Professional Documents
Culture Documents
248 T Bearing (Sliding) H
248 T Bearing (Sliding) H
Uploaded by
manoj_structureOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
248 T Bearing (Sliding) H
248 T Bearing (Sliding) H
Uploaded by
manoj_structureCopyright:
Available Formats
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
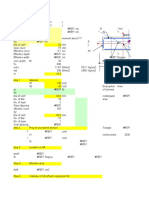
DESIGN CALCULATION FOR FIXED BEARING
Design Data
Span of bridge
Standard Temp.
Rotation ( Total)
Rotation(due to permanent action)
Rotation ( due to variable action)
Grade of concrete
Concrete stress ( Non seismic)
Concrete stress ( seismic)
Neoprene Pad stress
PTFE stress (working )
Steel stress(working ) for design use
65
+-25
0.01 x
0.0075 x
0.0025 x
M40
20
25
35
40
280
m
C
1.30 =
1.30 =
1.30 =
Mpa
Mpa
Mpa
Mpa
Mpa
DESIGN DIMENSION OF FIXED BEARING
Neoprene pad dia
Neoprene pad thickness
Pot base effective dia (actual)
Pot base thickness
Pot internal dia
Pot depth
Pot wall thickness
Piston effective contact dia
Piston thickness above spiggot
Spiggot projection
Bolt diameter
No. of bolt per component
Bolt flange thickness
No of sealing ring
Total thickness of rings
Dia of pedestal
Vertical face of Piston
Length of Lug
Thickness of distribution plate
Dia of distribution plate
Kailash Builders
372.0
26.0
480.00
28.00
372.00
47.00
44.00
480.00
30.00
36.00
20.00
12
16.00
2
4.00
960.00
9.00
20.00
25
620
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
nos
mm
nos
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
0.013 radian
0.00975 radian
0.00325 radian
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Loading and Requirement
Non Seismic Case
Load
MT
Vertical Load
Dead Load + Live load
250.00
Total
250.00
Horizental Load
Total
Longitudinal
Transverse
Resultant
25.00
0.00
25
Seismic Case
Load
MT
Vertical Load
Dead Load + Live load
250.00
Total
250.00
Horizental Load
Total
Longitudinal
Transverse
Resultant
41.20
0.00
41.20
Movement of superstructure
0.00 +
0.00 +
0.00 =
Calculation for permissible stresses in Pedestal concrete
Loaded area ( A2 )
x 480.00
^ 2.00
/ 4 = 180955.7368 mm^2
Dispersed area( A1)
x 960.00
^ 2.00
/ 4 = 723822.9474 mm^2
Permissible concrete stress
A1
A2
x 0.25 fck
20 Mpa
Non Seismic Case
Design of Neoprene Pad (IRC-83 part (iii) clause 926.2.3)
Neoprene pad stress
Kailash Builders
250.00
0.785
x 10000
=
x 372 ^ 2
23 Mpa <
Hence OK
35 Mpa
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Concrete stress at Pot Base (IRC-83 part (iii) clause 926.1.5)
I . Direct Bearing stress due to vertical load
=
250.00
0.785
14 Mpa <
x 10000
x 480 ^ 2
20 Mpa
Hence OK
II.Flexural stress due to active resulting from acting horizontal force
Eccentricity
Stress
28 +
26 +
4 =
25 x
10000 x
0.0982 x
480.0 ^ 3
1.336 Mpa
58
mm
58
III.Flexural stress due to induced resulting from resistance to Rotation
1) M. e.d. =
di^3 x ( k1 .p + k2. v)
di =
k1=
k2 =
p =
v =
M .ed =
=
=
2)
372.0 mm
2.09
89.314
0.00975 radian
0.00325 radian
372.0
51478848
15991389.3 N-mm
di / he =
^3 x(
x 0.311
M . R.d =
M . R.d =
Total induced moment =
=
=
15
2.2
k2
14.31
89.314
12.5
58.8
15
101
0.0098 +
89.3 x
186.00 x
9300000 N-mm
M .ed +
15991389 +
25291389
0.0982 x
Kailash Builders
12.5
1.8
372.0
186
186.00 mm
25.00 t
= 14.31
14.31
2.089
2.09 x
0.20 x
=
372.0
26.0
k1
0.2 x C x H
C=
H=
Stress
IRC- 83 Part (iii) clause 926.1.5.1
2.3
M . R.d
9300000
25291389
480.0 ^ 3
Mpa
25.00 x
10000
0.0033
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Total flexual stress
1.336 +
2.33 =
3.665 Mpa
<
15.00 Mpa
Hence OK
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.3)
IV.Coexisting direct and Flexural stress check (IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.3)
Stress =
13.82
20
3.66 =
15.00
<
0.94
1.00
Hence OK
Concrete stress at Piston Base
I.Direct bearing stress due to Vertical load (IRC-83-iii-clause 926.1.5)
Stress =
250.00 x
0.785
10000
x 480 ^ 2
<
13.82 Mpa
172.5 Mpa
Hence OK
II.Flexual stress due to active moment resulting from acting horizental force
e =
Stress
30 +
=
=
36 -
4.00 =
62 mm
25 x
10000 x
0.0982 x
480.0 ^ 3
1.428 Mpa
62
III.Flexural stress due to induced moment resulting from resistance to Rotation
1) M. e.d. =
di =
k1=
k2 =
p =
v =
Kailash Builders
di^3 x ( k1 .p + k2. v)
372.0 mm
2.09
89.314
0.00975 radian
0.00325 radian
IRC- 83 Part (iii) clause 926.1.5.1
di / he =
372.0
26.0
= 14.31
k1
14.31
2.089
12.5
1.8
15
2.2
k2
14.31
89.314
12.5
58.8
15
101
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
M .ed =
=
=
2)
372.0
51478848
15991389.3 N-mm
^3 x(
x 0.311
M . R.d =
89.3 x
0.0033
372.0
186
186.00 mm
25.00 t
M . R.d =
0.20 x
=
186.00 x
25.00 x
10000
9300000 N-mm
Total induced moment =
M .ed +
15991389 +
25291389
=
=
=
0.0982 x
Total flexual stress
0.0098 +
0.2 x C x H
C=
H=
Stress
2.09 x
2.3
1.428 +
M . R.d
9300000
25291389
480.0 ^ 3
Mpa
2.33 =
3.757 Mpa
<
151.80 Mpa
Hence OK
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.)
IV.Coexisting direct and Flexural stress check (IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.3)
Stress =
13.82
172.5
Design of Pot Wall
Force from Pad
3.76 =
151.80
1.00
Hence OK
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.3.1.1.7)
=
Pressure from Pad ( P1 ) =
=
Total horizental force on wall =
372.00 x
26.00 x
222474.651634
2 x
47.00 x 44.00
53.79 Mpa
25.00 t
Total Horizental stress into wall due to horizental force ( P2 )
Kailash Builders
<
0.10
23
= 222474.652 N ( per one section of ring)
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Total P
=
=
=
25 x
10000
2 x
47.00 x 44.00
60.44 Mpa
P1 + P2
53.79 + 60.44
114.23
Mpa
<
168 Mpa
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.2.)
