Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mm'mon FOR MAKIN: Filed Aug. 8, 1925
Mm'mon FOR MAKIN: Filed Aug. 8, 1925
Uploaded by
arufatoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Preparation of Methylamine Hydrochloride From Acetamide by Means of Calcium HypochloriteDocument3 pagesThe Preparation of Methylamine Hydrochloride From Acetamide by Means of Calcium Hypochloritegeovani2100% (1)
- Nalco New Approach For MacrofoulingDocument73 pagesNalco New Approach For Macrofoulingarufato100% (2)
- J. N. CarothersDocument4 pagesJ. N. CarothershaviedNo ratings yet
- United States Patent Office: Patented Jan. I9, 1954Document2 pagesUnited States Patent Office: Patented Jan. I9, 1954JavierNo ratings yet
- UNITED Starts: Patented Apr. 16, 1935Document2 pagesUNITED Starts: Patented Apr. 16, 1935shalsinia chantalNo ratings yet
- Translate Paten US5976485Document24 pagesTranslate Paten US5976485Lenywulandari AyundaNo ratings yet
- Us 2021699Document5 pagesUs 2021699haviedNo ratings yet
- United States Patent Office: Production of Disopum PhosphateDocument2 pagesUnited States Patent Office: Production of Disopum PhosphatefredyNo ratings yet
- United States: Patent OfficeDocument3 pagesUnited States: Patent OfficefredyNo ratings yet
- United States Patent 0: '3, l50, l74 ICCDocument2 pagesUnited States Patent 0: '3, l50, l74 ICCMuhammadAmdadulHoqueNo ratings yet
- Patent Office: 5 Claims. (CL 260-69)Document2 pagesPatent Office: 5 Claims. (CL 260-69)Teleson MarquesNo ratings yet
- Storage: o - InzoDocument4 pagesStorage: o - InzoOscar SobradosNo ratings yet
- US3689216Document5 pagesUS3689216PABLO URIZ CEREZONo ratings yet
- A Safe Method For Preparation of Uncontaminated Hydrazoic AcidDocument1 pageA Safe Method For Preparation of Uncontaminated Hydrazoic Acidgeovani2No ratings yet
- Facturing Fertilizer Containing Potassium, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous CompoundsDocument1 pageFacturing Fertilizer Containing Potassium, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous CompoundsBharat A. KaduNo ratings yet
- A To The OF A Preliminary Study of Hitherto AND: ProcedureDocument11 pagesA To The OF A Preliminary Study of Hitherto AND: ProcedureMariaNo ratings yet
- United States Patent 0 "Ice: Patented May 9, 1972Document4 pagesUnited States Patent 0 "Ice: Patented May 9, 1972Nguyễn Thanh TùngNo ratings yet
- US3347627Document3 pagesUS3347627Nuttapong JongjitsatitmunNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: Inoue Et A) - (11) Patent Number: (45) Date of PatentDocument4 pagesUnited States Patent (191: Inoue Et A) - (11) Patent Number: (45) Date of PatentShrutiNo ratings yet
- US2321218Document3 pagesUS2321218shirazizadehsinaNo ratings yet
- Us 744128Document2 pagesUs 744128haviedNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: GermanyDocument5 pagesUnited States Patent (191: GermanyChem2014EngNo ratings yet
- United States Patent PO: Patented Nov. 20, 1956Document2 pagesUnited States Patent PO: Patented Nov. 20, 1956shenn0No ratings yet
- Unite Sites Fret (19) : DahlinDocument3 pagesUnite Sites Fret (19) : Dahlintrinh xuan hiepNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Assay of Acetyl PhosphateDocument4 pagesPreparation and Assay of Acetyl PhosphatecataawwwNo ratings yet
- United States Patent 0 ": Patented Dec. 15, 1959Document2 pagesUnited States Patent 0 ": Patented Dec. 15, 1959Aaron CurrieNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: Macdonald 145) Feb. 25, 1975Document4 pagesUnited States Patent (191: Macdonald 145) Feb. 25, 1975Javier Alejandro Rodriguez MelgozaNo ratings yet
- Pentaeritritol 2Document6 pagesPentaeritritol 2Ibnul BaasithNo ratings yet
- US3014784Document2 pagesUS3014784SatyamSahuNo ratings yet
- Us 2375054Document3 pagesUs 2375054haviedNo ratings yet
- Matrix Acidizing of Sandstone4Document5 pagesMatrix Acidizing of Sandstone4HelyaNo ratings yet
- Arsenal Philadelphia, Pa. 19137: FrankfordDocument23 pagesArsenal Philadelphia, Pa. 19137: FrankfordPutri PramodyaNo ratings yet
- Ingles CDocument8 pagesIngles Coscar rodriguezNo ratings yet
- US2301231Document2 pagesUS2301231Abu Mejza'atNo ratings yet
- July 20, 1954 J. L. Krieger 2,684,286: InventorDocument4 pagesJuly 20, 1954 J. L. Krieger 2,684,286: InventorNurhafizah Abd JabarNo ratings yet
