Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gears - Gear Efficiency PDF
Gears - Gear Efficiency PDF
Uploaded by
barukomkssCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Price Action Market Traps 7 Trap PDFDocument85 pagesPrice Action Market Traps 7 Trap PDFPradeep Chandra71% (7)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Designing Urea ReactorDocument21 pagesDesigning Urea ReactorAdawiyah Al-jufri100% (4)
- V3i9 Ijertv3is090001 PDFDocument3 pagesV3i9 Ijertv3is090001 PDFbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- Kobelco - Kobe Steel PDFDocument6 pagesKobelco - Kobe Steel PDFbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- AWSPipeWeld - American Welding SocietyDocument2 pagesAWSPipeWeld - American Welding Societybarukomkss100% (1)
- Corrosion Rate Calculator: All CountriesDocument1 pageCorrosion Rate Calculator: All CountriesbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- NGR - Ohm Calc Trafo 5MVA-20kVDocument6 pagesNGR - Ohm Calc Trafo 5MVA-20kVbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- Jembatan Bellie PDFDocument2 pagesJembatan Bellie PDFbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- BSM Vol 1 Sec 15 Aug 2007 PDFDocument2 pagesBSM Vol 1 Sec 15 Aug 2007 PDFbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission: Schaberweg 30-34 61348 Bad Homburg Germany Telephone +49 6172 275-0 Telefax +49 6172 275-275Document5 pagesPower Transmission: Schaberweg 30-34 61348 Bad Homburg Germany Telephone +49 6172 275-0 Telefax +49 6172 275-275barukomkssNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission: Schaberweg 30-34 61348 Bad Homburg Germany Telephone +49 6172 275-0 Telefax +49 6172 275-275Document5 pagesPower Transmission: Schaberweg 30-34 61348 Bad Homburg Germany Telephone +49 6172 275-0 Telefax +49 6172 275-275barukomkssNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission: Schaberweg 30-34 61348 Bad Homburg Germany Telephone +49 6172 275-0 Telefax +49 6172 275-275Document5 pagesPower Transmission: Schaberweg 30-34 61348 Bad Homburg Germany Telephone +49 6172 275-0 Telefax +49 6172 275-275barukomkssNo ratings yet
- Porosity by MassDocument1 pagePorosity by MassbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- Pro & Contra Hydropower: AdvantagesDocument16 pagesPro & Contra Hydropower: AdvantagesbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- HourGlass ErrorDocument10 pagesHourGlass ErrorbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- RTe BookGSDCalculatorDocument5 pagesRTe BookGSDCalculatorbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- General Apendice7Document4 pagesGeneral Apendice7jesusgomNo ratings yet
- Class Notes EMG 2404Document75 pagesClass Notes EMG 2404yassinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Latch and Flip-FlopDocument43 pagesLecture 10 Latch and Flip-FlopNagaNo ratings yet
- Nadia Karima Izzaty 1306369466 Dept. Teknik Sipil: Time (H) Rate (In/h) Direct Runoff (CFS) RM (In.)Document7 pagesNadia Karima Izzaty 1306369466 Dept. Teknik Sipil: Time (H) Rate (In/h) Direct Runoff (CFS) RM (In.)Nadia KarimaNo ratings yet
- Computer Mcqs For NTS or Other TestsDocument89 pagesComputer Mcqs For NTS or Other TestsBetNex ExtraNo ratings yet
- Sliding Mode Control Strategy For A 6 DOF Quadrotor HelicopterDocument7 pagesSliding Mode Control Strategy For A 6 DOF Quadrotor HelicopternaderjsaNo ratings yet
- Rake ReceiverDocument48 pagesRake ReceiverIk Ram100% (1)
- Most Repeated Concepts & QuestionsDocument44 pagesMost Repeated Concepts & Questionsanshika tembhareNo ratings yet
- Domain Specific Languages in Practice: International Journal of Computer Applications April 2015Document5 pagesDomain Specific Languages in Practice: International Journal of Computer Applications April 2015Radian Nata KristiantoNo ratings yet
- MuexamDocument1 pageMuexameema yoNo ratings yet
- Astm C796Document6 pagesAstm C796Abel ClarosNo ratings yet
- AB1014 - Performance Tuning - v2.0Document46 pagesAB1014 - Performance Tuning - v2.0sameer1562000No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document27 pagesChapter 10Yash GandhiNo ratings yet
