Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Neoplastic Disorders: Slow Rapid Localize Infiltrating Encapsulated No Capsule Unusual Common
Neoplastic Disorders: Slow Rapid Localize Infiltrating Encapsulated No Capsule Unusual Common
Uploaded by
Amiel Francisco ReyesCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Hemodialysis Patient's Endorsement FormDocument1 pageHemodialysis Patient's Endorsement FormHacienda Galea Resort and Events Place100% (1)
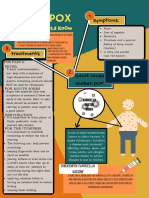
- Chicken Pox InfographicsDocument1 pageChicken Pox InfographicsBIANCA PILNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyKim GalamgamNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Module On Anti NeoplasticDocument7 pagesModule On Anti NeoplasticJojo JustoNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy For CancerDocument51 pagesChemotherapy For CancerHarshika KDGNo ratings yet
- Altretamine: Drug DosageDocument16 pagesAltretamine: Drug DosagePrincess CruzNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument11 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosusneu_gluhenNo ratings yet
- Antimetabolities: Route Onset Peak DurationDocument12 pagesAntimetabolities: Route Onset Peak DurationRichlle CortesNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 (Lecture)Document10 pagesNCM 106 (Lecture)e항해100% (3)
- Antineoplastic DrugsDocument38 pagesAntineoplastic DrugsTrixia CamporedondoNo ratings yet
- Name Mode of Action Indication Contraindicat ION Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: CV: Cardiotoxicity DermatologicDocument4 pagesName Mode of Action Indication Contraindicat ION Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: CV: Cardiotoxicity DermatologicAlexis Abigail de LeonNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy DrugsDocument43 pagesChemotherapy Drugsbrigette_lagat100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- NCP Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNCP Drug StudyArthadian De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- AntiNeoplastic AgentsDocument33 pagesAntiNeoplastic Agentsmers puno100% (1)
- Nutrition in Surgical PatientDocument26 pagesNutrition in Surgical Patient180045No ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationDocument6 pagesCellular AberrationCheysser FerolinoNo ratings yet
- Glomerulnephrities, Nephrotic SyndromDocument28 pagesGlomerulnephrities, Nephrotic SyndromJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Nausea Vomiting ReportDocument67 pagesNausea Vomiting Reportstephanie gayetaNo ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationsDocument37 pagesCellular AberrationsJess NinaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Regulation Student VersionDocument15 pagesCellular Regulation Student VersionCruz YrNo ratings yet
- Mitotic InhibitorsDocument17 pagesMitotic InhibitorsSamuel CamoronganNo ratings yet
- PrimDocument2 pagesPrimapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyJessie Cauilan CainNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Mesalamine MercaptopurineDocument15 pagesDrug Study On Mesalamine Mercaptopurineسوما الشمريNo ratings yet
- A 27Document10 pagesA 27NestleNo ratings yet
- Careplan 2Document11 pagesCareplan 2JulieRn2beNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressant DrugsDocument28 pagesImmunosuppressant DrugsimnasNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis-Medicine-PancreatitisDocument39 pagesCase Analysis-Medicine-PancreatitisAleks MendozaNo ratings yet
- DactinomycinDocument4 pagesDactinomycinKeith MadarangNo ratings yet
- A. Antineoplastic DrugsDocument48 pagesA. Antineoplastic DrugsKim Shyen BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Case 034: ConstipationDocument7 pagesCase 034: ConstipationZauza100% (1)
- Leukemias: by DR/ KhadigaDocument28 pagesLeukemias: by DR/ KhadigaDody ZainNo ratings yet
- Drugs Mechanism of Action Side Effect/Adverse Effect/Contraindication Nursing InterventionsDocument17 pagesDrugs Mechanism of Action Side Effect/Adverse Effect/Contraindication Nursing InterventionsJerome Vergel RubianesNo ratings yet
- Acute Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument37 pagesAcute Chronic GlomerulonephritisMadeline Jessica HuwaeNo ratings yet
