Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Selvam College of Technology, Namakkal - 03 PH: 9942099122: 2 Marks Question & Answers Unit - I Basics of Mechanisms
Selvam College of Technology, Namakkal - 03 PH: 9942099122: 2 Marks Question & Answers Unit - I Basics of Mechanisms
Uploaded by
Vijayan GopalsamyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Selvam College of Technology, Namakkal - 03 PH: 9942099122: 2 Marks Question & Answers Unit - I Basics of Mechanisms
Selvam College of Technology, Namakkal - 03 PH: 9942099122: 2 Marks Question & Answers Unit - I Basics of Mechanisms
Uploaded by
Vijayan GopalsamyCopyright:
Available Formats
www.Vidyarthiplus.
com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
2 Marks Question & Answers
Unit I
BASICS OF MECHANISMS
1. Define Degree if freedom (or) What is meant by mobility?
The Mobility of a mechanism or Degree of freedom is defined as the number of
input parameters (usually pair variables) which must be controlled independently in order
to bring the device into a particular position.
The number of degree of freedom of a mechanism (n) is given by,
n= 3(l-1)-2jh
l= Number of links,
j= Number of joints, and
h= Number of higher pairs.
2. What is meant by spatial mechanism?
Spatial ,mechanism have special geometric characteristics in that all revolute
axes are parallel and perpendicular to the plane of motion and all prism axes lie in the
plane of motion.
3. Classify the Constrained motion.
Constrained motions are classify into three types.
1.Completely constrained motion. (e.g., Square bar moving in a square hole)
2.Incompletely constrained motion (e.g., Circular shaft in a hole)
3.Successfully constrained motion (e.g., Piston and cylinder)
4. How to determine the given assemblage of links forms the kinematic chain or
not?
If the given assemblage satisfies the following two equations (for lower pair)
then it is called as kinematic chain.
Where,
l = 2p 4
j = 3/2 l 2
l= Number of links,
j= Number of pairs, and
h= Number of joints.
5. What is meant by number synthesis?
Expressing mobility (or) Degree of freedom of a mechanism in terms of the number
of
links and the number if pair connections of a given type is known as number
synthesis.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
6. What are the some important inversions of four bar chain mechanism?
1. Crank-rocker mechanism (or) Crank-lever mechanism (or) Rotary- oscillating
converter
2. Crank-crank mechanism (or) Double-rocker mechanism (or) Rotary-rotary
converter.
3. Rocker-rocker mechanism (or) Double-rocker mechanism (or) Double lever
mechanism (or) an Oscillating-oscillating converter.
7. What is toggle position?
It is the position of a mechanism at which the mechanical advantage is infinite and
the sine of angle between the coupler and driving link is zero.
8. What is pantograph?
Pantograph is a device which is used to reproduce a displacement exactly in an
enlarged or reduced scale. It is used in drawing officers, for duplicating the drawings,
maps, plans, etc. It works on the principle of 4 bar chain mechanism, i.e., Oscillatingoscillating converted mechanism.
9. What are the important applications of single slider crank mechanism?
1. Rotary (or) Gnome engines,
. Crank and slotted lever mechanism,
3. Oscillating cylinder engine,
4. Hand pump.
10. Compare machine and structure.
S.No.
Machine
1.
Relative motion exists between
its parts
2.
It transforms available energy
into useful work.
3.
Links are meant to transmit
motion and force.
4.
Example : Scooter, Car, Bus
Structure
No relative motion exists between
its members.
It does not convert the available
energy into work.
Members are meant for carrying
loads having action.
Example : Roof trusses, bridges.
11. Give some example for kinematic pairs.
1.Crank and connecting rod,
2.Connecting rod and piston rod, and
3.Piston and engine cylinder.
12. Cam and follower is ---------------type of pair.
[Ans: Higher and unclosed (force closed pair).]
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
13. All lower pairs are ------------------pair.
[Ans: Closed]
14. Side mirror and its attachment has-------------------pair.
[Ans: Spherical]
15.Discuss Elliptical trammel.
Elliptical trammel is an instrument used for drawing ellipses. It is the best
example for first inversion of double slider crank chain.
16. Second and third inversion of double slider crank chain are-------------and------[Ans: Scotch yoke mechanism; Oldhams coupling.]
17. Differentiate kinematic pair and kinematic chain.
Kinematic Pair
Kinematic Chain
1. A pair is a joint of two elements A Kinematic chain is a combination
that permits relative motion in
of pairs joined in such a way that the
such a way that their relative
relative motion between the links or
motion is completely or
elements is completely or
successfully constrained.
successfully constrained.
Example :
Example:
1. Crank and
1.Four bar chain.
connecting rod.
2. Double slider crank
2. Piston and cylinder chain.
18. Piston motion in a cylinder is ---------------------kind of constrained motion.
[Ans: Successfully constrained.]
19. Compare Movability and Mobility.
Movability includes the six degrees of freedom of the device as a whole, as
though the ground link were not fixed, and thus applies to a kinematic chain.Mobility
neglects these and considers only the internal relative motions, thus applying to a
mechanism.
20. Differentiate kinematic chain and mechanism.
S.No.
Kinematic chain
Mechanism
1.
It is a combination of
If any one of the link in the
kinematic pairs.
kinematic chain is fixed then the
kinematic chain is said to be a
mechanism.
2.
The relative motion
The relative motion between the
between the links is
links is completely (or)
completely or successfully successfully constrained.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
3.
constrained or locked.
Types: Four bar chain,
Slider crank chain, Double
slider crank chain, etc.
Types: Simple mechanism,
Compound mechanisam.
21. What is meant by transmission angle?
In a four bar chain mechanism, the angle between the coupler and the follower
(driven) link is called as the transmission angle.
22. What is Mechanical advantage in a mechanism?
The mechanical advantage is defined as the ratio of output torque to the input
torque. It is also defined as the ratio of the load to the effort.
Where ,
M.A. (ideal) =TB /TA
TB = Driven (resisting torque), and
TA = Driven torque
23. Quick return motion mechanism is the inversion of ----------------chain.
[Ans: Single slider crank chain.]
24. What is meant by Ackermann Steering?
Ackerman steering is the one of the mechanism used in vehicles. It is obtained by
inversion of four bar chain.
25. State the Kutzback criterion.
A kinematic chain having l links and j binary joints then what is the mobility
n, according to Kutzback criterion. n = 3(l-1)- 2j provided the chain should be a plane
mechanism.