- Semi-Active Fuzzy Control of A Wind-Excited Tall Building Using Multi-Objectivegenetic AlgorithmDocument16 pagesSemi-Active Fuzzy Control of A Wind-Excited Tall Building Using Multi-Objectivegenetic Algorithmalexkoch2No ratings yet
- App 34Document4 pagesApp 34kagisokhoza000No ratings yet
- Homework Help Geometry HoltDocument8 pagesHomework Help Geometry Holtafnofbfqearczc100% (1)
- Daa Lab Manual 2021Document21 pagesDaa Lab Manual 2021H S ParangiNo ratings yet
- 2013 / 1 6 Power System Analysis and Stability Representation of Power System ComponentsDocument32 pages2013 / 1 6 Power System Analysis and Stability Representation of Power System ComponentsPooja AshishNo ratings yet
- The Use of Hec-Ras Modelling in Flood Risk Analysis PDFDocument8 pagesThe Use of Hec-Ras Modelling in Flood Risk Analysis PDFaNo ratings yet
- Vdtuev FLEETWELD 5P PLUS enDocument1 pageVdtuev FLEETWELD 5P PLUS enfsasas asfaasNo ratings yet
- Cognos Report Development Tips and Tricks Ver3Document24 pagesCognos Report Development Tips and Tricks Ver3Angshusmita Baruah SegraNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document15 pagesModule 1An Neh GynNo ratings yet
- Editing, Coding, Data Entry, TabulationDocument3 pagesEditing, Coding, Data Entry, TabulationNutukurthi Venkat Ramji100% (1)
- Cost-Effectiveness of Supervised Exercise Therapy Compared With Endovascular Revascularization For Intermittent ClaudicationDocument10 pagesCost-Effectiveness of Supervised Exercise Therapy Compared With Endovascular Revascularization For Intermittent ClaudicationUday PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Powershore CatalogoDocument8 pagesPowershore CatalogoSimon HerediaNo ratings yet
- Deep Excavation BasementDocument8 pagesDeep Excavation BasementTan 程惠萍No ratings yet
- An Anatomical and Pathological Examination of The First Recorded Stranding of A Fraser's DolphinDocument7 pagesAn Anatomical and Pathological Examination of The First Recorded Stranding of A Fraser's DolphinStephanie Aeriel OcampoNo ratings yet
- Service & Operating Manual: 1/2" Elima-Matic Bolted MetalDocument14 pagesService & Operating Manual: 1/2" Elima-Matic Bolted MetalCalNo ratings yet
Gears - Gear Efficiency PDF
Gears - Gear Efficiency PDF
Uploaded by
barukomkssOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gears - Gear Efficiency PDF
Gears - Gear Efficiency PDF
Uploaded by
barukomkssCopyright:
Available Formats
Gears- Gear Efficiency
Disclaimer: The information on this page has not been checked by an independent person. Use this information at your own risk.
ROYMECH
Compact Geared Motors
framo-morat.com
Type Compacta for Reversing tasks Torque u pto 1600Nm; Speed upto 193
Click arrows to page adverts
Mechanical Engineer's
Pocket Book,
Roger Timings
Buy New 30.59
Privacy Information
Home
Drive_Index
Gear Efficiency
Introduction
Important Note:
The equations used are mainly derived from the technical information provided in the SDP/SI technical library see links below.
I recommend that for serious work the linked information is more suitable.
The efficiency of a gear system is simple calculated as the
[output shaft power /Input shaft power ].100 %.
The output power is the (input power - the power losses). Power losses in gear systems are associated primarily with tooth friction and
lubrication churning losses. Churning losses are relatively independent of the nature of the gears and the gear ratios - they are primarily
realated to the peripheral speed of the gears passing through the fluid.Churning losses are difficult to calculate and estimates based on
experience are often used in initial gear design. The frictional losses are related to the gear design,the reduction ratio,the pressure angle,
gear size, and the coefficient of friction.
The notes below relate primarily to estimating /calculating the the part of the efficiency of gear trains which is associated with the tooth
friction.
A simple table is provided below showing the efficiencies of various gear types. These efficiencies related to tooth friction losses only for
single tooth meshes.For drive trains the efficiencies or each mesh in the line is multiplied together ( 2 gears pairs of 90% efficiency result
in a gear train efficiency of 81%.
