Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adaptive Control
Adaptive Control
Uploaded by
Anonymous E4Rbo2sOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adaptive Control
Adaptive Control
Uploaded by
Anonymous E4Rbo2sCopyright:
Available Formats
Adaptive control
Dual Adaptive Controllers [based on Dual control
theory]
Adaptive control is the control method used by a controller which must adapt to a controlled system with parameters which vary, or are initially uncertain. For example, as an aircraft ies, its mass will slowly decrease
as a result of fuel consumption; a control law is needed
that adapts itself to such changing conditions. Adaptive
control is dierent from robust control in that it does not
need a priori information about the bounds on these uncertain or time-varying parameters; robust control guarantees that if the changes are within given bounds the control law need not be changed, while adaptive control is
concerned with control law changing themselves.
Optimal Dual Controllers [dicult to design]
Suboptimal Dual Controllers
Nondual Adaptive Controllers
Adaptive Pole Placement
Extremum Seeking Controllers
Iterative learning control
Gain scheduling
Model Reference Adaptive Controllers
(MRACs) [incorporate a reference model
dening desired closed loop performance]
Parameter estimation
The foundation of adaptive control is parameter estimation. Common methods of estimation include recursive
least squares and gradient descent. Both of these methods provide update laws which are used to modify estimates in real time (i.e., as the system operates). Lyapunov
stability is used to derive these update laws and show
convergence criterion (typically persistent excitation).
Projection (mathematics) and normalization are com- MRAC
monly used to improve the robustness of estimation algorithms. It is also called adjustable control.
REFERENCE
MODEL
ref
ADJUSTMENT
MECHANISM
Parameters
CONTROLLER
Plant identification
MECHANISM
Classication of adaptive control
techniques
CONTROLLER
In general one should distinguish between:
MODEL REFERENCE ADAPTIVE CONTROL (MRAC)
ADJUSTMENT
PLANT
SYSTEM
Plant uncertainty
IDENTIFICATION
PLANT
MODEL IDENTIFICATION ADAPTIVE CONTROL (MIAC)
MIAC
1. Feedforward Adaptive Control
Gradient Optimization MRACs [use local rule for adjusting params when performance diers from reference. Ex.: MIT
rule.]
Stability Optimized MRACs
2. Feedback Adaptive Control
as well as between
1. Direct Methods and
Model Identication Adaptive Controllers
(MIACs) [perform System identication while
the system is running]
2. Indirect Methods
Direct methods are ones wherein the estimated parameters are those directly used in the adaptive controller.
In contrast, indirect methods are those in which the estimated parameters are used to calculate required controller parameters[1]
Cautious Adaptive Controllers [use current SI to modify control law, allowing for
SI uncertainty]
Certainty Equivalent Adaptive Controllers [take current SI to be the true
system, assume no uncertainty]
There are several broad categories of feedback adaptive
control (classication can vary):
1
6 FURTHER READING
Nonparametric Adaptive Controllers
Parametric Adaptive Controllers
Explicit Parameter Adaptive Controllers
Implicit Parameter Adaptive Controllers
Some special topics in adaptive control can be introduced
as well:
1. Adaptive Control Based on Discrete-Time Process
Identication
2. Adaptive Control Based on the Model Reference
Technique
3. Adaptive Control based on Continuous-Time Process Models
4 See also
Nonlinear control
Intelligent control
Lyapunov optimization
5 References
[1] Astrom, Karl (2008). Adaptive Control. Dover. pp. 25
26.
6 Further reading
4. Adaptive Control of Multivariable Processes
5. Adaptive Control of Nonlinear Processes
Applications
When designing adaptive control systems, special consideration is necessary of convergence and robustness issues. Lyapunov stability is typically used to derive control
adaptation laws and show convergence.
Typical applications of adaptive control are (in general):
Self-tuning of subsequently xed linear controllers
during the implementation phase for one operating
point;
Self-tuning of subsequently xed robust controllers
during the implementation phase for whole range of
operating points;
B. Egardt, Stability of Adaptive Controllers. New
York: Springer-Verlag, 1979.
I. D. Landau, Adaptive Control: The Model Reference Approach. New York: Marcel Dekker, 1979.
P. A. Ioannou and J. Sun, Robust Adaptive Control.
Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1996.
K. S. Narendra and A. M. Annaswamy, Stable
Adaptive Systems. Englewood Clis, NJ: Prentice
Hall, 1989; Dover Publications, 2004.
