Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Development Management: Sustainable Agriculture
Development Management: Sustainable Agriculture
Uploaded by
vsrajeshvsCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Kendall Hunt-Chemcom - Chemistry in The Community-Kendall Hunt Pub Co (1996) PDFDocument662 pagesKendall Hunt-Chemcom - Chemistry in The Community-Kendall Hunt Pub Co (1996) PDFFranklin Manrique100% (1)
- Recent Leaks From Hanford's High-Level Nuclear Waste Tanks: USDOE's Failure To Monitor, Report or Characterize Tank LeaksDocument77 pagesRecent Leaks From Hanford's High-Level Nuclear Waste Tanks: USDOE's Failure To Monitor, Report or Characterize Tank Leaksscribd3No ratings yet
- Forests Sustainable Development Environmental: SFM Sustainable Forest Management (SFM) Is The Management ofDocument1 pageForests Sustainable Development Environmental: SFM Sustainable Forest Management (SFM) Is The Management ofMc ChNo ratings yet
- Forest PolicyDocument41 pagesForest PolicyShivani SinghNo ratings yet
- SFM For ExitDocument45 pagesSFM For ExittengertdereNo ratings yet
- G2Document3 pagesG2judylyn elizagaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Sustainable Tropical Forest Management Where Wood Production Is The Primary ObjectiveDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Sustainable Tropical Forest Management Where Wood Production Is The Primary ObjectiveLM LaguertaNo ratings yet
- Forest ManagementDocument6 pagesForest ManagementSUMIT naikNo ratings yet
- Nama: Rizky Pratama NIM: 18/427456/KT/08768: Kehutanan InternasionalDocument2 pagesNama: Rizky Pratama NIM: 18/427456/KT/08768: Kehutanan InternasionalRIZKY PRATAMA PRATAMANo ratings yet
- Forest Resource 12345Document5 pagesForest Resource 12345HARSH TELKARNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Forest ManagementDocument26 pagesSustainable Forest ManagementAkanksha kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Management of ResourcesDocument11 pagesSustainable Management of ResourcesSTUDENTS addaNo ratings yet
- Towards An Economic Approach To Sustainable Forest DevelopmentDocument36 pagesTowards An Economic Approach To Sustainable Forest DevelopmentRalph QuejadaNo ratings yet
- DeforestationDocument1 pageDeforestationzaineb chzkibNo ratings yet
- Sergu Negn Yene NewDocument23 pagesSergu Negn Yene Newgetachew girmayNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Forest and WildlifeDocument10 pagesConservation of Forest and WildlifegowdanihalsagarNo ratings yet
- Forest OdtDocument1 pageForest OdtvinothasoniNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Chapter 4Document8 pagesGroup 3 Chapter 4Franz PampolinaNo ratings yet
- Draft National Forest Policy 2018Document11 pagesDraft National Forest Policy 2018Byron heartNo ratings yet
- Chapter IV Envi SciDocument5 pagesChapter IV Envi SciAs YangNo ratings yet
- Intro ForestryDocument41 pagesIntro Forestryravidharu6No ratings yet
- Review: Forest Management and Conservation Practices in Ethiopia: Opportunities and ConstraintsDocument6 pagesReview: Forest Management and Conservation Practices in Ethiopia: Opportunities and ConstraintsBegna BulichaNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Sustainable Land Management To Minimize Rampant DeforestationDocument6 pagesGroup 5 Sustainable Land Management To Minimize Rampant DeforestationRobert Bruce HammertonNo ratings yet
- Forest ManagementDocument3 pagesForest Managementsandeep0109No ratings yet
- Evs Assignment 1STDocument17 pagesEvs Assignment 1STkailash katariyaNo ratings yet
- Eco-NaRM Profile DraftDocument13 pagesEco-NaRM Profile DraftMathewos AlemuNo ratings yet
- Forestry Forest ManagementDocument2 pagesForestry Forest ManagementbharanikantNo ratings yet
- Forest Management-Working PlanDocument40 pagesForest Management-Working PlanHarsh KotechaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Forest ConservationDocument33 pagesImportance of Forest ConservationGeehthanJINo ratings yet
- Sustainable Forest Management,: Biodiversity and LivelihoodsDocument39 pagesSustainable Forest Management,: Biodiversity and LivelihoodsrisalNo ratings yet
- Final Report Write UpbackupDocument22 pagesFinal Report Write Upbackupapi-245426452No ratings yet
- Forest ResourcesDocument14 pagesForest Resourcessebastian victorioNo ratings yet
- Finals Lesson 1 Envi SciDocument24 pagesFinals Lesson 1 Envi SciGie Apilado RanayNo ratings yet
- Forest EcosystemDocument14 pagesForest Ecosystemadityabusiness924No ratings yet
- Range LandDocument83 pagesRange Landmoges lakeNo ratings yet
- Assignment in SFFG11Document3 pagesAssignment in SFFG11Jose S. Cabato IIINo ratings yet
- FRM 503 Lecture Notes Forest Management PDFDocument35 pagesFRM 503 Lecture Notes Forest Management PDFNakash Chauhan100% (1)
- National Wildlife Action Plan (2002-2016) : Preamble BackgroundDocument6 pagesNational Wildlife Action Plan (2002-2016) : Preamble BackgroundParth MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Deforestation Sample 1Document2 pagesDeforestation Sample 1LECHMY A/P VENGADASALEM MoeNo ratings yet
- Forest ManagementDocument9 pagesForest ManagementLynn CrastoNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Natural ResourcesDocument24 pagesConservation of Natural Resourcesmcheche1292% (13)
