Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp2 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3
Exp2 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3
Uploaded by
EnesVSCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Mental Math Number Talk Strategies PDFDocument26 pagesMental Math Number Talk Strategies PDFwargoNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT NO 12 (Electrical Engineering)Document8 pagesLAB REPORT NO 12 (Electrical Engineering)Malik Hassaan SangraalNo ratings yet
- EEE 805 Assignment Questions For Chapter 20Document11 pagesEEE 805 Assignment Questions For Chapter 20ayeniNo ratings yet
- Areva p132 p139 612 Xrio Converter Manual Enu Tu2.30 v1.000Document8 pagesAreva p132 p139 612 Xrio Converter Manual Enu Tu2.30 v1.000Robert MihayoNo ratings yet
- 6121 Catalog DC Crane ControlDocument30 pages6121 Catalog DC Crane ControlcenicercNo ratings yet
- 3 545 398aDocument78 pages3 545 398aezze72x5058No ratings yet
- Leakage Inductance Behavior of Power Transformer Windings Under Mechanical FaultsDocument5 pagesLeakage Inductance Behavior of Power Transformer Windings Under Mechanical Faultshosein bahramian habilNo ratings yet
- "Bridge B2HZ" For The Control of A DC MotorDocument16 pages"Bridge B2HZ" For The Control of A DC MotorhadiNo ratings yet
- Characteristic of DC Compound Wound Generators - Electrical4uDocument8 pagesCharacteristic of DC Compound Wound Generators - Electrical4uM Kumar MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- A Technical Review On Solar-Net MeteringDocument5 pagesA Technical Review On Solar-Net MeteringMax SteeleNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Single Phase Induction Motor For Numerical Machine ComplexDocument55 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Single Phase Induction Motor For Numerical Machine Complexmugisa aloysiousNo ratings yet
- Problems in PSADocument12 pagesProblems in PSArameshsme100% (1)
- Multi Amp 830280 Transformer OhmmeterDocument40 pagesMulti Amp 830280 Transformer OhmmeterJonathan LayedraNo ratings yet
- EE 340L - Experiment 6: Synchronous Generator - Operation With The GridDocument6 pagesEE 340L - Experiment 6: Synchronous Generator - Operation With The GridMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Thyripol Ingles - ExcitacaoDocument14 pagesCatalogo Thyripol Ingles - ExcitacaoErbil KeskinNo ratings yet
- Magenetic Chip Collector New 2Document27 pagesMagenetic Chip Collector New 2Hemasundar Reddy JolluNo ratings yet
- Lab MachineDocument9 pagesLab MachineAnonymous ryvoPIDNo ratings yet
- Ata 24Document9 pagesAta 24Prince AbbasNo ratings yet
- EE333 Electrical Machines Lab IIDocument2 pagesEE333 Electrical Machines Lab IIvpzfarisNo ratings yet
- Color Sensor WorkingDocument3 pagesColor Sensor WorkingsureshmagixNo ratings yet
- Solid State Drives Short BookDocument48 pagesSolid State Drives Short BookGomathi Raja MNo ratings yet
- Stepup and Stepdown Transformers in Proteus IDEDocument29 pagesStepup and Stepdown Transformers in Proteus IDEArmand YoumbiNo ratings yet
- Datasheet SKHI 22A PDFDocument12 pagesDatasheet SKHI 22A PDFGlauber GoncalvesNo ratings yet
- Basic SVPWMDocument6 pagesBasic SVPWMVAMSIKRISHNAEEENo ratings yet
- Wound Rotor Induction MotorDocument4 pagesWound Rotor Induction MotorAnonymous zeISoBNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machine ProblemsDocument5 pagesSynchronous Machine Problemsbhuvana71No ratings yet
- Two Generators Rated 10 MVADocument2 pagesTwo Generators Rated 10 MVAvlkumashankardeekshithNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Short Questions and Answers EE1251 Electrical Machines II - Mosybk Getto19 - Academia - EduDocument14 pages(PDF) Short Questions and Answers EE1251 Electrical Machines II - Mosybk Getto19 - Academia - EduSolomon MebrahtuNo ratings yet
- Optimal Power Flow Analysis For 23MW Microgrid Using ETAPDocument6 pagesOptimal Power Flow Analysis For 23MW Microgrid Using ETAPInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- K&H - Em-3000Document9 pagesK&H - Em-3000waleed.murad@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Motor Programmable Controller Report 2Document3 pages3 Phase Motor Programmable Controller Report 2Solomon VargheseNo ratings yet
- Electric Drives and Control: Classes of Motor DutyDocument12 pagesElectric Drives and Control: Classes of Motor DutyAnonymous xaeuoo4No ratings yet