Type
Normal
Ratio Range
Pitch Line
Velocity (m/s)
Efficiency
Range
Spur
1:1 to 6:1
25
98-99%
Helical
1:1 to 10:1
50
98-99%
Double Helical
1:1 to 15:1
150
98-99%
Bevel
1:1 to 4:1
20
98-99%
Worm
5:1 to 75:1
30
20-98%
Crossed Helical
1:1 to 6:1
30
70-98%
Symbols
R g = Gear ratio
a n = normal pressure angle
v s = gear surface sliding velocity (m/s)
r o = Outside Diameter of pinion(m)
a = pressure angle
Rp = Pitch Diameter of gear (m)
= helix angle (deg)
r p = Pitch Diameter of pinion(m)
? = worm lead angle (deg)
E = efficiency of gear pair (%)
? = worm lead angle (deg)
P = Power loss of gear pair as a percentage of input power
= coefficient of friction
Ro = Outside Diameter of gear (m)
(%)
Spur Gears / Helical Gears
Considering a spur gear a good first approximation for average operating conditions is that the power loss at each mesh can be
http://www.roymech.co.uk/Useful_Tables/Drive/Gear_Efficiency.html[19/08/2014 9:32:11]
Gears- Gear Efficiency
approximated as P% of the potential power transmitted through the mesh. The efficiency is therefore..
Clarification of formula terms.
Gear Type
sign of Rg term
External spur
cos a
(R g +1)
Internal Spur
(R g -1)
Single Helical
cos f n / cos 2
tan f n = tan a.cos
(R g +1)
= helix angle
Worm Gears
The theoretical efficiency of a worm gear is provided on page worm gears and is shown again below as.
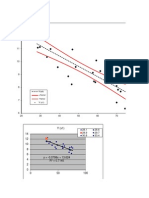
Chart of Worm Gear Efficiency
The graph below shows a worm gear efficiencies plotted against the lead angle for different coefficient of friction
Notes:
This chart agrees with the equation for worm gears having a normal pressure angle of 20 degrees...
An approximation for the friction coefficient for worm gears (Bronze -steel) is
= 0,04 v s -0,25
v s = sliding velocity (m/s)
http://www.roymech.co.uk/Useful_Tables/Drive/Gear_Efficiency.html[19/08/2014 9:32:11]
Gears- Gear Efficiency
Epicyclic Gears
Consider the two meshing gears below which are part of an epicyclic gear train.This is provided as and example of a typical component
in an epicyclic gear. The two gears and the arms are rotating as shown .
Now it the arm was stationary the contact point P would have a instantaneous velocity = -?2 R2 . (velocities to the right are positive ).
Now if the whole system was rotating as a rigid assembly with the velocity of the arm the instantaneous velocity -?3 R2 .Combining these
two motions together, the linear velocity of the tooth engagement (gear 2 -> gear 1)is therefore
v 12 = - ( ?2 R 2 - ?3 R 2 ) = - (?2 - ? 3 )R 2
Now the magnitude of the transmitted tangential force F12 x the tooth engagement velocity v 12 is called the potential power and the
power loss due to tooth friction is proportional to this power.Generally for spur gears ( and helical gears) it is sufficient to estimate the
power loss as 1% of the potential power.For more accurate estimations the equations above can be used.
P = 0,01 F12 v 12
The potential power is not the actual power but is the but is the power transmitted by the same gears operating on fixed centres at angular
velocities of ( ?2 - ?3 ) for gear 2 and ( ?1 - ?3 ) for gear 2.
The actual pitch line velocity of the gear mesh is -(?2 ) and therefore the ration of the potential power to the actual power is
http://www.roymech.co.uk/Useful_Tables/Drive/Gear_Efficiency.html[19/08/2014 9:32:11]
Gears- Gear Efficiency
Now in cases where the arm is rotating faster than the gear the potential power can be greater than the actual power and the losses
proportionally greater.
Example Epicyclic Gear efficiency calculation.