- Hepatic FailureDocument37 pagesHepatic FailureWinston Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Dub, Dys, MenoDocument64 pagesDub, Dys, MenoRebecca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology: Anti-Neoplastic Chemotherapeutic DrugsDocument42 pagesNursing Pharmacology: Anti-Neoplastic Chemotherapeutic DrugswokorowNo ratings yet
- Is The Most Common Extracranial Solid Tumor of InfancyDocument7 pagesIs The Most Common Extracranial Solid Tumor of InfancyEdamarie ChuaNo ratings yet
- AmoxicillinDocument5 pagesAmoxicillinKyle DelrosarioNo ratings yet
- Ulecerative ColitisDocument14 pagesUlecerative ColitisnizaNo ratings yet
- Fluorouracil Drug StudyDocument8 pagesFluorouracil Drug StudyAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis Case PresDocument77 pagesLiver Cirrhosis Case Presmarlx580% (5)
- FLUOROURACIL Drug StudyDocument8 pagesFLUOROURACIL Drug StudyAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Dr. J.A. Dogbe: Cosultant Paediatrician/Public Health Specialist Sms-Knust/KathDocument53 pagesDr. J.A. Dogbe: Cosultant Paediatrician/Public Health Specialist Sms-Knust/KathAnastasiafynnNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Journal Club Presentation: Presented byDocument54 pagesWelcome To Journal Club Presentation: Presented byneptorNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- LithiumDocument4 pagesLithiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Induced Liver Diseases (DILD) : M. DeepalakshmiDocument22 pagesDrug Induced Liver Diseases (DILD) : M. DeepalakshmicrissNo ratings yet
- Case Study OF Hypokalemia Periodic ParalysisDocument34 pagesCase Study OF Hypokalemia Periodic ParalysisVivian Montesena BreganzaNo ratings yet
- By DR.: Haitham Mokhtar Mohamed Abd AllahDocument101 pagesBy DR.: Haitham Mokhtar Mohamed Abd AllahMohamed ElkadyNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument8 pagesLiver CirrhosisgoyaNo ratings yet
- Definition and Etiology: PancreatitisDocument24 pagesDefinition and Etiology: PancreatitisAliyah Tofani PawelloiNo ratings yet
- UlcerativecolitisDocument27 pagesUlcerativecolitisMohamed Abdulrazaq100% (1)
- Medroxyprogesterone AcetateDocument3 pagesMedroxyprogesterone Acetateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Complete Drug StudyDocument239 pagesComplete Drug StudyRPh Krishna Chandra Jagrit0% (1)
- Anti-NenoplasticsDocument1 pageAnti-NenoplasticsBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudySandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Document6 pagesConcept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Ran PioloNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument11 pagesAcute Pancreatitispeter_soósNo ratings yet
- Semis 2 - Drugs Acting On The Endocrine System 2Document11 pagesSemis 2 - Drugs Acting On The Endocrine System 2Amiel Francisco Reyes100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document11 pagesChapter 1Amiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ni For LMSDocument10 pagesNi For LMSAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- TutorialsDocument3 pagesTutorialsAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ni For LMS Chapter 2Document11 pagesNi For LMS Chapter 2Amiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Adv of Distance LearningDocument1 pageAdv of Distance LearningAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Activity and ExerciseDocument45 pagesActivity and ExerciseAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- In Service Exam For Breast DR Paul BalisiDocument11 pagesIn Service Exam For Breast DR Paul BalisiAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Temperature RegulationDocument48 pagesTemperature RegulationAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Health StratDocument11 pagesHealth StratAmiel Francisco Reyes100% (1)