- US1960211 (Sudah)Document3 pagesUS1960211 (Sudah)aris_nurhidayatNo ratings yet
- Filed June l5, 1935Document6 pagesFiled June l5, 1935Yustinus Selis ToronNo ratings yet
- This Invention Relates To A Process For Making A Stable CopperDocument3 pagesThis Invention Relates To A Process For Making A Stable CopperAngel BuenoNo ratings yet
- US3718545 (1) PatenteDocument8 pagesUS3718545 (1) PatenteAndrés BelloniNo ratings yet
- Launcelot: Massachusetts Health, Analysis, BostonDocument6 pagesLauncelot: Massachusetts Health, Analysis, BostonMaxi GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Patent Nines,: Nited StatesDocument2 pagesPatent Nines,: Nited Statesjeque661No ratings yet
- Arease: Nov. 8, 1966 W. Wogt Et Al 3,284,495 Process For The Continuous Manufacture, Purification andDocument3 pagesArease: Nov. 8, 1966 W. Wogt Et Al 3,284,495 Process For The Continuous Manufacture, Purification andRachmad HermawanNo ratings yet
- Us 3229777Document4 pagesUs 3229777Parth AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Us1951789 PDFDocument5 pagesUs1951789 PDFJames EdwardsNo ratings yet
- United States Patent Office: Patented Sept. 1, 1959Document4 pagesUnited States Patent Office: Patented Sept. 1, 1959هیمن مNo ratings yet
- Per Acetic AcidDocument5 pagesPer Acetic AcidMaruthi KNo ratings yet
- US3416887Document6 pagesUS3416887khairulNo ratings yet
- Patente 2Document3 pagesPatente 2Saul MamaniNo ratings yet
- AAS Methods 2520of 2520 ProductionDocument4 pagesAAS Methods 2520of 2520 Productionapi-3714811No ratings yet
- Copie de US2899444-1Document4 pagesCopie de US2899444-1KHALED KHALEDNo ratings yet
- Indigo Prodn. From Phenyl-Glycine Carboxylic Acid Salt - by Fusion in Mixed Potassium Hydroxide and Sodium Hydroxide Melt, Then OxidnDocument4 pagesIndigo Prodn. From Phenyl-Glycine Carboxylic Acid Salt - by Fusion in Mixed Potassium Hydroxide and Sodium Hydroxide Melt, Then OxidnCillian CreedonNo ratings yet
- Us2094573-Production of Potassumsulphate Ammonium Sulphate Double SaltDocument2 pagesUs2094573-Production of Potassumsulphate Ammonium Sulphate Double Saltkvsj2001No ratings yet
- Removal of Fluorine From Wet Process Phosphoric AcidDocument2 pagesRemoval of Fluorine From Wet Process Phosphoric AcidAdios ANo ratings yet
- Benzoic Acid To Benzaldehyde, P-Nitrobenzoic Acid To Nitrobenzene and More.Document3 pagesBenzoic Acid To Benzaldehyde, P-Nitrobenzoic Acid To Nitrobenzene and More.banjo010% (1)
- Rile From NH4Document10 pagesRile From NH4rrivera7396No ratings yet
- United States: Patent Office. VDocument2 pagesUnited States: Patent Office. VAmir HamzahNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: MercadeDocument4 pagesUnited States Patent (191: MercadeSoufi BadrNo ratings yet
- Determination of Gamma No and TSDocument3 pagesDetermination of Gamma No and TSAditya ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- United States Patent Office: Patented Mar. 13, 1951 ... ."Document2 pagesUnited States Patent Office: Patented Mar. 13, 1951 ... ."Ruchita PoilkarNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: Wu Et Al. (451 Nov. 6, 1979Document6 pagesUnited States Patent (191: Wu Et Al. (451 Nov. 6, 1979FatonaRifkyPNo ratings yet
- 5991-6846EN BrosurDocument8 pages5991-6846EN BrosurarufatoNo ratings yet
- Tolerance Chart: (Maximum Permissible Error)Document3 pagesTolerance Chart: (Maximum Permissible Error)arufatoNo ratings yet
- Catalog KaoDocument1 pageCatalog KaoarufatoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Temperature On PH v4 - TSP-01-2Document7 pagesEffects of Temperature On PH v4 - TSP-01-2Aridita AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- 14.12 Kulcsar U PDFDocument6 pages14.12 Kulcsar U PDFarufatoNo ratings yet
- ASTM D7740 Optimizing AASDocument9 pagesASTM D7740 Optimizing AASarufatoNo ratings yet
- Doc316 53 01486 PDFDocument6 pagesDoc316 53 01486 PDFarufatoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Temperature On PH v4 - TSP-01-2 PDFDocument7 pagesEffects of Temperature On PH v4 - TSP-01-2 PDFarufatoNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Design ProcedDocument30 pagesIon Exchange Design ProcedFajar IndrawanNo ratings yet