- Lab 3 - DC Separately-Excited MotorDocument3 pagesLab 3 - DC Separately-Excited MotorAhmad Hudzaifah100% (1)
- Lec 17Document3 pagesLec 17Karthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- All - Inverter PDFDocument35 pagesAll - Inverter PDFVinod MuruganNo ratings yet
- Motor Control Fundamentals WikiDocument49 pagesMotor Control Fundamentals WikiAleksandar PetrusevskiNo ratings yet
- Speeed ControlDocument3 pagesSpeeed ControlChristine GomezNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual For Electrical Technology Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT (ISM) DhanbadDocument4 pagesInstruction Manual For Electrical Technology Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT (ISM) DhanbadSHUBHAM SINGHAL100% (1)
- PSAFDocument212 pagesPSAFEduardo Rivas CéspedesNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed ControllerDocument22 pagesDC Motor Speed ControllerShafqt MbrkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 SensorsDocument48 pagesChapter 9 Sensorsامجد الغالبيNo ratings yet
- ELG3311: Solutions For Assignment 1: Problem 2-6Document14 pagesELG3311: Solutions For Assignment 1: Problem 2-6tesfayregs gebretsadik100% (1)
- Presentation On Instrument TransformersDocument20 pagesPresentation On Instrument TransformersVishal Bhardwaj100% (1)
- Data Sheet For MUT2200 MC608Document8 pagesData Sheet For MUT2200 MC608Camila DezanNo ratings yet
- Speed Control IM (Edited)Document37 pagesSpeed Control IM (Edited)مصطفى حمدىNo ratings yet
- EMMI Lab PDFDocument31 pagesEMMI Lab PDFSarithareddy AvuluriNo ratings yet
- Temperature Rise of An Electrical MachineDocument9 pagesTemperature Rise of An Electrical MachinePurna RathnayakeNo ratings yet
- JISDocument153 pagesJIStulogmulat100% (3)
- Oscilloscope & Function Generator Operation: Department of Electrical Engineering Network Analysis LabDocument3 pagesOscilloscope & Function Generator Operation: Department of Electrical Engineering Network Analysis LabUsairum MirzaNo ratings yet
- Induction Machines: Torque Speed CharacteristicsDocument22 pagesInduction Machines: Torque Speed CharacteristicsGogioman Myhay100% (1)
- Tests On Single Phase Transformer (Procedure) - Analog Signals, Network and Measurement Laboratory - Electrical Engineering - IIT KHARAGPUR Virtual LabDocument4 pagesTests On Single Phase Transformer (Procedure) - Analog Signals, Network and Measurement Laboratory - Electrical Engineering - IIT KHARAGPUR Virtual Labvjvijay88No ratings yet
- Zab Abb Unitrol 1010 1020 e RevaDocument12 pagesZab Abb Unitrol 1010 1020 e RevaGavinsiauNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 DC Drives Part2Document75 pagesChapter 1 DC Drives Part2Mohammad MunzirNo ratings yet
- Radial Feeder ProtectionDocument14 pagesRadial Feeder Protectionanandhuravindran2002No ratings yet
- Lec9 - Basics of Electric Drives - IMDocument10 pagesLec9 - Basics of Electric Drives - IMTeofilo DedietroNo ratings yet
- Publication 1 19208 6043Document13 pagesPublication 1 19208 6043Stephen Velasco Villaruz0% (1)
- 1.4 Electrical Registration Overseas ApplicantsDocument7 pages1.4 Electrical Registration Overseas ApplicantsBlairNo ratings yet
- Diesel & Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument39 pagesDiesel & Gas Turbine Power PlantvigneshgeminiNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Squirrel Cage Induction Machine-1Document8 pagesLab 3 Squirrel Cage Induction Machine-1max100% (1)
- Which Is Defined By:: Synchronous SpeedDocument15 pagesWhich Is Defined By:: Synchronous SpeedYudhy SufbrataNo ratings yet
- Exp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3Document3 pagesExp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Micro Lecture 4Document47 pagesMicro Lecture 4EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Eed3018 Experiment 6Document1 pageEed3018 Experiment 6EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Loop Out (01H), A: Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 8: Non-Maskable Interrupt and Simple I/O With Z80 PioDocument1 pageLoop Out (01H), A: Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 8: Non-Maskable Interrupt and Simple I/O With Z80 PioEnesVSNo ratings yet
- Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 5: Z80 I/O Operations: Preliminary WorkDocument1 pageEed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 5: Z80 I/O Operations: Preliminary WorkEnesVSNo ratings yet