- 2006-07 CITIZEN CHARTER ForestsDocument20 pages2006-07 CITIZEN CHARTER Forestspujari chaithanyaNo ratings yet
- SC Mains 2022 Essay FrameworkDocument14 pagesSC Mains 2022 Essay Frameworklone survivorNo ratings yet
- Natural Resource Management Law - NoteDocument8 pagesNatural Resource Management Law - NoteDinberu GetachewNo ratings yet
- FM 101Document54 pagesFM 101VIKASH KOLNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of Social ForestryDocument94 pagesPrinciples and Practices of Social ForestryGary Bhullar90% (10)
- Natural Resource Management Law - NoteDocument8 pagesNatural Resource Management Law - NoteDinberu GetachewNo ratings yet
- 12042020171215forest Management B.Sc. Forestry IInd YearDocument92 pages12042020171215forest Management B.Sc. Forestry IInd YearSudip PandeyNo ratings yet
- Kats EvsDocument14 pagesKats EvsPooja JainNo ratings yet
- Envi 118 - Principles in Watershed Management (Chapter IV)Document17 pagesEnvi 118 - Principles in Watershed Management (Chapter IV)Gilbert D. ManongsongNo ratings yet
- Sustaining Biodiversity: The Ecosystem ApproachDocument42 pagesSustaining Biodiversity: The Ecosystem ApproachChristian Ralph Manzanero SabalaNo ratings yet
- Threats and Conservation For The Forest BiomeDocument2 pagesThreats and Conservation For The Forest Biomehlungwanethobeka43No ratings yet
- Introduction To IFRMDocument7 pagesIntroduction To IFRMJecejane LanticseNo ratings yet
- Forest Management in IndiaDocument4 pagesForest Management in Indiazodika khiangteNo ratings yet
- CSMFL Agroforestry TrainingDocument49 pagesCSMFL Agroforestry TrainingAwol She-AliNo ratings yet
- Ecological Components of Endangered ForestsDocument37 pagesEcological Components of Endangered ForestsforestethicsNo ratings yet
- Value of Forest and Biodiversity: Dr. Ranjan RoyDocument4 pagesValue of Forest and Biodiversity: Dr. Ranjan RoyEmdad YusufNo ratings yet
- FORESTSDocument5 pagesFORESTSMinahil FattaniNo ratings yet
- New One Role of Forests in Sustainable DevelopmentDocument6 pagesNew One Role of Forests in Sustainable DevelopmentAbhijit NayakNo ratings yet
- Deforestation and Forest DegradationDocument5 pagesDeforestation and Forest DegradationAniket MishraNo ratings yet
- Conservation of BiodiversityDocument70 pagesConservation of BiodiversitynarasimhanpondyNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Finance: Innovative Tools for a Flourishing PlanetFrom EverandBiodiversity Finance: Innovative Tools for a Flourishing PlanetNo ratings yet
- SAFe Implementation RoadmapDocument5 pagesSAFe Implementation Roadmapvsrajeshvs50% (4)
- Brainstorm Checklist 2018Document1 pageBrainstorm Checklist 2018vsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Kanbanworkbook SampleDocument23 pagesKanbanworkbook Samplevsrajeshvs100% (2)
- Scrum Checklist All PDFDocument1 pageScrum Checklist All PDFvsrajeshvs0% (1)
- Scrum Checklist All PDFDocument1 pageScrum Checklist All PDFvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Scrum Checklist Prio1 PDFDocument1 pageScrum Checklist Prio1 PDFvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Scrum in Large Companies Public Edition v1.1 PDFDocument4 pagesScrum in Large Companies Public Edition v1.1 PDFvsrajeshvs100% (1)
- 01 AdministrativeLawDocument11 pages01 AdministrativeLawvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Software - Components & CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesSoftware - Components & CharacteristicsvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument20 pagesUnit IiivsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Kurien UNIT 2Document46 pagesKurien UNIT 2vsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- SDLC Models: Linear ApproachDocument10 pagesSDLC Models: Linear ApproachvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- MBA: Unit III (Contd.) Integrated Environmental Management (IEM)Document8 pagesMBA: Unit III (Contd.) Integrated Environmental Management (IEM)vsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing & Variance AnalysisDocument4 pagesStandard Costing & Variance AnalysisvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Environmental AwarenessDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Awarenessvsrajeshvs100% (2)
- Full & Direct CostingDocument2 pagesFull & Direct CostingvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Science Chapter 8Document6 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 8Purnima Kadarasen100% (1)
- Bioremediation of Radioactive WasteDocument20 pagesBioremediation of Radioactive WastenickNo ratings yet
- Accident Radio Logic GOIANIADocument157 pagesAccident Radio Logic GOIANIACatalin CuraliucNo ratings yet
- City Limits Magazine, November 1985 IssueDocument32 pagesCity Limits Magazine, November 1985 IssueCity Limits (New York)No ratings yet
- Energy and Power Ib2Document24 pagesEnergy and Power Ib2Gkid GkidNo ratings yet
- Non Renewable Energy Guided NotesDocument20 pagesNon Renewable Energy Guided NotesLogan RoushNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Waste ManagementDocument427 pagesRadioactive Waste ManagementأحمدآلزهوNo ratings yet
