Professional Documents
Culture Documents
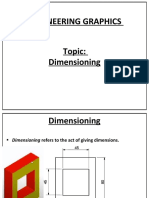
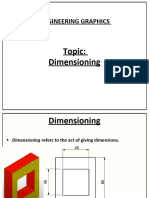
Rinciples of Imensioning: y y y y
Rinciples of Imensioning: y y y y
Uploaded by
Hasi De RustafariOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rinciples of Imensioning: y y y y
Rinciples of Imensioning: y y y y
Uploaded by
Hasi De RustafariCopyright:
Available Formats
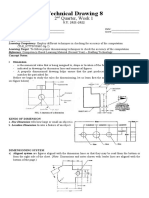
PRINCIPLES
DIMENSIONING
OF
y A Drawing from which a component is to be manufactured
q
y
information by:
must communicate all of the required
Describing the Shape of the component, by using
Orthographic Views or Pictorial Views
Views.
Giving actual Dimensions of all features.
Giving information about any special manufacturing
processes and materials required
required.
The Engineer should have a good understanding of
Projection methods, dimension methods and manufacturing
methods to be used
used.
2
TYPES OF DIMENSIONS
GENERAL
y Types of dimensioning can be classified as:
y Each dimension necessary for the complete
y Size Dimensions - Used to describe heights, widths,
definition of a finished product should be given on
the drawing
drawing.
diameters etc.
30
y Should appear once only.
y It
I should
h ld not b
be necessary ffor a di
dimension
i to b
be
48
calculated from other dimensions.
y It should not be necessary for the drawing to be
scaled.
y There should be no more dimensions than are
necessary to define the product.
y Dimensions for a particular feature should be placed on a
single
g view rather than on several, and on that view
which shows the relevant feature most clearly.
y Location Dimensions - Used to place various
features of a component relative to each other
other.
72
22
TYPES OF DIMENSIONS
ELEMENTS OF DIMENSIONING
y Mating Dimensions
Dimensions. Used for parts that fit together
requiring a certain degree of accuracy.
SMALL GAP - 2
82
EXTENSION LINE
SHORT EXTENSION - 2
16
6
72
72
40
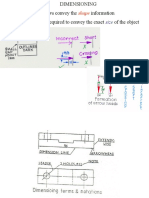
VALUE OF DIMENSION
12
PART - A
22
DIMENSION LINE
10
35
PART - B
55
DIMENSION LINES WELL SPACED
TO ENSURE CLARITY
Drawings for products must be dimensioned so that production
personnel all over the world can make mating parts that will fit
properly when assembled or when used to replace parts
5
ARROWHEADS
DIMENSION NUMBER ORIENTATION
Landscape Longest Side Horizontal
3X
Portrait Longest Side Vertical
X
Oblique
q Tick
Architectural Tick
B
Dot
A
Aligned Method
Arrowheads are typical dimension line terminators
terminators.
Arrowheads point directly to the extension lines at the end
off the
th dimension.
di
i
Arrowheads are made three times long as their width.
The dimension figures are placed so that they are
readable from the bottom or right side of the drawing.
LINEAR DIMENSIONING
DIMENSIONING
24
122
10
25
24
2
22
20
24
4
10
C-2
C-1
15
20
22
32
52
Chain or Continuous
Di
i i
Dimensioning
Parallel or Baseline
Di
i i
Dimensioning
Larger dimensions placed outside smaller dimensions
dimensions.
9
METHODS OF DIMENSIONING COMMON FEATURES
LEADER LINE
40
24
24
16
12
16
12
S12
SR12
16
METHODS OF DIMENSIONING COMMON FEATURES
10
applied to features by Leader Lines
Dimensions .applied
Lines.
Dimensioning to show applicable shape identification.