- Health Education Prelims TopicsDocument36 pagesHealth Education Prelims TopicsAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ni Semifinals Topics 2 COVID 19Document11 pagesNi Semifinals Topics 2 COVID 19Amiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Internal Examination: Course Audit FHC Mid 2Document4 pagesInternal Examination: Course Audit FHC Mid 2Amiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Finals Core Competencies Under The Eleven Key of Responsibility of NursingDocument8 pagesFinals Core Competencies Under The Eleven Key of Responsibility of NursingAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Table of The Cognitive Domain (Original)Document8 pagesTable of The Cognitive Domain (Original)Amiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chaptre 17 - Substance AbuseDocument40 pagesChaptre 17 - Substance AbuseAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Funda SyllabusDocument10 pagesFunda SyllabusAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Saturday, November 24, 2018: SubscribeDocument24 pagesSaturday, November 24, 2018: SubscribeAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development: Anthony P. Olalia JRDocument31 pagesGrowth and Development: Anthony P. Olalia JRAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Literature Matrix HappinessDocument1 pageLiterature Matrix HappinessAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Poor Blood Travels Through The INFRIOR or SUPERIOR VENA CAVADocument2 pagesOxygen Poor Blood Travels Through The INFRIOR or SUPERIOR VENA CAVAAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- NP1 Family Nursing 3Document2 pagesNP1 Family Nursing 3Jonas Marvin AnaqueNo ratings yet
- 2024-06-24 Politics, Private Interests, and The Biden Administration's Deviation From Agency Regulations in The COVID-19 Pandemic (With Appendix)Document623 pages2024-06-24 Politics, Private Interests, and The Biden Administration's Deviation From Agency Regulations in The COVID-19 Pandemic (With Appendix)The FederalistNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Infulenza Flue 1Document6 pagesChapter 7 - Infulenza Flue 1Jonathan SaydeNo ratings yet
- Shu ACT 2Document4 pagesShu ACT 2John Daniel CapituloNo ratings yet
- OSCE ReviewDocument45 pagesOSCE ReviewKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Jurnal MataDocument7 pagesJurnal MatatrianaamaliaNo ratings yet
- 16.nephrotic SyndromeDocument115 pages16.nephrotic SyndromeRhomizal MazaliNo ratings yet
- L4 - Assessment of Nasal ObstructionDocument17 pagesL4 - Assessment of Nasal ObstructionAmirul HamudinNo ratings yet
- A Case Study in Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever - MicrobiologyDocument1 pageA Case Study in Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever - MicrobiologyAnna PriskaNo ratings yet
- NCP OrthoDocument6 pagesNCP OrthoRuth Anne Arriesgado NañozNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Engineerng: Ehsan TahamiDocument30 pagesBiomedical Engineerng: Ehsan TahamiAmin Derakhshan100% (1)
- Minimally Invasive Vertical Preparation Design For Ceramic VeneersDocument12 pagesMinimally Invasive Vertical Preparation Design For Ceramic VeneersdanielaNo ratings yet
- Tinjauan Keakuratan Data Pada Sensus Harian Rawat Inap Di Rumah Sakit Khusus Bedah Banjarmasin SiagaDocument5 pagesTinjauan Keakuratan Data Pada Sensus Harian Rawat Inap Di Rumah Sakit Khusus Bedah Banjarmasin SiagaSaiful RizalNo ratings yet
- Manual of Obstetrics and GynecologyDocument183 pagesManual of Obstetrics and GynecologyMiraf MesfinNo ratings yet
- The New Parkland Hospital CampusDocument1 pageThe New Parkland Hospital CampusThe Dallas Morning NewsNo ratings yet
- NCM108 Module 1-CDocument9 pagesNCM108 Module 1-Cmirai desuNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Keperawatan Muhammadiyah: Suhenny Zainuddin, Ariyanti Saleh, Kusrini KadarDocument6 pagesJurnal Keperawatan Muhammadiyah: Suhenny Zainuddin, Ariyanti Saleh, Kusrini KadarristaNo ratings yet
- Modified Halterman Appliance-A Key To Alter Bilateral Ectopic Eruption of Maxillary Permanent First MolarsDocument5 pagesModified Halterman Appliance-A Key To Alter Bilateral Ectopic Eruption of Maxillary Permanent First MolarsLjubomirErdoglijaNo ratings yet
- Home Program and Councelling For CaregiversDocument6 pagesHome Program and Councelling For CaregiversAkhila SudheerbabuNo ratings yet
- Varicose VeinsDocument13 pagesVaricose VeinsTomus ClaudiuNo ratings yet
- Learning Needs and Quality Care Among Family Caregivers and Elderly Patients of Guadalupe, Cebu City, Central PhilippinesDocument22 pagesLearning Needs and Quality Care Among Family Caregivers and Elderly Patients of Guadalupe, Cebu City, Central PhilippinesLianne VergaraNo ratings yet
