Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Binary Liquid Systems Handout
Binary Liquid Systems Handout
Uploaded by
alyssa_marie_keCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Chbe 346 Lecture 23 ReviewDocument72 pagesChbe 346 Lecture 23 ReviewJamie SamuelNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Fluids Lecture 8Document39 pagesReservoir Fluids Lecture 8ChanseNo ratings yet
- 01 Lecture Human OrganismDocument26 pages01 Lecture Human Organismalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Lab CHM 261Document5 pagesLab CHM 261Mustafidzul Mustapha56% (9)
- Phase Equilibria Two-Component System: I. Liquid-Liquid System Ideal SolutionDocument16 pagesPhase Equilibria Two-Component System: I. Liquid-Liquid System Ideal SolutionChelsea MartinezNo ratings yet
- 20 Sistem 2 KomponenDocument5 pages20 Sistem 2 KomponenSiti Halimatus Sa'diahNo ratings yet
- 7 1. Vapor Liquid EquilibriumDocument9 pages7 1. Vapor Liquid Equilibriumwaseemkhan49No ratings yet
- Distillation SDFVBDocument57 pagesDistillation SDFVBbishuNo ratings yet
- Goal 1: Design A Flash DrumDocument16 pagesGoal 1: Design A Flash DrumGago_88No ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To VleDocument53 pages1 - Introduction To VleEko Putra BayuNo ratings yet
- Vapor Pressure: Pº Pressure of A Substance in Equilibrium With Its Pure Condensed (Liquid or Solid) PhaseDocument32 pagesVapor Pressure: Pº Pressure of A Substance in Equilibrium With Its Pure Condensed (Liquid or Solid) Phaseashoku2No ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Physical TransformationsDocument40 pagesChapter 04 Physical TransformationsRuby DalyNo ratings yet
- Vle For DummiesDocument8 pagesVle For Dummiesira_rancicNo ratings yet
- Physical ChemistryDocument13 pagesPhysical ChemistryAdamJoElaticoNo ratings yet
- ChE 421 Lec 1Document34 pagesChE 421 Lec 1alyssaNo ratings yet
- 9-Chapter 8-Chemical Reaction Equilibria-27March Online Class-STDNDocument15 pages9-Chapter 8-Chemical Reaction Equilibria-27March Online Class-STDNMahamed HusseinNo ratings yet
- Reactor Design - CREDocument22 pagesReactor Design - CREAliRashidNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium in Solution: TPC TPRTC TPRT A TPDocument6 pagesEquilibrium in Solution: TPC TPRTC TPRT A TPsgybleeNo ratings yet
- APC - Chapter 5 - Part 1 SP22Document20 pagesAPC - Chapter 5 - Part 1 SP22iB13eNo ratings yet
- DistillatnDocument149 pagesDistillatnVinayak ThalangeNo ratings yet
- Distillation - Dr.K.Suresh - NotesDocument63 pagesDistillation - Dr.K.Suresh - NotesRoyalNo ratings yet
- 5 60 Lecture23Document4 pages5 60 Lecture23sgybleeNo ratings yet
- Bubble Point of Liqued PropaneDocument128 pagesBubble Point of Liqued PropaneKhalil RehmanNo ratings yet
- CMT 405 - Distillation PDFDocument72 pagesCMT 405 - Distillation PDFMuhammad Azri Haziq100% (1)
- Pure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: LiquidsDocument8 pagesPure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: Liquidsahad_shiraziNo ratings yet
- October 1, 2001 Reading: Chapter VI Homework: 6.1,6.3,6.5,6.7,6.9,6.10 The Change in Enthalpy For A Chemical Reaction at Constant P and TDocument4 pagesOctober 1, 2001 Reading: Chapter VI Homework: 6.1,6.3,6.5,6.7,6.9,6.10 The Change in Enthalpy For A Chemical Reaction at Constant P and TclaudioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Volumetric Properties of Pure Fluids PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Volumetric Properties of Pure Fluids PDFNikko ManaleseNo ratings yet
- Thermo Test 1 SolutionDocument5 pagesThermo Test 1 SolutionBernie TanNo ratings yet
- 01 Lecture Note - Binary Flash DistillationDocument21 pages01 Lecture Note - Binary Flash DistillationtimNo ratings yet