26. Write down the Kutzback and Grublers criterin for spatial mechanism.
(i) According to Kutzback criterian,
Mobility, n = 6(l-1)-5p1-4p2-3p3-2p4-1p5
(ii) According to Grublers criterian,
6l-5p1-7=0
[For only single degree of freedom]
Where,
l=Number of links in the mechanism,
P1=Number of pairs having one degree of freedom, and
P2=Number of pairs having 2 degree of freedom and so on.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
27. Discuss the difference between mechanism and machine.
S.No.
Mechanism
Machine
1.
Mechanism transmits and
Machine transmits forces and couples
modities motion.
2.
A Mechanism is the skeleton
Machine may have many mechanisms
outline of the machine to
for transmitting power or mechanical
produce definite motion between work.
various links.
Example: Clock work,
Example: Shaper and lathe in
3.
typewriter
workshop.
28. Write down the Grashofs law for a four bar mechanism.
Grashofs law states that the sum of the shortest and longest links cannot be
greater than the sum of the remaining two links lengths, if there is to be continuous
relative motion between two members.
29. What are the significance of Grashofs law.
(i)Grashofs law specifies the order in which the links are connected in a
kinematic chain.
(ii)Grashofs law specifies which link of the four-bar chain is fixed.
(iii)(s+l)(p+q) should be satisfied, if not, no link will make a complete
revolution relative to another.
Where,
s = Length of the shortest link,
l = Length of the longest link, and
p & q are the lengths of other two links.
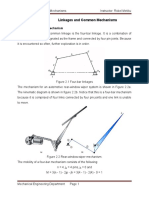
30. Explain the working mechanism of bicycle bells.
Bicycle bells are working on the principle of snap action mechanism (or otherwise
called as toggle mechanism of flip-flop mechanism.) Refer Fig.1.74, for pictorial
explanation.
31. --------------mechanism is used in screw jack.
[Ans:Linear actuator.]
32. What is meant by motion adjustment mechanism?
The mechanism used to adjust or modify the motion of the link are known as
motion adjustment mechanism. Motion adjustment is obtained by wedges, levers and
rack and pinion.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
33. Carpentry vices and collets are working under ----------mechanism.
[Ans: Clamping]
34. Locks, jacks and clockwork are working under ---------mechanism.
[Ans: Ratchets and escapement]
35. The Grublers criterion for plane mechanism is-----------.
[Ans:l and d]
36. A slider crank chain has ---------------links and-----------------inversions.
[Ans: Four, four]
37.An elliptic trammel consists of ---------------and---------------pairs.
[Ans:Tow sliding; two turning pairs.]
38. Whether a cycle chain is kinematic chain or not?
A cycle chain is a combination of several links with turning pair. Hence it is not a
kinematic chain.
39. In an Oldhams coupling the distance between the axles of the two parallel shafts to
be connected is 30 mm. What is the maximum speed of sliding of each tongue of the
intermediate piece along its slot if the shaft revolve at a speed of 250 r.p.m?
Solution:
Distance between the axes, r = 30mm.
Speed of the shaft, N = 250 r.p.m.
Angular speed of the shaft, = 2N/60
= 2X250/60=26.18r/s
Maximum sliding speed of each tongue = r
= 30X10-X26.18
= 0.7854 m/s
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
UNIT-II
KINEMATICS OF MOTION
1. Define instantaneous centre and instantaneous axis.
Instantaneous centre: Instantaneous centre of a moving body may be defined as
that centre which goes on changing from one instant to another.
Instantaneous axis: instantaneous axis is a line drawn through an instantaneous
centre and perpendicular to the plane of motion.
2. A pin joins two links A and B, A rotates with A angular velocity and B rotates which
B
angular velocity in opposite direction. What is the rubbing velocity of that pin?
Running velocity of pin = (1+ 2)Xr
Where r is the radius of the pin.
3. What is meant by the efficiency of a mechanism?
Efficiency of a mechanism is defined as the ratio of product of force and velocity
in driven link to the product of force and velocity in driving link.
= FBVB/FA VA
(or)
= TB B/TA A
Where,
A = Driving link, B = Driven link,
T = Torque.
F = Force,
V = Velocity, and
= Angular velocity.
4. How to represent the direction of linear velocity of any point on a link with
respect to another point on the same link?
The direction of linear velocity of any point on a link with respect to another point
on the same link is perpendicular to the line joining the points.
5. What is the magnitude of linear velocity of a point B on a link AB relative to A?
The magnitude of linear velocity of a point B on a link AB, which rotates with
angular velocity with respect to A is:
vBA =
BA xAB
6. What is the expression for Coriolis component of acceleration?
ACBC = 2 v
Where = Angular velocity of OA, and
V = Linear velocity of B.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
7. What are the properties of instantaneous centre?
(i)A rigid link rotates instantaneously relative to another link at the instantaneous
centre for the configuration of the mechanism.
(ii)The two rigid links have no linear velocity relative to each other at the
instantaneous centre. At this point the two rigid links have the same linear velocity relative
to the rigid link. In other words, the velocity of the instantaneous centre relative to any
third rigid link will be same whether the instantaneous centre is regarded as a point on the
first rigid link or on the second rigid link.
8. How many instantaneous centres are possible in a four bar chain mechanism?
Number of instantaneous centres, N = n(n-1)/2
Where ,
n = Number of links.
In four bar chain mechanism,
n=4
N = 4(4-1)/2=6centres are possible.
9. What are the two components of acceleration?
1. Radial component of acceleration,
arOB = 2OBxOB
2. Tangential component of acceleration,
atOB = aOBX OB
where, OB = Angular velocity of link OB,
OB = Angular acceleration of link OB, and
OB = Length of link OB.
10. Radial component of acceleration is ---------------------to the velocity of the component
and
tangential component is perpendicular to---------------------.
[Ans: Perpendicular ; Radial component (or) to the link.
11. Define Kennedys theorem.
The Kennedys theorem states that if three bodies move relatively to each other,
they have three instantaneous centres and lie on a straight line.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
12. In a four bar chain mechanism crank AB = 0.3 metre rotates with 100 r.p.m. and lever
CD
oscillates with a linear velocity of 5 m/s and what is the mechanical advantage of the
system.
Solution:
Mechanical advantage = VAB/VDC
VAB = ABxAB
= 2NAB/60xAB
= 2X100/60=0.3=3.14m/s
VDC = 5m/s
=3.14/55=0.628m/s
13. In the four bar chain, considering mechanical advantage of 0.7, F B = 50N, what is the
force
acting on pin C.
Given Data:
M.A = 0.7
FB = 50N
FC = ?
Solution:
M.A = FC/FB
0.7 = FC/50
FC=35N (Ans)
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
UNIT-III
KINEMATICS OF CAM
1. What is a cam?
A cam is a rotating machine element which gives reciprocating (or) oscillating
motion to another element known as follower.