- TB PolicyDocument174 pagesTB PolicyDrashua AshuaNo ratings yet
- Ape CopdDocument6 pagesApe Copdnina purnamasariNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic SetupDocument3 pagesDiagnostic SetupPatricia DasoveanuNo ratings yet
- Pleasure 1951Document4 pagesPleasure 1951Andres Espinosa de los MonterosNo ratings yet
- Staff Nurse - PrintDocument8 pagesStaff Nurse - PrintMark Joseph Felicitas CuntapayNo ratings yet
- CS FORM 41 Medical Certificate 2Document1 pageCS FORM 41 Medical Certificate 2Leonor BagnosNo ratings yet
Neoplastic Disorders: Slow Rapid Localize Infiltrating Encapsulated No Capsule Unusual Common
Neoplastic Disorders: Slow Rapid Localize Infiltrating Encapsulated No Capsule Unusual Common
Uploaded by
Amiel Francisco ReyesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Neoplastic Disorders: Slow Rapid Localize Infiltrating Encapsulated No Capsule Unusual Common
Neoplastic Disorders: Slow Rapid Localize Infiltrating Encapsulated No Capsule Unusual Common
Uploaded by
Amiel Francisco ReyesCopyright:
Available Formats
NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS
Pathogenesis of Cancer
Cellular Transformation and Derangement Theory
Failure of the Immune Response Theory
Etiologic Factors
Virus
Chemical carcinogens
Industrial Compounds
Hormones
Food, preservatives
Physical Agents
Radiation
Trauma/physical irritation
Hormones
Genetics
Predisposing Factors
Age
Sex
Urban vs rural residence
Geographic distribution
Occupation
Heredity
Stress
Precancerous lesions
Obesity
Warning Signs of Cancer
C- change in bowel or bladder habits
A- sore throat that does not heal
U- unusual bleeding or discharge
U- unexplained sudden weight loss
U- unexplained anemia
T- thickening or lump in the breast or elsewhere
I- indigestion or difficulty in swallowing
O- obvious change in warts or moles
N- nagging cough or hoarseness of voice
Comparison of Benign & Malignant Neoplasm
Characteristics
Benign
Malignant
Speed of growth
Slow
Rapid
Mode of growth
Localize
Infiltrating
Capsule
Encapsulated
No capsule
Recurrence
Unusual
Common
Metastasis
None
Common
Effect
Harmless to host
Harmful
Prognosis
Very good
Poor
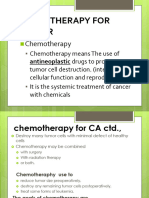
Chemotherapy
1. Objectives
To destroy Ca cells w/o excessive destruction of normal cells
To control tumor growth if cure is no longer possible
Used as adjuvant therapy
2. Contraindications
Infection
Recent surgery
Impaired renal/hepatic function
Pregnancy
Bone marrow depression
Recent radiation
Safe Handling of Chemotherapeutic Agents
1. Wear mask, gloves and back-closing gown
2. Avoid skin contact
3. Sterile/alcohol-wet cotton pledgets should be used in opening vials
4. Expel air bubbles on wet cottons
5. Vent vials to reduce pressure after mixing
6. Wipe external surface of syringes and IV bottles
7. Avoid needle stab
8. Clearly label the hanging bottle with ANTINEOPLASTIC CHEMOTHERAPY
9. Contaminated needles should be disposed in a clearly marked special container
10. Dispose half-empty ampules, vials, IV bottles in a sealed plastic bag with label
11. Handwashing should be done before and after removal of gloves
12. Trained personnel only should be involved in the use of drugs
13. Ideally preparation of drugs should be in laminar flow condition with filtered air
Nursing Intervention for Chemotherapeutic Side-effects
1. GI system nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation
Administer antiemetic
Replace fluid & electrolyte loss, low fiber diet to relieve diarrhea
High fiber diet to relieve constipation
2. Integumentary system
Pruritus, urticaria
Provide good skin care
Stomatitis
Provide good oral care, avoid hot & spicy food
Alopecia
Skin pigmentation
Nail changes
3. Hematopoietic system
Anemia
Provide frequent rest periods
Neutropenia
Protect from infection
Thrombocytopenia
Protect from trauma, avoid ASA
3. Genito-urinary system
Hemorrhagic cystitis
Provide 2-3 L of fluids/day
Urine color changes
Reassure client that it is harmless
3. Reproductive system
Premature menopause or amenorrhea
Reassure that menstruation will resume after chemotherapy
Summary of Effects of Chemotherapy
Antineoplastic drugs affects both normal and Ca cells by
disrupting cell function and division at various points
of cell cycle.