S. Sastry and M. Bodson, Adaptive Control: Stability, Convergence and Robustness. Prentice Hall,
1989.
K. J. Astrom and B. Wittenmark, Adaptive Control.
Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1995.
Self-tuning of xed controllers on request if the process behaviour changes due to ageing, drift, wear
etc.;
I. D. Landau, R. Lozano, and M. MSaad, Adaptive
Control. New York, NY: Springer-Verlag, 1998.
Adaptive control of linear controllers for nonlinear
or time-varying processes;
G. Tao, Adaptive Control Design and Analysis.
Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Interscience, 2003.
Adaptive control or self-tuning control of nonlinear
controllers for nonlinear processes;
Adaptive control or self-tuning control of multivariable controllers for multivariable processes (MIMO
systems);
Usually these methods adapt the controllers to both the
process statics and dynamics. In special cases the adaptation can be limited to the static behavior alone, leading to adaptive control based on characteristic curves for
the steady-states or to extremum value control, optimizing the steady state. Hence, there are several ways to apply adaptive control algorithms.
P. A. Ioannou and B. Fidan, Adaptive Control Tutorial. SIAM, 2006.
G. C. Goodwin and K. S. Sin, Adaptive Filtering Prediction and Control. Englewood Clis, NJ:
Prentice-Hall, 1984.
M. Krstic, I. Kanellakopoulos, and P. V. Kokotovic,
Nonlinear and Adaptive Control Design. Wiley Interscience, 1995.
P. A. Ioannou and P. V. Kokotovic, Adaptive Systems with Reduced Models. Springer Verlag, 1983.
External links
Shankar Sastry and Marc Bodson, Adaptive Control: Stability, Convergence, and Robustness,
Prentice-Hall, 1989-1994 (book)
K. Sevcik: Tutorial on Model Reference Adaptive
Control (Drexel University)
8 TEXT AND IMAGE SOURCES, CONTRIBUTORS, AND LICENSES
Text and image sources, contributors, and licenses
8.1
Text
Adaptive control Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adaptive%20control?oldid=608144854 Contributors: Jdpipe, David Gerard, Jason
Quinn, Billymac00, Mdd, Pol098, Pjetter, Vonkje, Encyclops, SmackBot, Trebor, Misrom, Wizard191, JForget, Letranova, James086,
MSBOT, Celithemis, Sonymontuno, User A1, STBot, Pekaje, Jiuguang Wang, Taggard, Tomas e, Control.optimization, Albambot, Addbot,
1971, Daniele Pugliesi, Jim1138, Materialscientist, LilHelpa, Xqbot, J04n, Sympatycznyfacet, RjwilmsiBot, 1, Kasirbot,
JamesQueue, Rjpbi, Lengzhe and Anonymous: 17
8.2
Images
File:MIAC.svg Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/ad/MIAC.svg License: Public domain Contributors: Originally
from en.wikipedia; description page is/was here. Original artist: Original uploader was Pekaje at en.wikipedia
File:MRAC.svg Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/14/MRAC.svg License: Public domain Contributors: Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons. Original artist: Pekaje at English Wikipedia
8.3
Content license
Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0
You might also like
- Action Research in ReadingDocument40 pagesAction Research in ReadingJosenia Constantino96% (82)
- Modelado Rotary Pendulum Workbook InstructorDocument60 pagesModelado Rotary Pendulum Workbook Instructorsolid34No ratings yet
- Extended State Observer Based ControllerDocument5 pagesExtended State Observer Based ControllerD.Viswanath50% (2)
- Nandi-Markweta Languages PDFDocument6 pagesNandi-Markweta Languages PDFAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Maus Unit Plan PDFDocument5 pagesMaus Unit Plan PDFcollin_macdonal6612No ratings yet
- Adaptive ControlDocument46 pagesAdaptive ControlAhmet Halilovic100% (1)
- Model Reference Adaptive ControlDocument22 pagesModel Reference Adaptive Controlasusd112550% (4)
- Adaptive Control PDFDocument380 pagesAdaptive Control PDFSanjiv CrNo ratings yet
- State Observers DesignDocument11 pagesState Observers DesignNileshNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 QUBE-Servo Bump Test Modeling Workbook (Student)Document6 pagesLab 4 QUBE-Servo Bump Test Modeling Workbook (Student)Luis EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Phase Plane Analysis PDFDocument27 pagesPhase Plane Analysis PDFjooooooNo ratings yet