- Simulation Mixed BedDocument13 pagesSimulation Mixed BedarufatoNo ratings yet
- 30265527A V03.16 KarlFischer Titrators Broch EN LR PDFDocument16 pages30265527A V03.16 KarlFischer Titrators Broch EN LR PDFarufatoNo ratings yet
- 2015 11 06 - Cetamine Technology in Power Plants - Swedish Conference 2015Document42 pages2015 11 06 - Cetamine Technology in Power Plants - Swedish Conference 2015arufatoNo ratings yet
- Gfps Chemicals PowerPlantsDocument2 pagesGfps Chemicals PowerPlantsarufatoNo ratings yet
- History of Fluorine Recovery ProcessesDocument21 pagesHistory of Fluorine Recovery ProcessesmahaNo ratings yet
- Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (Pafc)Document10 pagesPhosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (Pafc)Else Feba Paul0% (1)
- Phosphoric Acid - MSDSDocument3 pagesPhosphoric Acid - MSDSSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2213343722017419 MainDocument21 pages1 s2.0 S2213343722017419 MainIkram ADNANENo ratings yet
- PiperacilinDocument2 pagesPiperacilinivaNo ratings yet
- Buffer SolutionsDocument6 pagesBuffer SolutionsIrmey Hamidi100% (1)
- 900 Inorganic Questions For IIT JEE ADVANCEDDocument64 pages900 Inorganic Questions For IIT JEE ADVANCEDSourabh Dhavala95% (19)
- Naval JellyDocument4 pagesNaval JellyjohnsopranaNo ratings yet
- GST Food Item ListDocument88 pagesGST Food Item ListgeorgiinaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1877705812045341 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S1877705812045341 MainJavier Alejandro RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Solubility and Complex-Ion Equilibria: Practice ExamplesDocument33 pagesSolubility and Complex-Ion Equilibria: Practice Exampleskennethleo69No ratings yet
- Uses of Phosphoric AcidDocument3 pagesUses of Phosphoric AcidMarnel Roy MayorNo ratings yet
- Di-Calcium Phosphate by Direct Acidulation of Phosphate RockDocument111 pagesDi-Calcium Phosphate by Direct Acidulation of Phosphate RockAshutosh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sciencedirect: The Use of Advanced Process Controls in A Phosphoric Acid ReactorDocument7 pagesSciencedirect: The Use of Advanced Process Controls in A Phosphoric Acid ReactorJavier Alejandro RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of The Wet Process Phosphor PDFDocument8 pagesFundamentals of The Wet Process Phosphor PDFVandenberg Soares de AndradeNo ratings yet
- EtanolDocument57 pagesEtanolexe241293No ratings yet
- History of Phosphoric Acid Technology (Evolution and Future Perspectives)Document7 pagesHistory of Phosphoric Acid Technology (Evolution and Future Perspectives)Fajar Zona67% (3)
- P-Block 15 To 16 GroupDocument38 pagesP-Block 15 To 16 GroupBharti GoelNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Technology Section 1Document14 pagesFertilizer Technology Section 1Roed Alejandro LlagaNo ratings yet
- LiteraturDocument94 pagesLiteraturMuhammad Iqbal MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Che 329 - Lectre - 2Document95 pagesChe 329 - Lectre - 2anandseshadri901No ratings yet
- June 2018 QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Chemistry AS-LevelDocument24 pagesJune 2018 QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Chemistry AS-LevelRunNo ratings yet
- Panamax Cargo Hold Cleaning Manual Rev00Document36 pagesPanamax Cargo Hold Cleaning Manual Rev00Cenk ÇobanNo ratings yet
- Cleaning & Sanitising - Food Processing IndustryDocument21 pagesCleaning & Sanitising - Food Processing Industrydrmarvin2k5100% (1)
- Lecture 21 PhosphorousDocument53 pagesLecture 21 PhosphorousAnilKumar100% (2)
- L Uk SulphDocument24 pagesL Uk SulphypyeeNo ratings yet
- Calcium Sulfate Crystallization in Phosphoric Acid PDFDocument133 pagesCalcium Sulfate Crystallization in Phosphoric Acid PDFabderrahimnNo ratings yet
- TSP Tour ReportDocument16 pagesTSP Tour ReportArefin ShahriarNo ratings yet
- Chemicalcleaning For BoilerDocument16 pagesChemicalcleaning For Boilerak_thimiriNo ratings yet
Mm'mon FOR MAKIN: Filed Aug. 8, 1925
Mm'mon FOR MAKIN: Filed Aug. 8, 1925
Uploaded by
arufatoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mm'mon FOR MAKIN: Filed Aug. 8, 1925
Mm'mon FOR MAKIN: Filed Aug. 8, 1925
Uploaded by
arufatoCopyright:
Available Formats
0a. so, 1928.