- PollutionDocument29 pagesPollutionPratham PatelNo ratings yet
- Seguridad en Reactores de Investigación PDFDocument152 pagesSeguridad en Reactores de Investigación PDFJorge PáezNo ratings yet
- ENVPEP1412003Document5 pagesENVPEP1412003south adventureNo ratings yet
- Environmental Aspects of Nuclear Energy Production: Thomas H. PigfordDocument45 pagesEnvironmental Aspects of Nuclear Energy Production: Thomas H. PigforddenisaNo ratings yet
- Code of Practice & Safety Guide by Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety AgencyDocument63 pagesCode of Practice & Safety Guide by Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agencyj李枂洙No ratings yet
- Nuclear Fission and Fusion Lesson 16Document6 pagesNuclear Fission and Fusion Lesson 16Angel Alyza SisonNo ratings yet
- 6150 Saving The PlanetDocument2 pages6150 Saving The PlanetLeidy Fernanda VelandiaNo ratings yet
- RA 6969 Chemicals Management and Hazardous Waste ManagementDocument126 pagesRA 6969 Chemicals Management and Hazardous Waste ManagementJerome BungalowNo ratings yet
- Nuclear FukusimaDocument386 pagesNuclear Fukusimasigit wibisonoNo ratings yet
- Attomic Accident by James MahaffeyDocument9 pagesAttomic Accident by James MahaffeyAbdul basitNo ratings yet
- ENV 107 Introduction To Environmental Science: Alternative Energy ResourcesDocument45 pagesENV 107 Introduction To Environmental Science: Alternative Energy ResourcesMd Hasibul Karim 1811766630No ratings yet
- TMP Skeleton OutlineDocument5 pagesTMP Skeleton Outlinequraan.h.jNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 2 - Argument With Counter-Argument StructureDocument3 pagesIELTS Writing Task 2 - Argument With Counter-Argument StructureClementineNo ratings yet
- A Proposal To Research The Storage FacilityDocument5 pagesA Proposal To Research The Storage Facilityarthur_perez_3No ratings yet
- RA 6969 Toxic and Hazardous Waste Act PDFDocument6 pagesRA 6969 Toxic and Hazardous Waste Act PDFIrene AceroNo ratings yet
- America's Energy ChoicesDocument24 pagesAmerica's Energy ChoicesAmber AllenNo ratings yet
- UI TRIGA Decom Published PaperDocument5 pagesUI TRIGA Decom Published Papermoritati5No ratings yet
- Pertamina (Part 2 of 3) BOOT-003.compressed PDFDocument143 pagesPertamina (Part 2 of 3) BOOT-003.compressed PDFJonathan100% (1)
- Nuclear Energy: Nuclear Potential Energy Is The Potential Energy of The Particles Inside An Atomic Nucleus. The NuclearDocument26 pagesNuclear Energy: Nuclear Potential Energy Is The Potential Energy of The Particles Inside An Atomic Nucleus. The NuclearNur Umi RasyidahNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4. Environmental Issues and Problems Waste and PollutionDocument34 pagesMODULE 4. Environmental Issues and Problems Waste and PollutionFrank Joseph CatarigNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Pollution ProjectDocument19 pagesRadioactive Pollution ProjectMega No01No ratings yet
Development Management: Sustainable Agriculture
Development Management: Sustainable Agriculture
Uploaded by
vsrajeshvsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Development Management: Sustainable Agriculture
Development Management: Sustainable Agriculture
Uploaded by
vsrajeshvsCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Development Management
Sustainable Agriculture
<<Unit1>>
Sustainable Forestry Management
Thecommercialuseofforestsnowadayshasreachedsuchanextentthatithasbecomeathreattothe
environmentintheformof:
Increaseintemperature,
Lesserprecipitation,
Increasedrateofsoilerosion,
Increaseinfrequencyandvolumeoffloods,
Lossofsoilproductivity,
Extinctionofseveralspecies,
Nonavailabilityofseveralessentialforestproducts,and
Imbalanceinecosystem.
SFMisthemanagementofforestsaccordingtotheprinciplesofsustainabledevelopment.SFMhave
verybroadsocial,economic&envgoals.
KeyobjectiveofSFMistheattainmentofbalanceabalancebetweensociety'sincreasingdemandsof
forestproductsandbenefitsandthepreservationofforesthealth&diversity.Thisbalanceiscriticalto
thesurvivalofforestsandtotheprosperityofforestdependentcommunities.
KeyelementsofSFMare
Extentofforestresources
Biologicaldiversity
Foresthealthandvitality
Productivefunctionsandforestresources
Protectivefunctionsofforestresources
Socioeconomicfunctions
Legal,policyandinstitutionalframework.
Asetoflaws,regulations&programsareestablishedtoachieveSFM.
Laws
IndianForestActwhichprovideslegalframeworkformanagementofforestin
thecountry.
ForestConservationActwhichmandatescentralgovernmentapprovalfor
diversionofforestlandsforthenonforestrypurposes.
WildlifeProtection&preservationact
Regulations
Programs
SocialForestrymanagementandprotectionofforestsandafforestationon
barrenlandswiththepurposeofhelpingintheenvironmental,socialandrural
development.
JointForestManagement(JFM)partnershipsinforestmanagementinvolving
boththestateforestdepartmentsandlocalcommunities.
VanVigyanKendratodisseminatevarioustechnologiesdevelopedbyfarmers,
forestbasedindustriesandforestresearchinstitutes
Other
Institutions
IndianInstituteofForestManagement.
Mainforestconservationmethods:
Regulated&plannedcuttingoftreesclear,selective&shelterwoodcutting
Controloverforestfire.
