Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochem MSK
Biochem MSK
Uploaded by
caneman2014Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biochem MSK
Biochem MSK
Uploaded by
caneman2014Copyright:
Available Formats
MSK Hepato:
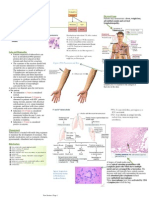
Extracellular propeptidases cleave disulfide-rich terminal extensions from the
procollagen molecule. This results in formation of water-insoluble triple helical
collagen fibrils.
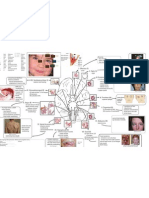
Alkaptonuria is an autosomal-recessive disorder in which the lack of homogentisic
oxidase blocks the metabolism of phenylalanine and tyrosine at the level of
homogentisic acid, leading to an accumulation of homogentisic acid. Homogentisic
acid excreted in the urine imparts a black color to urine, if allowed to undergo
oxidation. Alkaptonuria also causes ochronosis, a blue-black pigmentation that is
most evident in the ears, nose, and cheeks.
Marfans syndrome is due to a defect in fibrillin, an extracellular glycoprotein that is
abundant in the zonular fibers of the lens, the periosteum and the aortic media. The
different locations of fibrillin production explain the varied clinical manifestations of
Marfans syndrome.
Alkaptonuria is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by a deficiency of the
enzyme homogentisic acid oxidase, which normally breaks down the tyrosine
byproduct homogentisic acid (also called alkapton). Accumulated homogentisic acid
causes pigment deposits in connective tissues throughout the body.
Gout can occur with increased frequency in patients with activating mutations in 5'-phosphoribosyl-1'-pyrophosphate
(PRPP) synthetase due to an increased production of purines which results in hyperurlcemla.
Colchicine is useful in the acute management of gouty arthritis because it inhibits the chemotaxis of
neutrophils by preventing microtubule formation.
The IP3 second messenger system begins with hormone binding and G-protein
activation leading to activation of phospholipase C. Phospholipase C forms
diacylglycerol and IP3 from phospholipids, and IP3 causes an increase in intracellular
calcium, which then activates protein kinase C.
snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) are synthesized by RNA polymerase II in the nucleus. They
help to remove introns from the RNA transcript and are thus necessary for synthesis of messenger RNA.
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is a heritable connective tissue disease typically associated
with abnormal collagen. EDS usually manifests clinically as over-flexible
(hypermobile) joints over-elastic (hyperelastic) skin, and fragile tissue susceptible to
bruising, wounding, and hemarthrosis.
Procollagen is synthesized by a series of steps within the endoplasmic reticulum of
cells such as fibroblasts. This molecule is then released into the extracellular space
by transport through the Golgi apparatus and converted into collagen by procollagen
peptidases that cleave the water soluble, non-helical N- and C-terminal portions of
the procollagen molecule from procollagen to form collagen. Collagen monomers are
then covalently crosslinked with each other after certain residues are oxidized by
lysyl oxidase.
Glycogen degradation is coupled with skeletal muscle contraction due to calciummediated myophosphorylase activation. Muscle is stimulated to contract by the
neurotransmitter acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. This stimulation
causes depolarization of the muscle cell and release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic
reticulum into the cytosol. Increased calcium in the cytosol binds troponin C to cause
muscle contraction, and it also activates muscle glycogen phosphorylase to provide
energy for the working muscle.
Hydroxylation of proline and lysine residues in the collagen precursor occurs in the
RER and requires vitamin C as a cofactor. Terminal peptide cleavage and collagen
fibril crosslinking occur in the extracellular space.