Hence OK
Seismic Case
Design of Neoprene Pad (IRC-83 part (iii) clause 926.2.3)
Neoprene pad stress
250.00
0.785
x 10000
=
x 372 ^ 2
23 Mpa <
x 10000
x 480 ^ 2
14 Mpa <
35 Mpa
Hence OK
Concrete stress at Pot Base (IRC-83 part (iii) clause 926.1.5)
I . Direct Bearing stress due to vertical load
=
250.00
0.785
25 Mpa
Hence OK
II.Flexural stress due to active resulting from acting horizontal force
Eccentricity
Stress
=
=
28 +
26 +
4 =
41 x
10000 x
0.0982 x
480.0 ^ 3
2.201 Mpa
58
mm
58
III.Flexural stress due to induced resulting from resistance to Rotation
1) M. e.d. =
di =
k1=
k2 =
p =
v =
Kailash Builders
di^3 x ( k1 .p + k2. v)
372.0 mm
2.09
89.314
0.00975 radian
0.00325 radian
IRC- 83 Part (iii) clause 926.1.5.1
di / he =
372.0
26.0
= 14.31
k1
14.31
2.089
12.5
1.8
15
2.2
k2
14.31
89.314
12.5
58.8
15
101
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
M .ed =
=
=
2)
372.0
51478848
15991389.3 N-mm
^3 x(
x 0.311
M . R.d =
89.3 x
186.00 x
25.00 x
10000
0.20 x
=
9300000 N-mm
Total induced moment =
M .ed +
15991389 +
25291389
=
=
=
0.0982 x
=
2.3
2.201 +
M . R.d
9300000
25291389
480.0 ^ 3
Mpa
2.33 =
4.530 Mpa
<
15.00 Mpa
Hence OK
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.3)
IV.Coexisting direct and Flexural stress check (IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.3)
Stress =
13.82
25
4.53 =
19.50
<
0.78
Hence OK
Concrete stress at Piston Base
I.Direct bearing stress due to Vertical load (IRC-83-iii-clause 926.1.5)
Stress =
250.00 x
0.785
10000
x 480 ^ 2
<
13.82 Mpa
Hence OK
Kailash Builders
0.0033
186.00 mm
25.00 t
M . R.d =
Total flexual stress
0.0098 +
0.2 x C x H
C=
H=
Stress
2.09 x
172.5 Mpa
1.00
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
II.Flexual stress due to active moment resulting from acting horizontal force
e =
30 +
Stress
=
=
36 -
4.00 =
62 mm
41 x
10000 x
0.0982 x
480.0 ^ 3
2.353 Mpa
62
III.Flexural stress due to induced moment resulting from resistance to Rotation
1) M. e.d. =
di^3 x ( k1 .p + k2. v)
di =
k1=
k2 =
p =
v =
M .ed =
=
=
2)
372.0 mm
2.09
89.314
0.00975 radian
0.00325 radian
372.0
51478848
15991389.3 N-mm
di / he =
= 14.31
14.31
2.089
12.5
1.8
15
2.2
k2
14.31
89.314
12.5
58.8
15
101
2.09 x
0.0098 +
89.3 x
186.00 x
41.20 x
10000
0.2 x C x H
C=
H=
M . R.d =
186.00 mm
41.20 t
0.20 x
Total induced moment =
=
=
15326400 N-mm
M .ed +
15991389 +
31317789
=
0.0982 x
=
Kailash Builders
372.0
26.0
k1
^3 x(
x 0.311
M . R.d =
Stress
IRC- 83 Part (iii) clause 926.1.5.1
2.9
M . R.d
15326400
31317789
480.0 ^ 3
Mpa
0.0033
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Total flexual stress
2.353 +
2.88 =
5.237 Mpa
<
151.80 Mpa
Hence OK
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.)
IV.Coexisting direct and Flexural stress check (IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.3)
Stress =
13.82
172.5
Design of Pot Wall
Force from Pad
5.24 =
151.80
<
0.11
1.00
Hence OK
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.3.1.1.7)
=
372.00 x
Pressure from Pad ( P1 ) =
26.00 x
23
= 222474.652 N ( per one section of ring)
222474.651634
2 x
47.00 x 44.00
53.79 Mpa
Total horizental force on wall =
41.20 t
Total Horizental stress into wall due to horizental force ( P2 )
=
Total P
=
=
=
41 x
10000
2 x
47.00 x 44.00
99.61 Mpa
P1 + P2
53.79 + 99.61
153.40
Mpa
<
Hence OK
Kailash Builders
168 Mpa
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.2.)
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
MISCELLANEOUS DESIGN CHECKS
Rotation capacity
( IRC-83 part III - clause 926.2.3)
Check compression at edge of Neoprene Pad
Max . Permitted =
=
=
0.15
Rotation ( Radius )
15 % of T
x 22.00
3.3 mm
( T is the thickness of neoprene pad less thick of ring)
( IRC-83 part -III - clause 926.2.3)
=
372
=
3.3
x 0.5
0.018 radian
>
0.01 radian
Hence OK
D/ T ratio of Neoprene Pad
( IRC-83 part -III - clause 926.2.3)
=
372.0
26.0
14.31
< 15
Hence OK
Vertical face of Piston required
Width =
( IRC-83 part -III - clause 926.3.1.3.1)
1.3 x Seismic H Load x
( Pot dia
- 1.50 )
1.30 x
370.50
41.20 x
x 0.75
6.884
<
10000
x 0.75 x 280
10000
x 280
9.00 mm
Hence OK
Bolt Design ( Non Seismic )
Total horizental force
Kailash Builders
( IRC-83 part -III - clause 926.3.6)
25 t
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Contribution to resistance by Bolts ( F1 )
Nos of Bolts
Diameter of Bolt
Cross section area
Total cross section area
Shear strenght of bolt Gr 8.8
Shear strenght of bolt Gr 8.8
=
=
=
=
=
=
12
20.00
245.00
2940.0
190
190
Total shear force offer by the Bolts ( F1 ) =
nos
mm
mm
mm
Mpa
Mpa ( Seismic case )
2940.00
x 190
10000
55.9 t ( Non -Seismic Case)