- Phase DiagramsDocument19 pagesPhase Diagramsget2cs100% (1)
- Eso201A: Thermodynamics 2020-21 Ist Semester IIT Kanpur Instructor: P.A.ApteDocument19 pagesEso201A: Thermodynamics 2020-21 Ist Semester IIT Kanpur Instructor: P.A.ApteJitesh HemjiNo ratings yet
- Isothermal ReactorDocument10 pagesIsothermal Reactorsmith muñozNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance For Nonreactive Processes-P1Document12 pagesEnergy Balance For Nonreactive Processes-P1Aby JatNo ratings yet
- Lec. 3 DR, MarwaDocument25 pagesLec. 3 DR, MarwaFathi ShokryNo ratings yet
- L13 Equilibrium ConversionDocument21 pagesL13 Equilibrium ConversionLukas EstivaresNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document40 pagesCH 02정민교No ratings yet
- ChE422 Topic 8Document40 pagesChE422 Topic 8Elle EmmNo ratings yet
- CH 15 - Chemical Equilibrium Compatibility ModeDocument16 pagesCH 15 - Chemical Equilibrium Compatibility ModeIcha Meisyarani IINo ratings yet
- The Effect of Applied Pressure On Vapor Pressure:) (M, Equilibriu atDocument20 pagesThe Effect of Applied Pressure On Vapor Pressure:) (M, Equilibriu atVeliyana Londong AlloNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Ideal Gases and Ideal Gas LawDocument12 pagesModule 3 Ideal Gases and Ideal Gas LawHazel AdoNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY (CY11003) : Autumn 2021 - 2022Document15 pagesCHEMISTRY (CY11003) : Autumn 2021 - 2022Ashish RanjanNo ratings yet
- Termodinamica ch03Document35 pagesTermodinamica ch03Rebeca AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- 1basics of Process Calculations by Dr. Chetan M. PatelDocument10 pages1basics of Process Calculations by Dr. Chetan M. PatelYash JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Properties of Pure FluidsDocument38 pagesVolumetric Properties of Pure Fluidsrezarizqi09No ratings yet
- Properties of GasesDocument11 pagesProperties of GasessalasineNo ratings yet
- Two Component Phase Equilibria IDocument6 pagesTwo Component Phase Equilibria IRojo JohnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2. Ch1-Phase EquilibriaDocument26 pagesLesson 2. Ch1-Phase EquilibriaDuy Anh ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Steady State Nonisothermal Reactor DesignDocument47 pagesSteady State Nonisothermal Reactor DesignMohamad IezanyNo ratings yet
- Atkins' Physical Chemistry: Peter Atkins - Julio de PaulaDocument37 pagesAtkins' Physical Chemistry: Peter Atkins - Julio de PaulaAmalia AnggreiniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Reactor Design Che 3K4: Kevin Dunn, 2013Document17 pagesIntroduction To Reactor Design Che 3K4: Kevin Dunn, 2013Khalil LasferNo ratings yet
- Fe Chemical EngineeringDocument5 pagesFe Chemical EngineeringJudith LugoNo ratings yet
- Properties of Pure SubstancesDocument19 pagesProperties of Pure SubstancesaathithyayanNo ratings yet
- 2E + H2 (G, 1 Bar) + 2agcl (S) 2H+ (1M) +2Cl - (1M) +2ag (S) + 2E (.2223 V) Rxn3: O2 (G) + 2H+ (Aq) +2cytc (Fe2+) 2cytc (Fe3+) + H2ODocument2 pages2E + H2 (G, 1 Bar) + 2agcl (S) 2H+ (1M) +2Cl - (1M) +2ag (S) + 2E (.2223 V) Rxn3: O2 (G) + 2H+ (Aq) +2cytc (Fe2+) 2cytc (Fe3+) + H2OSam ClarotNo ratings yet
- L16 Unsteady State and Reaction EngrDocument25 pagesL16 Unsteady State and Reaction EngrFitrya ChiequzaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering 301 Lecture Notes: (Revised 9/04)Document9 pagesChemical Engineering 301 Lecture Notes: (Revised 9/04)shiv kr dubeyNo ratings yet
- Bubble Point Dan Dew PointDocument20 pagesBubble Point Dan Dew Pointastri0% (1)
- 2024 Recapitulation Part 2 Chapter 12-13Document26 pages2024 Recapitulation Part 2 Chapter 12-13httam12022005No ratings yet