Most Ca drugs are most effective against cells that multipl
rapidly neoplasm, bone marrow cells, cells in the GI tract,
and cells in the skin or hair follicles. Adverse reaction to
cancer drugs tend to occur in these organs.
Chemotherapeutic agents should not be used during
pregnancy or lactation. Congenital defects may occur in the
fetus.
Antiemetics
Dronabinol (Marinol)
Odansetron (Zofran)
Granisetron (Kytril)
Alprazolam (Zanax)
Lorazepam (Ativan)
Haloperidol (Haldol)
Prochlorperazine (Compazine)
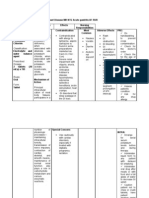
Antimetabolites
(foster cancer cell death by interfering with cellular metabolic process.)
Alkalyting agents
(produces cytoxic effects by damaging DNA and interfering with cell replication. Most effective against rapidly
dividing cells ).
Adverse effects:
gonadal suppression,
hemorrhagic and nonhemorrhagic cystitis,
N/V.(Reglan for vomiting).
Related drugs: (cytoxan, platinol, myeleran, leukeran).
Nursing implication:
force fluids
assess for signs and symptoms of unexplained bleeding.
Assess leukocytes count frequently.
Monitor CBC,uric acid, electrolytes, thrombocytosis and hepatic/renal function at least twice a week.
Instruct client to report hematuria or dysuria immediately
Plants or vinca alkaloids
(acts on cells undergoing mitosis, thus stopping cell division).
Adverse effects:
peripheral neuropathy
Cramps
Constipation
N/V
Stomatitis
alopecia,
leukopenia,
photosensitivity.
Nursing implications:
do not give IM or SC as tissue necrosis can occur.
Monitor bowel function, frequent neuro checks,monitor CBC and platelets,advise client to avoid
overexposure to sun.
Related drugs:
vincristine(oncovin), vinblastine(velban
Antibiotic Antineoplastic agents
(attaches to DNA and prevents DNA synthesis in vulnerable cells)
Adverse effects:
N/V,stomatitis,
hyper pigmentation of skin and nails,
alopecia.
Related drugs: Mitomycin, Plicamycin Blenoxane, Dactinomycin.
Nursing implication
dont give SC or IM- local reaction and skin necrosis may occur.
Do not mix with other drugs,
monitor CBC,serum uric acid levels,
frequent mouth care,
client needs sufficient fluids to prevent hyperuricemia,
assist client with information on wigs and head coverings before hair loss starts,
wear gloves to prepare this drug,
wash skin with soap and water if powder or solution contacts skin,
urine is red colored for 1-2 days after administration, clears within 48 hours.
Antineoplastic affecting hormonal balance
(keeps cancer cells in resting phase/alter the endocrine environment to make it less conducive for growth of the
cancer cells)
Related drugs: nolvadex, cytadren, lupron.