V "
v , _
I J. .N. CAROTHERS
,
_
mm'mon FOR MAKIN G
1,689,547.
TRI'-SODIUM PHOSPHATE.
Filed Aug. 8, 1925
J. . QRROTHER":
55a:
@2192:
'
1,689,547
Patented Oct. 30, 1928.
UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE. ,
JOHN R. CABOTHEBS, 0F ANNISTON, ALABAMA, ASSIGLIOB TO FEDERAL PHOSPHOBUS
COMPANY, OF BIRMINGHAM, ALABAMA, A COBIOP'ATION OF ALABAMA.
METHOD FOR MAKING TERI-SODIUM PHOSPHATE.
Application ?led August a, 1925. Serial m3. mass.
This invention relates to a method for by the chemical formula Na,PO.12H,O,
from which an inspection shows there is
making tri-sodium-phosphate, especially present
approximatel 57% water of crystaladapted to the use of concentrated phos
phoric acid.
5
I ,
lization. I proceed by adding sodium car
strong phosphoric acid simul
The object is td provide a method which bonate and
in a mixingtank, where vdi-sodium
requires less e uipment and is therefore less taneously
phosphate is formed. By strong phos
costly, and w ich at the same time, has
acid I mean an acid of such concen
greater e?iciency than existing methods phoric
tration
that it will not be necessary to em~
which are adapted to the use, of dilute phos
ploy any evaporation step in my process,
the water with the phosphoricacid, the
With these and other objects in view, the but
di-sodium
phosphate ?lter press water, and
invention consists in the novel details of a
that necessary to dissolve the caustic soda"
method embodying features of construcw will
provide enough to supply the water of
tion and combination of equipment consti
16 tuting my invention, more fully disclosed crystallization in the product. This acid 70
and particularly set forth in the appended may range from 50% to 75% HsPO? de
pendiInIg on operatingconditions, and while
,PO, may be continuously used pro
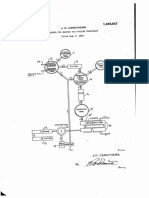
Referring to the accompanying drawing, 50%
vided
the
di-sodiuin ?lter press water be re
forming part of this speci cation, the appas
20 ratus comprises an acid tank 1 containing duced in proportion to the additional water
strong phosphoric acid, which is neutralized added by such acid, it is preferable to employ
by the addition of sodium carbonate to di acid of higher concentrations. The phos
sodium phosphate solution in mixing tank phoric acid and sodium carbonate are added
2, from which the solution passes through until di-sodium phosphate is formed, having,
10 phoric acid.
claims.
25 ?lter 3 into the receiving and mixing tank 4, in case iron tanks are used, a slight excess of
where caustic soda solution is added from sodium carbonate. Where acid resistant
dissolving tank 5.' After thoroughly mix-' tanks are used no excess of sodium carbonate
ing the resultant tri-sodium phosphate solu is needed. The chemical reaction is repre
tion in tank 4 it is assed through ?lter 6 and sented by the following equation:
30-,into receiving ta ,7, from which it ?ows
through crystallizers 8 which may have arti
?cial coolers 81 if desired. From the crystal-
lizers the crystals and a portion of the mother The solution is heated approximately 100
liquor pass into the centrifuge 9 where the ' C. by a heating coil 14 to expel all dissolved
35 crystals are de-watered. The mother liquor carbonic acid (00,) and to coagulate the
passes from the centrifuge 9 into the sump precipitate of iron, aluminum, calcium or
tank 10 and thence is returned by pump 11 magnesium phosphates, which will form if
to mixing tank 2 or'4, according to opera these impurities be present. In case this so
tion requirements, while the crystals pass lution is higher than 1.30-1.36 speci?c grav
40 ?rst through dryer 12" and then through ity at 85 0., wash water or mother liquor 95
be added to reduce the speci?c grav
cooler 13, after which they may be shipped should
as dried or screened crystals in any well ity to that mentioned. From the mixing
known manner. The elements of the, fore tank 2 the di-sodium phosphate solution
going apparatus are conveniently illus-\ passes through a ?lter of any standard type
45 trated as they constitute severally standard to remove the precipitate from the solution. 100
The clear solution of di-sodium phosphate
equipment.