- October 2, 2001 Reading: Chapter VI Homework: 6.1, 6.3, 6.5, 6.7, 6.9, 6.10 The Changes in Gibbs Free EnergyDocument4 pagesOctober 2, 2001 Reading: Chapter VI Homework: 6.1, 6.3, 6.5, 6.7, 6.9, 6.10 The Changes in Gibbs Free EnergyclaudioNo ratings yet
- Uses of Maxwell RelationsDocument17 pagesUses of Maxwell RelationsArun EbenezerNo ratings yet
- Ceic3001 NotesDocument3 pagesCeic3001 NotesZooy2012No ratings yet
- 1 (1) - Overview of Moral Situations and Contemporary Moral TrendsDocument52 pages1 (1) - Overview of Moral Situations and Contemporary Moral TrendsIvy TanNo ratings yet
- Human BiochemistryDocument167 pagesHuman Biochemistryalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- 3 Component Systems HandoutDocument9 pages3 Component Systems Handoutalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates 2: OligosaccharidesDocument71 pagesCarbohydrates 2: Oligosaccharidesalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology: 2 Semester 2013 - 2014Document16 pagesPharmaceutical Microbiology: 2 Semester 2013 - 2014alyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Microscopy: The InstrumentsDocument5 pagesMicroscopy: The Instrumentsalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: William H. Brown & Christopher S. FooteDocument67 pagesOrganic Chemistry: William H. Brown & Christopher S. Footealyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Apa DocumentationDocument51 pagesApa Documentationalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Nervous System LectureDocument234 pagesNervous System Lecturealyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The HeartDocument34 pagesPhysiology of The Heartalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document1 pageQuiz 1alyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesThe Human Respiratory Systemalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Talasanggunian: Health Disparities Research & Practice, 3 (3), 57-67Document1 pageTalasanggunian: Health Disparities Research & Practice, 3 (3), 57-67alyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Exercise 11 The Appendicular SkeletonDocument23 pagesExercise 11 The Appendicular Skeletonalyssa_marie_ke100% (1)
- Absorption and StrippingDocument52 pagesAbsorption and StrippingTomasz KobaNo ratings yet
- Gilson TRILUTION LC SoftwareDocument828 pagesGilson TRILUTION LC SoftwareIvanNo ratings yet
- IOHEXOLDocument5 pagesIOHEXOLArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Answer - Unit 3 PDFDocument11 pagesAnswer - Unit 3 PDFVicky AnggaraNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases 0620Document4 pagesAcids and Bases 0620Gono TakaduuNo ratings yet
- Henry's Law - WikipediaDocument14 pagesHenry's Law - WikipediaZakria Shah100% (1)
- Silica Gel: A Keystone in Chromatographic Techniques: IJPSR (2019), Volume 10, Issue 1 (Review Article)Document11 pagesSilica Gel: A Keystone in Chromatographic Techniques: IJPSR (2019), Volume 10, Issue 1 (Review Article)VinayNo ratings yet
- Potentiometric Determination of Captopril in Pharmaceutical FormulationsDocument6 pagesPotentiometric Determination of Captopril in Pharmaceutical FormulationsNurAfifahNo ratings yet
- Lss Exam 2023Document2 pagesLss Exam 2023Alibert NchoNo ratings yet
- Flow Injection AnalysisDocument17 pagesFlow Injection AnalysisUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- GC Lab ManualDocument5 pagesGC Lab ManualJC100% (1)
- Laporan Resmi Praktikum Dasar-Dasar Kimia Analitik Titrasi ArgentometriDocument33 pagesLaporan Resmi Praktikum Dasar-Dasar Kimia Analitik Titrasi Argentometrimawar khasaniyahNo ratings yet
- Ostwald's Theory of Acid and Base IndicatorsDocument12 pagesOstwald's Theory of Acid and Base IndicatorsPushkar WaneNo ratings yet