2. Give some example for cams.
(i)Radial (or) disc cams
(ii)Cylindrical cams (or) barrel cams
(iii)End (or) Face cams
(iv)Wedge cams
3. What is the maximum acceleration of a follower moving with cycloidal motion?
(i)Maximum acceleration of follower during out stroke: a 0 = 22s/02
(ii)Maximum acceleration of follower during return stroke: aR = 22s/R2
4. In a cylindrical cam with motion of the follower is --------------and------------------.
[Ans: Reciprocating; Oscillating]
5. Define tangent cam?
When the flanks of the cam are straight and tangential to the base circle and nose
circle, the cam is known as tangent cam.
6. Distinguish radial and cylindrical cams.
Radial Cam: In this cam, the follower reciprocates (or) oscillates in a direction
perpendicular to the cam axis.
Cylindrical Cam: In this the follower reciprocates (or) oscillates in a direction
parallel to the cam axis.
7. What are the different motions of the follower?
(i) Uniform motion,
(ii) Simple harmonic motion,
(iii) Uniform acceleration and retardation, and
(iv) Cycloidal motion.
8. How can high surface stress in flat faced follower be minimised?
High surface stress in the followers is minimized by machining the flat end of the
follower to a spherical shape.
9. Compare Roller and mushroom follower of a cam.
S.No.
Roller Follower
Mushroom Follower
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
1.
Roller followers are extensively
used where more space is available.
2.
It is used in stationary gas engines,
oil engines and aircraft valves in
engines.
The mushroom followers are
generally used where space is
limited.
It is used in cams which operate
the valves in automobile engines.
10. Where are the roller follower extensively used?
Roller followers are extensively used where more space is available such as in
stationary gas oil engines, and aircraft engines.
11. Define dwell period?
The period during which the follower remains at rest is called dwell period.
12. What is the principle used in constructing the cam profile?
[Ans: Kinematic inversion.]
13. In automobile engines-------------------follower is generally used.
[Ans: Spherical faced.]
14.Explain offset follower.
When the motion of the follower is along as axis away from the axis of the cam
centre, it is called offset follower.
15. The velocity diagram of the follower moving simple harmonic motion consists of a -----------curve and the acceleration diagram is a------------------------curve.
[Ans: Sine; cosine]
16. For high speed engines, the cam follower should move with-----------------.
[Ans: Cycloidal motion]
17.Simple harmonic motion of the follower is generally used for-----------------engines.
[Ans: High and medium speed.]
18. In a radial cam, the follower moves in a direction---------------------to the axis.
[Ans: Perpendicular]
19.Define trace point in the study of cams.
It is a reference point on the follower and is used to generate the pitch curve. In
case of knife edge follower the knife edge represents the trace point and the pitch curve
corresponds to the cam profile. In a roller follower the centre of the roller represents the
trace point.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
20. Define pressure angle with respect to cams.
It is the angle between the direction of the follower motion and a normal to the
pitch curve. This angle is very important in designing a cam profile. If the pressure angle
is too large, a reciprocating follower will jam in its bearings.
21. ----------------- is a point on the pitch curve having the maximum pressure angle.
[Ans: Pitch point]
22. ---------------- is the curve generated by the trace point as the follower moves
relative to the cam.
[Ans: Pitch curve]
23. Define Life (or) Stroke in cam.
It is the maximum travel of the follower from its lowest position to the topmost
position.
24. What is the maximum acceleration of a follower moving with simple harmonic
motion?
Maximum acceleration of follower during out stroke,
ao = 22s/2(o)2
Maximum acceleration of follower during return stroke,
aR = 22s/2(R)2
Where,
= Angular velocity of the cam,
S = Stroke length,
o = Out stroke angle, and
R = Return stroke angle.
25. The velocity and acceleration curves are continuous with respect to angular
displacement of cam, in----------------cams.
[Ans: High speed]
26. Define undercutting in cam. How it occurs?
The cam profile must be continuous curve without any loop. If the curvature of
the pitch curve is too sharp, then the part of the cam shape would be lost and thereafter
the intended cam motion would not be achieved. Such a cam is said to be undercut.
Undercutting occurs in the cam because of attempting to achieve too great a follower lift
with very small cam rotation with a smaller cam.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
27. What do you know about Nomogram?
In nomogram, by knowing the values of total lift of the follower (L) and the can
rotation angle () for each segment of the displacement diagram, we can read directly the
maximum pressure angle occurring in the segment for a particular choice of prime circle
radius (Ro).
28.How can you prevent undercutting in cam?
1. By decreasing the follower lift.
2. By increasing cam rotation angle.
3. By increasing the cam size (i.e., Base circle).
29. What do you know about gravity cam?
In this type, the rise of the cam is achieved by the rising surface of the cam and
the return by the force of gravity or due to the weight of the cam.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
UNIT-IV
TOOTHED GEARING
1. What is an angle of obliquity in gears?
It is the angle between the common normal to two gear teeth at the point of contact
and the common tangent at the pitch point. It is also called as pressure angle.
2. What is bevel gearing? Mention its types.
When the non-parallel (or) intersecting but coplanar shafts connected by gears,
they are called bevel gears and the arrangement is bevel gearing.It is of two types namely
skew bevel gearing and spiral gearing.
3. What is meant by are of approach, arc of recess and arc of contact?
Arc of approach is the portion of the path of contact from the beginning of the
engagement to the pitch point.
Arc of recess is the position of the path of contact from pitch point to the end of
the engagement of a pair of teeth.
Arc of contact is the path traced by a point on the pitch circle from the beginning
to the end of engagement of a pair of teeth.
4. State law of Gearing.
The law of gearing states that for obtaining a constant velocity ratio, at any instant
of teeth the common normal at each point of contact should always pass through a pitch
point, situated on the line joining the centre of rotation of the pair of mating gears.
5. To take heavy load---------------------system of gear teeth are used.
[Ans: 20o stub involute]
6. If double helical gears are cut on a same cylindrical surface then it is called as--------------.[Ans: Herringbone gears]
7. What is the abbreviation of P.I.V. drive?
Positive, Infinitely, Variable drive.
8. Define normal and axial pitch in helical gears.
Normal pitch is the distance between similar faces of adjacent teeth, along a helix
on the pitch cylinder normal to the teeth.
Axial pitch is the distance measured parallel to the axis between similar faces of a
adjacent teeth.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
9. Two intersecting and coplanar shafts are connected by---------------------gears.
[Ans: Bevel]
10. The product of the circular pitch and diametral pitch is equal to---------------.
[Ans: ].
11. What is the involute function in terms of pressure angle ?
Involute functions in terms of pressure angle [INV ()] = tan -
12. In involute teeth, the tangent to the base circle is--------------------------to the involute.
[Ans: Normal]
13. The path of contact in involute gear is a---------------------.
[Ans: Straight line]
14. Write down the differences between involute and cycloidal tooth profile.
S.No.