2940.00
x 190
10000
55.9 t ( Seismic Case)
Total shear force offer by the Bolts ( F1 ) =
Contribution to resistance by Friction ( F2 )
Vertical load ( min)
0 t ( Non-seismic )
Vertical load ( min)
0 t ( Seismic )
Co-efficient of friction between concrete and steel
Friction Force ( F2 )
0 x
0 =
0 t( Non-seismic case )
Friction Force ( F2 )
0 x
0 =
0 t ( Seismic case )
Total resistance offered =
( Non seismic case )
55.9 +
0 =
Total resistance offered =
( Seismic case )
55.9 +
DEWEL DESIGN
0.2
55.9 t
> 25.00 t
Hence OK
0 =
55.9 t
> 41.20 t
Hence OK
( IRC-83 part -III - clause 926.3.6.5)
Dia =
50 mm
Length
190 mm
Non-seismic case and Seismic case
Horizental force over Dowel by Bolt
=
3 x
245 x
Stress =
50 x
139650
190
190 =
=
139650 N
14.70 Mpa
< 15.00 Mpa
Hence OK
Kailash Builders
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
POT INTERFACE
( IRC-83 part -III - clause 926.3.1.1.7)
Non - Seismic
Shear stress at cylinder and base interface considering 1mm slice
Fluid Pressure ( P1 )
=
=
=
Horizental force ( P2) =
=
=
Total stress
he x cc
bp
26.0 x 23.00
44.00
13.59
Mpa
1.5
di
1.5 x
372.0 x
22.911
13.59 +
x H
x bp
250000
44.00
Mpa
22.91 =
36.5 Mpa
< 126.0 Mpa
Hence OK
51.3 Mpa
< 126.0 Mpa
Hence OK
Seismic
Shear stress at cylinder and base interface considering 1mm slice
Fluid Pressure ( P1 )
=
=
=
Horizental force ( P2) =
=
=
Total stress
Kailash Builders
he x cc
bp
26.0 x 23.00
44.00
13.59
Mpa
1.5
di
1.5 x
372.0 x
37.757
13.59 +
x H
x bp
412000
44.00
Mpa
37.76 =
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Bearing stress at cylinder and base interface 1mm slice
Non-seismic case
Fluid pressuse( P1 )
Horizental force (P2)
6 x cc x he^
2 x
bp ^
6.0 x
2.0 x
Total stress
23.0 x 676.0
1936.00
24.1 Mpa
1.5 x
2
2
6.0 x H x ha
di x bp ^
2
1.5 x
6.0 x
372.0 x
250000 x 30.00
1936.00
93.7 Mpa
24.1 +
93.7 =
117.8 Mpa
< 184.8 Mpa
Hence OK
combine stressat cylindrical base interface considering 1mm slice
=
13881.55285396
133.7119050167 <
3997.32068922
252
Hence OK
Seismic case
Fluid pressuse( P1 )
Horizental force (P2)
6.0 x
2.0 x
2
2
23.0 x 676.0
1936.00
24.1 Mpa
1.5 x
Kailash Builders
6 x cc x he^
2 x
bp ^
1.5 x
154.5 Mpa
6.0 x H x ha
di x bp ^
2
6.0 x
372.0 x
412000 x 30.00
1936.00
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Total stress
24.1 +
154.5 =
178.6 Mpa
< 184.8 Mpa
Hence OK
combine stressat cylindrical base interface considering 1mm slice
=
31881.5
7910.05059985
199.48 <
252
Hence OK
Stress into Lugs because of Horizontal force
Non-Seismic case
Total horizental force on bearing
Effective length of Lug taking shear
=
=
3.0 x
Thickness of Lug
Total cross sectional area of Lug
(Each Lug)
Total nos of Lug in each bearin
Horizental force on each Lug
Stress on Lug due to Horizental force
25 t
20.0 =
60.0 mm
16.00 mm
60.0 x
16.0 =
960 mm^2
12 nos
25
12
2t
20833.3333333
960
= 22 Mpa
<
126.0 Mpa
Hence OK
Seismic case
Total horizental force on bearing
Effective length of Lug taking shear
=
=
3.0 x
Thickness of Lug
Total cross sectional area of Lug
(Each Lug)
Total nos of Lug in each bearin
Horizental force on each Lug
Kailash Builders
25 t
20.0 =
60.0 mm
16.00 mm
60.0 x
16.0 =
12 nos
41.20
12
3t
960 mm^2
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Stress on Lug due to Horizental force
34333.3333333
960
<
= 36 Mpa
Check for thickness of Piston in bending : Top
Maximum Vertical load
Effective dia of Piston
=
=
250.00 t
480.00 mm
Effective area of the Top plate which contact with concrete
=
3.142 x
480.000 ^ 2
4
=
180955.7 mm^2
Stress on Top Plate
250.000 x 10000
180955.7
13.8 Mpa
Diameter of loaded area (Pad) =
Projection of piston
372.0 mm
480.00
372.0
Bending moment on the Top Plate =
54.0 mm
13.8 x
54.0^ 2
2
20143.05 N-mm
Thickness of Top Plate reqd to cater the B.M. =
20143.05
1 x
=
25.6 mm
6
184.8
<
30.0 mm
Hence OK
Check for thickness of pot in bending : Bottom
Maximum Vertical load
Effective dia of Piston
=
=
250.00 t
480.00 mm
Effective area of the Bottom plate which contact with concrete
=
3.142 x
480.000 ^ 2
4
=
180955.7 mm^2
Stress on Bot Plate
=
Diameter of loaded area (Pad) =
Projection of piston
Kailash Builders
250.000 x 10000
180955.7
13.8 Mpa
372.0 mm
480.00
372.0
126.0 Mpa
Hence OK
54.0 mm
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Bending moment on the Bot Plate =
13.8 x
54.0^ 2
2
20143.05 N-mm
Thickness of bottom Plate reqd to cater the B.M. =
20143.05
1 x
=
25.6 mm
6
184.8
<
28.0 mm
Hence OK
Kailash Builders
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
DESIGN CALCULATION FOR SLIDING BEARING
Design Data
Span of bridge
Standard Temp.
