: Part-ADocument4 pagesDrought in Bangladesh and Its Adaptive Measures: Part-ASADIA AFRINNo ratings yet
- CU-2020 B.Sc. (General) Chemistry Semester-III Paper-CC3-GE3 QPDocument4 pagesCU-2020 B.Sc. (General) Chemistry Semester-III Paper-CC3-GE3 QPSatyajitDeyNo ratings yet
- 03 RA4133 RL20 LTE KPI Architecture E01Document46 pages03 RA4133 RL20 LTE KPI Architecture E01Teguh YuliantoNo ratings yet
- IDEA Series Light Oil Burners: Manual of Installation - Use - MaintenanceDocument40 pagesIDEA Series Light Oil Burners: Manual of Installation - Use - MaintenancesanjayNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia Team Member Left To Right-Brenda Carr, John Gross, Dan Zacharias, Aroea Knox, Sean Hughley, Kevin Knox, and Travis KolderDocument4 pagesEthiopia Team Member Left To Right-Brenda Carr, John Gross, Dan Zacharias, Aroea Knox, Sean Hughley, Kevin Knox, and Travis KolderJohn GrossNo ratings yet
- LC320EM9 Service EmersonDocument61 pagesLC320EM9 Service EmersonDamon BrungerNo ratings yet
- Analayo - A Brief Criticism of The Two Paths To Liberation Theory PDFDocument14 pagesAnalayo - A Brief Criticism of The Two Paths To Liberation Theory PDFWuNo ratings yet
- AaDocument4 pagesAaCheck OndesNo ratings yet
- Compressibility FactorsDocument38 pagesCompressibility FactorssuruNo ratings yet
- 1 - Norovirus Care Home Poster 2018Document1 page1 - Norovirus Care Home Poster 2018GarryNo ratings yet
- Myhumandesign Analysis As A PseudoscienceDocument1 pageMyhumandesign Analysis As A PseudoscienceDavid HukomNo ratings yet
- SOCIOLOGICAL FOUNDATION ReportDocument14 pagesSOCIOLOGICAL FOUNDATION Reportᜃᜒᜈ᜔ᜎᜒ ᜇᜒᜋᜈ᜔ᜇᜒᜋᜈ᜔No ratings yet
- Education Presentation On Speech Organization: HB Dayaratne ACB, ALBDocument11 pagesEducation Presentation On Speech Organization: HB Dayaratne ACB, ALBHB DayaratneNo ratings yet
Four Types of Repetition JO
Four Types of Repetition JO
Uploaded by
Muhammad FikriOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Four Types of Repetition JO
Four Types of Repetition JO
Uploaded by
Muhammad FikriCopyright:
Available Formats
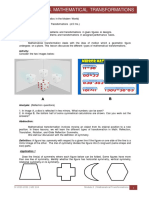
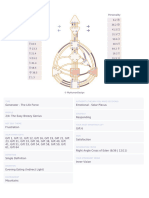
Four Types of Repetition
The five isometries above are the only isometries that map L onto itself. We will refer to these
isometries as I, R, T, H, V and G respectively.
Since these are the only isometries that map L onto itself, frieze patterns must be generated by
repeating combinations of these actions. Repeating the action T indefinitely, results in a frieze
pattern that we call Pattern 1
Frieze Pattern 1
Simularly repeating the action G indefinitely also results in a frieze pattern, Pattern 2
Frieze Pattern 2
In this pattern the tile is
but the pattern is generated from a single R by the repeated action of a glide reflection. This
samll piece of the pattern that has no symmetry and generates the entire design by
applications of I, R, T, H, V, and G is called a cell.
Repeating any of the other actions does not generate a strip required to be a frieze design. To
generate other patterns we are going to have to combine Pattern 1 or Pattern 2 with the other
actions. Again this can be done constructively on transparencies. Produce two copies each of
Patterns 1 and 2 and, in each case, place one copy on top of the other and then apply one of
the other actions on the top transparency.
For example applying the action V to Pattern 1 generates the pattern
Frieze Pattern 3
which we call Pattern 3. As above the vertical reflection is in the dashed green line.
Simularly applying action R by rotating Pattern 1 by 180o around the green dot yields
Pattern 4.
Frieze Pattern 4
Applying the rotation R to Pattern 2 gives rise to Pattern 5
Frieze Pattern 5
and the horizontal reflection H applied to Pattern 1 gives Pattern 6.
Frieze Pattern 6
Verify that no additional patterns result from applying any of the five isometries
to Pattern 1 or 2.
We now have to ask if additional patterns arise from applying any of the five isometries to
Patterns 3, 4, 5 or 6. Some experimentation shows that the horizontal reflection H applied to
Pattern 3 yields Pattern 7.