Involute Tooth profile
Cycloidal Tooth Profile
1.
Variation in centre distance
The centre distance should not vary.
does not affect the velocity
ratio.
2.
Pressure angle remains
Pressure angle varies. It is zero at the
constant throughout the
pitch point and maximum at the start
teeth.
and end of engagement.
3.
Interference occurs.
No interference occurs.
4.
Weaker teeth
Stronger teeth.
15. What are the standard interchangeable tooth profiles.
1. 14o composite system,
2. 14o full depth involute system, and
3. 20o full depth involute system.
16. What are the methods to avoid interference?
1. The height of the teeth may be reduced.
2. The pressure angel may be increased.
3. The radial flank of the pinion may be cut back (undercutting).
17. The centre distance between two meshing involute gears is directly proportional to-----------and inversely proportional to----------------------.
[Ans: The sum of base circle radii; Cosine of pressure angle.]
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
18. What is the advantage when arc of recess is equal to arc of approach in a meshing
gears?
When arc of recess equal to arc of approach, the work wasted by friction is
minimum and efficiency of drive is maximum.
19. Write down the expression for normal circular pitch and axial pitch in helical
gears.
Normal pitch = Pc x cos
Axial pitch = Pc/tan
Where
Pc = Circular pitch, and
= Helix angle.
20. What is the condition and expression for maximum efficiency in spiral gears?
1. Condition for maximum efficiency: = +/2
2. Maximum efficiency:
max = 1+cos(+)/1+cos(-)
Where ,
= Spiral angle,
= Shaft angle, and
= Friction angle.
21. What is the sum of the number of teeth on pinion and gear (z p+zw) to avoid
interference in
case of pressure angle of 14o and 20o?
1. For 14o system, (zp+zw) = 64
2. For 20o system, (zp+zw) = 35
22. What is the maximum efficiency in worm and worm gear?
max = 1-sin /1+sin
23. Two gears having involute teeth are in mesh. If the path of approach and path of
recess are half of their maximum possible values, then what is the length of path of
contact?
Length of path of contact = (R + r)sin /2
Where , R = Pitch circle radius of wheel,
r = Pitch circle radius of pinion, and
= Pressure angle.
24. Spur gears of equal diameter and pitch are called as------------------.
[Ans: Mitre gears]
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
25. What are the advantages and limitations of gear drive? Write any two.
Advantages:
1. Since there is no slip, so exact velocity ratio is obtained.
2. It is more efficient and effective means of power transmission.
Limitations:
1. Manufacture of gear is complicated.
2. The error in cutting teeth may cause vibration and noise during operation.
26. Define contact ratio.
It is the ratio of the length of arc contact to the circular pitch is known as contact
ratio. The value gives the number of pairs of teeth in contact.
27. The motion transmitted between the teeth of two spur gears is generally by---------[Ans: Partly sliding and partly rolling.]
28. When will the interference occur in an involute pinion and gear are in mesh having
same
size of addendum.
There will be an interference between the tip of pinion and flank of gear.
29. In involute gears, the pressure angle depends on---------------.
[Ans: Size of the teeth]
30. What do you know about tumbler gear?
Tumbler gears are those which are used in lathes for reversing the direction of
rotation of driven gears.
31. What is the minimum number of teeth pinion which will mesh with any gear
without interference?
System of gear teeth
Maximum number of teeth on the
pinion
o
14 composite
12
14o full depth involute
32
o
20 full depth involute
18
20o stub involute
14
32. The gear box in an automobile utilizes---------------------gear train.
[Ans: Epicyclic gear train.]
33. What is the arc of contact between two gears of pressure angle is-----------------------.
[Ans: Path of contact/cos ]
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
34. Part of flank of pinion tooth and part of face of gear tooth made cycloidal to avoid-------------in-----------------------teeth.
[Ans: Interference;Involute]
35. Define interference.
The phenomenon when the tip of tooth undercuts the roots on its mating gear is
known as interference.
36. What is the minimum number of teeth on a pinion for involute rack in order to
avoid interference?
Tp = 2AR/sin2
Where,
AR= Fraction by which the standar addendum of one module for the rack is to
be multiplied.
= Pressure angle
37. What you meant by non-standard gear teeth?
The gear teeth obtained by modifying the standard proportions of gear teeth
parameters is known as non-standard gear teeth.
38. Define cycloidal tooth profile and involute tooth profile.
A cycloid is the curve traced by a point on the circumference of a circle which
rolls without slipping on a fixed straight line.
Involute profile is defined as the locus of a point on a straight line which rolls without
slipping on the circumference of a circle.
39. Define circular pitch and diametral pitch in spur gears.
Circular pitch (PC):
It is the distance measured along the circumference of the pitch circle from a
point on one teeth to the corresponding point on the adjacent tooth.
PC = D/T
Diametral pitch(PD):
It is the ratio of number of teeth to the pitch circle diameter.
PD = T/D = /PC
40. Define Backlash.
It is the difference between the tooth space and the tooth thickness along the
pitch circle.
Backlash = Tooth space Tooth thickness
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
GEAR TRAIN
1. What is gear train of wheels?
Two or more gears re made to mesh with each other to transmit power from one
shaft to another. Such a combination is called a gear train or train of wheels.
2. What are the types of gear trains?
1. Simple gear train,
2. Compound gear train,
3. Reverted gear train, and
4. Epicyclic gear train.
3. Write velocity ratio in compound train of wheels?
Speed of last follower Product of teeth on drivers.
Speed of first driver Product of teeth on followers.
4. Train value of a gear train is-----------------.
[Ans: Reciprocal of the speed ratio]
5. Define simple gear train.
When there is only one gear on each shaft, it is known as simple gear train.
6. What is meant by compound gear train?
When there are more than one gear on shaft, it is called a compound gear
train.
7. What is the advantage of a compound gear train over a simple gear train.
The advantage of a compound gear train over a simple gear train is that a much
larger speed reduction from the first shaft to the last shaft can be obtained with small
gears.
8. What is reverted gear train?
When the axes of the first and last wheels are co-axial, the train is known as
reverted gear train.
9. In watch mechanism--------------------type of gear train is used.
[Ans: Reverted gear train]
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
10. How epicyclic gear train differs from the other types of gear trains?
In epicyclic gear trains, the axes of the shafts on which the gears mounted may
move relative to a fixed axis.
But in other types, the axes of the shafts over which the gears are mounted are
fixed relative to each other.
11. State the methods to find the velocity ratio of epicyclic gear train.
Two methods are: 1. Tabulation method, and 2. Algebraic method.