1
In order that the operation of my method is then mixed with a caustic soda solution to
carried out in my apparatus may be clearly form tri-sodium phosphate. This reaction
understood and practiced by those skilled in is represented by the following equation:
50 the art, I will outline the procedure in NaJIPO, 121L120 +NaOH=
volved. In the production of tri-sodium phos
phate a large percentage of the compound
'
106
Na3PO,,.12H2O+H,O
is water which is present as water of crystals Caustic soda solution may be prepared by
lization. The compound is represented dissolving solid caustic, or commercial caus
1,689,547
tie solution may be used. The strength of
the solution may be varied, but if made from
solid caustic a solution containing approxi
mately 70-72% NaOH is preferred. Since
Having thus described my invention, what
claim as new and desire to secure by Let
ters Patent, is :
_
rocess for the
_ l. The hereindescribed
commercial caustic soda solution contains production of tri-sodium p osphate, whlch 70"
only approximately 50% NaOH, this may consists in subjecting sodium carbonate to
not be used exclusively; however, a mixture the action of phosphoric acid having more
of solid caustic dissolved in the commercial, than 50% HsPO4 to form di-sodium phos
solution may be' satisfactorily used. The phate, then adding su?icient caustic soda to
10 tri-sodium phos hate solution is then ?ltered
convert said dil-sodium phosphate into tri .75
in any standar ?lter to remove solid mat
ter introduced b the caustic, as well as an
precipitate whic
'ay result from the addi
tion of caustic so a to the di-sodium phos
phate solution. In the addition of caustic
soda, su?lcient is added until titration with
half normal acid of a sample of the solution
being causticized, shows a relation of the
end point of phenolphthalein and the end
points of phenolphthalein and methyl or
20
an e
sodium phosphate, substantially as de
scribed.
2. The hereindescribed process for the
production of tri-sodium' phosphate, which
consists in subjecting sodium carbonate to
the action of stron phosphoric acid havingv
more than 50% ,PO, to form .di-sodium
phosphate, then removing all solid matter,
then adding caustic soda to convert said d1
sodium phosphate to tri-sodium phosphate,
varying between 0.53 and 0.56, arrived substantially as described.
. at by dividin the reading from the phenol
phthalein en point, by t e sum of the phe
3. The hereindescribed
rocess for the
production of tri-sodium osphate, which
nolphthalein and methyl orange end points. consists in subjecting sodlum carbonate in
This relation of titrations is a simple and
to the action of strong ghosphoric
quick means of controlling the addition of solution,
acid having more than 50% HSP ,, to form
caustic. After causticizing, the solution. di-sodium phosphate, then remov'
all
should have a speci?c gravity from 1.36'to solid matter, then adding caustic so a so
1.40 at 85 C. for best operation. After ?l lution to convert said di-sodium phosphate
tration, the solution is run into any suitable into tri-sodium phosphate, then cooling said
crystallizing uipment. The use of a con tri-sodium- phosphate solution until crystals
tinuous. 'crysta izer is referred, as thereb of tri-sodium phosphate form, substantially
30
a continuous feed and 'scharge is obtaine . as described.
It is desirable to add a certain percentage of
mother liquor, from
4. The hereindescribed
revious crystalliza production
of tri-sodium
rocess for the
osphate, which
100
tions, to aid in suspen in the crystals and consists in subjecting a sodium carbonate so
to facilitate han/dling. g.lhe quantity of - lution
to the action of stron phosphoric
mother liquor added Wlll vary depending on acid to ,form a di-sodium phospiate
solution
operating conditions at the time, .andsthe
approximately 1.33 speci?c gravity at 85
only means of judging is the fact that crys- - of
(1., t en'removing all so id matter, then add
tals produced are of the size desired, and in? caustic soda solution to convert said di
hand e readily in the crystallizer. From the so ium phosphate into tri-sodium phos
(0
crystallizer, the crystals pass into a centri
_fuge where they are d'e-watered before pass
15 mg to the dryer. '
. "
ince the I melting point of tri-sodium
phate, then cooling said tri-s'odium phos
phosphate form, thenseparatin said crys
105
phate solution until crystals of tri-sodium
'110
tals from the accompanying s?ution', sub
phos hate is very' ow, it is necessary to stantially
as described.
avoiw overheating and either melting or
5. The hereindescribed rocess for the ,
partly de-hydrating the crystals. _ In order
of tri-sodium osphate, which
that the dried crystals may be .in the best production
consists in subjecting SOdluIII carbonate to 115
physical condition, it is preferable that they the action of stron phosphoric acid to form
passed through a cooler aftenthe dryer, 1a di-sodium phosg ate solution of approxi~ I
that they may be at atmospheric tempera mately 1.33 speci c gravity at 85 0., then
ture when stored or packed.
55
The solution, elimlnated from the. crys removing all solid matter therefrom, then
" tals in the centrifu e, ?ows to a sump tank adding caustic soda solution to convert said
di-sodium phosphate into tri-sodium phos
from w ere it may
e returned by pump 11, phate in a solution of ap roximately 1.38
4 as conditions of pper speci?c gravity at 85 _C., t en cooling said
[nation require._
'~ $By the use of strong phosphoric acid and tri~sodium phosphate solution until crystals
the apparatus as described, I am enabled to of tri-sodium (phosphate are formed, then
separatingso1sai
"cr?stals from the accom
roduce .tri-sodium phosphate more ef panying
ution, t on d in said 0 stals
- to mixing tank 2 or
.cientlyv and less expensively than otherwise, substantially as described.y g
ry
,
"smce the expensive evaporation step em
6.
