Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modulation
Modulation
Uploaded by
Junjun BedrijoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modulation
Modulation
Uploaded by
Junjun BedrijoCopyright:
Available Formats
Modulation
the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal,
with a modulating signal that typically contains information to be transmitted.
Digitization
Digitization is the process of converting information into a digital format . In this
format, information is organized into discrete units of data (called bit s) that can be
separately addressed (usually in multiple-bit groups called byte s). This is
the binary data that computers and many devices with computing capacity (such
as digital camera s and digital hearing aid s) can process.
A codec is a device or computer program capable of encoding or decoding a digital data
stream or signal.[1][2][3] Codec is a portmanteau of coder-decoder or, less commonly,compressordecompressor.
A codec encodes a data stream or signal for transmission, storage or encryption, or decodes it for
playback or editing. Codecs are used in videoconferencing, streaming mediaand video
editing applications. A video camera's analog-to-digital converter (ADC) converts its analog signals
into digital signals, which are then passed through a video compressor for digital transmission or
storage. A receiving device then runs the signal through a video decompressor, then a digital-toanalog converter (DAC) for analog display
The sampling frequency or sampling rate, fs, is the average number of samples obtained in one
second (samples per second), thus fs = 1/T.
Definition - What does Synchronization mean?
Synchronization, in the context of .NET, is a process that involves coordinating the execution of
multiple threads to ensure a desired outcome without corrupting the shared data and preventing any
occurrence of deadlocks and race conditions.
Synchronization also occurs between network nodes to ensure that data streams are received and
transmitted correctly, and to prevent data collision. It usually uses a clock signal transmitted in
sequence with a data stream to maintain proper signal timing.
Pulse-code modulation (PCM) is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is
the standard form of digital audio in computers, Compact Discs, digital telephony and other digital
audio applications. In a PCM stream, the amplitude of the analog signal is sampled regularly at
uniform intervals, and each sample is quantized to the nearest value within a range of digital steps.
1.
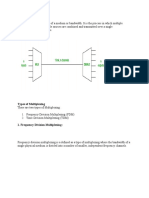
In telecommunications and computer networks, multiplexing(sometimes
contracted to muxing) is a method by which multiple analog message signals or digital
data streams are combined into one signal over a shared medium. The aim is to share
an expensive resource.
This page is all about Space-Division Multiplexing (SDM).
What is SDM: When we want to transmit multiple messages, the goal is maximum reuse of
the given resources: time and frequency. Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM), operates by dividing
the time up into time slices, so that the available time can be reused. Frequency-Division
Multiplexing (FDM), operates by dividing up the frequency into transmission bands, so that the
frequency spectrum can be reused. However, if we remember our work with directional
antennas, we can actually reuse both time and frequency, by transmitting our information along
parallel channels. This is known as Space-Division Multiplexing.
You might also like
- CT660 2012Document58 pagesCT660 2012Eduardo Alvarez100% (2)
- R.I.P. Dead Words ListDocument3 pagesR.I.P. Dead Words ListTanesha FisherNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Notes Form 2: Ms. G. BonniciDocument52 pagesMathematics Notes Form 2: Ms. G. BonnicijayweinxNo ratings yet
- Data CommunicationDocument114 pagesData CommunicationShikha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Data CommunicationDocument114 pagesData Communicationpawan100% (2)
- Priority SlotDocument6 pagesPriority Slotravijangde10No ratings yet
- MUTIPLEXINGDocument5 pagesMUTIPLEXINGMadhu SwtyNo ratings yet
- Overview Coding TheoryDocument2 pagesOverview Coding TheoryManal SaadNo ratings yet
- Encoder DecoderDocument6 pagesEncoder Decodermarkcelis1No ratings yet
- GSM NotesDocument3 pagesGSM NotesRamakant BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: Data CommunicationDocument89 pagesUnit - 1: Data CommunicationnavecNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument76 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAnonymous VtCR0qNo ratings yet
- NETWORKING BCA WBUT 5th SEM NOTESDocument135 pagesNETWORKING BCA WBUT 5th SEM NOTESapi-1958925986% (22)
- Chapter - 2 Network BasicsDocument5 pagesChapter - 2 Network BasicsRoopaNo ratings yet