You might also like
- Hemodialysis Patient's Endorsement FormDocument1 pageHemodialysis Patient's Endorsement FormHacienda Galea Resort and Events Place100% (1)
- Chicken Pox InfographicsDocument1 pageChicken Pox InfographicsBIANCA PILNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyKim GalamgamNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Module On Anti NeoplasticDocument7 pagesModule On Anti NeoplasticJojo JustoNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy For CancerDocument51 pagesChemotherapy For CancerHarshika KDGNo ratings yet
- Altretamine: Drug DosageDocument16 pagesAltretamine: Drug DosagePrincess CruzNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument11 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosusneu_gluhenNo ratings yet
- Antimetabolities: Route Onset Peak DurationDocument12 pagesAntimetabolities: Route Onset Peak DurationRichlle CortesNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 (Lecture)Document10 pagesNCM 106 (Lecture)e항해100% (3)
- Antineoplastic DrugsDocument38 pagesAntineoplastic DrugsTrixia CamporedondoNo ratings yet
- Name Mode of Action Indication Contraindicat ION Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: CV: Cardiotoxicity DermatologicDocument4 pagesName Mode of Action Indication Contraindicat ION Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: CV: Cardiotoxicity DermatologicAlexis Abigail de LeonNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy DrugsDocument43 pagesChemotherapy Drugsbrigette_lagat100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- NCP Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNCP Drug StudyArthadian De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- AntiNeoplastic AgentsDocument33 pagesAntiNeoplastic Agentsmers puno100% (1)
- Nutrition in Surgical PatientDocument26 pagesNutrition in Surgical Patient180045No ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationDocument6 pagesCellular AberrationCheysser FerolinoNo ratings yet
- Glomerulnephrities, Nephrotic SyndromDocument28 pagesGlomerulnephrities, Nephrotic SyndromJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Nausea Vomiting ReportDocument67 pagesNausea Vomiting Reportstephanie gayetaNo ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationsDocument37 pagesCellular AberrationsJess NinaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Regulation Student VersionDocument15 pagesCellular Regulation Student VersionCruz YrNo ratings yet
- Mitotic InhibitorsDocument17 pagesMitotic InhibitorsSamuel CamoronganNo ratings yet
- PrimDocument2 pagesPrimapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyJessie Cauilan CainNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Mesalamine MercaptopurineDocument15 pagesDrug Study On Mesalamine Mercaptopurineسوما الشمريNo ratings yet
- A 27Document10 pagesA 27NestleNo ratings yet
- Careplan 2Document11 pagesCareplan 2JulieRn2beNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressant DrugsDocument28 pagesImmunosuppressant DrugsimnasNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis-Medicine-PancreatitisDocument39 pagesCase Analysis-Medicine-PancreatitisAleks MendozaNo ratings yet
- DactinomycinDocument4 pagesDactinomycinKeith MadarangNo ratings yet
- A. Antineoplastic DrugsDocument48 pagesA. Antineoplastic DrugsKim Shyen BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Case 034: ConstipationDocument7 pagesCase 034: ConstipationZauza100% (1)
- Leukemias: by DR/ KhadigaDocument28 pagesLeukemias: by DR/ KhadigaDody ZainNo ratings yet
- Drugs Mechanism of Action Side Effect/Adverse Effect/Contraindication Nursing InterventionsDocument17 pagesDrugs Mechanism of Action Side Effect/Adverse Effect/Contraindication Nursing InterventionsJerome Vergel RubianesNo ratings yet
- Acute Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument37 pagesAcute Chronic GlomerulonephritisMadeline Jessica HuwaeNo ratings yet
- Hepatic FailureDocument37 pagesHepatic FailureWinston Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Dub, Dys, MenoDocument64 pagesDub, Dys, MenoRebecca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology: Anti-Neoplastic Chemotherapeutic DrugsDocument42 pagesNursing Pharmacology: Anti-Neoplastic Chemotherapeutic DrugswokorowNo ratings yet