Rotation ( Total)
Rotation(due to permanent action)
Rotation ( due to variable action)
Grade of concrete
Concrete stress ( Non seismic)
Concrete stress ( seismic)
Neoprene Pad stress
PTFE stress (working )
Steel stress(working ) for design use
65
+-25
0.01 x
0.0075 x
0.0025 x
M40
20
25
35
40
280
m
C
1.30 =
1.30 =
1.30 =
Mpa
Mpa
Mpa
Mpa
Mpa
DESIGN DIMENSION OF SLIDING BEARING
Neoprene pad dia
Neoprene pad thickness
PTFE size
Pot base effective dia (actual)
Pot base thickness
Pot internal dia
Pot depth
Pot wall thickness
Slide plate contact area dia
Slide plate thickness
Stainless steel thick( Gr 304 )
Effective thickness of slide plate
Piston outer diameter
Piston thickness above spiggot
Spiggot projection
Slide plate dimension (Rect )
Height of Guide Bar
Width of Guide Bar
Length of piston flat
Bolt diameter
No. of bolt per component
Bolt flange thickness
No of sealing ring
Total thickness of rings
Dia of pedestal
Vertical face of Piston
Width of Lug
Thickness of distribution plate
Size of Distribution plate
Kailash Builders
480.0
480.0
380.0
26.0
380.0
480.00
28.00
380.00
47.00
40.00
430.00
22.00
3.00
24.00
420.00
15.00
36.00
490.00
20.00
27.50
360.00
20.00
10
16.00
2
4.00
960.00
10.00
20.00
25
630
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
nos
mm
nos
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
mm
0.013 radian
0.00975 radian
0.00325 radian
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Loading and Requirement
Non Seismic Case
Load
MT
Vertical Load
Dead Load + Live load
Total
250.00
250.00
Horizontal Load
Total
Longitudinal
Transverse
Resultant
25.00
0.00
25
Seismic Case
Load
MT
Vertical Load
Dead Load + Live load
Total
250.00
250.00
Horizontal Load
Total
Longitudinal
Transverse
Resultant
25.00
0.00
25.00
Movement of superstructure
13 mm
Calculation for permissible stresses in Pedestal concrete
Loaded area ( A2 )
x 480.0
^ 2.00
/ 4 =
180955.737 mm^2
Dispersed area( A1)
x 960.0
^ 2.00
/ 4 =
723822.947 mm^2
Permissible concrete stress
A1
A2
x 0.25 fck
20 Mpa
Non Seismic Case
Design of Neoprene Pad (IRC-83 part (iii) clause 926.2.3)
Neoprene pad stress
PTFE stress
Kailash Builders
250.00
0.785
x 10000
=
x 380 ^ 2
22 Mpa <
250.00
0.785
x 10000
=
x 380 ^ 2
22 Mpa <
35 Mpa
Hence OK
Hence OK
40 Mpa
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Concrete stress at Pot Base (IRC-83 part (iii) clause 926.1.5)
I . Direct Bearing stress due to vertical load
=
250.00
0.785
14 Mpa <
x 10000
x 480 ^ 2
20 Mpa
Hence OK
II.Flexural stress due to active resulting from acting horizontal force
Eccentricity
Stress
28 +
26 +
4 =
25 x
10000 x
0.0982 x
480.0 ^ 3
1.336 Mpa
58
mm
58
III.Flexural stress due to induced resulting from resistance to Rotation
1) M. e.d. =
di^3 x ( k1 .p + k2. v)
di =
k1=
k2 =
p =
v =
M .ed =
=
=
2)
380.0 mm
2.14
94.508
0.00975 radian
0.00325 radian
di / he =
380.0
^3 x(
54872000
x 0.328
17998016 N-mm
M . R.d =
M . R.d =
Total induced moment =
=
=
15
2.2
k2
14.62
94.508
12.5
58.8
15
101
0.0098 +
94.5 x
190.0 x
9500000 N-mm
M .ed +
17998016 +
27498016
0.0982 x
Kailash Builders
12.5
1.8
380.0
190
190.00 mm
25.00 t
= 14.62
14.62
2.138
2.14 x
0.20 x
=
380.0
26.0
k1
0.2 x C x H
C=
H=
Stress
IRC- 83 Part (iii) clause 926.1.5.1
2.5
M . R.d
9500000
27498016
480.0 ^ 3
Mpa
25.00 x
10000
0.0033
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Total flexual stress
1.336 +
2.53 =
3.868 Mpa
<
15.00 Mpa
Hence OK
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.3)
IV.Coexisting direct and Flexural stress check (IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.3)
Stress =
13.82
20
3.87 =
15.00
0.95
<
Hence OK
1.00
Concrete stress at Top Plate
I.Direct bearing stress due to Vertical load (IRC-83-iii-clause 926.1.5)
Stress =
250.00 x
0.785
10000
x 430 ^ 2
<
17.22 Mpa
172.5 Mpa
Hence OK
II.Flexual stress due to active moment resulting from acting horizental force
e =
Stress
22 +
=
=
3 =
25 mm
25 x
10000 x
0.0982 x
430.0 ^ 3
0.801 Mpa
25
III.Flexural stress due to induced moment resulting from resistance to Rotation
1) M. e.d. =
di =
k1=
k2 =
p =
v =
M .ed =
=
=
2)
di^3 x ( k1 .p + k2. v)
380.0 mm
2.14
94.508
0.00975 radian
0.00325 radian
di / he =
380.0
^3 x(
54872000
x 0.328
17998016 N-mm
M . R.d =
190.00 mm
380.0
26.0
= 14.62
k1
14.62
2.138
12.5
1.8
15
2.2
k2
14.62
94.508
12.5
58.8
15
101
0.0098 +
94.5 x
2.14 x
0.2 x C x H
C=
Kailash Builders
IRC- 83 Part (iii) clause 926.1.5.1
380.0
190
0.0033
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
H=
25.00 t
M . R.d =
0.20 x
=
M .ed +
17998016 +
27498016
=
=
=
0.0982 x
Total flexual stress
25.00 x
10000
9500000 N-mm
Total induced moment =
Stress
190.00 x
3.5
0.801 +
M . R.d
9500000
27498016
430.0 ^ 3
Mpa
3.52 =
4.324 Mpa
<
151.80 Mpa
Hence OK
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.)
IV.Coexisting direct and Flexural stress check (IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.3)
Stress =
13.82
172.5
Design of Pot Wall
4.32 =
151.80
0.11
<
Hence OK
1.00
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.3.1.1.7)
Force from Pad
380.00 x
Pressure from Pad ( P1 ) =
26.00 x
22
217791 N ( per one section of ring)
217790.97476
2 x
47.00 x 40.00
57.92 Mpa
Total horizental force on wall =
25.00 t
Total Horizental stress into wall due to horizontal force ( P2 )
=
Total P
=
=
=
25 x
10000
2 x
47.00 x 40.00
66.49 Mpa
P1 + P2
57.92 + 66.49
124.41
Mpa
<
Hence OK
Kailash Builders
168 Mpa
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.2.)