12. Mention two methods to transmit power between two wheels when the distance
between them is great?
1. By providing the large sized wheels, or
2. By providing one or more intermediate wheels.
13. What are the externally applied torques used to keep the gear train in
equilibrium?
1. Impart torque on the driving member.
2. Resisting or holding torque on the driven member.
3. Holding or braking torque on the fixed member.
14. Where the epicyclic gear trains are used?
The epicyclic gear trains are used in the back gear of lathe, differential gears of
the automobiles, pulley blocks, wrist watches, etc.
15. An idler has----------------effect on velocity ratio.
[Ans: No]
16. The function of a gear box in a car is to--------------------.
[Ans: Provide variable speed]
17. In a simple gear train the direction of rotation of the last wheel will be opposite to that
of the
first wheel, if the number of intermediate wheel is----------------------.
[Ans: even]
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
UNIT-V
FRICTION
1. Compare Dry, Greasy and Fluid Friction.
Object
Dry Friction
Greasy Friction
Definition:
The friction that
When the two
exists between
surfaces in contact
two unlubricated
have a minute thin
surfaces.
layer of lubricant
between them,
then it is called as
greasy friction.
Other names
Solid friction
Skin friction
Fluid Friction
When the two
surfaces in contact
are completely
separated by a
lubricant, then it is
called as fluid
friction.
Film friction (or)
Viscous friction.
2. Compare the laws of solid friction and Fluid Friction.
S.No. Law of Solid (or) Dry Friction
Laws of Fluid Friction
1
The frictional force is directly
The frictional force is almost
proportional to the normal
independent of load.
reaction between the surfaces.
2.
The frictional force opposes the
The frictional force is independent of
motion (or) its tendency to the
the substances of the bearing surfaces
motion and depends upon the
and opposing tendency is less.
nature of the surfaces in contact.
3.
The frictional force is
The frictional force reduces with
independent of the area and the
increase in temperature of the
shape of the contacting surfaces. lubricant.
3. What is meant by slope of a thread?
It is the inclination of the thread with horizontal.
Slope of thread = tan-1[Lead screw/Circumference of screw]
4. Differentiate between angle of repose and limiting angle of friction.
S.No.
Angle of Repose
Limiting Angle of
Friction
1.
The angle of repose is defined as the
The limiting angle of
maximum inclination of a plane at which a
friction () is defined as
body remains in equilibrium over the
the angle at which the
inclined plane by the assistance of friction
resultant reaction R
only.
makes with the normal
reaction RN.
2.
The angle of repose is equal to the limiting
The limiting angle is not
angle of friction ().
equal to angle of repose.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
5. What are the effects of limiting angle of friction?
1. If limiting angle of friction () is equal to tan-1 , then the body will move over
the plane irrespective of the magnitude of the force (F) (Limiting force of friction).
2. If < tan-1 , then no motion of body on plane is possible irrespective of how
large the magnitude of F may be.
6. Define co-efficient of friction ().
It is defined as the ratio of the limiting friction (F) to the normal reaction (R N)
between the two bodies.
= Limiting force of friction/Normal reaction=F/RN
7. Differentiate coefficient of friction in square thread and V-thread.
(a) In square thread, = F/RN
(b) In V thread, 1
= /cos
Where ,
F = Limiting force of friction,
RN = Normal reaction, and
2 = Angle of V in a V thread.
8. A block of 50 N rests on a horizontal plane and whose co-efficient of friction is
0.25. What is the force required to pull the block at an angle 30 o to the
horizontal.
Given Date:
W = 50 N
= 0.25
= 30o
[ = tan -1 () = 14.04]
Solution:
Required force (pulling), P = W sin /cos ( - )
P = 50 sin 14.04/cos (30 14.04) = 12.62 N
9. In the above problem what is the minimum force required to just pull the body?
Given Data: W = 50kg
= 0.25
[ = tan -1 () = 14.04]
Solution:
Pmin = W sin
At minimum force position, =
Pmin = W sin = 50 sin 14.04
Pmin = 12.129N
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
10. What is the mechanical advantage for a block whose weight W which rests on
a inclined plane whose angle is a to the horizontal by a pulling force P , at
degrees with vertical plane (neglecting friction).
Mechanical advantage = W/ P = sin ( = a)/ sin a
11. What is the efficiency of inclined plane?
The efficiency of an inclined plane is defined as the ratio between effort without
friction (P ) and the effort with friction (P).
12. Compare laws of static friction and dynamic friction.
S.No.
Law of Static Friction
Laws of Dynamic Friction
1.
The frictional force always acts
The frictional force always acts in a
in a direction, opposite to the
direction, opposite to the direction of
direction of motion of the body.
motion of the body.
2.
The magnitude of frictional force Frictional force remains constant for
is exactly equal to the force.
moderate speeds.
3.
The magnitude of the limiting
The magnitude of the limiting friction
friction bears a constant ratio to
bears a constant ratio to the normal
the normal reaction between the
reaction between the two surfaces.
two surfaces.
13. A body of 50N is placed on a 20o inclined plane whose coefficient of friction =
0.3 what is the force required to hold the body at its position in the horizontal
direction.
Given Data: W = 50N
= 0.3 [ = tan-1 () = 16.69]
= 20o
Solution:
Since = 90o [indirectly given Horizontal force]
Holding Force,P = W sin (=)/sin (--) = 50sin (20o+16.69)/sin(90-20-16.69)
P = 37.255N
14. What is the mechanical advantage of the above system.
Mechanical advantage = W/P
= 50N/37.255N = 1.342
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
15. What is the mechanical efficiency of an inclined plane which needs 50N of force to
raise a block on its surface when it is purely lubricated and 65 N when the surface
is dry.
Given Data:
P0 = 50N [without friction]
P = 65N [with considering friction]
Solution:
Efficiency of the inclined surface is given by,
up = P0/P=50/65=0.79
up = 76.92%
16. A inclined plane ( inclination to the horizontal) having limiting angle of friction
is used to lower a load down, what is the efficiency of the inclined plane if the effort
is applied in the horizontal direction.
Solution: down = cot /cot (-)
(or)
down = tan (-)/tan
17. What is the effort required to lift a 50 tone of lorry using screw jack?
( = 0.3 and = 20o)
Solution:
= tan-1 () = 16.69o
W = 50tonne = 50x10x9.81
= 490.5KN
Effort required to lift lorry P = W tan ( + )
= 490.5 tan (16.69 + 20)
= 365.56KN
18. What is the preferred value for a screw to have maximum efficiency?
= /4-/2
19. What is the maximum efficiency of a screw jack?
max = 1- sin /1+ sin
where , = tan-1
20.Why self-locking screws have lesser efficiency?