- ELISA HandbookDocument31 pagesELISA HandbookShahil AlamNo ratings yet
- Chemical EqiulibriumDocument41 pagesChemical EqiulibriumZunaira Noreen100% (1)
- Physical Chemistry 2Document30 pagesPhysical Chemistry 2Michelle MenciasNo ratings yet
- Course InformationDocument3 pagesCourse Informationariff udinNo ratings yet
- PH Indicator - ExperimentDocument2 pagesPH Indicator - ExperimentHana BabićNo ratings yet
- To Determine Equilibrium Constant: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesTo Determine Equilibrium Constant: ObjectiveTim JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Determination Of Water-Soluble Vitamins B, B, B, B, B, B Andconc Column With Particle Size 3 Μm In Some Manufactured Food Products By Hplc With Uv-Dad/Fld DetectionDocument6 pagesDetermination Of Water-Soluble Vitamins B, B, B, B, B, B Andconc Column With Particle Size 3 Μm In Some Manufactured Food Products By Hplc With Uv-Dad/Fld DetectionHITESH CHOPRANo ratings yet
- Buffer Lab ReportDocument3 pagesBuffer Lab Reportbobby indaeyoNo ratings yet
- 2009GA Stevia-rebaudianaPosterDocument1 page2009GA Stevia-rebaudianaPostermagdamayalagNo ratings yet
- IJPS - Volume 9 - Issue 2 - Pages 23-29Document8 pagesIJPS - Volume 9 - Issue 2 - Pages 23-29Alvin Wahyu Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- RP-HPLC Method For The Simultaneous Estimation of Benazepril andDocument21 pagesRP-HPLC Method For The Simultaneous Estimation of Benazepril andPrtap Kumar PatraNo ratings yet
- Multiple Stagesddd LLEDocument6 pagesMultiple Stagesddd LLEFikrie MuhdNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument10 pagesExamEllen MarksNo ratings yet
- BS-Chemistry 7 Semester-Org (Morning) : SubjectDocument5 pagesBS-Chemistry 7 Semester-Org (Morning) : SubjectMuhammad Asad FaroquiNo ratings yet
- Determination Paraben in ShampooDocument5 pagesDetermination Paraben in ShampooromaincharlesNo ratings yet
- Rose Anthocyanins As Acid Base IndicatorsDocument16 pagesRose Anthocyanins As Acid Base IndicatorsLoo Huan HaoNo ratings yet
Binary Liquid Systems Handout
Binary Liquid Systems Handout
Uploaded by
alyssa_marie_keOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Binary Liquid Systems Handout
Binary Liquid Systems Handout
Uploaded by
alyssa_marie_keCopyright:
Available Formats
11/29/2011
Phase Diagrams
of
Binary Liquid Systems
A. Completely miscible binary liquids
When C = 2,
Intensive Variables: P, T, C1/C2
If T or P = k
F=3P
If T = k, P vs. C
If P = k, T vs. C
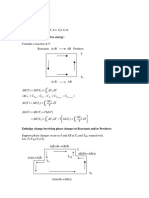
Raoults Law
For each volatile component of an ideal mixture of
liquids at constant T
T=k
Pi = i Pi
PA = A PA
PB
P = (1B) PA + B PB
and
P B = B P B
Since, Ptot = Pi
PB = B PB
P = PA + PB
=A PA + B PB
PA
PA = A PA
= (1B) PA + B PB
= (1 A)PA
B or YB
11/29/2011
For the vapor in equilibrium with the liquid
Pi = Yi Ptotal
T=k
PA = YA Ptotal
PB
and
PB = YB Ptotal
For the vapor above
the solution
V
L+V
B PB
YB =
(1B) PA + BPB
PA
B or YB
Ideal Solutions
1. IFA are completely balanced, A - - A = A - - B = B - - B
T=k
PB
L
P
L+V
PA
s
B or YB
v
B
11/29/2011
Nonideal Solutions
1. A - - A A - - B B - - B
closest to ideal behavior
intermediate values of Psoln
Intermediate values of Tsoln
T=k
PB
L
L+V
P
V
PA
B or YB
11/29/2011
Temperature Composition Diagram
P=k
TA
V
T
L+V
L
TB
B or YB
Fractional distillation
P=k
TA
V
T
L+V
L
TB
d1
B or YB
d2
11/29/2011
IFA are unbalanced
1. A - - A > A - - B < B - - B
Exhibits maximum vapor pressure
Exhibits minimum boiling point
Vapor Pressure Diagram
T=k
Pmax
L
L
L+V
L+V
PB
PA
E: Azeotrope
B or YB
11/29/2011
Poling Point Diagram
P=k
TA
V
L
L+V
TB
V
L+V L
Tmin
B or YB
2. A - - A < A - - B > B - - B