Consider the epicyclic gear chain shown below. The input speed = 250 RPM (ACW) and the input torque = 2.5 Nm
?2 = (250.2. p )/60 = 26,18rads/s.and ?1 = 0
The power into the gear = T?2 = 2,5.26,18 = 65 Watts. Calculating forces
The torque on the arm 2 = M2 = 2.5Nm
The force (F2) at Radius R2 (= R1 + R3) : = -(M2/R2) : F2 = -2.5 /(0,1m+.025m) = -20 N (forces to right are positive)
Now all forces and torques on the link between Arm(2) and gears (3) & (4) are in equilibrium therefore
For the gear mesh between gear 3 and the fixed sun 2 the velocity of tooth engagement is calculated by the product of the angular
velocity of the arm 2 at pitch radius of R2. = ?2 R1 = 26,18.0,075 = 1,96m/s
The potential power relates to the gear pair operated in isolation in this case for gear 3 to be in equilibrium (With forces and moments)
F2.R3 + F3.R3 = 0 and F2.R3 + F3R3 = 0 therefore F3 = -F2 = 20N
The potential power of the mesh between the sun gear 1 and the planet gear 3
= the gear engagement velocity(1,96m/s) x the tangential force (F3= 20N) = 1,96.20 =3,92W
Allowing 1% loss on a typical spur gear engagement the power loss at this engagement = 0,39W.
For the gear engagement between the gears 4 and 5 the angular velocity of gear five =
The velocity of tooth engagement between gear (4) and gear (5) =
R5 ( ?5 - ?2 ) = 0,068(-5,95- 26,18)=-2.18 m/s
The potential power at this tooth engagement =
the gear engagement velocity (2,18 m/s). x the tangential force (F4 = -167N) = 2,18.167 = 364 W
Assuming 1% power loss then the loss at this tooth engagement = 3,64 W
The power input to the epicyclic gear = 65 W therefore the Gear efficiency = 100(1 - (3,64 + 0,39) /65 ) = 94%
Links to Gear Efficiency
1. SDP/SI Technical Library...Lots of useful download documents with information of gear efficiency
2. Gear Efficiency comparison .. Short comparison -
http://www.roymech.co.uk/Useful_Tables/Drive/Gear_Efficiency.html[19/08/2014 9:32:11]
Gear Ratio
Worm Gear
Gears- Gear Efficiency
3. A second look at GearBox efficiencies .. A short informative download paper on spur gears /motors -
This Page is being developed
Home
Drive_Index
Send Comments to Roy Beardmore
Last Updated 20/01/2013
http://www.roymech.co.uk/Useful_Tables/Drive/Gear_Efficiency.html[19/08/2014 9:32:11]
Drive Gear
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Price Action Market Traps 7 Trap PDFDocument85 pagesPrice Action Market Traps 7 Trap PDFPradeep Chandra71% (7)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Designing Urea ReactorDocument21 pagesDesigning Urea ReactorAdawiyah Al-jufri100% (4)
- V3i9 Ijertv3is090001 PDFDocument3 pagesV3i9 Ijertv3is090001 PDFbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- Kobelco - Kobe Steel PDFDocument6 pagesKobelco - Kobe Steel PDFbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- AWSPipeWeld - American Welding SocietyDocument2 pagesAWSPipeWeld - American Welding Societybarukomkss100% (1)
- Corrosion Rate Calculator: All CountriesDocument1 pageCorrosion Rate Calculator: All CountriesbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- NGR - Ohm Calc Trafo 5MVA-20kVDocument6 pagesNGR - Ohm Calc Trafo 5MVA-20kVbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- Jembatan Bellie PDFDocument2 pagesJembatan Bellie PDFbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- BSM Vol 1 Sec 15 Aug 2007 PDFDocument2 pagesBSM Vol 1 Sec 15 Aug 2007 PDFbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission: Schaberweg 30-34 61348 Bad Homburg Germany Telephone +49 6172 275-0 Telefax +49 6172 275-275Document5 pagesPower Transmission: Schaberweg 30-34 61348 Bad Homburg Germany Telephone +49 6172 275-0 Telefax +49 6172 275-275barukomkssNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission: Schaberweg 30-34 61348 Bad Homburg Germany Telephone +49 6172 275-0 Telefax +49 6172 275-275Document5 pagesPower Transmission: Schaberweg 30-34 61348 Bad Homburg Germany Telephone +49 6172 275-0 Telefax +49 6172 275-275barukomkssNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission: Schaberweg 30-34 61348 Bad Homburg Germany Telephone +49 6172 275-0 Telefax +49 6172 275-275Document5 pagesPower Transmission: Schaberweg 30-34 61348 Bad Homburg Germany Telephone +49 6172 275-0 Telefax +49 6172 275-275barukomkssNo ratings yet