A dimension giving the Diameter of a Circle or Cylinder is shown
y
in front of the numerals.
byy the symbol
R15
R10
Part or incomplete
Circles are dimensioned as a Radii.
p
11
12
ADDING TEXT
STANDARD CHARACTER HEIGHTS FOR
FRONT ELEVATION
A2 = 420x 594
ADDING TEXT
MAIN TITLE - 7 mm
FRONT ELEVATION
SUB TITLES - 5 mm
DIMENSION & NOTES - 3 mm
Underline ONLY the Sub Titles
FRONT ELEVATION
DIMENSION IN MILLIMETRES - 3 mm
END ELEVATION
DIMENSIONS IN MILLIMETRES
PLAN
13
14
You might also like
- Managerial Practices Survey 2012Document3 pagesManagerial Practices Survey 2012Leana Polston-Murdoch75% (4)
- Technical Drawing GuidelineDocument82 pagesTechnical Drawing GuidelineAyman AlhalfawyNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3From EverandSolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- HSE Information Sheet Ageing Semi-Submersible Installations Offshore Information Sheet No 5 2007Document5 pagesHSE Information Sheet Ageing Semi-Submersible Installations Offshore Information Sheet No 5 2007Saeed JabbariNo ratings yet
- Dimension and Projection Lines Are Narrow Continuous Lines 0Document5 pagesDimension and Projection Lines Are Narrow Continuous Lines 0Sulaiman OluwapelumiNo ratings yet
- Introduction of EGDocument17 pagesIntroduction of EGUjjWal MahAjanNo ratings yet
- CAD & Engineering DrawingDocument13 pagesCAD & Engineering DrawingLaiba Khan100% (1)
- Dr. Richard E. Link U.S. Naval Academy Department of Mechanical Engineering 590 Holloway Road Annapolis, MD 21402-5042 All Rights ReservedDocument12 pagesDr. Richard E. Link U.S. Naval Academy Department of Mechanical Engineering 590 Holloway Road Annapolis, MD 21402-5042 All Rights ReservedDaveB2008No ratings yet
- Tutorial On Dimensioning: Standard Grade and Higher Graphic CommunicationDocument7 pagesTutorial On Dimensioning: Standard Grade and Higher Graphic CommunicationSanjay GomastaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Introductory NotesDocument13 pagesEngineering Drawing Introductory Notesvipsdgr8No ratings yet
- TOPIC: How Drawings Are Controlled in Industry in Relevance With Various Quality Systems?Document14 pagesTOPIC: How Drawings Are Controlled in Industry in Relevance With Various Quality Systems?randapaaaNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning: Objectives ImportanceDocument19 pagesDimensioning: Objectives ImportancejfcalaywanNo ratings yet
- ME 104 Engineering Drawing Lec Malik Kamran ShakirDocument22 pagesME 104 Engineering Drawing Lec Malik Kamran ShakirMusaab MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Basics of Dimension IngDocument11 pagesBasics of Dimension IngChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument410 pagesEngineering DrawingAtul Pandey33% (3)
- Inst 12-2aDocument61 pagesInst 12-2asansagithNo ratings yet
- MDT 110-1 Dimensioning ReviewDocument17 pagesMDT 110-1 Dimensioning Reviewcbales99No ratings yet
- Building Construction & Materials-VI: AssignmentDocument20 pagesBuilding Construction & Materials-VI: AssignmentMeenuNo ratings yet
- CAD & Engineering DrawingDocument51 pagesCAD & Engineering DrawingTravel & tourism100% (1)
- CPE414 DimensionDocument27 pagesCPE414 DimensionMuhamad Baihakhi ShamsudinNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics (ME-101) - IntroductionDocument68 pagesEngineering Graphics (ME-101) - IntroductionSUSHIL SUSHILNo ratings yet
- Rules in DimensioningDocument44 pagesRules in DimensioningUg ug ShotiteNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing 8 (Quarter 2 - Week 1)Document4 pagesTechnical Drawing 8 (Quarter 2 - Week 1)cha0% (2)
- DimensioningDocument26 pagesDimensioningLav BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter B - DimensioningDocument30 pagesChapter B - DimensioningNur Hazirah SadonNo ratings yet
- Engg DrawingDocument45 pagesEngg DrawingRicky Pointing100% (1)