Exhibits minimum vapor pressure
Exhibits maximum boiling point
11/29/2011
Vapor Pressure Diagram
T=k
PA
L
V
L+V
PB
L
L+V V
Pmin
B or YB
Boiling PointDiagram
P=k
Tmax
V
V
L+V
L+V
TB
TA
B or YB
11/29/2011
Partially miscible liquid pairs
Unbalanced strength of IFA at certain concentration
range
A in B
A(l)
B(l)
B in A
Since only the liquid phase is involved, P = k
F=CP+1
=2P+1
=3P
1. Miscibility is enhanced by increase in T
A--A>A--B<B--B
p=k
P=1
F=31=2
(T, %A / %B)
cstmax
T2
P=2
F=1
(T / %A / %B)
Temp
T1
ccst
y y
composition, wt %
11/29/2011
Material Balance
Consider a mixture of
composition m kept at T1
p=k
x = comp. of Arich layer
y = comp. of Brich layer
Tf
wt of Arich layer
T2
wt of Brich layer
ym
mx
If mixture m is heated to T2
x = comp. of Arich layer
T1
y = comp. of Arich layer
wt of Arich layer
y y
wt of Brich layer
y m
m x
Tf = temp of complete
miscibility
composition, wt %
If while T1 is kept constant,
B is added to m until the
composition of the mixture
is m
p=k
x = comp. of Arich layer
y = comp. of Brich layer
wt of Arich layer
wt of Brich layer
y m
=
m x
T1
composition, wt %
11/29/2011
2. Miscibility is enhanced by decrease in T
A--A<A--B>B--B
p=k
T2
P=2
Temp
T1
cstmin
P=1
A
ccst
y y
composition, wt %
3. Miscibility is enhanced by increase or decrease in T
A- -AA- - B B - - B
p=k
cstmax
P=1
T2
P=2
Temp
T1
cstmin
A
Ccst
Ccst,
y y
composition, wt %
10
11/29/2011
Completely immiscible liquid pairs
For a pair of immiscible
liquids at constant T
Ptotal = PA + PB
At the boiling pt. of the mixt.
Patm
PA = vapor pressure of A
PB = vapor pressure of B
A+B
YA =
PA
nA
Ptot
nvap
PA
YA /YB
A
PB
nA / nB
wA / MA
wB / MB
T
Tb
PA / Ptot
PB / Ptot
nA/nvap
nB/nvap
= PA / PB
= PA / PB
wA / wB = MAPA / MBPB
11
You might also like
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Chbe 346 Lecture 23 ReviewDocument72 pagesChbe 346 Lecture 23 ReviewJamie SamuelNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Fluids Lecture 8Document39 pagesReservoir Fluids Lecture 8ChanseNo ratings yet
- 01 Lecture Human OrganismDocument26 pages01 Lecture Human Organismalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Lab CHM 261Document5 pagesLab CHM 261Mustafidzul Mustapha56% (9)
- Phase Equilibria Two-Component System: I. Liquid-Liquid System Ideal SolutionDocument16 pagesPhase Equilibria Two-Component System: I. Liquid-Liquid System Ideal SolutionChelsea MartinezNo ratings yet
- 20 Sistem 2 KomponenDocument5 pages20 Sistem 2 KomponenSiti Halimatus Sa'diahNo ratings yet
- 7 1. Vapor Liquid EquilibriumDocument9 pages7 1. Vapor Liquid Equilibriumwaseemkhan49No ratings yet
- Distillation SDFVBDocument57 pagesDistillation SDFVBbishuNo ratings yet
- Goal 1: Design A Flash DrumDocument16 pagesGoal 1: Design A Flash DrumGago_88No ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To VleDocument53 pages1 - Introduction To VleEko Putra BayuNo ratings yet
- Vapor Pressure: Pº Pressure of A Substance in Equilibrium With Its Pure Condensed (Liquid or Solid) PhaseDocument32 pagesVapor Pressure: Pº Pressure of A Substance in Equilibrium With Its Pure Condensed (Liquid or Solid) Phaseashoku2No ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Physical TransformationsDocument40 pagesChapter 04 Physical TransformationsRuby DalyNo ratings yet
- Vle For DummiesDocument8 pagesVle For Dummiesira_rancicNo ratings yet
- Physical ChemistryDocument13 pagesPhysical ChemistryAdamJoElaticoNo ratings yet
- ChE 421 Lec 1Document34 pagesChE 421 Lec 1alyssaNo ratings yet
- 9-Chapter 8-Chemical Reaction Equilibria-27March Online Class-STDNDocument15 pages9-Chapter 8-Chemical Reaction Equilibria-27March Online Class-STDNMahamed HusseinNo ratings yet