- The Input and Output Devices Are Assigned and Identified by 16-Bit AddressesDocument43 pagesThe Input and Output Devices Are Assigned and Identified by 16-Bit AddressesEnesVSNo ratings yet
- Z80 CPU Instruction Description: - 158 Different Instruction Types - Instruction GroupsDocument41 pagesZ80 CPU Instruction Description: - 158 Different Instruction Types - Instruction GroupsEnesVSNo ratings yet
- SBC (Subtract With Borrow)Document36 pagesSBC (Subtract With Borrow)EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Systems: Asst - Prof.Dr. Haldun SarnelDocument82 pagesMicroprocessor Systems: Asst - Prof.Dr. Haldun SarnelEnesVSNo ratings yet
- Eed3018 Experiment 3Document1 pageEed3018 Experiment 3EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Exp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3Document3 pagesExp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Exp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments EM3000Document4 pagesExp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments EM3000EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 4: Program Loops: Preliminary WorkDocument1 pageEed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 4: Program Loops: Preliminary WorkEnesVSNo ratings yet
- Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 1: Basic Operations in Z80: Preliminary WorkDocument1 pageEed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 1: Basic Operations in Z80: Preliminary WorkEnesVSNo ratings yet
- Control Systems - Experiment 3Document16 pagesControl Systems - Experiment 3EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Slide 2Document89 pagesSlide 2EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Report VDocument4 pagesReport VEnesVSNo ratings yet
- FM Questions of Risk and Return IDocument4 pagesFM Questions of Risk and Return ItamoorNo ratings yet
- Chp6-Testing Angular: Unit Testing and End-To-End TestingDocument19 pagesChp6-Testing Angular: Unit Testing and End-To-End TestingyugaselvanNo ratings yet
- DR EN Diffusion and Solution at High Pe Res in 316L Stainless Steel and Nickel-Base Heat-Resistant Alloys N. Kishimoto, - MumDocument9 pagesDR EN Diffusion and Solution at High Pe Res in 316L Stainless Steel and Nickel-Base Heat-Resistant Alloys N. Kishimoto, - MumRitu Raj RamanNo ratings yet
- OTM Glossary For LOL - 20190723Document17 pagesOTM Glossary For LOL - 20190723Rahul Harsh RajéNo ratings yet
- AHD-S 201: AHD-S 201 Hydrostatic Level Transmitter For Shipbuilding and OffshoreDocument4 pagesAHD-S 201: AHD-S 201 Hydrostatic Level Transmitter For Shipbuilding and OffshoreElimat EmbarcacionesNo ratings yet
- Din51524hlp Hydraulic CustDocument11 pagesDin51524hlp Hydraulic CustTAREK HAMADNo ratings yet
- SCCL SyllabusDocument1 pageSCCL SyllabusSainathNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Wise Weightage of Marks in IIT JEE For ChemistryDocument5 pagesChapter-Wise Weightage of Marks in IIT JEE For ChemistryFaltukaaccountNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Workbench - Simulation Introduction: Training ManualDocument4 pagesANSYS Workbench - Simulation Introduction: Training ManualShamik ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- CHEN3000 Process Plant Engineering Sem 2 2016 Miri Test 1 Samples v2 + SolutionsDocument17 pagesCHEN3000 Process Plant Engineering Sem 2 2016 Miri Test 1 Samples v2 + SolutionsVincent Ys TanNo ratings yet
- 327, BC A101 05 Oa As BSDocument9 pages327, BC A101 05 Oa As BSMiguel AngelNo ratings yet
- JBL tn-OACDDocument4 pagesJBL tn-OACDRoland HendriksNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16Document36 pagesLecture 16Elsayed ElazazyNo ratings yet
- CONNECT C Versão 5.X AcertosDocument81 pagesCONNECT C Versão 5.X AcertosWilsonWilsonNo ratings yet
- BOTANAL-A Comprehensive Sampling Andcomputing Procedure For Estimating Pasture Yield and Composition. 1. Field..Document24 pagesBOTANAL-A Comprehensive Sampling Andcomputing Procedure For Estimating Pasture Yield and Composition. 1. Field..Remzi ZarateNo ratings yet
- Torque Values For Isolating Gaskets On ASME B16.5 and ASME B16.47 Series....Document1 pageTorque Values For Isolating Gaskets On ASME B16.5 and ASME B16.47 Series....Shijumon Kp100% (2)