The
hereindescribed
continuous
.proc
ployed in\ common practice is eliminated.
ess of 'producing tri-sodium phosphate crys
120
meme-7v
3'
talsg which consists in producing a. tri- and returning the mother liquor to the tri
sodium phosphate solution from strong acid, sodium phosphate solution, substantially as
continuously feeding" such tri-sodium phos- described.
phete solution having an approximate spe~
In testimony whereof I al?x my signa
ci?o gravity of 1.36 to 1.410v at 85 vG. to a ture.
crystallizer, and continuously Withdrawing
crystals of tri-sodium phosphate therefrom,
JOHN N. CAROTHERS.
You might also like
- The Preparation of Methylamine Hydrochloride From Acetamide by Means of Calcium HypochloriteDocument3 pagesThe Preparation of Methylamine Hydrochloride From Acetamide by Means of Calcium Hypochloritegeovani2100% (1)
- Nalco New Approach For MacrofoulingDocument73 pagesNalco New Approach For Macrofoulingarufato100% (2)
- J. N. CarothersDocument4 pagesJ. N. CarothershaviedNo ratings yet
- United States Patent Office: Patented Jan. I9, 1954Document2 pagesUnited States Patent Office: Patented Jan. I9, 1954JavierNo ratings yet
- UNITED Starts: Patented Apr. 16, 1935Document2 pagesUNITED Starts: Patented Apr. 16, 1935shalsinia chantalNo ratings yet
- Translate Paten US5976485Document24 pagesTranslate Paten US5976485Lenywulandari AyundaNo ratings yet
- Us 2021699Document5 pagesUs 2021699haviedNo ratings yet
- United States Patent Office: Production of Disopum PhosphateDocument2 pagesUnited States Patent Office: Production of Disopum PhosphatefredyNo ratings yet
- United States: Patent OfficeDocument3 pagesUnited States: Patent OfficefredyNo ratings yet
- United States Patent 0: '3, l50, l74 ICCDocument2 pagesUnited States Patent 0: '3, l50, l74 ICCMuhammadAmdadulHoqueNo ratings yet
- Patent Office: 5 Claims. (CL 260-69)Document2 pagesPatent Office: 5 Claims. (CL 260-69)Teleson MarquesNo ratings yet
- Storage: o - InzoDocument4 pagesStorage: o - InzoOscar SobradosNo ratings yet
- US3689216Document5 pagesUS3689216PABLO URIZ CEREZONo ratings yet
- A Safe Method For Preparation of Uncontaminated Hydrazoic AcidDocument1 pageA Safe Method For Preparation of Uncontaminated Hydrazoic Acidgeovani2No ratings yet
- Facturing Fertilizer Containing Potassium, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous CompoundsDocument1 pageFacturing Fertilizer Containing Potassium, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous CompoundsBharat A. KaduNo ratings yet
- A To The OF A Preliminary Study of Hitherto AND: ProcedureDocument11 pagesA To The OF A Preliminary Study of Hitherto AND: ProcedureMariaNo ratings yet
- United States Patent 0 "Ice: Patented May 9, 1972Document4 pagesUnited States Patent 0 "Ice: Patented May 9, 1972Nguyễn Thanh TùngNo ratings yet
- US3347627Document3 pagesUS3347627Nuttapong JongjitsatitmunNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: Inoue Et A) - (11) Patent Number: (45) Date of PatentDocument4 pagesUnited States Patent (191: Inoue Et A) - (11) Patent Number: (45) Date of PatentShrutiNo ratings yet
- US2321218Document3 pagesUS2321218shirazizadehsinaNo ratings yet
- Us 744128Document2 pagesUs 744128haviedNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: GermanyDocument5 pagesUnited States Patent (191: GermanyChem2014EngNo ratings yet
- United States Patent PO: Patented Nov. 20, 1956Document2 pagesUnited States Patent PO: Patented Nov. 20, 1956shenn0No ratings yet
- Unite Sites Fret (19) : DahlinDocument3 pagesUnite Sites Fret (19) : Dahlintrinh xuan hiepNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Assay of Acetyl PhosphateDocument4 pagesPreparation and Assay of Acetyl PhosphatecataawwwNo ratings yet
- United States Patent 0 ": Patented Dec. 15, 1959Document2 pagesUnited States Patent 0 ": Patented Dec. 15, 1959Aaron CurrieNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: Macdonald 145) Feb. 25, 1975Document4 pagesUnited States Patent (191: Macdonald 145) Feb. 25, 1975Javier Alejandro Rodriguez MelgozaNo ratings yet
- Pentaeritritol 2Document6 pagesPentaeritritol 2Ibnul BaasithNo ratings yet
- US3014784Document2 pagesUS3014784SatyamSahuNo ratings yet
- Us 2375054Document3 pagesUs 2375054haviedNo ratings yet
- Matrix Acidizing of Sandstone4Document5 pagesMatrix Acidizing of Sandstone4HelyaNo ratings yet