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Seismic Case
Design of Neoprene Pad (IRC-83 part (iii) clause 926.2.3)
Neoprene pad stress
PTFE stress
250.00
0.785
x 10000
=
x 380 ^ 2
22 Mpa <
250.00
0.785
x 10000
=
x 380 ^ 2
22 Mpa <
35 Mpa
Hence OK
40 Mpa
Hence OK
Concrete stress at Pot Base (IRC-83 part (iii) clause 926.1.5)
I . Direct Bearing stress due to vertical load
=
250.00
0.785
14 Mpa <
x 10000
x 480 ^ 2
25 Mpa
Hence OK
II.Flexural stress due to active resulting from acting horizontal force
Eccentricity
Stress
28 +
26 +
4 =
25 x
10000 x
0.0982 x
480.0 ^ 3
1.336 Mpa
58
mm
58
III.Flexural stress due to induced resulting from resistance to Rotation
1) M. e.d. =
di^3 x ( k1 .p + k2. v)
di =
k1=
k2 =
p =
v =
M .ed =
=
=
2)
380.0 mm
2.14
94.508
0.00975 radian
0.00325 radian
di / he =
380.0
^3 x(
54872000
x 0.328
17998016 N-mm
M . R.d =
380.0
26.0
= 14.62
k1
14.62
2.138
12.5
1.8
15
2.2
k2
14.62
94.508
12.5
58.8
15
101
0.0098 +
94.5 x
25.00 x
10000
2.14 x
0.2 x C x H
C=
H=
M . R.d =
190.00 mm
25.00 t
0.20 x
Kailash Builders
IRC- 83 Part (iii) clause 926.1.5.1
190.00 x
9500000 N-mm
0.0033
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Total induced moment =
M .ed +
17998016 +
27498016
=
=
Stress
=
0.0982 x
Total flexual stress
2.5
1.336 +
M . R.d
9500000
27498016
480.0 ^ 3
Mpa
2.53 =
3.868 Mpa
<
18.75 Mpa
Hence OK
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.3)
IV.Coexisting direct and Flexural stress check (IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.3)
Stress =
13.82
25
3.87 =
19.50
0.75
<
Hence OK
1.00
stress at Top Plate
I.Direct bearing stress due to Vertical load (IRC-83-iii-clause 926.1.5)
Stress =
250.00 x
0.785
10000
x 430 ^ 2
<
17.22 Mpa
172.5 Mpa
Hence OK
II.Flexual stress due to active moment resulting from acting horizontal force
e =
Stress
22 +
=
=
3 =
25 mm
25 x
10000 x
0.0982 x
430.0 ^ 3
0.801 Mpa
25
III.Flexural stress due to induced moment resulting from resistance to Rotation
1) M. e.d. =
di =
k1=
k2 =
p =
v =
Kailash Builders
di^3 x ( k1 .p + k2. v)
380.0 mm
2.14
94.508
0.00975 radian
0.00325 radian
IRC- 83 Part (iii) clause 926.1.5.1
di / he =
380.0
26.0
= 14.62
k1
14.62
2.138
12.5
1.8
15
2.2
k2
14.62
94.508
12.5
58.8
15
101
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
M .ed =
=
=
2)
380.0
^3 x(
54872000
x 0.328
17998016 N-mm
M . R.d =
2.14 x
0.0098 +
94.5 x
25.00 x
10000
0.0033
0.2 x C x H
C=
H=
190.00 mm
25.00 t
M . R.d =
0.20 x
=
9500000 N-mm
Total induced moment =
M .ed +
17998016 +
27498016
=
=
Stress
=
0.0982 x
Total flexual stress
190.00 x
3.5
0.801 +
M . R.d
9500000
27498016
430.0 ^ 3
Mpa
3.52 =
4.324 Mpa
<
151.80 Mpa
Hence OK
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.)
IV.Coexisting direct and Flexural stress check (IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.1.3)
Stress =
13.82
172.5
Design of Pot Wall
4.32 =
151.80
0.11
<
Hence OK
1.00
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.3.1.1.7)
Force from Pad
380.00 x
Pressure from Pad ( P1 ) =
26.00 x
22
217791 N ( per one section of ring)
217790.97476
2 x
47.00 x 40.00
57.92 Mpa
Total horizental force on wall =
25.00 t
Total Horizental stress into wall due to horizental force ( P2 )
=
Total P
=
=
=
Kailash Builders
25 x
10000
2 x
47.00 x 40.00
66.49 Mpa
P1 + P2
57.92 + 66.49
124.41
Mpa
<
168 Mpa
( IRC-83-iii-clause 926.2.2.)
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Hence OK
MISCELLANEOUS DESIGN CHECKS
Rotation capacity
( IRC-83 part III - clause 926.2.3)
Check compression at edge of Neoprene Pad
Max . Permitted =
=
=
15 % of T
x 22.00
3.3 mm
0.15
Rotation ( Radius )
( T is the thickness of neoprene pad less thick of ring)
( IRC-83 part -III - clause 926.2.3)
3.3
x 0.5
380
=
0.017 radian
>
0.01 radian
Hence OK
D/ T ratio of Neoprene Pad
( IRC-83 part -III - clause 926.2.3)
=
380.0
26.0
14.6 Mpa
< 15 Mpa
Hence OK
Vertical face of Piston required
Width =
( Pot dia
( IRC-83 part -III - clause 926.3.1.3.1)
1.3 x Seismic H Load x
- 1.50 )
1.30 x
378.50
25.00 x
x 0.75
4.1
<
10000
x 0.75 x 280
10000
x 280
10.00 mm
Hence OK
Kailash Builders
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Slidling Capacity
( IRC-83 part -III - clause 926.3.1.1.6.1)
Slide plate dimension (Rect )
480.00
Effective dia of concrete at top
Preset in Long. Direction
Longitudinal movement
Movement possible in one direction
490.00 mm
430.00 mm
0 mm
480.00 430.00
50.00 0.00
2
50.00 0.00
2
Movement possible in other direction
=
=
50.00 mm
25.0 mm
>
25.0 mm
>
13.0 mm
13.0 mm
Hence OK
Guides
Inside Dimension of slide plate
Length of Piston
490.00 435.00 -
Bolt Design ( Non Seismic )
Total horizontal force
27.50 10.00 -
27.50
5.00
435.00 mm
420.00 mm
=
=
( IRC-83 part -III - clause 926.3.6)
25 t
Contribution to resistance by Bolts ( F1 )
Nos of Bolts
Biameter of Bolt
Cross section area
Total cross section area
Shear strenght of bolt Gr 8.8
Shear strenght of bolt Gr 8.8
=
=
=
=
=
=
10
20.00
245.00
2450.0
190
190
Total shear force offer by the Bolts ( F1 ) =
nos
mm
mm
mm
Mpa
Mpa ( Seismic case )
2450.00
x 190
10000
46.6 t ( Non -Seismic Case)
2450.00
x 190
10000
46.6 t ( Seismic Case)
Total shear force offer by the Bolts ( F1 ) =
Contribution to resistance by Friction ( F2 )
Vertical load ( min)
0 t ( Non-seismic )
Vertical load ( min)
0 t ( Seismic )
Co-efficient of friction between concrete and steel
0.2
Friction Force ( F2 )
0 x
0 =
0 t( Non-seismic case )
Friction Force ( F2 )
0 x
0 =
0 t ( Seismic case )
Total resistance offered =
46.6 +
0 =
Kailash Builders
46.6 t
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
> 25.00 t
Hence OK
( Non seismic case )
Total resistance offered =