- 44 001gb-Er 8-Er 11-AusterasDocument22 pages44 001gb-Er 8-Er 11-AusterasWi DuddaaNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Gadget Terhadap Tumbuh Kembang Anak Siswa Kelas 4 - 6 Di SDN 213 Lapongkoda Kecamatan Tempe Kabupaten WajoDocument9 pagesPengaruh Gadget Terhadap Tumbuh Kembang Anak Siswa Kelas 4 - 6 Di SDN 213 Lapongkoda Kecamatan Tempe Kabupaten WajoMesines IdNo ratings yet
- GPA Calculator Using VisualDocument4 pagesGPA Calculator Using VisualOmotara AkinsowonNo ratings yet
- K3G400PW0301 KM220251 Data SheetDocument7 pagesK3G400PW0301 KM220251 Data Sheetsamuel christianNo ratings yet
- FIR Filters-Concept of Linear PhaseDocument38 pagesFIR Filters-Concept of Linear PhaseJaynil PatelNo ratings yet
- Volvo 760 Gle Turbo Diesel Owners Manual 1984Document121 pagesVolvo 760 Gle Turbo Diesel Owners Manual 1984Ciprian Clapa100% (2)
- North: Mean Rainfall Over Mauritius: 2260Mm Mean Annual Rainfall (1931 - 60)Document3 pagesNorth: Mean Rainfall Over Mauritius: 2260Mm Mean Annual Rainfall (1931 - 60)Manusha MaureeNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Setting Out HZ Alignment - 10Document10 pagesModule 8 - Setting Out HZ Alignment - 10Hisham Abou HalimaNo ratings yet
- Sicor Geared 10 Feb20Document8 pagesSicor Geared 10 Feb20Pritesh NaikNo ratings yet
- Basic AerodynamicsDocument36 pagesBasic AerodynamicsMohamed ArifNo ratings yet
- SUPRA50®: Chemical Composition (Weight %)Document3 pagesSUPRA50®: Chemical Composition (Weight %)malaya tripathyNo ratings yet
Exp2 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3
Exp2 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3
Uploaded by
EnesVSOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exp2 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3
Exp2 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3
Uploaded by
EnesVSCopyright:
Available Formats
DOKUZ EYLL UNIVERSITY
Department of Electrical and Electronics
Engineering
EED3012 Energy Conversion II Experimental Work
Experiment 2
Torque-Speed Characteristic of a Wound-Rotor
Induction Motor
The object of this experiment is to investigate the relationship between
the speed/torque characteristic of wound rotor induction motor with added
rotor resistance
EQUIPMENT REQUIRED:
EQUIPMENT
FH2 MkllI Test Bed
INITIAL SETTINGS
Speed Range 1800 rev / min
External/Internal Torque Switch to INT,
Torque Reverse Switch to give positive meter
deflection.
Brake Control to minimum.
Slip Ring Starter Switch to infinity.
FH100 Slip Ring Machine
Test Machine.
FH3 MkllI Instrumentation Frame
V3 A.C. Voltmeter
250VRange.
A3 A.C. Ammeter
1ARange.
A30 A.C. Ammeter
3ARange.
W1 A.C. Wattmeter
100W Range
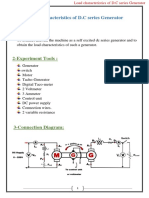
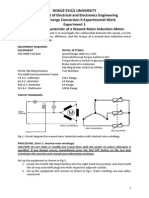
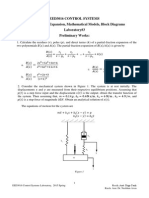
CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS:
Fig-1. Circuit diagram for wound-rotor induction motor with added rotor
resistance
PROCEDURE: (Part-1: added rotor resistance)
CAUTION: Do not make or modify any connections with the power
on unless otherwise is specified. If any danger occurs,
immediately press the EMERGENCY OFF button on the threephase power supply module. Terminate this exercise and consult
your laboratory assistant.
1
DOKUZ EYLL UNIVERSITY
Department of Electrical and Electronics
Engineering
EED3012 Energy Conversion II Experimental Work
Set up the equipment as shown in Fig-1.
1. Locate the FH100 Slip Ring Machine into the right-hand test position
and insert both the 10-way and earth plugs into their respective
adjacent sockets.
2. Set up the equipment and connect as shown in Fig.1.
3. Switch on the power to the FH2 MkIII Test Bed, first at the Mains
Switch and then press the Green ON push-button to activate the
contactor.
4. Rotate the FH2 Slip Ring Starter Switch slowly clockwise to the zero
position. The rotor winding are now shorted. The motor will start to
rotate.
5. Adjust the brake control so that the motor develops an indicated
torque of approximately 0.8 Nm. Allow the motor to warm up for
approximately 15 minutes.
6. Reset the brake control to minimum.
7. In steps, as indicated in the Table-1, increase the torque on the
motor and record corresponding values of torque, speed, and
current. CAUTION: If the rotor is locked by a heavy brake
torque, immediately press the red OFF button on the test
bed and terminate this exercise.