- Arsenal Philadelphia, Pa. 19137: FrankfordDocument23 pagesArsenal Philadelphia, Pa. 19137: FrankfordPutri PramodyaNo ratings yet
- Ingles CDocument8 pagesIngles Coscar rodriguezNo ratings yet
- US2301231Document2 pagesUS2301231Abu Mejza'atNo ratings yet
- July 20, 1954 J. L. Krieger 2,684,286: InventorDocument4 pagesJuly 20, 1954 J. L. Krieger 2,684,286: InventorNurhafizah Abd JabarNo ratings yet
- US1960211 (Sudah)Document3 pagesUS1960211 (Sudah)aris_nurhidayatNo ratings yet
- Filed June l5, 1935Document6 pagesFiled June l5, 1935Yustinus Selis ToronNo ratings yet
- This Invention Relates To A Process For Making A Stable CopperDocument3 pagesThis Invention Relates To A Process For Making A Stable CopperAngel BuenoNo ratings yet
- US3718545 (1) PatenteDocument8 pagesUS3718545 (1) PatenteAndrés BelloniNo ratings yet
- Launcelot: Massachusetts Health, Analysis, BostonDocument6 pagesLauncelot: Massachusetts Health, Analysis, BostonMaxi GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Patent Nines,: Nited StatesDocument2 pagesPatent Nines,: Nited Statesjeque661No ratings yet
- Arease: Nov. 8, 1966 W. Wogt Et Al 3,284,495 Process For The Continuous Manufacture, Purification andDocument3 pagesArease: Nov. 8, 1966 W. Wogt Et Al 3,284,495 Process For The Continuous Manufacture, Purification andRachmad HermawanNo ratings yet
- Us 3229777Document4 pagesUs 3229777Parth AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Us1951789 PDFDocument5 pagesUs1951789 PDFJames EdwardsNo ratings yet
- United States Patent Office: Patented Sept. 1, 1959Document4 pagesUnited States Patent Office: Patented Sept. 1, 1959هیمن مNo ratings yet
- Per Acetic AcidDocument5 pagesPer Acetic AcidMaruthi KNo ratings yet
- US3416887Document6 pagesUS3416887khairulNo ratings yet
- Patente 2Document3 pagesPatente 2Saul MamaniNo ratings yet
- AAS Methods 2520of 2520 ProductionDocument4 pagesAAS Methods 2520of 2520 Productionapi-3714811No ratings yet
- Copie de US2899444-1Document4 pagesCopie de US2899444-1KHALED KHALEDNo ratings yet
- Indigo Prodn. From Phenyl-Glycine Carboxylic Acid Salt - by Fusion in Mixed Potassium Hydroxide and Sodium Hydroxide Melt, Then OxidnDocument4 pagesIndigo Prodn. From Phenyl-Glycine Carboxylic Acid Salt - by Fusion in Mixed Potassium Hydroxide and Sodium Hydroxide Melt, Then OxidnCillian CreedonNo ratings yet
- Us2094573-Production of Potassumsulphate Ammonium Sulphate Double SaltDocument2 pagesUs2094573-Production of Potassumsulphate Ammonium Sulphate Double Saltkvsj2001No ratings yet
- Removal of Fluorine From Wet Process Phosphoric AcidDocument2 pagesRemoval of Fluorine From Wet Process Phosphoric AcidAdios ANo ratings yet
- Benzoic Acid To Benzaldehyde, P-Nitrobenzoic Acid To Nitrobenzene and More.Document3 pagesBenzoic Acid To Benzaldehyde, P-Nitrobenzoic Acid To Nitrobenzene and More.banjo010% (1)
- Rile From NH4Document10 pagesRile From NH4rrivera7396No ratings yet
- United States: Patent Office. VDocument2 pagesUnited States: Patent Office. VAmir HamzahNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: MercadeDocument4 pagesUnited States Patent (191: MercadeSoufi BadrNo ratings yet
- Determination of Gamma No and TSDocument3 pagesDetermination of Gamma No and TSAditya ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- United States Patent Office: Patented Mar. 13, 1951 ... ."Document2 pagesUnited States Patent Office: Patented Mar. 13, 1951 ... ."Ruchita PoilkarNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: Wu Et Al. (451 Nov. 6, 1979Document6 pagesUnited States Patent (191: Wu Et Al. (451 Nov. 6, 1979FatonaRifkyPNo ratings yet
- 5991-6846EN BrosurDocument8 pages5991-6846EN BrosurarufatoNo ratings yet
- Tolerance Chart: (Maximum Permissible Error)Document3 pagesTolerance Chart: (Maximum Permissible Error)arufatoNo ratings yet
- Catalog KaoDocument1 pageCatalog KaoarufatoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Temperature On PH v4 - TSP-01-2Document7 pagesEffects of Temperature On PH v4 - TSP-01-2Aridita AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- 14.12 Kulcsar U PDFDocument6 pages14.12 Kulcsar U PDFarufatoNo ratings yet
- ASTM D7740 Optimizing AASDocument9 pagesASTM D7740 Optimizing AASarufatoNo ratings yet