- 18 Adaptive ControlDocument7 pages18 Adaptive ControlFathi MusaNo ratings yet
- Data AcquisitionDocument18 pagesData Acquisitionwanted_JMTINo ratings yet
- Modeling An Inverted PendulumDocument45 pagesModeling An Inverted Pendulumjunaid_honey83896770% (1)
- Observer DesignDocument20 pagesObserver DesignRamaDinakaranNo ratings yet
- Use of Kalman Filters in Time and Frequency AnalysisDocument78 pagesUse of Kalman Filters in Time and Frequency AnalysisJaya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Particle Swarm Optimization - TutorialDocument4 pagesParticle Swarm Optimization - TutorialBiswajit DebnathNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 QUBE-Servo First Principles Modeling Workbook (Student)Document6 pagesLab 3 QUBE-Servo First Principles Modeling Workbook (Student)Luis EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Motor Speed - Simulink ControlDocument9 pagesMotor Speed - Simulink ControlJesamarsNo ratings yet
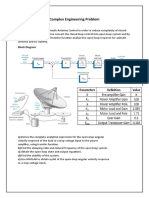
- Complex Engineering Problem StatementDocument10 pagesComplex Engineering Problem StatementMuhammad MashamNo ratings yet
- Kalman Filters For Parameter Estimation of Nonstationary SignalsDocument21 pagesKalman Filters For Parameter Estimation of Nonstationary Signalshendra lamNo ratings yet
- T7 - State Feedback Analysis and Design - 2021Document35 pagesT7 - State Feedback Analysis and Design - 2021James ChanNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Kalman FiltersDocument73 pagesDifferent Types of Kalman Filtersankit bansalNo ratings yet
- Particle Swarm OptimizationDocument13 pagesParticle Swarm OptimizationSaumil ShahNo ratings yet
- Operation in Fuzzy SetsDocument10 pagesOperation in Fuzzy SetsAnuj SamariyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture SlidesDocument21 pagesLecture SlidesAyodeji Samuel BinuyoNo ratings yet
- Sliding Mode Control Strategy For A 6 DOF Quadrotor HelicopterDocument7 pagesSliding Mode Control Strategy For A 6 DOF Quadrotor HelicopternaderjsaNo ratings yet
- Inverted PendulumDocument4 pagesInverted PendulumFerbNo ratings yet
- Kalman Filter Algorithm Design For HC-SR04 UltrasoDocument5 pagesKalman Filter Algorithm Design For HC-SR04 Ultrasomartinez_cvmNo ratings yet
- Transient Stability For IEEE 14 Bus Power System Using Power WorldDocument8 pagesTransient Stability For IEEE 14 Bus Power System Using Power Worldcristian_miranda_mNo ratings yet
- Neural Controller of DC MotorDocument81 pagesNeural Controller of DC MotorGanesan Ganesh50% (2)
- Advanced Control, Lecture 2,3, Modeling and LinearizationDocument48 pagesAdvanced Control, Lecture 2,3, Modeling and LinearizationsepehrNo ratings yet
- Files 2-Chapters 10 5 Transient Response SpecificationsDocument9 pagesFiles 2-Chapters 10 5 Transient Response SpecificationsYalemwork Yargal100% (1)
- Modeling, Implementation, Simulation and Comparison of Different Control Theories On A Two Wheel Self Balancing Robot Model in SimulinkDocument5 pagesModeling, Implementation, Simulation and Comparison of Different Control Theories On A Two Wheel Self Balancing Robot Model in SimulinkMario CavazosNo ratings yet
- Iterative Feedback Tuning, Theory and ApplicationsDocument16 pagesIterative Feedback Tuning, Theory and ApplicationsHao LuoNo ratings yet
- Ac3 SsiDocument13 pagesAc3 SsiAli Imam SunnyNo ratings yet
- Cs Pole Placement DesignDocument15 pagesCs Pole Placement Design18U208 - ARJUN A100% (1)
- Modeling and Position Control of Mobile RobotDocument6 pagesModeling and Position Control of Mobile RobotAmin EslamiNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Control 2Document30 pagesAdaptive Control 2kanchiNo ratings yet
- Inverted Pendulum Systems: Rotary and Arm-Driven A Mechatronic System Design Case StudyDocument6 pagesInverted Pendulum Systems: Rotary and Arm-Driven A Mechatronic System Design Case StudyWan Nizam Wan SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Model Predictive Control For UAVsDocument24 pagesModel Predictive Control For UAVsJulio BVNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 6 Four-Quadrant Operation of DC MotorDocument12 pagesExperiment - 6 Four-Quadrant Operation of DC Motoreng_abdelghany1979No ratings yet