- Reactor Design - CREDocument22 pagesReactor Design - CREAliRashidNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium in Solution: TPC TPRTC TPRT A TPDocument6 pagesEquilibrium in Solution: TPC TPRTC TPRT A TPsgybleeNo ratings yet
- APC - Chapter 5 - Part 1 SP22Document20 pagesAPC - Chapter 5 - Part 1 SP22iB13eNo ratings yet
- DistillatnDocument149 pagesDistillatnVinayak ThalangeNo ratings yet
- Distillation - Dr.K.Suresh - NotesDocument63 pagesDistillation - Dr.K.Suresh - NotesRoyalNo ratings yet
- 5 60 Lecture23Document4 pages5 60 Lecture23sgybleeNo ratings yet
- Bubble Point of Liqued PropaneDocument128 pagesBubble Point of Liqued PropaneKhalil RehmanNo ratings yet
- CMT 405 - Distillation PDFDocument72 pagesCMT 405 - Distillation PDFMuhammad Azri Haziq100% (1)
- Pure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: LiquidsDocument8 pagesPure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: Liquidsahad_shiraziNo ratings yet
- October 1, 2001 Reading: Chapter VI Homework: 6.1,6.3,6.5,6.7,6.9,6.10 The Change in Enthalpy For A Chemical Reaction at Constant P and TDocument4 pagesOctober 1, 2001 Reading: Chapter VI Homework: 6.1,6.3,6.5,6.7,6.9,6.10 The Change in Enthalpy For A Chemical Reaction at Constant P and TclaudioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Volumetric Properties of Pure Fluids PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Volumetric Properties of Pure Fluids PDFNikko ManaleseNo ratings yet
- Thermo Test 1 SolutionDocument5 pagesThermo Test 1 SolutionBernie TanNo ratings yet
- 01 Lecture Note - Binary Flash DistillationDocument21 pages01 Lecture Note - Binary Flash DistillationtimNo ratings yet
- Phase DiagramsDocument19 pagesPhase Diagramsget2cs100% (1)
- Eso201A: Thermodynamics 2020-21 Ist Semester IIT Kanpur Instructor: P.A.ApteDocument19 pagesEso201A: Thermodynamics 2020-21 Ist Semester IIT Kanpur Instructor: P.A.ApteJitesh HemjiNo ratings yet
- Isothermal ReactorDocument10 pagesIsothermal Reactorsmith muñozNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance For Nonreactive Processes-P1Document12 pagesEnergy Balance For Nonreactive Processes-P1Aby JatNo ratings yet
- Lec. 3 DR, MarwaDocument25 pagesLec. 3 DR, MarwaFathi ShokryNo ratings yet
- L13 Equilibrium ConversionDocument21 pagesL13 Equilibrium ConversionLukas EstivaresNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document40 pagesCH 02정민교No ratings yet
- ChE422 Topic 8Document40 pagesChE422 Topic 8Elle EmmNo ratings yet
- CH 15 - Chemical Equilibrium Compatibility ModeDocument16 pagesCH 15 - Chemical Equilibrium Compatibility ModeIcha Meisyarani IINo ratings yet
- The Effect of Applied Pressure On Vapor Pressure:) (M, Equilibriu atDocument20 pagesThe Effect of Applied Pressure On Vapor Pressure:) (M, Equilibriu atVeliyana Londong AlloNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Ideal Gases and Ideal Gas LawDocument12 pagesModule 3 Ideal Gases and Ideal Gas LawHazel AdoNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY (CY11003) : Autumn 2021 - 2022Document15 pagesCHEMISTRY (CY11003) : Autumn 2021 - 2022Ashish RanjanNo ratings yet
- Termodinamica ch03Document35 pagesTermodinamica ch03Rebeca AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- 1basics of Process Calculations by Dr. Chetan M. PatelDocument10 pages1basics of Process Calculations by Dr. Chetan M. PatelYash JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Properties of Pure FluidsDocument38 pagesVolumetric Properties of Pure Fluidsrezarizqi09No ratings yet
- Properties of GasesDocument11 pagesProperties of GasessalasineNo ratings yet