- Is The Most Common Extracranial Solid Tumor of InfancyDocument7 pagesIs The Most Common Extracranial Solid Tumor of InfancyEdamarie ChuaNo ratings yet
- AmoxicillinDocument5 pagesAmoxicillinKyle DelrosarioNo ratings yet
- Ulecerative ColitisDocument14 pagesUlecerative ColitisnizaNo ratings yet
- Fluorouracil Drug StudyDocument8 pagesFluorouracil Drug StudyAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis Case PresDocument77 pagesLiver Cirrhosis Case Presmarlx580% (5)
- FLUOROURACIL Drug StudyDocument8 pagesFLUOROURACIL Drug StudyAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Dr. J.A. Dogbe: Cosultant Paediatrician/Public Health Specialist Sms-Knust/KathDocument53 pagesDr. J.A. Dogbe: Cosultant Paediatrician/Public Health Specialist Sms-Knust/KathAnastasiafynnNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Journal Club Presentation: Presented byDocument54 pagesWelcome To Journal Club Presentation: Presented byneptorNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- LithiumDocument4 pagesLithiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Induced Liver Diseases (DILD) : M. DeepalakshmiDocument22 pagesDrug Induced Liver Diseases (DILD) : M. DeepalakshmicrissNo ratings yet
- Case Study OF Hypokalemia Periodic ParalysisDocument34 pagesCase Study OF Hypokalemia Periodic ParalysisVivian Montesena BreganzaNo ratings yet
- By DR.: Haitham Mokhtar Mohamed Abd AllahDocument101 pagesBy DR.: Haitham Mokhtar Mohamed Abd AllahMohamed ElkadyNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument8 pagesLiver CirrhosisgoyaNo ratings yet
- Definition and Etiology: PancreatitisDocument24 pagesDefinition and Etiology: PancreatitisAliyah Tofani PawelloiNo ratings yet
- UlcerativecolitisDocument27 pagesUlcerativecolitisMohamed Abdulrazaq100% (1)
- Medroxyprogesterone AcetateDocument3 pagesMedroxyprogesterone Acetateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Complete Drug StudyDocument239 pagesComplete Drug StudyRPh Krishna Chandra Jagrit0% (1)
- Anti-NenoplasticsDocument1 pageAnti-NenoplasticsBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudySandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Document6 pagesConcept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Ran PioloNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument11 pagesAcute Pancreatitispeter_soósNo ratings yet
- Semis 2 - Drugs Acting On The Endocrine System 2Document11 pagesSemis 2 - Drugs Acting On The Endocrine System 2Amiel Francisco Reyes100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document11 pagesChapter 1Amiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ni For LMSDocument10 pagesNi For LMSAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- TutorialsDocument3 pagesTutorialsAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ni For LMS Chapter 2Document11 pagesNi For LMS Chapter 2Amiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Adv of Distance LearningDocument1 pageAdv of Distance LearningAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Activity and ExerciseDocument45 pagesActivity and ExerciseAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- In Service Exam For Breast DR Paul BalisiDocument11 pagesIn Service Exam For Breast DR Paul BalisiAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Temperature RegulationDocument48 pagesTemperature RegulationAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Health StratDocument11 pagesHealth StratAmiel Francisco Reyes100% (1)
- Health Education Prelims TopicsDocument36 pagesHealth Education Prelims TopicsAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ni Semifinals Topics 2 COVID 19Document11 pagesNi Semifinals Topics 2 COVID 19Amiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Internal Examination: Course Audit FHC Mid 2Document4 pagesInternal Examination: Course Audit FHC Mid 2Amiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Finals Core Competencies Under The Eleven Key of Responsibility of NursingDocument8 pagesFinals Core Competencies Under The Eleven Key of Responsibility of NursingAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Table of The Cognitive Domain (Original)Document8 pagesTable of The Cognitive Domain (Original)Amiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chaptre 17 - Substance AbuseDocument40 pagesChaptre 17 - Substance AbuseAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Funda SyllabusDocument10 