Reforestation&Afforestation
CheckoverForestClearanceforAgriculturalandHabitationPurposes
Protectionofforestsforestdiseasesresultingfromparasiticfungi,rusts,mistletoes,viruses
andnematodeswhichcausethedestructionoftrees.Theforestsshouldbeprotectedeitherby
useofchemicalspray,antibioticsorbydevelopmentofdiseaseresistantstrainsoftrees.
ProperUtilisationofForestProductsandForests
Thesustainedyieldconceptdictatesthatwhenevertimberisremoved,eitherbyblockcuttingorby
selectivecutting,thedenudedareamustbereforested.Thismaybedonebynaturalorartificial
methods.Similarly,anyforestedlandwhichhasbeendestroyedbyfireorminingactivitiesshouldbe
reforested.Inruggedterrainaerialseedingisthemethodofchoice.
Besidesallthis,freshafforestationprogrammesshouldbestarted.Newplantationswillnotonly
increasetheforestcoverbutalsohelpinmakinguptheecobalance.Forafforestation,selectionoftrees
shouldbedoneaccordingtolocalgeographicalconditionsandcaremustbetakenduringinitialgrowth
ofthetrees.
Water Resource Management
Waterresourcesaresourcesofwaterthatareusefultohumans.Usesofwaterinclude
Agricultural65%
Industrial15%
Household
Recreational
Environmental
Virtuallyallofthehumanusesrequiresfreshwater.
Freshwaterisrenewableresourcelikesoil&air.However,wateristheoneofthecriticalresources,
butaroundtheworlditisunderthreat.Waterdemandalreadyexceedssupplyinmanypartsofthe
world,astheworldpopulationcontinuestorise,sotoodoesthewaterdemand.
Waterresourcescanbedividedintotwodistinctcategoriessurface&groundwatersources.
Surfacewateriswaterinariver,lakeorfreshwaterland.Surfacewaterisnaturallyreplenishedby
precipitationandnaturallylostthroughdischargetotheoceans,evaporationetc.
Waterresourcemanagementisthecontrolofwaterusage&alsothequalityofwater.Thisisvery
importantwithregardtotheconservation&theprotectionofwater.Waterdemandmanagementis
meanttomanagetheavailablewaterresourceswiselyandtodeliverthenecessaryamountfor
sustainabledevelopment.
<<benefits>>
<<stakeholders>>
<<framework>>awareness
Someavailabletechniquesare
Meter/Measure/Manage
Rainwaterharvesting
IncorporateLandscapeIrrigation/Xeriscaping
Waste Management
AsperBaselConvention,wastereferstosubstancesorobjectswhich
DisposedofOR
IntendedtobedisposedofOR
Requiredtobedisposedof
bytheprovisionofthelaw.
Wastescanbeclassifiedas
1. SolidWastewastesinsolidform.Examplesareplastic,bottles,cans,papers,scrapiron.
2. LiquidWastewastesinliquidform.Examplesarechemicals,oils,wastewateretc.
Basedonproperties,wastescanbeclassifiedas
1. Biodegradablethosethatcanbedegradedlikepaper,wood,fruitsetc.
2. NonBiodegradablethosethatcantbedegradedlikeplastics,bottles,oldmachines,cans.
Accordingtotheireffectonhumanhealth&env,wastescanbeclassifiedas
1. Hazardouswastethesearesubstancesunsafetousecommercially,industrially,agriculturally
oreconomically.
2. NonHazardouswastethesesubstancesusuallycreatedisposalproblems.
Wastescanbeclassifiedbasedonorigin
1. MunicipalSolidWasteSolidwastesthatincludehouseholdgarbage,rubbish,construction&
demolitiondebris,sanitationresidues,packagingmaterials,traderefugesetc.aremanagedby
anymunicipality.
2. BiomedicalWasteSolidorliquidwastesincludingcontainers,intermediateorendproducts
generatedduringdiagnosis,treatment&researchactivitiesofmedicalsciences.
3. IndustrialWasteLiquidandsolidwastesthataregeneratedbymanufacturing&processing
unitsofvariousindustrieslikechemical,petroleum,coal,metalgas,sanitary&paperetc.
4. AgriculturalWasteWastesgeneratedfromfarmingactivities.Thesesubstancesaremostly
biodegradable.
5. FisheryWasteWastesgeneratedduetofisheryactivities.Theseareextensivelyfoundin
coastal&estuarineareas.
6. RadioactiveWasteWastecontainingradioactivematerials.Usuallythesearebyproductsof
nuclearprocesses.Sometimesindustriesthatarenotdirectlyinvolvedinnuclearactivities,may
alsoproducesomeradioactivewastes,e.g.radioisotopes,chemicalsludgeetc.
7. EWasteElectronicwastesgeneratedfromanymodernestablishments.Theymaybe
describedasdiscardedelectricalorelectronicdevices.Someelectronicscrapcomponents,such
asCRTs,maycontaincontaminantssuchasPb,Cd,Beorbrominatedflameretardants.
Ifwastesarenotmanagedwisely,itcanimpact
Affectourhealthcancer,congenitalmalformations,neurologicaldiseasesetc.
Affectoursocioeconomicconditions.
Affectourcoastal&marineenv.
Affectourclimate.
<<Climatechange>>
Overthepastsomanyyears,communities,envgroups&otherconcernedindividualsandorghave
adoptedthewastebattlecryofReduceReuseRecycle.These3RsareoftendescribedastheWaste
Hierarchy.
Recently,Replacealsogotaddedtothishierarchy.ThemodifiedWasteHierarchyisshownas.