- Notes - Digital Communication Lecture-1Document63 pagesNotes - Digital Communication Lecture-1shakeebsadiqNo ratings yet
- Notes Digital Communication Lecture 1Document63 pagesNotes Digital Communication Lecture 1Faraz HumayunNo ratings yet
- Advance Digital CommunicationDocument31 pagesAdvance Digital CommunicationatifNo ratings yet
- Pulse-Code Modulation: "PCM" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument6 pagesPulse-Code Modulation: "PCM" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeesubrampatiNo ratings yet
- Lecture #2 Digital Communications EE 725Document33 pagesLecture #2 Digital Communications EE 725Aamir HabibNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Telecommunication PrinciplesDocument3 pagesAssignment - Telecommunication PrinciplesShanu ThariNo ratings yet
- Notes Digital Communication Lecture 1 - 4Document63 pagesNotes Digital Communication Lecture 1 - 4dinkarbhombe100% (2)
- Notes Digital Communication Lecture 1 - 3Document63 pagesNotes Digital Communication Lecture 1 - 3dinkarbhombeNo ratings yet
- Mid PreparationDocument18 pagesMid Preparationshadequl islamNo ratings yet
- Keywords - 9608 - Computer Science - Section - 1Document12 pagesKeywords - 9608 - Computer Science - Section - 1Ayesha TahirNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication TechniquesDocument5 pagesDigital Communication TechniquesmuralitejasNo ratings yet
- Pulse-Code Modulation (PCM) Is A Method Used ToDocument8 pagesPulse-Code Modulation (PCM) Is A Method Used ToMwesigye KennethNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Assigned By: Department: Roll #: Data Communication Chatrapathi Shhibaji Informatin Technology 2K8-BS-28Document5 pagesCourse Title: Assigned By: Department: Roll #: Data Communication Chatrapathi Shhibaji Informatin Technology 2K8-BS-28Deep AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- Topic 9-10 Data Communication and Computer NetworksDocument12 pagesTopic 9-10 Data Communication and Computer NetworksBENSON NGARI100% (1)
- Communication System NotesDocument26 pagesCommunication System NotesSammar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Assignments: Communication Technology (MC 0018)Document14 pagesAssignments: Communication Technology (MC 0018)amitavamudiNo ratings yet
- EC307 Fundamentals of Data CommunicationDocument15 pagesEC307 Fundamentals of Data CommunicationSwet SheershNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document115 pagesUnit 1rajNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Digital Communications TechniquesDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 7 Digital Communications TechniquesPatrick GarciaNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Lecture-1Document175 pagesDigital Communication Lecture-1Vijay JanyaniNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Lecture-1Document175 pagesDigital Communication Lecture-1Vijay JanyaniNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Lecture-1Document175 pagesDigital Communication Lecture-1Ahmed Hassan MohammedNo ratings yet
- Networking & Data CommunicationDocument30 pagesNetworking & Data CommunicationMR PAINTERNo ratings yet
- Notes Digital Communication Lecture 1Document61 pagesNotes Digital Communication Lecture 1Igho Silva0% (1)
- DC All Units-Dcet - Umar CoderDocument165 pagesDC All Units-Dcet - Umar Coderritif59968No ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Lab FileDocument17 pagesMobile Computing Lab FileSimarjot SinghNo ratings yet
- WMN w-23Document15 pagesWMN w-23atharvbowlekarNo ratings yet
- Qustion 2Document11 pagesQustion 2Yohannis DanielNo ratings yet
- Unit1-Chapter1 - CS-2-uddar SirDocument147 pagesUnit1-Chapter1 - CS-2-uddar SirRaghu BNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication - Quick GuideDocument75 pagesDigital Communication - Quick Guidearif8932869039No ratings yet
- ModemDocument5 pagesModemanishmohan0601No ratings yet
- Digital Communication: Student Report Mahmoud Mohamed KhodeirDocument9 pagesDigital Communication: Student Report Mahmoud Mohamed Khodeirالبياتي محمدNo ratings yet
- Digital FormsDocument13 pagesDigital FormsRobin VargheseNo ratings yet
- Data CompDocument4 pagesData CompAnjeche TomNo ratings yet
- DSP CasestudyDocument23 pagesDSP CasestudyShayani BatabyalNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Quick GuideDocument62 pagesDigital Communication Quick GuideArun avNo ratings yet
- Networking & Data CommunicationDocument30 pagesNetworking & Data Communicationodhiambopaul139No ratings yet
- Nformations Ommunications Echnology: DictionaryDocument53 pagesNformations Ommunications Echnology: Dictionarykz_bautistaNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Assignment 2 Etinosa Enomayo 1.1Document8 pagesUnit 10 Assignment 2 Etinosa Enomayo 1.1eet1nosa15No ratings yet