- Doc316 53 01486 PDFDocument6 pagesDoc316 53 01486 PDFarufatoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Temperature On PH v4 - TSP-01-2 PDFDocument7 pagesEffects of Temperature On PH v4 - TSP-01-2 PDFarufatoNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Design ProcedDocument30 pagesIon Exchange Design ProcedFajar IndrawanNo ratings yet
- Simulation Mixed BedDocument13 pagesSimulation Mixed BedarufatoNo ratings yet
- 30265527A V03.16 KarlFischer Titrators Broch EN LR PDFDocument16 pages30265527A V03.16 KarlFischer Titrators Broch EN LR PDFarufatoNo ratings yet
- 2015 11 06 - Cetamine Technology in Power Plants - Swedish Conference 2015Document42 pages2015 11 06 - Cetamine Technology in Power Plants - Swedish Conference 2015arufatoNo ratings yet
- Gfps Chemicals PowerPlantsDocument2 pagesGfps Chemicals PowerPlantsarufatoNo ratings yet
- History of Fluorine Recovery ProcessesDocument21 pagesHistory of Fluorine Recovery ProcessesmahaNo ratings yet
- Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (Pafc)Document10 pagesPhosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (Pafc)Else Feba Paul0% (1)
- Phosphoric Acid - MSDSDocument3 pagesPhosphoric Acid - MSDSSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2213343722017419 MainDocument21 pages1 s2.0 S2213343722017419 MainIkram ADNANENo ratings yet
- PiperacilinDocument2 pagesPiperacilinivaNo ratings yet
- Buffer SolutionsDocument6 pagesBuffer SolutionsIrmey Hamidi100% (1)
- 900 Inorganic Questions For IIT JEE ADVANCEDDocument64 pages900 Inorganic Questions For IIT JEE ADVANCEDSourabh Dhavala95% (19)
- Naval JellyDocument4 pagesNaval JellyjohnsopranaNo ratings yet
- GST Food Item ListDocument88 pagesGST Food Item ListgeorgiinaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1877705812045341 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S1877705812045341 MainJavier Alejandro RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Solubility and Complex-Ion Equilibria: Practice ExamplesDocument33 pagesSolubility and Complex-Ion Equilibria: Practice Exampleskennethleo69No ratings yet
- Uses of Phosphoric AcidDocument3 pagesUses of Phosphoric AcidMarnel Roy MayorNo ratings yet
- Di-Calcium Phosphate by Direct Acidulation of Phosphate RockDocument111 pagesDi-Calcium Phosphate by Direct Acidulation of Phosphate RockAshutosh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sciencedirect: The Use of Advanced Process Controls in A Phosphoric Acid ReactorDocument7 pagesSciencedirect: The Use of Advanced Process Controls in A Phosphoric Acid ReactorJavier Alejandro RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of The Wet Process Phosphor PDFDocument8 pagesFundamentals of The Wet Process Phosphor PDFVandenberg Soares de AndradeNo ratings yet
- EtanolDocument57 pagesEtanolexe241293No ratings yet
- History of Phosphoric Acid Technology (Evolution and Future Perspectives)Document7 pagesHistory of Phosphoric Acid Technology (Evolution and Future Perspectives)Fajar Zona67% (3)
- P-Block 15 To 16 GroupDocument38 pagesP-Block 15 To 16 GroupBharti GoelNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Technology Section 1Document14 pagesFertilizer Technology Section 1Roed Alejandro LlagaNo ratings yet
- LiteraturDocument94 pagesLiteraturMuhammad Iqbal MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Che 329 - Lectre - 2Document95 pagesChe 329 - Lectre - 2anandseshadri901No ratings yet
- June 2018 QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Chemistry AS-LevelDocument24 pagesJune 2018 QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Chemistry AS-LevelRunNo ratings yet
- Panamax Cargo Hold Cleaning Manual Rev00Document36 pagesPanamax Cargo Hold Cleaning Manual Rev00Cenk ÇobanNo ratings yet
- Cleaning & Sanitising - Food Processing IndustryDocument21 pagesCleaning & Sanitising - Food Processing Industrydrmarvin2k5100% (1)
- Lecture 21 PhosphorousDocument53 pagesLecture 21 PhosphorousAnilKumar100% (2)
- L Uk SulphDocument24 pagesL Uk SulphypyeeNo ratings yet
- Calcium Sulfate Crystallization in Phosphoric Acid PDFDocument133 pagesCalcium Sulfate Crystallization in Phosphoric Acid PDFabderrahimnNo ratings yet
- TSP Tour ReportDocument16 pagesTSP Tour ReportArefin ShahriarNo ratings yet
- Chemicalcleaning For BoilerDocument16 pagesChemicalcleaning For Boilerak_thimiriNo ratings yet