Glycine is the most abundant amino acid in the collagen molecule. It occurs in AT
LEAST every third amino acid position. The amino acid formula of collagen is (-Gly-XY-) 333.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Goljan Step 1 HY 36 Pages Notes PDFDocument36 pagesGoljan Step 1 HY 36 Pages Notes PDFTyler Lawrence CoyeNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Think AgainDocument85 pagesThink AgainSkyler BushNo ratings yet
- Effect of Sunlight Against Green Beans GrowthDocument4 pagesEffect of Sunlight Against Green Beans GrowthDanny Ramadhan0% (1)
- Cranial NerveshDocument1 pageCranial Nerveshcorreiodesportivo8071No ratings yet
- Joe Green: Objective ExperienceDocument1 pageJoe Green: Objective Experiencecaneman2014No ratings yet
- Medicine - Picmonics List - List of PicmonicsDocument21 pagesMedicine - Picmonics List - List of Picmonicscaneman2014100% (1)
- Tuberculosis: Adventitial Sounds and Cervical LymphadenopathyDocument2 pagesTuberculosis: Adventitial Sounds and Cervical Lymphadenopathycaneman2014No ratings yet
- GT AnatomyDocument1 pageGT Anatomycaneman2014No ratings yet
- My #Scipolicy News Archive Jan 2011 Part ADocument83 pagesMy #Scipolicy News Archive Jan 2011 Part AIno AgrafiotiNo ratings yet
- Consent For Circumcision FormDocument11 pagesConsent For Circumcision FormMohammed Abdel-Fattah ShalabyNo ratings yet
- NanozymesDocument10 pagesNanozymesdd donNo ratings yet
- WHO Reveals Leading Causes of Death and Disability Worldwide: 2000-2019Document5 pagesWHO Reveals Leading Causes of Death and Disability Worldwide: 2000-2019GhaniNo ratings yet
- LeprosyDocument32 pagesLeprosySiselle FajardoNo ratings yet
- Cri Du Chat SyndromeDocument3 pagesCri Du Chat SyndromeIbrahim GulamaliwalaNo ratings yet
- Clairvoyance - Seeing-With-Your-Spiritual-Eyes PDFDocument7 pagesClairvoyance - Seeing-With-Your-Spiritual-Eyes PDFeddddf67% (3)
- WJ Ms Paper Sir 2013Document13 pagesWJ Ms Paper Sir 2013Rohan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Vulovic - Brskovo Final PDFDocument27 pagesVulovic - Brskovo Final PDFDraganaNo ratings yet
- Penicillin Allergy DelabelingDocument31 pagesPenicillin Allergy Delabelingapi-506607906No ratings yet
- ScriptDocument12 pagesScriptTrishia Nhicole HoNo ratings yet
- The Heavy Truth About Obesity in The UKDocument14 pagesThe Heavy Truth About Obesity in The UKGymRoomNo ratings yet
- A Technical Study On Biomedical Image Classification Using Mining AlgorithmsDocument4 pagesA Technical Study On Biomedical Image Classification Using Mining AlgorithmsthamilselvanpNo ratings yet
- DDS Glycerin Supp PostlabDocument33 pagesDDS Glycerin Supp PostlabGRACE MAR CABAHUGNo ratings yet
- Rizal NotesDocument6 pagesRizal NotesKara GamerNo ratings yet
- CHNDocument136 pagesCHNSapiah RamanNo ratings yet
- Hearing Status of Children Under Five Years Old in Jatinangor DistrictDocument5 pagesHearing Status of Children Under Five Years Old in Jatinangor DistricterickNo ratings yet
- Introduction To UrinalysisDocument8 pagesIntroduction To UrinalysisKyle PicocNo ratings yet
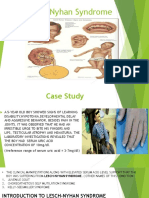
- Lesch-Nyhan SyndromeDocument8 pagesLesch-Nyhan SyndromevrindaNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument2 pagesCancerkatyaNo ratings yet
- Protocol 7Document9 pagesProtocol 7HimanshuNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia 110616032010 Phpapp02Document82 pagesPolycythemia 110616032010 Phpapp02Ahmad Ripani Musyaffa AhdanLabNo ratings yet
- Basic HaematologyDocument32 pagesBasic HaematologyAhtshamtaeiq AhtshamtariqNo ratings yet
- The Chronopolitics of The Anthropocene: The Pandemic and Our Sense of TimeDocument25 pagesThe Chronopolitics of The Anthropocene: The Pandemic and Our Sense of TimeJoão Francisco PinhoNo ratings yet
- Aortic Aneurysm Classification: SL No Time Specific Objective Content Av Aids EvaluationDocument2 pagesAortic Aneurysm Classification: SL No Time Specific Objective Content Av Aids EvaluationArunNo ratings yet
- Icd 11 Introduction ClinicalDocument50 pagesIcd 11 Introduction ClinicalMuhammad Farooq Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Problem Oriented Medical Record: Non Hodgkin LymphomaDocument25 pagesProblem Oriented Medical Record: Non Hodgkin Lymphomaphyna27No ratings yet
- Consent CraniotomyDocument9 pagesConsent CraniotomyAbhinav Gupta100% (1)