- RNNDocument16 pagesRNNSourabh AttriNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Advanced Control TheoryDocument17 pagesUnit 1 Advanced Control TheoryMuskan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Review - 3 - Load Forecasting PDFDocument25 pagesReview - 3 - Load Forecasting PDFhabte gebreial shrashrNo ratings yet
- Adaptive ControlDocument382 pagesAdaptive ControlAnonymous QakmLc3kTINo ratings yet
- Full Order Observer Controller Design For DC Motor Based On State Space ApproachDocument5 pagesFull Order Observer Controller Design For DC Motor Based On State Space ApproachSelaRajNo ratings yet
- Signal SummaryDocument11 pagesSignal Summaryaryaman58No ratings yet
- MCT Unit 2 State Space DesignDocument92 pagesMCT Unit 2 State Space DesignHarshal Giri100% (1)
- Volterra SeriesDocument50 pagesVolterra Seriessaleh1978No ratings yet
- CuckooDocument9 pagesCuckooshaliniNo ratings yet
- Updated Self Balancing Report (F16mte28)Document25 pagesUpdated Self Balancing Report (F16mte28)Shahrukh Aleem JhatialNo ratings yet
- Soft Computing and Optimization AlgorithmsDocument27 pagesSoft Computing and Optimization AlgorithmsAndrew GarfieldNo ratings yet
- Week 7A - Online Classes - S2020Document16 pagesWeek 7A - Online Classes - S2020Muhammad Tayyab YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Energy Conversion Systems, Fundamentals and Hard-switching ConvertersFrom EverandPower Electronics and Energy Conversion Systems, Fundamentals and Hard-switching ConvertersNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Control - Wikipedia PDFDocument20 pagesAdaptive Control - Wikipedia PDFig: sidaryNo ratings yet
- Classification of Adaptive Control TechniquesDocument3 pagesClassification of Adaptive Control TechniquesLOKESHWARAN K CHEM-UG- 2017 BATCHNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document25 pagesLecture 1Munazzah TaimuriNo ratings yet
- EE5104 Adaptive Control Systems/ EE6104 Adaptive Control Systems (Advanced)Document5 pagesEE5104 Adaptive Control Systems/ EE6104 Adaptive Control Systems (Advanced)sujingthetNo ratings yet
- Classification of Adaptive Control TechniquesDocument4 pagesClassification of Adaptive Control TechniquesUmesh AhirraoNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Control: According To Webster's DictionaryDocument20 pagesAdaptive Control: According To Webster's DictionaryMukesh Kumar VarmaNo ratings yet
- Jerky: Jerky Is Lean Trimmed Meat That Has Been Cut Into StripsDocument6 pagesJerky: Jerky Is Lean Trimmed Meat That Has Been Cut Into StripsAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Mountain RangeDocument5 pagesMountain RangeAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Sierra Morena: Central Plateau and Providing The Watershed Between The Valleys of TheDocument7 pagesSierra Morena: Central Plateau and Providing The Watershed Between The Valleys of TheAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Tariq Ibn ZiyadDocument5 pagesTariq Ibn ZiyadAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Konakovsky District (Russian: КонакDocument7 pagesKonakovsky District (Russian: КонакAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Jebel Musa (Morocco)Document3 pagesJebel Musa (Morocco)Anonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Adel Sedra: Adel S. Sedra Is An Egyptian Canadian Electrical Engineer andDocument4 pagesAdel Sedra: Adel S. Sedra Is An Egyptian Canadian Electrical Engineer andAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Bantoid Languages PDFDocument2 pagesBantoid Languages PDFAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Kipsigis LanguageDocument3 pagesKipsigis LanguageAnonymous E4Rbo2s100% (1)