( Seismic case )
46.6 +
46.6 t
> 25.00 t
Hence OK
DOWEL DESIGN
Dia =
Length =
0 =
( IRC-83 part -III - clause 926.3.6.5)
50 mm
190 mm
Non-seismic case and Seismic case
Horizental force over Dowel by Bolt
=
3 x
245 x
Stress =
190 =
139650.00
50 x
190
139650 N
14.70 Mpa
< 15.00 Mpa
Hence OK
Stress in Guide Bar
(Non Seismic )
Shear stress
25.00 x 10000
27.50 x 360.00
Eccentricity
Moment
5 +
25.00 x
Flexual stress
0.5 x
10000 x
25 Mpa
15 =
12.5 =
<
126 Mpa
Hence OK
12.5 mm
3125000 N-mm
M
x
6
L x H^ 2
=
=
360.00 x
69 Mpa
3125000 x 6
27.50 ^ 2
<
168 Mpa
Hence OK
Combine stress at the Top Plate Guide Bar inter face
4743.1
82 Mpa
1913.07
<
252 Mpa
Hence OK
Stress in Guide Bar
( Seismic )
Shear stress
25.00 x 10000
27.50 x 360.00
Eccentricity
Moment
5 +
25.00 x
Kailash Builders
0.5 x
10000 x
25 Mpa
15 =
12.5 =
<
126 Mpa
Hence OK
12.5 mm
3125000 N-mm
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Flexual stress
M
x
6
L x H^ 2
=
=
360.00 x
69 Mpa
3125000 x 6
27.50 ^ 2
<
168 Mpa
Hence OK
Combine stress at the Top Plate Guide Bar inter face
4743.1
82 Mpa
1913.07
<
252 Mpa
Hence OK
POT INTERFACE
( IRC-83 part -III - clause 926.3.1.1.7)
Non - Seismic
Shear stress at cylinder and base interface considering 1mm slice
Fluid Pressure ( P1 )
=
=
=
Horizental force ( P2) =
=
=
Total stress
Kailash Builders
he x cc
bp
26.0 x 22.04
40.00
14.33
Mpa
1.5
di
1.5 x
380.0 x
24.671
14.33 +
x H
x bp
250000
40.00
Mpa
24.67 =
39.0 Mpa
< 126 Mpa
Hence OK
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Seismic
Shear stress at cylinder and base interface considering 1mm slice
Fluid Pressure ( P1 )
he x cc
bp
26.0 x 22.04
40.00
14.33
Mpa
=
=
=
Horizental force ( P2) =
1.5
di
1.5 x
380.0 x
24.671
=
=
Total stress
14.33 +
x H
x bp
250000
40.00
Mpa
24.67 =
39.0 Mpa
< 126 Mpa
Hence OK
Bearing stress at cylinder and base interface 1mm slice
Non-seismic case
Fluid pressuse( P1 )
Horizental force (P2)
6 x cc x he^
2 x
bp ^
6.0 x
2.0 x
Total stress
22.0 x 676.0
1600.00
27.9 Mpa
1.5 x
1.5 x
6.0 x H x ha
di x bp ^ 2
6.0 x
380.0 x
19309.888928
154.50809036 <
27.9 +
4562.86105982
252
Hence OK
Kailash Builders
250000 x 30.00
1600.00
111.0 Mpa
111.0 =
combine stressat cylindrical base interface considering 1mm slice
=
2
2
139.0 Mpa
<
185 Mpa
Hence OK
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Seismic case
Fluid pressuse( P1 )
6 x cc x he^
2 x
bp ^
6.0 x
2.0 x
Horizental force (P2)
22.0 x 676.0
1600.00
27.9 Mpa
1.5 x
1.5 x
Total stress
2
2
6.0 x H x ha
di x bp ^ 2
6.0 x
380.0 x
250000 x 30.00
1600.00
111.0 Mpa
27.9 +
111.0 =
139.0 Mpa
<
185 Mpa
Hence OK
combine stressat cylindrical base interface considering 1mm slice
=
19309.9
4562.86105982
154.51 <
252
Hence OK
Stress into Lugs because of Horizontal force
Non-Seismic case
Total horizontal force on bearing
Effective length of Lug taking shear
=
=
3.0 x
Thickness of Lug
Total cross sectional area of Lug
(Each Lug)
Total nos of Lug in each bearin
Horizental force on each Lug
Stress on Lug due to Horizental force
Kailash Builders
25 t
20.0 =
60 mm
16.00 mm
60.0 x
16.0 =
960 mm^2
12 nos
25
12
2t
20833.333333
960
= 22 Mpa
<
126 Mpa
Hence OK
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Seismic case
Total horizental force on bearing
Effective length of Lug taking shear
3.0 x
Thickness of Lug
Total cross sectional area of Lug
(Each Lug)
Total nos of Lug in each bearin
Horizental force on each Lug
Stress on Lug due to Horizental force
25 t
20.0 =
60 mm
16.00 mm
60.0 x
16.0 =
960 mm^2
10 nos
25.00
10
3t
25000
960
= 26 Mpa
<
126 Mpa
Hence OK
Check for thickness of Piston in bending : Top
Maximum Vertical load
Effective dia of Piston
=
=
250.00 t
430.00 mm
Effective area of the Top plate which contact with concrete
=
3.142 x
430.000 ^ 2
4
=
145220.1 mm^2
Stress on Top Plate
250.000 x 10000
145220.1
17.2 Mpa
Diameter of loaded area (Pad) =
Projection of piston
380.0 mm
430.00
Bending moment on the Top Plate =
380.0
25.0 mm
17.2 x
25.0^ 2
2
5379.76 N-mm
Thickness of Top Plate reqd to cater the B.M. =
5379.76
1 x
=
13.2 mm
6
184.8
<
24 mm
Hence OK
Kailash Builders
Design of Bearings for Gangnani Bridge
Check for thickness of pot in bending : Bottom
Maximum Vertical load
Effective dia of Piston
=
=
250.00 t
480.00 mm
Effective area of the Bottom plate which contact with concrete
=
3.142 x
480.000 ^ 2
4
=
180955.7 mm^2
Stress on Bot Plate
250.000 x 10000
180955.7
13.8 Mpa
Diameter of loaded area (Pad) =
Projection of piston
380.0 mm
480.00
Bending moment on the Bot Plate =
380.0
50.0 mm
13.8 x
50.0^ 2
2
17269.42 N-mm
Thickness of bottom Plate reqd to cater the B.M. =
17269.42
1 x
=
23.7 mm
6
184.8
<
28 mm
Hence OK
Kailash Builders
You might also like
- Final Pot Ptfe Design Sheet - 02.01.13Document47 pagesFinal Pot Ptfe Design Sheet - 02.01.13Sandeep Kumar75% (4)
- CribDocument1 pageCribskumarsrNo ratings yet
- Underground Winding SystemsDocument58 pagesUnderground Winding SystemsRuben Castro Quispe100% (1)
- ELASTOMERIC and POT PTFEDocument10 pagesELASTOMERIC and POT PTFESwapnil KNo ratings yet
- 2850-1992 KN S (Type - A1) Span P 51 Anti Uplift ArrangementDocument9 pages2850-1992 KN S (Type - A1) Span P 51 Anti Uplift ArrangementGaurav PatilNo ratings yet
- Design of Elastomeric BearingsDocument6 pagesDesign of Elastomeric BearingsHarshitha GaneshNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation of Spherical MSM Slide Guide (T) Bearing - 1800 KN (GB7) PDFDocument6 pagesDesign Calculation of Spherical MSM Slide Guide (T) Bearing - 1800 KN (GB7) PDFDusmantaKumarSahooNo ratings yet