8. Switch off the power to the FH2 MkIII Test Bed, first press the Red
OFF push-button to deactivate the contactor and then at the Mains
Switch.
9. Using the results of Table-1, plot the graphs of torque, current, and
output power versus speed.
Table-1. Measured values of wound-rotor induction motor with added rotor
resistance
Torqu
e
(N.m)
1 (500 )
n
I
(rpm) (A)
2 (300 )
n
I
(rpm) (A)
Knob Position
3 (100 )
4 (50 )
n
I
n
I
(rpm) (A) (rpm) (A)
5 (0 )
n
I
(rpm) (A)
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
0.50
0.60
0.70
0.8
0.90
1.00
1.10
1.20
Calculate the power using the following formula:
2
DOKUZ EYLL UNIVERSITY
Department of Electrical and Electronics
Engineering
EED3012 Energy Conversion II Experimental Work
Pout = (rad / s) T ( N .m)
Unit conversions: 1 kg .m = 9.81 N .m , 1 rpm =
2
rad / s
60
PROCEDURE: (Part-2: blocked rotor test)
CAUTION: Do not make or modify any connections with the power
on unless otherwise is specified. If any danger occurs,
immediately press the Red OFF button on the test bed. Terminate
this exercise and consult your laboratory assistant.
1. Measure the Starting Torque and Current, for each of the Slip_Ring
Starter switch settings, using the rotor locking pin provided. Insert
the pin into the hole located in the right-hand Dynamometer boss (It
may be necessary to rotate the shaft to align the holes in the shaft
and the boss).
2. Disconnect the lead between the dynamometer supply and the
dynamometer,
3. Set the Slip-Ring starter switch to infinity.
4. Remove A3 ammeter and, in one line, insert A30 ammeter on the 3A
Range.
5. Activate the contactor by pressing the Green ON button, rotate the
Slip-Ring Starter switch to each position in-turn, and read the torque
and current values at each step to complete Table-2. CAUTION:
This procedure must be completed as quickly as possible in
order to avoid overheating, and care must be taken to check
the zero of the torque measuring system.
6. Switch off the power to the FH2 MkIII Test Bed, first press the Red
OFF push-button to deactivate the contactor and then at the Mains
Switch.
7. Using the results of Table-2, complete the graphs of torque, current,
and output power versus speed characteristics obtained in part-1.
Table-2. Measured values of starting torque and current of wound-rotor
induction motor with added rotor resistance
1 (500 )
T
I
(N.m) (A)
2 (300 )
T
I
(N.m) (A)
Knob Position
3 (100 )
4 (50 )
T
I
T
I
(N.m) (A) (N.m) (A)
5 (0 )
T
I
(N.m) (A)
RESULTS:
Explain the main features you have learned from the experiments. Discuss
on the tables/graphics obtained from the tests and comment on the results
in your report.
You might also like
- Mental Math Number Talk Strategies PDFDocument26 pagesMental Math Number Talk Strategies PDFwargoNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT NO 12 (Electrical Engineering)Document8 pagesLAB REPORT NO 12 (Electrical Engineering)Malik Hassaan SangraalNo ratings yet
- EEE 805 Assignment Questions For Chapter 20Document11 pagesEEE 805 Assignment Questions For Chapter 20ayeniNo ratings yet
- Areva p132 p139 612 Xrio Converter Manual Enu Tu2.30 v1.000Document8 pagesAreva p132 p139 612 Xrio Converter Manual Enu Tu2.30 v1.000Robert MihayoNo ratings yet
- 6121 Catalog DC Crane ControlDocument30 pages6121 Catalog DC Crane ControlcenicercNo ratings yet
- 3 545 398aDocument78 pages3 545 398aezze72x5058No ratings yet
- Leakage Inductance Behavior of Power Transformer Windings Under Mechanical FaultsDocument5 pagesLeakage Inductance Behavior of Power Transformer Windings Under Mechanical Faultshosein bahramian habilNo ratings yet
- "Bridge B2HZ" For The Control of A DC MotorDocument16 pages"Bridge B2HZ" For The Control of A DC MotorhadiNo ratings yet
- Characteristic of DC Compound Wound Generators - Electrical4uDocument8 pagesCharacteristic of DC Compound Wound Generators - Electrical4uM Kumar MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- A Technical Review On Solar-Net MeteringDocument5 pagesA Technical Review On Solar-Net MeteringMax SteeleNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Single Phase Induction Motor For Numerical Machine ComplexDocument55 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Single Phase Induction Motor For Numerical Machine Complexmugisa aloysiousNo ratings yet