- Two Component Phase Equilibria IDocument6 pagesTwo Component Phase Equilibria IRojo JohnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2. Ch1-Phase EquilibriaDocument26 pagesLesson 2. Ch1-Phase EquilibriaDuy Anh ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Steady State Nonisothermal Reactor DesignDocument47 pagesSteady State Nonisothermal Reactor DesignMohamad IezanyNo ratings yet
- Atkins' Physical Chemistry: Peter Atkins - Julio de PaulaDocument37 pagesAtkins' Physical Chemistry: Peter Atkins - Julio de PaulaAmalia AnggreiniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Reactor Design Che 3K4: Kevin Dunn, 2013Document17 pagesIntroduction To Reactor Design Che 3K4: Kevin Dunn, 2013Khalil LasferNo ratings yet
- Fe Chemical EngineeringDocument5 pagesFe Chemical EngineeringJudith LugoNo ratings yet
- Properties of Pure SubstancesDocument19 pagesProperties of Pure SubstancesaathithyayanNo ratings yet
- 2E + H2 (G, 1 Bar) + 2agcl (S) 2H+ (1M) +2Cl - (1M) +2ag (S) + 2E (.2223 V) Rxn3: O2 (G) + 2H+ (Aq) +2cytc (Fe2+) 2cytc (Fe3+) + H2ODocument2 pages2E + H2 (G, 1 Bar) + 2agcl (S) 2H+ (1M) +2Cl - (1M) +2ag (S) + 2E (.2223 V) Rxn3: O2 (G) + 2H+ (Aq) +2cytc (Fe2+) 2cytc (Fe3+) + H2OSam ClarotNo ratings yet
- L16 Unsteady State and Reaction EngrDocument25 pagesL16 Unsteady State and Reaction EngrFitrya ChiequzaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering 301 Lecture Notes: (Revised 9/04)Document9 pagesChemical Engineering 301 Lecture Notes: (Revised 9/04)shiv kr dubeyNo ratings yet
- Bubble Point Dan Dew PointDocument20 pagesBubble Point Dan Dew Pointastri0% (1)
- 2024 Recapitulation Part 2 Chapter 12-13Document26 pages2024 Recapitulation Part 2 Chapter 12-13httam12022005No ratings yet
- October 2, 2001 Reading: Chapter VI Homework: 6.1, 6.3, 6.5, 6.7, 6.9, 6.10 The Changes in Gibbs Free EnergyDocument4 pagesOctober 2, 2001 Reading: Chapter VI Homework: 6.1, 6.3, 6.5, 6.7, 6.9, 6.10 The Changes in Gibbs Free EnergyclaudioNo ratings yet
- Uses of Maxwell RelationsDocument17 pagesUses of Maxwell RelationsArun EbenezerNo ratings yet
- Ceic3001 NotesDocument3 pagesCeic3001 NotesZooy2012No ratings yet
- 1 (1) - Overview of Moral Situations and Contemporary Moral TrendsDocument52 pages1 (1) - Overview of Moral Situations and Contemporary Moral TrendsIvy TanNo ratings yet
- Human BiochemistryDocument167 pagesHuman Biochemistryalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- 3 Component Systems HandoutDocument9 pages3 Component Systems Handoutalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates 2: OligosaccharidesDocument71 pagesCarbohydrates 2: Oligosaccharidesalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology: 2 Semester 2013 - 2014Document16 pagesPharmaceutical Microbiology: 2 Semester 2013 - 2014alyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Microscopy: The InstrumentsDocument5 pagesMicroscopy: The Instrumentsalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: William H. Brown & Christopher S. FooteDocument67 pagesOrganic Chemistry: William H. Brown & Christopher S. Footealyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Apa DocumentationDocument51 pagesApa Documentationalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Nervous System LectureDocument234 pagesNervous System Lecturealyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The HeartDocument34 pagesPhysiology of The Heartalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document1 pageQuiz 1alyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesThe Human Respiratory Systemalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Talasanggunian: Health Disparities Research & Practice, 3 (3), 57-67Document1 pageTalasanggunian: Health Disparities Research & Practice, 3 (3), 57-67alyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Exercise 11 The Appendicular SkeletonDocument23 pagesExercise 11 The Appendicular Skeletonalyssa_marie_ke100% (1)