- Planning Your Engineering DrawingDocument14 pagesPlanning Your Engineering Drawingapi-3707012100% (1)
- Sub-Module of Basic Drawing & Cad: Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka Fakulti Kejuruteraan PembuatanDocument20 pagesSub-Module of Basic Drawing & Cad: Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka Fakulti Kejuruteraan Pembuatanstamford_bridgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 Demtol1 - Dimensioning StandardsDocument100 pagesChapter7 Demtol1 - Dimensioning Standardsapi-265554570No ratings yet
- Gamtek - DimensioningDocument19 pagesGamtek - DimensioningIqbal Haryono PutraNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning ME DrawingsDocument50 pagesDimensioning ME DrawingsLuis NunesNo ratings yet
- Class 3Document12 pagesClass 3amrithakhubaNo ratings yet
- EGCD Unit-1Document86 pagesEGCD Unit-1Bhuma Naga PavanNo ratings yet
- Section 8: Dimensioning Identification: Completion GuidanceDocument9 pagesSection 8: Dimensioning Identification: Completion GuidancemithuwanNo ratings yet
- Inst 12-2aDocument61 pagesInst 12-2aDyerom Consulta DacirNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning 07-08Document50 pagesDimensioning 07-08Ankit KumarNo ratings yet
- DimensioningDocument23 pagesDimensioningAditya Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Drafting and Dimensioning StandardsDocument30 pagesDrafting and Dimensioning StandardskrristinNo ratings yet
- DimensioningDocument23 pagesDimensioningsai ganeshNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawings ManualDocument48 pagesEngineering Drawings ManualHowo4DieNo ratings yet
- Orthographic Projection - WWW - Helenhudspith.com-Slash-Resources-Slash-Graphics-Slash-John - H-Slash-Orthographic PDFDocument26 pagesOrthographic Projection - WWW - Helenhudspith.com-Slash-Resources-Slash-Graphics-Slash-John - H-Slash-Orthographic PDFjeroldscdNo ratings yet
- OrthographicDocument27 pagesOrthographicAmit RajputNo ratings yet
- 11/26/2013 Engineering Drawing & GraphicsDocument20 pages11/26/2013 Engineering Drawing & GraphicsSam ChaduaryNo ratings yet
- JJ306 Autodesk Inventor Week 2 - Project 2 - Flange Manifold PartDocument42 pagesJJ306 Autodesk Inventor Week 2 - Project 2 - Flange Manifold PartAh TiangNo ratings yet
- Concrete Bridge Design - Conception To Fabrication: Learning ObjectivesDocument58 pagesConcrete Bridge Design - Conception To Fabrication: Learning ObjectivesServet Süha SariakçaliNo ratings yet
- Production DrawingDocument98 pagesProduction DrawingThangadurai Senthil Ram PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Types of Drawings: S P D (D D)Document42 pagesTypes of Drawings: S P D (D D)umeshNo ratings yet
- Developments - Cont'D: Mechanical Engineering Graphics MECH 211Document139 pagesDevelopments - Cont'D: Mechanical Engineering Graphics MECH 211psomNo ratings yet
- Orthographic ProjectionsDocument26 pagesOrthographic ProjectionssynayakNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing NotesDocument81 pagesEngineering Drawing NotesAnonymous OFP2ygPIdNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning As Per BIS StandardDocument33 pagesDimensioning As Per BIS StandardBhuban Limbu100% (7)
- Computer Aided Technical DrawingDocument8 pagesComputer Aided Technical DrawinggurksyNo ratings yet
- Sketching, Constraining & DimensioningDocument29 pagesSketching, Constraining & DimensioningjtpmlNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing - VivaDocument20 pagesEngineering Drawing - VivaAshmit PaulNo ratings yet
- C A D - BPD Manual 23.07.2018Document68 pagesC A D - BPD Manual 23.07.2018Akash RangkameNo ratings yet
- Autocad Assignment Group G and IDocument7 pagesAutocad Assignment Group G and IJaks AnxamNo ratings yet
- Basic Autocad Start UpDocument22 pagesBasic Autocad Start UpuntoniNo ratings yet
- SMEA1304Document164 pagesSMEA1304y2k405 kaosNo ratings yet