Reducebuyless&useless.Theultimategoalistodecreasethevolume&toxicityofwasteseach
persongeneratesinthecourseofdailylife.Italsomeansthatbyreducingconsumption,valuable
resourceslikewaterandenergyareconserved.
Avoidunnecessarypackaging.
Avoiditemsdesignedtobeusedonlyonce.
Usedurable,reusableproducts
Exampleclothbagsinsteadofplastic&paperbags,extrachargetoreducetheoverall
disposablebagusage.
Reuseisconcernedwithextendingthelifecycleofamaterialorproductwithminimalorno
conversionofform.Reusecanbedefinedassimplyfindingmoreand/ordifferentwaystouseanitem.
Reusingitemscansaveenergy&money.
Purchase&usedurableitemswithlonglives.
Reuseofcars,autoparts,books,jars,packingmaterials,containersetc.
Donateusablegoodssuchastoys,clothing&eyeglassestocharity.
Recycleisthemostrecognizedoptionof4Rs.Recyclingcanbedoneathome(milkjugs&soda
cans),atwork(cardboard&papers)&onthego(plastic&paperrecyclingatairports,citystreetsetc).
Inessence,recycletakesdiscardeditemsandseparatesthemintomaterialsthatcanberemanufactured
intonewproducts.
Upcyclingreferstotheconversionoflowvaluematerialsintohighvalueproducts.
Downcyclingreferstotheconversionofhighvalueproductsintolowvaluematerials.
Ingeneral,upcyclingismoredesirable,totheextentthatitismorelikelytoresultinalonglived
productandtherebykeepthematerialoutofthewastestreamforalongerperiodoftime.However,
bothupcycling&downcyclingaddresstheprimaryobjectiveofminimizingwastedisposalinlandfills.
Replaceproduction&useofrenewable,biobasedproductsalmostalwaysresultinlowerenvimpacts
thanproductsmadeofnonrenewablematerials.Productswithhighembodiedenergyshouldbe
replacedwithproductsrequiringalowerenergytoproduce.Thatmeans,thestrategyofreplaceis
focussedoncaseswhererenewableproducts(suchaswood)canreplacenonrenewableproducts(such
asconcrete&steel)resultinginanetenvbenefit.Anotherwayofphrasingthisstrategyistousebio
basedmaterialsinsteadoffossilfuelbasedmaterials,especiallywherethesubstitutionadvantageis
higher.IndustrialWasteManagement
Industrial Waste Management
Itisthewasteproducedbybusinessfromanindustrialormanufacturingprocess.Someoftheexamples
arechemicalsolvents,paints,metals,radioactivewastesetc.
Inabroadersense,industrialwastescanbeclassifiedas
Hazardous
NonHazardous
Hazardouswaste,,whichmaybeinsolid,liquidorgaseousformmaycausedangertohealthorenv,
eitheraloneorwhenincontactwithotherwastes.
Listofindustrialwastesare
Agriculturewaste
Clinicalwaste
Animalbyproducts
Commercialwaste
Biodegradablewastes
Foodwaste
Biomedicalwaste
Electronicwaste
Businesswaste
Nonbiodegradablewaste
Chemicalwaste
Remove
Dontgeneratewaste
Reduce
Generatelesswastebybettermanagement.
Sourcereductioncanbeachievedthroughequipmentortechnologymodifications,
processorproceduremodifications,reformulationorredesignofproducts,substitution
ofrawmaterials,
Replace
Materialsubstitution
Reuse
Reuseinitsoriginal.
Recycle
Recycleorreprocesstheitemtoincorporateitintoanewproductornewuse.
Recover
Extractmaterialsorenergyfromwaste.
Treat
Mitigatetheinherenthazardofthewaste.
BiologicalMethodscomposting,landfarming
ThermalMethodsincineration
ChemicalMethodsstabilization,neutralization
PhysicalMethodsfiltration,centrifugation,shreddingetc.
Dispose
Mitigatethehazardthroughpathwaymodifications
DeepInjection
Dischargetowaterorland
Landfill
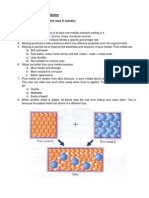
Nuclear Waste Management
Radiowastesarewastesthatcontainradioactivematerial.Radioactivematerialsareusuallythe
byproductofnuclearpowergeneration.However,otherindustriescanalsogenerateradioactivewastes
sometimes.(Hospitals).
Radiowastesishazardoustomostformsoflifeandtheenvironment,andisregulatedbyGovt.
agenciesinordertoprotecthumanhealthandtheenvironment.Notallnuclearwasteareparticularly
hazardousorhardtomanageascomparedtoothertoxicindustrialwastes.
Radioactivewastescanbesegregatedintoseveralclassifications.
LowlevelWasteisgeneratedfromhospitals,laboratoriesandindustry,aswellasthenuclearfuel
cycle.Itcomprisespaper,rags,tools,clothing,filtersetc.whichcontainsmallamountsofmostly
shortlivedradioactivity.Itisnotdangeroustohandle,butmustbedisposedofmorecarefullythan
normalgarbage.Usuallyitisburiedinshallowlandfillsites.Toreduceitsvolume,itisoften
compactedorincinerated(inaclosedcontainer)beforedisposal.Worldwideitcomprises90%ofthe
volumebutonly1%oftheradioactivityofallradwaste.