- Absorption and StrippingDocument52 pagesAbsorption and StrippingTomasz KobaNo ratings yet
- Gilson TRILUTION LC SoftwareDocument828 pagesGilson TRILUTION LC SoftwareIvanNo ratings yet
- IOHEXOLDocument5 pagesIOHEXOLArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Answer - Unit 3 PDFDocument11 pagesAnswer - Unit 3 PDFVicky AnggaraNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases 0620Document4 pagesAcids and Bases 0620Gono TakaduuNo ratings yet
- Henry's Law - WikipediaDocument14 pagesHenry's Law - WikipediaZakria Shah100% (1)
- Silica Gel: A Keystone in Chromatographic Techniques: IJPSR (2019), Volume 10, Issue 1 (Review Article)Document11 pagesSilica Gel: A Keystone in Chromatographic Techniques: IJPSR (2019), Volume 10, Issue 1 (Review Article)VinayNo ratings yet
- Potentiometric Determination of Captopril in Pharmaceutical FormulationsDocument6 pagesPotentiometric Determination of Captopril in Pharmaceutical FormulationsNurAfifahNo ratings yet
- Lss Exam 2023Document2 pagesLss Exam 2023Alibert NchoNo ratings yet
- Flow Injection AnalysisDocument17 pagesFlow Injection AnalysisUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- GC Lab ManualDocument5 pagesGC Lab ManualJC100% (1)
- Laporan Resmi Praktikum Dasar-Dasar Kimia Analitik Titrasi ArgentometriDocument33 pagesLaporan Resmi Praktikum Dasar-Dasar Kimia Analitik Titrasi Argentometrimawar khasaniyahNo ratings yet
- Ostwald's Theory of Acid and Base IndicatorsDocument12 pagesOstwald's Theory of Acid and Base IndicatorsPushkar WaneNo ratings yet
- ELISA HandbookDocument31 pagesELISA HandbookShahil AlamNo ratings yet
- Chemical EqiulibriumDocument41 pagesChemical EqiulibriumZunaira Noreen100% (1)
- Physical Chemistry 2Document30 pagesPhysical Chemistry 2Michelle MenciasNo ratings yet
- Course InformationDocument3 pagesCourse Informationariff udinNo ratings yet
- PH Indicator - ExperimentDocument2 pagesPH Indicator - ExperimentHana BabićNo ratings yet
- To Determine Equilibrium Constant: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesTo Determine Equilibrium Constant: ObjectiveTim JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Determination Of Water-Soluble Vitamins B, B, B, B, B, B Andconc Column With Particle Size 3 Μm In Some Manufactured Food Products By Hplc With Uv-Dad/Fld DetectionDocument6 pagesDetermination Of Water-Soluble Vitamins B, B, B, B, B, B Andconc Column With Particle Size 3 Μm In Some Manufactured Food Products By Hplc With Uv-Dad/Fld DetectionHITESH CHOPRANo ratings yet
- Buffer Lab ReportDocument3 pagesBuffer Lab Reportbobby indaeyoNo ratings yet
- 2009GA Stevia-rebaudianaPosterDocument1 page2009GA Stevia-rebaudianaPostermagdamayalagNo ratings yet
- IJPS - Volume 9 - Issue 2 - Pages 23-29Document8 pagesIJPS - Volume 9 - Issue 2 - Pages 23-29Alvin Wahyu Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- RP-HPLC Method For The Simultaneous Estimation of Benazepril andDocument21 pagesRP-HPLC Method For The Simultaneous Estimation of Benazepril andPrtap Kumar PatraNo ratings yet
- Multiple Stagesddd LLEDocument6 pagesMultiple Stagesddd LLEFikrie MuhdNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument10 pagesExamEllen MarksNo ratings yet
- BS-Chemistry 7 Semester-Org (Morning) : SubjectDocument5 pagesBS-Chemistry 7 Semester-Org (Morning) : SubjectMuhammad Asad FaroquiNo ratings yet
- Determination Paraben in ShampooDocument5 pagesDetermination Paraben in ShampooromaincharlesNo ratings yet
- Rose Anthocyanins As Acid Base IndicatorsDocument16 pagesRose Anthocyanins As Acid Base IndicatorsLoo Huan HaoNo ratings yet