- Demonstrative PDFDocument8 pagesDemonstrative PDFAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Crumple ZoneDocument7 pagesCrumple ZoneAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Function OverloadingDocument4 pagesFunction OverloadingAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Class (Computer Programming)Document12 pagesClass (Computer Programming)Anonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Eispack: DocumentationDocument1 pageEispack: DocumentationAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Cleve MolerDocument2 pagesCleve MolerAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Cephalopod LimbDocument9 pagesCephalopod LimbAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- American Anthropologist - August 1963 - Aberle - Culture and Behavior Collected Essays of Clyde KluckhohnDocument3 pagesAmerican Anthropologist - August 1963 - Aberle - Culture and Behavior Collected Essays of Clyde KluckhohnJesicca PajaresNo ratings yet
- Certificate: Cv. Solas Marine IndonesiaDocument8 pagesCertificate: Cv. Solas Marine Indonesiamasyithah fadhaniNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics: Zero - Gee Ergonomic Computer and Gaming WorkstationDocument38 pagesErgonomics: Zero - Gee Ergonomic Computer and Gaming WorkstationsoumikhalderNo ratings yet
- FIFA Video Game - Players ClassificationDocument26 pagesFIFA Video Game - Players Classificationimmi1989No ratings yet
- Golisano Children Hospital GRD FloorDocument1 pageGolisano Children Hospital GRD FloorMuhammad IlyasNo ratings yet
- CC Confirmation FinalDocument3 pagesCC Confirmation FinalEd CacalNo ratings yet
- 3656 8873 1 SMDocument10 pages3656 8873 1 SMDino KaninoNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2-NOTES - Self Management Skills-IXDocument8 pagesUNIT-2-NOTES - Self Management Skills-IXVaishnavi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Welding and Cutting Do's and Don'Ts Global EHS DD 004Document6 pagesWelding and Cutting Do's and Don'Ts Global EHS DD 004SYED AHMEDNo ratings yet
- 29 - MSC Sonia Crew Menber Burned Steam PDFDocument8 pages29 - MSC Sonia Crew Menber Burned Steam PDFKwabena KwakyeNo ratings yet
- Item Analysis MPS-Q1Document6 pagesItem Analysis MPS-Q1Acebron AcederaNo ratings yet
- UAV Positioning For Throughput Maximization: Research Open AccessDocument15 pagesUAV Positioning For Throughput Maximization: Research Open AccessAbhishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- LithiumBattery EnglishDocument7 pagesLithiumBattery EnglishgojarooNo ratings yet
- Tablet Machine Qualification ProtocolDocument22 pagesTablet Machine Qualification ProtocolScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Foundations of PlanningDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Foundations of PlanningAndrea KhoNo ratings yet
- Dissociative Identity DisorderDocument4 pagesDissociative Identity DisorderRyan Turtoga ZafeNo ratings yet
- Transfer: SectionDocument76 pagesTransfer: SectionmohhizbarNo ratings yet
- DHL550UDM-EG: 55'' FHD Video Wall Display Unit (Ultra Narrow Bezel 1.8mm)Document2 pagesDHL550UDM-EG: 55'' FHD Video Wall Display Unit (Ultra Narrow Bezel 1.8mm)ParvizNo ratings yet
- FAQ - Transfer Plate Example (General) PDFDocument6 pagesFAQ - Transfer Plate Example (General) PDFStevenNo ratings yet
- LMC7001-7004-R4!10!100 Compact Med Conv ManualDocument4 pagesLMC7001-7004-R4!10!100 Compact Med Conv ManualMarco Enrique Rodriguez LeivaNo ratings yet
- Trelleborg Elastomeric Bridge Bearings PDFDocument4 pagesTrelleborg Elastomeric Bridge Bearings PDFMad WonderNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 1 (Dsa)Document6 pagesLab Assignment 1 (Dsa)Rajan MahatoNo ratings yet
- ws15 4Document5 pagesws15 4Sierra LeeNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Screening Performance: Where To StartDocument6 pagesEvaluating Screening Performance: Where To StartParthNo ratings yet
- Lsa DWG 190703 98 Ejm SignedDocument1 pageLsa DWG 190703 98 Ejm SignedAgung PerbowoNo ratings yet
- Management La Distanta-Tipuri de ManagememtDocument9 pagesManagement La Distanta-Tipuri de ManagememtAndreeaDeEaNo ratings yet
- Angel Correa-Pedreros - LSA 3 Final Lesson Plan - DELTA Module 2Document11 pagesAngel Correa-Pedreros - LSA 3 Final Lesson Plan - DELTA Module 2ÁngelNo ratings yet
- Pothole DetectionDocument28 pagesPothole DetectionSwati Sharma0% (1)