IntermediatelevelWastecontainshigheramountsofradioactivityandmayrequirespecialshielding.It
typicallycomprisesresins,chemicalsludgesandreactorcomponents,aswellascontaminatedmaterials
fromreactordecommissioning.Worldwideitmakesup7%ofthevolumeandhas4%ofthe
radioactivityofallradwaste.Itmaybesolidifiedinconcreteorbitumenfordisposal.Generally
shortlivedwaste(mainlyfromreactors)isburied,butlonglivedwaste(fromreprocessingnuclear
fuel)isdisposedofdeepunderground.
HighlevelWastemaybetheusedfuelitself,ortheprincipalwasteseparatedfromreprocessingthis.
Whileonly3%ofthevolumeofallradwaste,itholds95%oftheradioactivity.Itcontainsthe
highlyradioactivefissionproductsandsomeheavyelementswithlonglivedradioactivity.Itgenerates
aconsiderableamountofheatandrequirescooling,aswellasspecialshieldingduringhandlingand
transport.Iftheusedfuelisreprocessed,theseparatedwasteisvitrifiedbyincorporatingitinto
borosilicate(Pyrex)glasswhichissealedinsidestainlesssteelcanistersforeventualdisposaldeep
underground.
Nuclearwasteisgeneratedatallpointsofthefuelcycle.Frontendwasteconsistsprimarilyoflow
levelalphaemissionwaste.ServiceperiodwastetypicallyincludesLLW&ILWsuchascontaminated
reactorhousingsandwastefromdailyoperation.Backendwastenormallyisthemostradioactiveand
includesspentfuelrodsandreactorcores.
Threegeneralprinciplesareemployedinthemanagementofradioactivewastes:
Concentrateandcontain
Diluteanddisperse
Delayanddecay.
Thefirsttwoarealsousedinthemanagementofnonradioactivewastes.Thewasteiseither
concentratedandthenisolated,oritisdilutedtoacceptablelevelsandthendischargedtothe
environment.
Delayanddecayhoweverisuniquetoradioactivewastemanagementitmeansthatthewasteisstored
anditsradioactivityisallowedtodecreasenaturallythroughdecayoftheradioisotopesinit.
Inaccordancewithinternationalguidelines,acoherentcomprehensiveandconsistentsetofprinciples
andstandardsarebeingpracticedinIndiaforNuclearWasteManagementinconformitywith
Internationalguidelines.
AbriefsummaryofthevariousradioactiveWasteManagementpracticesfollowedinIndiaispresented
below.
Municipal Waste Management
ss
HospitalWasteManagement
AirQualityManagement
Coastal&MarineResourceManagement
NIMBYNotInMyBackYard
You might also like
- Kendall Hunt-Chemcom - Chemistry in The Community-Kendall Hunt Pub Co (1996) PDFDocument662 pagesKendall Hunt-Chemcom - Chemistry in The Community-Kendall Hunt Pub Co (1996) PDFFranklin Manrique100% (1)
- Recent Leaks From Hanford's High-Level Nuclear Waste Tanks: USDOE's Failure To Monitor, Report or Characterize Tank LeaksDocument77 pagesRecent Leaks From Hanford's High-Level Nuclear Waste Tanks: USDOE's Failure To Monitor, Report or Characterize Tank Leaksscribd3No ratings yet
- Forests Sustainable Development Environmental: SFM Sustainable Forest Management (SFM) Is The Management ofDocument1 pageForests Sustainable Development Environmental: SFM Sustainable Forest Management (SFM) Is The Management ofMc ChNo ratings yet
- Forest PolicyDocument41 pagesForest PolicyShivani SinghNo ratings yet
- SFM For ExitDocument45 pagesSFM For ExittengertdereNo ratings yet
- G2Document3 pagesG2judylyn elizagaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Sustainable Tropical Forest Management Where Wood Production Is The Primary ObjectiveDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Sustainable Tropical Forest Management Where Wood Production Is The Primary ObjectiveLM LaguertaNo ratings yet
- Forest ManagementDocument6 pagesForest ManagementSUMIT naikNo ratings yet
- Nama: Rizky Pratama NIM: 18/427456/KT/08768: Kehutanan InternasionalDocument2 pagesNama: Rizky Pratama NIM: 18/427456/KT/08768: Kehutanan InternasionalRIZKY PRATAMA PRATAMANo ratings yet
- Forest Resource 12345Document5 pagesForest Resource 12345HARSH TELKARNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Forest ManagementDocument26 pagesSustainable Forest ManagementAkanksha kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Management of ResourcesDocument11 pagesSustainable Management of ResourcesSTUDENTS addaNo ratings yet
- Towards An Economic Approach To Sustainable Forest DevelopmentDocument36 pagesTowards An Economic Approach To Sustainable Forest DevelopmentRalph QuejadaNo ratings yet
- DeforestationDocument1 pageDeforestationzaineb chzkibNo ratings yet
- Sergu Negn Yene NewDocument23 pagesSergu Negn Yene Newgetachew girmayNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Forest and WildlifeDocument10 pagesConservation of Forest and WildlifegowdanihalsagarNo ratings yet
- Forest OdtDocument1 pageForest OdtvinothasoniNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Chapter 4Document8 pagesGroup 3 Chapter 4Franz PampolinaNo ratings yet
- Draft National Forest Policy 2018Document11 pagesDraft National Forest Policy 2018Byron heartNo ratings yet
- Chapter IV Envi SciDocument5 pagesChapter IV Envi SciAs YangNo ratings yet
- Intro ForestryDocument41 pagesIntro Forestryravidharu6No ratings yet