- Introduction To Digital CommunicationsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Digital CommunicationsYashwanthReddyNo ratings yet
- ECE - Modems in Data CommunicationDocument7 pagesECE - Modems in Data CommunicationLLoydDomingoMandocdocNo ratings yet
- Igital Ignal Rocessing: at SivagangaiDocument21 pagesIgital Ignal Rocessing: at SivagangaidhivakargunalanNo ratings yet
- Modem: What Is A Modem? Types of Modems: Modulator ConvertsDocument7 pagesModem: What Is A Modem? Types of Modems: Modulator ConvertsthiruNo ratings yet
- Audio Visual Speech Recognition: Advancements, Applications, and InsightsFrom EverandAudio Visual Speech Recognition: Advancements, Applications, and InsightsNo ratings yet
- LCF MeterDocument7 pagesLCF MeterJunjun BedrijoNo ratings yet
- Thesis Ii Progress Report: Edgardo Bedrijo Jr. Mario Borromeo Jr. Genel Pornillos Jestoni ImperialDocument2 pagesThesis Ii Progress Report: Edgardo Bedrijo Jr. Mario Borromeo Jr. Genel Pornillos Jestoni ImperialJunjun BedrijoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Radio Transmission SystemsDocument148 pagesChapter 2 Radio Transmission SystemsJunjun BedrijoNo ratings yet
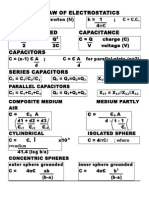
- Coulomb'S Law of Electrostatics Energy Stored Capacitance Capacitors Series CapacitorsDocument4 pagesCoulomb'S Law of Electrostatics Energy Stored Capacitance Capacitors Series CapacitorsJunjun BedrijoNo ratings yet
- Edgardo Bedrijo Jr. Genel Pornillos Mario BorromeoDocument1 pageEdgardo Bedrijo Jr. Genel Pornillos Mario BorromeoJunjun BedrijoNo ratings yet
- All ElectronicsDocument9 pagesAll ElectronicsJunjun BedrijoNo ratings yet
- Application LayerDocument12 pagesApplication LayerJunjun BedrijoNo ratings yet
- Project STA108Document25 pagesProject STA108meliszaNo ratings yet
- Caputo Et Al., 2017Document12 pagesCaputo Et Al., 2017ManoakiNo ratings yet
- Properties of Materials With Temperature VariationDocument50 pagesProperties of Materials With Temperature Variationcliffrajjoel100% (1)
- Giant - Anthem Advanced Pro 29 2 - 2466Document1 pageGiant - Anthem Advanced Pro 29 2 - 2466KM MuiNo ratings yet
- Arch MLCDocument471 pagesArch MLCJoseNo ratings yet
- Sustained Controlled ReleaseDocument43 pagesSustained Controlled Releasesukanya100% (1)
- Successful SAP BW Implementation and Upgrade Tips Part One - V.2Document55 pagesSuccessful SAP BW Implementation and Upgrade Tips Part One - V.2Vyas BhargavNo ratings yet
- Storyboard Example StudentsDocument6 pagesStoryboard Example Studentsbrianzuch2002No ratings yet
- AbstDocument3 pagesAbstcrazz1No ratings yet
- Safety Instructions Trouble Shooting: SituationDocument1 pageSafety Instructions Trouble Shooting: SituationHAITHM MURSHEDNo ratings yet
- Elliot Wave TheoryDocument56 pagesElliot Wave TheoryThanongkij45100% (1)
- Graphical Analysis: Velocity and Time GraphDocument9 pagesGraphical Analysis: Velocity and Time GraphDarwyn RiosNo ratings yet
- D 395 - 02 - RDM5NS0WMG - PDFDocument6 pagesD 395 - 02 - RDM5NS0WMG - PDFAndré BerninzonNo ratings yet
- Experiments With An Axial Fan: Page 1/3 10/2010Document3 pagesExperiments With An Axial Fan: Page 1/3 10/2010Priyam ParasharNo ratings yet
- Class X Science (Magnetic Effect of Electric Current)Document10 pagesClass X Science (Magnetic Effect of Electric Current)Mohammad RezaullahNo ratings yet
- Patinkins Real Balance EffectDocument16 pagesPatinkins Real Balance EffectAshu KhatriNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths 314648 Foundation Tier Terminal Unit 3 Section B Mark Scheme (Specimen)Document3 pagesGCSE Maths 314648 Foundation Tier Terminal Unit 3 Section B Mark Scheme (Specimen)gcsemathstutor100% (1)
- Kylin85T 0 PDFDocument2 pagesKylin85T 0 PDFlomie100% (1)
- DMC RepairDocument155 pagesDMC RepairАndrey100% (1)
- Design and Analysis of Coupling Matrix For Microwave Filter ApplicationsDocument13 pagesDesign and Analysis of Coupling Matrix For Microwave Filter ApplicationskhadimthiamNo ratings yet
- Hindak 2008 - Chlorogloeopsis PDFDocument18 pagesHindak 2008 - Chlorogloeopsis PDFHigor LessaNo ratings yet
- Exp 0013Document24 pagesExp 0013chandra9000No ratings yet
- Long Quiz 1-BDocument11 pagesLong Quiz 1-BEthel FajardoNo ratings yet
- Connectable Devices TEMS Investigation 19.0Document30 pagesConnectable Devices TEMS Investigation 19.0Devesh GargNo ratings yet
- Finite Element - Exam PrepDocument5 pagesFinite Element - Exam PrepLil A Nano World schwiftyNo ratings yet
- Re: Find Material Stock To Given Date: Ravi Kanth TalaganaDocument11 pagesRe: Find Material Stock To Given Date: Ravi Kanth TalaganainfosapabapNo ratings yet
- Um TQ GC Ms 7000e 7010c Series Concepts Guide g7006 90008 en AgilentDocument52 pagesUm TQ GC Ms 7000e 7010c Series Concepts Guide g7006 90008 en AgilentxdshkiperNo ratings yet