Self locking needs some friction on the thread surface of the screw and nut hence
it needs higher efforts to lift a body and hence automatically the efficiency decreases.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
FRICTION CLUTCHES
1. What are the functions of clutches?
1. It supplies power to the transmission system.
2. It stops the vehicle by disconnecting the engine from transmission system.
3. It is used to change the gear and idling the engine.
4. It gives gradual increment of speed to the wheels.
2. On solving clutch problems, it is assumed the old cluth works under uniform-------------------and the new clutch works under uniform--------------------.
[Ans: Wear; Pressure]
3. In a five plate clutch drive, the inner and outer radii of friction plate are 100 mm and
200 mm on the plate using uniform wear principle.
Given Data:
np = 5 and n = 5-1=4;
r1 = 100 mm;
r2 = 200 mm;
= 0.25;
W = 15KN;
T=?
Solution:
T =nWR
= n W(r1+ r2/2)
= 4x0.25x15x103 (100+200/2)x10-3
T = 2250N-m
4. What is the axial force required at the engagement and disengagement of cone
clutch?
Axial force required: W =Wn (1+ cot )
Where ,
Wn = Normal load,
= Coefficient of friction, and
= Cone angle of the clutch.
5. What is the difference between cone clutch and centrifugal clutch.
Cone clutch works on the principle of friction alone. But centrifugal clutch uses
principle of centrifugal force in addition with it.
6. Compare plate clutches and cone clutches.
S.No.
Plate clutches
Cone clutches
1.
Works on the principle of friction. Works on the principle of friction.
2.
Friction lined flat plates are used.
Friction lined frustum of cone is used.
3.
Single plate and multiplate clutch
It is not possible.
is possible depending on the load
condition.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
4.
It uses principle of uniform wear
and uniform pressure
It also uses the principle of uniform
wear and uniform pressure.
7. Why friction is called as necessary evil?
Friction is the important factor in engineering and physical applications such as belt
and ropes, jibs, clutches and brakes, nut and bolts, so it is the necessary one.If the friction
exceeds certain value it will cause heat, damage and wear when applied. So it is
called necessary evil.
BELT AND ROPE DRIVES
1. What are the belt materials?
1. Leather, 2. Cotton or fabric, 3. Rubber, 4. Balata, and 5. Nylon.
2. What are the types of belt drive?
1. Parallel belt drives
2. Angular belt drives
a) Open belt
(with or without idler pulley)
b) Cross belt
a) Right angle drive,
c) One idler pulley
b) Intersecting drives
d) Many idler pulley
c) Non-intersecting drives
e) Intermediate pulley
3. Explain velocity ratio.
It is defined as the ratio between velocity of the driver and the follower (or)
driven.
4. Whether the thickness of belt affects the velocity ratio?
Yes, but it is negligible.
N2/N1 = d1+t/d2+t
Where ,N1 and N2 = Speed of the driver and the driven respectively,
d1 and d2 = Diameters of the driver and the driven
respectively, and t = Belt thickness.
5. What is the effect of slip on velocity ratio of a belt drive?
N2/N1 = d1/d2[1-s/100]
s = Slip of the belt drive.
6. State the law of belting?
Law of belting states that the centre line of the belt as it approaches the pulley must
lie in a plane perpendicular to the axis of the pulley or must lie in the plane of the pulley,
otherwise the belt will runoff the pulley.
7. In a open belt drive, distance between pulleys is x and their diameters are D 1 and
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
D2 What is the length of belt required by this system?
L = /2 (D1+ D2)+2x+( D1-D2)2/4x
8. What is meant by angle of contact? (Lap angle)
It is the angle made by a common normal drawn to the tangent line at the point of
engagement and at the point of disengagement of the belt on a pulley, at its centre.
Lap angle for open belt drive = = (180 o-2)/180 rad
Lap angle for cross belt drive = = (180+2)/180 rad
9. Compare slip and creep in belt drive. Write any two points.
S.No.
Slip
Creep
1.
The relative motion between belt The phenomenon of sudden
and pulley due to insufficient
contraction and expansion of belt
friction is called as slip.
when it passes from slack side to
tight side is called as creep.
2.
The effect of slip is to reduce the The effect of creep is to reduce the
speed of driven.
speed of the driven pulley.
3.
It can be avoided by proper
It can be improved (avoided) by
friction lining on the surface pf
arranging the driving system such
the pulley or on belt.
that the tight side should be the
lower one and slack side be upper
one.
4.
Its effect on velocity ratio,
N2/N1 = d1/d2xE+2/ E+1
N2/N1 = d1/d2[1-s/100]
Where E = Youngs modulus of
the belt material, and
1, 2 stress on tight side and slack
sides of the belt.
10. What is the centrifugal effect on belts?
During operation, as the belt passes over a pulley the centrifugal effect due to its self
weight tends to lift the belt from the pulley surface. This reduces the normal reaction and
hence the frictional resistance. The centrifugal force produce additional tension in the
belt.
11. Write down the condition for maximum power transmission in belts.
P = (TV-mv3) x C
Where, C = 1-1/e
12. What are the disadvantages of V-belt drive over flat belt?
1. V belt cannot be used in large distance.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
2. It is not as durable as flat belt.
3. Since the V belt subjected to certain amount of creep therefore it is not suitable
for constant speed applications such as synchronous machines, and timing
devices.
4. It is a costlier system.
13. What is the ratio of driving tension in flat belt, V belt and in rope drives?
(a)
T1/T2 = e (For flat belt drive)
(b)
T1/T2 = e cosec (For V belt and rope drive)
Where
T1 = Tension in tight side,
T2 = Tension in loose side,
= Angle of contact, and
2 = Angle of V groove.
14. What is the condition for transmission of optimum or maximum power in belt
drive?
Power transmitted shall be a maximum when the centrifugal tension TC is one third
of the belt strength T or when the belt runs at the velocity of T/3m
Where ,
T = Total belt tension, and
m = Mass of belt per unit length.
15. When is the cross belt used instead of open belt?
1. Cross belt is used where the direction of rotation of driven pulley is opposite to
driving pulley.
2. Where we need more power transmission there we can use cross belt drive.
16. What is wipping? How it can be avoided in belt driver?
It the centre distance between two pulleys are too long then the belt begins to
vibrate in a direction perpendicular to the direction of motion of belt. This phenomenon is
called as wipping. Wipping can be avoided by using idler pulleys.
17. Centrifugal tension in belt depends on--------------and--------------and it effects----------------.
Ans: Mass of the belt per unit length (or) Density of belt material; Velocity of the belt;
Effects the power transmission.
18. What will be the effect on the limiting ratio of tensions of a belt if the coefficient of
friction between the belt and rim of pulley is doubled while angle of lap remains
same?