- Review: Forest Management and Conservation Practices in Ethiopia: Opportunities and ConstraintsDocument6 pagesReview: Forest Management and Conservation Practices in Ethiopia: Opportunities and ConstraintsBegna BulichaNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Sustainable Land Management To Minimize Rampant DeforestationDocument6 pagesGroup 5 Sustainable Land Management To Minimize Rampant DeforestationRobert Bruce HammertonNo ratings yet
- Forest ManagementDocument3 pagesForest Managementsandeep0109No ratings yet
- Evs Assignment 1STDocument17 pagesEvs Assignment 1STkailash katariyaNo ratings yet
- Eco-NaRM Profile DraftDocument13 pagesEco-NaRM Profile DraftMathewos AlemuNo ratings yet
- Forestry Forest ManagementDocument2 pagesForestry Forest ManagementbharanikantNo ratings yet
- Forest Management-Working PlanDocument40 pagesForest Management-Working PlanHarsh KotechaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Forest ConservationDocument33 pagesImportance of Forest ConservationGeehthanJINo ratings yet
- Sustainable Forest Management,: Biodiversity and LivelihoodsDocument39 pagesSustainable Forest Management,: Biodiversity and LivelihoodsrisalNo ratings yet
- Final Report Write UpbackupDocument22 pagesFinal Report Write Upbackupapi-245426452No ratings yet
- Forest ResourcesDocument14 pagesForest Resourcessebastian victorioNo ratings yet
- Finals Lesson 1 Envi SciDocument24 pagesFinals Lesson 1 Envi SciGie Apilado RanayNo ratings yet
- Forest EcosystemDocument14 pagesForest Ecosystemadityabusiness924No ratings yet
- Range LandDocument83 pagesRange Landmoges lakeNo ratings yet
- Assignment in SFFG11Document3 pagesAssignment in SFFG11Jose S. Cabato IIINo ratings yet
- FRM 503 Lecture Notes Forest Management PDFDocument35 pagesFRM 503 Lecture Notes Forest Management PDFNakash Chauhan100% (1)
- National Wildlife Action Plan (2002-2016) : Preamble BackgroundDocument6 pagesNational Wildlife Action Plan (2002-2016) : Preamble BackgroundParth MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Deforestation Sample 1Document2 pagesDeforestation Sample 1LECHMY A/P VENGADASALEM MoeNo ratings yet
- Forest ManagementDocument9 pagesForest ManagementLynn CrastoNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Natural ResourcesDocument24 pagesConservation of Natural Resourcesmcheche1292% (13)
- 2006-07 CITIZEN CHARTER ForestsDocument20 pages2006-07 CITIZEN CHARTER Forestspujari chaithanyaNo ratings yet
- SC Mains 2022 Essay FrameworkDocument14 pagesSC Mains 2022 Essay Frameworklone survivorNo ratings yet
- Natural Resource Management Law - NoteDocument8 pagesNatural Resource Management Law - NoteDinberu GetachewNo ratings yet
- FM 101Document54 pagesFM 101VIKASH KOLNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of Social ForestryDocument94 pagesPrinciples and Practices of Social ForestryGary Bhullar90% (10)
- Natural Resource Management Law - NoteDocument8 pagesNatural Resource Management Law - NoteDinberu GetachewNo ratings yet
- 12042020171215forest Management B.Sc. Forestry IInd YearDocument92 pages12042020171215forest Management B.Sc. Forestry IInd YearSudip PandeyNo ratings yet
- Kats EvsDocument14 pagesKats EvsPooja JainNo ratings yet
- Envi 118 - Principles in Watershed Management (Chapter IV)Document17 pagesEnvi 118 - Principles in Watershed Management (Chapter IV)Gilbert D. ManongsongNo ratings yet
- Sustaining Biodiversity: The Ecosystem ApproachDocument42 pagesSustaining Biodiversity: The Ecosystem ApproachChristian Ralph Manzanero SabalaNo ratings yet
- Threats and Conservation For The Forest BiomeDocument2 pagesThreats and Conservation For The Forest Biomehlungwanethobeka43No ratings yet
- Introduction To IFRMDocument7 pagesIntroduction To IFRMJecejane LanticseNo ratings yet
- Forest Management in IndiaDocument4 pagesForest Management in Indiazodika khiangteNo ratings yet
- CSMFL Agroforestry TrainingDocument49 pagesCSMFL Agroforestry TrainingAwol She-AliNo ratings yet
- Ecological Components of Endangered ForestsDocument37 pagesEcological Components of Endangered ForestsforestethicsNo ratings yet
- Value of Forest and Biodiversity: Dr. Ranjan RoyDocument4 pagesValue of Forest and Biodiversity: Dr. Ranjan RoyEmdad YusufNo ratings yet
- FORESTSDocument5 pagesFORESTSMinahil FattaniNo ratings yet
- New One Role of Forests in Sustainable DevelopmentDocument6 pagesNew One Role of Forests in Sustainable DevelopmentAbhijit NayakNo ratings yet
- Deforestation and Forest DegradationDocument5 pagesDeforestation and Forest DegradationAniket MishraNo ratings yet
- Conservation of BiodiversityDocument70 pagesConservation of BiodiversitynarasimhanpondyNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Finance: Innovative Tools for a Flourishing PlanetFrom EverandBiodiversity Finance: Innovative Tools for a Flourishing PlanetNo ratings yet
- SAFe Implementation RoadmapDocument5 pagesSAFe Implementation Roadmapvsrajeshvs50% (4)
- Brainstorm Checklist 2018Document1 pageBrainstorm Checklist 2018vsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Kanbanworkbook SampleDocument23 pagesKanbanworkbook Samplevsrajeshvs100% (2)
- Scrum Checklist All PDFDocument1 pageScrum Checklist All PDFvsrajeshvs0% (1)