pagesFunda SyllabusAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Saturday, November 24, 2018: SubscribeDocument24 pagesSaturday, November 24, 2018: SubscribeAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development: Anthony P. Olalia JRDocument31 pagesGrowth and Development: Anthony P. Olalia JRAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Literature Matrix HappinessDocument1 pageLiterature Matrix HappinessAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Poor Blood Travels Through The INFRIOR or SUPERIOR VENA CAVADocument2 pagesOxygen Poor Blood Travels Through The INFRIOR or SUPERIOR VENA CAVAAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- NP1 Family Nursing 3Document2 pagesNP1 Family Nursing 3Jonas Marvin AnaqueNo ratings yet
- 2024-06-24 Politics, Private Interests, and The Biden Administration's Deviation From Agency Regulations in The COVID-19 Pandemic (With Appendix)Document623 pages2024-06-24 Politics, Private Interests, and The Biden Administration's Deviation From Agency Regulations in The COVID-19 Pandemic (With Appendix)The FederalistNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Infulenza Flue 1Document6 pagesChapter 7 - Infulenza Flue 1Jonathan SaydeNo ratings yet
- Shu ACT 2Document4 pagesShu ACT 2John Daniel CapituloNo ratings yet
- OSCE ReviewDocument45 pagesOSCE ReviewKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Jurnal MataDocument7 pagesJurnal MatatrianaamaliaNo ratings yet
- 16.nephrotic SyndromeDocument115 pages16.nephrotic SyndromeRhomizal MazaliNo ratings yet
- L4 - Assessment of Nasal ObstructionDocument17 pagesL4 - Assessment of Nasal ObstructionAmirul HamudinNo ratings yet
- A Case Study in Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever - MicrobiologyDocument1 pageA Case Study in Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever - MicrobiologyAnna PriskaNo ratings yet
- NCP OrthoDocument6 pagesNCP OrthoRuth Anne Arriesgado NañozNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Engineerng: Ehsan TahamiDocument30 pagesBiomedical Engineerng: Ehsan TahamiAmin Derakhshan100% (1)
- Minimally Invasive Vertical Preparation Design For Ceramic VeneersDocument12 pagesMinimally Invasive Vertical Preparation Design For Ceramic VeneersdanielaNo ratings yet
- Tinjauan Keakuratan Data Pada Sensus Harian Rawat Inap Di Rumah Sakit Khusus Bedah Banjarmasin SiagaDocument5 pagesTinjauan Keakuratan Data Pada Sensus Harian Rawat Inap Di Rumah Sakit Khusus Bedah Banjarmasin SiagaSaiful RizalNo ratings yet
- Manual of Obstetrics and GynecologyDocument183 pagesManual of Obstetrics and GynecologyMiraf MesfinNo ratings yet
- The New Parkland Hospital CampusDocument1 pageThe New Parkland Hospital CampusThe Dallas Morning NewsNo ratings yet
- NCM108 Module 1-CDocument9 pagesNCM108 Module 1-Cmirai desuNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Keperawatan Muhammadiyah: Suhenny Zainuddin, Ariyanti Saleh, Kusrini KadarDocument6 pagesJurnal Keperawatan Muhammadiyah: Suhenny Zainuddin, Ariyanti Saleh, Kusrini KadarristaNo ratings yet
- Modified Halterman Appliance-A Key To Alter Bilateral Ectopic Eruption of Maxillary Permanent First MolarsDocument5 pagesModified Halterman Appliance-A Key To Alter Bilateral Ectopic Eruption of Maxillary Permanent First MolarsLjubomirErdoglijaNo ratings yet
- Home Program and Councelling For CaregiversDocument6 pagesHome Program and Councelling For CaregiversAkhila SudheerbabuNo ratings yet
- Varicose VeinsDocument13 pagesVaricose VeinsTomus ClaudiuNo ratings yet
- Learning Needs and Quality Care Among Family Caregivers and Elderly Patients of Guadalupe, Cebu City, Central PhilippinesDocument22 pagesLearning Needs and Quality Care Among Family Caregivers and Elderly Patients of Guadalupe, Cebu City, Central PhilippinesLianne VergaraNo ratings yet
- TB PolicyDocument174 pagesTB PolicyDrashua AshuaNo ratings yet
- Ape CopdDocument6 pagesApe Copdnina purnamasariNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic SetupDocument3 pagesDiagnostic SetupPatricia DasoveanuNo ratings yet
- Pleasure 1951Document4 pagesPleasure 1951Andres Espinosa de los MonterosNo ratings yet
- Staff Nurse - PrintDocument8 pagesStaff Nurse - PrintMark Joseph Felicitas CuntapayNo ratings yet
- CS FORM 41 Medical Certificate 2Document1 pageCS FORM 41 Medical Certificate 2Leonor BagnosNo ratings yet