The ratio of tension will be squared.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
19. What is the (force) effort required to down a 50kg block on a inclined plane whose
angle of inclination is equal to limiting angle of friction?
There is no effort is required to move the body down.
20. Why lubrication reduces friction?
In practical all the mating surfaces are having roughness with it. It causes friction. If
the surfaces are smooth then friction is very less. Lubrication smoothens the mating
surface by introducing oil film between it. The fluids are having high smoothness than
solids and thus lubrication reduces friction.
21. What is the S.I. unit for frictional moment?
Frictional moment = N-m
22. What is the maximum angle of wedge for self locking?
= 2
= Angle of wedge
= Limiting friction angle
23. What you meant by Crowning in pulley?
The process of increasing the frictional resistance on the pulley surface is known as
crowning. It is done in order to avoid slipping of the belt.
24. What is meant by initial tension in belts?
In order to increase the frictional grip between the belt and pulleys, the belt is
tightened up. Due to this the belt gets subjected to some tension even when the pulleys
are stationary. This tension in the belt is called initial tension (T 0).
BRAKES
1. List out the commonly used breaks.
1. Hydraulic brakes: e.g., Pumps or hydrodynamic brake and fluid agitator.
2. Electric brakes: e.g., Eddy current brakes.
3. Mechanical brakes: e.g., Radial brakes and Axial brakes
2. Write an expression for the ratio of tension between the tight and slack sides of a
band and block brake.
T1/T2 =[1+ tan /1+ tan ]n
Where,
T1 = Tension in tight side,
T2 = Tension in slack side,
= Coefficient of friction between block and drum.
20 = Subtending angle, and
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL
03 Ph: 9942099122
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG.| 080120068 KINEMATICS OF
MACHINERY
II YEAR 3th SEMESTER)
n = Number of blocks.
3. What do you mean by a brake?
Brake is a device by means of which motion of a body is retarded for slowing down
(or) to bring it to rest which works on the principle of frictional force, it acts against the
driving force.
4. Function of dynamometer is-------------and it works on the principle of-----------------------.[Ans: To measure driving force; Brakes.]
5. Explain self-energising.
When moments of efforts applied on the break drum and frictional force are in the
same direction, the breaking torque becomes maximum (frictional force aids the braking
action). In such a case the brake is said to be partially self actuating or self energizing.
6. When is the intensity of pressure acting brake shoe is assumed to be uniform?
The intensity of pressure is assumed to be constant when the break shoe has small
angle of contact.For large angle of contact, it is assumed that the rate of wear of the shoe
remains constant.
7. Where does the P.I.V. drive system used?
P.I.V. (Positive Infinitely Variable) drive is used in an infinitely varying speed
systems.
Prepared by
(J.RAMESHKUMAR)
Ap/Mech
Success is the sum of small efforts, repeated day in and day out
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
You might also like
- Musical Acoustics PDFDocument26 pagesMusical Acoustics PDFGino Mendoza0% (1)
- Professional Practice Session 1Document23 pagesProfessional Practice Session 1Dina HawashNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Outline + Essay TemplateDocument7 pagesSynthesis Outline + Essay TemplatefirdausNo ratings yet
- Arthur Clifton GuytonDocument2 pagesArthur Clifton GuytonArlyn SanchezNo ratings yet
- BIACS 2 - Seville Biennial: The Unhomely (Review)Document3 pagesBIACS 2 - Seville Biennial: The Unhomely (Review)foggy_notionNo ratings yet
- Kom Two MarksDocument21 pagesKom Two MarksNavNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machines (Me1252) UNIT-1 Simple Mechanism. Two MarksDocument32 pagesKinematics of Machines (Me1252) UNIT-1 Simple Mechanism. Two MarksRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Lecturer Notes - Kinematics of MachineryDocument65 pagesLecturer Notes - Kinematics of Machineryehsan_shameli100% (1)
- Final TOM Lab Manual New PDFDocument10 pagesFinal TOM Lab Manual New PDFdab111No ratings yet
- Lab Manual For Kinematics of MachinesDocument18 pagesLab Manual For Kinematics of Machinesshailendra_236No ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery NotesDocument65 pagesKinematics of Machinery NotesVenkatesh Rajamani100% (1)
- Me6401 Kom Notes RejinpaulDocument64 pagesMe6401 Kom Notes RejinpaulkjsdjsdaNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Question Bank: 1. Differentiate Between Machine and MechanismDocument15 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Question Bank: 1. Differentiate Between Machine and MechanismSyed RoshanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineryDocument65 pagesKinematics of Machinerykumaravel07No ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineryDocument64 pagesKinematics of MachineryarulmuruganNo ratings yet
- Module 1 & First Half of 2 - Two Marks Q & ADocument8 pagesModule 1 & First Half of 2 - Two Marks Q & AMOHAMMED ZAHID BNo ratings yet
- KOM 2 Marks - Edition 3Document24 pagesKOM 2 Marks - Edition 3rajeshNo ratings yet
- Kinematics OF Machinery: Adithya Institute of TechnologyDocument34 pagesKinematics OF Machinery: Adithya Institute of TechnologybalajimetturNo ratings yet
- Pimpri Chinchwad Polytechnic, Nigdi: Chapter 01-Inversions of MechanismDocument43 pagesPimpri Chinchwad Polytechnic, Nigdi: Chapter 01-Inversions of MechanismNarendra ChavdaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineryDocument64 pagesKinematics of MachineryStar SathishNo ratings yet
- Ijsrdv1i9084 PDFDocument2 pagesIjsrdv1i9084 PDFKanaga VaratharajanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery (Me35) - 1 PDFDocument15 pagesKinematics of Machinery (Me35) - 1 PDFPraveen RajaNo ratings yet
- KOM 2 Marks - Edition 2Document16 pagesKOM 2 Marks - Edition 2Rajakumar SundaramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 HandoutDocument12 pagesChapter 2 HandoutRobel Metiku100% (1)
- Modeling and Simulation of Inverted Pendulum System Using Matlab: OverviewDocument4 pagesModeling and Simulation of Inverted Pendulum System Using Matlab: OverviewMuhammad Zubair SheikhNo ratings yet
- MEC291 Dynamic Crank and Slider2Document9 pagesMEC291 Dynamic Crank and Slider2Amir ArsyadNo ratings yet