Frieze Pattern 7
No.
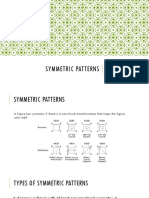
Types
1.
Translations
FOUR TYPES OF REPETITION
Directions
Examples of Transformations
Repeating Motif Slides Up or
Down
Either
Vertical, Horizontal or Diagonal
Vertical, Horizontal, Diagonal
When motif turns around a
point.
Rotation can be
60,
Order 6 in 60 Rotation
Diagonal
2.
Rotation
Directions
Rotations
90,
Oder 4 in 90 Rotation
120
Oder 3 in 120 Rotation
or
180
Oder 2 in 180 Rotation
Figure 5: Order 2 in 180o
Rotation
3.
Reflections
When motif reflects and the
image reverses as in a mirror.
Vertical Reflection
Vertical & Horizontal
Vertical
vvflectionflection
4.
Glide Reflections
When motif translates along the
axis and at the same time
reflects across an axis.
Glide Reflection
NO
STRUCTURE
TYPES
11
12
1g
m1
1m
mg
mm
Frieze pattern types and structures
Frieze Patterns (Types & Structures)
You might also like
- Pattern & Isometries AND Fibonacci Sequence & Golden RatioDocument11 pagesPattern & Isometries AND Fibonacci Sequence & Golden Ratiokirsten ching100% (1)
- 4 Types of Symmetry in The PlaneDocument5 pages4 Types of Symmetry in The PlaneRohit MaldeNo ratings yet
- 878 Chapter 14 Partial DerivativesDocument14 pages878 Chapter 14 Partial DerivativesdannisaackNo ratings yet
- Dayanand Wandre Sept 2016 Estimation and Cost AnalystDocument4 pagesDayanand Wandre Sept 2016 Estimation and Cost AnalystVIJETA YADAVNo ratings yet
- Library Management SystemDocument58 pagesLibrary Management SystemPurushottam Choudhary100% (9)
- Mathematics in The Modern World Chapter 8Document26 pagesMathematics in The Modern World Chapter 8dreih MadrigNo ratings yet
- Frieze PaperDocument6 pagesFrieze PaperbelluomoNo ratings yet
- Final ModuleDocument5 pagesFinal ModuledatumanongnormalahNo ratings yet
- MMW Module 2C IsometriesDocument7 pagesMMW Module 2C Isometrieselmer.platiljrNo ratings yet
- 5.mathematics of Symmetry Part 2 For StudentsDocument22 pages5.mathematics of Symmetry Part 2 For StudentsPrincess SingNo ratings yet
- Mit18 900s23 Lec1Document5 pagesMit18 900s23 Lec1Htike HtikeNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of Symmetry in The PlaneDocument5 pages4 Types of Symmetry in The PlaneDent KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- The Four Type of Symmetry in The PlaneDocument4 pagesThe Four Type of Symmetry in The PlaneHimansu MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- Frieze Symmetries: ThereDocument2 pagesFrieze Symmetries: ThereTiffany GeluzNo ratings yet
- m208 3 Section 5Document11 pagesm208 3 Section 5pigcowdog100% (1)
- Redelmeier's AlgorithmDocument13 pagesRedelmeier's Algorithmluis lopezNo ratings yet
- Lecture#6Document14 pagesLecture#6tokaliabdelrahman05No ratings yet
- Transformations: Wjec MathematicsDocument20 pagesTransformations: Wjec MathematicsEff0% (1)
- Gec104 Module 3Document5 pagesGec104 Module 3MicsjadeCastillo100% (1)
- Drawing Polygons: Loops and Arrays: 5.1. The Repeat LoopDocument8 pagesDrawing Polygons: Loops and Arrays: 5.1. The Repeat LooplaoraculoNo ratings yet
- Geometry Crns 12-13 4th Nine WeeksDocument15 pagesGeometry Crns 12-13 4th Nine Weeksapi-201428071No ratings yet
- Symmetric Patterns: The Nature of Mathematics and Mathematics in NatureDocument23 pagesSymmetric Patterns: The Nature of Mathematics and Mathematics in NaturejennaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical TransformationsDocument15 pagesGeometrical Transformationswahyupreneur92No ratings yet
- Cohen A. Group Theory For Maths, Physics and Chemistry Students 2002Document91 pagesCohen A. Group Theory For Maths, Physics and Chemistry Students 2002Thongkool CtpNo ratings yet
- Symmetric Fractals: Seeking Sangaku Ramanujan, Hardy, and OnoDocument5 pagesSymmetric Fractals: Seeking Sangaku Ramanujan, Hardy, and Onoياسر عوض اللّهNo ratings yet