- Production Drawing: 3 Basic Principles of Dimensioning in Production DrawingsDocument5 pagesProduction Drawing: 3 Basic Principles of Dimensioning in Production DrawingsManoj KbNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Engineering DrawingDocument18 pagesFundamentals of Engineering DrawingyanpainNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing - BookDocument150 pagesEngineering Drawing - Bookgurumahesh gNo ratings yet
- Installation Manual: ModelDocument20 pagesInstallation Manual: ModelJohan VargasNo ratings yet
- 2009 Chery TiggoDocument69 pages2009 Chery TiggoMtto Proyecto FúqueneNo ratings yet
- SP Catalogue JAN-DECDocument20 pagesSP Catalogue JAN-DECRiverland Welding and Tool SuppliesNo ratings yet
- Landscape and Urban Planning: Jie Su, Alexandros GasparatosDocument15 pagesLandscape and Urban Planning: Jie Su, Alexandros GasparatosMaria Claudia VergaraNo ratings yet
- Dimond Structural Systems Manual Aug2016Document272 pagesDimond Structural Systems Manual Aug2016Erwin Mars UyNo ratings yet
- Color Atlas of Diagnostic MicrobiologyDocument223 pagesColor Atlas of Diagnostic MicrobiologyOana Herea100% (2)
- CHAPTER 6 - HOMEWORK - With KeyDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 6 - HOMEWORK - With KeyVõ Ngọc HânNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Lesson ADocument17 pagesUnit 6 Lesson ADianaNo ratings yet
- Technical Offer Sama Baghdad Company 31st DEC 2020 Solicitation W56KGZ21Q7017Document120 pagesTechnical Offer Sama Baghdad Company 31st DEC 2020 Solicitation W56KGZ21Q7017Ra'ad HaniNo ratings yet
- Saha, 2003Document16 pagesSaha, 2003LA ArenqueNo ratings yet
- Summer Issue of The Dirt 2021Document28 pagesSummer Issue of The Dirt 2021Vermont Nursery & Landscape AssociationNo ratings yet
- 5AMCAT Coding Questions and Answers PDF Test 2018 Java - Geek Plac.Document4 pages5AMCAT Coding Questions and Answers PDF Test 2018 Java - Geek Plac.ROHIT KUMAR GUPTANo ratings yet
- Hubungan Jumlah Cd4 Dengan Kualitas Hidup Pada Orang Dengan Hiv/Aids (Odha)Document12 pagesHubungan Jumlah Cd4 Dengan Kualitas Hidup Pada Orang Dengan Hiv/Aids (Odha)WihelaNo ratings yet
- Whitman Resume AnnotatedDocument1 pageWhitman Resume Annotatedapi-664114983No ratings yet
- UHV II D4 S1 Recap v1Document10 pagesUHV II D4 S1 Recap v1Ram MurthyNo ratings yet
- Assessment Plan Developmental Domain/Subject Grade Level/Grading Period Content Standard Performance StandardDocument2 pagesAssessment Plan Developmental Domain/Subject Grade Level/Grading Period Content Standard Performance StandardHenry Kahal Orio Jr.No ratings yet
- Design Technology Coursework ExamplesDocument4 pagesDesign Technology Coursework Examplesf5e28dkq100% (2)
- Method For Estimating Carbon in BiocharDocument5 pagesMethod For Estimating Carbon in BiocharCharlesNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Week 1 - Day 4Document3 pagesQ2 - Week 1 - Day 4Erwin TusiNo ratings yet
- Observation Activity For Young LearnersDocument2 pagesObservation Activity For Young LearnersRifqi HidayatNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Minerals, Energy, Water and ResourcesDocument9 pagesMinistry of Minerals, Energy, Water and ResourcesRefilwe GarebaitseNo ratings yet
- Real Time Characteristic Value CombinationDocument5 pagesReal Time Characteristic Value CombinationHari KrishnaNo ratings yet
- CH 19 Cash and Liquidity Management Appendix Class WorkDocument4 pagesCH 19 Cash and Liquidity Management Appendix Class WorkMhmd KaramNo ratings yet
- Team6 Legend 5BVLCDocument8 pagesTeam6 Legend 5BVLCAna Sofia MuñizNo ratings yet
- Solved MbaDocument16 pagesSolved MbaJayaram SreevarahamNo ratings yet
- المنطق غير المحكم في علم الكلامDocument28 pagesالمنطق غير المحكم في علم الكلامهند خابةNo ratings yet
- Checklist For IE - UNESCODocument4 pagesChecklist For IE - UNESCOelaine marieNo ratings yet
- GNU Solfege 3.9.4 User ManualDocument66 pagesGNU Solfege 3.9.4 User Manualinfobits0% (1)