- Elastomeric Bearing 21.6mDocument8 pagesElastomeric Bearing 21.6mnaresh KUMARNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Bearing-38.973 (Skew)Document37 pages1.0 Bearing-38.973 (Skew)vinoraamNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal BearingDocument6 pagesLongitudinal BearingDPJAIN INFRASTRUCTURENo ratings yet
- FB. 60M - Free Bearing DesignDocument10 pagesFB. 60M - Free Bearing DesignBasava SowmyaNo ratings yet
- Section Modulus CalculatorDocument14 pagesSection Modulus CalculatorSuyenthan SathishNo ratings yet
- Shear Conection Design - IS 800-2007Document4 pagesShear Conection Design - IS 800-2007Swapnil ToraskarNo ratings yet
- Bearing Design-30.0m - PSCDocument5 pagesBearing Design-30.0m - PSCSHARATH VASUPRADA100% (1)
- Elastromatric Bearing PadDocument7 pagesElastromatric Bearing PadIlancheral NedumaranNo ratings yet
- Loads On Pot - Ptfe Bearing - 3x17m SpanDocument12 pagesLoads On Pot - Ptfe Bearing - 3x17m SpanMalayKumarDebNo ratings yet
- Idn - 4Document5 pagesIdn - 4Anh KyNo ratings yet
- Bearing Design Method ADocument6 pagesBearing Design Method ALartit LIANTHAVYVANHNo ratings yet
- Bolted Connections: DR S R Satish Kumar, IIT MadrasDocument30 pagesBolted Connections: DR S R Satish Kumar, IIT MadraspjuvvadiNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Check in Prestressed GirderDocument3 pagesFatigue Check in Prestressed GirderViplawNo ratings yet
- Plate GirderDocument74 pagesPlate Girderarif_rubin100% (1)
- Cost Comparison PCC Vs RCC ReturnDocument3 pagesCost Comparison PCC Vs RCC Returndesign MridcNo ratings yet
- Elastomeric Bearings: 6 (1) Design Load On BearingsDocument8 pagesElastomeric Bearings: 6 (1) Design Load On BearingsCivil MexNo ratings yet
- 70R Loading, Live LoadDocument12 pages70R Loading, Live LoadTashi TamangNo ratings yet
- SDPL CH 148-160 Shuttering Design For Girder-Layout-23Document1 pageSDPL CH 148-160 Shuttering Design For Girder-Layout-23Sudeep JoshiNo ratings yet
- Bolted Splice DesignDocument8 pagesBolted Splice DesignAnonymous sfkedkymNo ratings yet
- TSR NIRMAN Bow String Girder Launching Design Note-06.05.2022Document1 pageTSR NIRMAN Bow String Girder Launching Design Note-06.05.2022sups madiNo ratings yet
- Bearing Pot Cum 27-08-2020Document48 pagesBearing Pot Cum 27-08-2020Hymavathi MNo ratings yet
- Design of Pot Ptfe Bearing (Free Bearing) As Per Irc 83:2002 (Part 3)Document7 pagesDesign of Pot Ptfe Bearing (Free Bearing) As Per Irc 83:2002 (Part 3)DPJAIN INFRASTRUCTURENo ratings yet
- 4.3 Design Values of Bending Moments and Shear ForcesDocument7 pages4.3 Design Values of Bending Moments and Shear Forcesmn4webNo ratings yet
- Design of Welded Plate GirderDocument25 pagesDesign of Welded Plate GirderJinshad UppukodenNo ratings yet
- Spliced ColumnsDocument10 pagesSpliced ColumnsgvlanushaNo ratings yet
- HMM Infra LTD, Anbala: Design of Trestle (Cribs)Document10 pagesHMM Infra LTD, Anbala: Design of Trestle (Cribs)Anonymous sfkedkymNo ratings yet
- Bridge PortionDocument16 pagesBridge PortionNagara SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Thulo Neti Khola Bridge - Abutment Design: Fig: Abutment (All Dimensions in Metres)Document4 pagesThulo Neti Khola Bridge - Abutment Design: Fig: Abutment (All Dimensions in Metres)Himal KafleNo ratings yet
- Design of POT-PTFE (Fixed)Document8 pagesDesign of POT-PTFE (Fixed)NONGTHONNo ratings yet
- Design of Cantilever Slab As Per Is 456 2000Document2 pagesDesign of Cantilever Slab As Per Is 456 2000airtelNo ratings yet
- Spread Sheet of Plate Girder-Is800-2007Document3 pagesSpread Sheet of Plate Girder-Is800-2007yedida v r aviswanadh100% (1)
- JSPL SectionsDocument7 pagesJSPL SectionsDebasish MondalNo ratings yet
- 2000 MM 1900 MM: Check For Crack Width As Per Is 456-2000Document1 page2000 MM 1900 MM: Check For Crack Width As Per Is 456-2000karthikmr85No ratings yet
- Elastomeric Bearing 13-09-13Document27 pagesElastomeric Bearing 13-09-13bulganinganguliNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Bearing ForcesDocument15 pagesCalculation of Bearing ForcesSajib DasNo ratings yet
- 2 - Axle Load PDFDocument17 pages2 - Axle Load PDFDebanjan MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- IRC Rigid Pavement DesignDocument15 pagesIRC Rigid Pavement DesignAjay SastryNo ratings yet
- Beam Bending Strenght Aisc 9th EditionDocument17 pagesBeam Bending Strenght Aisc 9th EditionKory Estes100% (1)
- DistributionTheory RevBDocument102 pagesDistributionTheory RevBNasser AmmariNo ratings yet
- Base Plate Design - Concrete Beam TheoryDocument3 pagesBase Plate Design - Concrete Beam TheoryDarsHan MoHanNo ratings yet
- Column Splice End Plate DesignDocument3 pagesColumn Splice End Plate DesigninnovativekarthiNo ratings yet
- Seismic ArrestorDocument8 pagesSeismic ArrestorankitNo ratings yet
- Pipe CulvertDocument14 pagesPipe CulvertPraveen M balaramNo ratings yet
- Design of Elastomeric Bearing Based On IRC 083-2-1987Document4 pagesDesign of Elastomeric Bearing Based On IRC 083-2-1987Babita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Plate Girder&GantryGirder NotesDocument18 pagesUnit 5 Plate Girder&GantryGirder NotesGautham SgNo ratings yet
- Precast Rib Beam DesignDocument1 pagePrecast Rib Beam Designanshutomar7915100% (1)
- SteelDocument80 pagesSteelAnonymous HJ7hmihhNo ratings yet
- Aci BeamDocument6 pagesAci BeamkumsbamaNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Design of PSC Girder by Working Stress MethodDocument50 pagesStep by Step Design of PSC Girder by Working Stress Methodpravin100% (3)
- Wing Wall DesignDocument19 pagesWing Wall DesignMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Retaining WallDocument41 pagesRetaining Wallp_ignatiusNo ratings yet