- Problems in PSADocument12 pagesProblems in PSArameshsme100% (1)
- Multi Amp 830280 Transformer OhmmeterDocument40 pagesMulti Amp 830280 Transformer OhmmeterJonathan LayedraNo ratings yet
- EE 340L - Experiment 6: Synchronous Generator - Operation With The GridDocument6 pagesEE 340L - Experiment 6: Synchronous Generator - Operation With The GridMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Thyripol Ingles - ExcitacaoDocument14 pagesCatalogo Thyripol Ingles - ExcitacaoErbil KeskinNo ratings yet
- Magenetic Chip Collector New 2Document27 pagesMagenetic Chip Collector New 2Hemasundar Reddy JolluNo ratings yet
- Lab MachineDocument9 pagesLab MachineAnonymous ryvoPIDNo ratings yet
- Ata 24Document9 pagesAta 24Prince AbbasNo ratings yet
- EE333 Electrical Machines Lab IIDocument2 pagesEE333 Electrical Machines Lab IIvpzfarisNo ratings yet
- Color Sensor WorkingDocument3 pagesColor Sensor WorkingsureshmagixNo ratings yet
- Solid State Drives Short BookDocument48 pagesSolid State Drives Short BookGomathi Raja MNo ratings yet
- Stepup and Stepdown Transformers in Proteus IDEDocument29 pagesStepup and Stepdown Transformers in Proteus IDEArmand YoumbiNo ratings yet
- Datasheet SKHI 22A PDFDocument12 pagesDatasheet SKHI 22A PDFGlauber GoncalvesNo ratings yet
- Basic SVPWMDocument6 pagesBasic SVPWMVAMSIKRISHNAEEENo ratings yet
- Wound Rotor Induction MotorDocument4 pagesWound Rotor Induction MotorAnonymous zeISoBNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machine ProblemsDocument5 pagesSynchronous Machine Problemsbhuvana71No ratings yet
- Two Generators Rated 10 MVADocument2 pagesTwo Generators Rated 10 MVAvlkumashankardeekshithNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Short Questions and Answers EE1251 Electrical Machines II - Mosybk Getto19 - Academia - EduDocument14 pages(PDF) Short Questions and Answers EE1251 Electrical Machines II - Mosybk Getto19 - Academia - EduSolomon MebrahtuNo ratings yet
- Optimal Power Flow Analysis For 23MW Microgrid Using ETAPDocument6 pagesOptimal Power Flow Analysis For 23MW Microgrid Using ETAPInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- K&H - Em-3000Document9 pagesK&H - Em-3000waleed.murad@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Motor Programmable Controller Report 2Document3 pages3 Phase Motor Programmable Controller Report 2Solomon VargheseNo ratings yet
- Electric Drives and Control: Classes of Motor DutyDocument12 pagesElectric Drives and Control: Classes of Motor DutyAnonymous xaeuoo4No ratings yet
- Lab 3 - DC Separately-Excited MotorDocument3 pagesLab 3 - DC Separately-Excited MotorAhmad Hudzaifah100% (1)
- Lec 17Document3 pagesLec 17Karthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- All - Inverter PDFDocument35 pagesAll - Inverter PDFVinod MuruganNo ratings yet
- Motor Control Fundamentals WikiDocument49 pagesMotor Control Fundamentals WikiAleksandar PetrusevskiNo ratings yet
- Speeed ControlDocument3 pagesSpeeed ControlChristine GomezNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual For Electrical Technology Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT (ISM) DhanbadDocument4 pagesInstruction Manual For Electrical Technology Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT (ISM) DhanbadSHUBHAM SINGHAL100% (1)
- PSAFDocument212 pagesPSAFEduardo Rivas CéspedesNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed ControllerDocument22 pagesDC Motor Speed ControllerShafqt MbrkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 SensorsDocument48 pagesChapter 9 Sensorsامجد الغالبيNo ratings yet
- ELG3311: Solutions For Assignment 1: Problem 2-6Document14 pagesELG3311: Solutions For Assignment 1: Problem 2-6tesfayregs gebretsadik100% (1)
- Presentation On Instrument TransformersDocument20 pagesPresentation On Instrument TransformersVishal Bhardwaj100% (1)
- Data Sheet For MUT2200 MC608Document8 pagesData Sheet For MUT2200 MC608Camila DezanNo ratings yet
- Speed Control IM (Edited)Document37 pagesSpeed Control IM (Edited)مصطفى حمدىNo ratings yet
- EMMI Lab PDFDocument31 pagesEMMI Lab PDFSarithareddy AvuluriNo ratings yet