- VCS REPORT FinalDocument7 pagesVCS REPORT Finalasd108533No ratings yet
- KOM Lect5Document36 pagesKOM Lect5Pranav C PNo ratings yet
- Kinematics-Of-Machinery 2 Mark QuestionsDocument33 pagesKinematics-Of-Machinery 2 Mark QuestionsNishanth ShannmugamNo ratings yet
- AE 2201 MOM.2marksDocument9 pagesAE 2201 MOM.2marksdennyfrancis19No ratings yet
- AE2201 2marks PDFDocument30 pagesAE2201 2marks PDFSathis KumarNo ratings yet
- Crank and Slotted Lever Quick Return (Rev2)Document9 pagesCrank and Slotted Lever Quick Return (Rev2)Vipin YadavNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Actuation SystemDocument34 pagesMechanical Actuation Systemdildar123100% (2)
- 2marks With AnswerDocument17 pages2marks With AnswerMECH HODNo ratings yet
- Precise Modelling of A Gantry Crane System Including Friction, 3D Angular Swing and Hoisting Cable FlexibilityDocument7 pagesPrecise Modelling of A Gantry Crane System Including Friction, 3D Angular Swing and Hoisting Cable FlexibilityPhạm Ngọc HòaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDocument18 pagesKinematics of Machinery 2 Marks All 5 UnitsvelavansuNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 19BME069Document14 pagesTutorial 3 19BME06920BME005 INAM SABRINo ratings yet
- Introduction To Theory of Machines, Mechanics of Machines, Mechanics of MaterialsDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Theory of Machines, Mechanics of Machines, Mechanics of MaterialsArif ZainNo ratings yet
- Class Note: 3 Inversions of MechanismDocument8 pagesClass Note: 3 Inversions of MechanismShweta PradhanNo ratings yet
- MoM Expt03 Theory Pos SliderCrank Ver01Document9 pagesMoM Expt03 Theory Pos SliderCrank Ver01krunal07786No ratings yet
- Simulation of Slider Crank Mechanism Using Adams ViesDocument5 pagesSimulation of Slider Crank Mechanism Using Adams Vieskiran_wakchaureNo ratings yet
- Kom Unit 1 PDFDocument18 pagesKom Unit 1 PDFDEVENDRA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines Part 1Document27 pagesMechanics of Machines Part 1kimosave99No ratings yet
- TOM EME-653 lAB MANUAL1Document41 pagesTOM EME-653 lAB MANUAL1kotika_somarajuNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Structural Analysis AND Design Optimization: OF Industrial RobotsDocument29 pagesMechanical Structural Analysis AND Design Optimization: OF Industrial RobotsAhsan AmjadNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Mass and Stiffness Distribution For Efficient Bipedal WalkingDocument6 pagesOptimization of Mass and Stiffness Distribution For Efficient Bipedal WalkingDaniel Sanz MerodioNo ratings yet
- TOM Exp.Document9 pagesTOM Exp.Aneesh KumarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER THREE ACTUATOR InterfacingDocument40 pagesCHAPTER THREE ACTUATOR InterfacingdanielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Mechanism and Linkages - Part BDocument37 pagesChapter 03 - Mechanism and Linkages - Part BMuaz FadzilNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines - Lab ManualDocument28 pagesTheory of Machines - Lab ManualHoneyNo ratings yet
- GS01 System Modeling PDFDocument3 pagesGS01 System Modeling PDFJerald Morelos HabilNo ratings yet
- Me6401 KomDocument128 pagesMe6401 KomThomas LafontaineNo ratings yet
- Composite Robust Control of A Laboratory Flexible ManipulatorDocument6 pagesComposite Robust Control of A Laboratory Flexible ManipulatorinfodotzNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesFrom EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Robot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlFrom EverandRobot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 1 Activity 4Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 1 Activity 4CLAUDIA ELISABET BECERRA GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Toolkit 1Document3 pagesComprehension Toolkit 1api-510893209No ratings yet
- Logging Best Practices Guide PDFDocument12 pagesLogging Best Practices Guide PDFbnanduriNo ratings yet
- Dedication Certificate John Clyde D. Cristobal: This Certifies ThatDocument1 pageDedication Certificate John Clyde D. Cristobal: This Certifies ThatAGSAOAY JASON F.No ratings yet
- The Politics of Plural SocietiesDocument14 pagesThe Politics of Plural SocietiesAngel StephensNo ratings yet
- Steve Nison - Candlestick Patterns - RezumatDocument22 pagesSteve Nison - Candlestick Patterns - RezumatSIightlyNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Segmentation Targeting Positioning FINAL PDFDocument13 pagesModule 3 Segmentation Targeting Positioning FINAL PDFLusiana Lie100% (1)
- M HealthDocument81 pagesM HealthAbebe ChekolNo ratings yet
- Saving Trees Comprehension QuestionsDocument3 pagesSaving Trees Comprehension QuestionsJayamathiVeerapa100% (1)
- Manual Mycom InglêsDocument158 pagesManual Mycom InglêsJorge Palinkas100% (1)
- If ملخص قواعدDocument2 pagesIf ملخص قواعدAhmed GaninyNo ratings yet
- Rhetorical Appeals Composition and TranslationDocument54 pagesRhetorical Appeals Composition and Translationteacher briculNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument9 pagesReportshobhaNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten HandbookDocument5 pagesKindergarten HandbookElizabeth MoorlagNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and Patent LawDocument4 pagesArtificial Intelligence and Patent LawSaksham TyagiNo ratings yet
- Power Point Skripsi UmarDocument12 pagesPower Point Skripsi UmarMuchamad Umar Chatab NasserieNo ratings yet
- Ie 2e Level 4 Unit 9-4Document4 pagesIe 2e Level 4 Unit 9-4Stasya EgorovaNo ratings yet
- How To Cook Pork AdoboDocument3 pagesHow To Cook Pork AdoboJennyRoseVelascoNo ratings yet
- Republic of Rhetoric by Abhinav ChandrachudDocument356 pagesRepublic of Rhetoric by Abhinav ChandrachudVinayak Gupta100% (1)
- The Oris Aquis Depth GaugeDocument2 pagesThe Oris Aquis Depth GaugeLord VarioNo ratings yet
- The Entrepreneurial and Entrepreneurial Mind: Week #2Document20 pagesThe Entrepreneurial and Entrepreneurial Mind: Week #2Mr.BaiGNo ratings yet
- Influence of Cooling Rate On The Structure and Formation of Oxide Scale in LowDocument7 pagesInfluence of Cooling Rate On The Structure and Formation of Oxide Scale in LowVarun MangaloreNo ratings yet
- Sap Fico Blueprint-1Document32 pagesSap Fico Blueprint-1Deepak AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Guiberon Well Service SytemsDocument66 pagesGuiberon Well Service SytemsRonald LlerenaNo ratings yet
- Event - Vsphere 7.0 DayDocument71 pagesEvent - Vsphere 7.0 Dayrico devizaNo ratings yet