- 2.10 Rearranging Formulas 1: I V R R V IDocument2 pages2.10 Rearranging Formulas 1: I V R R V ISam LankaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Ug Module 4Document2 pagesModule 3 Ug Module 4Ellorvie Carcueva SandoyNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 TransformationDocument28 pagesTOPIC 2 Transformationjonathanmaithya9No ratings yet
- Frieze PatternsDocument7 pagesFrieze PatternsAndRos Chin Yong KeatNo ratings yet
- Airline Tickets: Unit SquareDocument1 pageAirline Tickets: Unit SquareCarol LizardoNo ratings yet
- Geometric Design 1Document61 pagesGeometric Design 1Kaius VezirNo ratings yet
- Geometry Book-Chapter 5.2Document6 pagesGeometry Book-Chapter 5.2alternativoNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument28 pagesFormulasA CNo ratings yet
- Graph of Tangent and CotangentDocument13 pagesGraph of Tangent and CotangentlpuelearningNo ratings yet
- The Derivatives of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument29 pagesThe Derivatives of Trigonometric FunctionsM Arifin RasdhakimNo ratings yet
- Taylor PolynomialDocument22 pagesTaylor Polynomialjakharviru009No ratings yet
- Formulae and TranspositionDocument8 pagesFormulae and TranspositiontitserNo ratings yet
- Lesson Presentation Warm Up: Holt Algebra 1 Holt Algebra 1Document22 pagesLesson Presentation Warm Up: Holt Algebra 1 Holt Algebra 1Puvaneswary SegharanNo ratings yet
- The Mathematics of Patterns and SymmetriesDocument22 pagesThe Mathematics of Patterns and SymmetriesED PradoNo ratings yet
- Theorem (Sum of Degrees of Vertices Theorem)Document17 pagesTheorem (Sum of Degrees of Vertices Theorem)Harsh RajNo ratings yet
- Mock AcetDocument100 pagesMock AcetKasumi ChanNo ratings yet
- Frieze PatternsDocument9 pagesFrieze Patternstaziaboy_91No ratings yet
- WS 3Document12 pagesWS 3Christian LerrickNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 25: Frieze PatternsDocument4 pagesWorksheet 25: Frieze PatternsMayaNo ratings yet
- Geometric Transformations 23-24Document47 pagesGeometric Transformations 23-24Jose Arturo Gonzalez GomezNo ratings yet
- MPM2D - Unit 7 Notes Solutions ThurnerDocument12 pagesMPM2D - Unit 7 Notes Solutions ThurnerAndre-Malique DavisNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of The Planarity Condition of Grötzsch's TheoremDocument10 pagesAn Investigation of The Planarity Condition of Grötzsch's TheoremEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Greenwood Tejay TransformationsDocument2 pagesGreenwood Tejay Transformationsapi-316353237No ratings yet
- Lecture#3Document19 pagesLecture#3ahmedessamaee654No ratings yet
- Tesselations Video Notes 1Document3 pagesTesselations Video Notes 1api-264764674No ratings yet
- What Is Differentiation?: Rate of Change of The Distance Compared To The Time. The Slope Is Positive All TheDocument14 pagesWhat Is Differentiation?: Rate of Change of The Distance Compared To The Time. The Slope Is Positive All TheWuey MeiiNo ratings yet
- Three-Octave Scales: ObjectivesDocument1 pageThree-Octave Scales: ObjectivesVictor ChangNo ratings yet
- Partial DerivativesDocument5 pagesPartial DerivativeshussainboiNo ratings yet
- TrigratiosanysizeDocument8 pagesTrigratiosanysizeDaiszyBarakaNo ratings yet
- Translation - Reflections - Rotations - Glide ReflectionsDocument24 pagesTranslation - Reflections - Rotations - Glide ReflectionsMat KingNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument27 pagesUntitledErjohn OcaNo ratings yet
- Wallpaper GroupDocument30 pagesWallpaper GroupCallMe NumberSixteenNo ratings yet
- Drum PDFDocument13 pagesDrum PDFAntonio Almenara LópezNo ratings yet
- Frieze Groups PDFDocument6 pagesFrieze Groups PDFanon_164463578No ratings yet
- Vectors Exercises - PrintDocument6 pagesVectors Exercises - PrintMuhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Answer ALL The QuestionsDocument2 pagesInstruction: Answer ALL The QuestionsMuhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- 7 Amalgamation PDFDocument8 pages7 Amalgamation PDFMuhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- Panofsky ATH701 1Document9 pagesPanofsky ATH701 1Muhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- Translation Rotation Reflection 1 - TZQTQ PDFDocument2 pagesTranslation Rotation Reflection 1 - TZQTQ PDFMuhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- FemaleDocument72 pagesFemaleMuhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- Bio L 2281 Experiment 6Document8 pagesBio L 2281 Experiment 6karyanNo ratings yet