- Porosity by MassDocument1 pagePorosity by MassbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- Pro & Contra Hydropower: AdvantagesDocument16 pagesPro & Contra Hydropower: AdvantagesbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- HourGlass ErrorDocument10 pagesHourGlass ErrorbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- RTe BookGSDCalculatorDocument5 pagesRTe BookGSDCalculatorbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- General Apendice7Document4 pagesGeneral Apendice7jesusgomNo ratings yet
- Class Notes EMG 2404Document75 pagesClass Notes EMG 2404yassinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Latch and Flip-FlopDocument43 pagesLecture 10 Latch and Flip-FlopNagaNo ratings yet
- Nadia Karima Izzaty 1306369466 Dept. Teknik Sipil: Time (H) Rate (In/h) Direct Runoff (CFS) RM (In.)Document7 pagesNadia Karima Izzaty 1306369466 Dept. Teknik Sipil: Time (H) Rate (In/h) Direct Runoff (CFS) RM (In.)Nadia KarimaNo ratings yet
- Computer Mcqs For NTS or Other TestsDocument89 pagesComputer Mcqs For NTS or Other TestsBetNex ExtraNo ratings yet
- Sliding Mode Control Strategy For A 6 DOF Quadrotor HelicopterDocument7 pagesSliding Mode Control Strategy For A 6 DOF Quadrotor HelicopternaderjsaNo ratings yet
- Rake ReceiverDocument48 pagesRake ReceiverIk Ram100% (1)
- Most Repeated Concepts & QuestionsDocument44 pagesMost Repeated Concepts & Questionsanshika tembhareNo ratings yet
- Domain Specific Languages in Practice: International Journal of Computer Applications April 2015Document5 pagesDomain Specific Languages in Practice: International Journal of Computer Applications April 2015Radian Nata KristiantoNo ratings yet
- MuexamDocument1 pageMuexameema yoNo ratings yet
- Astm C796Document6 pagesAstm C796Abel ClarosNo ratings yet
- AB1014 - Performance Tuning - v2.0Document46 pagesAB1014 - Performance Tuning - v2.0sameer1562000No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document27 pagesChapter 10Yash GandhiNo ratings yet
- Semi-Active Fuzzy Control of A Wind-Excited Tall Building Using Multi-Objectivegenetic AlgorithmDocument16 pagesSemi-Active Fuzzy Control of A Wind-Excited Tall Building Using Multi-Objectivegenetic Algorithmalexkoch2No ratings yet
- App 34Document4 pagesApp 34kagisokhoza000No ratings yet
- Homework Help Geometry HoltDocument8 pagesHomework Help Geometry Holtafnofbfqearczc100% (1)
- Daa Lab Manual 2021Document21 pagesDaa Lab Manual 2021H S ParangiNo ratings yet
- 2013 / 1 6 Power System Analysis and Stability Representation of Power System ComponentsDocument32 pages2013 / 1 6 Power System Analysis and Stability Representation of Power System ComponentsPooja AshishNo ratings yet
- The Use of Hec-Ras Modelling in Flood Risk Analysis PDFDocument8 pagesThe Use of Hec-Ras Modelling in Flood Risk Analysis PDFaNo ratings yet
- Vdtuev FLEETWELD 5P PLUS enDocument1 pageVdtuev FLEETWELD 5P PLUS enfsasas asfaasNo ratings yet
- Cognos Report Development Tips and Tricks Ver3Document24 pagesCognos Report Development Tips and Tricks Ver3Angshusmita Baruah SegraNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document15 pagesModule 1An Neh GynNo ratings yet
- Editing, Coding, Data Entry, TabulationDocument3 pagesEditing, Coding, Data Entry, TabulationNutukurthi Venkat Ramji100% (1)
- Cost-Effectiveness of Supervised Exercise Therapy Compared With Endovascular Revascularization For Intermittent ClaudicationDocument10 pagesCost-Effectiveness of Supervised Exercise Therapy Compared With Endovascular Revascularization For Intermittent ClaudicationUday PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Powershore CatalogoDocument8 pagesPowershore CatalogoSimon HerediaNo ratings yet
- Deep Excavation BasementDocument8 pagesDeep Excavation BasementTan 程惠萍No ratings yet
- An Anatomical and Pathological Examination of The First Recorded Stranding of A Fraser's DolphinDocument7 pagesAn Anatomical and Pathological Examination of The First Recorded Stranding of A Fraser's DolphinStephanie Aeriel OcampoNo ratings yet
- Service & Operating Manual: 1/2" Elima-Matic Bolted MetalDocument14 pagesService & Operating Manual: 1/2" Elima-Matic Bolted MetalCalNo ratings yet