- Trafo Found DesignDocument6 pagesTrafo Found DesignIrshad Khan100% (1)
- Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsDocument26 pagesWorkbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsShubham mishraNo ratings yet
- Combined Gusset Plate DesignDocument3 pagesCombined Gusset Plate Designkalpanaadhi100% (3)
- Front ElevationDocument1 pageFront Elevationmanoj_structureNo ratings yet
- DeflectionDocument22 pagesDeflectionrobertantoreniNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Analysis and Design of TDocument49 pagesPresentation On Analysis and Design of Tmanoj_structureNo ratings yet
- B 10 MM 8" C/C 10 MM 6" C/C A: Reinf. Schedule in Slab Reinf. Dia Spacing MarkDocument1 pageB 10 MM 8" C/C 10 MM 6" C/C A: Reinf. Schedule in Slab Reinf. Dia Spacing Markmanoj_structureNo ratings yet
- Hamesh Manchanda GF Slab 1Document1 pageHamesh Manchanda GF Slab 1manoj_structureNo ratings yet
- Asi 810 05 R1Document1 pageAsi 810 05 R1manoj_structureNo ratings yet
- Concrete Design Excel SheetDocument16 pagesConcrete Design Excel SheetCleth Hiren Santos25% (4)
- 14-Apr-07 24-May-2013 11:38 Vented Causeway 3M X 3M Analysis For Class A Double Lane Loading - STDDocument1 page14-Apr-07 24-May-2013 11:38 Vented Causeway 3M X 3M Analysis For Class A Double Lane Loading - STDmanoj_structureNo ratings yet
- Is 802 - Load CombinationDocument3 pagesIs 802 - Load Combinationmanoj_structureNo ratings yet
- Stringers ISMC MM Th. CHQ Plate Decking X Girder ISMCDocument1 pageStringers ISMC MM Th. CHQ Plate Decking X Girder ISMCmanoj_structureNo ratings yet
- PLAN1a PDFDocument1 pagePLAN1a PDFmanoj_structureNo ratings yet
- First Floor Layout PlanDocument1 pageFirst Floor Layout Planmanoj_structureNo ratings yet
- Structural MechanicsDocument649 pagesStructural MechanicsNanda Moreira100% (1)
- Rpt. 195 Load Rating Bridges W o Plans 1j0rx7yDocument66 pagesRpt. 195 Load Rating Bridges W o Plans 1j0rx7yMahmoud BayatNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Automatic Shoe Polishing Machine: Technical ReportDocument5 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Automatic Shoe Polishing Machine: Technical Reportesubalew tadesseNo ratings yet
- M.tech ME Machine Design R17Document51 pagesM.tech ME Machine Design R17Lakshmi Narayana SNo ratings yet
- IRC 112-2011 Concrete Road Bridges PDFDocument289 pagesIRC 112-2011 Concrete Road Bridges PDFBiswa Balla89% (18)
- Ahammed & Melchers 1996Document6 pagesAhammed & Melchers 1996Michael McconnellNo ratings yet
- Life Assessment Ship Unloader CraneDocument5 pagesLife Assessment Ship Unloader CraneArif SugihartoNo ratings yet
- Plate Theory Slides From WEB PDFDocument20 pagesPlate Theory Slides From WEB PDFHarish ShridharamurthyNo ratings yet
- Collings, David - Steel Concrete Composite Bridges (2005, Thomas Telford Publishing) PDFDocument195 pagesCollings, David - Steel Concrete Composite Bridges (2005, Thomas Telford Publishing) PDFjasmina100% (2)
- At 14 2Document7 pagesAt 14 2Icz Fuentes100% (1)
- Static Analysis of Tractor Trolley AxleDocument5 pagesStatic Analysis of Tractor Trolley AxleseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- Material Properties: (ESE - 1992) (ESE - 1992)Document121 pagesMaterial Properties: (ESE - 1992) (ESE - 1992)Sanket ManeNo ratings yet
- Análisis e Investigación de Fallas de Fractura en El Eje de Transmisión de PositivoDocument18 pagesAnálisis e Investigación de Fallas de Fractura en El Eje de Transmisión de Positivojohnny oreNo ratings yet
- Ship Collision Finite Element AnalysisDocument29 pagesShip Collision Finite Element AnalysisGobinda SinhaNo ratings yet
- Thesis FulltextDocument472 pagesThesis FulltextBhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Tool LifeDocument22 pagesTool LifeDhruv Bhalala100% (1)
- AISC Design Guide 29 - Vertical Bracing Connections - Analysis and Design 2 de 2 PDFDocument196 pagesAISC Design Guide 29 - Vertical Bracing Connections - Analysis and Design 2 de 2 PDFMartin Cristobal CupitayNo ratings yet
- Study On The Residual Stress of Bar With Straightening by Two RollsDocument6 pagesStudy On The Residual Stress of Bar With Straightening by Two RollsArmando FaríasNo ratings yet
- Mahalakshmi: Engineering CollegeDocument16 pagesMahalakshmi: Engineering CollegeVijeesh VijayalayamNo ratings yet
- UNIT-5 SpringsDocument6 pagesUNIT-5 SpringsUday Narasimha100% (2)
- Eng TipsDocument5 pagesEng TipsBenedictus MurdonoNo ratings yet
- 59-Numerical Analysis of Masonry Arch Bridges Benefits and Limits of Damage MechanicsDocument8 pages59-Numerical Analysis of Masonry Arch Bridges Benefits and Limits of Damage MechanicsvttrlcNo ratings yet
- ICMPT 2019 Proceedindgs PDFDocument762 pagesICMPT 2019 Proceedindgs PDFBiswajitRoyNo ratings yet
- Design Provisions For Shear WallsDocument13 pagesDesign Provisions For Shear WallsRm1262No ratings yet
- Filling and Emptying State of Silos Above DischargDocument6 pagesFilling and Emptying State of Silos Above DischargBartłomiej MinorNo ratings yet
- AP-T188-11 - Review of Structural Design Procedures For Foamed Bitumen PavementsDocument82 pagesAP-T188-11 - Review of Structural Design Procedures For Foamed Bitumen Pavementsaskarah100% (1)
- Mechanics:-: AS Level Physics: Terms & DefinitionsDocument7 pagesMechanics:-: AS Level Physics: Terms & DefinitionsJenniferNo ratings yet
- Eaton Metal SealsDocument60 pagesEaton Metal SealsmyegnrNo ratings yet
- Design For Punching Shear Strength With ACI 318-95: Aci Structural Journal Technical PaperDocument11 pagesDesign For Punching Shear Strength With ACI 318-95: Aci Structural Journal Technical PaperJoseph AsfourNo ratings yet