- Itr 22-23 PDFDocument1 pageItr 22-23 PDFPixel computerNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Pumps: Reliable & Long-LastingDocument2 pagesWastewater Pumps: Reliable & Long-LastingMina IskanderNo ratings yet
- EDA VHDL SimulationDocument19 pagesEDA VHDL SimulationYQ WNo ratings yet
- Stock 2014 DiopsDocument770 pagesStock 2014 DiopsHoàng Minh HuyềnNo ratings yet
- AdvBiomedRes61134-4368627 120806Document11 pagesAdvBiomedRes61134-4368627 120806dzaky fadhilNo ratings yet
- Microsoft-Case StudyDocument26 pagesMicrosoft-Case StudyHiten GuptaNo ratings yet
- DejectionDocument6 pagesDejectionMani Kandan100% (1)
- IcrmnDocument26 pagesIcrmnAbhishek ThakurNo ratings yet
- Biological Conservation: Policy AnalysisDocument8 pagesBiological Conservation: Policy AnalysisEmilio Lecaros BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.2 - Material HandlingDocument23 pagesUnit 3.2 - Material Handlinglamao123No ratings yet
- 7 25 12 0204 62337 242 Pages 61901 26405 ROA From RMC To 2JDC CR12-1262-3049796 (Appeal From Municipal's Court) Digitized Ocr A9 DigitizedDocument242 pages7 25 12 0204 62337 242 Pages 61901 26405 ROA From RMC To 2JDC CR12-1262-3049796 (Appeal From Municipal's Court) Digitized Ocr A9 DigitizedNevadaGadflyNo ratings yet
- PLANTILLA de Animales para PresentaciónDocument53 pagesPLANTILLA de Animales para PresentaciónoliNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 News Clips Unit OutlineDocument6 pagesGrade 10 News Clips Unit Outlineapi-245846103No ratings yet
- Devoir de Synthèse N°1 Collège Pilote - Anglais - 7ème (2015-2016) Mme Saadaoui Nesrya PDFDocument5 pagesDevoir de Synthèse N°1 Collège Pilote - Anglais - 7ème (2015-2016) Mme Saadaoui Nesrya PDFmethnani chaimaNo ratings yet
- Drought in Bangladesh and Its Adaptive Measures: Part-ADocument4 pagesDrought in Bangladesh and Its Adaptive Measures: Part-ASADIA AFRINNo ratings yet
- CU-2020 B.Sc. (General) Chemistry Semester-III Paper-CC3-GE3 QPDocument4 pagesCU-2020 B.Sc. (General) Chemistry Semester-III Paper-CC3-GE3 QPSatyajitDeyNo ratings yet
- 03 RA4133 RL20 LTE KPI Architecture E01Document46 pages03 RA4133 RL20 LTE KPI Architecture E01Teguh YuliantoNo ratings yet
- IDEA Series Light Oil Burners: Manual of Installation - Use - MaintenanceDocument40 pagesIDEA Series Light Oil Burners: Manual of Installation - Use - MaintenancesanjayNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia Team Member Left To Right-Brenda Carr, John Gross, Dan Zacharias, Aroea Knox, Sean Hughley, Kevin Knox, and Travis KolderDocument4 pagesEthiopia Team Member Left To Right-Brenda Carr, John Gross, Dan Zacharias, Aroea Knox, Sean Hughley, Kevin Knox, and Travis KolderJohn GrossNo ratings yet
- LC320EM9 Service EmersonDocument61 pagesLC320EM9 Service EmersonDamon BrungerNo ratings yet
- Analayo - A Brief Criticism of The Two Paths To Liberation Theory PDFDocument14 pagesAnalayo - A Brief Criticism of The Two Paths To Liberation Theory PDFWuNo ratings yet
- AaDocument4 pagesAaCheck OndesNo ratings yet
- Compressibility FactorsDocument38 pagesCompressibility FactorssuruNo ratings yet
- 1 - Norovirus Care Home Poster 2018Document1 page1 - Norovirus Care Home Poster 2018GarryNo ratings yet
- Myhumandesign Analysis As A PseudoscienceDocument1 pageMyhumandesign Analysis As A PseudoscienceDavid HukomNo ratings yet
- SOCIOLOGICAL FOUNDATION ReportDocument14 pagesSOCIOLOGICAL FOUNDATION Reportᜃᜒᜈ᜔ᜎᜒ ᜇᜒᜋᜈ᜔ᜇᜒᜋᜈ᜔No ratings yet
- Education Presentation On Speech Organization: HB Dayaratne ACB, ALBDocument11 pagesEducation Presentation On Speech Organization: HB Dayaratne ACB, ALBHB DayaratneNo ratings yet