- Scrum Checklist All PDFDocument1 pageScrum Checklist All PDFvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Scrum Checklist Prio1 PDFDocument1 pageScrum Checklist Prio1 PDFvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Scrum in Large Companies Public Edition v1.1 PDFDocument4 pagesScrum in Large Companies Public Edition v1.1 PDFvsrajeshvs100% (1)
- 01 AdministrativeLawDocument11 pages01 AdministrativeLawvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Software - Components & CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesSoftware - Components & CharacteristicsvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument20 pagesUnit IiivsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Kurien UNIT 2Document46 pagesKurien UNIT 2vsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- SDLC Models: Linear ApproachDocument10 pagesSDLC Models: Linear ApproachvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- MBA: Unit III (Contd.) Integrated Environmental Management (IEM)Document8 pagesMBA: Unit III (Contd.) Integrated Environmental Management (IEM)vsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing & Variance AnalysisDocument4 pagesStandard Costing & Variance AnalysisvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Environmental AwarenessDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Awarenessvsrajeshvs100% (2)
- Full & Direct CostingDocument2 pagesFull & Direct CostingvsrajeshvsNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Science Chapter 8Document6 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 8Purnima Kadarasen100% (1)
- Bioremediation of Radioactive WasteDocument20 pagesBioremediation of Radioactive WastenickNo ratings yet
- Accident Radio Logic GOIANIADocument157 pagesAccident Radio Logic GOIANIACatalin CuraliucNo ratings yet
- City Limits Magazine, November 1985 IssueDocument32 pagesCity Limits Magazine, November 1985 IssueCity Limits (New York)No ratings yet
- Energy and Power Ib2Document24 pagesEnergy and Power Ib2Gkid GkidNo ratings yet
- Non Renewable Energy Guided NotesDocument20 pagesNon Renewable Energy Guided NotesLogan RoushNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Waste ManagementDocument427 pagesRadioactive Waste ManagementأحمدآلزهوNo ratings yet
- PollutionDocument29 pagesPollutionPratham PatelNo ratings yet
- Seguridad en Reactores de Investigación PDFDocument152 pagesSeguridad en Reactores de Investigación PDFJorge PáezNo ratings yet
- ENVPEP1412003Document5 pagesENVPEP1412003south adventureNo ratings yet
- Environmental Aspects of Nuclear Energy Production: Thomas H. PigfordDocument45 pagesEnvironmental Aspects of Nuclear Energy Production: Thomas H. PigforddenisaNo ratings yet
- Code of Practice & Safety Guide by Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety AgencyDocument63 pagesCode of Practice & Safety Guide by Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agencyj李枂洙No ratings yet
- Nuclear Fission and Fusion Lesson 16Document6 pagesNuclear Fission and Fusion Lesson 16Angel Alyza SisonNo ratings yet
- 6150 Saving The PlanetDocument2 pages6150 Saving The PlanetLeidy Fernanda VelandiaNo ratings yet
- RA 6969 Chemicals Management and Hazardous Waste ManagementDocument126 pagesRA 6969 Chemicals Management and Hazardous Waste ManagementJerome BungalowNo ratings yet
- Nuclear FukusimaDocument386 pagesNuclear Fukusimasigit wibisonoNo ratings yet
- Attomic Accident by James MahaffeyDocument9 pagesAttomic Accident by James MahaffeyAbdul basitNo ratings yet
- ENV 107 Introduction To Environmental Science: Alternative Energy ResourcesDocument45 pagesENV 107 Introduction To Environmental Science: Alternative Energy ResourcesMd Hasibul Karim 1811766630No ratings yet
- TMP Skeleton OutlineDocument5 pagesTMP Skeleton Outlinequraan.h.jNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 2 - Argument With Counter-Argument StructureDocument3 pagesIELTS Writing Task 2 - Argument With Counter-Argument StructureClementineNo ratings yet
- A Proposal To Research The Storage FacilityDocument5 pagesA Proposal To Research The Storage Facilityarthur_perez_3No ratings yet
- RA 6969 Toxic and Hazardous Waste Act PDFDocument6 pagesRA 6969 Toxic and Hazardous Waste Act PDFIrene AceroNo ratings yet
- America's Energy ChoicesDocument24 pagesAmerica's Energy ChoicesAmber AllenNo ratings yet
- UI TRIGA Decom Published PaperDocument5 pagesUI TRIGA Decom Published Papermoritati5No ratings yet
- Pertamina (Part 2 of 3) BOOT-003.compressed PDFDocument143 pagesPertamina (Part 2 of 3) BOOT-003.compressed PDFJonathan100% (1)
- Nuclear Energy: Nuclear Potential Energy Is The Potential Energy of The Particles Inside An Atomic Nucleus. The NuclearDocument26 pagesNuclear Energy: Nuclear Potential Energy Is The Potential Energy of The Particles Inside An Atomic Nucleus. The NuclearNur Umi RasyidahNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4. Environmental Issues and Problems Waste and PollutionDocument34 pagesMODULE 4. Environmental Issues and Problems Waste and PollutionFrank Joseph CatarigNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Pollution ProjectDocument19 pagesRadioactive Pollution ProjectMega No01No ratings yet