Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formulas in Math IV: Linear Function
Formulas in Math IV: Linear Function
Uploaded by
GracePadillaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formulas in Math IV: Linear Function
Formulas in Math IV: Linear Function
Uploaded by
GracePadillaCopyright:
Available Formats
Formulas in Math IV
Linear Function A linear function is a first
degree
equation that can be written in the form
y=mx+b
and can be written as f(x)=mx+b, where
m and b
are real numbers.
Formulas:
m=
Slope of a line:
y2 y1
x2 x1
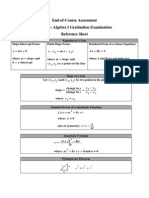
Standard Form: Ax+By=C
Slope and y-intercept : y= mx+b
x and y- intercept:
x y
+ =1
a b
Slope and a point:
y y 1=m(x x1 )
Passing through points:
y y 1=
y 2 y 1
(xx 1)
x 2x 1
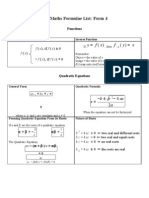
Quadratic Function A function defined by
equation
f ( x )=ax +bx +c
where a, b, and c are real
numbers and a 0
Formulas:
Vertex Form:
x/h formula:
f ( x )=a ( x h2 ) +k
b
2a
4 acb
4a
y/k formula:
f ( x )=ax 2
Vertex of the origin:
Vertex of the parabola in k unit:
f ( x )=ax 2 k
2
Vertex of the parabola in h unit:
xh
f ( x )=a
b b24 ac
2a
Nature of Zeros:
b24 ac
Discriminant:
Polynomial Function A function P that is
defined by
the equation:
n
p ( x )=an x + an1 x
where
n1
+a2 x + a1 x +a0
a0
an , an1 , a1a 0
, n ia a non-negative integer and
are real numbers.
Formulas:
Remainder Theorem:
Rational Zero Theorem:
p ( x )= ( x c ) Q ( x ) + R( x )
p
q
Exponential Function Exponential functions are
equations of the form
and
b x =a
, where
b1
Logarithmic Function the inverse of an
exponential functions,
y=2 x
is
x=2 y
. The
b>0
exponent y is called the logarithm of x to the base 2.
Written as log x= y
2
Formulas:
Logarithm of a Product:
log b xy=log b x + log b y
Logarithm of a Quotient:
log b
Logarithm of a Power:
( xy )=log xlog y
b
log b x = p log b x
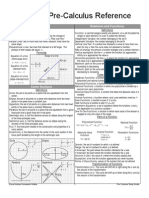
Circular Function The graph of the
equation
x 2+ y 2 =1
is a circle in the rectangular coordinate
system. This
graph is called the unit circle and has its
center at
the origin and has a radius of 1 unit.
Formulas:
Degree to Radian:
Radian to Degree:
1 =
180
1radian=
180
You might also like
- HSC 3U Maths FormulaeDocument7 pagesHSC 3U Maths FormulaeHotz InatorNo ratings yet
- Algebra FormulasDocument2 pagesAlgebra FormulasKhan100% (1)
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form4 PDFDocument16 pagesSPM Add Maths Formula List Form4 PDFNicholas Rogers83% (6)
- H2 Maths Detailed SummaryDocument82 pagesH2 Maths Detailed SummarythatsparklexNo ratings yet
- Math Resources Algebra FormulasDocument4 pagesMath Resources Algebra FormulasSanjiv GautamNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Formulae ListDocument8 pagesAdd Maths Formulae ListWong Hui SeanNo ratings yet
- A Catalog of Essential Functions: Linear ModelsDocument27 pagesA Catalog of Essential Functions: Linear ModelsTuan Anh TranNo ratings yet
- Pops Jaminey MDocument7 pagesPops Jaminey Mlaur33nNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument5 pagesMathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryabhiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument5 pagesMathematics Revision of Formulae and Results: Surds Co-Ordinate GeometryDarrenPurtillWrightNo ratings yet
- 4.6 1 TransformationsDocument4 pages4.6 1 TransformationsBradley SinghNo ratings yet
- Alg I Reference SheetDocument1 pageAlg I Reference Sheety2kmvrNo ratings yet
- Types of FunctionsDocument7 pagesTypes of FunctionsAbdul Basit SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Linear, Quadratic FunctionsDocument14 pagesLinear, Quadratic FunctionsRolando AlbinaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument13 pagesQuadratic FunctionsNur AmiraNo ratings yet
- 6.6 Analyzing Graphs of Quadratic FunctionsDocument22 pages6.6 Analyzing Graphs of Quadratic FunctionsCikgu Shaiful Kisas100% (1)
- Ultimate Algebra 2 Notes! (1st Semester)Document1 pageUltimate Algebra 2 Notes! (1st Semester)Addison CollingsworthNo ratings yet
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form 4Document16 pagesSPM Add Maths Formula List Form 4Hasbull97No ratings yet
- Ad Maths Formula ListDocument16 pagesAd Maths Formula ListZareena CarrimNo ratings yet
- Topics Entry Test IBEB NonCD Version 2014Document5 pagesTopics Entry Test IBEB NonCD Version 2014YonYonNo ratings yet
- Graphs and Properties of The Graphs of Polynomial FunctionsDocument11 pagesGraphs and Properties of The Graphs of Polynomial FunctionsAaron SantillanNo ratings yet
- Math ReviewDocument2 pagesMath Reviewrockpaperscissors427No ratings yet
- Fungsi KuadratDocument10 pagesFungsi KuadratDwi WulandariNo ratings yet
- Edexcel - As Levels MathsDocument4 pagesEdexcel - As Levels MathsAhmad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Function and Factoring Quadractic EquationDocument14 pagesQuadratic Function and Factoring Quadractic EquationYvan OmayanNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics - List of Formulae (Form 4)Document19 pagesAdditional Mathematics - List of Formulae (Form 4)Syazleen Nabilah AkmalNo ratings yet
- Mathematical I PDFDocument124 pagesMathematical I PDFProfessor Dr. Nabeel Al-Bayati-Consultant EngineerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document25 pagesLecture 8Gia Huy LạiNo ratings yet
- Maths Concepts and Formulae: y FX F y XDocument16 pagesMaths Concepts and Formulae: y FX F y XAt TanwiNo ratings yet
- Day 3 (Constant and Linear Functions)Document3 pagesDay 3 (Constant and Linear Functions)Jerome InfanteNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Function Form4Document1 pageQuadratic Function Form4akuzaraNo ratings yet
- Mella Triana - Teaching MaterialDocument14 pagesMella Triana - Teaching MaterialMella TrianaNo ratings yet
- Pre CalcDocument2 pagesPre Calcapi-213604106No ratings yet
- Formulae,,key Points,, Algorithm (For Class 12 TH Maths)Document23 pagesFormulae,,key Points,, Algorithm (For Class 12 TH Maths)angusingh60No ratings yet
- Linear Functions Linear FunctionsDocument8 pagesLinear Functions Linear FunctionsNerinel CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Study NotesDocument61 pagesAdd Maths Study NotesElisha James100% (1)
- Polynomial FunctionsDocument40 pagesPolynomial Functionsnur hashimahNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Lesson NotesDocument22 pagesUnit 9 Lesson Notesapi-291793268No ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Hyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandHyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"From EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Functional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)From EverandFunctional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)No ratings yet