- Temperature Rise of An Electrical MachineDocument9 pagesTemperature Rise of An Electrical MachinePurna RathnayakeNo ratings yet
- JISDocument153 pagesJIStulogmulat100% (3)
- Oscilloscope & Function Generator Operation: Department of Electrical Engineering Network Analysis LabDocument3 pagesOscilloscope & Function Generator Operation: Department of Electrical Engineering Network Analysis LabUsairum MirzaNo ratings yet
- Induction Machines: Torque Speed CharacteristicsDocument22 pagesInduction Machines: Torque Speed CharacteristicsGogioman Myhay100% (1)
- Tests On Single Phase Transformer (Procedure) - Analog Signals, Network and Measurement Laboratory - Electrical Engineering - IIT KHARAGPUR Virtual LabDocument4 pagesTests On Single Phase Transformer (Procedure) - Analog Signals, Network and Measurement Laboratory - Electrical Engineering - IIT KHARAGPUR Virtual Labvjvijay88No ratings yet
- Zab Abb Unitrol 1010 1020 e RevaDocument12 pagesZab Abb Unitrol 1010 1020 e RevaGavinsiauNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 DC Drives Part2Document75 pagesChapter 1 DC Drives Part2Mohammad MunzirNo ratings yet
- Radial Feeder ProtectionDocument14 pagesRadial Feeder Protectionanandhuravindran2002No ratings yet
- Lec9 - Basics of Electric Drives - IMDocument10 pagesLec9 - Basics of Electric Drives - IMTeofilo DedietroNo ratings yet
- Publication 1 19208 6043Document13 pagesPublication 1 19208 6043Stephen Velasco Villaruz0% (1)
- 1.4 Electrical Registration Overseas ApplicantsDocument7 pages1.4 Electrical Registration Overseas ApplicantsBlairNo ratings yet
- Diesel & Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument39 pagesDiesel & Gas Turbine Power PlantvigneshgeminiNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Squirrel Cage Induction Machine-1Document8 pagesLab 3 Squirrel Cage Induction Machine-1max100% (1)
- Which Is Defined By:: Synchronous SpeedDocument15 pagesWhich Is Defined By:: Synchronous SpeedYudhy SufbrataNo ratings yet
- Exp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3Document3 pagesExp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Micro Lecture 4Document47 pagesMicro Lecture 4EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Eed3018 Experiment 6Document1 pageEed3018 Experiment 6EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Loop Out (01H), A: Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 8: Non-Maskable Interrupt and Simple I/O With Z80 PioDocument1 pageLoop Out (01H), A: Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 8: Non-Maskable Interrupt and Simple I/O With Z80 PioEnesVSNo ratings yet
- Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 5: Z80 I/O Operations: Preliminary WorkDocument1 pageEed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 5: Z80 I/O Operations: Preliminary WorkEnesVSNo ratings yet
- The Input and Output Devices Are Assigned and Identified by 16-Bit AddressesDocument43 pagesThe Input and Output Devices Are Assigned and Identified by 16-Bit AddressesEnesVSNo ratings yet
- Z80 CPU Instruction Description: - 158 Different Instruction Types - Instruction GroupsDocument41 pagesZ80 CPU Instruction Description: - 158 Different Instruction Types - Instruction GroupsEnesVSNo ratings yet
- SBC (Subtract With Borrow)Document36 pagesSBC (Subtract With Borrow)EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Systems: Asst - Prof.Dr. Haldun SarnelDocument82 pagesMicroprocessor Systems: Asst - Prof.Dr. Haldun SarnelEnesVSNo ratings yet
- Eed3018 Experiment 3Document1 pageEed3018 Experiment 3EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Exp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3Document3 pagesExp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Exp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments EM3000Document4 pagesExp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments EM3000EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 4: Program Loops: Preliminary WorkDocument1 pageEed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 4: Program Loops: Preliminary WorkEnesVSNo ratings yet
- Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 1: Basic Operations in Z80: Preliminary WorkDocument1 pageEed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 1: Basic Operations in Z80: Preliminary WorkEnesVSNo ratings yet
- Control Systems - Experiment 3Document16 pagesControl Systems - Experiment 3EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Slide 2Document89 pagesSlide 2EnesVSNo ratings yet
- Report VDocument4 pagesReport VEnesVSNo ratings yet
- FM Questions of Risk and Return IDocument4 pagesFM Questions of Risk and Return ItamoorNo ratings yet
- Chp6-Testing Angular: Unit Testing and End-To-End TestingDocument19 pagesChp6-Testing Angular: Unit Testing and End-To-End TestingyugaselvanNo ratings yet
- DR EN Diffusion and Solution at High Pe Res in 316L Stainless Steel and Nickel-Base Heat-Resistant Alloys N. Kishimoto, - MumDocument9 pagesDR EN Diffusion and Solution at High Pe Res in 316L Stainless Steel and Nickel-Base Heat-Resistant Alloys N. Kishimoto, - MumRitu Raj RamanNo ratings yet
- OTM Glossary For LOL - 20190723Document17 pagesOTM Glossary For LOL - 20190723Rahul Harsh RajéNo ratings yet
- AHD-S 201: AHD-S 201 Hydrostatic Level Transmitter For Shipbuilding and OffshoreDocument4 pagesAHD-S 201: AHD-S 201 Hydrostatic Level Transmitter For Shipbuilding and OffshoreElimat EmbarcacionesNo ratings yet
- Din51524hlp Hydraulic CustDocument11 pagesDin51524hlp Hydraulic CustTAREK HAMADNo ratings yet
- SCCL SyllabusDocument1 pageSCCL SyllabusSainathNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Wise Weightage of Marks in IIT JEE For ChemistryDocument5 pagesChapter-Wise Weightage of Marks in IIT JEE For ChemistryFaltukaaccountNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Workbench - Simulation Introduction: Training ManualDocument4 pagesANSYS Workbench - Simulation Introduction: Training ManualShamik ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- CHEN3000 Process Plant Engineering Sem 2 2016 Miri Test 1 Samples v2 + SolutionsDocument17 pagesCHEN3000 Process Plant Engineering Sem 2 2016 Miri Test 1 Samples v2 + SolutionsVincent Ys TanNo ratings yet
- 327, BC A101 05 Oa As BSDocument9 pages327, BC A101 05 Oa As BSMiguel AngelNo ratings yet
- JBL tn-OACDDocument4 pagesJBL tn-OACDRoland HendriksNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16Document36 pagesLecture 16Elsayed ElazazyNo ratings yet
- CONNECT C Versão 5.X AcertosDocument81 pagesCONNECT C Versão 5.X AcertosWilsonWilsonNo ratings yet
- BOTANAL-A Comprehensive Sampling Andcomputing Procedure For Estimating Pasture Yield and Composition. 1. Field..Document24 pagesBOTANAL-A Comprehensive Sampling Andcomputing Procedure For Estimating Pasture Yield and Composition. 1. Field..Remzi ZarateNo ratings yet
- Torque Values For Isolating Gaskets On ASME B16.5 and ASME B16.47 Series....Document1 pageTorque Values For Isolating Gaskets On ASME B16.5 and ASME B16.47 Series....Shijumon Kp100% (2)
- 44 001gb-Er 8-Er 11-AusterasDocument22 pages44 001gb-Er 8-Er 11-AusterasWi DuddaaNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Gadget Terhadap Tumbuh Kembang Anak Siswa Kelas 4 - 6 Di SDN 213 Lapongkoda Kecamatan Tempe Kabupaten WajoDocument9 pagesPengaruh Gadget Terhadap Tumbuh Kembang Anak Siswa Kelas 4 - 6 Di SDN 213 Lapongkoda Kecamatan Tempe Kabupaten WajoMesines IdNo ratings yet
- GPA Calculator Using VisualDocument4 pagesGPA Calculator Using VisualOmotara AkinsowonNo ratings yet
- K3G400PW0301 KM220251 Data SheetDocument7 pagesK3G400PW0301 KM220251 Data Sheetsamuel christianNo ratings yet
- FIR Filters-Concept of Linear PhaseDocument38 pagesFIR Filters-Concept of Linear PhaseJaynil PatelNo ratings yet
- Volvo 760 Gle Turbo Diesel Owners Manual 1984Document121 pagesVolvo 760 Gle Turbo Diesel Owners Manual 1984Ciprian Clapa100% (2)
- North: Mean Rainfall Over Mauritius: 2260Mm Mean Annual Rainfall (1931 - 60)Document3 pagesNorth: Mean Rainfall Over Mauritius: 2260Mm Mean Annual Rainfall (1931 - 60)Manusha MaureeNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Setting Out HZ Alignment - 10Document10 pagesModule 8 - Setting Out HZ Alignment - 10Hisham Abou HalimaNo ratings yet
- Sicor Geared 10 Feb20Document8 pagesSicor Geared 10 Feb20Pritesh NaikNo ratings yet
- Basic AerodynamicsDocument36 pagesBasic AerodynamicsMohamed ArifNo ratings yet
- SUPRA50®: Chemical Composition (Weight %)Document3 pagesSUPRA50®: Chemical Composition (Weight %)malaya tripathyNo ratings yet